Abstract
Background
Plastid gene loss and pseudogenization has been widely documented in parasitic and mycoheterotrophic plants, which have relaxed selective constraints on photosynthetic function. More enigmatic are sporadic reports of pseudogenization and loss of important photosynthesis genes in lineages thought to be fully photosynthetic. Here we report the complete plastid genome of Saniculiphyllum guangxiense, a critically endangered and phylogenetically isolated plant lineage, along with genomic evidence of reduced chloroplast function. We also report 22 additional plastid genomes representing the diversity of its containing clade Saxifragales, characterizing gene content and placing variation in a broader phylogenetic context.
Results
We find that the plastid genome of Saniculiphyllum has experienced pseudogenization of five genes of the ndh complex (ndhA, ndhB, ndhD, ndhF, and ndhK), previously reported in flowering plants with an aquatic habit, as well as the surprising pseudogenization of two genes more central to photosynthesis (ccsA and cemA), contrasting with strong phylogenetic conservatism of plastid gene content in all other sampled Saxifragales. These genes participate in photooxidative protection, cytochrome synthesis, and carbon uptake. Nuclear paralogs exist for all seven plastid pseudogenes, yet these are also unlikely to be functional.
Conclusions
Saniculiphyllum appears to represent the greatest degree of plastid gene loss observed to date in any fully photosynthetic lineage, perhaps related to its extreme habitat specialization, yet plastid genome length, structure, and substitution rate are within the variation previously reported for photosynthetic plants. These results highlight the increasingly appreciated dynamism of plastid genomes, otherwise highly conserved across a billion years of green plant evolution, in plants with highly specialized life history traits.
Keywords: Plastid genome, Plastome, Pseudogene, Organelle, Saxifragaceae, Saniculiphyllum
Background
Plastid genome structure and content is highly conserved among most of the ~ 500,000 species of land plants and their closest green algal relatives [1]. Widespread loss or pseudogenization of photosynthetic genes is a familiar feature of the plastids of diverse non-photosynthetic plant lineages, reflecting the reduced need for photosynthetic genes in lineages with heterotrophic strategies [2]. Accumulating evidence, however, has increasingly documented the pseudogenization and loss of “accessory” photosynthetic genes, only conditionally essential under stress, in fully photosynthetic plants. Although not universal, many of these pseudogenizations and losses are associated with highly specialized life history traits such as aquatic habit [3–5], carnivory [6, 7], and a mycoheterotrophic life-stage [1]; the functional significance of these losses remains enigmatic [8].
Plastid gene loss and pseudogenization is currently best studied in mycoheterotrophic, primarily non-photosynthetic plants, which are under relatively relaxed selection on photosynthetic function. Remarkably, these plant lineages tend to follow a relatively predictable gene loss sequence, with early loss of photosynthetic accessory genes, primarily restricted to the ndh complex [2], which is involved in photooxidative protection under stressful conditions [8, 9]. This is eventually followed, in taxa with a longer evolutionary history of mycoheterotrophy, by loss of core photosynthetic genes. Housekeeping genes unrelated to photosynthesis, such as plastid ribosomal genes, are very resistant to loss [2]. Plastid gene content is less well-studied in fully photosynthetic life histories, but examples so far are consistent with this model. Gene loss to date has been restricted to portions of the ndh complex [3, 8, 10–12], which appears to be non-essential in model systems in the absence of abiotic stress [9, 13]. Whether such losses of a functional copy from the plastid genome truly represent a loss of function remains uncertain, as there are many examples of gene loss or pseudogenization in organellar genomes accompanied by functional transfer to the nuclear genome [14, 15].
Saniculiphyllum guangxiense C.Y. Wu & T.C. Ku is a semi-aquatic flowering plant now restricted to a miniscule area in Yunnan province, China. It grows partially submersed in the flow of small shaded waterfalls, and is critically endangered, with only four small extant populations in an area ~ 10 km2 known to science, as well as several other populations known to have been extirpated within the last 30 years [16]. Consistent with the isolated morphological and ecological traits of this lineage within the family Saxifragaceae, its phylogenetic affinities remain uncertain. The most recent attempts to place this species [16–18] exhibit strong disagreement. Xiang et al. [16], using six loci generated by Sanger sequencing, could not confidently place this lineage beyond its membership in the Heucheroid clade, while [17], using the same genetic loci, were able to place this lineage with 0.93–1.0 posterior probability (depending on the analysis) as sister to the Boykinia group, a difference Deng et al. [17] attribute to alignment differences in a single rapidly evolving genetic locus (ITS). Relationships in these studies based on Sanger sequencing data differ substantially in several areas from those recovered on the basis of more than 300 nuclear genes [18], where Saniculiphyllum was placed with moderate bootstrap support (80%) as sister to a clade containing the Astilbe and Boykinia groups.
In the course of organellar genome surveys across Saxifragales, we found anomalous photosynthetic gene sequences in Saniculiphyllum. Here, we report new plastid genome sequences of phylogenetically pivotal taxa, analyze plastid gene evolution across the Saxifragales, and place the Saniculiphyllum plastid genome in a phylogenetic context to assess evolutionary relationships and rates of plastid evolution. We seek to test whether Saniculiphyllum (1) has evidence for reduced photosynthetic function via pseudogenization of accessory photosynthetic genes, and (2) whether there is evidence for restored function of plastid pseudogenes via nuclear paralogs.
Results
Assembly results
For all samples, we successfully assembled a complete circular genome using NOVOPlasty. We individually confirmed all sequence features noted below by mapping the reads back to the assembly and found no evidence of misassembly.
