Recent genomic and epigenomic analyses have pointed out the heterogeneity of tumors from a same histopathological group and have identified key oncogenic alterations that enabled the description of novel tumor entities. Thus, pediatric high-grade gliomas (HGG) comprise a heterogeneous group of tumors, including H3 K27M-mutant, H3 G34-mutant, IDH-mutant and H3/IDH-wildtype HGG. Furthermore, the H3/IDH-wildtype HGG group has recently been divided into three molecular entities based on their DNA methylation profile: Receptor tyrosine kinase type I (RTK I) and II (RTKII), and MYCN-amplified, the latter representing the most frequent subgroup (41% of cases, 36/87) [4]. However, the current 2016 WHO classification does not discriminate between them. In addition, data on these entities came from large series collectively deciphering molecular landscape of HGG. Therefore, the HGG-MYCN subgroup remains poorly characterized and clinical, imaging and pathological data are scarce (Supplementary Table S1).
We investigated data from five pediatric supratentorial HGG-MYCN diagnosed by DNA methylation profiling at our institution (one case included in [7]) and we pooled them with methylation class pediatric HGG-MYCN of the literature (n = 59) [4, 5, 7]. Therefore, we analyzed clinical, histopathological and molecular data of pediatric supratentorial HGG-MYCN and compared them to their pontine counterparts [9] and did a systematic review of four groups of supratentorial pediatric HGG (including 62 H3 K27M-mutant gliomas, 31 H3-G34 mutant gliomas, 44 HGG-RTKI and 16 HGG-RTKII) [1–8, 10].
Clinical data of our cases are summarized in Table S2. The median age of pediatric HGG-MYCN (published cases and our own) was 9.0 years (range from 2 to 18) which was lower than H3 K27M (11.0 years) and H3 G34-mutant (13.0 years), RTKI (10.0 years) and RTKII subgroups (10.0 years) [1–8, 10]. This difference was only significant between HGG-MYCN and H3-G34 mutant gliomas (p < 0.001) [4, 5, 7, 8]. The sex ratio male/female for HGG-MYCN was 1.3 and 3.4, 0.6, 1.2 and 1.3 respectively for H3 G34-mutant gliomas, H3 K27M-mutant gliomas, HGG-RTKI and RTK2 (but without significant difference) [1–8, 10]. HGG-MYCN were mostly located in the hemispheres (31/37 cases with available data, 83.8%), but 5 (13.5%) were thalamic and one arose from the sellar area [4, 5, 7]. There was a slight predilection for temporal lobes (16/37 cases, 43.2%), which was significantly higher than in other subgroups (p < 0.001).
By imaging, no calcifications were observed and only one tumor was hemorrhagic (Case 5). They were well-circumscribed with meningeal attachment (except for thalamic tumors). They appeared as solid hypercellular masses with a restricted apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in the main part of the tumors. They displayed slight peri-lesional edema and homogeneous enhancement after contrast injection (Fig. 1). These imaging characteristics were quite similar to their pontine counterparts [9].
Fig. 1.
Radiological features of two supratentorial HGG-MYCN. First line: Case 3. (a) T1-weighted images after contrast media injection, (b) T2-weighted images, and (c) diffusion-weighted images: a solid lesion with peri-lesional edema, homogeneous enhancement and hypercellularity (apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) on diffusion weighted images is restricted in the main part of the tumor). Second line: Case 1. (d) T1-weighted images after contrast media injection, (e) FLAIR-weighted images and (f) cerebral blood flow map using arterial spin labeling: a solid and infiltrative lesion with homogeneous enhancement and high cerebral blood flow
The mean/median progression-free survival was 9.3/9.0 months for HGG-MYCN, 8.8/9.0 months for HGG-RTKI, 8.7/6.3 months for supratentorial H3 K27M-mutant HGG and 10.5/10.0 months for H3 G34-mutant HGG without significant differences in univariate analysis (p = 0.421) (Fig. 2) [1–3, 5–8, 10]. The mean/median overall survival (OS) was 16.4/16.5 months for HGG-MYCN, 12.0/11.5 months for HGG-RTKI, 13.9/12.0 months for supratentorial HGG-K27M and 17.6/15.0 months for HGG-G34 without significant differences in univariate analysis (p = 0.109) (Fig. 2) [1–3, 5–8, 10]. This median OS was significantly longer (p < 0.001) than pontine HGG-MYCN (median OS of 1.5 months, likely due to tumor location) [7, 9].
Fig. 2.
