Abstract
The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors (TFs) have been identified and functionally characterized in many plants. However, no comprehensive analysis of the bHLH family in papaya (Carica papaya L.) has been reported previously. Here, a total of 73 CpbHLHs were identified in papaya, and these genes were classified into 18 subfamilies based on phylogenetic analysis. Almost all of the CpbHLHs in the same subfamily shared similar gene structures and protein motifs according to analysis of exon/intron organizations and motif compositions. The number of exons in CpbHLHs varied from one to 10 with an average of five. The amino acid sequences of the bHLH domains were quite conservative, especially Leu-27 and Leu-63. Promoter cis-element analysis revealed that most of the CpbHLHs contained cis-elements that can respond to various biotic/abiotic stress-related events. Gene ontology (GO) analysis revealed that CpbHLHs mainly functions in protein dimerization activity and DNA-binding, and most CpbHLHs were predicted to localize in the nucleus. Abiotic stress treatment and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) revealed some important candidate CpbHLHs that might be responsible for abiotic stress responses in papaya. These findings would lay a foundation for further investigate of the molecular functions of CpbHLHs.
Keywords: Papaya, Genome-wide analysis, bHLH transcription factors, Abiotic stress, Expression analysis
Introduction
Since plants are unable to move, plant growth and development are regularly affected by abiotic and biotic stresses, which impair yields and result in losses to farmers. For better growth and development, plants have to make use of a series of physiological and biochemical processes in their responses to multiple abiotic stresses by regulating gene expression (Agarwal et al., 2006; Feller et al., 2011; Pires & Dolan, 2010). Previous studies have demonstrated that these physiological and biochemical mechanisms are more likely to be a polygenic cooperative defense response induced by various stresses, rather than the single response of a single gene (Zhang, Creelman & Zhu, 2004). Therefore, the traditional method of obtaining the stress tolerance of plants by modification a single resistance/sensitive gene is limited. Comprehensive analysis of important gene families are very important for molecular breeding.
As an important and popular fruit, papaya is famous for its high nutritional and medical values. Papaya is widely grown in southern China, the tropics and subtropics areas, and its demand is increasing every year. However, the production and quality of papaya were often threatened by various abiotic stresses, such as salt, drought, and cold. These stresses often cause severe economic losses in papaya production in China. Therefore, it is very important to study the functions of gene families that involved in abiotic stresses response in papaya. Since obtaining the whole genome sequences of papaya (Ming et al., 2008), several important gene families have been identified by the tool of genome-wide analysis in papaya, including Aux/IAA gene family, ARF family, SQUAMOSA promoter binding protein-like (SPL) gene family, NBS resistance gene family and NPR1 family. These families were essential for papaya fruit ripening, flower and fruit development, fitness and disease resistance (Liu et al., 2017a; Liu et al., 2015; Peraza-Echeverria, Santamaría & Fuentes, 2012; Porter et al., 2009; Xu et al., 2020).
In various stresses regulation network and signaling pathways, transcription factors (TFs) are important proteins that regulate gene expression by activating and repressing related downstream genes. Among them, WRKY and bHLH families are the most common TF families in higher plants (Kosugi & Ohashi, 2002). The WRKY transcription factors has been reported to be related to abiotic and biotic stresses responses in papaya (Pan & Jiang, 2014). Basic/helix-loop-helix (bHLH) TFs are widely found in almost all eukaryotes and are the second largest TFs family in plants (Carretero-Paulet et al., 2010; Feller et al., 2011; Jones, 2004; Pires & Dolan, 2010). The bHLH superfamily proteins are defined by one highly conserved bHLH domain, which comprises approximately 60 amino acids in length and contains two different functional regions: the basic region and the HLH region (Li et al., 2006; Toledo-Ortiz, Huq & Quail, 2003). The basic region is located at the N-terminal end of the bHLH domain and consists approximately 15 amino acids. It is a DNA-binding region that enables bHLH TFs to bind to a specific E-boxes (CANNTG) (Atchley & Fitch, 1997; Atchley, Terhalle & Dress, 1999). The HLH region, at the C-terminal end, is mainly composed of hydrophobic residues, containing two amphipathic α-helices linked by a loop region that has variable sequences and acts as a dimerization domain (Heim et al., 2003; Li et al., 2006). Outside of the two conserved regions, the rest of the bHLH protein sequences are usually very different (Morgenstern & Atchley, 1999).
In animals, the bHLH TFs can be divided into six main groups (designated A to F) based on phylogenetic analysis, functional properties and DNA-binding specificity (Atchley & Fitch, 1997). These bHLH groups can be divided into several small subfamilies (Ledent & Vervoort, 2001; Simionato et al., 2007). The bHLHs mainly function in sensing the external environment, cell cycle regulation and tissue differentiation (Amoutzias, Robertson & Bornberg-Bauer, 2004; Atchley & Fitch, 1997; Stevens, Roalson & Skinner, 2008; Vervoort & Ledent, 2001). Compared to animals, the research on bHLH proteins in plants is limited, even the exact number subfamilies of bHLH TFs has not been determined. Generally, the bHLH proteins is thought to cover 15–25 subfamilies (Buck & Atchley, 2003; Pires & Dolan, 2010), but some atypical bHLHs have extended the number to 32 based on phylogenetic analysis in plants (Carretero-Paulet et al., 2010). With the availability of genome sequence data and the rapid development of molecular biology, increasing numbers of bHLH subfamily genes have been identified and characterized in a wide range of plant species, including Arabidopsis (Toledo-Ortiz, Huq & Quail, 2003), peanut (Gao et al., 2017), apple (Mao et al., 2017), tomato (Sun, Fan & Ling, 2015), potato (Wang et al., 2018b), peach (Zhang et al., 2018), grapes (Wang et al., 2018a), sweet orange (Geng & Liu, 2018), and bamboo (Cheng et al., 2018). The results from these research have shown that bHLH TFs have versatile biological functions, such as regulating light morphogenesis (Leivar et al., 2008; Roig-Villanova et al., 2007), hormone signals (Friedrichsen et al., 2002; Lee et al., 2006), the developmental of root (Feng et al., 2017) and anther (Farquharson, 2016), regulating epidermal cell fate determination (Bernhardt et al., 2003), participating in various biotic and abiotic stress responses (Jiang, Yang & Deyholos, 2009; Liu et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2018b), etc.
In recent years, some studies demonstrated that bHLH transcription factors play important roles in the stress-related regulation network and signaling pathways in many species. However, no systematic analysis of the bHLH TFs have previously been performed in papaya. In this study, a total of 73 CpbHLH genes were identified in papaya, and phylogenetic analyses were carried out to analyze the relationships among these genes. Meanwhile, gene structure, protein physicochemical properties and conserved motifs, the cis-element of the promoter region, and gene ontology (GO) analysis were investigated. Furthermore, to analyze the functions of CpbHLHs responsible for responding to abiotic stresses, the expression profiles of 22 selected genes under salt, drought, ABA and cold stresses were investigated by using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). We identified several important candidate genes that might be responsible for abiotic stress responses. We completed the first comprehensive genome-wide analysis of the bHLH gene family in papaya, and our results provide information necessary for further functional research of the bHLH family in papaya.
Materials & Methods
Identification of CpbHLH genes, gene structure and physicochemical analysis
Papaya (Carica papaya L.) bHLH protein sequences were downloaded from the Plant TFDB V4.0 database (Jin et al., 2017). Furthermore, we used the SMART online software (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) and the InterProScan tool (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/pfa/iprscan/) to identify integrated bHLH domains in putative papaya bHLH proteins. The physicochemical properties of CpbHLH proteins were predicted by ProPAS (Wu & Zhu, 2012). The genomic sequences, ID numbers and coding sequences (CDS) corresponding to each predicted CpbHLH gene were obtained from the Phytozome database (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html). The intron numbers, exon–intron organizations and locations of the CpbHLH genes were analyzed by Gene Structure Display Server (GSDS) v2.0 (Hu et al., 2015).
Phylogenetic tree building, motif identification and multiple sequence alignment
To research the phylogenetic relationship of CpbHLH proteins, protein sequences of papaya were pre-aligned using HMM align (Eddy, 1998) and the pHMM HLH ls.hmm from PFAM (https://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00010) to identify the domains of bHLH TFs. Based on the manually aligned bHLH region of 158 bHLH proteins from Arabidopsis and 173 from rice (Pires & Dolan, 2010), the identified bHLH domains were later aligned using MAFFT v7.305b (Kaotoh, Kuma & Miyata, 2002) with default settings. Phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the neighbor-joining method using FastTree v2.1.11 (Price, Dehal & Arkin, 2009) with default settings. Bootstrapping with 1000 replicates was used to assess the statistical reliability of nodes in the tree. Multiple sequence alignment based on protein sequences of these 73 CpbHLH TFs was generated by MAFFT v7.305b (Kaotoh, Kuma & Miyata, 2002) with default settings.
