Abstract
Given an unsatisfiable formula F in CNF, i.e. a set of clauses, the problem of Minimal Unsatisfiable Subset (MUS) seeks to identify a minimal subset of clauses  such that N is unsatisfiable. The emerging viewpoint of MUSes as the root causes of unsatisfiability has led MUSes to find applications in a wide variety of diagnostic approaches. Recent advances in identification and enumeration of MUSes have motivated researchers to discover applications that can benefit from rich information about the set of MUSes. One such extension is that of counting the number of MUSes. The current best approach for MUS counting is to employ a MUS enumeration algorithm, which often does not scale for the cases with a reasonably large number of MUSes.
such that N is unsatisfiable. The emerging viewpoint of MUSes as the root causes of unsatisfiability has led MUSes to find applications in a wide variety of diagnostic approaches. Recent advances in identification and enumeration of MUSes have motivated researchers to discover applications that can benefit from rich information about the set of MUSes. One such extension is that of counting the number of MUSes. The current best approach for MUS counting is to employ a MUS enumeration algorithm, which often does not scale for the cases with a reasonably large number of MUSes.
Motivated by the success of hashing-based techniques in the context of model counting, we design the first approximate MUS counting procedure with  guarantees, called
guarantees, called 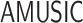 . Our approach avoids exhaustive MUS enumeration by combining the classical technique of universal hashing with advances in QBF solvers along with a novel usage of union and intersection of MUSes to achieve runtime efficiency. Our prototype implementation of
. Our approach avoids exhaustive MUS enumeration by combining the classical technique of universal hashing with advances in QBF solvers along with a novel usage of union and intersection of MUSes to achieve runtime efficiency. Our prototype implementation of  is shown to scale to instances that were clearly beyond the realm of enumeration-based approaches.
is shown to scale to instances that were clearly beyond the realm of enumeration-based approaches.
Introduction
Given an unsatisfiable Boolean formula F as a set of clauses 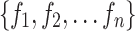 , also known as conjunctive normal form (CNF), a set N of clauses is a Minimal Unsatisfiable Subset (MUS) of F iff
, also known as conjunctive normal form (CNF), a set N of clauses is a Minimal Unsatisfiable Subset (MUS) of F iff  , N is unsatisfiable, and for each
, N is unsatisfiable, and for each 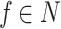 the set
the set  is satisfiable. Since MUSes can be viewed as representing the minimal reasons for unsatisfiability of a formula, MUSes have found applications in wide variety of domains ranging from diagnosis
[45], ontologies debugging
[1], spreadsheet debugging
[29], formal equivalence checking
[20], constrained counting and sampling
[28], and the like. As the scalable techniques for identification of MUSes appeared only about decade and half ago, the earliest applications primarily focused on a reduction to the identification of a single MUS or a small set of MUSes. With an improvement in the scalability of MUS identification techniques, researchers have now sought to investigate extensions of MUSes and their corresponding applications. One such extension is MUS counting, i.e., counting the number of MUSes of F. Hunter and Konieczny
[26], Mu
[45], and Thimm
[56] have shown that the number of MUSes can be used to compute different inconsistency metrics for general propositional knowledge bases.
is satisfiable. Since MUSes can be viewed as representing the minimal reasons for unsatisfiability of a formula, MUSes have found applications in wide variety of domains ranging from diagnosis
[45], ontologies debugging
[1], spreadsheet debugging
[29], formal equivalence checking
[20], constrained counting and sampling
[28], and the like. As the scalable techniques for identification of MUSes appeared only about decade and half ago, the earliest applications primarily focused on a reduction to the identification of a single MUS or a small set of MUSes. With an improvement in the scalability of MUS identification techniques, researchers have now sought to investigate extensions of MUSes and their corresponding applications. One such extension is MUS counting, i.e., counting the number of MUSes of F. Hunter and Konieczny
[26], Mu
[45], and Thimm
[56] have shown that the number of MUSes can be used to compute different inconsistency metrics for general propositional knowledge bases.
In contrast to the progress in the design of efficient MUS identification techniques, the work on MUS counting is still in its nascent stages. Reminiscent of the early days of model counting, the current approach for MUS counting is to employ a complete MUS enumeration algorithm, e.g., [3, 12, 34, 55], to explicitly identify all MUSes. As noted in Sect. 2, there can be up to exponentially many MUSes of F w.r.t. |F|, and thus their complete enumeration can be practically intractable. Indeed, contemporary MUS enumeration algorithms often cannot complete the enumeration within a reasonable time [10, 12, 34, 47]. In this context, one wonders: whether it is possible to design a scalable MUS counter without performing explicit enumeration of MUSes?
The primary contribution of this paper is a probabilistic counter, called 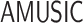 , that takes in a formula F, tolerance parameter
, that takes in a formula F, tolerance parameter  , confidence parameter
, confidence parameter  , and returns an estimate guaranteed to be within
, and returns an estimate guaranteed to be within  -multiplicative factor of the exact count with confidence at least
-multiplicative factor of the exact count with confidence at least  . Crucially, for F defined over n clauses,
. Crucially, for F defined over n clauses,  explicitly identifies only
explicitly identifies only  many MUSes even though the number of MUSes can be exponential in n.
many MUSes even though the number of MUSes can be exponential in n.
The design of  is inspired by recent successes in the design of efficient XOR hashing-based techniques
[15, 17] for the problem of model counting, i.e., given a Boolean formula G, compute the number of models (also known as solutions) of G. We observe that both the problems are defined over a power-set structure. In MUS counting, the goal is to count MUSes in the power-set of F, whereas in model counting, the goal is to count models in the power-set that represents all valuations of variables of G. Chakraborty et al.
[18, 52] proposed an algorithm, called
is inspired by recent successes in the design of efficient XOR hashing-based techniques
[15, 17] for the problem of model counting, i.e., given a Boolean formula G, compute the number of models (also known as solutions) of G. We observe that both the problems are defined over a power-set structure. In MUS counting, the goal is to count MUSes in the power-set of F, whereas in model counting, the goal is to count models in the power-set that represents all valuations of variables of G. Chakraborty et al.
[18, 52] proposed an algorithm, called  , for approximate model counting that also provides the (
, for approximate model counting that also provides the ( ,
,  ) guarantees.
) guarantees.  is currently in its third version,
is currently in its third version, 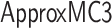 [52]. The base idea of
[52]. The base idea of 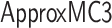 is to partition the power-set into nCells small cells, then pick one of the cells, and count the number inCell of models in the cell. The total model count is then estimated as
is to partition the power-set into nCells small cells, then pick one of the cells, and count the number inCell of models in the cell. The total model count is then estimated as  . Our algorithm for MUS counting is based on
. Our algorithm for MUS counting is based on 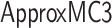 . We adopt the high-level idea to partition the power-set of F into small cells and then estimate the total MUS count based on a MUS count in a single cell. The difference between
. We adopt the high-level idea to partition the power-set of F into small cells and then estimate the total MUS count based on a MUS count in a single cell. The difference between 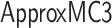 and
and 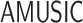 lies in the way of counting the target elements (models vs. MUSes) in a single cell; we propose novel MUS specific techniques to deal with this task. In particular, our contribution is the following:
lies in the way of counting the target elements (models vs. MUSes) in a single cell; we propose novel MUS specific techniques to deal with this task. In particular, our contribution is the following:
We introduce a QBF (quantified Boolean formula) encoding for the problem of counting MUSes in a single cell and use a
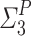 oracle to solve it.
oracle to solve it.Let
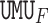 and
and  be the union and the intersection of all MUSes of F, respectively. We observe that every MUS of F (1) contains
be the union and the intersection of all MUSes of F, respectively. We observe that every MUS of F (1) contains 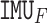 and (2) is contained in
and (2) is contained in  . Consequently, if we determine the sets
. Consequently, if we determine the sets 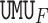 and
and  , then we can significantly speed up the identification of MUSes in a cell.
, then we can significantly speed up the identification of MUSes in a cell.We propose a novel approaches for computing the union
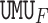 and the intersection
and the intersection 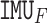 of all MUSes of F.
of all MUSes of F.We implement
 and conduct an extensive empirical evaluation on a set of scalable benchmarks. We observe that
and conduct an extensive empirical evaluation on a set of scalable benchmarks. We observe that  is able to compute estimates for problems clearly beyond the reach of existing enumeration-based techniques. We experimentally evaluate the accuracy of
is able to compute estimates for problems clearly beyond the reach of existing enumeration-based techniques. We experimentally evaluate the accuracy of  . In particular, we observe that the estimates computed by
. In particular, we observe that the estimates computed by  are significantly closer to true count than the theoretical guarantees provided by
are significantly closer to true count than the theoretical guarantees provided by  .
.
Our work opens up several new interesting avenues of research. From a theoretical perspective, we make polynomially many calls to a  oracle while the problem of finding a MUS is known to be in
oracle while the problem of finding a MUS is known to be in 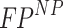 , i.e. a MUS can be found in polynomial time by executing a polynomial number of calls to an NP-oracle
[19, 39]. Contrasting this to model counting techniques, where approximate counter makes polynomially many calls to an NP-oracle when the underlying problem of finding satisfying assignment is NP-complete, a natural question is to close the gap and seek to design a MUS counting algorithm with polynomially many invocations of an
, i.e. a MUS can be found in polynomial time by executing a polynomial number of calls to an NP-oracle
[19, 39]. Contrasting this to model counting techniques, where approximate counter makes polynomially many calls to an NP-oracle when the underlying problem of finding satisfying assignment is NP-complete, a natural question is to close the gap and seek to design a MUS counting algorithm with polynomially many invocations of an 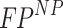 oracle. From a practitioner perspective, our work calls for a design of MUS techniques with native support for XORs; the pursuit of native support for XOR in the context of SAT solvers have led to an exciting line of work over the past decade
[52, 53].
oracle. From a practitioner perspective, our work calls for a design of MUS techniques with native support for XORs; the pursuit of native support for XOR in the context of SAT solvers have led to an exciting line of work over the past decade
[52, 53].
Preliminaries and Problem Formulation
A Boolean formula 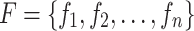 in a conjunctive normal form (CNF) is a set of Boolean clauses over a set of Boolean variables
in a conjunctive normal form (CNF) is a set of Boolean clauses over a set of Boolean variables  . A Boolean clause is a set
. A Boolean clause is a set 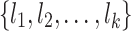 of literals. A literal is either a variable
of literals. A literal is either a variable  or its negation
or its negation  . A truth assignment I to the variables
. A truth assignment I to the variables 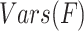 is a mapping
is a mapping 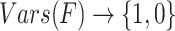 . A clause
. A clause 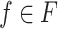 is satisfied by an assignment I iff
is satisfied by an assignment I iff 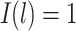 for some
for some 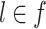 or
or  for some
for some 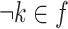 . The formula F is satisfied by I iff I satisfies every
. The formula F is satisfied by I iff I satisfies every  ; in such a case I is called a model of F. Finally, F is satisfiable if it has a model; otherwise F is unsatisfiable.
