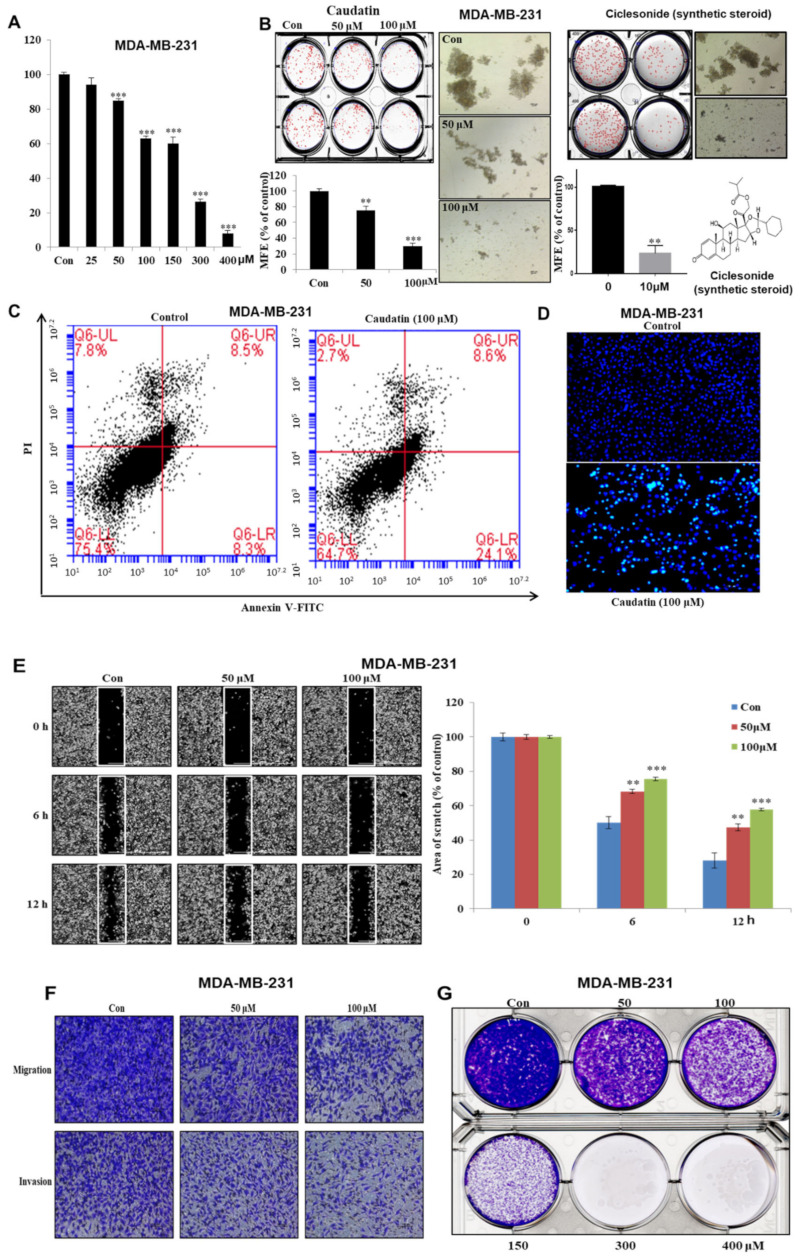
Figure 3.
The effects of caudatin on the proliferation and mammosphere formation of breast cancer cells. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured in a 96-well plate with caudatin for 24 h. MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation was assayed with an EZ-Cytox kit. (B) Caudatin and ciclesonide reduced mammosphere formation by breast cancer cells. Mammospheres derived from MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured in ultralow-attachment 6-well plates with CSC culture medium for seven days. The mammosphere formation efficiency (MFE) was examined with increasing concentrations of caudatin and ciclesonide. Images show representative mammospheres and were obtained by microscopy (scale bar: 100 μm). (C) Caudatin induced apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells. Apoptosis was determined using Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining. (D) Apoptotic cells induced by caudatin were stained with Hoechst 33,342 dye (scale bar: 50 μm). (E) The migration of MDA-MB-231 cells with/without caudatin (Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM)/0.5% fetal bovine serum (FBS)) was imaged at 0, 6 h and 12 h by a scratch assay (scale bar: 100 μm). The percent of inhibition in cell migration was expressed using untreated well at 100%. (F) The cell migration (without Matrigel) and invasion (with Matrigel) of MDA-MB-231 cells exposed to caudatin were determined by transwell assays (scale bar: 100 μm). (G) MDA-MB-231 cells were incubated in 6-well plates and treated with caudatin. Representative colony formation data were collected. The data from triplicate experiments are represented as the mean ± SD. ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 versus the DMSO-treated control group.