To identify the conserved motifs among the CpbHLH proteins, we uploaded the 73 amino acid sequences of the CpbHLH family to the Multiple EM for Motif Elicitation (MEME, version 5.1.1) (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme). The parameter settings were as follows: zero or one, occurrence of a single motif per sequence; 3, maximum number of motifs found. All other parameters were set to the default values.
Promoter cis-acting regulatory element analysis and gene ontology (GO) annotation
To predict and compare the putative promoter cis-elements of bHLHs in papaya and Arabidopsis, the upstream 2,000 bp genomic DNA sequences of 73 CpbHLH genes in papaya, and 47 AtbHLH genes in Arabidopsis (the putative orthologous genes corresponding to CpbHLHs) were downloaded and then submitted to the PlantCARE (Magali et al., 2002). The GO annotations of papaya bHLH proteins were downloaded from AgriGOv2.0 (http://systemsbiology.cau.edu.cn/agriGOv2/download/508_slimGO). For GO enrichment analysis, the full-length protein sequences of papaya bHLH were blasted against Arabidopsis proteins with default parameters. The best hits were submitted to AgriGOv2.0 for GO enrichment analysis (Tian et al., 2017). Fisher’s exact test was used to evaluate enriched GO terms. GO terms include three aspects: biological process, cellular component and molecular function.
Plant materials, growth conditions and stress treatments
In this experiment, stems with axillary buds were selected as explants from two-year-old ‘Yi Chi Gua’ papaya trees grown under standard field conditions in the Institute of Fruit Tree Research, Guangdong Academy of Agriculture Science, Guangzhou, China, and cultured in vitro to obtain the complete papaya seedlings with normal leaves and roots using tissue culture techniques. Healthy and uniform papaya seedlings were used for different treatments. For the selection of stress conditions for papaya, we designed different gradients of stress conditions for pre-experiments: the concentration gradients of salt stress are 100 mM Nacl, 200 mM Nacl, and 300 mM Nacl; the concentration gradients of PEG6000 (to mimic drought stress) are 15% PEG6000, 20% PEG6000, 25% PEG6000 and 30% PEG6000; the concentration gradients of ABA are 50 µM ABA, 100 µM ABA and 150 µM ABA; the temperature gradients are 0 °C, 4 °C and 10 °C, and finally determined the suitable stress conditions used in this manucript. For salt, drought and ABA stresses, seedlings were treated with MS liquid medium containing 200 mM Nacl, 25% PEG6000 and 100 µM ABA for 2 h respectively, and then the roots were collected. For cold treatment, seedlings were subjected to 4 °C for 2 h and the leaves were collected. All of the collected materials were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C for RNA isolation. Untreated seedlings were used as the control groups. Three biological replications were carried out for each treatment.
RNA extraction and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis
Total RNA from papaya after different treatments was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). The extracted RNA was treatment with DNase (TaKaRa), and then reverse transcribed into cDNA using the PrimeScriptTM RT Reagent Kit (TaKaRa). The qRT-PCR was conducted on the ABI StepOne Real Time PCR system using 2X SG Fast qPCR Master Mix (High Rox) (TaKaRa) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. TATA binding protein 2 (CpTBP2) amplification was used as an internal control (Zhu et al., 2012). The qRT-PCR reactions used three biological replicates, and each biological repeat had three technical replicates. Gene-specific primers for qRT-PCR of the 22 CpbHLH genes were designed based on the CDSs of the CpbHLH genes using Primer Premier 5.0 (Data S1). The relative expression levels of each gene were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method, the raw data was showed in File S1.
Results
Identification and characterization of CpbHLHs
A total of 105 putative bHLH transcription factors of papaya (C. papaya) were downloaded from the PlantTFDBv2.0 (http://planttfdb.cbi.pku.edu.cn/). To verify the reliability of these results, the 105 Cp bHLH proteins sequences were filtered by Interproscan and SMART domain annotation, and a total of 73 predicted CpbHLH proteins were identified. They were named CpbHLH001 to CpbHLH073 at random except for 32 proteins that were explicitly excluded by Interproscan and SMART (Table S1). The detailed information on these predicted Cp bHLHs, including protein ID, locus ID, opening reading frame (ORF) lengths, amino acid sequences/lengths, molecular weight, isoelectric point and exon/intron numbers, are listed in Data S2. In previous studies, 129/132, 188, 159, 147, 124, 95, 94 and 56 bHLH genes were identified in peanut (Gao et al., 2017), apple (Mao et al., 2017), tomato (Sun, Fan & Ling, 2015), Arabidopsis (Toledo-Ortiz, Huq & Quail, 2003), potato (Wang et al., 2018b), peach (Zhang et al., 2018), grapes (Wang et al., 2018a) and sweet orange (Geng & Liu, 2018), respectively. Compared with the above dicotyledonous plants, the density of bHLHs genes in papaya genome was about 0.26%, which is lower than the density of peanut (Gao et al., 2017), apple (Mao et al., 2017), tomato (Sun, Fan & Ling, 2015), Arabidopsis (Toledo-Ortiz, Huq & Quail, 2003), potato (Wang et al., 2018b) and sweet orange (Geng & Liu, 2018), and similar to peach (Zhang et al., 2018) and wine grapes (Wang et al., 2018a) (Table 1). This is probably associated with the whole-genome duplications during evolution. Among the above plants, some plants with recent whole-gene duplication like peanut, apple, tomato, Arabidopsis, potato and sweet orange while the plants without whole-gene duplication like papaya, peach and wine grapes.
Table 1. Summary of TFs identified from dicotyledonous plant species with genome sequences.
| Plant species | Common name | bHLH | Proteins | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. papaya | Papaya | 73 | 27829 | 0.26 |
| A. ipaensis/A. duranensis | Peanut | 129/132 | 7243 | 1.78/1.82 |
| Malus x domestica | Apple | 188 | 15173 | 1.24 |
| S. lycopersicum | Tomato | 159 | 15722 | 1.01 |
| A. thaliana | Arabidopsis | 147 | 32125 | 0.46 |
| S. tuberosum | Potato | 124 | 17445 | 0.71 |
| P. persica | Peach | 95 | 28299 | 0.34 |
| V. vinifera | Wine Grapes | 94 | 47097 | 0.20 |
| C. sinensis | Valencia Orange | 56 | 13522 | 0.41 |
To further characterize the bHLHs in papaya, the physicochemical properties of these putative proteins were analyzed and are shown in Data S2. The size of deduced CpbHLHs ranged from 100 (CpbHLH053) to 679 (CpbHLH068) amino acids, the corresponding molecular weights from 11.525 KDa to 75.899 KDa. The predicted theoretical isoelectric points (PI) values of CpbHLHs were between 4.71(CpbHLH028) and 11.07(CpbHLH003). Similar molecular weights and isoelectric points have been made in potato (Wang et al., 2018b). And all of predicted CpbHLH proteins were hydrophilic characteristic proteins, the grand average of hydropathy values were negative, ranging from −0.2098(CpbHLH033) to −1.0125(CpbHLH006). Similar result has been made in Brachypodium distachyo n (Niu et al., 2017). That is, the predicted CpbHLH proteins showed diversities in their length, molecular weight, PI and the grand average of hydropathy values.
