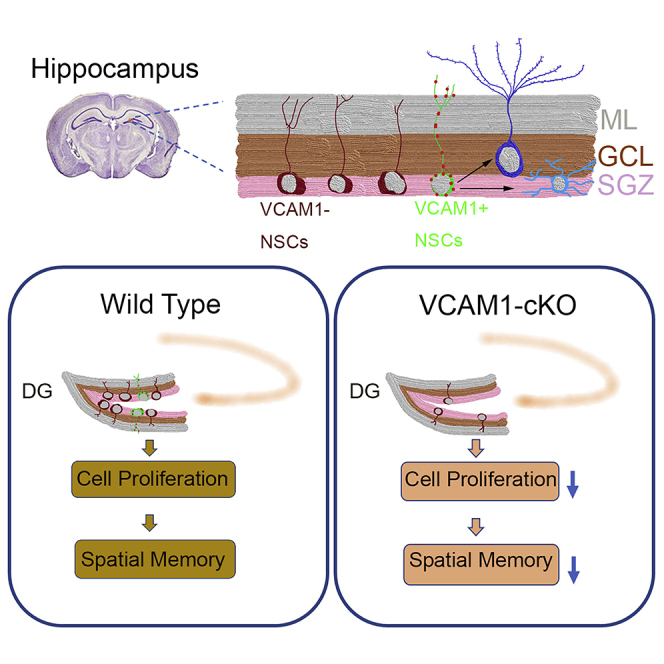
Summary
Active neural stem cells (aNSCs) and quiescent neural stem cells (qNSCs) are two distinct subpopulations found in the adult hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG). However, to date, no cell surface marker has been established to identify and profile qNSCs in the adult hippocampus. Here, we identified expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM1) on the cell surface of NSCs, through which we identified a previously unrecognized subpopulation of NSCs in the adult mouse DG. Interestingly, most VCAM1-expressing NSCs were largely quiescent. By injecting virus into Ai14 reporter mice to conduct lineage tracing in the adult DG, we confirmed that VCAM1-expressing cells were multipotent and capable of generating neurons and astrocytes. Furthermore, depletion of Vcam1 during the embryonic or adult stage impaired spatial learning and memory in mice, accompanied by a reduced number of radial glial-like cells and proliferating NSCs in the subgranular zone of Vcam1 knockout mice.
Key words: adult NSCs, hippocampus, quiescent, VCAM1, memory, GZ, multipotent, Lineage tracing
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
-
•
VCAM1 expresses on the cell surface of qNSCs in adult hippocampus
-
•
VCAM1+ cells were multipotent and capable of generating neurons and astrocytes
-
•
Loss of VCAM1+ cells impaired spatial learning and memory in mice.
In this article, Hu and colleagues show that VCAM1 expresses on the cell surface of qNSCs in adult hippocampus. These VCAM1-expressing NSCs were multipotent and capable of generating neurons and astrocytes. Loss of VCAM1-expressing NSCs during the embryonic or adult stage impaired spatial memory in mice, which indicates that VCAM1+ NSCs in the SGZ were critical for spatial learning and memory.
Introduction
In adult mammalian brains, the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG), and the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricles, are the two principal regions in which newborn neurons and glia are continually generated throughout life (Kriegstein and Alvarez-Buylla, 2009, Ming and Song, 2011). Therefore, these two regions are regarded as specific neural stem cell (NSC)-containing niches supporting the self-renewal and proliferation of stem cells throughout life (Kriegstein and Alvarez-Buylla, 2009). Noticeably, adult hippocampal neurogenesis is required for, and indeed enhanced in, hippocampus-dependent spatial learning and memory (Anacker and Hen, 2017), but not non-hippocampus-dependent learning (Lieberwirth et al., 2016, Zhao et al., 2008). The age-dependent reduction of adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus has also been linked to learning impairments in the Morris water maze task (Driscoll et al., 2006, Van der Borght et al., 2005). The above evidence suggests that adult NSCs play a pivotal role in hippocampal functions.
Generally, NSCs in the adult hippocampus are thought to be radial glia-like cells, and their cell bodies located in the SGZ. Their prominent processes project through the granule cell layer (GCL), while their short tangential processes branch in the outer GCL and inner molecular layer (Ming and Song, 2005). Increasing evidence suggested that NSCs may comprise heterogeneous populations identified with different markers, such as NES, glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP), and SOX2 (Semerci and Maletic-Savatic, 2016). NES is a well-established marker of hippocampal NSCs, and NES+ cells can differentiate into cells with different neuronal and glial characteristics (Dahlstrand et al., 1995, Renfranz et al., 1991). Clonal analysis of NSCs using Nestin-CreERT2 transgenic mice revealed that NES+ NSCs have self-renewal and multipotent capacities (Bonaguidi et al., 2011). GFAP+ glia-like radial astrocytes located in the DG of the adult mammalian hippocampus give rise to new neurons (Seri et al., 2001). However, the NES+ cell population contains GFAP+ early progenitors and GFAP− late progenitors (Fukuda et al., 2003). Moreover, single-cell gene expression profiling of NES+ NSCs in the adult hippocampus demonstrated the heterogeneity and molecular diversity between active NSCs (aNSCs) with a short-term cell cycle and quiescent NSCs (qNSCs) with a long-term cell cycle (Shin et al., 2015). Transgenic reporter mice were infected with viruses to trace SOX2+ neural precursors in the adult SGZ. Suh et al. (2007) revealed that the majority of labeled cell clusters contained only a single cell (neuron, astrocyte, or SOX2+ precursor), suggesting that these cells have a limited capacity for self-renewal and multipotency. In addition to the molecular differences in NSC subpopulations, Lugert et al. (2010) found that morphological differences, such as radial and horizontal NSCs, exist in the SGZ, and demonstrated that morphologically different NSCs exhibit distinctive responses to various stimuli, including aging, exercise, and seizures.
Previously, we reported that vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM1), a cell surface sialoglycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, is expressed in an embryonic subpopulation of NSCs that persists into adulthood (Hu et al., 2017, Kokovay et al., 2012) and is exclusively enriched in qNSCs (Codega et al., 2014). Here, we found that VCAM1 can readily label a subpopulation of NSCs in the adult mouse hippocampus. Using amplified immunohistochemical and acute staining, we observed that VCAM1 was selectively expressed in SGZ cells and co-localized with known NSC markers (NES, GFAP, and SOX2) in the adult hippocampus. We performed lineage tracing of VCAM1+ cells, and identified that these cells were quiescent and multipotent. Interestingly, when we investigated the effects of VCAM1 deletion during the embryonic or adult stage, we found that VCAM1+ NSCs in the SGZ were critical for spatial learning and memory.
Results
VCAM1 Labels a Subpopulation of Adult NSCs in the Mouse Hippocampus
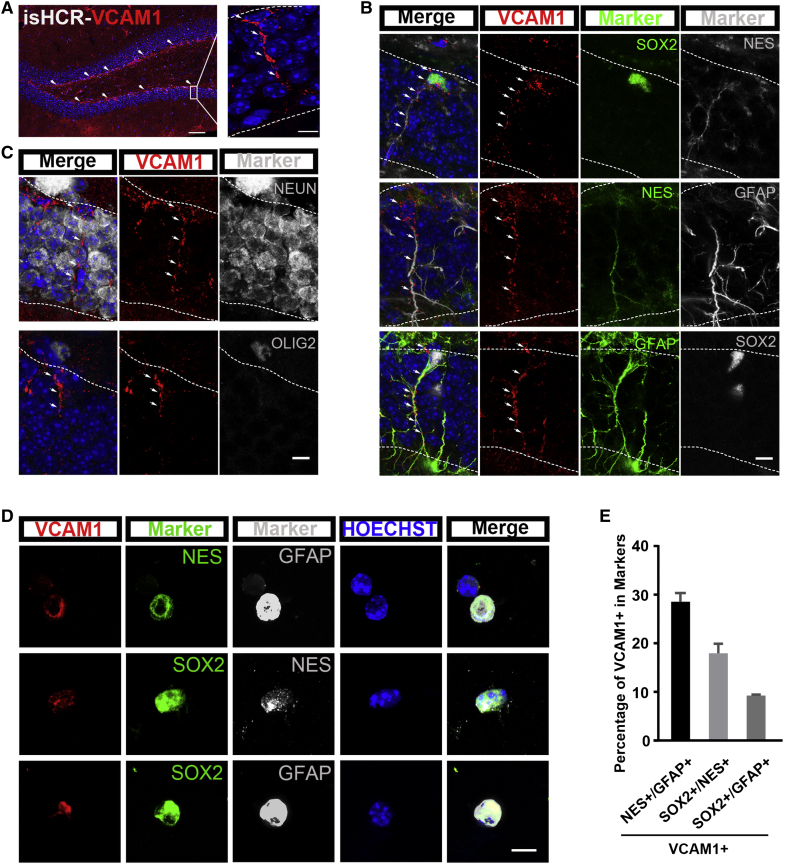
NSCs in the SVZ continually express VCAM1 from embryo stage to adulthood (Hu et al., 2017). However, it is unclear whether VCAM1 is expressed in NSCs in the adult hippocampus, another neurogenic niche in adult mammalian brains. To address this question, we first performed immunostaining of hippocampal sections from adult WT mice but observed no VCAM1 signal. Taking into consideration the possibility that VCAM1 expression may be outside the detection range of normal immunostaining, we then adopted the immunosignal hybridization chain reaction (isHCR) method. This combines antibody-antigen interactions with hybridization chain reaction technology and amplifies immunofluorescent signal intensity by up to 10,000-fold compared with normal immunostaining (Lin et al., 2018). Using the isHCR method, we detected endogenous VCAM1 expression in the SGZ of the adult hippocampus (Figure 1A). We performed co-staining for other NSC markers, and found that VCAM1 was co-localized with NES, GFAP, and SOX2 (Figure 1B). However, VCAM1 was not expressed in terminally differentiated neural cells, such as mature neurons and oligodendrocytes, which were identified by neuronal nuclei (NEUN) and oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 (OLIG2) staining, respectively (Lu et al., 2000, Teng et al., 2001) (Figure 1C).
