Abstract
Coming off psychotropic drugs can cause physical as well as mental withdrawal, resulting in failed withdrawal attempts and unnecessary long-term drug use. The first reports about withdrawal appeared in the 1950s, but although patients have been complaining about psychotropic withdrawal problems for decades, the first tentative acknowledgement by psychiatry only came in 1997 with the introduction of the ‘antidepressant-discontinuation syndrome’. It was not until 2019 that the UK Royal College of Psychiatrists, for the first time, acknowledged that withdrawal can be severe and persistent. Given the lack of a systematic professional response, over the years, patients who were experiencing withdrawal started to work out practical ways to safely come off medications themselves. This resulted in an experience-based knowledge base about withdrawal which ultimately, in The Netherlands, gave rise to the development of person-specific tapering medication (so-called tapering strips). Tapering medication enables doctors, for the first time, to flexibly prescribe and adapt the medication required for responsible and person-specific tapering, based on shared decision making and in full agreement with recommendations in existing guidelines. Looking back, it is obvious that the simple practical solution of tapering strips could have been introduced much earlier, and that the traditional academic strategy of comparisons from randomised trials is not the logical first step to help individual patients. While randomised controlled trials (RCTs) are the gold standard for evaluating interventions, they are unable to accommodate the heterogeneity of individual responses. Thus, a more individualised approach, building on RCT knowledge, is required. We propose a roadmap for a more productive way forward, in which patients and academic psychiatry work together to improve the recognition and person-specific management of psychotropic drug withdrawal.
Keywords: patient participation, psychotropic drugs, tapering, withdrawal
Introduction
In this perspective review, we explain, from a user perspective, how the issue of psychotropic drug withdrawal divided, and to a degree continues to divide, physicians and patients; how this has hampered the development of practical solutions for a very long time; and how closer collaboration between users and professionals can remedy this situation.
The first reports of withdrawal from older psychotropic drugs appeared in the 1950s. The first selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) was introduced in 1988, the first reports of withdrawal from these drugs occurred in the 1990s.1–6 These reports demonstrated that withdrawal can cause physical as well as mental problems. This, in turn, can lead to failed withdrawal attempts of drugs like antidepressants, and unnecessary drug use contributing to a growing number of long-term antidepressant users. Part of the reason for increasing numbers of psychotropic drug long-term users is because patients are unable to get off the drugs and are compelled to remain on indefinitely, often having tried, and failed, to withdraw many times.7,8 It seems that for many years, critical questions about withdrawal effects were rarely asked and if they were, were not addressed properly. Drug research has always been, and mostly still is, focused on short-term efficacy and not on long-term adverse effects. Pharmaceutical companies were not, and surprisingly, still are not, obliged to investigate if and how patients can safely come off the drugs they want to register, for example, after (long-term) therapeutic use.
Withdrawal problems have been recognised in the scientific literature,9 and recently, there has been pressure to modify National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines in order to start considering withdrawal a severe, and long-term problem.10 But overall, for a long time, withdrawal problems were not considered a significant issue in academic psychiatry. This remained until 2019, when the UK Royal College of Psychiatrists (RCPsych), for the first time, admitted that the reality for many patients was quite different: withdrawal symptoms could be more severe and last longer than had always been assumed. Also, there was no evidence base on how to come off medications safely.11 The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, in an announcement about future revision of antidepressant guidelines, has come to similar conclusions,12 as did the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)13 and Center for Disease Control (CDC),14 in the context of opioid withdrawal. These recent updates acknowledged what many patients had been reporting for years:15 that they had great difficulties when they tried to come off medications and that their doctors did not seem to be able to help them with this. As a result, patients started to find solutions on their own, and to advise other patients how to stop safely.15–19
In their respective statements, RCPsych, NICE, FDA and CDC made clear that from now on, doctors must let their patients taper gradually, that no standard tapering schedules exist, and that tapering must be individualised. However, they did not make clear how this can or should be done. Further research was deemed necessary.
In this review, we will discuss if it is possible to improve clinical practice without first having to do new studies, using the knowledge, information and tools we already have. In order to do this, it is not enough to merely draw from professional knowledge. Rather, we acknowledge that there is an extensive and important body of user knowledge, based on the work of users who experienced withdrawal themselves.15–20 This area of user knowledge, however, to date, has not been appreciated and was largely ignored by psychiatry and medical science.
In the medical scientific literature, the focus in reviews is mostly on the development and testing of theoretical models with the goal to gather ‘evidence-based’ proof to improve daily clinical practice by establishing evidence-based guidelines. These are rarely clear cut, and commonly accompanied by statements such as ‘this may lead to’ and ‘further research is needed’. Patients looking for solutions, however, generally adopted a much more pragmatic course, with a strong focus on practical experimentation, resulting in a rich knowledge base outside mainstream psychiatry,15–20 and many concrete suggestions for new and practical medication-withdrawal strategies.21,22
In this review, the user perspective is allowed a leading role. One of the authors (PCG) started as a patient and wrote about his experiences,23 before he became, in fact coincidentally, involved in the development of tapering medication.21,24,25 Being a patient and not a doctor provides a perspective which makes it easier to ask questions that are not commonly asked by medical professionals. Service users want to develop practical solutions for the problems they encounter. Theories remain a means to an end and do not become an end in itself. In the medical literature about withdrawal, the usual conclusion is that ‘more research is necessary’, before clinical practice can be improved later. It can be argued, however, that after more than half a century of poor-quality clinical practice which largely ignored withdrawal, the case for referring patients to ‘further research’ that may never provide answers in the first place and will take at least a decade to conduct and interpret, should funding ever be found, is ethically and logistically untenable. A decade more of waiting for patients and their doctors is simply not acceptable.