Phylogenetic analysis, gene structure, conserved motifs analysis and multiple sequence alignment of CpbHLHs
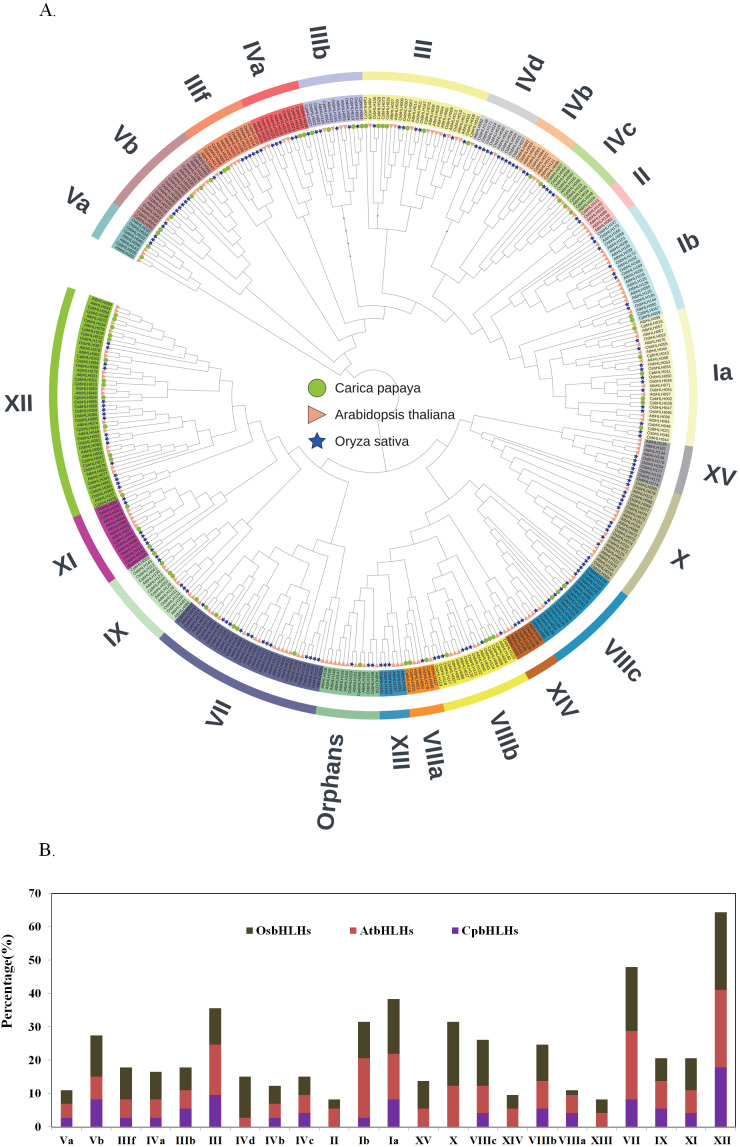
To evaluate the evolutionary relationships of the CpbHLH proteins, a neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree was generated using conserved bHLH domains from papaya, Arabidopsis and rice. The phylogenetic tree showed that the 73 CpbHLH members were clustered into 18 subfamilies with one orphan (Fig. 1A and Data S3), consistent with the earlier results showing that the bHLH subfamily in plants can be divided into 15–25 subfamilies (Pires & Dolan, 2010). Previous research have named the bHLH subfamilies using English letters (Li et al., 2006; Mao et al., 2017), Roman numerals (Song et al., 2017; Sun, Fan & Ling, 2015), or Arabic numerals (Chen et al., 2015; Toledo-Ortiz, Huq & Quail, 2003), In this study, we named CpbHLH subfamilies using Roman numerals. As shown in Fig. 1, the subfamily XII was the largest subfamily among all three species, and all of subfamilies include at least two species. In papaya, none of the bHLHs were grouped into IV d, II, X V, X, XI V and XIII subfamilies compared to rice and Arabidopsis, which may be due to these bHLHs were lost during the process of evolution.
Figure 1. Phylogenic and family members analysis of bHLHs from papaya, rice and Arabidopsis.
(A) The 73 CpbHLHs are clustered into 18 subfamilies. Phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the neighbor-joining method. Bootstrapping with 1,000 replicates was used to assess the statistical reliability of nodes in the tree. (B) Comparison of bHLH family members from papaya, rice and Arabidopsis. Different colors represent the different plants. Black: OsbHLHs, red: AtbHLHs, purple: CpbHLHs.
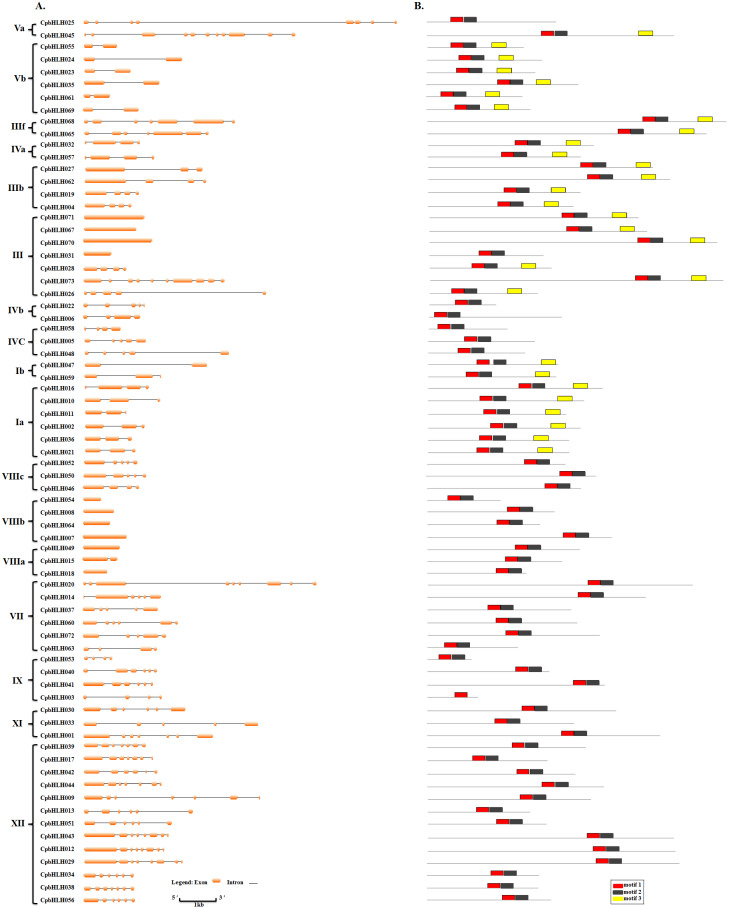
Exon/intron organization, as a type of structural divergence, plays an important role in the evolution of multiple gene families (Xu et al., 2012). The annotation features of the CpbHLH genes were submitted to Gene Structure Display Server (GSDS) together to show their gene structures. As described in Data S2 and Fig. 2A, the number of introns varied from zero to ten, representing a complex distribution pattern. Most (63 (86.3%)) of the CpbHLHs were found to possess introns among the 73 CpbHLH genes, while 10 (13.7%) of the genes were intron-less, 8 (11.0%) genes contained one intron, and the remaining genes had two or more introns. In addition, members of the same subfamily also displayed similar intron distribution patterns in view of the full-length genome sequences. For instance, all of the CpbHLHs in subfamily V b had one intron and two exons, the whole members of subfamily III f had six introns and seven exons, the IV a subfamily members showed three introns and four exons, and all members of VIII b subfamily consisted only one exon.
Figure 2. Gene structure and motif distribution of the papaya bHLH family.
(A) Exon-intron organization of CpbHLH genes. Exons and introns are presented as filled orange lines and thin black single lines, respectively. The brackets and Roman numerals separate each subfamily and clearly present the member conservation of each subfamily. (B) Arrangements of conserved motifs in 73 CpbHLH proteins. Three predicted motifs are represented by different colored boxes, motif 1 (red block), motif 2 (black block) and motif 3 (yellow block).
Most importantly, members of the same bHLHs subfamily are usually participated in the same signaling pathway or biological process, and the functions of these members are often partially or totally redundant (Pires & Dolan, 2010). For example, AtbHLH10, AtbHLH89 and AtbHLH91, corresponding rice orthologs OsbHLH141, OsbHLH142 are members of subfamily II, they are all involved in the process of pollen development (Li et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2015). Especially in Arabidopsis, there is no obvious phenotype in single mutant of AtbHLH10, AtbHLH89 or AtbHLH91, only their various double or triple mutants showed the phenotype of pollen development deficiency (Liu et al., 2017). In subfamily III b, OsbHLH001 (OsICE2), OsbHLH002 (OsICE1), CpbHLH027, CpbHLH062, AtbHLH116 (ICE1) and AtbHLH33 (ICE2) were clustered within one clade. In previous studies, AtbHLH116(ICE1) and AtbHLH33(ICE2) and corresponding orthologs in rice (Os bHLH001/OsICE2, OsbHLH002/OsICE1) have been reported to function in the stress of chilling (Chinnusamy et al., 2003; Deng et al., 2017; Fursova, Pogorelko & Tarasov, 2009; Li et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2017). And we also found transcripts of CpbHLH027 and CpbHLH062 were increased under chilling stress in this study, implying that CpbHLH027 and CpbHLH062 are involved in the process of chilling stress in papaya.