Basic genome features
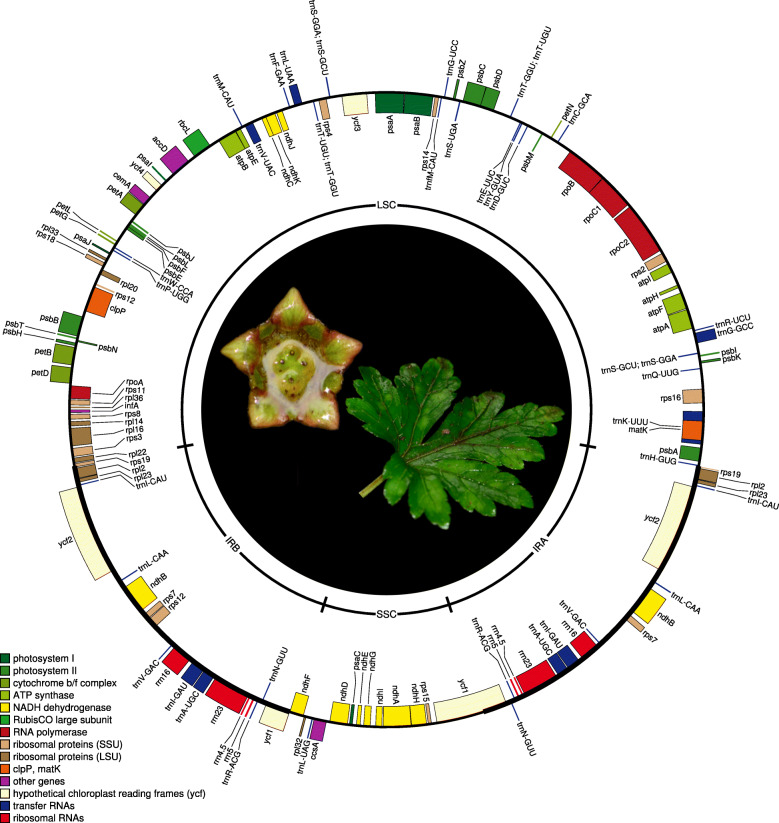
Saniculiphyllum has a chloroplast genome 151,704 bp long (Fig. 1). The large-scale structure of the genome is canonical for land plants, with an inverted repeat (26,109 bp) separating the large-single-copy region (LSC; 84,479 bp) and small-single-copy region (SSC, 15,007 bp). Excluding putative pseudogenes (below), gene content was as expected [20], comprising 73 distinct protein-coding genes, 30 tRNA genes, and 4 rRNA genes.
Fig. 1.
Gene map of the Saniculiphyllum plastome built using OrganellarGenomeDRAW [19]; genes marked on the outside face of the circle are transcribed counter-clockwise and those inside the circle are transcribed clockwise. Center photo: Saniculiphyllum flower and leaf; photo credit: C.-L. X
Evidence for pseudogenization
We used the presence of premature stop codons, frame shift mutations, missing canonical stop codons, and very large deletions as our criteria for pseudogenization (reviewed in [21]). We used gene models in the previously published H. parviflora var. saurensis genome [22] as well as comparisons across the newly annotated Saxifragales genomes presented here. We found genomic evidence for pseudogenization in 5 genes of the ndh complex (ndhA, ndhB, ndhD, ndhF, and ndhK), and two other photosynthetic genes (cemA, ccsA), summarized in Table S2, Additional file 1). These were either driven by frame-shift mutations (ccsA, ndhA, ndhD, and ndhF) or by premature stop codons without a frameshift (due to a point mutation in ndhB and a short inversion in ndhK). Three genes (cemA, ndhD, and ndhF) lack much of the conserved gene sequence due to large deletions > 100 bp. Among these, cemA has no premature stop codons, but it has an unconventional predicted protein size (5 extra amino acids) in a gene that otherwise shows no size variation in Saxifragales; while lacking 18% of the 3′ end of this gene, the Saniculiphyllum copy has 137 additional bp before a novel stop codon, the sequence of which is homologous with adjacent intergenic spacers in its relatives, making it unlikely that this sequence is functional. Additionally, frameshift has resulted in the loss of the conserved stop codon site of ndhA. Predicted proteins of the three genes with large deletions (cemA, ndhD, and ndhF) have hydrophobicity outside the range of variation of other Saxifragales (cemA 50% hydrophobic amino acids vs. the 95% confidence interval for other Saxifragales [50.4, 52.2%]; ndhD 47.8% vs. [62.2, 63.6%]; ndhF 54.9% vs. [55.6, 58.2%]).
Evidence for paralogs of pseudogenes
For the three genes with large deletions (cemA, ndhD, and ndhF), we used the Leptarrhena sequence for the missing DNA to probe for potential nuclear or mitochondrial paralogs that could be functional; otherwise we used the entire CDS of this taxon. For all seven novel pseudogenes, we found evidence of paralogs outside of the assembled chloroplast genome, some of which are more conserved in sequence and lack the anomalous features of plastid pseudogenes (Supplementary Figs. S1–7). This includes copies of cemA, ndhD, and ndhF without the large deletions found in the plastid copy. However, with the exception of partial assembled sequences of ndhF, these paralogs all have either the same premature stop codons of the plastid copy or novel premature stop codons and are also unlikely to be functional. These paralogs likely originate in the nucleus on the basis of sequence coverage, which was orders of magnitude lower (SPAdes calculated k-mer coverage ~ 1-5X) than that expected for either the plastid or the mitochondrion (k-mer coverage 100-2000X).
With the exception of ndhK, where we recovered 4 independent lineages of Saniculiphyllum paralogs, gene genealogies (Figs. S1–7, Additional file 1) were consistent with a recent origin of paralogs of the seven pseudogenes. In the ccsA gene genealogy, the Saxifraga stolonifera Curtis plastid ortholog was placed within a Saniculiphyllum clade without support, but otherwise (cemA, ndhA, ndhB, ndhD, ndhF) the Saniculiphyllum paralogs were recovered as monophyletic.
Other anomalous features
Several genes show slight variations in within-frame start and stop codon positions in Saxifragales, but Saniculiphyllum shows more variation than any other species we sampled, with four genes showing unique CDS terminations (atpB, cemA, rpl20, ycf2; Table S2, Additional file 1), of which none but rpl20 show any size variation in other Saxifragales species. While still within the typical length of photosynthetic plastid genomes, the Saniculiphyllum plastid genome as a whole was significantly smaller than the mean for Saxifragales species (one-tailed t-test, p = 1.485e-10).