Figure 1.
VCAM1 Labels Adult NSCs in the SGZ of the Hippocampus
(A) Representative images illustrate isHCR staining (red) of VCAM1 in brain sections from the adult mice hippocampal DG (left). A high-magnification image of the box (left) is shown on the right. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue).
(B and C) Representative images illustrate co-staining of VCAM1 (red) with NES, GFAP, or SOX2 (green or gray) (B), but not with NEUN or OLIG2 (green or gray) (C), in brain sections of adult WT mice by isHCR method.
(D) Representative images illustrate co-staining of VCAM1 (red) with GFAP, SOX2, and NES (green or gray) from acutely isolated single cells of DG in adult WT mice.
(E) Quantification of the proportion of VCAM1+ cells in NES+ GFAP+ cells, SOX2+ NES+ cells, and SOX2+ GFAP+ cells from acute staining of adult WT mice.
Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars, 250 μm (A, left), 10 μm (A, right), and 7.5 μm (B–D). Data represent mean ± SEM. (D–E) At least 1,000 cells were counted for each group.
To quantify the proportion of VCAM1+ adult hippocampal NSCs, we stained acutely isolated single cells from the hippocampal DG of adult WT mice. VCAM1 was expressed in 28.56% ± 1.80% of NES+ GFAP+ cells, 17.93% ± 2.00% of SOX2+ NES+ cells, and 9.30% ± 0.17% of SOX2+ GFAP+ cells (Figures 1D, 1E, and S1A–S1C), suggesting that VCAM1 was expressed by a small subpopulation of adult DG NSCs.
The Distribution and Identity of VCAM1-Expressing Cells in the Adult DG In Vivo
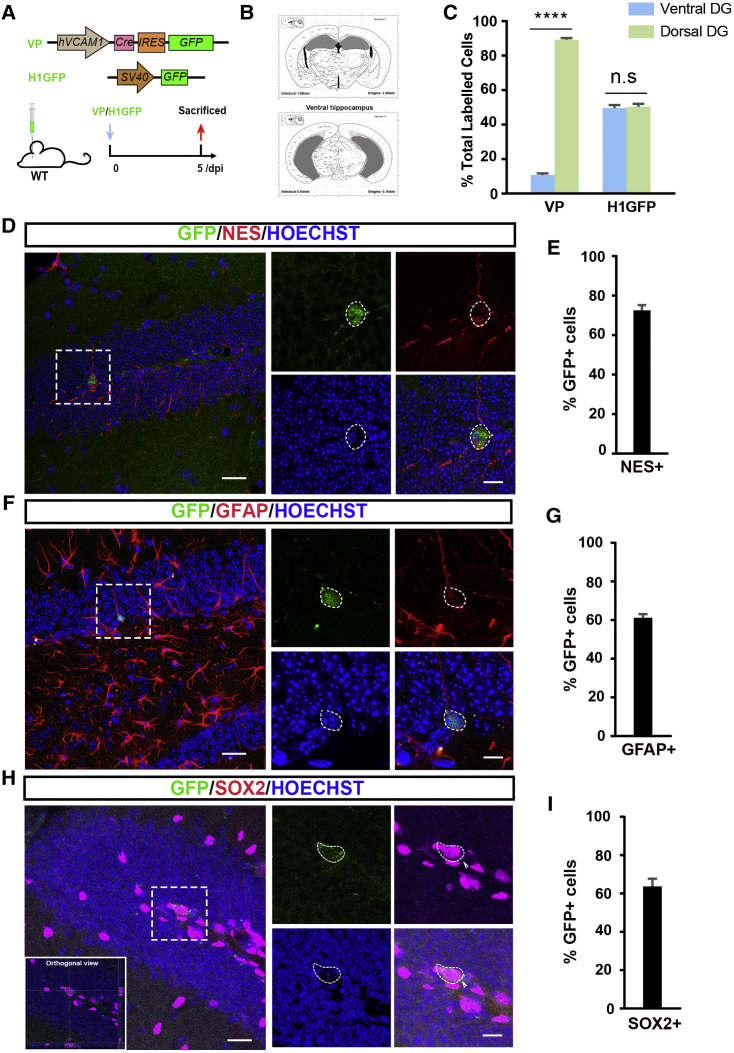
After we identified the existence of VCAM1-expressing NSCs in the adult DG, we next explored their distribution and characteristics in vivo. To label and visualize these VCAM1-expressing cells, we constructed a lentiviral vector named VP, in which a human VCAM1 promoter drives CRE and green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression (Neish et al., 1992) (Figure 2A). The specificity of this VP lentiviral vector was confirmed by infection of a VCAM1-expressing or non-VCAM1-expressing cell line in vitro (Figures S2A–S2C). Meanwhile, we constructed a nonspecific lentiviral vector, H1GFP, in which an SV40 promoter drives GFP expression, and injected this vector into the DG of adult mice (Figure 2A). We found that the H1GFP lentivirus infected almost all SGZ cells throughout the DG, confirming that lentivirus can specifically infect most SGZ cells throughout the DG as reported previously (van Hooijdonk et al., 2009) (Figure S2D).
Figure 2.
The Distribution and Identification of VCAM1-Expressing Cells in the Adult DG In Vivo
(A) The schematic shows components of VP-GFP and H1GFP lentiviral plasmids and the experimental design of viral microinjection.
(B and C) Representative location of dorsal and ventral hippocampus according to the Mouse Brain Atlas (B). The dorsal hippocampus was defined as the dorsal part of the hippocampus in coronal section before AP-2.50; the ventral hippocampus was defined as the ventral part of the hippocampus in coronal section after AP-3.16. (C) Quantitative distribution analysis of GFP+ cells is shown for the dorsal versus ventral DG at 5 dpi after infecting GFP or H1GFP+.
(D, F, and H) Representative staining images of NES (D), GFAP (F), and SOX2 (H) in the adult DG after VP lentivirus injection. Low-magnification images are shown on the left, with four high-magnification images derived from a dotted box in the left images shown on the right (H) (GFP in green and NES/GFAP/SOX2 in red, arrowhead indicates the SOX2+ cell).
(E, G, and I) Quantification of the proportion of NES+ cells (E), GFAP+ cells (G), and SOX2+ cells (I) in total GFP+ cells in SGZ through the entire DG.
Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars: (D, F, and H) 25 μm (left) and 10 μm (right). Data represent mean ± SEM. (C) Six mice for each group; (E) 3 mice/75 GFP+ cells; (G) 5 mice/118 GFP+ cells; (I) 5 mice/101 GFP+ cells. Two-way ANOVA for (B). ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; n.s., not significant. WT, wild type; dpi, days post injection.
On the fifth day post injection (dpi), we observed a small number of VP-GFP+ cells throughout the SGZ. These cells also expressed VCAM1, as determined using the isHCR method (Figures S2E–S2G). The dorsal-ventral distribution of these VP-GFP+ cells was studied: 89.25% ± 0.98% located in the dorsal part of the DG and 10.75% ± 1.70% located in the ventral part of the DG (Figure 2C). The dorsal and ventral hippocampus are marked in gray in the Mouse Brain Atlas presented in Figure 2B. In contrast, H1GFP+ cells were not differentially distributed throughout the DG (Figure 2C). These results suggest that VCAM1+ cells were primarily located in the dorsal DG, suggesting that their function might be involved in dorsal hippocampus-associated learning and memory (Kheirbek et al., 2013).
Moreover, quantitative co-localization analysis of GFP with NES/GFAP/SOX2 in the SGZ of hippocampal slices revealed that 72.55% ± 2.63% of cells were GFP+ NES+ (Figures 2D and 2E), 61.20% ± 1.91% were GFP+ GFAP+ (Figures 2F and 2G), and 63.67% ± 4.00% were GFP+ SOX2+ (Figures 2H and 2I), indicating that a large proportion of VCAM1+ cells co-express NSC markers.