Discussions about withdrawal, in the scientific literature and elsewhere, have often been confusing and even polarised because for a long time, many within psychiatry considered withdrawal to be much less of a problem than patients did.26 Currently, however, it is safe to say that there is consensus about the following:11–14 (a) withdrawal can be severe and persistent; (b) there is extensive variation in withdrawal experience between and even within people in terms of symptoms, severity, level of persistence, recurrence and tolerated rate of reduction, making it unlikely that an ‘evidence-based’ standard approach will ever emerge; (c) withdrawal should involve the dosage being tapered or slowly decreased, which may occur over several months or (much) longer; (d) this should be done at a reduction rate that is tolerable for the patient; (e) ongoing monitoring is required; (f) shared decision making is important.
In this perspective review, it will be argued that it is not necessary to wait for the uncertain outcomes of future research before clinical practice can be improved. Indeed, we will demonstrate that valid solutions exist, based on the body of user knowledge and pioneering observational studies to date.
A divide between patients and doctors about withdrawal
The first withdrawal symptoms were reported in the 1950s,1–3 but it was not until 1997 when, at a conference funded by Eli Lilly, a ‘Discontinuation Consensus Panel’ defined the so-called ‘antidepressant-discontinuation syndrome’ or ADS.4 This name has been criticised for obscuring and minimising withdrawal, perhaps for commercial reasons.27 Fact is that until 2019,11 psychiatry remained relatively insensitive to signals from patients about withdrawal.
There was and probably still is a divide between what many doctors thought or think about withdrawal and what patients experience. Advice in patient leaflets and guidelines often stops with the recommendation to taper the dose gradually over a period of several weeks, according to the patient’s need, without being specific about what this precisely means and how this should be made practically possible (see Box 1).
Box 1.
Manufacturers’ recommendations in fact show gradual tapering is impossible.
| For venlafaxine it has never been possible for doctors to let patients taper gradually as suggested by the manufacturer. Under the heading ‘If you stop taking Efexor XL’, the patient information leaflet of Efexor XL (venlafaxine, last updated August 2019) states the following:28
‘ Side effects are known to occur when people stop using this medicine, especially when it is stopped suddenly or the dose is reduced too quickly. Some patients may experience symptoms such as tiredness, dizziness, light-headedness, headache, sleeplessness, nightmares, dry mouth, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhoea, nervousness, agitation, confusion, ringing in the ears, tingling or rarely electric shock sensations, weakness, sweating, seizures, or flu-like symptoms. Your doctor will advise you on how you should gradually discontinue Efexor XL treatment. If you experience any of these or other symptoms that are troublesome, ask your doctor for further advice’. By stating that ‘your doctor will advise you on how you should gradually discontinue Efexor XL treatment’, Pfizer, the manufacturer of Efexor, not only suggests that doctors know how to let their patients taper gradually and safely, but also that they have the proper tools to do this. In practice, however, using the dosages mentioned in the patient leaflet, this has never been and still is not possible. The lowest available dose for venlafaxine of 37.5 mg comes in capsules, which, according to the patient leaflet, may not be opened, crushed, chewed or dissolved. Because 37.5 mg is too high a dose to taper safely from in one single step, the logical conclusion is that for more than 25 years, doctor’s prescribing venlafaxine were not given the tools they needed to help their patients come off venlafaxine safely. For most other drugs, in theory, it would be possible for doctors to let their patients taper gradually using the medication provided. In practice, however, due to a lack of dosages which are (much) lower than the registered doses, very often this did not and still does not happen. |
When patients started to try to taper safely at home by applying ‘do-it-yourself (DIY) pharmacotherapy’ (fiddling with medication at home in order to obtain lower dosages),15–19 they made clear that they wanted (and needed29) to have access to lower strengths of the drugs they wished to taper than were available. For a pharmaceutical company, making yet another strength is technically not more demanding or more expensive than making any of the strengths already registered. The question therefore arises, why did they not provide the strengths patients required? Why did medical associations and guideline committees not ask pharmaceutical companies to do this, when they noticed that patients were falling back to ‘DIY pharmacotherapy’? Why do not more people ask critical questions about the current dosing system which puts such strong limits on the choices doctors and patients can make? A system that is very much at odds with the choices we have when we use everyday products (see Box 2).
Box 2.
Peculiarities of the current dosing system leave doctors with inadequate options to help patients properly.

|
(a) Most things we use are customised. (b) For most drugs pharmaceutical companies bring on the market, only a limited number of different strengths are registered. This has made it difficult for doctors or even impossible (see Box 1) to prevent withdrawal symptoms by prescribing gradual enough tapering schedules. |
Patient experiences and initiatives
Over the years, in response to the perceived or real failure of their doctors in helping them safely come off prescribed drugs, a growing number of patients have started trying to find solutions on their own, which has resulted in a knowledge base complementary to the existing psychiatric and the scientific literature, in the form of a number of well-moderated fora on the internet, with unofficial and sometimes very elaborate guidelines,16,17,20 and with systematically gathered personal accounts, in some cases, of thousands of patients.15 It is not an exaggeration to state that many patients have felt that they were, or were indeed, helped better by these initiatives than by their doctors.
Important for the recognition of withdrawal problems is the fact that among those who experienced withdrawal were also medical professionals. In 2019, two of them, Mark Horowitz and David Taylor, published an important and insightful scientific article about how to taper antidepressants29 in which they made clear that withdrawal is a piece of a complex puzzle which should be interpreted under a pharmacokinetic, as well as a pharmacodynamic, model.30 Horowitz and Taylor had inferred correctly that what they had experienced was very different from what they had learned and from what guidelines said. Horowitz elaborated on this in an interview:
‘I think if a patient had come to me (before I’d experienced it) and said they had real trouble coming off an antidepressant, I would probably be inclined not to believe them … and I think that’s one of the reasons for doctors being skeptical of this’.31
Likewise, Taylor said: ‘Why do clinicians continue to tell people that withdrawal symptoms are mild and really nothing to worry about? Maybe it’s because there is a tendency for clinicians to want to believe that new drugs are innocuous panaceas’.32
The title of his short piece, ‘It’s not quite like the standard texts say’, clearly hinted at the need to adapt current guidelines and was published in 1999, 20 years before the official recognition of the possible severity and duration of withdrawal symptoms by psychiatry.11
How many patients suffer from withdrawal?