We indirectly measured plastid genome copy number relative to background (mostly nuclear) DNA by calculating the percent of total genomic DNA mapping to the plastid genome. Lower values suggest lower copy number, either through fewer plastids or fewer genome copies per plastid. Interestingly, this was significantly smaller in Saniculiphyllum (3.4%) compared to other Saxifragales (one-tailed t-test, p = 1.629e-07); the mean of our Saxifragales species sampled here was 10.1%, identical to a mean of 10.1% recovered with further Saxifragaceae species sampled in [22].
Plastid genome diversity in Saxifragales
The new plastid genomes sequenced in this study have no evidence of any structural rearrangements, underlining the strong conservatism of plastid genome structure in Saxifragales [20, 23] (the rare exception is Haloragaceae, distantly related to taxa discussed here; see [23, 24]). Other than Saniculiphyllum, we found no evidence at the DNA sequence level for pseudogenes beyond those previously documented for Saxifragales [20, 23] and many other angiosperms, namely ycf15 and pseudogenes created by IR (inverted repeat) region boundaries within ycf1 and ycf2 (cf. Table S2, Additional file 1). The IR region, a major contributor to plastid genome size variation [25], shows similar trends (Table 1) to those documented previously in Saxifragales, where much like genome structure it is highly conserved [20]. However, the family Saxifragaceae shows a trend towards reduction, with some of the smallest IR regions in Saxifragales.
Table 1.
Summary of new chloroplast genome sequences reported in this paper
| Species | Field collecting location | Sequencing technology | Collection data (Herbarium) | Genbank accession | Total sequencing effort (millions of reads) | Plastid genome mean coverage (reduced data) | Plastid assembly length | Inverted repeat length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boykinia aconitifolia | Alleghany County, North Carolina, U.S.A. | BGI-SEQ | Folk 249 (FLAS) | MN496058 | 734.3 | 374.8× | 154,368 bp | 25,769 bp |
| Cercidiphyllum japonicum | Cultivation | BGI-SEQ | Whitten 5886 (FLAS) | MN496059 | 799.1 | 394.8× | 159,897 bp | 26,434 bp |
| Daphniphyllum macropodum | Cultivation | BGI-SEQ | Whitten 5884 (FLAS) | MN496060 | 684.5 | 66.0× | 160,408 bp | 26,605 bp |
| Fortunearia sinensis | Cultivation | BGI-SEQ |
Folk 253 (FLAS) |
MN496061 | 727.7 | 90.2× | 159,413 bp | 26,274 bp |
| Heuchera abramsii | Los Angeles County, California, U.S.A. | Illumina HiSeq | Folk I-40 (OS) | MN496062 | 211.8 | 710.3× | 155,527 bp | 25,838 bp |
| Heuchera alba | Pendleton County, West Virginia, U.S.A. | Illumina HiSeq | Folk 63 (OS) | MN496063 | 160.8 | 252.4× | 155,360 bp | 25,632 bp |
| Heuchera caespitosa | Ventura County, California, U.S.A. | Illumina HiSeq | Folk 48 (OS) | MN496064 | 171.7 | 490.5× | 155,520 bp | 25,834 bp |
| Heuchera eastwoodiae | Yavapai County, Arizona, U.S.A. | Illumina HiSeq | Folk 35 (OS) | MN496065 | 82.3 | 336.0× | 155,174 bp | 25,605 bp |
| Heuchera grossulariifolia var. grossulariifolia | Idaho County, Idaho, U.S.A. | Illumina HiSeq | Folk 160 (OS) | MN496066 | 226.6 | 742.7× | 155,493 bp | 25,645 bp |
| Heuchera longipetala var. longipetala | Cultivation | Illumina HiSeq | Folk I-21 (OS) | MN496067 | 223.6 | 768.3× | 155,418 bp | 25,638 bp |
| Heuchera mexicana var. mexicana | Cultivation | BGI-SEQ | Folk I-51 (OS) | MN496068 | 710.8 | 150.3× | 155,451 bp | 25,638 bp |
| Heuchera parvifolia var. utahensis | Cultivation | Illumina HiSeq | Folk I-56 (OS) | MN496069 | 273.3 | 738.5× | 155,350 bp | 25,633 bp |
| Leptarrhena pyrolifolia | Skagit County, Washington, U.S.A. | BGI-SEQ | J.V. Freudenstein 3069 (FLAS) | MN496070 | 752.2 | 253.8× | 155,055 bp | 25,781 bp |
| Mitella diphylla | Monroe County, Ohio, U.S.A. | Illumina HiSeq | Folk 88 (OS) | MN496071 | 230.8 | 357.0× | 155,646 bp | 25,753 bp |
| Mitella pentandra | King County, Washington, U.S.A. | Illumina HiSeq | Folk 128 (OS) | MN496072 | 264.4 | 341.2× | 155,470 bp | 25,620 bp |
| Mukdenia rossii | Cultivation | BGI-SEQ | Folk 259 (FLAS) | MN496073 | 799.0 | 330.9× | 156,927 bp | 25,585 bp |
| Oresitrophe rupifraga | Cultivation | BGI-SEQ |
Folk 257 (FLAS) |
MN496074 | 678.1 | 261.3× | 156,787 bp | 25,586 bp |
| Ribes nevadense | Shasta County, California, U.S.A. | BGI-SEQ | Nelson 2018–028 (FLAS) | MN496075 | 782.7 | 234.3× | 157,715 bp | 25,887 bp |
| Ribes roezlii | Shasta County, California, U.S.A. | BGI-SEQ | Nelson 2018–027 (FLAS) | MN496076 | 723.6 | 262.7× | 157,781 bp | 25,967 bp |
| Rodgersia sambucifolia | Cultivation | BGI-SEQ | R.A. Folk 266 (FLAS) | MN496077 | 637.3 | 193.2× | 157,289 bp | 25,556 bp |