VCAM1 Is Preferentially Expressed in qNSCs in the Adult DG
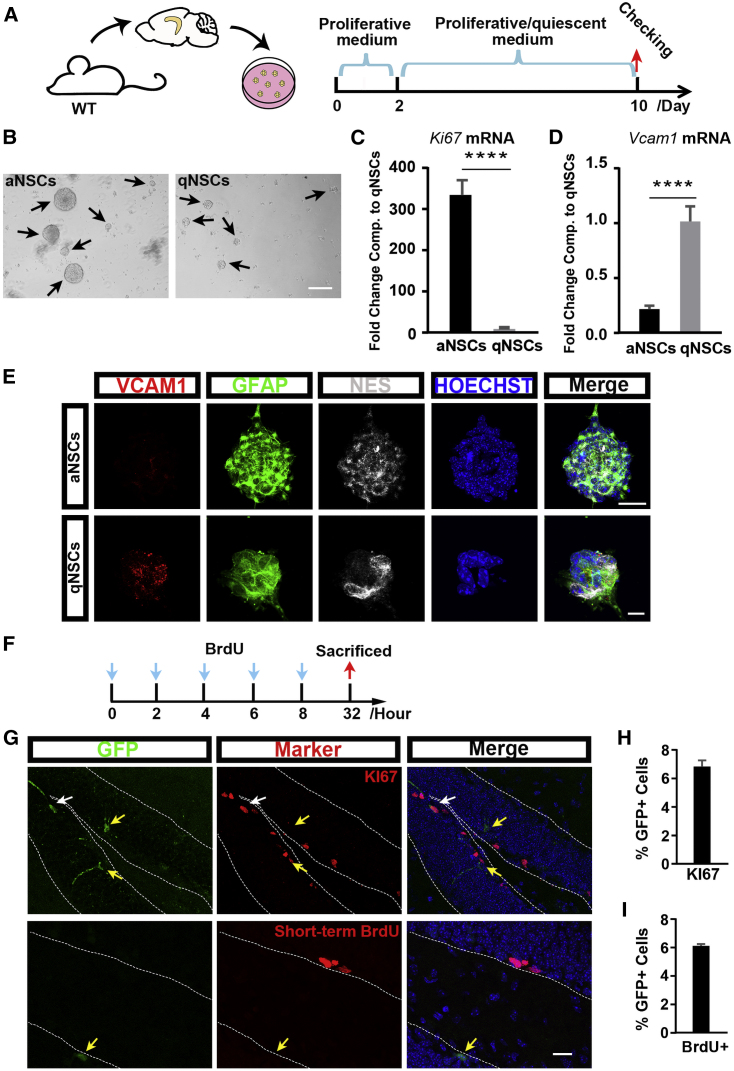
Actively proliferating and quiescent NSCs coexist in adult tissues but differ from each other with respect to many features (Lugert et al., 2010, Wang et al., 2011). Therefore, we investigated whether VCAM1 is differentially expressed in aNSCs and qNSCs in the adult hippocampus. We cultured adult hippocampal NSCs and induced quiescence by adding brain morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) into the culture system as reported previously (Knobloch et al., 2017, Mira et al., 2010) (Figure 3A). We first confirmed successful qNSC induction by determining the number and diameter of neurospheres after 8 days of BMP4 treatment in culture (Figures 3B, S3A, and S3B). We found that the expression of Ki67, a marker of cell proliferation (Starborg et al., 1996), was significantly higher in aNSCs than in qNSCs (Figure 3C). Furthermore, the expression of the NSC markers Nes and Sox2 was higher in aNSCs than in qNSCs (Figure S3C), while the expression of the intermediate progenitor marker achaete-scute Family BHLH transcription factor 1 (Ascl1) was lower in qNSCs (Figure S3D). Interestingly, the expression of Vcam1 was higher in qNSCs than in aNSCs (Figure 3D).
Figure 3.
VCAM1 Is Preferentially Expressed in qNSCs in the Adult DG
(A) Schematic outline illustrates the experiment procedure of aNSCs/qNSCs harvested from the DG of adult mice in vitro.
(B) Representative images show neurospheres of aNSCs and qNSCs in the adult DG. Arrows indicate neurospheres.
(C and D) Expression of Ki67(C) and Vcam1 (D) mRNA in aNSCs versus qNSCs at the checking time revealed by qPCR.
(E) Representative staining images for neurosphere from aNSC and qNSC cultures (VCAM1 in red, GFAP in green, and NES in gray).
(F) Experimental schemes depict the short-term (left) BrdU pulse injections in adult mice infected by VP lentivirus.
(G) Representative images show Ki67 or BrdU staining (red) and GFP+ (green) cells in the SGZ of adult DG. Yellow arrows indicate GFP+ cells only, and white arrows indicate Ki67+ GFP+ cells.
(H and I) Quantification of the proportion of Ki67+ (H) and short-term BrdU+ (I) cells in total GFP+ cells through the SGZ of the entire DG.
Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars: (B) 100 μm, (E) 25 μm (top) and 7.5 μm (bottom), and (G) 25 μm. Data represent mean ± SEM. (C and D) Twelve repeats for each group; (H) 4 mice/147 GFP+ cells; (I) 3 mice/100 GFP+ cells; Student's t test for (C) and (D). ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
To confirm the above results, we then analyzed Waterfall single-cell RNA sequencing data published by Shin et al. (2015), who reconstructed somatic stem cell dynamics with unprecedented temporal resolution. According to their data, we found that Vcam1 trajectory showed higher levels at the beginning of pseudotime and then downregulated (Figure S3E), indicating that Vcam1 expression was higher in qNSCs and was downregulated after qNSC activation (Shin et al., 2015). On the other hand, we found that the expression pattern of Vcam1 according to pseudotime was similar with that of Gfap, Sox2, and Nes (Figures S3F–S3H).
Combined with the evidence that Vcam1 is preferentially expressed in neurospheres of a smaller size (Figure 3E) and the results of the isHCR staining in the SGZ, we conclude that Vcam1 expression is higher in qNSCs in the adult hippocampus than in aNSCs and terminally differentiated cells in the adult DG.
To repeat these results in vivo, we injected the aforementioned VP lentivirus into the DG of mice and performed bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) pulse labeling. As a thymidine analog, BrdU can integrate into the genome during DNA synthesis at the S phase of the cell cycle, which is approximately 12 h long in hippocampal progenitor cells (Brandt et al., 2012, Mandyam et al., 2007). Thus, 24 h survival time after the last injection can allow us label most of the fast-dividing cells in 1 day (Wojtowicz and Kee, 2006) (Figure 3F). Quantitative analysis showed that 6.13% ± 0.12% of GFP+ cells were co-labeled with BrdU in the short-term BrdU labeling experiment (Figures 3G and 3I), which is consistent with the proportion of Ki67+ GFP+ cells in the SGZ of the adult DG (6.84% ± 0.42%, Figures 3G and 3H).
Taken together, these data demonstrate that Vcam1 expression is higher in qNSCs than in aNSCs in the adult hippocampus.
Lineage Tracing of VCAM1-Expressing NSCs in the Adult DG.
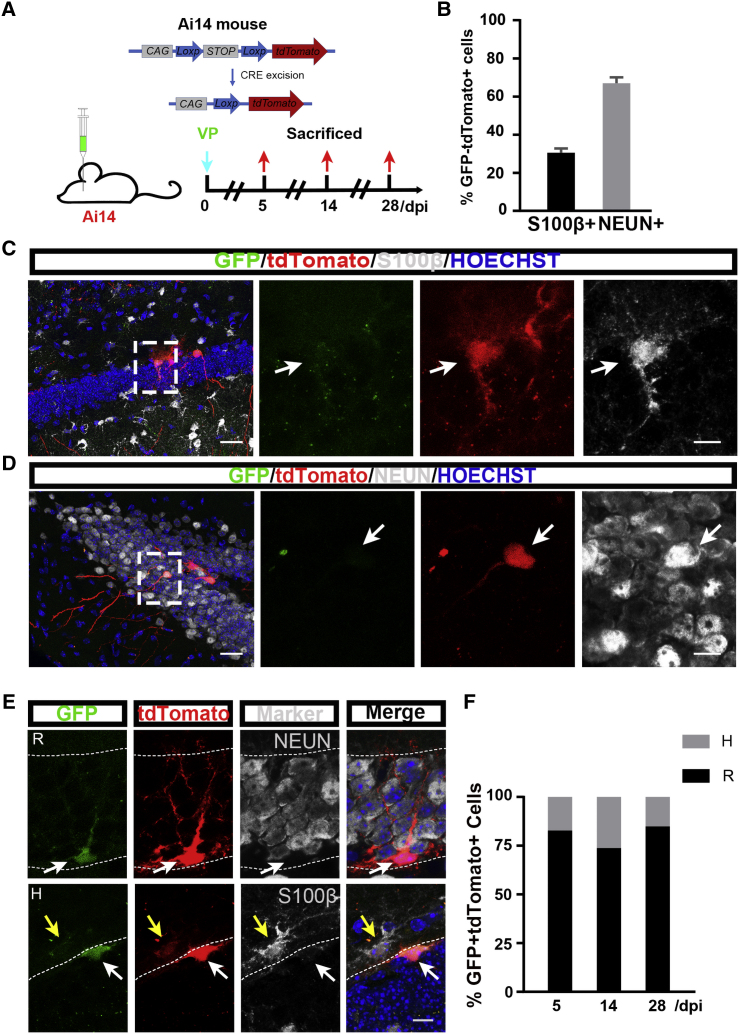
To explore the lineage identity of VCAM1-expressing NSCs in vivo, we injected the VP lentivirus into the DG of adult Ai14 Cre reporter mice. In the Ai14 mice, a loxP-flanked STOP cassette preventing transcription of a CAG promoter-driven red fluorescent protein variant (tdTomato) has been inserted into the Gt (ROSA)26Sor locus. After VCAM1+ cells are infected with the VP virus, the Vcam1 promotor initiates Cre transcription, promoting the expression of GFP protein and Cre-mediated recombination through removal of the STOP cassette, which leads to the expression of tdTomato protein in VCAM1 cells in the SGZ. As a result, the progenies of VCAM1-expressing cells should express tdTomato only, and most should migrate out of the SGZ (Madisen et al., 2010, Suh et al., 2018) (Figure 4A). Surprisingly, we observed some GFP+ tdTomato− cells exhibiting typical neuronal morphology and migrating out of the SGZ. This phenomenon is discussed in the Discussion section. To characterize the fate of GFP− tdTomato+ progenies of VCAM1-expressing cells at 28 dpi, we stained the tdTomato+ cells for specific markers, namely S100β, a marker of mature astrocytes (Zelentsova et al., 2017), and NEUN, a marker of mature neurons (Gusel'nikova and Korzhevskiy, 2015). We observed that 30.60% ± 2.27% of GFP- tdTomato+ cells were S100β+ and 66.96% ± 3.08% were NEUN+ (Figures 4B–4D). These results suggest that VCAM1-expressing NSCs can differentiate into two types of neural cells, namely neurons and astrocytes. Neurons were the major cell type generated from VCAM1+ cells.