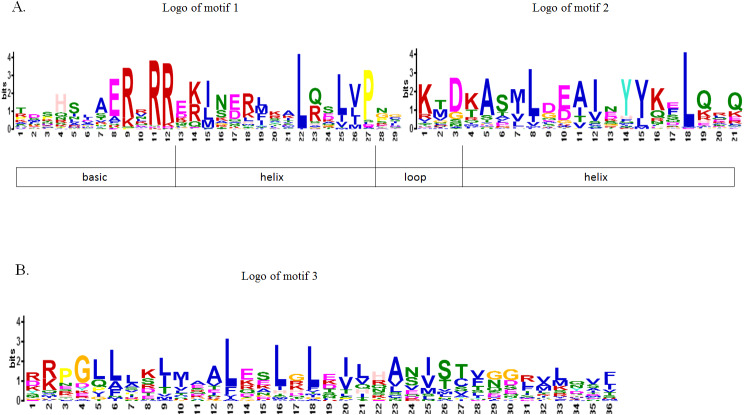
To further study the sequence characteristics of the predicted bHLH domains at the amino acid level, we carried out a multiple sequence alignment of the 73 predicted CpbHLH protein sequences (Fig. 3). The result showed that the 73 putative CpbHLH proteins contained two conserved regions in the bHLH domains: the basic region plus helix 1 and the loop region plus helix 2 (Fig. 3 and Table S2). Additionally, we used the online MEME program to identify the conserved motifs (Bailey & Elkan, 1994). The result also showed that most of the sequences (exclude CpbHLH003) exhibited two highly conserved motifs: one is contains 29 amino acids, and the other consists of 21 amino acids, are shown in red and black blocks, respectively (Fig. 2B). Among the two motifs, motif 1 comprises basic residues and helix 1, and motif 2 comprises a loop and helix 2. And the space between motif 1 and 2 consists of a loop, which is variable in length in some bHLH proteins. The sequence logos of motif 1 (in red) and motif 2 (in black) are shown in Fig. 4A. The backbones of motif 1 and 2 are also conserved in most plant species (Guo & Wang, 2017; Heim et al., 2003; Sun, Fan & Ling, 2015), and these highly conserved residues in bHLH domains may be responsible for protein dimerization (Heim et al., 2003).
Figure 3. Multiple sequence alignment of the bHLH domains in papaya.
Amino acids with more than 50% identity are labeled with colored boxes.
Figure 4. Motif composition and logos of papaya bHLH proteins.
(A) The logos of motif 1 and 2, which together constitute the bHLH domain in papaya. The overall height of the character represents the conservation of an amino acid at the specific position. Each color of the English letters represents a type of amino acid residue. (B) The logo of motif 3, which is another conserved motif.
Besides these two common conserved motifs, some CpbHLHs that are mainly distributed into eight subfamilies (including V a, V b, III f, IV a, III b, III, I b and I a subfamilies) harbor another conserved motif (motif 3) with a length of 36 amino acids. The motif 3 is indicated by the yellow blocks and the sequence logo is visualized as logo3 (Fig. 2B and Fig. 4B). This result is accord with the previous studies that members of a given subfamily exhibited another conserved nonbHLH motif (motif 3) in plant bHLH superfamily (Pires & Dolan, 2010). However, in papaya, members of the bHLH proteins have the same motif that is distributed into eight subfamilies, not just one subfamily. In addition, among the 73 CpbHLHs, one atypical bHLH protein (Cp bHLH003) exhibited incomplete bHLH domains, whereas the remaining 72 CpbHLH proteins all presented complete bHLH domains. Similar observations have been made in other plant species, such as peach and blueberry (Song et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2018).
Promoter analysis of bHLH genes in papaya
To further understand CpbHLHs functions and regulation patterns, cis-elements in CpbHLH genes promoter sequences were investigated. Regions of 2,000 bp upstream from the start codons of each CpbHLH gene were analyzed using PlantCARE. The results showed that the cis-elements could be divided into three main categories (Fig. 5A and Data S4). Category one contained a ubiquitous class of plant light responsive elements among which G-Box, G-box, GT1-motif and Box 4 were common in the CpbHLH promoters. Category two contained important elements that were involved in the process of stress-responsiveness, including MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility (MBS), low temperature response elements (LTR), defense and stress responsive elements (TC-rich) and wound-responsive elements (WUN-motifs). In addition, more than ten kinds of hormone-responsive cis-elements were identified (e.g., gibberellin-GA, auxin-IAA, methyl jasmonate-MeJA, salicylic acid-SA, and abscisic acid-ABA). Among them, the most common response elements were ABA (ABRE), MeJA (CGTCA-motif and TGACG-motif) and SA (TCA-element and SARE), which included 158 (29.15%), 128 (23.62%) and 53 (9.78%), respectively (Fig. 5B). Category three contained plant growth and development elements, such as anaerobic induction elements (ARE), O2-site, CAT-box and so on. Additionally, we also analyze the cis-elements in the promoter regions of putative orthologous genes that corresponding to CpbHLH in Arabidopsis, and the similar result has been obtained in Arabidopsis (Fig. S1 and Data S4). There also existed three main categories: plant light, abiotic and biotic stresses and plant growth and development responsive elements. And the percentage of most stress-responsive elements in Arabidopsia were similar to papaya, including ABA responsive elements, drought-responsive elements, wound-responsive elements, low temperature-responsive elements and IAA responsive elements, implying that most of the promoter cis-elements of bHLH family were conserved in Arabidopsis and papaya.
Figure 5. Cis-acting element analysis of the promoter of bHLH genes in papaya.
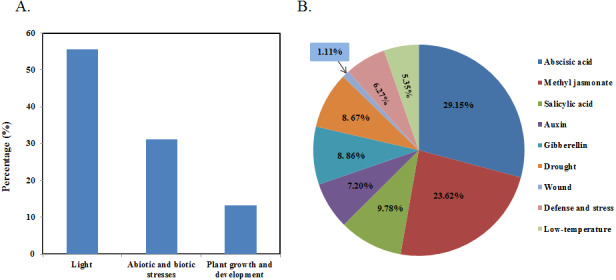
(A) Percentage of total cis-acting elements in the promoter region of CpbHLH genes. (B) The percentage of each cis-acting element in the abiotic and biotic stresses categories. Abscisic acid (29.15%), methyl jasmonate (23.62%), salicylic acid (9.78%), auxin (7.20%), gibberellin (8.86%), drought (8.67%), wound (1.11%), defense and stress (6.27%), low temperature (5.35%).
GO annotation of CpbHLH proteins
To understand the functions of papaya bHLHs, we performed a GO annotation of CpbHLHs, and the results are shown in Data S5 . A total of 70 CpbHLHs were involved in protein dimerization activity (GO: 0046983). The result is consistent with the earlier studies, which show that the HLH domain was necessary for protein dimerization and DNA binding (Murre, Mccaw & Baltimore, 1989). Some conserved amino acid residues are important to the function of bHLH proteins, especially the Leu-27 in helix 1 and the Leu-73 in helix 2 (Carretero-Paulet et al., 2010). In this study, we found 72 (out of 73) CpbHLH proteins have Leu-27 (corresponding to Leu-27 in AtbHLHs), and all of the CpbHLH proteins have Leu-63 (corresponding to Leu-73 in AtbHLHs) (Fig. 3 and Table S2). Because of a lack of reported experimental data and databases, we used Arabidopsis as the reference species to perform a GO enrichment analysis of CpbHLH proteins, and 54 of 73 predicted CpbHLH proteins were obtained with results compared to Arabidopsis. We summarized the results in Fig. 6 and Data S6. The majority of predicted CpbHLH proteins were enriched in DNA binding. Almost all of the predicted CpbHLH proteins (37, 68.5%) were predicted to localize in the nucleus, whereas the remaining predicted CpbHLH proteins were located in other organelles, including plastids, the cytoplasm, and chloroplasts. Additionally, some predicted CpbHLH proteins existed in multiple cellular components. For example, CpbHLH013 was located in three cellular components: chloroplasts, part of the cytoplasm, and the nucleus, which may reflect its multiple functions in various biological processes. The metabolic processes involved the greatest number of putative CpbHLH proteins (47, 87.0%). Biosynthetic processes and gene expression involved the second greatest number of putative CpbHLH proteins (46, 85.2%). In addition, CpbHLH proteins could respond to stimulus, morphogenesis, cell differentiation, and developmental process.
Figure 6. Gene ontology (GO) annotation of Cp bHLH proteins.
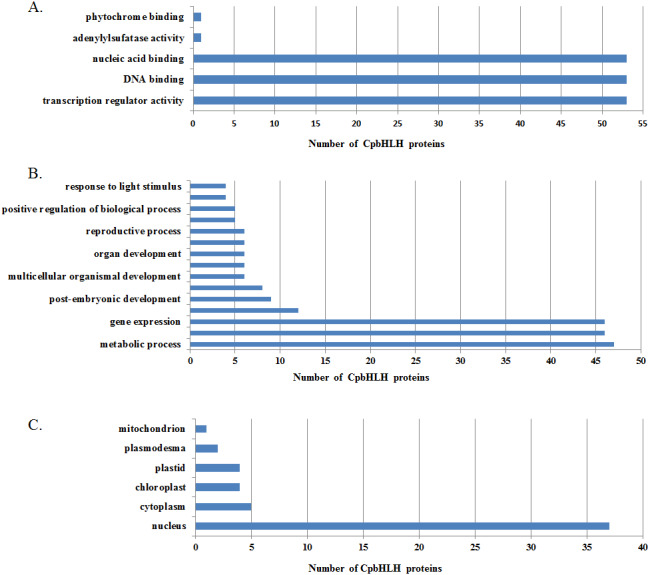
The annotation was performed on three categories: (A) molecular function, (B) biological processes and (C) cellular components.