How many patients who suffer from withdrawal is not clear. In 17 different studies, ranging from small, industry-funded drug trials to large independent online surveys, incidence rates were reported ranging from 5% to 97%.33 According to the most recent online survey among 867 people from 31 countries who had tried to come off antidepressants, 61% reported withdrawal effects, with 44% describing these as severe.34 These rough estimates do not tell us what the numbers are for a specific drug. A problem is that not only do we not have enough data but that the incidence, severity and duration of withdrawal and relapse are probably all contingent on how a patient tapers; abrupt withdrawal causes more problems than gradual tapering.
Very little is known about the distribution of the severity of withdrawal over groups of patients. In an attempt to find a preliminary answer about such a distribution, we used available prescription data for tapering strips for a group of patients who had tapered venlafaxine successfully from 37.5 mg to zero. Of 810 patients, 299 (36.9%) chose to taper in 28 days, 169 (20.9%) in 56 days, 255 (31.5%) in 84 days, 65 (8,0%) in 112 days and 22 (2.9%) in 140 days or more, using one, two, three, four or five or more tapering strips, respectively (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
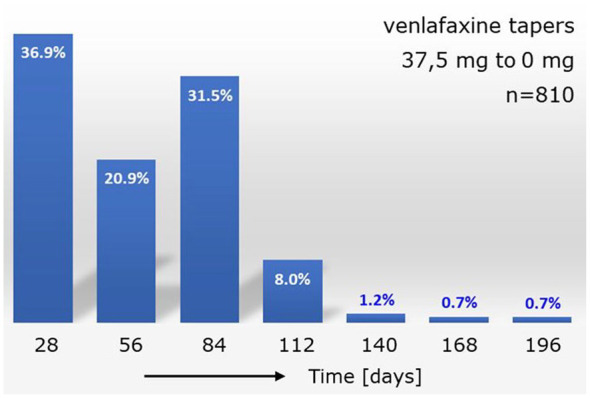
How many patients suffer from withdrawal?
The histogram shows the duration of successful tapers for 810 patients who successfully tapered venlafaxine from the lowest available registered dose of 37.5 mg to zero. The duration of the taper is used as a proxy for the severity of experienced withdrawal (see main text).
These preliminary data must be interpreted with caution because they hinge on the assumption that (a) the time patients took to taper is a proxy for the severity of withdrawal; and (b) that shared decision making was used when the tapering strips were prescribed. Furthermore, it is likely that a number of patients would have taken more time to taper had their health insurer reimbursed their medication.
Skewed distribution reconciles opposing views on the severity of withdrawal
What was observed in Figure 1 is that 90% of patients tapered in 3 months or less, and about 10% in 4 or more months. We think that this is precisely the kind of skewed distribution we would expect if we would want to reconcile currently opposing views on the true severity of withdrawal. With, on the one hand, a majority of patients who suffer less from withdrawal, and on the other hand, a much smaller group which suffers severely. The larger group with little withdrawal can be helped properly with the recent recommendations as laid out in the RCPsych position statement11, tapering over a period of several months. The smaller group with severe withdrawal, among which many of the (self-selected) patients found on internet fora, as well as those reported on in recent, larger observational studies,33,34 require much more time to be able to taper their medications.
Results of RCTs are not valid for patients at the tail of a skewed distribution
A skewed distribution would also be expected for other medications causing withdrawal. This has a number of implications. To begin with, results of randomised studies to examine properties which are very unevenly distributed over a population will yield results which can have meaning for a majority of patients, but will not be valid for the subgroup of patients at the tail of a skewed distribution.35 Any attempt to use such results to determine what will be the proper treatment for an individual patient at the tail of the distribution must be considered poor-quality clinical practice which can potentially be damaging for such patients, and also for the doctors who must help them. Yet, this is, in our view, precisely what has been happening and what is still happening in the case of withdrawal.
We can also infer that recommendations about withdrawal in past and current medical guidelines were not only not useful for these ‘rare’ patients but were, and still are, also harmful. A concrete example of how this harm is done was observed in The Netherlands, where a number of health insurers refuse(d) to reimburse tapering medication to patients to whom doctors wanted to prescribe more gradual tapering schedules of longer duration because they suffered from (severe) withdrawal. The argument these health insurers use(d) is that ‘there is no evidence in the literature’ that the patient in question would need this medication. However, the health insurer does not, and cannot, know what the position of the patient in the distribution is, even if data about the distribution would be available, which is currently not the case.
In such a situation, the only reasonable thing to do would be to rely on the judgement of the doctor regarding the severity of the withdrawal the patient is suffering from. But instead of doing this, the argument that there was no ‘evidence’ was considered the only valid statement. This was also the case for the Dutch National Healthcare Institute, which advised in favour of the health insurers in all cases where patients issued an official complaint, even when their doctors had attested to the severity of their withdrawal complaints.36–40 Ironically and sadly, what we see here is that the ‘evidence-based model’ of medical science has led to a culture of substantially ignoring patient experiences.41
Institutional resistance
The Dutch health insurers and the Dutch National Healthcare Institute are not the only parties who have been using the argument that there is a lack of ‘evidence’ for the need to taper much more gradually and over much longer periods of time than what has been standard clinical practice. It is safe to say that many within psychiatry have used or are still using the argument that we need more ‘evidence’ from randomised group studies first. This, despite the fact that such studies, as explained above, will not help to identify patients who are most at risk because they are in the tail of a skewed distribution.
A surprising issue we had to deal with in The Netherlands is the fact that, in recent years, it was difficult for us to inform or to discuss these issues with the relevant parties such as our health insurers, the Dutch Psychiatric Association, General Practitioners Association, the patient umbrella organisation MIND, the Dutch National Healthcare Institute and even the Ministry of Health. In our view, we experienced what so many patients had experienced for so many years when they tried to discuss their withdrawal problems. Theory, assumptions and a narrow interpretation of the literature was what counted, other things were found to be less relevant, or not relevant at all.