| Saniculiphyllum guangxiense | Funing County, Yunnan, China | Illumina HiSeq | Xiang 1271 (KUN) | MN496078 | 180.9 | 179.6× | 151,704 bp | 26,109 bp |
| Saxifraga stolonifera | Cultivation | BGI-SEQ | Folk 258 (FLAS) | MN496079 | 623.5 | 238.2× | 151,060 bp | 25,412 bp |
| Sycopsis sinensis | Cultivation | BGI-SEQ |
Folk 256 (FLAS) |
MN496080 | 746.2 | 117.7× | 159,043 bp | 26,230 bp |
Phylogenetic analysis
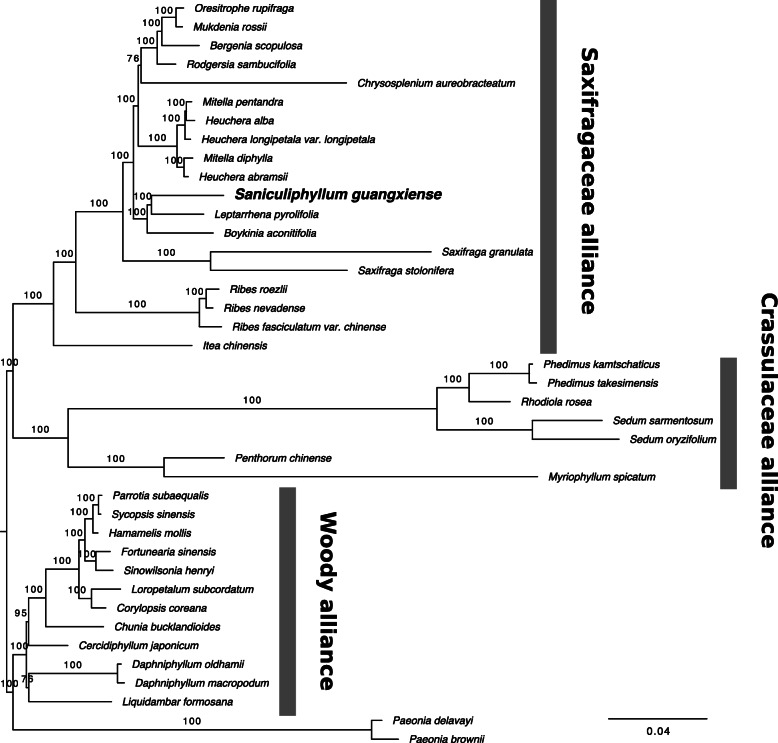
The plastome alignment length was 172,773 bp, with 9.9% of the alignment comprising gap characters, and 38,332 parsimony-informative characters excluding the gap characters. Backbone relationships in the chloroplast genome phylogeny were congruent with recent phylogenomic work [18] (Fig. 2). Although receiving maximal bootstrap support, the placement of Saniculiphyllum we recovered is different from all previous efforts to place this taxon, none of which agree among themselves and none of which achieved greater than moderate support [16–18]. Our placement resembles previous work [17, 18] in placing Saniculiphyllum in a clade comprising the Astilbe Buch.-Ham., Boykinia Raf., and Leptarrhena groups, but the novel placement reported here is sister to Leptarrhena.
Fig. 2.
ML phylogeny of Saxifragales plastid genomes. Saniculiphyllum shown in bold; labelled clades correspond to the terminology of [26]. The scale bar represents per-site substitution rate. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies
Substitution rate analysis
Despite its divergent plastome features, genome-wide substitution rates did not appear elevated in Saniculiphyllum on the basis of phylogenetic branch length (Fig. 2), suggesting that at the nucleotide level negative selection is not substantially relaxed in this lineage. We further explored this hypothesis by explicitly testing for the presence of relaxed selection in the seven plastid gene copies with evidence of pseudogenization in Saniculiphyllum. We implemented this via ω (dN/dS) ratios in PAML [27]. We used a model comparison approach on each gene tree to test whether the Saniculiphyllum branch experienced a shift in selection regime compared to its immediately ancestral branch. We did not find evidence of shifts in selection regimes (all p > 0.05); likewise, we estimated dN/dS < 1 for the Saniculiphyllum branch across all seven pseudogenes (mean 0.0319), consistent with strong negative selection.
Discussion
Pseudogenization
In total, we found genomic evidence for seven putative pseudogenes in the Saniculiphyllum plastid genome. Five of these (ndhA, ndhB, ndhD, ndhF, and ndhK), are genes of the ndh complex. These genes are highly conserved across the land plants and related green algae [8]. Most losses of plastid gene function have been associated with parasitic and mycoheterotrophic plants, which presumably have few functional constraints on photosynthetic gene evolution. Pseudogenization or loss of genes in the ndh complex has nevertheless been observed in several fully photosynthetic lineages with a variety of often highly specialized life history traits: woody perennials in Pinaceae and Gnetales (both gymnosperms), short-lived perennials in Geraniaceae (eudicots: rosids), alpine Circaeasteraceae (eudicots: Ranunculales), carnivorous and often aquatic plants of Lentibulariaceae (eudicots: asterids), various photosynthetic members of Orchidaceae (monocot), and aquatic members of Alismatales (monocot) and Podostemataceae (rosid [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 13, 28–30];). The primary function of the ndh complex is thought to be reduction of photooxidative stress under fluctuating light conditions. While the ndh complex appears dispensable under mild growth conditions [9], experimental evidence from knockouts of single ndh genes shows that a complete and intact complex is essential for efficient photosynthesis and robust plant growth under stressful conditions [13].
More unusual than loss of ndh function is the clear pseudogenization of two other photosynthesis-specific genes, for which we report the first absence in a fully photosynthetic plant. The gene cemA encodes a protein involved in carbon uptake; while not essential for photosynthesis, photosynthetic efficiency is reduced under high light environments in Chlamydomonas Ehrenb. mutants lacking this gene [31]. The gene ccsA encodes a protein involved in heme attachment to chloroplast cytochrome c [32]. ccsA, at least in Chlamydomonas, is essential for System II photosynthesis [32]. Both cemA and ccsA are conserved across primary photosynthetic eukaryotes and even cyanobacteria [31, 33].
