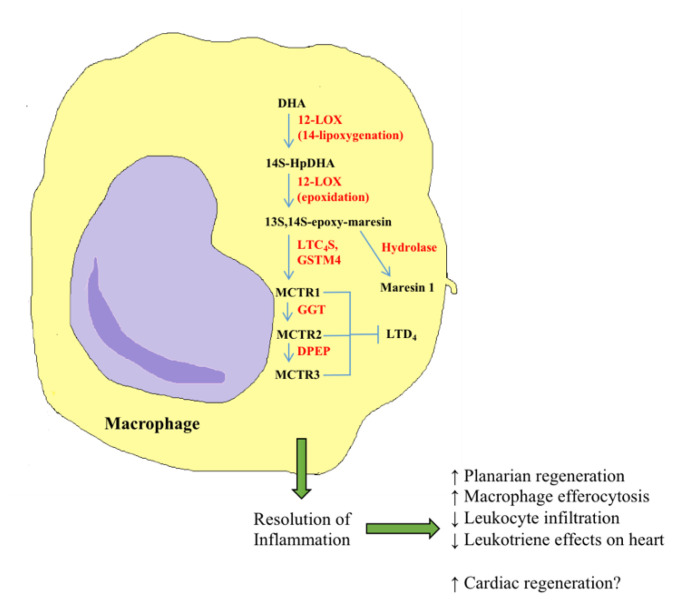
Figure 4.
Maresin biosynthetic pathways in the resolution of inflammation. In human macrophages, DHA is converted to a 13,14-epoxide intermediate through the actions of LOX enzymes. This intermediate can then be hydrolyzed into maresin 1 or conjugated to peptides at position 13 on the DHA backbone to form MCTRs. The bioactive maresins and MCTRs produced by macrophages play a role in the resolution of inflammation, partly through countering the pro-inflammatory effects of leukotrienes, and this activity may be key to facilitating cardiac regeneration. Abbreviations: DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; DPEP, dipeptidase; GGT, γ-glutamyl transferase; GSTM4, glutathione S-transferase µ4; HpDHA, hydroperoxy-docosahexaenoic acid; LOX, lipoxygenase; LTC4S, leukotriene C4 synthase; LTD4, leukotriene D4; MaR1, maresin 1; MCTR1/2/3, maresin conjugate in tissue regeneration 1/2/3.