In The Netherlands, this, in our view, unscientific attitude, has led to several hearings,42–44 court cases,45–47 parliamentary questions48–51 and even a parliamentary hearing,52 the outcome of which was ignored by the Minister of Health,53 perhaps because it was organised by the main opposition parties. An erroneous interpretation of the theory was deemed more important than what patients and their doctors reported. As a result, patients to whom reimbursement of their medication was refused could either choose to pay for the medication themselves or taper faster than they wished or their doctors found responsible, thus running the risk of withdrawal and associated undue consequences.
To a large extent, we think that what we observe here has been happening over the last 50 years to many patients who had problems coming off medication. Theoretical considerations and expert opinion were considered more valid than the experiences of patients themselves, perhaps also as a result of other financial and institutional interests.54
To be able to stop this unwanted situation, we think that it is crucial to be more honest about existing uncertainties and gaps in knowledge, many of which will not likely go away anytime soon.55 Patients experiences, ideas and initiatives must be taken much more seriously, also when these are not published in the scientific literature and even when they are considered to contain ‘critical’ messages. This will require another attitude and another way of valuing information but will be worth the effort.
How to improve the practice of coming off medications: which studies do we need?
Medical science appreciates randomised studies much more than other types of studies. For improving the practice of coming off medications, this has been highly problematic because (a) few randomised studies about withdrawal have been carried out thus far;8,56–58 (b) most of these were (too) small, had methodological issues and used words like ‘gradual’ in a confusing way, which, for example, has led to the erroneous claim that there would be no significant advantage of slow tapering compared with abrupt withdrawal;5,6,57,59–62 (c) the largely unknown effects on withdrawal of polypharmacy, which is not uncommon in daily clinical practice, are not taken into account; (d) there are perhaps more reviews6,63–68 than original randomised studies about withdrawal, which has led to the echoing of results that were not to be trusted in the first place; (e) outcomes are not meaningful for the most vulnerable patients at the end of skewed distributions (see above). We find it not surprising that the combined contribution to improving daily clinical practice of all these studies has been worryingly low.8,58,59
What is true for withdrawal studies is also true for most other randomised clinical trials in psychiatry. The yield of thousands of RCTs, which have cost billions of dollars, has been disappointing. As John Ioannidis put it, ‘There is enormous investment in basic neuroscience research and intensive searches for informative biomarkers of treatment response and toxicity. The yield is close to nil . . . even optimists acknowledge that, currently, there is still no clinically useful way to predict which patients will respond best to widely used medications such as antidepressants.’69 It is not realistic to expect much from randomised studies for improvement of prediction models. It seems better to accept existing uncertainties and work with them,55 as explained below.
The availability of tapering medication makes it possible to obtain prospective observational data for different drugs from daily clinical practice for large groups of patients within a few years. We propose performing such studies because they will provide much needed data which cannot easily be obtained in other ways.
Dealing with or preventing withdrawal symptoms
It is without question that proper guidance, by a doctor or other health professionals, is important and should always be available70 and can help to endure and overcome withdrawal symptoms if they occur, but only gradual tapering helps prevent them. Therefore, the first job of a doctor should be to make safe tapering possible by prescribing the right (tapering) medication. All patients who have been trying, or are still trying, to achieve this through DIY pharmacotherapy have understood this better than many of their doctors and many investigators, who did not address the question how to taper first.
Tapering medication (tapering strips)
A patient’s initiative
In 2010, a project was started in The Netherlands, based on the idea for the development of a ‘medication-withdrawal strip’ that was published in 2004.22 In 2013, this led to the development of the first tapering strips for paroxetine and venlafaxine21 (see Box 3). In the years that followed, a flexible system for prescribing tapering medication was developed for a host of different other medications: antidepressants, antipsychotics, sedatives like benzodiazepines, centrally acting analgesics like opioid painkillers,71 antiepileptics and some other drugs.72 The list is still growing because requests for other medications which turn out to cause withdrawal symptoms keep coming in, from patients as well as from clinicians; a clear indication that withdrawal problems are not limited to antidepressants and that they have been, and perhaps still are, being underestimated by medical science.
Box 3.
Tapering strips: how it works.
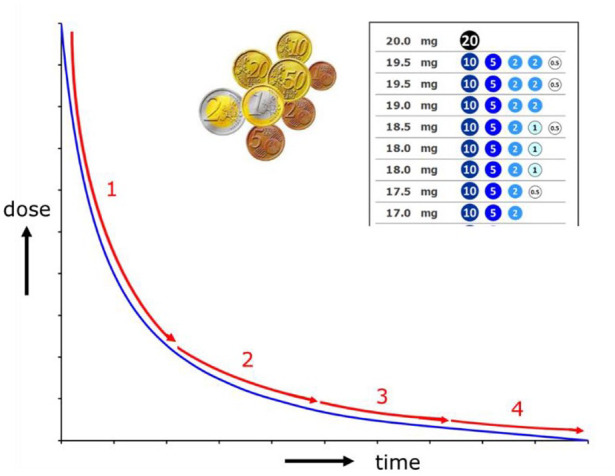
| Tapering strips were based on an idea of a patient, published in 2004,22 and were developed to make flexible and hyperbolic dose reduction29 practically possible in accordance with older, as well as very recent recommendations,11–14 of which it was never clear how they should or could be followed (see Box 1). A tapering strip is ‘medication on a roll’ for 28 days packaged by an automatic dispensing system. Using tapering medication, a tapering trajectory can last 28 or a multiple of 28 days, using one of more tapering strips one after another. Each prescribed daily dose is separately packaged and is composed of one or a limited number of capsules or tablets of different strengths. A system analogous to how a limited number of different denominations is being used for efficient payment traffic. If necessary, a prescriber can flexibly adjust a tapering schedule based on shared decision making, by stabilisation, by slowing down or by going back to a (slightly) higher dose. For stabilisation, so-called stabilisation strips can be prescribed in any required dosage, that is, also in dosages which are (much) lower than the limited number of available registered dosage accesible thus far, which could never be prescribed previously and which were difficult or impossible to come by for patients, even when they tried to do this at home using DIY pharmacotherapy (see Box 1). |
|
Tolerating uncertainty: using knowledge patients have
Shared decision making can perhaps best be prescribed as making an educated guess together, which is necessary when there is uncertainty.55 For withdrawal, this is less a problem than many investigators who want to develop prediction models first, seem to think. One of the reasons why this is so is that patients often have a pretty good idea of what they want or need; arguably, even better than their doctors. This is especially true for patients who have tried to taper a drug in the past and failed. Many of these patients know how gradually and slowly they want to taper, or perhaps, how fast they do not want to taper. Making use of this knowledge is not only in line with the growing emphasis on practising shared decision making, it also makes much more sense than relying on limited and not concrete advice in patient leaflets and existing guidelines, based on expert opinion, not on evidence-based medicine. In this situation, we should ask ourselves, ‘Who is the expert: the doctor or the patient?’