Evidence for paralogs in the nucleus
We successfully found and assembled paralogs for all seven novel putative chloroplast pseudogenes in Saniculiphyllum. Many of these paralogs are of more conserved sequence than that of the assembled plastid genome; with the exception of ndhK these appear to have originated primarily after the divergence of Saniculiphyllum from other Saxifragaceae lineages sampled here. On the basis of coverage, these are likely to represent NUPTs (nuclear sequences of plastid origin [34];). Our results are consistent with growing evidence of a slow transfer of organellar gene content into nuclear genomes [14, 34], a process associated with frequent non-homologous recombinational repair between these genomes [35]. While in some cases NUPTs are associated with restoration of function by coding for an imported functional photosynthetic protein [15], it is unlikely that Saniculiphyllum has any functional copies of these genes because almost all nuclear paralogs show signs of pseudogenization.
Other genome anomalies
We also observed unusual CDS terminations upstream or downstream of closely related Saxifragales plastid genomes in four genes (Table S2, Additional file 1); these do not result in frameshifts but expected protein products are of unexpected length. Although less dramatic than the pseudogenization patterns we observed, the lack of length conservation in Saniculiphyllum is markedly greater compared to close relatives. Likewise, while the Saniculiphyllum plastome is far longer than many non-photosynthetic plants (reviewed in [2]), it is among the shortest in Saxifragales due to large deletions in coding and non-coding regions throughout the plastome.
Despite having one of the most divergent plastid genomes in Saxifragales, there is no evidence for elevated substitution rates in Saniculiphyllum based on phylogenetic branch length estimated from the entire plastid genome (Fig. 2). Likewise, we implemented tests on dN/dS ratios in the seven putative pseudogenes, demonstrating that Saniculiphyllum does not show significantly different selection regimes at the codon level compared to related lineages. These results suggest that Saniculiphyllum primarily differs in its plastid genome evolution via deletions and rare novel stop codons without any detectable global relaxation of purifying selection at the nucleotide level. Dosage of plastid DNA relative to the nucleus also appears to be low in Saniculiphyllum compared to relatives, likely representing either a reduction in plastids per cell or a reduction in genome copy number per plastid.
Evolutionary relationships
This work also represents the first robust phylogenomic placement of Saniculiphyllum, an important group for interpreting morphological evolution in Saxifragaceae [16]. We confirm a close relationship with the Boykinia and Leptarrhena groups, with which it shares axile placentation, determinate cymose inflorescences, and a strongly rhizomatous habit. However, representatives of the Astilbe group and several others have yet to be sampled; denser taxon sampling is needed to confirm the placement reported here.
Conclusions
Although chloroplast genome evolution in Saxifragales has been previously understood as very conservative [20], further sampling has revealed surprising plastid variation in one of its rarest and most unusual lineages. Similar but less extreme patterns of gene loss have been observed before in aquatic members of order Alismatales and Podostemaceae, and appear to represent multiple independent evolutionary events [3, 5], suggesting a possible relationship with life history. Like these lineages, Saniculiphyllum is highly specialized for partially submerged shaded waterfall environments, a stable habitat possibly conducive to relaxed selection on and loss of photosynthetic accessory genes. Nevertheless, this putative correlation is imperfect; while Alismatales contains some of the most thoroughly aquatic-adapted angiosperms, including the only examples of aquatic pollination [3], Myriophyllum, a completely aquatic Saxifragales lineage, shows conventional gene content [23], as do many other aquatic plastid genomes (e.g., Nelumbo Adans. [36], Nymphaea L. [37], Lemna L. [38]).
It is tempting to speculate on the relationship between loss of photosynthetic gene content and the imperiled conservation status of Saniculiphyllum since loss of abiotic stress-response genes would suggest a poor ability to respond to cope with environmental change. Unfortunately, we understand little of the functional significance of plastid gene content outside of model organisms. We highlight the need for characterization of plastid genome evolution, further examination its relationship to life history traits, and the continued promise of comparative phylogenomic approaches [39] for shedding light on this enigmatic pattern.
Methods
Sampling
We sequenced 23 plastomes in total to increase phylogenetic representation. Other than Saniculiphyllum, we sampled 16 further taxa of Saxifragaceae to cover most of the major recognized clades recognized in [17], and six further Saxifragales outgroups to increase representation in the woody alliance (cf. [26]). Most materials were obtained from horticultural sources; wild materials were collected with permission from the U.S. National Forest Service. Materials of Saniculiphyllum, which unfortunately does not currently have a legal conservation designation, were collected from an unprotected natural area. Sampling localities are given in Table 1. The species sampled in total, listed by major clade names, were: Darmera group: Mukdenia rossii, Oresitrophe rupifraga, Rodgersia sambucifolia; Boykinia group: Boykinia aconitifolia; Leptarrhena group: Leptarrhena pyrolifolia; Heuchera group: Heuchera abramsii, Heuchera alba, Heuchera caespitosa, Heuchera eastwoodiae, Heuchera grossulariifolia var. grossulariifolia, Heuchera longipetala var. longipetala, Heuchera mexicana var. mexicana, Heuchera parvifolia var. utahensis, Mitella diphylla, and Mitella pentandra; Saxifraga group: Saxifraga stolonifera; incertae sedis: Saniculiphyllum guangxiense. Outgroup taxa, listed by family, were: Cercidiphyllaceae: Cercidiphyllum japonicum. Daphniphyllaceae: Daphniphyllum macropodum; Grossulariaceae: Ribes nevadense and Ribes roezlii; Hamamelidaceae: Fortunearia sinensis and Sycopsis sinensis.
DNA extraction and sequencing
Whole genomic DNAs were isolated from silica-dried leaf material (Saniculiphyllum) or fresh material (all other taxa) using a modified CTAB extraction protocol [40]. Although our target was plastid DNA, we sequenced total DNA to enable paralog assembly (see below) and other future related work on mitochondrial and nuclear genomes. Taxa were chosen to represent lineages across Saxifragales. Sequencing was performed either at RAPiD Genomics (Gainesville, Florida, U.S.A.) with 150 bp paired-end Illumina HiSeq sequencing or with 100 bp paired-end BGISEQ-500 sequencing at BGI (Shenzhen, Guangdong, P.R. China), in both cases with an insert size of approximately 300 bp (summarized in Table 1).
