Abstract
Immediate removal of staghorn stones is compulsory to prevent life-threatening complications. The advancement of endoscopic technology makes retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) a favorable treatment to remove large stones over the standard percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL). Without careful considerations, it can cause the formation of steinstrasse. Here, we present the case of a 68-year-old man with multiple stones along his right urogenital duct after being treated with RIRS to remove a staghorn stone. After 2 years of multiple interventions, the steinstrasse was completely removed. To prevent this complication, detailed assessment of the stone (size, location) and renal anatomy should be performed prior to the procedure.
Keywords: retrograde intrarenal surgery, staghorn stones, steinstrasse, complication
Introduction
The term “staghorn” describes the configuration of large, branched renal stones that occupy the pelvis and extent to at least two renal calices. Immediate removal of the stones is compulsory to prevent serious kidney injury and life-threatening sepsis 1. According to the American Urological Association, percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is the standard treatment for staghorn removal 2. Recently, urologists started using retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) to treat large stones since it is less invasive and simpler than PCNL 3. However, this procedure might cause the formation of steinstrasse as a complication especially in stones of size 2–3 cm, which require more invasive removal procedures. This multi-procedure approach in the treatment of renal stone can impact the patients’ quality of life, especially when the stone is hard (measured with Hounsfield unit of more than 1000) 4, 5. This study shows and discusses the formation of steinstrasse and the need of follow up procedures, which led to depression in the patient after the use of RIRS for staghorn stone removal.
Case presentation
A 68-year-old man came to our hospital in April 2016 with multiple stones along his right urogenital system. He had been experiencing flank pain that was not influenced by body position for 1 month. He denied any treatment relating to the pain that he experienced in this period. He also denied having a family history of this symptom nor ever he had this symptom before. Physical examination only revealed tenderness of the right flank.
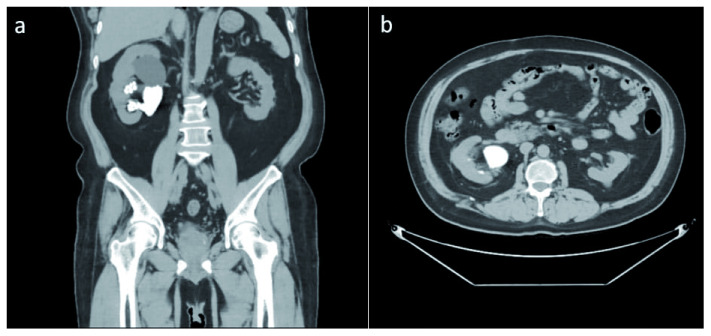
Computed tomography (CT) urography at the previous hospital showed a staghorn stone at the right inferior calyx with a size of 45.7 × 59.3 × 27.5 mm (Hounsfield unit not available), a left renal cyst with size of 19.2 × 22.2 × 18.9 mm, and a third-grade right-side hydronephrosis ( Figure 1). Post-RIRS photo showed a double J stent with multiple tiny stones from the right pelvio-calyces to vesico-ureteral junction ( Figure 2a).
Figure 1. Initial computed tomography (CT) urography.
The first CT Urography of the patient shows right staghorn stone with grade 3 hydronephrosis and left renal cyst.
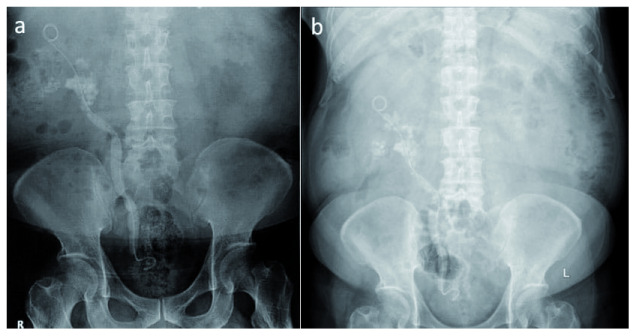
Figure 2. Steinstrasse formation.
An immediate ( a) and 1 month (April 2016) ( b) Plain abdominal photo following retrograde intrarenal surgery shows multiple tiny stones along the right genitourinary system.
A month later at when he come to our hospital for a second opinion, his plain abdominal X-ray result had not changed ( Figure 2b). Right ureteroscopy (URS), right nephrostomy, and right PCNL was performed and post-operative X-ray imaging was conducted ( Figure 3a). Another right URS was performed 2 weeks later, resulting in the remaining 8-mm stone at the ureter-pelvic junction (UPJ) ( Figure 3b).
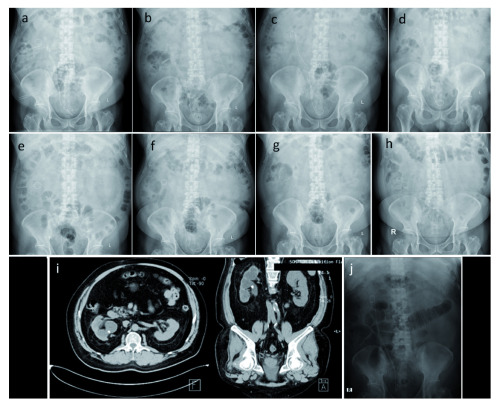
Figure 3. Sequential imaging photos.