How useful are risk criteria?
Risk criteria have been defined in order to try to identify patients who are more at risk than others73 but there is very little hard evidence in the literature to support them.74 These risk criteria may be helpful but a given patient without any risk factor may still be at risk and vice versa. It is currently not possible to predict this for an individual patient. More randomised group studies (RCTs) will not change this (see before). The availability of tapering medication makes it possible to deal with this uncertainty in a very practical way. It allows doctor and patient to decide upon a tapering trajectory together, using all the (patient) knowledge that is available. It is our view that the patient should be in the lead here, not the doctor. They both do not, and cannot, know if their choice will be for the optimal tapering schedule, but because it is practically possible to adapt when withdrawal symptoms occur, this is not a big problem. What is important here is that proper (self-)monitoring is also made practically possible.
Self-monitoring made simple
Proper (self-)monitoring is an important aspect of responsible tapering. To help make this possible, we designed a simple-to-use withdrawal self-monitoring form which is now provided with every prescribed tapering or stabilisation strip. Box 4 shows the first two self-monitoring forms that were returned to us (we only recently started a pilot project with these forms); one by a patient who tapered clomipramine from 75 mg to 50 mg in 28 days, and one by a patient who stabilised diazepam at a dose of 0.3 mg. Short and simple instructions enabled both patients to fill in the form without problems and to draw their own conclusions. The patient who tapered clomipramine concluded that tapering went well. The patient who stabilised diazepam on the low dose of 0.3 mg concluded that sleep had been restored completely. Both patients decided that they wished to taper further. We consider this to be helpful, as well as empowering for the patient and informative for the doctor, which should make it easier to have a fruitful conversation on how to proceed further.
Box 4.
Self-monitoring made simple.
| Recently, a prospective self-monitoring form for measuring subjective withdrawal complaints was designed, which is now being provided with each tapering or stabilisation strip. The goal is to help both the patient and the doctor determine if and how a changing (when tapering) or constant (when stabilising) dose affects the (dis)appearance of subjectively experienced withdrawal symptoms, not to obtain detailed information about specific withdrawal symptoms, for which more elaborate monitoring instruments would be needed. In order to allow as many patients as possible to be able to use it, the form and the instructions for the patient have deliberately been kept as simple as possible. The patient is asked to subjectively score how much they suffered from withdrawal on a scale from 1 (‘not at all’) complaint to 7 (‘very much’), and to write down withdrawal symptoms if they occur, especially if they are new or if the severity of the symptoms changes much. The name of drug that is being tapered or stabilised and the daily dose for each day are mentioned on the form. This makes it possible to see if and how a changing or constant daily dose affects the (dis)appearance of withdrawal symptoms, which will help doctor and patients to adapt a tapering schedule if they feel that this is needed. A unique number on each form, which only the pharmacist can trace back to the patient, can be used to make future, prospective, observational withdrawal research, using tapering medication, possible. Two examples of filled-in self-monitoring forms: Clomipramine tapering, 75 >50 mg Diazepam stabilisation at 0.3 mg 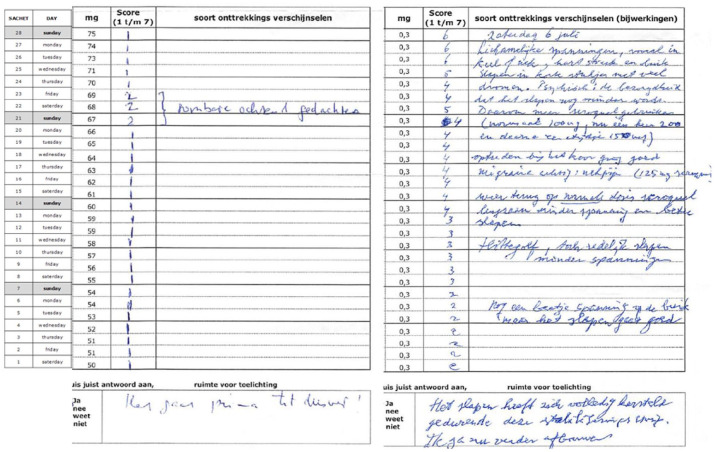
|
Experiences with the use of tapering strips
That the use of tapering strips works well in clinical practice and that it makes shared decision making practically possible, we have, in our opinion, shown, in our first observational study of a group of 1194 patients who had used tapering medication.24 In this first group were many patients who had previously suffered from withdrawal and had therefore been actively searching for better and safer ways to taper. When they found out that tapering medication existed, they had to explain this to their doctors who often did not know that this existed. Because these patients knew what they wanted, we believe that in this group, the use of tapering strips will often have been the result of shared decision making, and also that patients were educating their doctors about tapering, instead of the other way around.
That the efforts of these patients were not wasted is demonstrated by the result of our observational study. This first group probably contained a relatively large group of self-selected, difficult-to-help and vulnerable patients, located at the tail of the skewed distribution discussed earlier. The use of tapering medication enabled 70% of them to taper their antidepressant completely, which is a much higher percentage than any study we know of.
In our view, this shows that many of the current withdrawal problems are not the unfortunate result of a lack of knowledge, but the adverse iatrogenic effect of a system that has allowed the prescription of new drugs without providing the tools necessary to come off them safely.