; in such a case I is called a model of F. Finally, F is satisfiable if it has a model; otherwise F is unsatisfiable.
A QBF is a Boolean formula where each variable is either universally (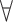 ) or existentially (
) or existentially ( ) quantified. We write
) quantified. We write  -QBF, where
-QBF, where  , to denote the class of QBF with a particular type of alternation of the quantifiers, e.g.,
, to denote the class of QBF with a particular type of alternation of the quantifiers, e.g.,  -QBF or
-QBF or  -QBF. Every QBF is either true (valid) or false (invalid). The problem of deciding validity of a formula in
-QBF. Every QBF is either true (valid) or false (invalid). The problem of deciding validity of a formula in 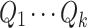 -QBF where
-QBF where 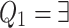 is
is 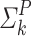 -complete
[43].
-complete
[43].
When it is clear from the context, we write just formula to denote either a QBF or a Boolean formula in CNF. Moreover, throughout the whole text, we use F to denote the input Boolean Formula in CNF. Furthermore, we will use capital letters, e.g., S, K, N, to denote other CNF formulas, small letters, e.g.,  , to denote clauses, and small letters, e.g.,
, to denote clauses, and small letters, e.g.,  , to denote variables.
, to denote variables.
Given a set X, we write 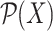 to denote the power-set of X, and |X| to denote the cardinality of X. Finally, we write
to denote the power-set of X, and |X| to denote the cardinality of X. Finally, we write  to denote the probability of an outcome O when sampling from a probability space
to denote the probability of an outcome O when sampling from a probability space 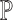 . When
. When  is clear from the context, we write just
is clear from the context, we write just 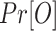 .
.
Minimal Unsatisfiability
Definition 1 (MUS)
A set N,  , is a minimal unsatisfiable subset (MUS) of F iff N is unsatisfiable and for all
, is a minimal unsatisfiable subset (MUS) of F iff N is unsatisfiable and for all 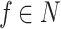 the set
the set  is satisfiable.
is satisfiable.
Note that the minimality concept used here is set minimality, not minimum cardinality. Therefore, there can be MUSes with different cardinalities. In general, there can be up to exponentially many MUSes of F w.r.t. |F| (see the Sperner’s theorem
[54]). We use  to denote the set of all MUSes of F. Furthermore, we write
to denote the set of all MUSes of F. Furthermore, we write  and
and  to denote the union and the intersection of all MUSes of F, respectively. Finally, note that every subset S of F can be expressed as a bit-vector over the alphabet
to denote the union and the intersection of all MUSes of F, respectively. Finally, note that every subset S of F can be expressed as a bit-vector over the alphabet 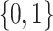 ; for example, if
; for example, if 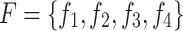 and
and 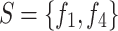 , then the bit-vector representation of S is 1001.
, then the bit-vector representation of S is 1001.
Definition 2
Let N be an unsatisfiable subset of F and  . The clause f is necessary for N iff
. The clause f is necessary for N iff 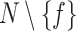 is satisfiable.
is satisfiable.
The necessary clauses are sometimes also called transition
[6] or critical
[2] clauses. Note that a set N is a MUS iff every 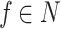 is necessary for N. Also, note that a clause
is necessary for N. Also, note that a clause  is necessary for F iff
is necessary for F iff 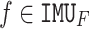 .
.
Example 1
We demonstrate the concepts on an example, illustrated in Fig. 1. Assume that  . In this case,
. In this case,  ,
, 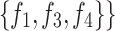 ,
,  , and
, and 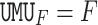 .
.
Fig. 1.

Illustration of the power set of the formula F from the Example 1. We denote individual subsets of F using the bit-vector representation. The subsets with a dashed border are the unsatisfiable subsets, and the others are satisfiable subsets. The MUSes are filled with a background color. (Color figure online)
Hash Functions
Let n and m be positive integers such that  . By
. By 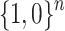 we denote the set of all bit-vectors of length n over the alphabet
we denote the set of all bit-vectors of length n over the alphabet  . Given a vector
. Given a vector 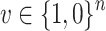 and
and  , we write v[i] to denote the i-th bit of v. A hash function h from a family
, we write v[i] to denote the i-th bit of v. A hash function h from a family  of hash functions maps
of hash functions maps 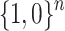 to
to 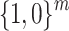 . The family
. The family 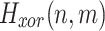 is defined as
is defined as  , where
, where  and
and  denote the Boolean XOR and AND operators, respectively, and
denote the Boolean XOR and AND operators, respectively, and  for all
for all  and
and 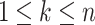 .
.
To choose a hash function uniformly at random from  , we randomly and independently choose the values of
, we randomly and independently choose the values of 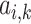 . It has been shown
[24] that the family
. It has been shown
[24] that the family 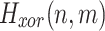 is pairwise independent, also known as strongly 2-universal. In particular, let us by
is pairwise independent, also known as strongly 2-universal. In particular, let us by 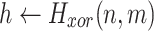 denote the probability space obtained by choosing a hash function h uniformly at random from
denote the probability space obtained by choosing a hash function h uniformly at random from  . The property of pairwise independence guarantees that for all
. The property of pairwise independence guarantees that for all  and for all distinct
and for all distinct  ,
, 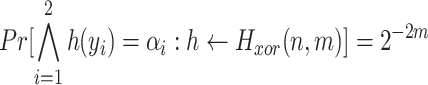 .
.
We say that a hash function  partitions
partitions
 into
into 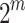 cells. Furthermore, given a hash function
cells. Furthermore, given a hash function  and a cell
and a cell 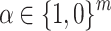 of h, we define their prefix-slices. In particular, for every
of h, we define their prefix-slices. In particular, for every  , the
, the  prefix of h, denoted
prefix of h, denoted  , is a map from
, is a map from 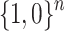 to
to 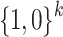 such that
such that  for all
for all  and for all
and for all 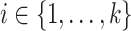 . Similarly, the
. Similarly, the 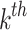 prefix of
prefix of  , denoted
, denoted 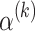 , is an element of
, is an element of  such that
such that 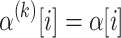 for all
for all  . Intuitively, a cell
. Intuitively, a cell  of
of 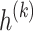 originates by merging the two cells of
originates by merging the two cells of  that differ only in the last bit.
that differ only in the last bit.
In our work, we use hash functions from the family  to partition the power-set
to partition the power-set  of the given Boolean formula F into
of the given Boolean formula F into 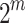 cells. Furthermore, given a cell
cells. Furthermore, given a cell  , let us by
, let us by 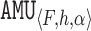 denote the set of all MUSes in the cell
denote the set of all MUSes in the cell 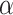 ; formally,
; formally, 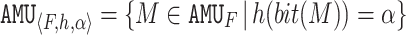 , where
, where  is the bit-vector representation of M. The following observation is crucial for our work.
is the bit-vector representation of M. The following observation is crucial for our work.
Observation 1
For every formula F, 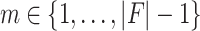 ,
,  , and
, and  it holds that:
it holds that:  for every
for every  .
.
Example 2
Assume that we are given a formula F such that 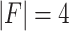 and a hash function
and a hash function  that is defined via the following values of individual
that is defined via the following values of individual  :
:
 |
The hash function partitions  into 4 cells. For example,
into 4 cells. For example, 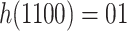 since
since 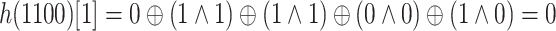 and
and 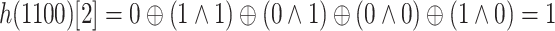 . Figure 2 illustrates the whole partition and also illustrates the partition given by the prefix
. Figure 2 illustrates the whole partition and also illustrates the partition given by the prefix 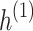 of h.
of h.
Fig. 2.
Illustration of the partition of  by
by 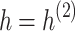 and
and  from Example 2. In the case of h, we use 4 colors, orange, pink, white, and blue, to highlight its four cells. In case of
from Example 2. In the case of h, we use 4 colors, orange, pink, white, and blue, to highlight its four cells. In case of  , there are only two cells: the white and the blue cells are merged into a white cell, and the pink and the orange cells are merged into an orange cell. (Color figure online)
, there are only two cells: the white and the blue cells are merged into a white cell, and the pink and the orange cells are merged into an orange cell. (Color figure online)
Problem Definitions
In this paper, we are concerned with the following problems.
Name:
 problem
problem
Input: A formula F, a tolerance  , and a confidence
, and a confidence  .
.
Output: A number c such that 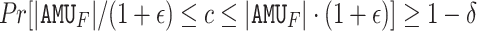 .
.
Name: MUS-membership problem
Input: A formula F and a clause 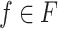 .
.
Output:
True if there is a MUS  such that
such that 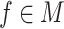 and False otherwise.
and False otherwise.
Name: MUS-union problem
Input: A formula F.
Output: The union  of all MUSes of F.
of all MUSes of F.
Name: MUS-intersection problem
Input: A formula F.
Output: The intersection 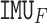 of all MUSes of F.
of all MUSes of F.
Name:
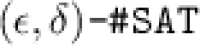 problem
problem
Input: A formula F, a tolerance  , and a confidence
, and a confidence 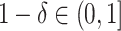 .
.
Output: A number m such that 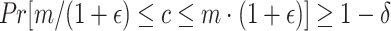 , where m is the number of models of F.
, where m is the number of models of F.
The main goal of this paper is to provide a solution to the
 problem. We also deal with the MUS-membership, MUS-union and MUS-intersection problems since these problems emerge in our approach for solving the
problem. We also deal with the MUS-membership, MUS-union and MUS-intersection problems since these problems emerge in our approach for solving the
 problem. Finally, we do not focus on solving the
problem. Finally, we do not focus on solving the
 problem, however the problem is closely related to the
problem, however the problem is closely related to the
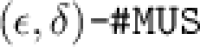 problem.
problem.
Related Work
It is well-known (see e.g.,
[21, 36, 51]) that a clause  belongs to
belongs to  iff f is necessary for F. Therefore, to compute
iff f is necessary for F. Therefore, to compute 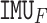 , one can simply check each
, one can simply check each  for being necessary for F. We are not aware of any work that has focused on the MUS-intersection problem in more detail.
for being necessary for F. We are not aware of any work that has focused on the MUS-intersection problem in more detail.
The MUS-union problem was recently investigated by Mencia et al.