Figure 4.
Lineage Tracing of VCAM1-Expressing NSCs in the Adult DG
(A) Experimental design for lineage tracing in vivo in the adult DG of Ai14 mice by VP lentivirus injection.
(B) Quantification of the proportion of mature astrocytes (S100β+) and mature neurons (NEUN+) in total progenies (GFP− tdTomato+) of VCAM1+ NSCs in the adult DG of Ai14 mice infected by VP lentivirus at 28 dpi.
(C and D) Representative images for progenies of VCAM1+ NSCs in the adult DG of Ai14 mice at 28 dpi. Immunostaining of S100β (C) and NEUN (D) is shown. High-magnification images from the dotted boxes from the left-most panels are shown on the right (GFP in green, tdTomato in red, and S100β/NEUN in gray). Arrows indicate progenies.
(E) Representative images of VCAM1-expressing NSCs with radial-like (R) and horizontal-like (H) morphologies in the SGZ of adult Ai14 mice (GFP in green, tdTomato in red, and S100β/NEUN in gray). White arrows indicate NSCs and yellow arrows indicate progenies.
(F) Quantification of proportion of R versus H morphology in VCAM1-expressing NSCs (GFP+ tdTomato+) in the adult SGZ of Ai14 mice at 28 dpi. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars: (D–E) 25 μm (left) and 7.5 μm (right). Data represent mean ± SEM or mean. (B) S100β, 3 mice/101 tdTomato+ cells; NEUN, 3 mice/223 tdTomato+ cells; (F) 5 dpi, 108 cells; 14 dpi, 178 cells; 28 dpi, 160 cells. Two-way ANOVA for (F).
Lugert et al. (2010) reported that NSCs in the adult SGZ were astrocytes exhibiting radial-like (R) and horizontal-like (H) morphology, which can be divided into quiescent R NSCs, quiescent H NSCs, and active H NSC subpopulations, demonstrating the existence of an association between morphology and activation state. Thus, we investigated whether VCAM1-expressing NSCs display specific morphology at different time points after VP lentivirus injection in adult Ai14 mice. The ratio of R to H VCAM1-expressing cells remained constant (82.76%–17.24% at 5 dpi, 73.77%–26.23% at 14 dpi, and 84.85%–15.15% at 28 dpi) (Figures 4F and 4G), suggesting that most VCAM1-expressing NSCs are radial-like shape and exist in a stable quiescent state in the adult DG.
To identify the spatial distribution of VCAM1 lineage cells (tdTomato+) across the adult DG, we subdivided the DG into four regions of uniform width (SGZ and GCL1, 2, and 3) as reported previously (van Hooijdonk et al., 2009) (Figure S4A). Quantification of the percentages of VCAM1 lineage cells (GFP+ tdTomato+ and GFP− tdTomato+) in each of these regions demonstrated that the majority cells resided in the SGZ at all time points. A small proportion of the cells migrated to GCL1 (1.72%, 16.39%, and 26.21% at 5, 14, and 28 dpi, respectively) or GCL2 (0.97% at 28 dpi). However, no cells reached GCL3 within 28 days (Figure S4B), indicating that they had a limited migration capacity.
Clonal Analysis of VCAM1-Expressing NSCs in the Adult DG.
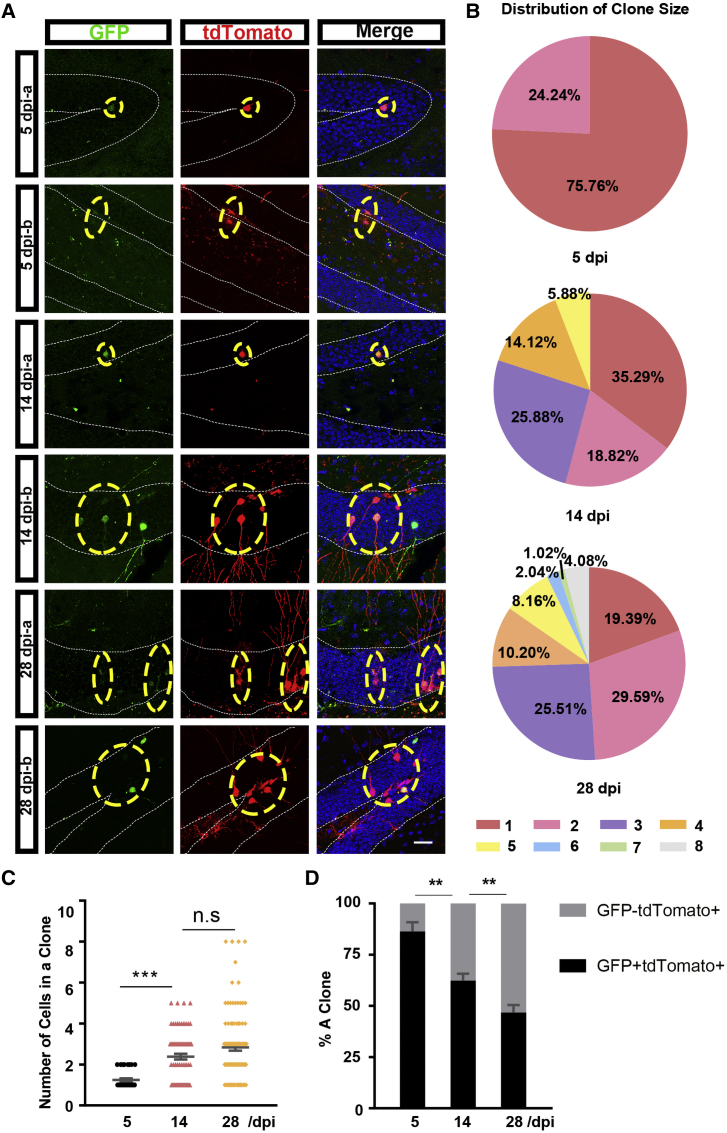
To collect reliable data on the properties of stem cells at the single-cell level, we adjusted the lentiviral titer and assessed the clonal progenies of VCAM1+ cells by measuring the distance between a GFP+ cell and the nearest GFP+ cell at 5 dpi. A ring with a radius of less than 200 μm from the clone center was used to determine the clone composition (Bonaguidi et al., 2011) (Figure S5A).
We injected Ai14 mice with the VP lentivirus and analyzed tdTomato-labeled VCAM1-expressing NSCs and their progenies at different time points. At 5 dpi, each clone was comprised of only one or two cells. At this time point, most clones contained only one cell (Figures 5A and 5B). At 14 dpi, the cell number within each clone increased, and ranged from one to five. Meanwhile, the proportion of clones containing one cell decreased to less than 40%, although this remained the predominant fraction (Figures 5A, 5B, and S5B). At 28 dpi, some clones continued to enlarge, and the maximum cell number was eight. At this time point, 19.39% of clones contained only one cell, and half of the clones were comprised of two or three cells (Figures 5A, 5B, and S5B). These results suggest that some VCAM1-expressing NSCs remained quiescent, while others underwent division during the 28-day experimental period. Furthermore, the mean clone size of VCAM1-expressing NSCs and their progenies increased significantly from 1.24 ± 0.08 at 5 dpi to 2.84 ± 0.16 at 28 dpi, suggesting that VCAM1-expressing NSCs exhibit slow proliferation (Figures 5C and 5D).
Figure 5.
Clonal Analysis of VCAM1-Expressing NSCs in the Adult DG
(A) Representative images of individual clones in the adult DG of Ai14 mice after VP lentivirus injection (GFP in green and tdTomato in red). Time points are indicated in each panel on the left. A dotted oval box represents a clone.