Results of the systematic review of supratentorial molecular subgroups of pediatric HGG. a There was no significant difference in terms of progression-free survival (PFS) between HGG-MYCN, HGG-RTKI, supratentorial H3 K27M-mutant HGG and H3 G34-mutant HGG in univariate analysis (p = 0.421). b There was no significant difference in terms of progression-free survival (PFS) between HGG-MYCN, HGG-RTKI, supratentorial H3 K27M-mutant HGG and H3 G34-mutant HGG in univariate analysis (p = 0.109). c There was a significant difference in terms of overall survival (OS) between supratentorial HGG-MYCN and pontine HGG-MYCN in univariate analysis (p < 0.001)
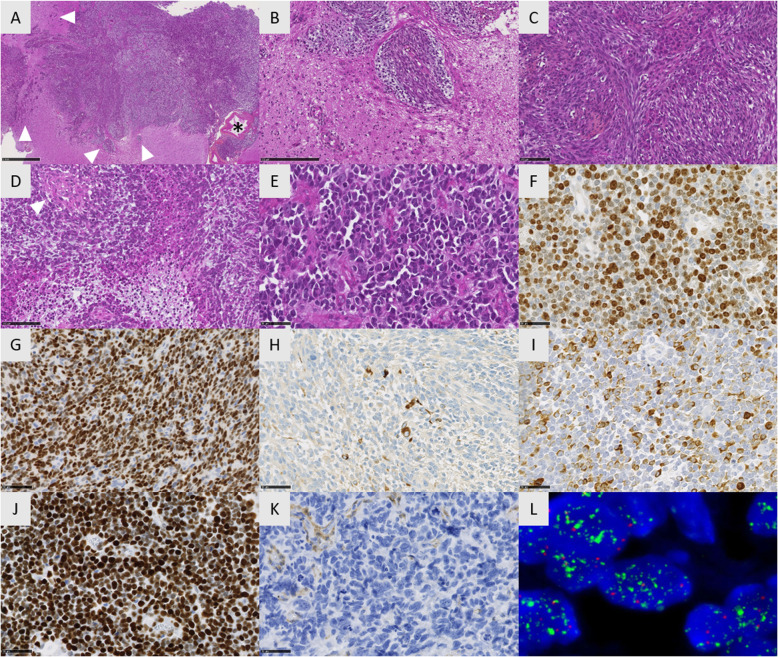
Histopathological features of all our HGG-MYCN were similar to those described in pontine HGG-MYCN [9]. These undifferentiated neoplasms presented circumscribed nodules and isolated tumoral cells infiltrating the brain (corresponding to the radiological peri-lesional edema). Leptomeningeal extension was common, (Fig. 3a and b). The proliferations were highly cellular, composed of alternating spindle and epithelioid cells with prominent nucleoli (Fig. 3c-e). In all five cases, malignancy was obvious with high mitotic count and proliferation index (mean MIB1 index 66%), necrosis, and microvascular proliferation (Fig. 3d-f). Immunohistochemical findings are summarized in supplementary Table S3. There was no expression of H3K27M, IDH1R132H, Lin28A and a preserved expression of H3K27me3, INI1 and ATRX in all tumors. Tumor cells co-expressed at least one glial and one neuronal marker (Fig. 3g-i). All these results were in line with the literature (20/25 reported cases were initially diagnosed as primary neuroepithelial tumors –PNET) [7]. Contrarily to pontine tumors, no pluriphenotypic pattern was observed in the supratentorial location [9]. In all 5 cases, tumor cells exhibited a strong nuclear and diffuse accumulation of p53 (Fig. 3j) and TP53 mutations were found by next-generation sequencing analyses (as in 56.2% of reported cases) [5, 7]. Interestingly, loss of PTEN expression was constantly observed in all 5 supratentorial HGG-MYCN (Fig. 3k), contrarily to their pontine counterparts [9]. Tumor cells presented a preserved expression of ATRX in all 5 cases which was consistent with the reported data (25/26) [4]. No hTERT promoter mutation was observed in the 5 tumors diagnosed at our institution (possibly due to the small size of our series), contrary to 18.7% (6/32) of reported cases [4, 5].
Fig. 3.