[42]. Their algorithm is based on gradually refining an under-approximation of 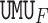 until the exact
until the exact  is computed. Unfortunately, the authors experimentally show that their algorithm often fails to find the exact
is computed. Unfortunately, the authors experimentally show that their algorithm often fails to find the exact 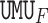 within a reasonable time even for relatively small input instances (only an under-approximation is computed). In our work, we propose an approach that works in the other way: we start with an over-approximation of
within a reasonable time even for relatively small input instances (only an under-approximation is computed). In our work, we propose an approach that works in the other way: we start with an over-approximation of  and gradually refine the approximation to eventually get
and gradually refine the approximation to eventually get 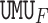 . Another related research was conducted by Janota and Marques-Silva
[30] who proposed several QBF encodings for solving the MUS-membership problem. Although they did not focus on finding
. Another related research was conducted by Janota and Marques-Silva
[30] who proposed several QBF encodings for solving the MUS-membership problem. Although they did not focus on finding 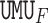 , one can clearly identify
, one can clearly identify 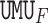 by solving the MUS-membership problem for each
by solving the MUS-membership problem for each  .
.
As for counting the number of MUSes of F, we are not aware of any previous work dedicated to this problem. Yet, there have been proposed plenty of algorithms and tools (e.g.,
[3, 9, 11, 12, 35, 47]) for enumerating/identifying all MUSes of F. Clearly, if we enumerate all MUSes of F, then we obtain the exact value of 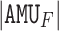 , and thus we also solve the
, and thus we also solve the
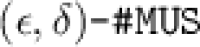 problem. However, since there can be up to exponentially many of MUSes w.r.t. |F|, MUS enumeration algorithms are often not able to complete the enumeration in a reasonable time and thus are not able to find the value of
problem. However, since there can be up to exponentially many of MUSes w.r.t. |F|, MUS enumeration algorithms are often not able to complete the enumeration in a reasonable time and thus are not able to find the value of 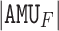 .
.
Very similar to the
 problem is the
problem is the
 problem. Both problems involve the same probabilistic and approximation guarantees. Moreover, both problems are defined over a power-set structure. In MUS counting, the goal is to count MUSes in
problem. Both problems involve the same probabilistic and approximation guarantees. Moreover, both problems are defined over a power-set structure. In MUS counting, the goal is to count MUSes in 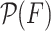 , whereas in model counting, the goal is to count models in
, whereas in model counting, the goal is to count models in 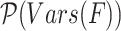 . In this paper, we propose an algorithm for solving the
. In this paper, we propose an algorithm for solving the
 problem that is based on
problem that is based on 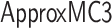 [15, 17, 52]. In particular, we keep the high-level idea of
[15, 17, 52]. In particular, we keep the high-level idea of  for processing/exploring the power-set structure, and we propose new low-level techniques that are specific for MUS counting.
for processing/exploring the power-set structure, and we propose new low-level techniques that are specific for MUS counting.
 : A Hashing-Based MUS Counter
: A Hashing-Based MUS Counter
We now describe  , a hashing-based algorithm designed to solve the (
, a hashing-based algorithm designed to solve the (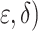 -#MUS problem. The name of the algorithm is an acronym for Approximate Minimal Unsatisfiable Subsets Implicit Counter.
-#MUS problem. The name of the algorithm is an acronym for Approximate Minimal Unsatisfiable Subsets Implicit Counter.  is based on
is based on 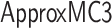 , which is a hashing-based algorithm to solve
, which is a hashing-based algorithm to solve  -#SAT problem. As such, while the high-level structure of
-#SAT problem. As such, while the high-level structure of 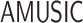 and
and 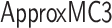 share close similarities, the two algorithms differ significantly in the design of core technical subroutines.
share close similarities, the two algorithms differ significantly in the design of core technical subroutines.
We first discuss the high-level structure of  in Sect. 4.1. We then present the key technical contributions of this paper: the design of core subroutines of
in Sect. 4.1. We then present the key technical contributions of this paper: the design of core subroutines of 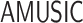 in Sects. 4.3, 4.4 and 4.5.
in Sects. 4.3, 4.4 and 4.5.
Algorithmic Overview
The main procedure of 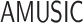 is presented in Algorithm 1. The algorithm takes as an input a Boolean formula F in CNF, a tolerance
is presented in Algorithm 1. The algorithm takes as an input a Boolean formula F in CNF, a tolerance 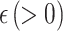 , and a confidence parameter
, and a confidence parameter  , and returns an estimate of
, and returns an estimate of  within tolerance
within tolerance 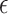 and with confidence at least
and with confidence at least  . Similar to
. Similar to 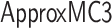 , we first check whether
, we first check whether 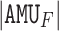 is smaller than a specific
is smaller than a specific  that is a function of
that is a function of  . This check is carried out via a MUS enumeration algorithm, denoted
. This check is carried out via a MUS enumeration algorithm, denoted 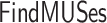 , that returns a set Y of MUSes of F such that
, that returns a set Y of MUSes of F such that  . If
. If 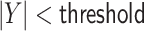 , the algorithm terminates while identifying the exact value of
, the algorithm terminates while identifying the exact value of  . In a significant departure from
. In a significant departure from 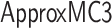 ,
,  subsequently computes the union (
subsequently computes the union (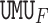 ) and the intersection (
) and the intersection ( ) of all MUSes of F by invoking the subroutines
) of all MUSes of F by invoking the subroutines 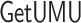 and
and 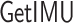 , respectively. Through the lens of set representation of the CNF formulas, we can view
, respectively. Through the lens of set representation of the CNF formulas, we can view  as another CNF formula, G. Our key observation is that
as another CNF formula, G. Our key observation is that  (see Sect. 4.2), thus instead of working with the whole F, we can focus only on G. The rest of the main procedure is similar to
(see Sect. 4.2), thus instead of working with the whole F, we can focus only on G. The rest of the main procedure is similar to  , i.e., we repeatedly invoke the core subroutine called
, i.e., we repeatedly invoke the core subroutine called 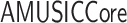 . The subroutine attempts to find an estimate c of
. The subroutine attempts to find an estimate c of 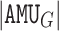 within the tolerance
within the tolerance  . Briefly, to find the estimate, the subroutine partitions
. Briefly, to find the estimate, the subroutine partitions 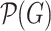 into
into 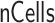 cells, then picks one of the cells, and counts the number
cells, then picks one of the cells, and counts the number 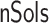 of MUSes in the cell. The pair
of MUSes in the cell. The pair  is returned by
is returned by  , and the estimate c of
, and the estimate c of 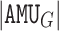 is then computed as
is then computed as 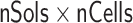 . There is a small chance that
. There is a small chance that  fails to find the estimate; it such a case
fails to find the estimate; it such a case  . Individual estimates are stored in a list C. After the final invocation of
. Individual estimates are stored in a list C. After the final invocation of 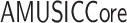 ,
, 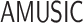 computes the median of the list C and returns the median as the final estimate of
computes the median of the list C and returns the median as the final estimate of 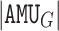 . The total number of invocations of
. The total number of invocations of  is in
is in  which is enough to ensure the required confidence
which is enough to ensure the required confidence  (details on assurance of the
(details on assurance of the 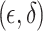 guarantees are provided in Sect. 4.2).
guarantees are provided in Sect. 4.2). 

We now turn to  which is described in Algorithm 2. The partition of
which is described in Algorithm 2. The partition of  into
into 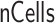 cells is made via a hash function h from
cells is made via a hash function h from  , i.e.
, i.e.  . The choice of m is a crucial part of the algorithm as it regulates the size of the cells. Intuitively, it is easier to identify all MUSes of a small cell; however, on the contrary, the use of small cells does not allow to achieve a reasonable tolerance. Based on
. The choice of m is a crucial part of the algorithm as it regulates the size of the cells. Intuitively, it is easier to identify all MUSes of a small cell; however, on the contrary, the use of small cells does not allow to achieve a reasonable tolerance. Based on 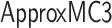 , we choose m such that a cell given by a hash function
, we choose m such that a cell given by a hash function  contains almost
contains almost 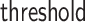 many MUSes. In particular, the computation of
many MUSes. In particular, the computation of  starts by choosing at random a hash function h from
starts by choosing at random a hash function h from 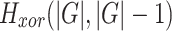 and a cell
and a cell 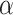 at random from
at random from  . Subsequently, the algorithm tends to identify
. Subsequently, the algorithm tends to identify 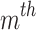 prefixes
prefixes 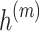 and
and 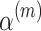 of h and
of h and  , respectively, such that
, respectively, such that  and
and  . Recall that
. Recall that  (Observation 1, Sect. 2). We also know that the cell
(Observation 1, Sect. 2). We also know that the cell  , i.e. the whole
, i.e. the whole 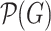 , contains at least
, contains at least  MUSes (see Algorithm 1, line 3). Consequently, there can exist at most one such m, and it exists if and only if
MUSes (see Algorithm 1, line 3). Consequently, there can exist at most one such m, and it exists if and only if  . Therefore, the algorithm first checks whether
. Therefore, the algorithm first checks whether  . The check is carried via a procedure
. The check is carried via a procedure  that returns the number
that returns the number  . If
. If  , then
, then  fails to find the estimate of
fails to find the estimate of  and terminates. Otherwise, a procedure
and terminates. Otherwise, a procedure  is used to find the required value of m together with the number
is used to find the required value of m together with the number  of MUSes in
of MUSes in  . The implementation of
. The implementation of 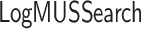 is directly adopted from
is directly adopted from  and thus we do not provide its pseudocode here (note that in
and thus we do not provide its pseudocode here (note that in  the procedure is called
the procedure is called  ). We only briefly summarize two main ingredients of the procedure. First, it has been observed that the required value of m is often similar for repeated calls of
). We only briefly summarize two main ingredients of the procedure. First, it has been observed that the required value of m is often similar for repeated calls of  . Therefore, the algorithm keeps the value mPrev of m from previous iteration and first test values near mPrev. If none of the near values is the required one, the algorithm exploits that
. Therefore, the algorithm keeps the value mPrev of m from previous iteration and first test values near mPrev. If none of the near values is the required one, the algorithm exploits that  , which allows it to find the required value of m via the galloping search (variation of binary search) while performing only
, which allows it to find the required value of m via the galloping search (variation of binary search) while performing only 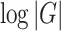 calls of
calls of 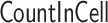 .
.
Note that in 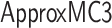 , the procedure
, the procedure 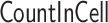 is called
is called  and it is implemented via an NP oracle, whereas we use a
and it is implemented via an NP oracle, whereas we use a 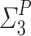 oracle to implement the procedure (see Sect. 4.3). The high-level functionality is the same: the procedures use up to
oracle to implement the procedure (see Sect. 4.3). The high-level functionality is the same: the procedures use up to  calls of the oracle to check whether the number of the target elements (models vs. MUSes) in a cell is lower than
calls of the oracle to check whether the number of the target elements (models vs. MUSes) in a cell is lower than 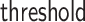 .