Expression analysis of bHLH superfamily genes under different abiotic stresses
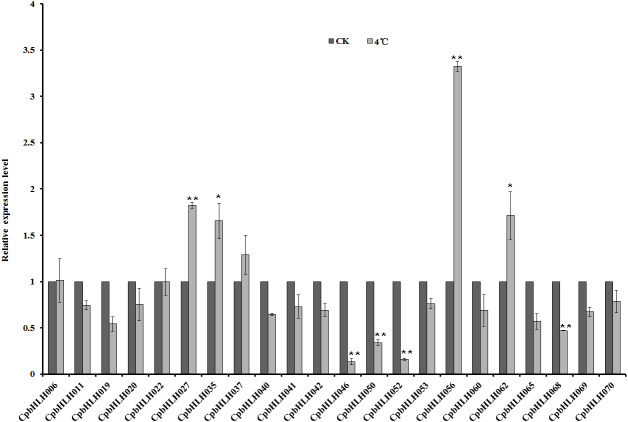
The bHLH proteins have been characterized functionally in many plants with a vital role in the regulation of diverse biological processes, but little is known about their role in papaya. To analyze the functions of CpbHLHs responding to abiotic stresses, the expression profiles of 22 selected genes under salt, drought, ABA and cold stresses were investigated by using qRT-PCR (Table 2 and Fig. 7). The results showed that 4 (CpbHLH011, CpbHLH022, CpbHLH027 and CpbHLH056) of 22 CpbHLH mRNAs were increased, and 3 CpbHLH (CpbHLH020, CpbHLH053 and CpbHLH062) mRNAs were reduced more than 2-fold in salt (200 mM Nacl) treated papaya seedlings. Under drought stress (25% PEG), 8 (CpbHLH011, CpbHLH022, CpbHLH027, CpbHLH046, CpbHLH050, CpbHLH052, CpbHLH056 and CpbHLH068) of 22 CpbHLH mRNAs were upregulated, and 3 CpbHLH (CpbHLH020, CpbHLH042 and CpbHLH053) mRNAs were downregulated more than 2-fold. Under ABA treatment (100 µM), 3 (CpbHLH027, CpbHLH052 and CpbHLH056) of 22 CpbHLH mRNAs were upregulated, and 5 CpbHLH (CpbHLH019, CpbHLH020, CpbHLH042, CpbHLH053 and CpbHLH062) mRNAs were downregulated. Under cold stress (4 °C), there were 4 CpbHLH genes (CpbHLH027, CpbHLH035, CpbHLH056 and CpbHLH062) whose expression increased more than 1.5-fold, and 4 CpbHLH (CpbHLH046, CpbHLH050, CpbHLH052 and CpbHLH068) mRNAs were reduced more than 2-fold.
Table 2. Expression levels of CpbHLH genes under salt, drought and ABA stresses.
| The name of CpbHLHs | CK | NaCl (200 mM) | PEG (25%) | ABA (100 µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpbHLH006 | 1 | 0.74 ± 0.13 | 0.95 ± 0.15 | 0.75 ± 0.07 |
| CpbHLH011 | 1 | 2.45 ± 0.04 | 4.06 ± 0.12 | 1.66 ± 0.12 |
| CpbHLH019 | 1 | 0.80 ± 0.03 | 0.64 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.02 |
| CpbHLH020 | 1 | 0.20 ± 0.003 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.01 |
| CpbHLH022 | 1 | 4.21 ± 0.03 | 3.05 ± 0.03 | 1.54 ± 0.08 |
| CpbHLH027 | 1 | 4.49 ± 0.09 | 2.32 ± 0.06 | 2.27 ± 0.12 |
| CpbHLH035 | 1 | 1.62 ± 0.08 | 1.79 ± 0.07 | 0.71 ± 0.02 |
| CpbHLH037 | 1 | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 1.04 ± 0.01 | 1.92 ± 0.07 |
| CpbHLH040 | 1 | 1.38 ± 0.04 | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 0.51 ± 0.03 |
| CpbHLH041 | 1 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.76 ± 0.03 | 0.70 ± 0.03 |
| CpbHLH042 | 1 | 0.55 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.04 | 0.26 ± 0.03 |
| CpbHLH046 | 1 | 0.78 ± 0.06 | 5.46 ± 0.10 | 0.53 ± 0.03 |
| CpbHLH050 | 1 | 0.53 ± 0.04 | 11.86 ± 0.10 | 1.18 ± 0.02 |
| CpbHLH052 | 1 | 1.64 ± 0.06 | 8.71 ± 0.06 | 4.42 ± 0.13 |
| CpbHLH053 | 1 | 0.44 ± 0.04 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 0.19 ± 0.01 |
| CpbHLH056 | 1 | 7.11 ± 0.04 | 32.65 ± 0.45 | 12.22 ± 0.21 |
| CpbHLH060 | 1 | 0.89 ± 0.07 | 0.76 ± 0.05 | 0.75 ± 0.11 |
| CpbHLH062 | 1 | 0.38 ± 0.02 | 0.65 ± 0.02 | 0.30 ± 0.02 |
| CpbHLH065 | 1 | 1.64 ± 0.06 | 1.04 ± 0.03 | 0.52 ± 0.05 |
| CpbHLH068 | 1 | 1.72 ± 0.05 | 2.37 ± 0.04 | 1.39 ± 0.07 |
| CpbHLH069 | 1 | 0.68 ± 0.07 | 0.89 ± 0.18 | 0.52 ± 0.08 |
| CpbHLH070 | 1 | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 1.17 ± 0.07 | 1.47 ± 0.04 |
Notes.
Quantitative RT-PCR was used to investigate the expression levels (shown in fold change) of the CpbHLHs. The expression level in the control (CK) was set at 1.0. The means of three replicates of qRT-PCR and standard deviations (SD) values are shown.
Figure 7. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of 22 selected CpbHLH genes under cold stress condition (4 °C).
The data are expressed as means ± SD of three independent biological determinations. Untreated seedlings were used as the control groups. ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01 (Student’s t test) indicate significant differences between treated seedlings and control groups.
Interestingly, a few transcripts of CpbHLH responded to all or multiple stresses. For instance, CpbHLH056 was sensitive to all four stresses and was upregulated distinctly under the four stresses. The orthologue of CpbHLH056 in Arabidopsis is BEE1 (AtbHLH044) (Fig. 1), which has been functionally characterized in previous reports. At low temperatures, BEE1 is a positive regulator of flavonoid accumulation (Petridis et al., 2016), which is consistent with our results. In addition, BEE1, BEE2 and BEE3 are functionally redundant positive regulators of BR (brassinosteroid) signaling, but these transcripts are repressed by ABA (Friedrichsen et al., 2002). However, we found the transcription of CpbHLH056 was notably upregulated (>10-fold) under ABA treatment. More interestingly, CpbHLH042, which is an orthologue of BEE2 (Fig. 1), was distinctly repressed by ABA (approximately 4-fold). These results suggested that CpbHLH056 and CpbHLH042 may provide different functionalities compared to Arabidopsis. Additionally, CpbHLH027 was also upregulated distinctly under four stresses. In Arabidopsis, the orthologue of CpbHLH027 is AtbHLH116 (ICE1) (Fig. 1), which can be induced by Nacl, ABA and cold stresses, playing an important role in the cold-responsive signaling pathway via an ABA-independent pathway (Chinnusamy et al., 2003). There are two orthologues of CpbHLH027 in rice, one ortholog is OsICE2/OsbHLH001, is induced by salt stress, and its overexpression can enhanced the tolerance to freezing and salt stress (Deng et al., 2017; Li et al., 2010). OsICE1/OsbHLH002 is another ortholog in rice, which is induced by chilling stress. OsbHLH002 can positively regulates cold signaling via targeting OsTPP1, which encodes a keyenzyme for trehalose biosynthesis (Zhang et al., 2017). These results implied CpbHLH027 plays essential roles in abiotic stresses in papaya. In addition, the transcript of CpbHLH062 was also increased under cold treatment, its orthologue is AtbHLH033/ICE2, which involving the cold response and the ABA pathway (Fursova, Pogorelko & Tarasov, 2009; Kurbidaeva, Ezhova & Novokreshchenova, 2014), implying the CpbHLH062 may involved in the cold stress. Cp bHLH053 was downregulated under salt, drought and ABA stresses. The orthologue of CpbHLH053 is AtbHLH129 (Fig. 1), which is a transcription repressor that negatively regulates the ABA response in Arabidopsis (Tian et al., 2015), implying CpbHLH053 may have the similar function with the AtbHLH129 in the process of ABA response.
