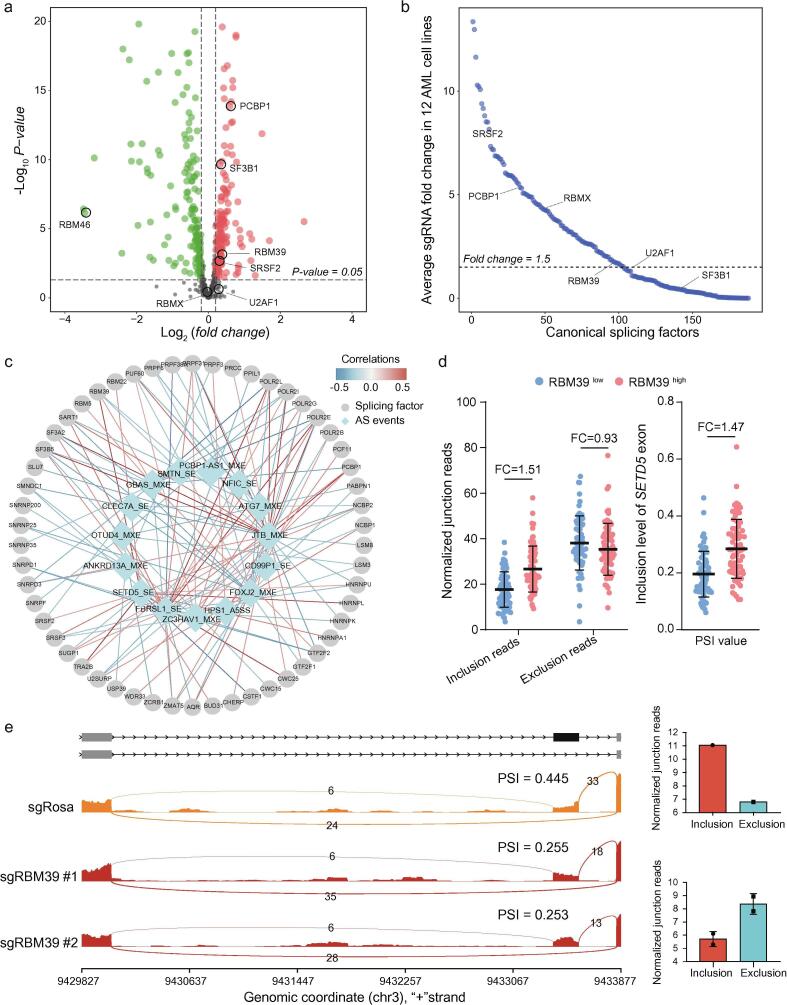
Fig. 6.
Splicing-regulatory network correlating splicing factors with prognostic AS events in AML. (a) Volcano plot of differentially expressed splicing factors in AML patient samples (N = 477) compared with normal human bone marrow/peripheral blood samples (N = 33). (b) Average fold change (initial/final) in sgRNA abundance in a pooled splicing factor-focused negative selection screen of 12 AML cell lines. Each dot represents the average of all the sgRNAs targeting a splicing factor. (c) A splicing co-expression network of 15 prognostic AS events and their associated splicing factor genes. (d) Quantification of the junction reads for the SETD5 exon are shown for RBM39low and RBM39high groups based on the RNA-seq data from AML patients. Exon inclusion and exclusion reads were normalized to the total number of reads in each sample. FC, fold change. (e) Sashimi plots showing SETD5 exon inclusion or exclusion in Molm13 cells before and after the RBM39 knockout based on RNA-seq junction reads.