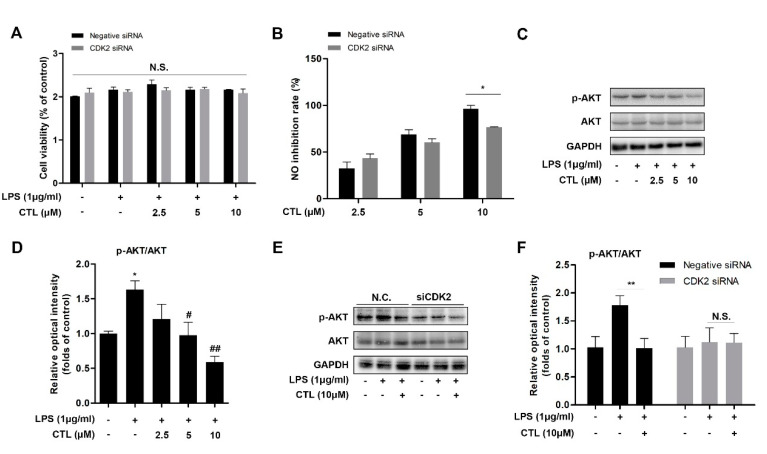
Figure 4.
Knockdown of CDK2 antagonized CTL effect on neuroinflammation, CDK2 is necessary for CTL-mediated anti-inflammatory activity. (A) CDK2 siRNA-transfected BV2 microglial cells were treated with gradient concentrations of CTL and 1 μg/mL of LPS or vehicle for anti-inflammation assay. The cell viability was determined by MTT method. (B) The level of NO production was detected by Griess assay, and subsequently calculated its inhibition rate. p values were calculated by two-tailed t-test. * p < 0.05. (C) Phosphorylation and total expressions of AKT was determined by Western blot assay. (D) Quantitative analysis for relative phosphorylation levels of AKT. * p < 0.05 vs. control group. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. LPS group. p values were calculated by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (E) CTL inhibition on AKT phosphorylation was significantly reversed in CDK2 knockdown group compared with negative control group. (F) Quantitative analysis of negative control group and CDK2 siRNA group for relative phosphorylation levels of AKT. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM for three individual experiments. p values were calculated by two-tailed t-test respectively. ** p < 0.01. N.S., no statistical difference.