.
Analysis and Comparison with 
Following from the discussion above, there are three crucial technical differences between  and
and  : (1) the implementation of the subroutine
: (1) the implementation of the subroutine 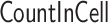 in the context of MUS, (2) computation of the intersection
in the context of MUS, (2) computation of the intersection  of all MUSes of F and its usage in
of all MUSes of F and its usage in  , and (3) computation of the union
, and (3) computation of the union 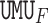 of all MUSes of F and invocation of the underlying subroutines with G (i.e.,
of all MUSes of F and invocation of the underlying subroutines with G (i.e.,  ) instead of F. The usage of
) instead of F. The usage of 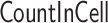 can be viewed as domain-specific instantiation of
can be viewed as domain-specific instantiation of  in the context of MUSes. Furthermore, we use the computed intersection of MUSes to improve the runtime efficiency of
in the context of MUSes. Furthermore, we use the computed intersection of MUSes to improve the runtime efficiency of  . It is perhaps worth mentioning that prior studies have observed that over 99% of the runtime of
. It is perhaps worth mentioning that prior studies have observed that over 99% of the runtime of 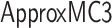 is spent inside the subroutine
is spent inside the subroutine  [52]. Therefore, the runtime efficiency of
[52]. Therefore, the runtime efficiency of  is crucial for the runtime performance of
is crucial for the runtime performance of  , and we discuss in detail, in Sect. 4.3, algorithmic contributions in the context of
, and we discuss in detail, in Sect. 4.3, algorithmic contributions in the context of  including usage of
including usage of  . We now argue that the replacement of F with G in line 4 in Algorithm 1 does not affect correctness guarantees, which is stated formally below:
. We now argue that the replacement of F with G in line 4 in Algorithm 1 does not affect correctness guarantees, which is stated formally below:
Lemma 1
For every 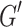 such that
such that 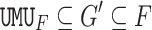 , the following hold:
, the following hold:
 |
1 |
 |
2 |
Proof
(1) Since  then every MUS of
then every MUS of 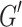 is also a MUS of F. In the other direction, every MUS of F is contained in the union
is also a MUS of F. In the other direction, every MUS of F is contained in the union  of all MUSes of F, and thus every MUS of F is also a MUS of
of all MUSes of F, and thus every MUS of F is also a MUS of 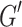 (
( ).
).
(2)  .
.
Equipped with Lemma 1, we now argue that each run of 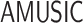 can be simulated by a run of
can be simulated by a run of 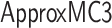 for an appropriately chosen formula. Given an unsatisfiable formula
for an appropriately chosen formula. Given an unsatisfiable formula  , let us by
, let us by 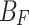 denote a satisfiable formula such that: (1)
denote a satisfiable formula such that: (1)  and (2) an assignment
and (2) an assignment  is a model of
is a model of  iff
iff  is a MUS of F. Informally, models of
is a MUS of F. Informally, models of 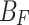 one-to-one map to MUSes of F. Hence, the size of sets returned by
one-to-one map to MUSes of F. Hence, the size of sets returned by  for F is identical to the corresponding
for F is identical to the corresponding 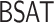 for
for  . Since the analysis of
. Since the analysis of 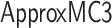 only depends on the correctness of the size of the set returned by
only depends on the correctness of the size of the set returned by 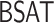 , we conclude that the answer computed by
, we conclude that the answer computed by  would satisfy
would satisfy 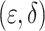 guarantees. Furthermore, observing that
guarantees. Furthermore, observing that  makes
makes 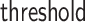 many queries to
many queries to 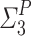 -oracle, we can bound the time complexity. Formally,
-oracle, we can bound the time complexity. Formally,
Theorem 1
Given a formula F, a tolerance 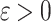 , and a confidence
, and a confidence 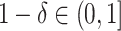 , let
, let  return c. Then
return c. Then 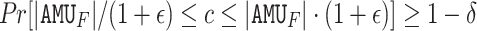 . Furthermore,
. Furthermore,  makes
makes 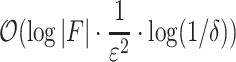 calls to
calls to  oracle.
oracle.
Few words are in order concerning the complexity of  . As noted in Sect. 1, for a formula on n variables, approximate model counters make
. As noted in Sect. 1, for a formula on n variables, approximate model counters make 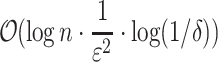 calls to an NP oracle, whereas the complexity of finding a satisfying assignment is NP-complete. In our case, we make calls to a
calls to an NP oracle, whereas the complexity of finding a satisfying assignment is NP-complete. In our case, we make calls to a 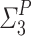 oracle while the problem of finding a MUS is in
oracle while the problem of finding a MUS is in  . Therefore, a natural direction of future work is to investigate the design of a hashing-based technique that employs an
. Therefore, a natural direction of future work is to investigate the design of a hashing-based technique that employs an  oracle.
oracle.
Counting MUSes in a Cell: 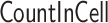
 In this section, we describe the procedure CountInCell. The input of the procedure is the formula G (i.e.,
In this section, we describe the procedure CountInCell. The input of the procedure is the formula G (i.e., 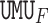 ), the set
), the set  , a hash function
, a hash function 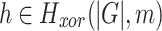 , a cell
, a cell  , and the
, and the  value. The output is
value. The output is 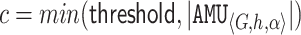 .
.
The description is provided in Algorithm 3. The algorithm iteratively calls a procedure GetMUS that returns either a MUS M such that  or null if there is no such MUS. For each M, the value of c is increased and M is added to
or null if there is no such MUS. For each M, the value of c is increased and M is added to  . The loop terminates either when c reaches the value of
. The loop terminates either when c reaches the value of 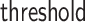 or when GetMUS fails to find a new MUS (i.e., returns null). Finally, the algorithm returns c.
or when GetMUS fails to find a new MUS (i.e., returns null). Finally, the algorithm returns c.
GetMUS. To implement the procedure GetMUS, we build an  -QBF formula MUSInCell such that each witness of the formula corresponds to a MUS from
-QBF formula MUSInCell such that each witness of the formula corresponds to a MUS from 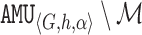 . The formula consists of several parts and uses several sets of variables that are described in the following.
. The formula consists of several parts and uses several sets of variables that are described in the following.
The main part of the formula, shown in Eq. (3), introduces the first existential quantifier and a set  of variables that are quantified by the quantifier. Note that each valuation I of P corresponds to a subset S of G; in particular let us by
of variables that are quantified by the quantifier. Note that each valuation I of P corresponds to a subset S of G; in particular let us by  denote the set
denote the set 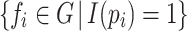 . The formula is build in such a way that a valuation I is a witness of the formula if and only if
. The formula is build in such a way that a valuation I is a witness of the formula if and only if 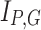 is a MUS from
is a MUS from 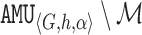 . This property is expressed via three conjuncts, denoted
. This property is expressed via three conjuncts, denoted
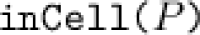 ,
,
 , and
, and
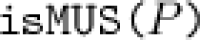 , encoding that (i)
, encoding that (i)  is in the cell
is in the cell 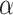 , (ii)
, (ii)  is not in
is not in 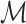 , and (iii)
, and (iii)  is a MUS, respectively.
is a MUS, respectively.
| 3 |
Recall that the family  of hash functions is defined as
of hash functions is defined as 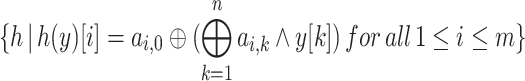 , where
, where 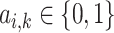 (Sect. 2). A hash function
(Sect. 2). A hash function 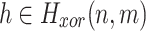 is given by fixing the values of individual
is given by fixing the values of individual 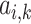 and a cell
and a cell 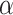 of h is a bit-vector from
of h is a bit-vector from 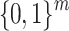 . The formula
. The formula  encoding that the set
encoding that the set 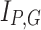 is in the cell
is in the cell  of h is shown in Eq. (4).
of h is shown in Eq. (4).
| 4 |
To encode that we are not interested in MUSes from  , we can simply block all the valuations of P that correspond to these MUSes. However, we can do better. In particular, recall that if M is a MUS, then no proper subset and no proper superset of M can be a MUS; thus, we prune away all these sets from the search space. The corresponding formula is shown in Eq. (5).
, we can simply block all the valuations of P that correspond to these MUSes. However, we can do better. In particular, recall that if M is a MUS, then no proper subset and no proper superset of M can be a MUS; thus, we prune away all these sets from the search space. The corresponding formula is shown in Eq. (5).
| 5 |
The formula  encoding that
encoding that  is a MUS is shown in Eq. (6). Recall that
is a MUS is shown in Eq. (6). Recall that 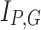 is a MUS if and only if
is a MUS if and only if 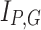 is unsatisfiable and for every closest subset
S of
is unsatisfiable and for every closest subset
S of  it holds that S is satisfiable, where closest subset means that
it holds that S is satisfiable, where closest subset means that  . We encode these two conditions using two subformulas denoted by
. We encode these two conditions using two subformulas denoted by  and
and 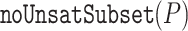 .
.
| 6 |
The formula
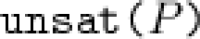 , shown in Eq. (7), introduces the set
, shown in Eq. (7), introduces the set 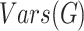 of variables that appear in G and states that every valuation of
of variables that appear in G and states that every valuation of 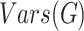 falsifies at least one clause contained in
falsifies at least one clause contained in 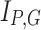 .
.
| 7 |
The formula
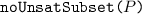 , shown in Eq. (8), introduces another set of variables:
, shown in Eq. (8), introduces another set of variables: 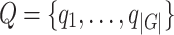 . Similarly as in the case of P, each valuation I of Q corresponds to a subset of G defined as
. Similarly as in the case of P, each valuation I of Q corresponds to a subset of G defined as 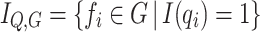 . The formula expresses that for every valuation I of Q it holds that
. The formula expresses that for every valuation I of Q it holds that  is satisfiable or
is satisfiable or 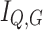 is not a closest subset of
is not a closest subset of  .
.
| 8 |
The requirement that  is satisfiable is encoded in Eq. (9). Since we are already reasoning about the satisfiability of G’s clauses in Eq. (7), we introduce here a copy
is satisfiable is encoded in Eq. (9). Since we are already reasoning about the satisfiability of G’s clauses in Eq. (7), we introduce here a copy 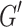 of G where each variable
of G where each variable 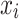 of G is substituted by its primed copy
of G is substituted by its primed copy  . Equation (9) states that there exists a valuation of
. Equation (9) states that there exists a valuation of 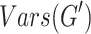 that satisfies
that satisfies 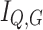 .
