ABSTRACT
Palliative care is an important component of the medical response to pandemics and other health emergencies. The principles of palliative care do not change, but the practice of palliative care has to change as a result of factors such as greater demand and infection control measures. This article makes suggestions for palliative care provision during a pandemic (in developed countries), based on a limited review of the literature and personal experience of the ongoing pandemic (COVID-19 infection).
KEYWORDS: Palliative, end-of-life, pandemic, COVID-19
‘to cure sometimes
to relieve often
to comfort always’
Anonymous, 15th century AD
Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) has stated that ‘humanitarian responses to emergencies and crises should include palliative care and symptom control’. Moreover, it has stated that ‘responses that do not include palliative care are medically deficient and ethically indefensible’.1 It should be noted that the WHO defines palliative care as ‘an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families facing the problem associated with life-threatening illness, through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems, physical, psychosocial and spiritual’.2
In ‘normal’ times, most palliative care is provided by non-specialists (in palliative care), although research suggests that many more patients would benefit from input from specialist palliative care services. Similarly, in times of pandemics and other healthcare emergencies, most palliative care will need to be provided by non-specialists, with specialist palliative care services providing targeted support for patients, families and colleagues. However, applying the principles of palliative care at such times is extremely challenging, particularly in the context of strict infection control measures and healthcare professionals working to capacity in highly stressful situations.
Principles of care
The guiding ethical principle of managing patients during pandemics and other healthcare emergencies is that ‘everyone matters equally’ (although ‘this does not mean that everyone is treated the same’).3 Patients who are not for escalation of treatment (or are for de-escalation of treatment) deserve adequate ‘basic care’, and timely/appropriate management of symptoms and other end-of-life care problems. Moreover, they need empathy and ‘safe’ personal interactions (especially in the absence of families) (Box 1). It is important that sufficient resources are ring-fenced for these patients in the same way that resources are ring-fenced for patients requiring intensive (interventional) treatments.
Box 1.
Considerations when caring for palliative care patients during a pandemic (in the context of strict infection control measures).
Engage as much as possible with patient:
Ensure that symptoms are controlled Facilitate remote contact with family, eg using mobile phones Facilitate direct contact with family for end-of-life care patients Communicate regularly with family Consider modifications to environment (to improve patient experience) Manage expectations, eg preferred place of care/death |
Utilisation of resources
Human resources (specialist palliative care)
As discussed, specialist palliative care is a finite resource, and during pandemics and other healthcare emergencies, it is important that this resource is utilised appropriately to manage those patients affected by the pandemic as well as those patients who make up the ‘normal’ palliative care population (eg patients with life-limiting conditions, cancer patients requiring supportive care).
Everyone's job plan/rota should be reviewed (and invariably be amended). Moreover, this needs to be an ongoing process, since the clinical situation will change as the pandemic progresses (and eventually subsides), and as workforce issues develop (ie isolation, illness, physical fatigue, psychological fatigue / ‘burnout’). Table 1 outlines a ‘Yes, Maybe, No’ approach to job planning during pandemics and other healthcare emergencies.
Table 1.
A ‘Yes, Maybe, No’ approach for job planning for specialist palliative care healthcare professionals during pandemics and other healthcare emergencies.
| Category | Yes | Maybe | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | ‘Specialist palliative care’ – activities related to specialist training | ‘General medical care’ – activities related to general medical training | Non-essential ‘usual’ activities |
| Examples | Symptom control – difficult cases End-of-life care – difficult cases Education and training – symptom control, end-of-life care [Audit and research] |
Medical management of patients [Decision making around escalation de-escalation] [Breaking ‘bad news’] |
Generally non-clinical activities |
| Role of other healthcare professionals / other staff | Many activities can be shared within specialist palliative care teams Some activities can be delegated to other healthcare professionals (with appropriate training/support) |
Medical management overseen by medical/support teams (eg ITU team). | Some activities can be delegated to administrative staff and/or volunteers Apply ‘3-D’ approach:
|
| Population of patients | Pandemic patients:
|
Pandemic patients (‘Normal’ palliative care patients) |
(‘Normal’ palliative care patients) |
It is important that job planning / task allocation reflects the person's specific knowledge and skills, and it should not be unduly influenced by what the person wants to do (eg managing acutely unwell patients) or what other people don't want to do (eg breaking ‘bad news’ to patients/carers). Nevertheless, everyone should expect to undertake activities outside their normal scope (including menial duties), and potentially outside their ‘comfort zone’. In the latter instance, it is essential that appropriate training/support is readily available.