(B) Pie charts reporting the fraction of clone size in the adult DG of Ai14 mice at 5, 14, and 28 dpi. Color-coded rectangles on the bottom stand for the cell number within a clone.
(C) Quantitative analysis of clone size among time points in adult Ai14 mice after VP lentivirus injection.
(D) Quantification of the proportion of VCAM1-expressing NSCs (GFP+ tdTomato+) in SGZ and of their progenies (GFP− tdTomato+) in the GCL of adult DG of Ai14 mice among the time points.
Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars: (A) 25 μm. Data represent mean or mean ± SEM. (B–D) 5 dpi, 33 clones; 14 dpi, 85 clones; 28 dpi, 98 clones. One-way ANOVA for (C) and two-way ANOVA for (D). ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; n.s, no significance.
Loss of VCAM1 Impairs Spatial Learning and Memory and Reduces Adult NSCs
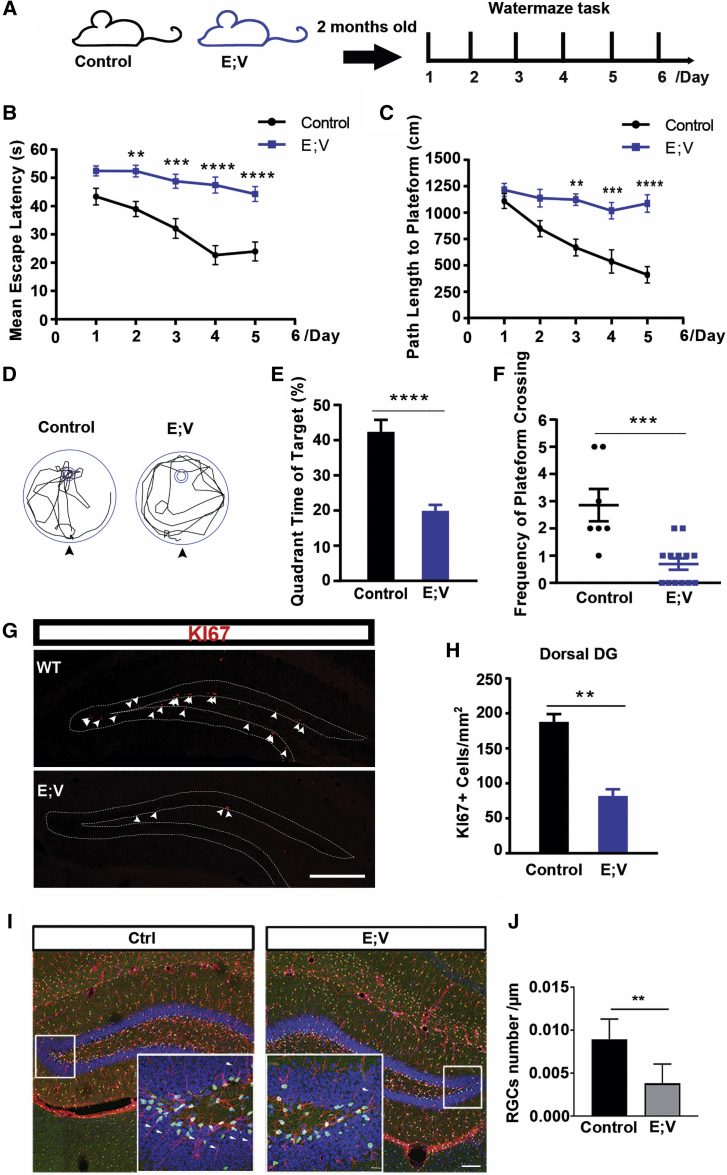
Given the predominant expression of VCAM1 in NSCs in the dorsal DG, an area involved in learning and memory (Fanselow and Dong, 2010, Goncalves et al., 2016), we wondered whether VCAM1+ NSCs play a role in spatial learning and memory. To test this hypothesis, we firstly generated EMX1-Cre; VCAM1fl/fl (E; V) VCAM1 conditional knockout mice (cKO) (Figure S6A). In these transgenic mice, Cre-mediated recombination of a loxP-flanked Vcam1 allele in EMX1-expressing cells results in region-specific deletion of the Vcam1 gene in the hippocampus during the embryonic period (Gorski et al., 2002). These mice were viable and displayed no overt developmental defects compared with their wild-type (WT) littermates.
Two-month-old E; V mice and their littermate controls were subjected to the Morris water maze task, a task commonly used to measure spatial learning and memory in rodents (Kee et al., 2007, Vorhees and Williams, 2006) (Figure 6A). Our data revealed that the length of time taken by the control mice to find the hidden platform (escape latency) decreased during the training period (Figure 6B). Remarkably, E; V mice failed to find the hidden platform throughout the acquisition trials, suggesting that these mice exhibit hippocampus-associated learning impairments. A path length parameter was also assessed, and similar differences were observed between control and E; V mice (Figure 6C), indicating a decrease in spatial learning in VCAM1 regional knockout mice. A probe trial in which the hidden platform was removed and the animal's ability to remember the location of the platform was assessed 24 h after the final acquisition trial. Control mice spent more time in the target quadrant and crossed the position of the hidden platform more frequently than E; V mice (Figures 6D–6F). In addition, every day swimming speed did not significantly differ between the control and E; V mice, demonstrating that E; V mice did not exhibit motor capability impairments (Figure S6B). These data indicate that the embryonic loss of VCAM1 in the hippocampus significantly impairs spatial learning and memory.
Figure 6.
Loss of VCAM1 Embryonically Impairs Spatial Learning and Memory Behavior and Reduces Adult NSCs
(A) Experimental design of the Morris water maze task for EMX-Cre; VCAM1fl/fl (E; V) and their littermate control (Control) mice, including EMX-Cre; VCAM1+/+, EMX-Cre; VCAM1fl/+ and VCAM1fl/fl mice at 2 months old.
(B and C) Quantification analysis of the escape latency (B) and path length to the platform (C) at each training day of acquiring trials between adult E; V and control mice.
(D) Representative swim paths during probe trial of adult E; V and control mice. The annulus stands for the position of removed hidden platform. Arrowheads indicate a start location.
(E and F) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of the time spent in the target quadrant (E) and the frequency of crossing the hidden platform (F) between adult E; V and control mice during probe trial.
(G and H) Representative images (G) and quantitative analysis (H) of Ki67 staining (red) in the dorsal DG between adult E; V and control mice. Arrowheads indicate Ki67+ signals along the SGZ. (I–J) Representative images (I) and quantitative analysis (J) of the radial process penetrating the whole GCL in SOX2+ GFAP+ stained (red) cells in dorsal DG between adult E; V and control mice. Arrowheads indicate radial processes of NSCs (SOX2+ GFAP+) along the SGZ.
Scale bars: (G and I) 250 μm and 12 μm (inset). Data represent mean ± SEM. (B, C, E, and F) E; V, 13 mice; control, 7 mice; (H and J) E; V, 4 mice; control, 3 mice. Two-way ANOVA for (B) and (C); Student's t test for (E), (F), (H), and (J). ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
To identify the type of cells affected by VCAM1 deletion, we compared the number of aNSCs (Ki67 staining) in the SGZ of E; V and control mice after the water maze test (Figure S6C). As expected, the number of Ki67+ cells in the dorsal and ventral DG were significantly lower in E; V mice than in control mice (Figures 6G–6H), suggesting that the proliferation of aNSCs in the SGZ dramatically decreased after the loss of VCAM1+ NSCs during the embryonic stage. When we stained for the NSC markers SOX2 and GFAP, we found that the radial processes of SOX2+ GFAP+ radial-like cells penetrating the whole GCL dramatically decreased in E; V mice (Figures 6I–6J). Given that a previous study reported that SOX2+ GFAP+ radial-like cells are qNSCs (Lugert et al., 2010), this result suggests that the number of qNSCs in the adult hippocampus dramatically reduces after Vcam1 deletion. Because the ventral DG is a brain structure associated with depressive behavior, we wondered whether the VCAM1-cKO mice would exhibit different depressive behavior. We tested depressive behavior using the forced swimming test, and found no significant difference between the E; V and control mice (Figures S6E–S6G).