.
| 9 |
Equation (10) encodes that 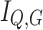 is a closest subset of
is a closest subset of  . To ensure that
. To ensure that  is a subset of
is a subset of 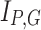 , we add the clauses
, we add the clauses 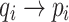 . To ensure the closeness, we use cardinality constraints. In particular, we introduce another set
. To ensure the closeness, we use cardinality constraints. In particular, we introduce another set  of variables and enforce their values via
of variables and enforce their values via  . Intuitively, the number of variables from R that are set to 1 equals to
. Intuitively, the number of variables from R that are set to 1 equals to 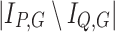 . Finally, we add cardinality constraints, denoted by
. Finally, we add cardinality constraints, denoted by
 , ensuring that exactly one
, ensuring that exactly one  is set to 1.
is set to 1.
| 10 |
Note that instead of encoding a closest subset in Eq. 10, we could just encode that 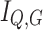 is an arbitrary proper subset of
is an arbitrary proper subset of 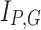 as it would still preserve the meaning of Eq. 6 that
as it would still preserve the meaning of Eq. 6 that  is a MUS. Such an encoding would not require introducing the set R of variables and also, at the first glance, would save a use of one existential quantifier. The thing is that the whole formula would still be in the form of
is a MUS. Such an encoding would not require introducing the set R of variables and also, at the first glance, would save a use of one existential quantifier. The thing is that the whole formula would still be in the form of  -QBF due to Eq. 9 (which introduces the second existential quantifier). The advantage of using a closet subset is that we significantly prune the search space of the QBF solver. It is thus matter of contemporary QBF solvers whether it is more beneficial to reduce the number of variables (by removing R) or to prune the searchspace via R.
-QBF due to Eq. 9 (which introduces the second existential quantifier). The advantage of using a closet subset is that we significantly prune the search space of the QBF solver. It is thus matter of contemporary QBF solvers whether it is more beneficial to reduce the number of variables (by removing R) or to prune the searchspace via R.
For the sake of lucidity, we have not exploited the knowledge of  (
(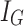 ) while presenting the above equations. Since we know that every clause
) while presenting the above equations. Since we know that every clause  has to be contained in every MUS of G, we can fix the values of the variables
has to be contained in every MUS of G, we can fix the values of the variables 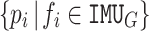 to 1. This, in turn, significantly simplifies the equations and prunes away exponentially many (w.r.t.
to 1. This, in turn, significantly simplifies the equations and prunes away exponentially many (w.r.t. 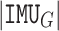 ) valuations of P, Q, and R, that need to be assumed. To solve the final formula, we employ a
) valuations of P, Q, and R, that need to be assumed. To solve the final formula, we employ a 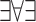 -QBF solver, i.e., a
-QBF solver, i.e., a 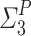 oracle.
oracle.
Finally, one might wonder why we use our custom solution for identifying MUSes in a cell instead of employing one of existing MUS extraction techniques. Conventional MUS extraction algorithms cannot be used to identify MUSes that are in a cell since the cell is not “continuous” w.r.t. the set containment. In particular, assume that we have three sets of clauses, K, L, M, such that  . It can be the case that K and M are in the cell, but L is not in the cell. Contemporary MUS extraction techniques require the search space to be continuous w.r.t. the set containment and thus cannot be used in our case.
. It can be the case that K and M are in the cell, but L is not in the cell. Contemporary MUS extraction techniques require the search space to be continuous w.r.t. the set containment and thus cannot be used in our case.
Computing 
We now turn our attention to computing the union 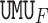 (i.e., G) of all MUSes of F. Let us start by describing well-known concepts of autark variables and a lean kernel. A set
(i.e., G) of all MUSes of F. Let us start by describing well-known concepts of autark variables and a lean kernel. A set 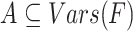 of variables is an autark of F iff there exists a truth assignment to A such that every clause of F that contains a variable from A is satisfied by the assignment
[44]. It holds that the union of two autark sets is also an autark set, thus there exists a unique largest autark set (see, e.g.,
[31, 32]). The lean kernel of F is the set of all clauses that do not contain any variable from the largest autark set. It is known that the lean kernel of F is an over-approximation of
of variables is an autark of F iff there exists a truth assignment to A such that every clause of F that contains a variable from A is satisfied by the assignment
[44]. It holds that the union of two autark sets is also an autark set, thus there exists a unique largest autark set (see, e.g.,
[31, 32]). The lean kernel of F is the set of all clauses that do not contain any variable from the largest autark set. It is known that the lean kernel of F is an over-approximation of  (see e.g.,
[31, 32]), and there were proposed several algorithms, e.g.,
[33, 38], for computing the lean kernel.
(see e.g.,
[31, 32]), and there were proposed several algorithms, e.g.,
[33, 38], for computing the lean kernel.
Algorithm. Our approach for computing  consists of two parts. First, we compute the lean kernel K of F to get an over-approximation of
consists of two parts. First, we compute the lean kernel K of F to get an over-approximation of  , and then we gradually refine the over-approximation K until K is exactly the set
, and then we gradually refine the over-approximation K until K is exactly the set  . The refinement is done by solving the MUS-membership problem for each
. The refinement is done by solving the MUS-membership problem for each 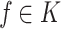 . To solve the MUS-membership problem efficiently, we reveal a connection to necessary clauses, as stated in the following lemma.
. To solve the MUS-membership problem efficiently, we reveal a connection to necessary clauses, as stated in the following lemma.
Lemma 2
A clause  belongs to
belongs to  iff there is a subset W of F such that W is unsatisfiable and f is necessary for W (i.e.,
iff there is a subset W of F such that W is unsatisfiable and f is necessary for W (i.e., 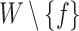 is satisfiable).
is satisfiable).
Proof
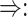 Let
Let 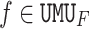 and
and 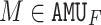 such that
such that  . Since M is a MUS then
. Since M is a MUS then  is satisfiable; thus f is necessary for M.
is satisfiable; thus f is necessary for M.
 If W is a subset of F and
If W is a subset of F and 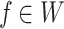 a necessary clause for W then f has to be contained in every MUS of W. Moreover, W has at least one MUS and since
a necessary clause for W then f has to be contained in every MUS of W. Moreover, W has at least one MUS and since  , then every MUS of W is also a MUS of F.
, then every MUS of W is also a MUS of F.
Our approach for computing 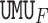 is shown in Algorithm 4. It takes as an input the formula F and outputs
is shown in Algorithm 4. It takes as an input the formula F and outputs 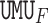 (denoted K). Moreover, the algorithm maintains a set
(denoted K). Moreover, the algorithm maintains a set  of MUSes of F. Initially,
of MUSes of F. Initially,  and K is set to the lean kernel of F; we use an approach by Marques-Silva et al.
[38] to compute the lean kernel. At this point, we know that
and K is set to the lean kernel of F; we use an approach by Marques-Silva et al.
[38] to compute the lean kernel. At this point, we know that  . To find
. To find 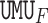 , the algorithm iteratively determines for each
, the algorithm iteratively determines for each 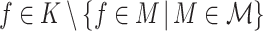 if
if  . In particular, for each f, the algorithm checks whether there exists a subset W of K such that f is necessary for W (Lemma 2). The task of finding W is carried out by a procedure
. In particular, for each f, the algorithm checks whether there exists a subset W of K such that f is necessary for W (Lemma 2). The task of finding W is carried out by a procedure
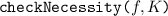 . If there is no such W, then the algorithm removes f from K. In the other case, if W exists, the algorithm finds a MUS of W and adds the MUS to the set
. If there is no such W, then the algorithm removes f from K. In the other case, if W exists, the algorithm finds a MUS of W and adds the MUS to the set  . Any available single MUS extraction approach, e.g.,
[2, 5, 7, 46], can be used to find the MUS.
. Any available single MUS extraction approach, e.g.,
[2, 5, 7, 46], can be used to find the MUS.
To implement the procedure
 we build a QBF formula that is true iff there exists a set
we build a QBF formula that is true iff there exists a set 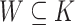 such that W is unsatisfiable and f is necessary for W. To represent W we introduce a set
such that W is unsatisfiable and f is necessary for W. To represent W we introduce a set  of Boolean variables; each valuation I of S corresponds to a subset
of Boolean variables; each valuation I of S corresponds to a subset 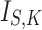 of K defined as
of K defined as  . Our encoding is shown in Eq. 11.
. Our encoding is shown in Eq. 11.
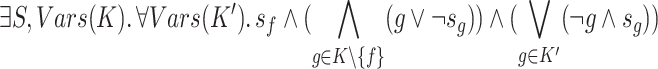 |
11 |
The formula consists of three main conjuncts. The first conjunct ensures that f is present in 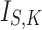 . The second conjunct states that
. The second conjunct states that 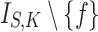 is satisfiable, i.e., that there exists a valuation of
is satisfiable, i.e., that there exists a valuation of 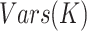 that satisfies
that satisfies 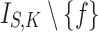 . Finally, the last conjunct express that
. Finally, the last conjunct express that 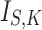 is unsatisfiable, i.e., that every valuation of
is unsatisfiable, i.e., that every valuation of 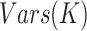 falsifies at least one clause of
falsifies at least one clause of 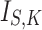 . Since we are already reasoning about variables of K in the second conjunct, in the third conjunct, we use a primed version (a copy)
. Since we are already reasoning about variables of K in the second conjunct, in the third conjunct, we use a primed version (a copy)  of K.
of K.
Alternative QBF Encodings. Janota and Marques-Silva
[30] proposed three other QBF encodings for the MUS-membership problem, i.e., for deciding whether a given  belongs to
belongs to  . Two of the three proposed encodings are typically inefficient; thus, we focus on the third encoding, which is the most concise among the three. The encoding, referred to as JM encoding (after the initials of the authors), uses only two quantifiers in the form of
. Two of the three proposed encodings are typically inefficient; thus, we focus on the third encoding, which is the most concise among the three. The encoding, referred to as JM encoding (after the initials of the authors), uses only two quantifiers in the form of 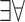 -QBF and it is only linear in size w.r.t. |F|. The underlying ideas by JM encoding and our encoding differ significantly. Our encoding is based on necessary clauses (Lemma 2), whereas JM exploits a connection to so-called Maximal Satisfiable Subsets. Both the encodings use the same quantifiers; however, our encoding is smaller. In particular, the JM uses
-QBF and it is only linear in size w.r.t. |F|. The underlying ideas by JM encoding and our encoding differ significantly. Our encoding is based on necessary clauses (Lemma 2), whereas JM exploits a connection to so-called Maximal Satisfiable Subsets. Both the encodings use the same quantifiers; however, our encoding is smaller. In particular, the JM uses 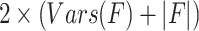 variables whereas our encoding uses only
variables whereas our encoding uses only 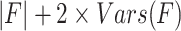 variables, and leads to smaller formulas.
variables, and leads to smaller formulas.