A roadmap for tapering
Withdrawal could become such a big problem because pharmaceutical companies were, and still are, allowed to bring drugs onto the market without having to investigate if problems can occur when patients stop using them after therapeutic use and to develop solutions if this happens. Academic psychiatry is also to be blamed. There always was and still is a lot of attention for the development and (short-term) efficacy of new drugs and for starting pharmacotherapeutic treatment, but not enough for stopping treatment and for long-term adverse effects. The too-limited number of registered strengths of drugs was questioned by patients, not by psychiatry. Clinical practice was adapted to what pharmaceutical companies sold and not the other way around. As a result, patients who needed other strengths had to fall back on DIY pharmacotherapy, pay out of their own pocket, or risk withdrawal symptoms that could have been prevented.
Tapering medication makes it possible to prescribe and adapt tapering schedules in a flexible way using shared decision making. But it is clear that this will not solve all withdrawal problems. Many questions remain. One very important question is if tapering, which is gradual enough to prevent withdrawal symptoms during and shortly after tapering, is also gradual enough to prevent relapse or withdrawal problems which occur (much) later. To know this, is highly clinically relevant. After successful tapering (without experiencing withdrawal symptoms), some patients start having complaints later, and for some, these can be very severe and longlasting and may perhaps not go away at all. Why this is so, is not completely clear.60,75 Can a (much) more gradual taper help these patients? We do not know. To find out, we need data, especially about the (perhaps rare) patients who are most vulnerable; those who are located at the end of a skewed distribution. The availability of tapering medication makes it possible to obtain prospective observational data for different drugs from daily clinical practice for large groups of patients within a few years if these patients are allowed to choose themselves (on the basis of shared decision making) and if they are willing to share self-monitoring data during and after tapering. Meta-analyses can then help find answers to questions for which there are no answers now.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. Tapering medication contains generic drugs and can be made by a compounding pharmacy. The authors have been involved in the development of and research into the use of taperingstrips, but not in producing them or providing them to patients. They do not receive any reimbursement or income from the provision of tapering medication. In the Netherlands, at the explicit request of the not-for-profit foundation Cinderella Therapeutics, tapering medication is being made and provided by the Regenboog Apotheek in Bavel.
Funding: The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
ORCID iD: Peter C. Groot  https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3339-1469
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3339-1469
Contributor Information
Peter C. Groot, User Research Centre NL, Utrecht University Medical Centre Postbus 85500, Utrecht 3508 GA, The Netherlands.
Jim van Os, UMC Utrecht Brain Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands.
References
- 1. Kramer JC, Klein DF, Fink M. Withdrawal symptoms following discontinuation of imipramine therapy. Am J Psychiatry 1961; 118: 549–550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Hollister LE, Motzenbecker FP, Degan RO. Withdrawal reactions from chlordiazepoxide (“Librium”). Psychopharmacologia 1961; 2: 63–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Selikoff IJ, Robitzek EH, Ornstein GG. Withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuance of iproniazid and isoniazid therapy. Am Rev Tuberc 1953; 67: 212–216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Schatzberg AF, Haddad P, Kaplan EM, et al. Possible biological mechanisms of the serotonin reuptake inhibitor syndrome. Discontinuation Consensus Panel. J Clin Psychiatry 1997; 58(Suppl. 7): 23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Fava GA, Gatti A, Belaise C, et al. Withdrawal symptoms after selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor discontinuation: a systematic review. Psychother Psychosom 2015; 84: 72–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Fava GA, Benasi G, Lucente M, et al. Withdrawal symptoms after serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor discontinuation: systematic review. Psychother Psychosom 2018; 87: 195–203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Bosman RC, Huijbregts KM, Verhaak PF, et al. Long-term antidepressant use: a qualitative study on perspectives of patients and GPs in primary care. Br J Gen Pract 2016; 66: e708–e719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Eveleigh R, Muskens E, Lucassen P, et al. Withdrawal of unnecessary antidepressant medication: a randomised controlled trial in primary care. BJGP Open 2017; 1: bjgpopen17X101265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Cosci F, Chouinard G. Acute and persistent withdrawal syndromes following discontinuation of psychotropic medications. Psychother Psychosom. Epub ahead of print 7 April 2020. DOI: 10.1159/000506868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Davies J, Read J, Hengartner MP, et al. Clinical guidelines on antidepressant withdrawal urgently need updating. BMJ 2019; 365: l2238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Royal College of Psychiatrists. Position statement on antidepressants and depression, www.rcpsych.ac.uk/docs/default-source/improving-care/better-mh-policy/position-statements/ps04_19—antidepressants-and-depression.pdf (2019, accessed 28 May 2019)
- 12. Iacobucci G. NICE updates antidepressant guidelines to reflect severity and length of withdrawal symptoms. BMJ 2019; 367: l6103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. US Food and Drug Administration Drug Safety Communication. FDA identifies harm reported from sudden discontinuation of opioid pain medicines and requires label changes to guide prescribers on gradual, individualized tapering, https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-identifies-harm-reported-sudden-discontinuation-opioid-pain-medicines-and-requires-label-changes (2019, accessed 24 September 2019).
- 14. Dowell D, Haegerich T, Chou R. No shortcuts to safer opioid prescribing. N Engl J Med 2019; 380: 2285–2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Surviving Antidepressants. Surviving Antidepressants is a site for peer support, documentation, and education of withdrawal symptoms and withdrawal syndrome caused by psychiatric drugs, specifically antidepressants, with more than 6000 reports of patients experiences, https://www.survivingantidepressants.org/ (accessed 6 January 2020).
- 16. The Withdrawal Project, https://withdrawal.theinnercompass.org (accessed 11 December 2019).
- 17. Hall W. Harm reduction guide to coming off psychiatric drugs. 2d Ed. The Icarus Project and Freedom Center, https://www.theicarusproject.net/resources/publications/harm-reduction-guide-to-coming-off-psychiatric-drugs-and-withdrawal/ (2012, accessed 11 December 2019) [Google Scholar]
- 18. Benzo buddies, www.benzobuddies.org (accessed 6 January 2020).