We should also noticed a few CpbHLHs that showed distinct increases or decreases in their mRNA levels under different treatments, and these CpbHLHs′ orthologues have not been reported in previous studies. For instance, CpbHLH050 is notably upregulated (>10-fold) under PEG treatment, CpbHLH046 is upregulated by PEG treatment, but sharply down regulated under ABA and cold treatments, implying these genes may have additional functions than response to drought by regulating root development. CpbHLH020 and CpbHLH053 were downregulated (>2-fold) by Nacl, PEG and ABA stresses distinctly. We should also pay attention to these genes in the following research.
Discussion
Transcription factors (TFs) play key roles in the stress regulation network and signal pathways in plants. Basic/helix-loop-helix (bHLH) TFs are the second largest TFs family in plants and have been identified in many species (Cheng et al., 2018; Gao et al., 2017; Geng & Liu, 2018; Mao et al., 2017; Sun, Fan & Ling, 2015; Toledo-Ortiz, Huq & Quail, 2003; Wang et al., 2018a; Wang et al., 2018b; Zhang et al., 2018). However, the bHLH TF family has not previously been reported in papaya (Carica papaya L.). In this paper, we found 73 CpbHLH genes in papaya. This TF family seemed to be one of the moderately sized families compared with other plant species, which might be because of the papaya has a relatively small reference genome, the size is only 372 Mb (Ming et al., 2008). The gene evolution changes the gene organization. In this study, we found that CpbHLH genes were diverse in their number introns, ranging from 0 to 10 (Data S2). This result implied these genes may have undergone numerous of genetic evolution events, and the genes in different subfamilies may have different functions (Cheng et al., 2018). Most CpbHLHs in the same subfamily shared similar gene structures and protein motifs according to the analysis of exon/intron organizations and motif compositions (Figs. 2, 3 and 4), indicating that the functions of encoded proteins in each subfamily are probably stable. However, the conserved motif analysis showed that some CpbHLHs, which are mainly distributed in eight subfamilies (including V a, V b, III f, IVa, IIIb, III, I b and I a subfamilies) from the phylogenetic tree, harbor another conserved motif (motif 3) with a length of 36 amino acids (Figs. 2 and 4), indicating that these proteins may have additional functions.
Promoter cis-acting regulatory element analysis showed that cis-elements could be divided into three main categories: light responsive, abiotic and biotic stresses and plant growth and development. Especially in abiotic and biotic stresses, the most common response elements were ABA (29.15%), MeJA (23.62%) and SA (9.78%), suggesting that these phytohormones may play important roles in the regulation of papaya growth and development (Fig. 5 and Data S4). In addition, the promoter cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness analysis is consistent with the qRT-PCR results (Data S4 and Table 2), showing four genes (CpHLH020/-027/-053/-056) involved in abscisic acid response. Another two genes (CpHLH020/-062) were also identified that were involved in abscisic acid response by GO enrichment analysis and qRT-PCR (Data S6 and Table 2). We also identified a large number of cis-acting elements in CpbHLH genes that may respond to drought (MBS, 8.67%), which is also consistent with the qRT-PCR (including seven genes: CpbHLH027/-050/-056/-011/-068/-042/-053). Other genes also had important elements, including LTR, TC-rich and WUN-motifs, which indicated plant responses to low temperatures, defense stresses and wound-responsiveness, respectively. These results implied CpbHLH genes may have a wide range of functions in papaya growth, disease resistance, and response to environmental conditions. We also analyze the cis-elements in the promoter regions of putative orthologous genes in Arabidopsis (Fig. S1 and Data S4). And we compared the promoter cis-elements of bHLH genes in Arabidopsis, papaya and previously reported bamboo (Cheng et al., 2018). The result showed that the promoter cis- elements of bHLH genes in these three plants were divided into three categories, and most of elements were the same. These similar results implied that most of the promoter cis-elements of bHLH family were conserved in Arabidopsis, papaya and bamboo. The most notable is, the percentage of MeJA responsive cis-elements in papaya and Arabidopsis (23.62%, 30.61%) were less than bamboo (43.39%). And the percentage of SA responsive cis-elements in papaya and Arabidopsis (9.78%, 5.87%) were also less than bamboo (10.31%). SA is a phytohormone that plays important roles in plant defenses against pathogens (Pokotylo, Kravets & Ruelland, 2019). MeJA also has been identified as a vital cellular regulator that mediates defense processes (Cheong & Choi, 2003). So, the stress-responsive elements in papaya and Arabidopsis were corresponding less than bamboo, including drought-responsive elements, wound-responsive elements, low temperature-responsive elements, and defense and stress responsive elements. These results may help explain why papaya is more sensitive to external stresses compared to bamboo.
Many studies have shown that bHLH genes are involved in various abiotic and biotic stresses responses. We randomly selected 22 genes to investigate their expression profiles by using qRT-PCR under salt, drought, ABA and cold stresses (Fig. 7 and Table 2). The results revealed some candidate CpbHLH genes that might be responsible for abiotic stress responses in papaya. For example, CpbHLH027, CpbHLH062, AtbHLH116 (ICE1), AtbHLH33 (ICE2), OsbHLH001 (OsICE2) and OsbHLH002 (OsICE1) were clustered within one clade. Among them, AtbHLH116 (ICE1), AtbHLH33 (ICE2), OsbHLH001 (OsICE2) and OsbHLH002 (OsICE1) have been reported function in chilling stress in Arabidopsis and rice (Chinnusamy et al., 2003; Deng et al., 2017; Fursova, Pogorelko & Tarasov, 2009; Li et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2017). And the transcripts of CpbHLH027, CpbHLH062 were increased under chilling stress in this study, implying that CpbHLH027 and CpbHLH062 may be also involved in the process of chilling stress. The orthologue of CpHLH056 in Arabidopsis is BEE1 (At1G18400), which is a positive regulator of flavonoid accumulation (Petridis et al., 2016). BEE1, BEE2 and BEE3 are functionally redundant positive regulators of BR signaling, and their transcription is repressed by ABA in Arabidopsis (Friedrichsen et al., 2002). However, we found that the transcription of CpbHLH056 is notably upregulated (> 10-fold) under ABA treatment rather than downregulated in this study. These results imply that CpbHLH056 may involved in the process of ABA stress but has different function compared to Arabidopsis. We have also noticed a few candidate CpbHLHs that showed distinct increases or decreases in their mRNA levels under different treatments, and these CpbHLHs’ orthologues have not been reported in other plants. For instance, CpbHLH050, CpbHLH020, CpbHLH046, CpbHLH053, and so on. These findings provide important candidate genes/proteins necessary for further functional research on the bHLH family in papaya.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the study performed a genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors in papaya. As a result, a total of 73 bHLH genes were identified in papaya, and these CpbHLHs were classified into 18 subfamilies with one orphan, which was consistent with the earlier results showing that the bHLH subfamily in plants can be divided into 15–25 subfamilies. Almost all of the CpbHLHs in the same subfamily shared similar gene structures and protein motifs according to analysis of exon/intron organizations and motif compositions. These results further supported the classification predicted by the phylogenetic tree. Compared to rice and Arabidopsis, the amino acid sequences of the CpbHLH domains were quite conservative, especially Leu-27 and Leu-63. Promoter cis-element and GO annotation analysis revealed that most of the CpbHLHs could respond to various biotic/abiotic stress-related events. Abiotic stress treatment and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) assay further supported promoter cis-acting regulatory element and GO annotation analysis, revealed some important candidate CpbHLHs that might be responsible for abiotic stress responses in papaya. We completed the first comprehensive genome-wide analysis of the bHLH gene family in papaya, and our results provide information necessary for further functional research of the bHLH family in papaya.
Supplemental Information
Fisher’s exact test was used to evaluate enriched GO terms. GO terms include three aspects: biological process, cellular component and molecular function.
(A) Percentage of total cis-acting elements in the promoter region of At bHLH genes. (B) The percentage of each cis-acting element in the abiotic and biotic stresses categories.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Presidential Foundation of Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China (No. 201820), the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (No. 2019B020214005), and the Innovation Team Program of Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System in Guangdong Province of China (2019KJ116). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Additional Information and Declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Author Contributions
Min Yang conceived and designed the experiments, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, prepared figures and/or tables, authored or reviewed drafts of the paper, and approved the final draft.
Chenping Zhou and Hu Yang performed the experiments, analyzed the data, prepared figures and/or tables, authored or reviewed drafts of the paper, and approved the final draft.
Ruibin Kuang and Bingxiong Huang performed the experiments, analyzed the data, authored or reviewed drafts of the paper, and approved the final draft.
Yuerong Wei conceived and designed the experiments, authored or reviewed drafts of the paper, and approved the final draft.
Data Availability
The following information was supplied regarding data availability:
The raw data are available in the Supplementary Files.