Implementation. Recall that we compute 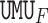 to reduce the search space, i.e. instead of working with the whole F, we work only with
to reduce the search space, i.e. instead of working with the whole F, we work only with 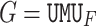 . The soundness of this reduction is witnessed in Lemma 1 (Sect. 4.2). In fact, Lemma 1 shows that it is sound to reduce the search space to any
. The soundness of this reduction is witnessed in Lemma 1 (Sect. 4.2). In fact, Lemma 1 shows that it is sound to reduce the search space to any 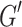 such that
such that 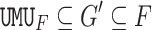 . Since our algorithm for computing
. Since our algorithm for computing  subsumes repeatedly solving a
subsumes repeatedly solving a 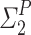 -complete problem, it can be very time-consuming. Therefore, instead of computing the exact
-complete problem, it can be very time-consuming. Therefore, instead of computing the exact  , we optionally compute only an over-approximation
, we optionally compute only an over-approximation 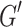 of
of 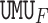 . In particular, we set a (user-defined) time limit for computing the lean kernel K of F. Moreover, we use a time limit for executing the procedure
. In particular, we set a (user-defined) time limit for computing the lean kernel K of F. Moreover, we use a time limit for executing the procedure
 ; if the time limit is exceeded for a clause
; if the time limit is exceeded for a clause  , we conservatively assume that
, we conservatively assume that  , i.e., we over-approximate.
, i.e., we over-approximate.
Sparse Hashing and
 . The approach of computation of
. The approach of computation of  is similar to, in spirit, computation of independent support of a formula to design sparse hash functions
[16, 28]. Briefly, given a Boolean formula H, an independent support of H is a set
is similar to, in spirit, computation of independent support of a formula to design sparse hash functions
[16, 28]. Briefly, given a Boolean formula H, an independent support of H is a set 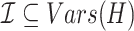 such that in every model of H, the truth assignment to
such that in every model of H, the truth assignment to  uniquely determines the truth assignment to
uniquely determines the truth assignment to  . Practically, independent support can be used to reduce the search space where a model counting algorithm searches for models of H. It is interesting to note that the state of the art technique reduces the computation of independent support of a formula in the context of model counting to that of computing (Group) Minimal Unsatisfiable Subset (GMUS). Thus, a formal study of computation of independent support in the context of MUSes is an interesting direction of future work.
. Practically, independent support can be used to reduce the search space where a model counting algorithm searches for models of H. It is interesting to note that the state of the art technique reduces the computation of independent support of a formula in the context of model counting to that of computing (Group) Minimal Unsatisfiable Subset (GMUS). Thus, a formal study of computation of independent support in the context of MUSes is an interesting direction of future work.
Computing 
Our approach to compute the intersection  (i.e.,
(i.e., 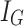 ) of all MUSes of G is composed of several ingredients. First, recall that a clause
) of all MUSes of G is composed of several ingredients. First, recall that a clause  belongs to
belongs to  iff f is necessary for G. Another ingredient is the ability of contemporary SAT solvers to provide either a model or an unsat core of a given unsatisfiable formula
iff f is necessary for G. Another ingredient is the ability of contemporary SAT solvers to provide either a model or an unsat core of a given unsatisfiable formula 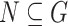 , i.e., a small, yet not necessarily minimal, unsatisfiable subset of N. The final ingredient is a technique called model rotation. The technique was originally proposed by Marques-Silva and Lynce
[40], and it serves to explore necessary clauses based on other already known necessary clauses. In particular, let f be a necessary clause for G and
, i.e., a small, yet not necessarily minimal, unsatisfiable subset of N. The final ingredient is a technique called model rotation. The technique was originally proposed by Marques-Silva and Lynce
[40], and it serves to explore necessary clauses based on other already known necessary clauses. In particular, let f be a necessary clause for G and  a model of
a model of 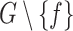 . Since G is unsatisfiable, the model I does not satisfy f. The model rotation attempts to alter I by switching, one by one, the Boolean assignment to the variables
. Since G is unsatisfiable, the model I does not satisfy f. The model rotation attempts to alter I by switching, one by one, the Boolean assignment to the variables 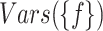 . Each variable assignment
. Each variable assignment  that originates from such an alternation of I necessarily satisfies f and does not satisfy at least one
that originates from such an alternation of I necessarily satisfies f and does not satisfy at least one 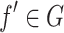 . If it is the case that there is exactly one such
. If it is the case that there is exactly one such 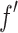 , then
, then 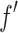 is necessary for G. An improved version of model rotation, called recursive model rotation, was later proposed by Belov and Marques-Silva
[6] who noted that the model rotation could be recursively performed on the newly identified necessary clauses.
is necessary for G. An improved version of model rotation, called recursive model rotation, was later proposed by Belov and Marques-Silva
[6] who noted that the model rotation could be recursively performed on the newly identified necessary clauses.
Our approach for computing 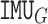 is shown in Algorithm 5. To find
is shown in Algorithm 5. To find  , the algorithm decides for each f whether f is necessary for G. In particular, the algorithm maintains two sets: a set C of candidates on necessary clauses and a set K of already known necessary clauses. Initially, K is empty and
, the algorithm decides for each f whether f is necessary for G. In particular, the algorithm maintains two sets: a set C of candidates on necessary clauses and a set K of already known necessary clauses. Initially, K is empty and 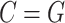 . At the end of computation, C is empty and K equals to
. At the end of computation, C is empty and K equals to  . The algorithm works iteratively. In each iteration, the algorithm picks a clause
. The algorithm works iteratively. In each iteration, the algorithm picks a clause  and checks
and checks 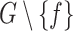 for satisfiability via a procedure
for satisfiability via a procedure  . Moreover,
. Moreover, 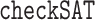 returns either a model I or an unsat core
returns either a model I or an unsat core 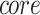 of
of  . If
. If 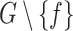 is satisfiable, i.e. f is necessary for G, the algorithm employs the recursive model rotation, denoted by
is satisfiable, i.e. f is necessary for G, the algorithm employs the recursive model rotation, denoted by
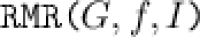 , to identify a set R of additional necessary clauses. Subsequently, all the newly identified necessary clauses are added to K and removed from C. In the other case, when
, to identify a set R of additional necessary clauses. Subsequently, all the newly identified necessary clauses are added to K and removed from C. In the other case, when 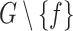 is unsatisfiable, the set C is reduced to
is unsatisfiable, the set C is reduced to  since every necessary clause of G has to be contained in every unsatisfiable subset of G. Note that
since every necessary clause of G has to be contained in every unsatisfiable subset of G. Note that 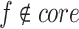 , thus at least one clause is removed from C.
, thus at least one clause is removed from C.
Experimental Evaluation
We employed several external tools to implement  . In particular, we use the QBF solver CAQE
[49] for solving the QBF formula MUSInCell, the 2QBF solver CADET
[50] for solving our
. In particular, we use the QBF solver CAQE
[49] for solving the QBF formula MUSInCell, the 2QBF solver CADET
[50] for solving our  -QBF encoding while computing
-QBF encoding while computing  , and the QBF preprocessor QRATPre+
[37] for preprocessing/simplifying our QBF encodings. Moreover, we employ muser2
[7] for a single MUS extraction while computing
, and the QBF preprocessor QRATPre+
[37] for preprocessing/simplifying our QBF encodings. Moreover, we employ muser2
[7] for a single MUS extraction while computing  , a MaxSAT solver UWrMaxSat
[48] to implement the algorithm by Marques-Silva et al.
[38] for computing the lean kernel of F, and finally, we use a toolkit called pysat
[27] for encoding cardinality constraints used in the formula MUSInCell. The tool along with all benchmarks that we used is available at https://github.com/jar-ben/amusic.
, a MaxSAT solver UWrMaxSat
[48] to implement the algorithm by Marques-Silva et al.
[38] for computing the lean kernel of F, and finally, we use a toolkit called pysat
[27] for encoding cardinality constraints used in the formula MUSInCell. The tool along with all benchmarks that we used is available at https://github.com/jar-ben/amusic.
Objectives. As noted earlier,  is the first technique to (approximately) count MUSes without explicit enumeration. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach via a comparison with two state of the art techniques for MUS enumeration:
is the first technique to (approximately) count MUSes without explicit enumeration. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach via a comparison with two state of the art techniques for MUS enumeration:  [35] and
[35] and 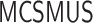 [3]. Within a given time limit, a MUS enumeration algorithm either identifies the whole
[3]. Within a given time limit, a MUS enumeration algorithm either identifies the whole 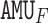 , i.e., provides the exact value of
, i.e., provides the exact value of  , or identifies just a subset of
, or identifies just a subset of 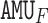 , i.e., provides an under-approximation of
, i.e., provides an under-approximation of 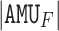 with no approximation guarantees.
with no approximation guarantees.
The objective of our empirical evaluation was two-fold: First, we experimentally examine the scalability of 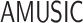 ,
,  , and
, and 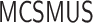 w.r.t.
w.r.t.  . Second, we examine the empirical accuracy of
. Second, we examine the empirical accuracy of  .
.
Benchmarks and Experimental Setup. Given the lack of dedicated counting techniques, there is no sufficiently large set of publicly available benchmarks to perform critical analysis of counting techniques. To this end, we focused on a recently emerging theme of evaluation of SAT-related techniques on scalable benchmarks1. In keeping with prior studies employing empirical methodology based on scalable benchmarks
[22, 41], we generated a custom collection of CNF benchmarks. The benchmarks mimic requirements on multiprocessing systems. Assume that we are given a system with two groups (kinds) of processes, 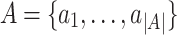 and
and 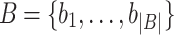 , such that
, such that 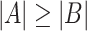 . The processes require resources of the system; however, the resources are limited. Therefore, there are restrictions on which processes can be active simultaneously. In particular, we have the following three types of mutually independent restrictions on the system:
. The processes require resources of the system; however, the resources are limited. Therefore, there are restrictions on which processes can be active simultaneously. In particular, we have the following three types of mutually independent restrictions on the system:
The first type of restriction states that “at most
 processes from the group A can be active simultaneously”, where
processes from the group A can be active simultaneously”, where 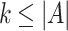 .
.The second type of restriction enforces that “if no process from B is active then at most
 processes from A can be active, and if at least one process from B is active then at most
processes from A can be active, and if at least one process from B is active then at most  processes from A can be active”, where
processes from A can be active”, where 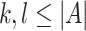 .