After right ureterorenoscopy, right nephrostomy, and right percutaneous nephrolithotomy in April 2016 ( a), after ureterorenoscopy and percutaneous nephrolithotomy in June 2016 ( b), after the second extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy in June 2016 ( c), after the third extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy in July 2016 ( d), after right laser ureterorenoscopy and replacement of right double J stent in July 2016 ( e), after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy in October 2016 ( f), double J stent removal in October 2016 ( g), routine control in January 2018 ( h & i), retrograde intrarenal surgery which shows no residual stone in June 2019 ( j).
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) was performed twice in June 2016, resulting in a decrease in stone size to 6 mm. ( Figure 3c). Another ESWL was performed the next month ( Figure 3d). In July 2016, he underwent a right laser URS followed by replacement of the DJ stent ( Figure 3e). Three months later, another ESWL was performed ( Figure 3f). Shortly after, the remaining DJ stent was removed. Plain abdominal X-ray still showed a residual right nephrolithiasis. ( Figure 3g). In 2017, the patient was so depressed from the numerous procedures that he decided to end the treatment for his remaining stone. He admitted lacking spirit throughout the day since the failure of the last ESWL procedure and feeling that his stone would not be able to be cured, along with his continuous need for pain medication.
Almost two years later (January 2018), routine plain abdominal X-ray and CT urography showed no change on his right nephrolithiasis ( Figure 3h, i). In June 2019, he was persuaded by his family to re-try stone management and had the last RIRS at another hospital to remove the remaining stone completely ( Figure 3j). In November 2019, he visited our hospital for DJ stent removal and plain abdominal X-ray. Neither stone nor DJ stent were observed. The summary of the patient’s history of illness can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1. Summary of the patient’s history of illness.
| Time | Initial condition | Procedure | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| December
2015 |
Plain abdominal photo showed right
staghorn stone (45,7 × 59,3 × 27,5 mm); Third grade hydronephrosis |
RIRS and DJ stent insertion | Multiple tiny stones along the right
genitourinary system from pelvio-calyces to vesico-ureteral junction ( Figure 2) |
| April 2016 | Plain abdominal photo showed multiple
tiny stones along the right genitourinary system from pelvio-calyces to vesico- ureteral junction |
Right URS; Right
nephrostomy; Right PCNL; Insertion of a new DJ stent |
A remaining radio opaque stone with a
diameter of 8 mm at the UPJ ( Figure 3a) |
| June 2016 | Plain abdominal photo showed a radio
opaque stone with the size of 8 mm |
ESWL twice | The stone size was decreased to 6 mm
( Figure 3b, c) |
| July 2016 | Plain abdominal photo showed a radio
opaque stone with the size of 6 mm |
ESWL; DJ stent
replacement; Right laser URS |
Small residual stones at the right kidney
( Figure 3d, e) |
| October 2016 | A residual right nephrolithiasis | ESWL; DJ stent removal | A residual right nephrolithiasis ( Figure 3f) |
| January 2018 | Plain abdominal photo and CT urography
showed right nephrolithiasis |
N/A | Figure 3g |
| June 2019 | CT urography showed right nephrolithiasis | RIRS and DJ stent insertion | Right DJ stent
in situ; No residual
stone ( Figure 3h, i) |
| November
2019 |
Right DJ stent in situ; No residual stone | DJ stent removal | No stone was found on the final BNO
( Figure 3j) |
RIRS, retrograde intrarenal surgery; URS, Ureteroscopy; PCNL, percutaneous nephrolithotomy; ESWL, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy.
Discussion
The management of nephrolithiasis has been changing dramatically over time, shifting from open surgery to less-invasive procedures, such as PCNL and ESWL 6. According to the American Urological Association and European Association of Urology guidelines, the standard treatment for staghorn stone removal is PCNL 2, 5. PCNL has a high stone-free rate (SFR), similar to that of an open surgery (93%). It also results in lower morbidity, shorter operative time, shorter hospital stays, and earlier back to work compared to open surgery. However, it can cause severe complications, such as renal trauma with severe uncontrollable bleeding 7, 8.
On the other hand, the development of flexible ureteroscopes allows for excellent visualization that makes it a favorable procedure for most urologists. The possibility of using holmium lasers alongside a ureteroscope, lowering the cost, has made this procedure even more popular 9. Compared to PCNL, RIRS has a slightly lower SFR of 87% and also lower morbidity and complication rate at 2% 10. In our case, the first option of RIRS instead of PCNL was because the patient preferred a less invasive method.
In Indonesia, PCNL is still the first choice for treating large renal calculi according to Ikatan Ahli Urologi Indonesia (the Indonesian Urologist Association). However, the use of PCNL in Indonesia is still limited due to the lack of technology and experts, particularly in remote areas 11. The incidence of steinstrasse formation after RIRS is 20% of large renal stone cases followed by hydronephrosis 4. The development of SS is also seen in our patient who were initially treated with RIRS. To avoid this complication, a scoring system was developed by Resorlu et al. 12 that includes four indicators: a renal stone size >20 mm, lower pole stone with an infundibulum-pelvic angle <45°, a stone number in different calyces >1, and abnormal renal anatomy. A greater score is associated with a lower SFR. This score can be calculated prior to RIRS.