Other resources
Pandemics and other healthcare emergencies often result in scarcities of drugs, equipment and consumables (eg personal protective equipment). Fortunately, the symptoms experienced by patients with COVID-19 are manageable with commonly available medications, and there are invariably alternatives to first-line options. For example, opioids are effective in managing shortness of breath, and while morphine is usually the first-line option, other opioids are equally effective.
Syringe pumps (‘syringe drivers’) are often used to give medication to patients at the end of life. However, syringe pumps are not essential to providing good end-of-life care, and patients’ symptoms can potentially be managed by either intermittent subcutaneous injections or the use of other routes of administration (ie intravenous, transdermal, oral transmucosal, intranasal, rectal).4,5 Indeed, syringe pumps only became established in the early 1990s, although they had been in use for a decade or so beforehand.6
Guidelines
The symptoms/problems experienced by patients with COVID-19 are not unique, and the management of patients should be based on the available evidence from analogous cohorts of patients (with necessary adjustments). Unfortunately, some promoted guidance is lacking in evidence (eg benzodiazepines to manage shortness of breath per se) or is impractical in many COVID-19 patients (eg breathing/relaxation techniques for shortness of breath).
The Palliative Care Formulary is a reputable source of information about symptom control (and end-of-life care management).5 An alternative is the British National Formulary.7 Table 2 gives an overview of symptom control in patients with COVID-19 infection.8–13 Patients with difficult-to-control symptoms / other problems should be referred to / discussed with the local specialist palliative care team in a timely manner (and advice from these teams should be available 24 hours per day / 7 days per week).
Table 2.
Principles of symptom control in patients with COVID-19 infection.
| Symptom | Intervention (first-line) | Comments |
| All symptoms | Exclude other conditions (Treat other conditions) |
Non-pharmacological interventions may not be practical at the end of life (especially in patients in isolation) |
| Fever | Cooling measures (not fan) Paracetamol – usual routes, usual doses |
Fans are not recommended (infection control) Concerns have been raised about the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, but at present the evidence is lacking to support these concerns8 |
| Cough (dry) | Simple linctus9 Opioids9 – usual routes, small doses (cf pain) |
Opioids are not indicated in a productive cough9 |
| Shortness of breath | Opioids10 – usual routes, small doses (cf pain) | Fans are not recommended (infection control) Oxygen may not improve shortness of breath (even in patients with severe hypoxia) Benzodiazepines do not improve shortness of breath, although they can be used to manage related anxiety11 |
| Delirium / terminal restlessness | Exclude reversible causes [Non-pharmacological interventions – see above] Haloperidol12 – usual routes, usual doses |
Second-line (sedating) pharmacological interventions include levomepromazine and midazolam |
| Audible upper airway secretions (‘death rattle’) | No evidence to support any pharmacological intervention (or non-pharmacological intervention)13 [Anticholinergics are generally prescribed] |
Patients are usually not distressed by these upper airway secretions Explanation/reassurance is needed for family members (and others) |
| Pain | Manage in usual way | Not a major feature of COVID-19 infection |
| Nausea and vomiting | Manage in usual way | Not a major feature of COVID-19 infection |
Learning the lessons
Lessons from previous pandemics
The medical literature contains a number of articles about the potential role of palliative care in healthcare emergencies,14,15 although there are limited reports about the actual role of palliative care (or specialist palliative care services) in previous healthcare emergencies.16,17 Indeed, there is no evidence to support any specific model of palliative care in these circumstances.18
Paladino and colleagues reported on the consequences of the Ebola outbreak in Africa in 2014–16:19 they highlighted high levels of psychological distress in Ebola survivors (eg depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)), in the general population (eg abnormal grief response, PTSD) and also among healthcare professionals (eg burnout, PTSD). Moreover, they reported ongoing physical health problems in Ebola survivors (eg insomnia, short-term memory problems).
We need to anticipate similar problems following the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, we need to anticipate problems arising from the cancellation, postponement or modification of treatment given to other groups of patients during this period. For example, some patients with cancer may have gone from being ‘curable’ to only ‘treatable’, and some from being ‘treatable’ to only suitable for palliative care. Indeed, we suggest that a national strategy should be developed to manage the potential ‘iceberg scenario’ of the current pandemic (Fig 1).
Fig 1.