References
- Agarwal et al. (2006).Agarwal PK, Agarwal P, Reddy MK, Sopory SK. Role of DREB transcription factors in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Reports. 2006;25:1263–1274. doi: 10.1007/s00299-006-0204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amoutzias, Robertson & Bornberg-Bauer (2004).Amoutzias GD, Robertson DL, Bornberg-Bauer E. The evolution of protein interaction networks in regulatory proteins. Comparative and Functional Genomics. 2004;5:79–84. doi: 10.1002/cfg.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchley & Fitch (1997).Atchley WR, Fitch WM. A natural classification of the basic helix-loop-helix class of transcription factors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1997;94:5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.10.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchley, Terhalle & Dress (1999).Atchley WR, Terhalle W, Dress A. Positional dependence, cliques, and predictive motifs in the bhlh protein domain. Journal of Molecular Evolution. 1999;48:501–516. doi: 10.1007/PL00006494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey & Elkan (1994).Bailey TL, Elkan C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology. 1994;2:28–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt et al. (2003).Bernhardt C, Lee MM, Gonzalez A, Zhang F, Lloyd A, Schiefelbein J. The bHLH genes GLABRA3 (GL3) and ENHANCER OF GLABRA3 (EGL3) specify epidermal cell fate in the Arabidopsis root. Development. 2003;130:6431–6439. doi: 10.1242/dev.00880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck & Atchley (2003).Buck MJ, Atchley WR. Phylogenetic analysis of plant basic helix-loop-helix proteins. Journal of Molecular Evolution. 2003;56:742–750. doi: 10.1007/s00239-002-2449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero-Paulet et al. (2010).Carretero-Paulet L, Galstyan A, Roig-Villanova I, Martinez-Garcia JF, Bilbao-Castro JR, Robertson DL. Genome-wide classification and evolutionary analysis of the bHLH family of transcription factors in Arabidopsis, poplar, rice, moss, and algae. Plant Physiology. 2010;153:1398–1412. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.153593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen et al. (2015).Chen YY, Li MY, Wu XJ, Huang Y, Ma J, Xiong AS. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix−loop−helix family transcription factors and their role in responses to abiotic stress in carrot. Molecular Breeding. 2015;35:125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng et al. (2018).Cheng X, Xiong R, Liu H, Wu M, Chen F, Hanwei Y, Xiang Y. Basic helix-loop-helix gene family: genome wide identification, phylogeny, and expression in Moso bamboo. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 2018;132:104–119. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.08.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong & Choi (2003).Cheong J-J, Choi YD. Methyl jasmonate as a vital substance in plants. Trends in Genetics. 2003;19:409–413. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(03)00138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnusamy et al. (2003).Chinnusamy V, Ohta M, Kanrar S, Lee BH, Hong X, Agarwal M, Zhu JK. ICE1: a regulator of cold-induced transcriptome and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Genes and Development. 2003;17:1043–1054. doi: 10.1101/gad.1077503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng et al. (2017).Deng C, Ye H, Fan M, Pu T, Yan J. The rice transcription factors OsICE confer enhanced cold tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Signaling & Behavior. 2017;12:e1316442. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2017.1316442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy (1998).Eddy SR. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics. 1998;14:755–763. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquharson (2016).Farquharson KL. A Domain in the bHLH transcription factor DYT1 is critical for anther development. The Plant Cell. 2016;28:997–998. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller et al. (2011).Feller A, Machemer K, Braun EL, Grotewold E. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. The Plant Journal. 2011;66:94–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng et al. (2017).Feng Y, Xu P, Li B, Li P, Wen X, An F, Gong Y, Xin Y, Zhu Z, Wang Y, Guo H. Ethylene promotes root hair growth through coordinated EIN3/EIL1 and RHD6/RSL1 activity in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2017;114:13834–13839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711723115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrichsen et al. (2002).Friedrichsen DM, Nemhauser J, Muramitsu T, Maloof JN, Alonso J, Ecker JR, Furuya M, Chory J. Three redundant brassinosteroid early response genes encode putative bHLH transcription factors required for normal growth. Genetics. 2002;162:1445–1456. doi: 10.1093/genetics/162.3.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fursova, Pogorelko & Tarasov (2009).Fursova OV, Pogorelko GV, Tarasov VA. Identification of ICE2, a gene involved in cold acclimation which determines freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 2009;429:98–103. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao et al. (2017).Gao C, Sun J, Wang C, Dong Y, Xiao S, Wang X, Jiao Z. Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix gene family in peanut and assessment of its roles in pod development. PLOS ONE. 2017;12:e0181843. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng & Liu (2018).Geng J, Liu JH. The transcription factor CsbHLH18 of sweet orange functions in modulation of cold tolerance and homeostasis of reactive oxygen species by regulating the antioxidant gene. Journal of Experimental Botany. 2018;69:2677–2692. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo & Wang (2017).Guo XJ, Wang JR. Global identification, structural analysis and expression characterization of bHLH transcription factors in wheat. BMC Plant Biology. 2017;17:90. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1038-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim et al. (2003).Heim MA, Jakoby M, Werber M, Martin C, Weisshaar B, Bailey PC. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in plants: a genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2003;20:735–747. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu et al. (2015).Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G. GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics. 2015;31:1296–1297. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Yang & Deyholos (2009).Jiang Y, Yang B, Deyholos MK. Functional characterization of the Arabidopsis bHLH92 transcription factor in abiotic stress. Molecular Genetics and Genomics. 2009;282:503–516. doi: 10.1007/s00438-009-0481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin et al. (2017).Jin J, Tian F, Yang DC, Meng YQ, Kong L, Luo J, Gao G. PlantTFDB 4.0: toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Research. 2017;45:D1040–D1045. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones (2004).Jones S. An overview of the basic helix-loop-helix proteins. Genome Biology. 2004;5:226. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-6-226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaotoh, Kuma & Miyata (2002).Kaotoh MK, Kuma K, Miyata T. MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Resarch. 2002;30:3059–3066. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosugi & Ohashi (2002).Kosugi S, Ohashi Y. DNA binding and dimerization specificity and potential targets for the TCP protein family. The Plant Journal. 2002;30:337. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurbidaeva, Ezhova & Novokreshchenova (2014).Kurbidaeva A, Ezhova T, Novokreshchenova M. Plant Science. 2014;229:10–22. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledent & Vervoort (2001).Ledent V, Vervoort M. The basic helix-loop-helix protein family: comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis. Genome Research. 2001;11:754–770. doi: 10.1101/gr.177001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee et al. (2006).Lee S, Lee S, Yang KY, Kim YM, Park SY, Kim SY, Soh MS. Overexpression of PRE1 and its homologous genes activates Gibberellin-dependent responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant and Cell Physiology. 2006;47:591–600. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcj026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leivar et al. (2008).Leivar P, Monte E, Al-Sady B, Carle C, Storer A, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Quail PH. The Arabidopsis phytochrome-interacting factor PIF7, together with PIF3 and PIF4, regulates responses to prolonged red light by modulating phyB levels. The Plant Cell. 2008;20:337–352. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.052142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li et al. (2010).Li F, Guo S, Zhao Y, Chen D, Chong K, Xu Y. Overexpression of a homopeptide repeat-containing bHLH protein gene (OrbHLH001) from Dongxiang Wild Rice confers freezing and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Reports. 2010;29:977–986. doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0883-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li et al. (2006).Li X, Duan X, Jiang H, Sun Y, Tang Y, Yuan Z, Guo J, Liang W, Chen L, Yin J, Ma H, Wang J, Zhang D. Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology. 2006;141:1167–1184. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.080580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu et al. (2017a).Liu K, Yuan C, Feng S, Zhong S, Li H, Zhong J, Shen C, Liu J. Genome-wide analysis and characterization of Aux/IAA family genes related to fruit ripening in papaya (Carica papaya L.) BMC Genomics. 2017a;18:351. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3722-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu et al. (2015).Liu K, Yuan C, Li H, Lin W, Yang Y, Shen C, Zheng X. Genome-wide identification and characterization of auxin response factor (ARF) family genes related to flower and fruit development in papaya (Carica papaya L.) BMC Genomics. 2015;16:901. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2182-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu et al. (2014).Liu W, Tai H, Li S, Gao W, Zhao M, Xie C, Li WX. bHLH122 is important for drought and osmotic stress resistance in Arabidopsis and in the repression of ABA catabolism. New Phytologist. 