.The third type of restriction includes the second restriction. Moreover, we assume that a process from B can activate a process from A. In particular, for every
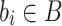 , we assume that when
, we assume that when  is active, then
is active, then 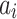 is also active.
is also active.
We encode the three restrictions via three Boolean CNF formulas,  ,
, 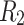 ,
,  . The formulas use three sets of variables:
. The formulas use three sets of variables: 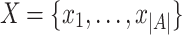 ,
, 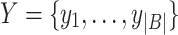 , and Z. The sets X and Y represent the Boolean information about activity of processes from A and B:
, and Z. The sets X and Y represent the Boolean information about activity of processes from A and B: 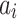 is active iff
is active iff  and
and  is active iff
is active iff 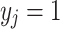 . The set Z contains additional auxiliary variables. Moreover, we introduce a formula
. The set Z contains additional auxiliary variables. Moreover, we introduce a formula 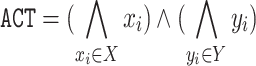 encoding that all processes are active. For each
encoding that all processes are active. For each  , the conjunction
, the conjunction  is unsatisfiable. Intuitively, every MUS of
is unsatisfiable. Intuitively, every MUS of 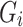 represents a minimal subset of processes that need to be active to violate the restriction. The number of MUSes in
represents a minimal subset of processes that need to be active to violate the restriction. The number of MUSes in  ,
,  , and
, and 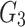 is
is 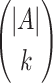 ,
,  , and
, and 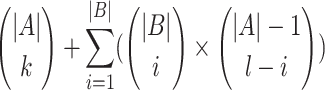 , respectively. We generated
, respectively. We generated 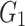 ,
, 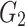 , and
, and  for these values:
for these values: 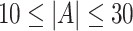 ,
, 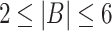 ,
,  , and
, and 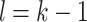 . In total, we obtained 1353 benchmarks (formulas) that range in their size from 78 to 361 clauses, use from 40 to 152 variables, and contain from 120 to
. In total, we obtained 1353 benchmarks (formulas) that range in their size from 78 to 361 clauses, use from 40 to 152 variables, and contain from 120 to  MUSes.
MUSes.
All experiments were run using a time limit of 7200 s and computed on an AMD EPYC 7371 16-Core Processor, 1 TB memory machine running Debian Linux 4.19.67-2. The values of 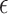 and
and 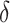 were set to 0.8 and 0.2, respectively.
were set to 0.8 and 0.2, respectively.
Accuracy. Recall that to compute an estimate c of 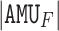 ,
, 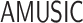 performs multiple iteration of executing
performs multiple iteration of executing 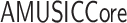 to get a list C of multiple estimates of
to get a list C of multiple estimates of  , and then use the median of C as the final estimate c. The more iterations are performed, the higher is the confidence that c is within the required tolerance
, and then use the median of C as the final estimate c. The more iterations are performed, the higher is the confidence that c is within the required tolerance  , i.e., that
, i.e., that  . To achieve the confidence
. To achieve the confidence  , 66 iterations need to be performed. In case of 157 benchmarks, the algorithm was not able to finish even a single iteration, and only in case of 251 benchmarks, the algorithm finished all the 66 iterations. For the remaining 945 benchmarks, at least some iterations were finished, and thus at least an estimate with a lower confidence was determined.
, 66 iterations need to be performed. In case of 157 benchmarks, the algorithm was not able to finish even a single iteration, and only in case of 251 benchmarks, the algorithm finished all the 66 iterations. For the remaining 945 benchmarks, at least some iterations were finished, and thus at least an estimate with a lower confidence was determined.
We illustrate the achieved results in Fig. 3. The figure consists of two plots. The plot at the bottom of the figure shows the number of finished iterations (y-axis) for individual benchmarks (x-axis). The plot at the top of the figure shows how accurate were the MUS count estimates. In particular, for each benchmark (formula) F, we show the number 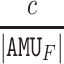 where c is the final estimate (median of estimates from finished iterations). For benchmarks where all iterations were completed, it was always the case that the final estimate is within the required tolerance, although we had only 0.8 theoretical confidence that it would be the case. Moreover, the achieved estimate never exceeded a tolerance of 0.1, which is much better than the required tolerance of 0.8. As for the benchmarks where only some iterations were completed, there is only a single benchmark where the tolerance of 0.8 was exceeded.
where c is the final estimate (median of estimates from finished iterations). For benchmarks where all iterations were completed, it was always the case that the final estimate is within the required tolerance, although we had only 0.8 theoretical confidence that it would be the case. Moreover, the achieved estimate never exceeded a tolerance of 0.1, which is much better than the required tolerance of 0.8. As for the benchmarks where only some iterations were completed, there is only a single benchmark where the tolerance of 0.8 was exceeded.
Fig. 3.
The number of completed iterations and the accuracy of the final MUS count estimate for individual benchmarks.
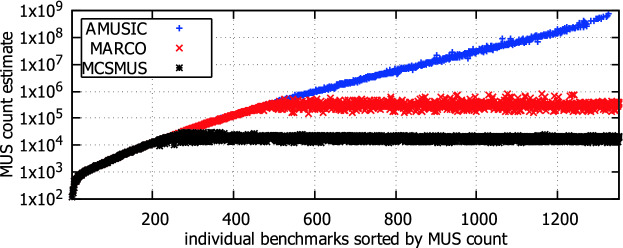
Scalability. The scalability of  ,
,  , and
, and  w.r.t. the number of MUSes (
w.r.t. the number of MUSes (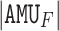 ) is illustrated in Fig. 4. In particular, for each benchmark (x-axis), we show in the plot the estimate of the MUS count that was achieved by the algorithms (y-axis). The benchmarks are sorted by the exact count of MUSes in the benchmarks.
) is illustrated in Fig. 4. In particular, for each benchmark (x-axis), we show in the plot the estimate of the MUS count that was achieved by the algorithms (y-axis). The benchmarks are sorted by the exact count of MUSes in the benchmarks.  and
and  were able to finish the MUS enumeration, and thus to provide the count, only for benchmarks that contained at most
were able to finish the MUS enumeration, and thus to provide the count, only for benchmarks that contained at most 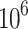 and
and 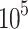 MUSes, respectively.
MUSes, respectively.  , on the other hand, was able to provide estimates on the MUS count even for benchmarks that contained up to
, on the other hand, was able to provide estimates on the MUS count even for benchmarks that contained up to  MUSes. Moreover, as we have seen in Fig. 3, the estimates are very accurate. Only in the case of 157 benchmarks where
MUSes. Moreover, as we have seen in Fig. 3, the estimates are very accurate. Only in the case of 157 benchmarks where  finished no iteration, it could not provide any estimate.
finished no iteration, it could not provide any estimate.
Fig. 4.
Scalability of  ,
,  , and
, and  w.r.t.
w.r.t.  .
.
Summary and Future Work
We presented a probabilistic algorithm, called 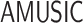 , for approximate MUS counting that needs to explicitly identify only logarithmically many MUSes and yet still provides strong theoretical guarantees. The high-level idea is adopted from a model counting algorithm
, for approximate MUS counting that needs to explicitly identify only logarithmically many MUSes and yet still provides strong theoretical guarantees. The high-level idea is adopted from a model counting algorithm 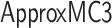 : we partition the search space into small cells, then count MUSes in a single cell, and estimate the total count by scaling the count from the cell. The novelty lies in the low-level algorithmic parts that are specific for MUSes. Mainly, (1) we propose QBF encoding for counting MUSes in a cell, (2) we exploit MUS intersection to speed-up localization of MUSes, and (3) we utilize MUS union to reduce the search space significantly. Our experimental evaluation showed that the scalability of
: we partition the search space into small cells, then count MUSes in a single cell, and estimate the total count by scaling the count from the cell. The novelty lies in the low-level algorithmic parts that are specific for MUSes. Mainly, (1) we propose QBF encoding for counting MUSes in a cell, (2) we exploit MUS intersection to speed-up localization of MUSes, and (3) we utilize MUS union to reduce the search space significantly. Our experimental evaluation showed that the scalability of  outperforms the scalability of contemporary enumeration-based counters by several orders of magnitude. Moreover, the practical accuracy of
outperforms the scalability of contemporary enumeration-based counters by several orders of magnitude. Moreover, the practical accuracy of  is significantly better than what is guaranteed by the theoretical guarantees.
is significantly better than what is guaranteed by the theoretical guarantees.
Our work opens up several questions at the intersection of theory and practice. From a theoretical perspective, the natural question is to ask if we can design a scalable algorithm that makes polynomially many calls to an 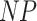 oracle. From a practical perspective, our work showcases interesting applications of QBF solvers with native XOR support. Since approximate counting and sampling are known to be inter-reducible, another line of work would be to investigate the development of an almost-uniform sampler for MUSes, which can potentially benefit from the framework proposed in UniGen
[14, 16]. Another line of work is to extend our MUS counting approach to other constraint domains where MUSes find an application, e.g., F can be a set of SMT
[25] or LTL
[4, 8] formulas or a set of transition predicates
[13, 23].
oracle. From a practical perspective, our work showcases interesting applications of QBF solvers with native XOR support. Since approximate counting and sampling are known to be inter-reducible, another line of work would be to investigate the development of an almost-uniform sampler for MUSes, which can potentially benefit from the framework proposed in UniGen
[14, 16]. Another line of work is to extend our MUS counting approach to other constraint domains where MUSes find an application, e.g., F can be a set of SMT
[25] or LTL
[4, 8] formulas or a set of transition predicates
[13, 23].
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by National Research Foundation Singapore under its NRF Fellowship Programme [NRF-NRFFAI1-2019-0004 ] and AI Singapore Programme [AISG-RP-2018-005], and NUS ODPRT Grant [R-252-000-685-13]. The computational work for this article was performed on resources of the National Supercomputing Centre, Singapore https://www.nscc.sg.
Footnotes
M. Y. Vardi, in his talk at BIRS CMO 18w5208 workshop, called on the SAT community to focus on scalable benchmarks in lieu of competition benchmarks. Also, see: https://gitlab.com/satisfiability/scalablesat (Accessed: May 10, 2020).
Work done in part while the first author visited National University of Singapore.
Contributor Information
Shuvendu K. Lahiri, Email: shuvendu.lahiri@microsoft.com
Chao Wang, Email: wang626@usc.edu.
Jaroslav Bendík, Email: xbendik@gmail.com.
