Figure 3.
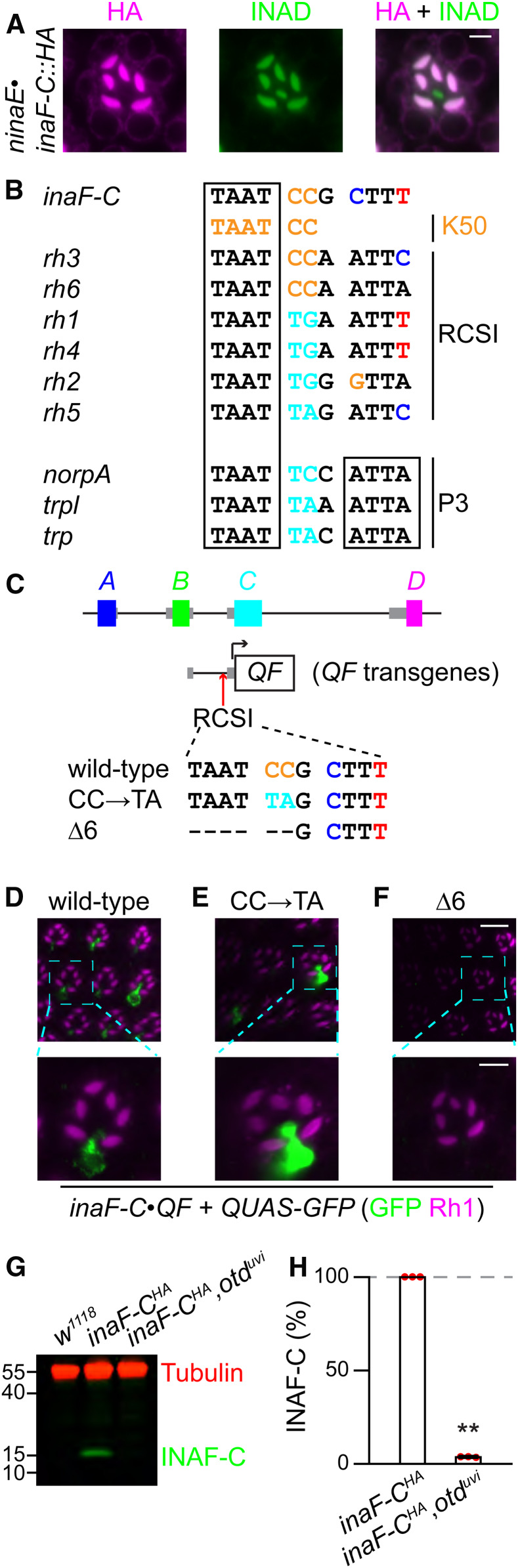
Expression of inaF-C in R7 cells depends on the rhodopsin core sequence I (RCSI). (A) An ommatidium (R7 layer) from flies expressing inaF-C::HA under control of the ninaE promoter (ninaE•inaF-C::HA) were costained with mouse anti-HA (magenta) and rabbit anti-INAD (green); bar, 3 μm. (B) Comparison between the RCSI elements in the promoter of rhodopsins, the palindromic P3 motif in several broadly expressed photoreceptor genes (norpA, trpl, and trp), and the K50 motif in the promoters of inaF-C, rh3, and rh6. (C) Mutations in the inaF-C RCSI sequence introduced into an 0.8 kb region of the inaF-C promoter (−770 to −1, relative to the translation start codon). The three inaF-C promoter versions were fused directed to the coding region of QF and used to generate transgenic flies. (D–F) The number of R7 cells expressing INAF-C is reduced or eliminated by mutations in the inaF-C RCSI sequence. QF expressed under control of either the wild-type or mutated inaF-C promoter sequences (inaF-C•QF) was used to drive QUAS-GFP. Shown are optical sections of compound eyes from the indicated flies stained with anti-GFP (Green) and anti-Rh1 (magenta). The scale bars in the upper and lower panels indicate 10 and 4 μm, respectively. (D) inaF-Cwild-type•QF. (E) inaF-CCC→TA•QF. (F) inaF-CΔ6•QF. (G) Extracts from 0.5 head equivalents from the indicated flies were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, and Western blots were probed with mouse anti-tubulin (loading control) and rabbit anti-HA (recognizes INAF-C::HA). Protein size markers are indicated (kDa). (H) Quantification of INAF-C levels obtained from Western blot analyses represented in (G).