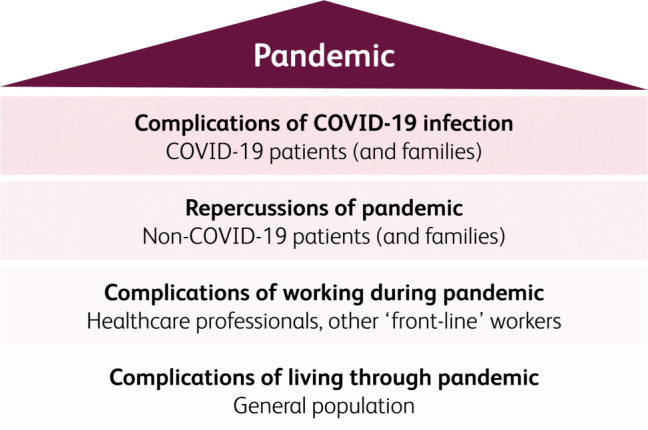
‘Iceberg scenario’ (potential consequences of COVID-19 pandemic).
Lessons from current pandemic
At the time of writing, the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic was expected in 1–2 weeks (in the UK). We have all learned lessons during this pandemic, and will surely learn further lessons over the coming weeks and months. We need to reflect on our experiences, and importantly share these experiences (both positive and negative). Moreover, we should not go back to doing things ‘the old way’, if contemporary initiatives have been successful (eg telephone/video consultations).
References
- 1.World Health Organization Integrating palliative care and symptom relief into the response to humanitarian emergencies and crises: a WHO guide. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2018. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/274565 [Accessed 23 April 2020]. [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization National cancer control programmes: policies and managerial guidelines, 2nd edn Geneva: World Health Organization, 2002. www.who.int/cancer/publications/nccp2002/en/ [Accessed 23 April 2020]. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cabinet Office and Department of Health Responding to pandemic influenza: the ethical framework for policy and planning. London: Department of Health, 2007; revised 2017. www.gov.uk/guidance/pandemic-flu#ethical-framework [Accessed 23 April 2020]. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hanks GW, Roberts CJ, Davies AN. Principles of drug use in palliative medicine. In: Doyle D, Hanks G, Cherny N, Calman K. (eds), Oxford Textbook of Palliative Medicine, 3rd edn Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2004:213–25. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Twycross R, Wilcock A, Howard P. Palliative Care Formulary, 6th edn Nottingham: Palliativedrugs.com Ltd, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Graham F, Clark D. The syringe driver and the subcutaneous route in palliative care: the inventor, the history and the implications. J Pain Symptom Manage 2005;29:32–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.BMJ Group and the Royal Pharmaceutical Society British National Formulary. London and Basingstoke: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press, 2019. https://bnf.nice.org.uk/ [Accessed 23 April 2020]. [Google Scholar]
- 8.GOV.UK Commission on Human Medicines advice on ibuprofen and coronavirus (COVID-19). www.gov.uk/government/news/ibuprofen-use-and-covid19coronavirus [Accessed 23 April 2020].
- 9.NHS Scotland Scottish Palliative Care Guidelines. www.palliativecareguidelines.scot.nhs.uk/guidelines/symptom-control/Cough.aspx [Accessed 23 April 2020].
- 10.Barnes H, McDonald J, Smallwood N, Manser R. Opioids for the palliation of refractory breathlessness in adults with advanced disease and terminal illness. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;3:CD011008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Simon ST, Higginson IJ, Booth S, Harding R, Weingärtner V, Bausewein C. Benzodiazepines for the relief of breathlessness in advanced malignant and non-malignant diseases in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;10:CD007354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Delirium: prevention, diagnosis and management. Clinical guideline (CG103). London: NICE, 2010. (updated 2019). www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg103 [Accessed 23 April 2020]. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wee B, Hillier R. Interventions for noisy breathing in patients near to death. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008;1:CD005177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Matzo M, Wilkinson A, Lynn J, Gatto M, Phillips S. Palliative care considerations in mass casualty events with scarce resources. Biosecur Bioterror 2009;7:199–210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Downar J, Seccareccia D. Palliating a pandemic: “All patients must be cared for”. J Pain Symptom Manage 2010;39:291–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Leong IYO, Lee AOK, Ng TW, et al. The challenge of providing holistic care in a viral epidemic: opportunities for palliative care. Palliat Med 2004;18:12–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen TJ, Lin MH, Chou LF, Hwang SJ. Hospice utilization during the SARS outbreak in Taiwan. BMC Health Serv Res 2006;6:94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nouvet E, Sivaram M, Bezanson K, et al. Palliative care in humanitarian crises: a review of the literature. J Int Humanit Action 2018;3:5. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Paladino L, Sharpe RP, Galwankar SC, et al. Reflections on the Ebola public health emergency of international concern, part 2: the unseen epidemic of posttraumatic stress among health-care personnel and survivors of the 2014–2016 Ebola outbreak. J Glob Infect Dis 2017;9:45–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


