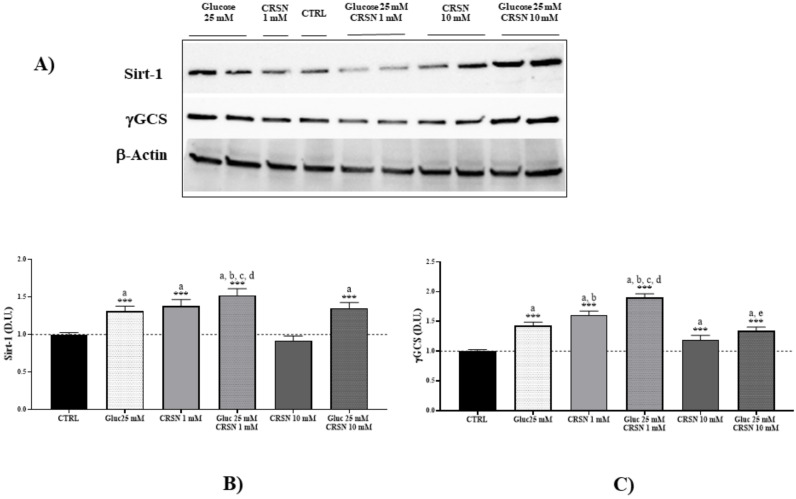
Figure 2.
Cellular sirtuin-1 (Sirt-1) and gamma-glutamyl cysteine synthetase (γ-GCS) protein concentrations (normalized to untreated cells) significantly increased in murine immortalized podocytes under glucose stress (25 mM; p = 1.4 × 10−3 and p = 5.5 × 10−7, respectively) or under carnosine addition (1 mM; p = 1.0 × 10−3 and p = 4.4 × 10−8, respectively). Co-incubation with carnosine (1 mM) and glucose (25 mM) induced further upregulation of Sirt-1 and γ-GCS proteins compared to single treatment (p = 0.002 vs. glucose and p = 0.03 vs. carnosine for Sirt-1; p = 1.6 × 10−6 vs. glucose and p = 6.7 × 10−3 vs. carnosine for γ-GCS) or control (p = 1.1 × 10−6 and p = 1.1 × 10−8 for Sirt-1 and γ-GCS, respectively), determined by western blotting (A) and quantified with an imaging software normalized to respective β-actin concentrations (B,C). Note: n = 5, a = significant increase vs. control, b = significant increase vs. glucose (25 mM), c = significant increase vs. carnosine (1 mM), d = significant increase vs. glucose (25 mM) + carnosine (10 mM), *** p < 0.001.