- 19. Recovery Road. Antidepressant & benzodiazepine withdrawal support, www.recovery-road.org (accessed 11 December 2019).
- 20. Ashton CH. Benzodiazepines: how they work and how to withdraw. (Revised edition 2011). Newcastle: University of Newcastle; 2002. (aka The Ashton Manual: www.benzo.org.uk/manual/). [Google Scholar]
- 21. Groot PC; Consensusgroup Tapering. Taperingstrips for paroxetine and venlafaxine. Tijdschr Psychiatr 2013; 55: 789–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Leurink H. De medicijnontwenningsstrip [The medication withdrawal strip]. NRC Handelsblad, December 31, https://www.nrc.nl/nieuws/2004/12/31/de-medicijnontwenningsstrip-7716777-a1039826 (2004, accessed 11 December 2019) [Google Scholar]
- 23. Groot PC. Patients can diagnose too: how continuous self-assessment aids diagnosis of, and recovery from, depression. J Ment Health 2010; 19: 352–362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Groot PC, Van Os J. Antidepressant tapering strips to help people come off medication more safely. Psychosis 2018; 10: 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- 25. Wichers M, Groot PC; Psychosystems, ESM Group, EWS Group. Critical slowing down as a personalized early warning signal for depression. Psychother Psychosom 2016; 85: 114–116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Bitter I, Filipovits D, Czobor P. Adverse reactions to duloxetine in depression. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2011; 10: 839–850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Nielsen M, Hansen EH, Gøtzsche PC. What is the difference between dependence and withdrawal reactions? A comparison of benzodiazepines and selective serotonin re–uptake inhibitors. Addiction 2012; 107: 900–908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Pfizer. Patient information leaflet Efexor, www.medicines.org.uk/emc/files/pil.1219.pdf (2019, accessed 16 December 2019).
- 29. Horowitz MA, Taylor D. Tapering of SSRI treatment to mitigate withdrawal symptoms. Lancet Psychiatry 2019; 6: 538–546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Fava GA, Cosci F. Understanding and managing withdrawal syndromes after discontinuation of antidepressant drugs. J Clin Psychiatry 2019; 80: 19com12794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Simons P. Peer-support groups were right, guidelines were wrong: Dr. Mark Horowitz on tapering off antidepressants, www.madinamerica.com/2019/03/peer-support-groups-right-official-guidelines-wrong-dr-mark-horowitz-tapering-off-antidepressants/ (2019, accessed 12 April 2019)
- 32. Taylor D. Truth withdrawal. Open Mind (National Association for Mental Health, London E14), https://www.socialaudit.org.uk/4200DTAY.htm (1999, accessed 15 March 2019).
- 33. Davies J, Read J. A systematic review into the incidence, severity and duration of antidepressant withdrawal effects: are guidelines evidence-based? Addict Behav 2019; 97: 111–121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Read J. How common and severe are six withdrawal effects from, and addiction to, antidepressants? The experiences of a large international sample of patients. Addict Behav. Epub ahead of print 30 November 2019. DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Fisher AJ, Medaglia JD, Jeronimus BF. Lack of group-to-individual generalizability is a threat to human subjects research. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018; 115: E6106–E6115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Dutch Foundation for Health Insurances Complaints and Disputes (SKGZ), Zeist. Case number 201700970, ruling 08-011-2017 (Dutch), www.kpzv.nl/pdf/1f5e874e-221c-4c5d-adc0-f94f22ba337e (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 37. Dutch Foundation for Health Insurances Complaints and Disputes (SKGZ), Zeist. Case number 201601537, ruling 05-07-2017 (Dutch), www.kpzv.nl/pdf/d7b130e2-f722-4169-b26e-57955cc58937 (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 38. Dutch Foundation for Health Insurances Complaints and Disputes (SKGZ), Zeist. Case number 201602636, ruling 07-06-2017 (Dutch), www.kpzv.nl/pdf/82856924-7081-4f00-b835-7118baff7b0a (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 39. Dutch Foundation for Health Insurances Complaints and Disputes (SKGZ), Zeist. Case number 201601423, ruling 22-03-2017 (Dutch), www.kpzv.nl/pdf/7e34753d-a253-4c81-88fa-d42792e9b3f5 (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 40. Dutch Foundation for Health Insurances Complaints and Disputes (SKGZ), Zeist. Case number 201601491, ruling 12-10-2016 (Dutch), www.kpzv.nl/pdf/c9785e4a-7de8-406e-9c4b-5dfe27c4736d (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 41. Healy D, Mangin D. Clinical judgments, not algorithms, are key to patient safety-an essay by David Healy and Dee Mangin. BMJ 2019; 367: l5777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Technical briefing. Organized by Dr. P.C. Groot and Prof. J. van Os at the request of the Dutch National Healthcare Institute, 29 March 2017, Utrecht. [Google Scholar]
- 43. Expert-meeting ‘Tapering antidepressants - how?’. Organized by the Dutch Institute for Responsible Medicine Use (IVM) at the request of the Dutch Minister of Health, Drs. B. Bruins, 21 November 2019, Utrecht www.rijksoverheid.nl/documenten/rapporten/2020/02/14/verslag-expertmeeting-afbouwen-antidepressiva-hoe (accessed 14 February 2020). [Google Scholar]
- 44. Scoping about tapering of (specific) antidepressants using tapering strips. Organized by the Dutch National Healthcare Institute, 24 August 2017, Diemen. [Google Scholar]
- 45. Court Gelderland, Case number NL18.23783, Ruling 19-12-2019, Arnhem, https://uitspraken.rechtspraak.nl/inziendocument?id=ECLI:NL:RBGEL:2019:5935 (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 46. Court Midden-Nederland, Case number C/16/468767 / KG ZA 18-644; Ruling 9-01-2019, Utrecht, https://uitspraken.rechtspraak.nl/inziendocument?id=ECLI:NL:RBMNE:2019:6614. [Google Scholar]
- 47. Court Gelderland, Case number C/05/345680 / KG ZA 18-505, Ruling 15-02-2019, Arnhem, https://uitspraken.rechtspraak.nl/inziendocument?id=ECLI:NL:RBGEL:2019:5935 (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 48. Parliamentary questions to the Dutch Minister of Health, 13-04-2017, Ref. 2017Z04977: ‘Antidepressants and tapering strips’ (Dutch), www.tweedekamer.nl/kamerstukken/kamervragen/detail?id=2017Z04977&did=2017D10390 (accessed 11 December 2019).