2014;201:1192–1204. doi: 10.1111/nph.12607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu et al. (2017).Liu Y, Li J, Wei G, Sun Y, Lu Y, Lan H, Li C, Zhang S, Cao M. Cloning, molecular evolution and functional characterization of ZmbHLH16, the maize ortholog of OsTIP2 (OsbHLH142) Biology Open. 2017;6:1654–1663. doi: 10.1242/bio.026393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magali et al. (2002).Magali L, Patrice D, Gert T, Kathleen M, Yves M, VdP Yves, Pierre R, Stephane R. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research. 2002;30:325–327. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao et al. (2017).Mao K, Dong Q, Li C, Liu C, Ma F. Genome wide identification and characterization of apple bhlh transcription factors and expression analysis in response to drought and salt stress. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2017;8:480. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming et al. (2008).Ming R, Hou S, Feng Y, Yu Q, Dionne-Laporte A, Saw JH, Senin P, Wang W, Ly BV, Lewis KL, Salzberg SL, Feng L, Jones MR, Skelton RL, Murray JE, Chen C, Qian W, Shen J, Du P, Eustice M, Tong E, Tang H, Lyons E, Paull RE, Michael TP, Wall K, Rice DW, Albert H, Wang ML, Zhu YJ, Schatz M, Nagarajan N, Acob RA, Guan P, Blas A, Wai CM, Ackerman CM, Ren Y, Liu C, Wang J, Wang J, Na JK, Shakirov EV, Haas B, Thimmapuram J, Nelson D, Wang X, Bowers JE, Gschwend AR, Delcher AL, Singh R, Suzuki JY, Tripathi S, Neupane K, Wei H, Irikura B, Paidi M, Jiang N, Zhang W, Presting G, Windsor A, Navajas-Pérez R, Torres MJ, Feltus FA, Porter B, Li Y, Burroughs AM, Luo MC, Liu L, Christopher DA, Mount SM, Moore PH, Sugimura T, Jiang J, Schuler MA, Friedman V, Mitchell-Olds T, Shippen DE, dePamphilis CW, Palmer JD, Freeling M, Paterson AH, Gonsalves D, Wang L, Alam M. The draft genome of the transgenic tropical fruit tree papaya (Carica papaya Linnaeus) Nature. 2008;452:991–996. doi: 10.1038/nature06856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern & Atchley (1999).Morgenstern B, Atchley WR. Evolution of bHLH transcription factors: modular evolution by domain shuffling? Molecular Biology & Evolution. 1999;16:1654–1663. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre, Mccaw & Baltimore (1989).Murre C, Mccaw PS, Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989;56:777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu et al. (2017).Niu X, Guan Y, Chen S, Li H. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genomics. 2017;18:619. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4044-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan & Jiang (2014).Pan LJ, Jiang L. Identification and expression of the WRKY transcription factors of Carica papaya in response to abiotic and biotic stresses. Molecular Biology Reports. 2014;41:1215–1225. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2966-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peraza-Echeverria, Santamaría & Fuentes (2012).Peraza-Echeverria S, Santamaría JM, Fuentes G. The NPR1 family of transcription cofactors in papaya: insights into its structure, phylogeny and expression. Genes & Genomics. 2012;34:379–390. doi: 10.1007/s13258-011-0218-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Petridis et al. (2016).Petridis A, Döll S, Nichelmann L, Bilger W, Mock HP. Arabidopsis thaliana G2-LIKE FLAVONOID REGULATOR and BRASSINOSTEROID ENHANCED EXPRESSION1 are low-temperature regulators of flavonoid accumulation. New Phytologist. 2016;211:912–925. doi: 10.1111/nph.13986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pires & Dolan (2010).Pires N, Dolan L. Origin and diversification of basic-helix-loop-helix proteins in plants. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2010;27:862–874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokotylo, Kravets & Ruelland (2019).Pokotylo I, Kravets V, Ruelland E. Salicylic acid binding proteins (sabps): the hidden forefront of salicylic acid signalling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019;20:4377. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter et al. (2009).Porter BW, Paidi M, Ming R, Alam M, Nishijima WT, Zhu YJ. Genome-wide analysis of Carica papaya reveals a small NBS resistance gene family. Molecular Genetics and Genomics. 2009;281:609–626. doi: 10.1007/s00438-009-0434-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price, Dehal & Arkin (2009).Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2009;26:1641–1650. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roig-Villanova et al. (2007).Roig-Villanova I, Bou-Torrent J, Galstyan A, Carretero-Paulet L, Portolés S. Interaction of shade avoidance and auxin responses: a role for two novel atypical bHLH proteins. Embo Journal. 2007;26:4756–4767. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionato et al. (2007).Simionato E, Ledent V, Richards G, Thomas-Chollier M, Kerner P, Coornaert D, Degnan BM, Vervoort M. Origin and diversification of the basic helix-loop-helix gene family in metazoans: insights from comparative genomics. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 2007;7:33. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song et al. (2017).Song Y, Liu H-D, Zhou Q, Zhang H-J, Zhang Z-D, Li Y-D, Wang H-B, Liu F-Z. High-throughput sequencing of highbush blueberry transcriptome and analysis of basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors. Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 2017;16:591–604. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61461-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, Roalson & Skinner (2008).Stevens JD, Roalson EH, Skinner MK. Phylogenetic and expression analysis of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor gene family: genomic approach to cellular differentiation. Differentiation. 2008;76:1006–1022. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2008.00285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Fan & Ling (2015).Sun H, Fan HJ, Ling HQ. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the bHLH gene family in tomato. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:9. doi: 10.1186/s12864-014-1209-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian et al. (2015).Tian H, Guo H, Dai X, Cheng Y, Zheng K, Wang X, Wang S. An ABA down-regulated bHLH transcription represor gene, bHLH129 regulates root elongation and ABA response when overexpressed in Arabidopsis. Scientific Reports. 2015;5:17587. doi: 10.1038/srep17587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian et al. (2017).Tian T, Liu Y, Yan H, You Q, Yi X, Du Z, Xu W, Su Z. agriGO v2.0: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2017;45:W122–W129. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo-Ortiz, Huq & Quail (2003).Toledo-Ortiz G, Huq E, Quail PH. The arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. The Plant Cell Online. 2003;15:1749–1770. doi: 10.1105/tpc.013839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vervoort & Ledent (2001).Vervoort M, Ledent V. The evolution of the neural basic Helix-Loop-Helix proteins. Scientific World Journal. 2001;1:396–426. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2001.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang et al. (2018a).Wang P, Su L, Gao H, Jiang X, Wu X, Li Y, Zhang Q, Wang Y, Ren F. Genome-Wide characterization of bhlh genes in grape and analysis of their potential relevance to abiotic stress tolerance and secondary metabolite biosynthesis. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2018a;9:64. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang et al. (2018b).Wang R, Zhao P, Kong N, Lu R, Pei Y, Huang C, Ma H, Chen Q. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the potato bHLH transcription factor family. Genes (Basel) 2018b;9:54–74. doi: 10.3390/genes9010054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu & Zhu (2012).Wu S, Zhu Y. ProPAS: standalone software to analyze protein properties. Bioinformation. 2012;8:167–169. doi: 10.6026/97320630008167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu et al. (2012).Xu G, Guo C, Shan H, Kong H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2012;109:1187–1192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109047109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu et al. (2020).Xu Y, Xu H, Wall MM, Yang J. Roles of transcription factor SQUAMOSA promoter binding protein-like gene family in papaya (Carica papaya) development and ripening. Genomics. 2020;112:2734–2747. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang et al. (2018).Zhang C, Feng R, Ma R, Shen Z, Cai Z, Song Z, Peng B, Yu M. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix superfamily members in peach. PLOS ONE. 2018;13:e0195974. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Creelman & Zhu (2004).Zhang JZ, Creelman RA, Zhu J-K. From Laboratory to field, using information from arabidopsis to engineer salt, cold, and drought tolerance in crops. Plant Physiology. 2004;135:615–621. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.040295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang et al. (2017).Zhang Z, Li J, Li F, Liu H, Yang W, Chong K, Xu Y. OsMAPK3 phosphorylates OsbHLH002/OsICE1 and inhibits its ubiquitination to activate ostpp1 and enhances rice chilling tolerance. Developmental Cell. 2017;43:731–743.e735. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu et al. (2015).Zhu E, You C, Wang S, Cui J, Niu B, Wang Y, Qi J, Ma H, Chang F. The DYT1-interacting proteins bHLH010, bHLH089 and bHLH091 are redundantly required for Arabidopsis anther development and transcriptome. The Plant Journal. 2015;83:976–990. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu et al. (2012).Zhu X, Li X, Chen W, Chen J, Lu W, Chen L, Fu D. Evaluation of new reference genes in papaya for accurate transcript normalization under different experimental conditions. PLOS ONE. 2012;7:e44405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Fisher’s exact test was used to evaluate enriched GO terms. GO terms include three aspects: biological process, cellular component and molecular function.
(A) Percentage of total cis-acting elements in the promoter region of At bHLH genes. (B) The percentage of each cis-acting element in the abiotic and biotic stresses categories.
Data Availability Statement
The following information was supplied regarding data availability:
The raw data are available in the Supplementary Files.