Meningiomas are the most common primary central nervous system tumor with an incidence rate of 8.33 per 100 000.1 The majority of meningiomas (80–90%) are low grade (grade I) and have a 7–20% recurrence risk. While more rare, high-grade meningiomas harbor an increased risk of recurrence and death: grade II occurring 5–15% with a 30–40% recurrence risk and grade III occurring 1–3% with a 50–80% recurrence risk.2,3
A total of 134 high-grade (grade II or grade III) meningiomas were screened for the presence of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and IDH2 mutations using next-generation exome sequencing.
This study was approved by the human subjects institutional review board and complied with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act guidelines. We identified 134 patients with high-grade meningioma (grade II or grade III) who underwent neurosurgical resection at our institution from 1995 to 2017 with available archival formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue. A board-certified neuropathologist reviewed histopathological diagnosis, grade, and purity of each case according to 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines.
DNA was extracted using Maxwell FFPE Plus DNA Purification Kit (Promega). DNA tissue libraries were generated using Ion AmpliSeq Oncomine Comprehensive research panel versions 2.0 and 3.0 as described previously.4 Sequencing data analysis performed using Torrent Suite (versions 5.6.0., 5.8.0) and Ion Reporter (versions 5.2, 5.6, 5.8).
We are the first to report recurrent IDH1/2 mutations in high-grade meningiomas using next-generation exome sequencing. Mutations in IDH1/2 were identified in 2.2% (3/134) of our cohort.
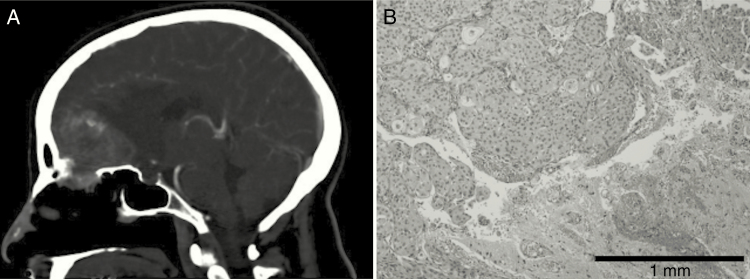
Case 1 involved a 53-year-old woman with a preoperative CT that revealed a heterogeneously enhancing, partially calcified extra-axial right frontal mass measuring 4.1 × 3.6 × 4.1 cm (Fig. 1A). Survival after neurosurgical resection is currently 10.1 years. Histopathologic evaluation demonstrated a primary grade II atypical meningioma with focal brain invasion (Fig. 1B) and epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) and progesterone receptor (PR) positivity. Targeted sequencing revealed an IDH1 p.Arg132His alteration (10.5%, 334x). However, IDH1 R132H immunohistochemistry was negative.
Fig. 1.
(A) Sagittal CT demonstrating right frontal mass measuring 4.1 cm × 3.6 cm × 4.1 cm. (B) WHO grade II atypical meningioma on hematoxylin and eosin (10x) with focal brain invasion (shown at the bottom right).
In order to provide orthogonal validation for the G395A mutation in the IDH1 gene, which results in a missense Arg to His mutation, we designed targeted primers to amplify this region as part of a targeted 250 bp amplicon where the G395A mutation in IDH1 is centered with up- and downstream flanks (hg19; chr2:209112972-209113205). Two hundred fifty nanograms of amplified DNA was used as input into library prep for downstream single molecule, real-time sequencing on the RSII platform (Pacific Biosciences). Following raw data collection, highly accurate (>99.9%) circular consensus sequences (CCS) were generated using web-based SMRTLink 7.0 bioinformatics suite in order to call single nucleotide polymorphism variants. A total of 50 497 CCS reads were generated, with 362 (0.7%) distinct molecules validating the G395A variant of interest at QV40.
Case 2 is from a 37-year-old woman with a preoperative MRI that revealed a left frontal mass measuring 5.4 × 7.5 × 6.9 cm. Histopathologic evaluation demonstrated a recurrent grade III anaplastic meningioma (papillary) with focal brain invasion and EMA and PR positivity. We identified an IDH1 p.Arg132Gly alteration (6.9%, 2000x). The only other single nucleotide variant found in this case was an NF2 p.Ile126fs; no BAP1 alteration was identified. The patient is currently alive after neurosurgical resection at 13.3 years.
Case 3 was a 67-year-old woman who survived for a total of 10.9 years after neurosurgical resection of a lesion from the parietal convexity. Histopathologic evaluation demonstrated a recurrent grade II atypical meningioma with focal necrosis and EMA positivity. This case harbored an IDH2 p.Arg140Gln alteration (5.0%, 2000x).
Importantly, all 3 patients in our cohort with an IDH1/2 mutation survived for at least 10 years after neurosurgical resection. Screening for IDH1/2 alterations in high-grade meningioma with exome sequencing is encouraged as patients with IDH1/2-mutated high-grade meningioma may benefit from IDH inhibitors that are currently in clinical trials. Future inter-institutional and collaborative group studies are warranted to validate these findings and elucidate how IDH1/2 mutation status affects survival outcomes in high-grade meningioma independent of tumor grade.
Funding
None.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Authorship statement.
Study design: CMG, RS, RKS, MF. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: CMG, JL, JWR, HA, NF, YW, NF, MP, MU, YK, RBM, JB, MD, MS, RS, RKS, MF. Manuscript preparation: CMG, JL, JWR, HA, NF, YW, NF, MP, MU, YK, RBM, JB, MD, MS, RS, RKS, MF. Final manuscript approval: CMG, JL, JWR, HA, NF, YW, NF, MP, MU, YK, RBM, JB, MD, MS, RS, RKS, MF.
References
- 1. Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Truitt G, Boscia A, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(suppl_4):iv1–iv86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114(2):97–109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathologica. 2016;131(6):803–820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Pain M, Wang H, Lee E, et al. Treatment-associated TP53 DNA-binding domain missense mutations in the pathogenesis of secondary gliosarcoma. Oncotarget. 2018;9(2):2603–2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]