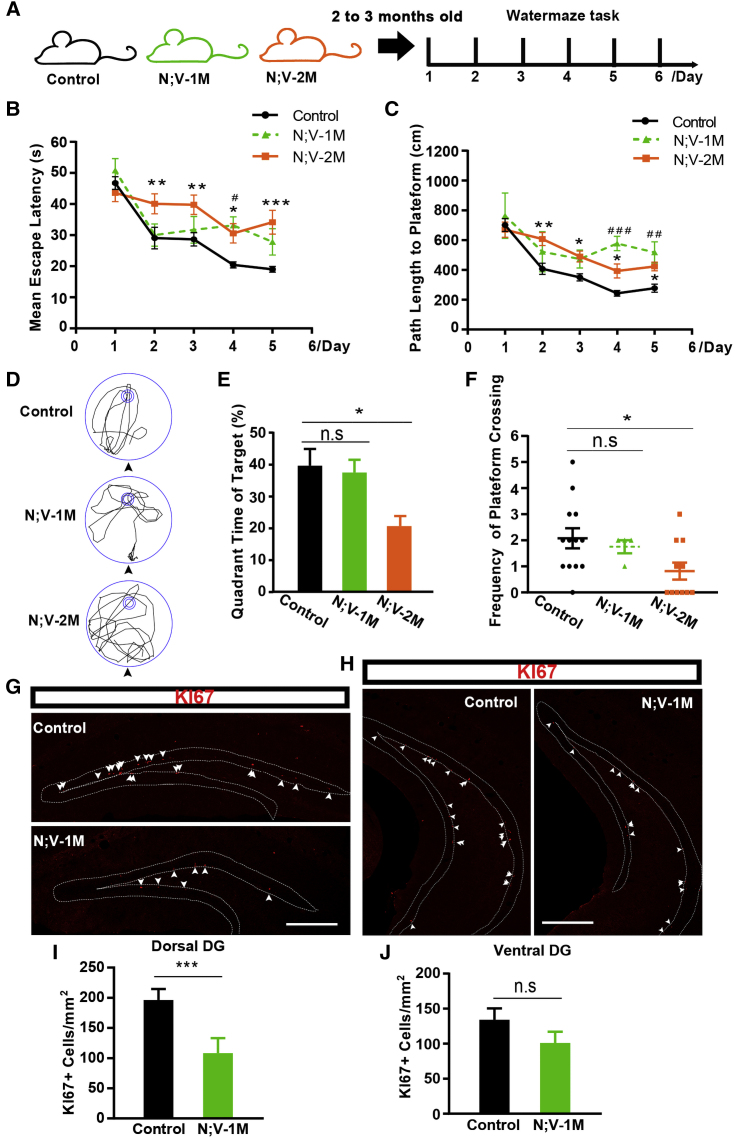
To further identify the role of VCAM1 in adult hippocampal NSCs, we generated another strain of knockout mice, Nestin-CreERT2; VCAM1fl/fl (N; V) mice. In these transgenic mice, CreERT2-mediated inducible recombination of a loxP-flanked Vcam1 allele in NES-expressing cells leads to cell-specific deletion of the Vcam1 in NSCs after tamoxifen (TAM) administration (Lagace et al., 2007) (Figure S7A).
One-month-old N; V mice and their littermate controls were administered TAM to induce the deletion of Vcam1 in NES+ cells (Figures S7B and S6A). All mice were subjected to the Morris water maze task, including N; V mice administered TAM for 1 month (N; V-1M), N; V mice administered TAM for 2 months (N; V-2M), and control mice (Figure 7A). The control mice performed well in the task. Our data showed that N; V-2M mice exhibited a longer escape latency than control mice (significant difference from days 2 to 5), while N; V-1M mice exhibited a slightly longer escape latency than control mice (Figure 7B). These results were confirmed by assessment of a path length parameter (Figure 7C). During the probe trail, the N; V-2M mice, but not the N; V-1M mice, spent less time in the target quadrant and exhibit a reduced number of platform crossings compared with the control mice (Figures 7D–7F). Meanwhile, every day swimming speed did not significantly differ between the N; V-1M, N; V-2M, and control mice (Figure S7C), indicating that all mice exhibited normal motor capability. However, when the number of aNSCs in the SGZ was compared between N; V-1M and control mice via KI67 staining, we found that the proliferation of aNSCs declined in the dorsal DG but not in the ventral DG (Figures 7G–7J). The above results suggest that VCAM1+ NSCs are involved in learning and memory in the adult brain.
Figure 7.
Loss of VCAM1 during Adulthood Weakens Spatial Learning and Memory Behavior and Reduces Adult aNSCs
(A) Experimental design of the Morris water maze task for Nestin-CreERT2;VCAM1fl/fl (N; V), including deletion for 1 month (N; V-1M) and 2 months (N; V-2M) mice, and their littermate control (control) mice, including VCAM1fl/fl, Nestin-CreERT2;VCAM1fl/+, and Nestin-CreERT2;VCAM1+/+ mice at 2 to 3 months old.
(B and C) Quantification analysis of the escape latency (B) and path length to the platform (C) at each training day of acquiring trials among adult N; V-1M, N; V-2M, and control mice.
(D) Representative swim paths during probe trial of adult N; V-1M, N; V-2M, and control mice. The annulus stands for the position of removed hidden platform. Arrowheads indicate a start location.
(E and F) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of the time spent in the target quadrant (E) and the frequency of crossing the hidden platform (F) among adult N; V-1M, N; V-2M, and control mice during probe trial.
(G and H) Representative images of KI67 staining (red) in dorsal (G) and ventral (H) DG between adult N; V-1M and control mice. Arrowheads indicate KI67+ signals along the SGZ.
(I and J) Quantitative analysis of KI67+ cells in dorsal (I) and ventral (J) DG between adult N; V-1M and control mice.
Scale bars: (G and H) 250 μm. Data represent mean ± SEM. (B–F) N; V-1M, 4 mice; N; V-2M, 11 mice; control, 13 mice; (I and J) N; V-1M, 3 mice; control, 3 mice. Two-way ANOVA for (B) and (C); one-way ANOVA for (E) and (F); Student's t test for (I) and (J). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001; n.s., not significant.
None of the above differences were noted when a visible platform was created in the water maze to test whether the transgenic mice exhibited vision defects (Figures S7D–S7G). These results confirm that the learning and memory impairments exhibited by the cKO mice were not a result of vision defects.
Discussion
The adult hippocampus houses heterogeneous populations of NSCs, which can be identified by different markers, such as NES, SOX2, GFAP, and HES5 (Bao and Song, 2018, Gebara et al., 2016, Wang et al., 2011). However, qNSCs, a subpopulation of NSCs, lack specific cell surface markers facilitating their isolation and identification. Although prominin-1 (CD133) has been identified as a cell surface marker for both SVZ and SGZ progenitors, its specificity and the identity for labeling NSCs have not been fully elucidated (Walker et al., 2013). Here, using magnified immunostaining and lineage tracing combined with lentivirus injection, we identified that VCAM1 is expressed on the cell surface of qNSCs in the adult hippocampus in vivo. Our results showed that VCAM1 was highly expressed in a subpopulation of adult NSCs, but not expressed in differentiated neurons and oligodendrocytes (Artegiani et al., 2017, Saunders et al., 2018, Shin et al., 2015). We characterized the quiescence and multipotency of VCAM1-expressing cells in the adult hippocampus in vivo. Furthermore, the loss of VCAM1 in NSCs during the embryonic or adult stage impaired hippocampus-associated learning and memory.
VCAM1-expressing cells and their progeny, which were identified by lineage tracing in this study, exhibited a low level of proliferation. A small number of cells made up each clone (1–2 or 2.84 ± 0.16 cells per clone at 5 or 28 dpi, respectively), whereas actively proliferating NSCs in the adult hippocampus have been reported to divide 2.3 ± 0.1 times and persist for 9.6 ± 1.4 days to give rise to clones containing an average of 4.8 ± 0.5 cells (Pilz et al., 2018). It seems that VCAM1-expressing NSCs are different from active NSCs but remain quiescent and serve as a steady pool of stem cells under normal conditions. The quiescent nature of VCAM1-expressing NSCs has also been demonstrated by pathway enrichment analysis of single-cell transcriptomes of adult NSCs from the hippocampus and SVZ (Codega et al., 2014). This analysis revealed that functional annotations relating to the process for maintenance of qNSCs enrich in ion or protein transport, cell communication, and cell adhesion. VCAM1 is significantly downregulated in the process of qNSC activation (Ganapathi et al., 2018, Morizur et al., 2018, Shin et al., 2015). Nevertheless, we noticed that more tdTomato+ cells appeared in one clone, while proportionally less GFP+ cells were labeled in the same clone (Figure 5D). This seems to indicate that VCAM1+ NSCs undergo gradual differentiation and simultaneously lose their self-renewal capability. Alternatively, the loss of GFP+ cells in the clone labeled by the VP lentiviral infection may result from gradual degradation of the ZsGreen GFP protein. Future studies in which VCAM1 is reliably labeled in a transgenic VCAM1 reporter mouse should therefore be conducted to clarify the biological explanation for this observation.
In this study, we found that some GFP+ cells (known to be VCAM1+ cells), particularly those located in the GCL, show typical neuron shape. Similarly, in Ai14 mice injected with the GFP virus, GFP+ tdTomato+ cells (assumed to be VCAM1+ cells) also exhibited typical neuronal morphology. These data contradict our earlier conclusion that VCAM1 is not expressed in mature neurons (Figure 1C). To explain this contradictory phenomenon, we proposed two possibilities. Firstly, following the initiation of GFP protein expression by the VCAM1 promoter, this GFP protein may not degrade sufficiently over time, and thus may ultimately persist in differentiated neurons. This may occur when VCAM1+ NSCs directly differentiate into neurons without dividing, as has been reported previously in the literature (Corish and Tyler-Smith, 1999). Alternatively, some injured neurons infected by the VP virus might express inflammation-related genes, such as VCAM1 (Zhang et al., 2015). Taken together, further investigation is needed to elucidate this phenomenon.