- 49. Parliamentary questions to the Dutch Minister of Health, 01-02-2018, Ref. 2018Z01656: ‘The use of compounding pharmacy preparations in tapering strips as a means to taper medication in a responsible manner’ (Dutch), www.tweedekamer.nl/kamerstukken/kamervragen/detail?id=2018Z01656&did=2018D03403 (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 50. Parliamentary questions to the Dutch Minister of Health, ref. 2018Z24807, 28-12-2018: ‘tapering strips and blunder with non-existent research’ (Dutch), www.tweedekamer.nl/kamerstukken/kamervragen/detail?id=2018Z24807&did=2018D61879 (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 51. Parliamentary questions to the Dutch Minister of Health, 24-09-2019, Ref. 2019Z17796: ‘Active opposition against reimbursement of tapering strips by the Dutch Healthcare Institute, the Dutch Association of Psychiatrists (NVvP) and health insurers. (Dutch), www.tweedekamer.nl/kamerstukken/kamervragen/detail?id=2019Z17796&did=2019D37112 (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 52. Parliamentary hearing/round table discussion, 20-06-2019: ‘Tapering Medication’, The Hague (Dutch), www.tweedekamer.nl/debat_en_vergadering/commissievergaderingen/details?id=2019A01954 (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 53. Report of the General Consultation with the Minister of Health on 26-06-2019, ref. 29689-1018, page 29. The Hague, www.tweedekamer.nl/kamerstukken/verslagen/detail?id=2019Z10536&did=2019D28840 (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 54. Whitaker R, Cosgrove L. Psychiatry under the influence. Institutional corruption, social injury, and prescriptions for reform. New York: Palgrave Macmillan Ltd, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 55. Simpkin AL, Schwartzstein RM. Tolerating uncertainty - the next medical revolution? N Engl J Med 2016; 375: 1713–1715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Rosenbaum JF, Fava M, Hoog SL, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor discontinuation syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Biol Psychiatry 1998; 44: 77–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Tint A, Haddad PM, Anderson IM. The effect of rate of antidepressant tapering on the incidence of discontinuation symptoms: a randomised study. J Psychopharmacol 2008; 22: 330–332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Scholten WD, Batelaan NM, van Oppen P, et al. The efficacy of a group CBT relapse prevention program for remitted anxiety disorder patients who discontinue antidepressant medication: a randomized controlled trial. Psychother Psychosom 2018; 87: 240–242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Fava GA, Belaise C. Discontinuing antidepressant drugs: lesson from a failed trial and extensive clinical experience. Psychother Psychosom 2018; 87: 257–267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Chouinard G, Chouinard VA. New classification of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor withdrawal. Psychother Psychosom 2015; 84: 63–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Gallagher JC, Strzinek RA, Cheng RJ, et al. The effect of dose titration and dose tapering on the tolerability of desvenlafaxine in women with vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2012; 21: 188–198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Khan A, Musgnung J, Ramey T, et al. Abrupt discontinuation compared with a 1-week taper regimen in depressed outpatients treated for 24 weeks with desvenlafaxine 50 mg/d. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2014; 34: 365–368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Lejoyeux M, Adès J. Antidepressant discontinuation: a review of the literature. J Clin Psychiatry 1997; 58(Suppl. 7): 11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Shelton RC. The nature of the discontinuation syndrome associated with antidepressant drugs. J Clin Psychiatry 2006; 67(Suppl. 4): 3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Schatzberg AF, Blier P, Delgado PL, et al. Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome: consensus panel recommendations for clinical management and additional research. J Clin Psychiatry 2006; 67(Suppl. 4): 27–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Haddad P, Lejoyeux M, Young A. Antidepressant discontinuation reactions. BMJ 1998; 316: 1105–1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Wilson E, Lader M. A review of the management of antidepressant discontinuation symptoms. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 2015; 5: 357–368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Zajecka J, Tracy KA, Mitchell S. Discontinuation symptoms after treatment with serotonin reuptake inhibitors: a literature review. J Clin Psychiatry 1997; 58: 291–297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Ioannidis JPA. Therapy and prevention for mental health: what if mental diseases are mostly not brain disorders? Behav Brain Sci 2019; 42: e13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Guy A, Davies J, Rizq R. Guidance for psychological therapists: enabling conversations with clients taking or withdrawing from prescribed psychiatric drugs. APPG for Prescribed Drug Dependence publication, www.prescribeddrug.info/download/279/ (2019, accessed 5 December 2019) [Google Scholar]
- 71. Groot PC, van Os J. Tackling rising numbers of opioid prescriptions users. Lancet Public Health 2020; 5: e16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Tapering strips. A not-for-profit website of the user research center NL of Maastricht/Utrecht Medical Center, www.taperingstrip.org (accessed 30 December 2019).
- 73. Ruhe HG, Horikx A, Groeneweg BF, et al. Multidisciplinary document “Discontinuation of SSRIs & SNRIs”. Supplement to: Ruhe HG, Horikx A, van Avendonk MJP, Woutersen-Koch H. Tapering of SSRI treatment to mitigate withdrawal symptoms. Lancet Psychiatry 2019; 6: 561–562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Muzina DJ. Discontinuing an antidepressant? Currenty Psychiatry 2010; 9: 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- 75. Fava GA, Offidani E. The mechanisms of tolerance in antidepressant action. Prog Neuro-psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2011; 35: 1593–1602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


