Correction to: BMC Nephrology (2020) 21:226
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-020-01879-6
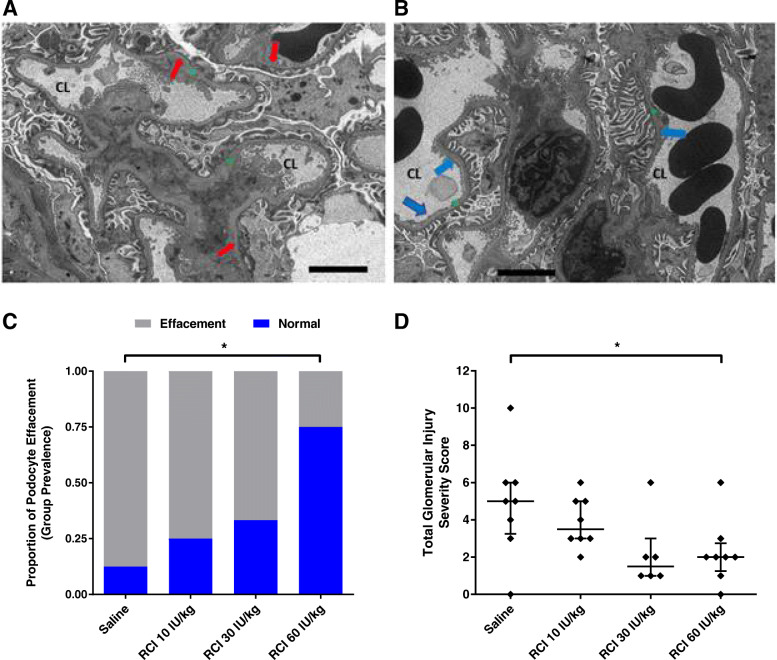
Following publication of the original article [1], the authors identified an error in Fig. 7. The correct figure is given below.
Fig. 7.
Podocyte and Glomerular Assessment in the 12-week PAN Model. a Saline EM image. Red arrows = podocyte effacement. b RCI 60 IU/kg EM image. Blue arrows = normal podocyte foot process structure. a, b Green * = capillary basement membrane; CL = capillary lumen; scale bar = 4 μM. c Group prevalence of podocyte effacement by EM analysis. *p < 0.05, Fisher’s exact test for group differences compared with saline, 2-tailed. d Total glomerular injury score. *p < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric ANOVA, Dunn’s post hoc test, comparing the RCI treatment groups with saline. Values are mean ± standard error of the mean. For all panels, naive samples are not shown because of low sample size. Abbreviations: ANOVA, analysis of variance; EM, electron microscopy; PAN, puromycin aminonucleoside; RCI, repository corticotropin injection
The original article has been corrected.
Reference
- 1.Hayes K, et al. Repository corticotropin injection versus corticosteroids for protection against renal damage in a focal segmental glomerulosclerosis rodent model. BMC Nephrol. 2020;21:226. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01879-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]