Urolithiasis is a painful chronic disease which significantly impacts the quality of life of the sufferers. In addition to chronic pain, the acute pain of urolithiasis resulting from stone movement often causes fear of recurrence. Recent studies have suggested an association between the disease and anxiety and depression 13. In the present study, our patient developed symptoms of depression during the second year of his treatment because he had to undergo multiple surgical procedures in a year. However, after receiving support from his family and reassurance from the clinicians, the patient finally decided to continue treatment for his leftover stones. The patient initially preferred RIRS to PCNL because it was less invasive, but after his negative experiences, he would prefer PCNL to RIRS.
RIRS may be used in cases where open surgery and ESWL are risky or inadequate, such as in patients with obesity, bleeding disorders, musculoskeletal deformities, renoureteral malformations, and infundibular stenosis 5.
One limitation of this study is that we did not know the hardness (Hounsfield units) of the stone prior to the patient presenting to our clinic, meaning we could not specifically determine the cause of his previous failure of treatment other than the size of the stone.
Conclusions
RIRS can be an alternative choice to remove large staghorn calculi in selected patients even though the efficacy is lower than PCNL. Detailed assessment should be made to prevent any complications. Patients with large staghorn calculi should be informed regarding the possible need for multiple procedures to completely remove the stones, otherwise receiving inadequate information will lead the patient to negative thinking and treatment avoidance.
Data availability
All data underlying the result are available as part of the article and no additional source data are required.
Consent
Written informed consent for publication of their clinical details and/or clinical images was obtained from the patient/parent/guardian/relative of the patient.
Funding Statement
The author(s) declared that no grants were involved in supporting this work.
[version 1; peer review: 1 approved
References
- 1. Healy KA, Ogan K: Pathophysiology and management of infectious staghorn calculi. Urol Clin N Am. 2007;34(3):363–74. 10.1016/j.ucl.2007.05.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Preminger GM, Assimos DG, Lingeman JE, et al. : Chapter 1: AUA guideline on management of staghorn calculi: diagnosis and treatment recommendations. J Urol. 2005;173(6):1991–2000. 10.1097/01.ju.0000161171.67806.2a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Zengin K, Tanik S, Karakoyunlu N, et al. : Retrograde intrarenal surgery versus percutaneous lithotripsy to treat renal stones 2-3 cm in diameter. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015: 914231. 10.1155/2015/914231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Hyams ES, Munver R, Bird VG, et al. : Flexible ureterorenoscopy and holmium laser lithotripsy for the management of renal stone burdens that measure 2 to 3 cm: a multi-institutional experience. J Endourol. 2010;24(10):1583–1588. 10.1089/end.2009.0629 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Turk C, Neisius A, Petrik A, et al. : EAU Guidelines on Urolithiasis.2018. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 6. Yuri P, Hariwibowo R, Soeroharjo I, et al. : Meta-analysis of Optimal Management of Lower Pole Stone of 10 - 20 mm: Flexible Ureteroscopy (FURS) versus Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) versus Percutaneus Nephrolithotomy (PCNL). Acta Med Indones. 2018;50(1):18–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Al-kohlany KM, Shokeir AA, Mosbah T, et al. : Treatment of complete staghorn stones: a prospective randomized comparison of open surgery versus percutaneous nephrolithotomy. [abstract]. J Urol. 2005;173(2):469–73. 10.1097/01.ju.0000150519.49495.88 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. El-Nahas AR, Shokeir AA, El-Assmy AM, et al. : Post-percutaneous nephrolithotomy extensive hemorrhage: a study of risk factors. J Urol. 2007;177(2):576–9. 10.1016/j.juro.2006.09.048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Krambeck AE, Murat FJ, Gettman MT, et al. : The evolution of ureteroscopy: a modern single-institution series. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006;81(4):468–73. 10.4065/81.4.468 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Prabhakar M: Retrograde ureteroscopic intrarenal surgery for large (1.6-3.5 cm) upper ureteric/renal calculus. Indian J Urol. 2010;26(1):46–9. 10.4103/0970-1591.60443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Rasyid N, Kusuma GW, Atmoko W, editor: Ikatan Ahli Urologi Indonesia: Panduan penatalaksanaan klinis batu saluran kemih Edisi pertama. Jakarta.2018. [Google Scholar]
- 12. Resorlu B, Unsal A, Gulec H, et al. : A new scoring system for predicting stone-free rate after retrograde intrarenal surgery: the “resorlu-unsal stone score”. Urology. 2012;80(3):512–8. 10.1016/j.urology.2012.02.072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Lien CS, Huang CP, Chung CJ, et al. : Increased risk of anxiety among patients with urolithiasis: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Int J Urol. 2015;22(10):937–42. 10.1111/iju.12865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]