References
-
1.Arif MF, Mencía C, Ignatiev A, Manthey N, Peñaloza R, Marques-Silva J. BEACON: an efficient SAT-based tool for debugging
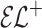 ontologies. In: Creignou N, Le Berre D, editors. Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing – SAT 2016; Cham: Springer; 2016. pp. 521–530. [Google Scholar]
ontologies. In: Creignou N, Le Berre D, editors. Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing – SAT 2016; Cham: Springer; 2016. pp. 521–530. [Google Scholar] - 2.Bacchus F, Katsirelos G. Using minimal correction sets to more efficiently compute minimal unsatisfiable sets. In: Kroening D, Păsăreanu CS, editors. Computer Aided Verification; Cham: Springer; 2015. pp. 70–86. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bacchus F, Katsirelos G. Finding a collection of MUSes incrementally. In: Quimper C-G, editor. Integration of AI and OR Techniques in Constraint Programming; Cham: Springer; 2016. pp. 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barnat J, Bauch P, Beneš N, Brim L, Beran J, Kratochvíla T. Analysing sanity of requirements for avionics systems. Formal Aspects Comput. 2015;28(1):45–63. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Belov A, Heule MJH, Marques-Silva J. MUS extraction using clausal proofs. In: Sinz C, Egly U, editors. Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing – SAT 2014; Cham: Springer; 2014. pp. 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Belov, A., Marques-Silva, J.: Accelerating MUS extraction with recursive model rotation. In: FMCAD, pp. 37–40. FMCAD Inc. (2011)
- 7.Belov A, Marques-Silva J. MUSer2: an efficient MUS extractor. JSAT. 2012;8:123–128. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bendík, J.: Consistency checking in requirements analysis. In: ISSTA, pp. 408–411. ACM (2017)
- 9.Bendík, J., Beneš, N., Černá, I., Barnat, J.: Tunable online MUS/MSS enumeration. In: FSTTCS. LIPIcs, vol. 65, pp. 50:1–50:13. Schloss Dagstuhl - Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik (2016)
- 10.Bendík, J., Černá, I.: Evaluation of domain agnostic approaches for enumeration of minimal unsatisfiable subsets. In: LPAR. EPiC Series in Computing, vol. 57, pp. 131–142. EasyChair (2018)
- 11.Bendík J, Černá I. MUST: minimal unsatisfiable subsets enumeration tool; Tools and Algorithms for the Construction and Analysis of Systems; Cham: Springer; 2020. pp. 135–152. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bendík J, Černá I, Beneš N. Recursive online enumeration of all minimal unsatisfiable subsets. In: Lahiri SK, Wang C, editors. Automated Technology for Verification and Analysis; Cham: Springer; 2018. pp. 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bendík J, Ghassabani E, Whalen M, Černá I. Online enumeration of all minimal inductive validity cores. In: Johnsen EB, Schaefer I, editors. Software Engineering and Formal Methods; Cham: Springer; 2018. pp. 189–204. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chakraborty S, Fremont DJ, Meel KS, Seshia SA, Vardi MY. On parallel scalable uniform SAT witness generation. In: Baier C, Tinelli C, editors. Tools and Algorithms for the Construction and Analysis of Systems; Heidelberg: Springer; 2015. pp. 304–319. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chakraborty S, Meel KS, Vardi MY. A scalable approximate model counter. In: Schulte C, editor. Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming; Heidelberg: Springer; 2013. pp. 200–216. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chakraborty, S., Meel, K.S., Vardi, M.Y.: Balancing scalability and uniformity in SAT witness generator. In: Proceedings of DAC (2014)
- 17.Chakraborty, S., Meel, K.S., Vardi, M.Y.: Algorithmic improvements in approximate counting for probabilistic inference: from linear to logarithmic SAT calls. In: Proceedings of IJCAI (2016)
- 18.Chakraborty, S., Meel, K.S., Vardi, M.Y.: Algorithmic improvements in approximate counting for probabilistic inference: from linear to logarithmic SAT calls. In: IJCAI, pp. 3569–3576. IJCAI/AAAI Press (2016)
- 19.Chen Z-Z, Toda S. The complexity of selecting maximal solutions. Inf. Comput. 1995;119(2):231–239. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Orly, C., Moran, G., Michael, L., Alexander, N., Vadim, R.: Designers work less with quality formal equivalence checking. In: DVCon. Citeseer (2010)
- 21.de Kleer J, Williams BC. Diagnosing multiple faults. Artif. Intell. 1987;32(1):97–130. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Elffers, J., Giráldez-Cru, J., Gocht, S., Nordström, J., Simon, L.: Seeking practical CDCL insights from theoretical sat benchmarks. In: IJCAI, pp. 1300–1308. International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization, July 2018
- 23.Ghassabani, E., Gacek, A., Whalen, M.W., Heimdahl, M.P.E., Wagner, L.G.: Proof-based coverage metrics for formal verification. In: ASE, pp. 194–199. IEEE Computer Society (2017)
- 24.Gomes, C.P., Sabharwal, A., Selman, B.: Near-uniform sampling of combinatorial spaces using XOR constraints. In: NIPS, pp. 481–488. MIT Press (2006)
- 25.Guthmann, O., Strichman, O., Trostanetski, A.: Minimal unsatisfiable core extraction for SMT. In: FMCAD, pp. 57–64. IEEE (2016)
- 26.Hunter, A., Konieczny, S.: Measuring inconsistency through minimal inconsistent sets. In: KR, pp. 358–366. AAAI Press (2008)
- 27.Ignatiev A, Morgado A, Marques-Silva J. PySAT: a Python toolkit for prototyping with SAT Oracles. In: Beyersdorff O, Wintersteiger CM, editors. Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing – SAT 2018; Cham: Springer; 2018. pp. 428–437. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ivrii A, Malik S, Meel KS, Vardi MY. On computing minimal independent support and its applications to sampling and counting. Constraints. 2015;21(1):41–58. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jannach D, Schmitz T. Model-based diagnosis of spreadsheet programs: a constraint-based debugging approach. Autom. Softw. Eng. 2014;23(1):105–144. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Janota M, Marques-Silva J. On deciding MUS membership with QBF. In: Lee J, editor. Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming – CP 2011; Heidelberg: Springer; 2011. pp. 414–428. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Büning, H.K., Kullmann, O.: Minimal unsatisfiability and autarkies. In: Handbook of Satisfiability. FAIA, vol. 185, pp. 339–401. IOS Press (2009)
- 32.Kullmann O. Investigations on autark assignments. Discrete Appl. Math. 2000;107(1–3):99–137. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kullmann O, Marques-Silva J. Computing maximal autarkies with few and simple Oracle queries. In: Heule M, Weaver S, editors. Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing – SAT 2015; Cham: Springer; 2015. pp. 138–155. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liffiton MH, Malik A. Enumerating infeasibility: finding multiple MUSes quickly. In: Gomes C, Sellmann M, editors. Integration of AI and OR Techniques in Constraint Programming for Combinatorial Optimization Problems; Heidelberg: Springer; 2013. pp. 160–175. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liffiton MH, Previti A, Malik A, Marques-Silva J. Fast, flexible MUS enumeration. Constraints. 2016;21(2):223–250. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Liffiton MH, Sakallah KA. Algorithms for computing minimal unsatisfiable subsets of constraints. J. Autom. Reasoning. 2008;40(1):1–33. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lonsing F, Egly U. QRATPre+: effective QBF preprocessing via strong redundancy properties. In: Janota M, Lynce I, editors. Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing – SAT 2019; Cham: Springer; 2019. pp. 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Marques-Silva, J., Ignatiev, A., Morgado, A., Manquinho, V.M., Lynce, I.: Efficient autarkies. In: ECAI. FAIA, vol. 263, pp. 603–608. IOS Press (2014)
- 39.Marques-Silva, J., Janota, M.: On the query complexity of selecting few minimal sets. Electron. Colloquium Comput. Complex. (ECCC) 21, 31 (2014)
- 40.Marques-Silva J, Lynce I. On improving MUS extraction algorithms. In: Sakallah KA, Simon L, editors. Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing - SAT 2011; Heidelberg: Springer; 2011. pp. 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Meel KS, Shrotri AA, Vardi MY. Not all FPRASs are equal: demystifying FPRASs for DNF-counting. Constraints. 2018;24(3):211–233. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mencía C, Kullmann O, Ignatiev A, Marques-Silva J. On computing the union of MUSes. In: Janota M, Lynce I, editors. Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing – SAT 2019; Cham: Springer; 2019. pp. 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Meyer, A.R., Stockmeyer, L.J.: The equivalence problem for regular expressions with squaring requires exponential space. In: SWAT (FOCS), pp. 125–129. IEEE Computer Society (1972)
-
44.Monien B, Speckenmeyer E. Solving satisfiability in less than 2
 steps. Discrete Appl. Math. 1985;10(3):287–295. [Google Scholar]
steps. Discrete Appl. Math. 1985;10(3):287–295. [Google Scholar] - 45.Kedian M. Formulas free from inconsistency: an atom-centric characterization in priest’s minimally inconsistent LP. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2019;66:279–296. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nadel A, Ryvchin V, Strichman O. Accelerated deletion-based extraction of minimal unsatisfiable cores. JSAT. 2014;9:27–51. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Narodytska, N., Bjørner, N., Marinescu, M.-C., Sagiv, M.: Core-guided minimal correction set and core enumeration. In: IJCAI, pp. 1353–1361 (2018). ijcai.org
- 48.Piotrów, M.: Uwrmaxsat-a new minisat+-based solver in maxsat evaluation 2019. In: MaxSAT Evaluation 2019, p. 11 (2019)
- 49.Rabe, M.N., Tentrup, L.: CAQE: a certifying QBF solver. In: FMCAD, pp. 136–143. IEEE (2015)
- 50.Rabe MN, Tentrup L, Rasmussen C, Seshia SA. Understanding and extending incremental determinization for 2QBF. In: Chockler H, Weissenbacher G, editors. Computer Aided Verification; Cham: Springer; 2018. pp. 256–274. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Reiter R. A theory of diagnosis from first principles. Artif. Intell. 1987;32(1):57–95. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Soos, M., Meel, K.S.: BIRD: engineering an efficient CNF-XOR SAT solver and its applications to approximate model counting. In: Proceedings of the AAAI (2019)
- 53.Soos M, Nohl K, Castelluccia C. Extending SAT solvers to cryptographic problems. In: Kullmann O, editor. Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing - SAT 2009; Heidelberg: Springer; 2009. pp. 244–257. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sperner E. Ein satz über untermengen einer endlichen menge. Math. Z. 1928;27(1):544–548. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Stern, R.T., Kalech, M., Feldman, A., Provan, G.M.: Exploring the duality in conflict-directed model-based diagnosis. In: AAAI. AAAI Press (2012)
- 56.Thimm, M.: On the evaluation of inconsistency measures. Meas. Inconsistency Inf. 73, 19–60 (2018)