Histomolecular features of HGG-MYCN. a Diffuse and solid proliferation with several nodules infiltrating the brain parenchyma (arrowheads) and the leptomeninge with large vessels (asterisk) (Case 2, HPS, × 100 magnification). b Dense proliferation of tumour cells organized in nodules following Virchow-Robin spaces around capillaries (Case 2, HPS, × 250 magnification). c Highly cellular and undifferenciated proliferation composed of alternating fascicles and nodules (Case 2, HPS, × 250 magnification). d Highly malignant tumor with microvascular proliferation (arrowhead) and necrosis (Case 2, HPS, × 400 magnification). e Embryonal proliferation composed of hyperchromatic cells presenting anisocaryotic nuclei with numerous apoptotic bodies (Case 3, HPS, × 400 magnification). f Elevated proliferation index (Case 2, MIB, × 400 magnification). g Diffuse expression of Olig2 (Case 2, × 400 magnification). h Focal expression of GFAP by tumor cells (Case 2, × 400 magnification). i Expression of neurofilament in numerous tumor cells (Case 3, × 400 magnification). j Nuclear accumulation of p53 (Case 2, × 400 magnification). k PTEN loss of expression in tumor cells (endothelial cells as positive internal controls). l High-level of MYCN amplification by FISH analysis with MYCN locus in green signals and control centromeric in red signals (Case 4). Black scale bars represent 1 mm (a), 100 μm (b) and 50 μm (C to K)
HGG-MYCN is a DNA methylation defined tumor entity based on clustering analyses, and tumors constituting this methylation cluster often exhibit MYCN amplification (52.3% of reported cases, 34/65) [4, 7]. MYCN amplification is easily detectable by FISH analysis and was observed in the 5 tumors diagnosed at our institution (Fig. 3l). ID2 amplification is frequently observed in this DNA methylation cluster (72.2%, 26/36 reported HGG-MYCN, including the 5 tumors from our institution), and was reported in one tumor lacking MYCN amplification (1/63 cases, 1.6%) [4, 7] suggesting that ID2 amplification is characteristic of this methylation class and might help diagnose this entity.
Here, we extend the knowledge of pediatric supratentorial HGG-MYCN and present their clinico-radiological and morpho-immunophenotypes. We recommend systematically adding MYCN and ID2 analyses to the diagnostic molecular panel for pediatric H3/IDH-wildtype malignant supratentorial tumors with glioneuronal phenotype. Nevertheless, considering the relatively high proportion of tumors belonging to this cluster lacking MYCN amplification, this diagnosis can only be made with certainty by DNA methylation profiling and further investigations are needed to better characterize this entity and identify alternative oncogenic drivers to MYCN amplification.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Summary of available data concerning pediatric HGG-MYCN in the literature.
Additional file 2: Table S2. Clinical data of pediatric HGG-MYCN of our series.
Additional file 3: Table S3. Immunohistochemical profile and molecular data of pediatric HGG-MYCN of our series.
Authors’ contributions
ATE, JG, SP, AR, VDR and NB compiled the MRI and clinical records; ATE, MP, AG, EL, FC and PV conducted the neuropathological examinations; MAD, DC and RS conducted the molecular studies; ATE and PV drafted the manuscript; all authors reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
JG received funding from the charity “l’Etoile de Martin” and from the Carrefour Foundation “Les Boucles du Coeur” for the sequencing programme RARE.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest directly related to the topic of this article.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s40478-020-00974-x.
References
- 1.Aihara K, Mukasa A, Gotoh K, Saito K, Nagae G, Tsuji S, Tatsuno K, Yamamoto S, Takayanagi S, Narita Y, Shibui S, Aburatani H, Saito N. H3F3A K27M mutations in thalamic gliomas from young adult patients. Neuro-Oncol. 2014;16:140–146. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Broniscer A, Hwang SN, Chamdine O, Lin T, Pounds S, Onar-Thomas A, Chi L, Shurtleff S, Allen S, Gajjar A, Northcott P, Orr BA. Bithalamic gliomas may be molecularly distinct from their unilateral high-grade counterparts. Brain Pathol Zurich Switz. 2018;28:112–120. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Mulcahy Levy JM. H3 K27M-mutant gliomas in adults vs. children share similar histological features and adverse prognosis. Clin Neuropathol. 2018;37(2018):53–63. doi: 10.5414/NP301085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Korshunov A, Schrimpf D, Ryzhova M, Sturm D, Chavez L, Hovestadt V, Sharma T, Habel A, Burford A, Jones C, Zheludkova O, Kumirova E, Kramm CM, Golanov A, Capper D, von Deimling A, Pfister SM, Jones DTW (2017) H3−/IDH-wild type pediatric glioblastoma is comprised of molecularly and prognostically distinct subtypes with associated oncogenic drivers. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 10.1007/s00401-017-1710-1 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 5.Mackay A, Burford A, Molinari V, Jones DTW, Izquierdo E, Brouwer-Visser J, Giangaspero F, Haberler C, Pietsch T, Jacques TS, Figarella-Branger D, Rodriguez D, Morgan PS, Raman P, Waanders AJ, Resnick AC, Massimino M, Garrè ML, Smith H, Capper D, Pfister SM, Würdinger T, Tam R, Garcia J, Thakur MD, Vassal G, Grill J, Jaspan T, Varlet P, Jones C. Molecular, pathological, radiological, and immune profiling of non-brainstem pediatric high-grade Glioma from the HERBY phase II randomized trial. Cancer Cell. 2018;33:829–842.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ryall S, Guzman M, Elbabaa SK, Luu B, Mack SC, Zapotocky M, Taylor MD, Hawkins C, Ramaswamy V. H3 K27M mutations are extremely rare in posterior fossa group a ependymoma. Childs Nerv Syst ChNS Off J Int Soc Pediatr Neurosurg. 2017;33:1047–1051. doi: 10.1007/s00381-017-3481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sturm D, Orr BA, Toprak UH, Hovestadt V, Jones DTW, Capper D, Sill M, Buchhalter I, Northcott PA, Leis I, Ryzhova M, Koelsche C, Pfaff E, Allen SJ, Balasubramanian G, Worst BC, Pajtler KW, Brabetz S, Johann PD, Sahm F, Reimand J, Mackay A, Carvalho DM, Remke M, Phillips JJ, Perry A, Cowdrey C, Drissi R, Fouladi M, Giangaspero F, Łastowska M, Grajkowska W, Scheurlen W, Pietsch T, Hagel C, Gojo J, Lötsch D, Berger W, Slavc I, Haberler C, Jouvet A, Holm S, Hofer S, Prinz M, Keohane C, Fried I, Mawrin C, Scheie D, Mobley BC, Schniederjan MJ, Santi M, Buccoliero AM, Dahiya S, Kramm CM, von Bueren AO, von Hoff K, Rutkowski S, Herold-Mende C, Frühwald MC, Milde T, Hasselblatt M, Wesseling P, Rößler J, Schüller U, Ebinger M, Schittenhelm J, Frank S, Grobholz R, Vajtai I, Hans V, Schneppenheim R, Zitterbart K, Collins VP, Aronica E, Varlet P, Puget S, Dufour C, Grill J, Figarella-Branger D, Wolter M, Schuhmann MU, Shalaby T, Grotzer M, van Meter T, Monoranu C-M, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Snuderl M, Forrester LA, Koster J, Versteeg R, Volckmann R, van Sluis P, Wolf S, Mikkelsen T, Gajjar A, Aldape K, Moore AS, Taylor MD, Jones C, Jabado N, Karajannis MA, Eils R, Schlesner M, Lichter P, von Deimling A, Pfister SM, Ellison DW, Korshunov A, Kool M. New brain tumor entities emerge from molecular classification of CNS-PNETs. Cell. 2016;164:1060–1072. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sturm D, Witt H, Hovestadt V, Khuong-Quang D-A, Jones DTW, Konermann C, Pfaff E, Tönjes M, Sill M, Bender S, Kool M, Zapatka M, Becker N, Zucknick M, Hielscher T, Liu X-Y, Fontebasso AM, Ryzhova M, Albrecht S, Jacob K, Wolter M, Ebinger M, Schuhmann MU, van Meter T, Frühwald MC, Hauch H, Pekrun A, Radlwimmer B, Niehues T, von Komorowski G, Dürken M, Kulozik AE, Madden J, Donson A, Foreman NK, Drissi R, Fouladi M, Scheurlen W, von Deimling A, Monoranu C, Roggendorf W, Herold-Mende C, Unterberg A, Kramm CM, Felsberg J, Hartmann C, Wiestler B, Wick W, Milde T, Witt O, Lindroth AM, Schwartzentruber J, Faury D, Fleming A, Zakrzewska M, Liberski PP, Zakrzewski K, Hauser P, Garami M, Klekner A, Bognar L, Morrissy S, Cavalli F, Taylor MD, van Sluis P, Koster J, Versteeg R, Volckmann R, Mikkelsen T, Aldape K, Reifenberger G, Collins VP, Majewski J, Korshunov A, Lichter P, Plass C, Jabado N, Pfister SM. Hotspot mutations in H3F3A and IDH1 define distinct epigenetic and biological subgroups of glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:425–437. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.08.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tauziède-Espariat A, Debily M-A, Castel D, Grill J, Puget S, Sabel M, Blomgren K, Gareton A, Dangouloff-Ros V, Lechapt E, Boddaert N, Varlet P. An integrative radiological, histopathological and molecular analysis of pediatric pontine histone-wildtype glioma with MYCN amplification (HGG-MYCN) Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7:87. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0738-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang L, Li Z, Zhang M, Piao Y, Chen L, Liang H, Wei Y, Hu Z, Zhao L, Teng L, Lu D. H3 K27M-mutant diffuse midline gliomas in different anatomical locations. Hum Pathol. 2018;78:89–96. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2018.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Summary of available data concerning pediatric HGG-MYCN in the literature.
Additional file 2: Table S2. Clinical data of pediatric HGG-MYCN of our series.
Additional file 3: Table S3. Immunohistochemical profile and molecular data of pediatric HGG-MYCN of our series.