Genome assembly
We used NOVOPlasty v. 3.2 [41] to assemble chloroplast genomes for all sequenced taxa. For each sample, we ran two assemblies using rbcL and matK seed reference genes from the plastid genome of Heuchera parviflora var. saurensis R.A. Folk [22]. Reads were not quality filtered following developer recommendations (see https://github.com/ndierckx/NOVOPlasty). We used the following parameters: k-mer = 39, expected genome range 120,000–200,000 bp, insert size 300 bp, insert range = 1.8, and insert range strict = 1.3. We also used insert range fine-tuning to account for insert size variation between samples. When running NOVOPlasty on the entire dataset, we found it returned only partial plastid genome assemblies; datasets were normalized to 8 million raw reads per sample for HiSeq data and 4 million for BGI-SEQ samples (~ 100-500X plastid coverage) using standard UNIX tools to achieve full-length assemblies of the plastid genome. Chloroplast genomes in most plants exist in both possible orientations of the small-single copy region relative to the rest of the genome [42], we manually standardized the orientation of the SSC region across samples prior to sequence alignment using Geneious R9.
Annotations were performed in Geneious R9 using the Heuchera parviflora reference plastid genome and a cutoff of 70% sequence identity, and draft annotated plastid genomes were aligned and manually examined for annotation accuracy. Additionally, all premature stop codons, inversions, frameshifting indels, and other unusual features were individually verified visually by mapping the original reads back to the assembled plastid genomes using the Geneious read mapping algorithm [43]. We also calculated the percent of chloroplast sequences in the total DNA from these mapped reads using SAMtools [44].
For the seven putative plastid pseudogenes, we searched for potential paralogs in the mitochondrial and nuclear genomes using aTRAM 2 [45, 46]. aTRAM is a method for iterative, targeted assembly that implements commonly used de novo assembly modules on a reduced read set that has sequence homology with a seed sequence. Seed sequences were derived from the CDS sequence of the closest identified relative among our taxa, Leptarrhena pyrolifolia (D. Don) Ser. Ten iterations were used per assembly, and the assembler used was SPAdes v. 3.13.0 [47]; other options correspond to defaults. For these analyses, we extracted matching reads from the full Saniculiphyllum dataset (~ 180,000,000 reads).
Phylogenetics
We conducted a maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis both to reassess the relationships of Saniculiphyllum [16–18], and to assess rates of plastid substitution in a phylogenetic context. We analyzed the single-copy plastid sequence from each genome (i.e., with one copy of the inverted repeat), aligned them with MAFFT v. 7.388 [48], and ran phylogenetic analyses in RaxML v. 8.2.10 [49] under a GTR-Γ model with 1000 bootstrap replicates (command “-f a”). Sites were partitioned as either coding (exonic protein-coding, rDNA, and tRNA) or non-coding. For this analysis, we sampled 22 further previously reported plastid genomes (Supplementary Table S1, Additional file 1), as well as generating a plastid genome assembly from previously reported short read data from Saxifraga granulata L. ([50]; SRA accession SRX665162), all chosen to represent phylogenetic diversity in Saxifragales, for a total of 40 taxa. We sampled 12 of 16 families, including complete representation of the Saxifragaceae alliance; the plastid of the parasitic family Cynomoriaceae has been sequenced, but this was deliberately excluded as it is on an extremely long branch [51]. Saxifragaceae sampling covers 8 of the 10 major clades recognized in [17]. Tree rooting follows [18].
For the paralog search in aTRAM, we placed recovered sequences in a phylogenetic context by extracting plastid sequences for each gene from the plastid genome alignment, trimming to the extent of chloroplast gene sequences and removing ambiguously aligned regions, and removing any sequences with fewer than 200 bp remaining after these steps. We then built individual gene trees following the RAxML methods above.
Tests for selection
To test for relaxed selection in putative pseudogenes in Saniculiphyllum, we built two models for each of the seven gene trees: a full model allowing ω to vary across all branches, and a constrained model where Saniculiphyllum was constrained to have the same ω as the branch immediately ancestral to it. We used a likelihood ratio test to determine whether the constrained model could be rejected (= a shift in selective regime along this phylogenetic branch). Since multiple tests were executed, multiple comparisons were corrected by the Hochberg method [52].
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Summary of chloroplast genome sequences downloaded from GenBank for phylogenetic analyses. Table S2. Summary of premature stop codons, large/frame-shifting indels, and other anomalous genome features unique to Saniculiphyllum.Figure S1. ML gene phylogeny of ccsA, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S2. ML gene phylogeny of cemA, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S3. ML gene phylogeny of ndhA, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S4. ML gene phylogeny of ndhB, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S5. ML gene phylogeny of ndhD, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S6. ML gene phylogeny of ndhF, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S7. ML gene phylogeny of ndhK, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted.
Acknowledgments
D. Soltis and G. Wong are thanked for facilitating access to pilot short read data in connection with the 10KP project. J. Nelson, J. Xiang, and J.V. Freudenstein are thanked for providing DNA materials; J. Ginori assisted with testing early assembly runs, and the late M. Whitten advised extensively on DNA extraction protocols.
Abbreviations
- CDS
Coding sequence
- CTAB
Cetrimonium bromide
- GTR-Γ
General time reversible with gamma
- ITS
Internal transcribed spacer
- LSC
Long single copy [region]
- NUPT
Nuclear plastid DNA
- SSC
Small single copy [region]
- SRA
Sequence Read Archive
Authors’ contributions
R.A.F. conceived the study; R.A.F. and N.S. performed analyses; B.T.S., C.-L. X., and R.P.G consulted on analyses and interpretation; R.A.F. wrote the first manuscript draft; and all authors contributed to the final manuscript draft. All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Funding
R.A.F. was supported by NSF DBI-1523667. There was no involvement of the funding providers in designing the study; collecting, analyzing or interpreting the data; or deciding to submit the paper for publication.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available at Dryad (alignments, partition files, and tree topologies; 10.5061/dryad.mgqnk98vt), and at GenBank (accession numbers in Table S1; Additional file 1). Supplemental figures are available in Additional file 1.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors have complied with all relevant institutional, national and international guidelines in collecting biological materials for this study. Collection permits for materials for sequencing were granted by the U.S. National Forest Service.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ryan A. Folk and Neeka Sewnath are co-first authors.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12870-020-02533-x.