Sparse labeling by VP lentivirus injection revealed that VCAM1-expressing NSCs in the adult hippocampus were long-lasting NSCs with the ability to proliferate and differentiate. Moreover, we found that VCAM1-expressing NSCs exhibited radial and, to a lesser extent, horizontal morphology, which may link them to a proliferative fraction in the VCAM1-expressing NSC pool (Lugert et al., 2010).
Functional differences along the dorsal-ventral axis of the hippocampus have been well documented. The dorsal DG appears to be involved in the learning and memory processes associated with navigation and exploration (Fanselow and Dong, 2010). A number of studies have provided evidence linking adult neurogenesis and spatial learning and memory (Anacker and Hen, 2017). We hypothesized that VCAM1-expressing NSCs are involved in hippocampus-dependent learning and memory given that more VCAM1 NSCs are located in the dorsal DG than in the ventral DG, which consistent with previous report (Huckleberry et al., 2018).
In the E; V cKO mice, deletion of VCAM1 during the embryonic period severely impaired learning and memory and profoundly reduced the numbers of aNSCs and radial-like NSCs in the adult hippocampus. In the N; V cKO mice, deletion of VCAM1 from adult NSCs slightly impaired learning and memory and slightly reduced the number of hippocampal aNSCs. These results suggest that VCAM1 is required for NSC-associated learning and memory at the embryonic and adult stages. Previous studies have demonstrated that the morphological maturation and functional integration of adult-born neurons from NSCs in the DG take 4 to 8 weeks (Duan et al., 2008, Esposito et al., 2005). Thus, a reduction in the adult NSC pool (VCAM1+ NSC pool) may result in fewer adult newborn neurons being integrated into neural networks, causing learning and memory impairments. Our data that behavioral impairment was more severe in N; V-2M than N; V-1M consistent with the reports, indicating that neural network integration of newborn neurons is required for intact learning and memory. In addition to neurons differentiated from NSCs, NSCs themselves may directly contribute to hippocampal plasticity and behavior by releasing factors such as gliotransmitters into the neurogenic niche (Han et al., 2015, Tang et al., 2019). Together, our results suggest that VCAM1 plays a key role in maintaining a critical mass of NSCs in the adult hippocampus. The deletion of VCAM1 impairs hippocampal learning and memory regardless of the stage of maturation (embryonic or adult).
Experimental Procedures
Animals
Animal procedures were performed according to protocols approved by the Capital Medical University Animal Care and Use Committee. All mice were housed in standard cages in a specific pathogen-free facility. Details of this procedure can be found in the Supplemental Experimental Procedure.
isHCR
isHCR was performed according to a protocol provided by Prof. Luo (Lin et al., 2018). Details of this procedure can be found in the Supplemental Experimental Procedure.
Viral Vector Production
VP-GFP and H1GFP lentiviruses were generated in the HEK293FT cell line by polyethylenimine (PEI) transfection. Details of this procedure can be found in the Supplemental Experimental Procedure.
Adult NSC Culture
Primary adult mouse hippocampal NSCs were cultured as described previously with minor modifications (Kokovay et al., 2012). Details of this procedure can be found in the Supplemental Experimental Procedure.
BrdU Labeling
For the short-term labeling experiments, the mice were intraperitoneally injected with the thymidine analog BrdU (100 mg/kg/injection, Sigma) in saline five times at 2-h intervals. The animals were killed 24 h later.
Immunostaining and Antibodies
Sections were blocked in 5% BSA-PBST (0.1 M PBS and 0.3% Triton X-100) at room temperature for 1 h and incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies diluted in blocking solution. The brain sections were then incubated with secondary antibodies for 2 h. Following this, the slides were counterstained with a nuclear counterstain, Hoechst 33342 (Life Technologies) for 10 min. The sections were mounted with anti-fade Fluoromount-G (Southern Biotech). Details of this procedure and antibodies can be found in the Supplemental Experimental Procedure.
Gene Expression Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from proliferative and quiescent NSCs and qPCR was performed to determine the expression of target genes. Details of this procedure can be found in the Supplemental Experimental Procedure subsection.
The Morris Water Maze Task
Adult E; V, N; V, and control mice were subjected to the Morris water maze task to test spatial learning and memory. Details of this procedure can be found in the Supplemental Experimental Procedure subsection.
Author Contributions
X.-L.H. and D.-Y.W. conceived and designed the experiments. D.-Y.W., A.-F.L. performed the experiments. Q.-R.B. constructed the viral plasmids. X.-L.G. and Y. Z. supported the experiments. Q.S., X.-M.W., X.-L.H., and D.-Y.W. wrote the manuscript. Q.S., X.-M.W., and X.-L.H. supervised the project. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. John Q. Wang from UMKC for his suggestions and comments on the manuscript, Prof. Minmin Luo and Dr. Rui Lin from NIBS for their help with the isHCR protocol, Prof. Yichang Jia from Tsinghua University for his kind support, Jingjing Wang from the Laboratory Animal Center of CCMU for her technical support, Prof. Huirong Liu from CCMU for her kind support. This work was supported by a grant from Ministry of Science and Technology of China to Q. S. (2019YFA0110102), a grant from the Beijing Natural Science Foundation Program and Scientific Research Key Program of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education, China to X.-L.H. (KZ201710025016), a grant from the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission National Major R&D Program to X.-M.W. (Z161100002616007), a grant from National Key R&D Program to X.-M.W. (2016YFC1306300).
Published: June 9, 2020
Footnotes
Supplemental Information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.05.012.
Contributor Information
Qin Shen, Email: shenqin@tongji.edu.cn.
Xiao-Ling Hu, Email: huxiaoling@ccmu.edu.cn.
Xiao-Min Wang, Email: xmwang@ccmu.edu.cn.
Supplemental Information
References
- Anacker C., Hen R. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive flexibility—linking memory and mood. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017;18:335–346. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artegiani B., Lyubimova A., Muraro M., van Es J.H., van Oudenaarden A., Clevers H. A single-cell RNA sequencing study reveals cellular and molecular dynamics of the hippocampal neurogenic niche. Cell Rep. 2017;21:3271–3284. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bao H., Song J. Treating brain disorders by targeting adult neural stem cells. Trends Mol. Med. 2018;24:991–1006. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaguidi M.A., Wheeler M.A., Shapiro J.S., Stadel R.P., Sun G.J., Ming G.L., Song H. In vivo clonal analysis reveals self-renewing and multipotent adult neural stem cell characteristics. Cell. 2011;145:1142–1155. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.05.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt M.D., Hubner M., Storch A. Brief report: adult hippocampal precursor cells shorten S-phase and total cell cycle length during neuronal differentiation. Stem Cells. 2012;30:2843–2847. doi: 10.1002/stem.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codega P., Silva-Vargas V., Paul A., Maldonado-Soto A.R., Deleo A.M., Pastrana E., Doetsch F. Prospective identification and purification of quiescent adult neural stem cells from their in vivo niche. Neuron. 2014;82:545–559. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.02.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corish P., Tyler-Smith C. Attenuation of green fluorescent protein half-life in mammalian cells. Protein Eng. 1999;12:1035–1040. doi: 10.1093/protein/12.12.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlstrand J., Lardelli M., Lendahl U. Nestin mRNA expression correlates with the central nervous system progenitor cell state in many, but not all, regions of developing central nervous system. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1995;84:109–129. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(94)00162-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll I., Howard S.R., Stone J.C., Monfils M.H., Tomanek B., Brooks W.M., Sutherland R.J. The aging hippocampus: a multi-level analysis in the rat. Neuroscience. 2006;139:1173–1185. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan X., Kang E., Liu C.Y., Ming G.L., Song H. Development of neural stem cell in the adult brain. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2008;18:108–115. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M.S., Piatti V.C., Laplagne D.A., Morgenstern N.A., Ferrari C.C., Pitossi F.J., Schinder A.F. Neuronal differentiation in the adult hippocampus recapitulates embryonic development. J. Neurosci. 2005;25:10074–10086. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3114-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanselow M.S., Dong H.W. Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron. 2010;65:7–19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.11.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda S., Kato F., Tozuka Y., Yamaguchi M., Miyamoto Y., Hisatsune T. Two distinct subpopulations of nestin-positive cells in adult mouse dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2003;23:9357–9366. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-28-09357.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M., Boles N.C., Charniga C., Lotz S., Campbell M., Temple S., Morse R.H. Effect of Bmi1 over-expression on gene expression in adult and embryonic murine neural stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:7464. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25921-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebara E., Bonaguidi M.A., Beckervordersandforth R., Sultan S., Udry F., Gijs P.J., Lie D.C., Ming G.L., Song H., Toni N. Heterogeneity of radial glia-like cells in the adult hippocampus. Stem Cells. 2016;34:997–1010. doi: 10.1002/stem.2266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goncalves J.T., Schafer S.T., Gage F.H. Adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus: from stem cells to behavior. Cell. 2016;167:897–914. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J.A., Talley T., Qiu M., Puelles L., Rubenstein J.L., Jones K.R. Cortical excitatory neurons and glia, but not GABAergic neurons, are produced in the Emx1-expressing lineage. J. Neurosci. 2002;22:6309–6314. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-15-06309.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusel'nikova V.V., Korzhevskiy D.E. NeuN as a neuronal nuclear antigen and neuron differentiation marker. Acta Nat. 2015;7:42–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Calvo C.F., Kang T.H., Baker K.L., Park J.H., Parras C., Levittas M., Birba U., Pibouin-Fragner L., Fragner P. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 controls neural stem cell activation in mice and humans. Cell Rep. 2015;10:1158–1172. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.01.049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu X.L., Chen G., Zhang S., Zheng J., Wu J., Bai Q.R., Wang Y., Li J., Wang H., Feng H. Persistent expression of VCAM1 in radial glial cells is required for the embryonic origin of postnatal neural stem cells. Neuron. 2017;95:309–325.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.06.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckleberry K.A., Shue F., Copeland T., Chitwood R.A., Yin W., Drew M.R. Dorsal and ventral hippocampal adult-born neurons contribute to context fear memory. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018;43:2487–2496. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0109-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kee N., Teixeira C.M., Wang A.H., Frankland P.W. Imaging activation of adult-generated granule cells in spatial memory. Nat. Protoc. 2007;2:3033–3044. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kheirbek M.A., Drew L.J., Burghardt N.S., Costantini D.O., Tannenholz L., Ahmari S.E., Zeng H., Fenton A.A., Hen R. Differential control of learning and anxiety along the dorsoventral axis of the dentate gyrus. Neuron. 2013;77:955–968. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.12.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch M., Pilz G.A., Ghesquiere B., Kovacs W.J., Wegleiter T., Moore D.L., Hruzova M., Zamboni N., Carmeliet P., Jessberger S. A fatty acid oxidation-dependent metabolic shift regulates adult neural stem cell activity. Cell Rep. 2017;20:2144–2155. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokovay E., Wang Y., Kusek G., Wurster R., Lederman P., Lowry N., Shen Q., Temple S. VCAM1 is essential to maintain the structure of the SVZ niche and acts as an environmental sensor to regulate SVZ lineage progression. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;11:220–230. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegstein A., Alvarez-Buylla A. The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2009;32:149–184. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagace D.C., Whitman M.C., Noonan M.A., Ables J.L., DeCarolis N.A., Arguello A.A., Donovan M.H., Fischer S.J., Farnbauch L.A., Beech R.D. Dynamic contribution of nestin-expressing stem cells to adult neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2007;27:12623–12629. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3812-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberwirth C., Pan Y., Liu Y., Zhang Z., Wang Z. Hippocampal adult neurogenesis: its regulation and potential role in spatial learning and memory. Brain Res. 2016;1644:127–140. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.05.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R., Feng Q., Li P., Zhou P., Wang R., Liu Z., Wang Z., Qi X., Tang N., Shao F. A hybridization-chain-reaction-based method for amplifying immunosignals. Nat. Methods. 2018;15:275–278. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q.R., Yuk D., Alberta J.A., Zhu Z., Pawlitzky I., Chan J., McMahon A.P., Stiles C.D., Rowitch D.H. Sonic hedgehog-regulated oligodendrocyte lineage genes encoding bHLH proteins in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuron. 2000;25:317–329. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80897-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugert S., Basak O., Knuckles P., Haussler U., Fabel K., Gotz M., Haas C.A., Kempermann G., Taylor V., Giachino C. Quiescent and active hippocampal neural stem cells with distinct morphologies respond selectively to physiological and pathological stimuli and aging. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;6:445–456. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madisen L., Zwingman T.A., Sunkin S.M., Oh S.W., Zariwala H.A., Gu H., Ng L.L., Palmiter R.D., Hawrylycz M.J., Jones A.R. A robust and high-throughput Cre reporting and characterization system for the whole mouse brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2010;13:133–140. doi: 10.1038/nn.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandyam C.D., Harburg G.C., Eisch A.J. Determination of key aspects of precursor cell proliferation, cell cycle length and kinetics in the adult mouse subgranular zone. Neuroscience. 2007;146:108–122. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.12.064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming G.L., Song H. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005;28:223–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.28.051804.101459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming G.L., Song H. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron. 2011;70:687–702. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mira H., Andreu Z., Suh H., Lie D.C., Jessberger S., Consiglio A., San Emeterio J., Hortiguela R., Marques-Torrejon M.A., Nakashima K. Signaling through BMPR-IA regulates quiescence and long-term activity of neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7:78–89. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morizur L., Chicheportiche A., Gauthier L.R., Daynac M., Boussin F.D., Mouthon M.A. Distinct molecular signatures of quiescent and activated adult neural stem cells reveal specific interactions with their microenvironment. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;11:565–577. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.06.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neish A.S., Williams A.J., Palmer H.J., Whitley M.Z., Collins T. Functional analysis of the human vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 promoter. J. Exp. Med. 1992;176:1583–1593. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilz G.A., Bottes S., Betizeau M., Jorg D.J., Carta S., Simons B.D., Helmchen F., Jessberger S. Live imaging of neurogenesis in the adult mouse hippocampus. Science. 2018;359:658–662. doi: 10.1126/science.aao5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renfranz P.J., Cunningham M.G., McKay R.D. Region-specific differentiation of the hippocampal stem cell line HiB5 upon implantation into the developing mammalian brain. Cell. 1991;66:713–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90116-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A., Macosko E.Z., Wysoker A., Goldman M., Krienen F.M., de Rivera H., Bien E., Baum M., Bortolin L., Wang S. Molecular diversity and specializations among the cells of the adult mouse brain. Cell. 2018;174:1015–1030.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semerci F., Maletic-Savatic M. Transgenic mouse models for studying adult neurogenesis. Front. Biol. (Beijing) 2016;11:151–167. doi: 10.1007/s11515-016-1405-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seri B., Garcia-Verdugo J.M., McEwen B.S., Alvarez-Buylla A. Astrocytes give rise to new neurons in the adult mammalian hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2001;21:7153–7160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07153.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin J., Berg D.A., Zhu Y., Shin J.Y., Song J., Bonaguidi M.A., Enikolopov G., Nauen D.W., Christian K.M., Ming G.L. Single-cell RNA-seq with Waterfall reveals molecular cascades underlying adult neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17:360–372. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.07.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starborg M., Gell K., Brundell E., Hoog C. The murine Ki-67 cell proliferation antigen accumulates in the nucleolar and heterochromatic regions of interphase cells and at the periphery of the mitotic chromosomes in a process essential for cell cycle progression. J. Cell Sci. 1996;109(Pt 1):143–153. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh H., Consiglio A., Ray J., Sawai T., D'Amour K.A., Gage F.H. In vivo fate analysis reveals the multipotent and self-renewal capacities of Sox2+ neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:515–528. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh H., Zhou Q.G., Fernandez-Carasa I., Clemenson G.D., Jr., Pons-Espinal M., Ro E.J., Marti M., Raya A., Gage F.H., Consiglio A. Long-term labeling of hippocampal neural stem cells by a lentiviral vector. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018;11:415. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C., Wang M., Wang P., Wang L., Wu Q., Guo W. Neural stem cells behave as a functional niche for the maturation of newborn neurons through the secretion of PTN. Neuron. 2019;101:32–44 e36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.10.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng J., Takei Y., Harada A., Nakata T., Chen J., Hirokawa N. Synergistic effects of MAP2 and MAP1B knockout in neuronal migration, dendritic outgrowth, and microtubule organization. J. Cell Biol. 2001;155:65–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200106025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Borght K., Wallinga A.E., Luiten P.G., Eggen B.J., Van der Zee E.A. Morris water maze learning in two rat strains increases the expression of the polysialylated form of the neural cell adhesion molecule in the dentate gyrus but has no effect on hippocampal neurogenesis. Behav. Neurosci. 2005;119:926–932. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.119.4.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hooijdonk L.W., Ichwan M., Dijkmans T.F., Schouten T.G., de Backer M.W., Adan R.A., Verbeek F.J., Vreugdenhil E., Fitzsimons C.P. Lentivirus-mediated transgene delivery to the hippocampus reveals sub-field specific differences in expression. BMC Neurosci. 2009;10:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorhees C.V., Williams M.T. Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat. Protoc. 2006;1:848–858. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T.L., Wierick A., Sykes A.M., Waldau B., Corbeil D., Carmeliet P., Kempermann G. Prominin-1 allows prospective isolation of neural stem cells from the adult murine hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2013;33:3010–3024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3363-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y.Z., Plane J.M., Jiang P., Zhou C.J., Deng W. Concise review: quiescent and active states of endogenous adult neural stem cells: identification and characterization. Stem Cells. 2011;29:907–912. doi: 10.1002/stem.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojtowicz J.M., Kee N. BrdU assay for neurogenesis in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2006;1:1399–1405. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelentsova K., Talmi Z., Abboud-Jarrous G., Sapir T., Capucha T., Nassar M., Burstyn-Cohen T. Protein S regulates neural stem cell quiescence and neurogenesis. Stem Cells. 2017;35:679–693. doi: 10.1002/stem.2522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D., Yuan D., Shen J., Yan Y., Gong C., Gu J., Xue H., Qian Y., Zhang W., He X. Up-regulation of VCAM1 relates to neuronal apoptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage in adult rats. Neurochem. Res. 2015;40:1042–1052. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1561-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao C., Deng W., Gage F.H. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell. 2008;132:645–660. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.