References
- 1.Wicke S, Schneeweiss GM, dePamphilis CW, Müller KF, Quandt D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol Biol. 2011;76:273–297. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9762-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Barrett CF, Freudenstein JV, Li J, Mayfield-Jones DR, Perez L, Pires JC, et al. Investigating the path of plastid genome degradation in an early-transitional clade of heterotrophic orchids, and implications for heterotrophic angiosperms. Mol Biol Evol. 2014;31:3095–3112. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Peredo EL, King UM, Les DH. The plastid genome of Najas flexilis: adaptation to submersed environments is accompanied by the complete loss of the NDH complex in an aquatic angiosperm. PLoS One. 2013;8:e68591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ross TG, Barrett CF, Soto Gomez M, Lam VKY, Henriquez CL, Les DH, et al. Plastid phylogenomics and molecular evolution of Alismatales. Cladistics. 2016;32:160–178. doi: 10.1111/cla.12133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bedoya AM, Ruhfel BR, Philbrick CT, Madriñán S, Bove CP, Mesterházy A, et al. Plastid genomes of five species of riverweeds (Podostemaceae): structural organization and comparative analysis in Malpighiales. Front Plant Sci. 2019;10:1035. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wicke S, Schäferhoff B, dePamphilis CW, Müller KF. Disproportional plastome-wide increase of substitution rates and relaxed purifying selection in genes of carnivorous Lentibulariaceae. Mol Biol Evol. 2014;31:529–545. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gruzdev EV, Kadnikov VV, Beletsky AV, Kochieva EZ, Mardanov AV, Skryabin KG, et al. Plastid genomes of carnivorous plants Drosera rotundifolia and Nepenthes × ventrata reveal evolutionary patterns resembling those observed in parasitic plants. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20. 10.3390/ijms20174107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Martín M, Sabater B. Plastid ndh genes in plant evolution. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010;48:636–645. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shikanai T, Endo T, Hashimoto T, Yamada Y, Asada K, Yokota A. Directed disruption of the tobacco ndhB gene impairs cyclic electron flow around photosystem I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:9705–9709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lin C-S, Chen JJW, Chiu C-C, Hsiao HCW, Yang C-J, Jin X-H, et al. Concomitant loss of NDH complex-related genes within chloroplast and nuclear genomes in some orchids. Plant J. 2017;90:994–1006. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chris Blazier J, Guisinger MM, Jansen RK. Recent loss of plastid-encoded ndh genes within Erodium (Geraniaceae) Plant Mol Biol. 2011;76:263–272. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9753-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ranade SS, García-Gil MR, Rosselló JA. Non-functional plastid ndh gene fragments are present in the nuclear genome of Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karsch): insights from in silico analysis of nuclear and organellar genomes. Mol Gen Genomics. 2016;291:935–941. doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-1159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ruhlman TA, Chang W-J, Chen JJW, Huang Y-T, Chan M-T, Zhang J, et al. NDH expression marks major transitions in plant evolution and reveals coordinate intracellular gene loss. BMC Plant Biol. 2015;15:100. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0484-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Richly E, Leister D. NUPTs in sequenced eukaryotes and their genomic organization in relation to NUMTs. Mol Biol Evol. 2004;21:1972–1980. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Magee AM, Aspinall S, Rice DW, Cusack BP, Sémon M, Perry AS, et al. Localized hypermutation and associated gene losses in legume chloroplast genomes. Genome Res. 2010;20:1700–1710. doi: 10.1101/gr.111955.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xiang C-L, Gitzendanner MA, Soltis DE, Peng H, Lei L-G. Phylogenetic placement of the enigmatic and critically endangered genus Saniculiphyllum (Saxifragaceae) inferred from combined analysis of plastid and nuclear DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2012;64:357–367. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2012.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Deng J-B, Drew BT, Mavrodiev EV, Gitzendanner MA, Soltis PS, Soltis DE. Phylogeny, divergence times, and historical biogeography of the angiosperm family Saxifragaceae. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2015;83:86–98. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2014.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Folk RA, Stubbs RL, Mort ME, Cellinese N, Allen JM, Soltis PS, et al. Rates of niche and phenotype evolution lag behind diversification in a temperate radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116:10874–10882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1817999116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lohse M, Drechsel O, Kahlau S, Bock R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW--a suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(Web Server issue):W575–W581. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dong W, Xu C, Cheng T, Zhou S. Complete chloroplast genome of Sedum sarmentosum and chloroplast genome evolution in Saxifragales. PLoS One. 2013;8:e77965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Albalat R, Cañestro C. Evolution by gene loss. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:379–391. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Folk RA, Mandel JR, Freudenstein JV. A protocol for targeted enrichment of intron-containing sequence markers for recent radiations: a phylogenomic example from Heuchera (Saxifragaceae) Appl Plant Sci. 2015;3:1500039. doi: 10.3732/apps.1500039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dong W, Xu C, Wu P, Cheng T, Yu J, Zhou S, et al. Resolving the systematic positions of enigmatic taxa: manipulating the chloroplast genome data of Saxifragales. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2018;126:321–330. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2018.04.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liao Y, Liu Y, Liu X, Lü T, Mbichi RW, Wan T, et al. The complete chloroplast genome of Myriophyllum spicatum reveals a 4-kb inversion and new insights regarding plastome evolution in Haloragaceae. Ecol Evol. 2020. 10.1002/ece3.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Wang R-J, Cheng C-L, Chang C-C, Wu C-L, Su T-M, Chaw S-M. Dynamics and evolution of the inverted repeat-large single copy junctions in the chloroplast genomes of monocots. BMC Evol Biol. 2008;8:36. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jian S, Soltis PS, Gitzendanner MA, Moore MJ, Li R, Hendry TA, et al. Resolving an ancient, rapid radiation in Saxifragales. Syst Biol. 2008;57:38–57. doi: 10.1080/10635150801888871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yang Z. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1586–1591. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Barrett CF, Sinn BT, Kennedy AH. Unprecedented parallel photosynthetic losses in a heterotrophic orchid genus. Mol Biol Evol. 2019. 10.1093/molbev/msz111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Weng M-L, Blazier JC, Govindu M, Jansen RK. Reconstruction of the ancestral plastid genome in Geraniaceae reveals a correlation between genome rearrangements, repeats, and nucleotide substitution rates. Mol Biol Evol. 2014;31:645–659. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sun Y, Deng T, Zhang A, Moore MJ, Landis JB, Lin N, et al. The draft genome of the endangered, relictual plant Kingdonia uniflora (Circaeasteraceae, Ranunculales) reveals potential mechanisms and perils of evolutionary specialization. bioRxiv. 2020. 10.1101/2020.01.08.898460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 31.Rolland N, Dorne AJ, Amoroso G, Sültemeyer DF, Joyard J, Rochaix JD. Disruption of the plastid ycf10 open reading frame affects uptake of inorganic carbon in the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas. EMBO J. 1997;16:6713–6726. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.22.6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Xie Z, Merchant S. The plastid-encoded ccsA gene is required for heme attachment to chloroplast c-type cytochromes. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:4632–4639. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hamel PP, Dreyfuss BW, Xie Z, Gabilly ST, Merchant S. Essential histidine and tryptophan residues in CcsA, a system II polytopic cytochrome c biogenesis protein. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:2593–2603. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208651200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Timmis JN, Ayliffe MA, Huang CY, Martin W. Endosymbiotic gene transfer: organelle genomes forge eukaryotic chromosomes. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:123–135. doi: 10.1038/nrg1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Huang CY, Ayliffe MA, Timmis JN. Simple and complex nuclear loci created by newly transferred chloroplast DNA in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:9710–9715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400853101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wu Z, Gui S, Quan Z, Pan L, Wang S, Ke W, et al. A precise chloroplast genome of Nelumbo nucifera (Nelumbonaceae) evaluated with sanger, Illumina MiSeq, and PacBio RS II sequencing platforms: insight into the plastid evolution of basal eudicots. BMC Plant Biol. 2014;14:289. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0289-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Goremykin VV, Hirsch-Ernst KI, Wölfl S, Hellwig FH. The chloroplast genome of Nymphaea alba: whole-genome analyses and the problem of identifying the most basal angiosperm. Mol Biol Evol. 2004;21:1445–1454. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mardanov AV, Ravin NV, Kuznetsov BB, Samigullin TH, Antonov AS, Kolganova TV, et al. Complete sequence of the duckweed (Lemna minor) chloroplast genome: structural organization and phylogenetic relationships to other angiosperms. J Mol Evol. 2008;66:555–564. doi: 10.1007/s00239-008-9091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Smith SD, Pennell MW, Dunn CW, Edwards SV. Phylogenetics is the new genetics (for most of biodiversity). Trends Ecol Evol. 2020;0. 10.1016/j.tree.2020.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 40.Doyle JJ. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull. 1987;19:11–15. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dierckxsens N, Mardulyn P, Smits G. NOVOPlasty: de novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:e18. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang W, Lanfear R. Long-reads reveal that the chloroplast genome exists in two distinct versions in most plants. Genome Biol Evol. 2019;11:3372–3381. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Matthew Kearse, Shane Sturrock, and Peter Meintjes. The Geneious 6.0.3 Read Mapper. https://assets.geneious.com/documentation/geneious/GeneiousReadMapper.pdf. Accessed 18 Sept 2019.
- 44.Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Allen JM, LaFrance R, Folk RA, Johnson KP, Guralnick RP. aTRAM 2.0: an improved, flexible locus assembler for NGS data. Evol Bioinformatics Online. 2018;14:1176934318774546. doi: 10.1177/1176934318774546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Allen JM, Huang DI, Cronk QC, Johnson KP. aTRAM - automated target restricted assembly method: a fast method for assembling loci across divergent taxa from next-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015;16:98. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0515-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, et al. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. 2012;19:455–477. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Katoh K, Asimenos G, Toh H. Multiple alignment of DNA sequences with MAFFT. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;537:39–64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-251-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stamatakis A. RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:2688–2690. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.van der Meer S, Van Houdt JKJ, Maes GE, Hellemans B, Jacquemyn H. Microsatellite primers for the gynodioecious grassland perennial Saxifraga granulata (Saxifragaceae) Appl Plant Sci. 2014;2:1400040. doi: 10.3732/apps.1400040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bellot S, Cusimano N, Luo S, Sun G, Zarre S, Gröger A, et al. Assembled plastid and mitochondrial genomes, as well as nuclear genes, place the parasite family Cynomoriaceae in the Saxifragales. Genome Biol Evol. 2016;8:2214–2230. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hochberg Y. A sharper Bonferroni procedure for multiple tests of significance. Biometrika. 1988;75:800–802. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Summary of chloroplast genome sequences downloaded from GenBank for phylogenetic analyses. Table S2. Summary of premature stop codons, large/frame-shifting indels, and other anomalous genome features unique to Saniculiphyllum.Figure S1. ML gene phylogeny of ccsA, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S2. ML gene phylogeny of cemA, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S3. ML gene phylogeny of ndhA, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S4. ML gene phylogeny of ndhB, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S5. ML gene phylogeny of ndhD, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S6. ML gene phylogeny of ndhF, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted. Figure S7. ML gene phylogeny of ndhK, showing the phylogenetic placement of Saniculiphyllum paralogs (bold) among plastid orthologs. The Saniculiphyllum plastid copy is marked ***. Branch labels represent bootstrap frequencies; those below 50 are not plotted.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available at Dryad (alignments, partition files, and tree topologies; 10.5061/dryad.mgqnk98vt), and at GenBank (accession numbers in Table S1; Additional file 1). Supplemental figures are available in Additional file 1.