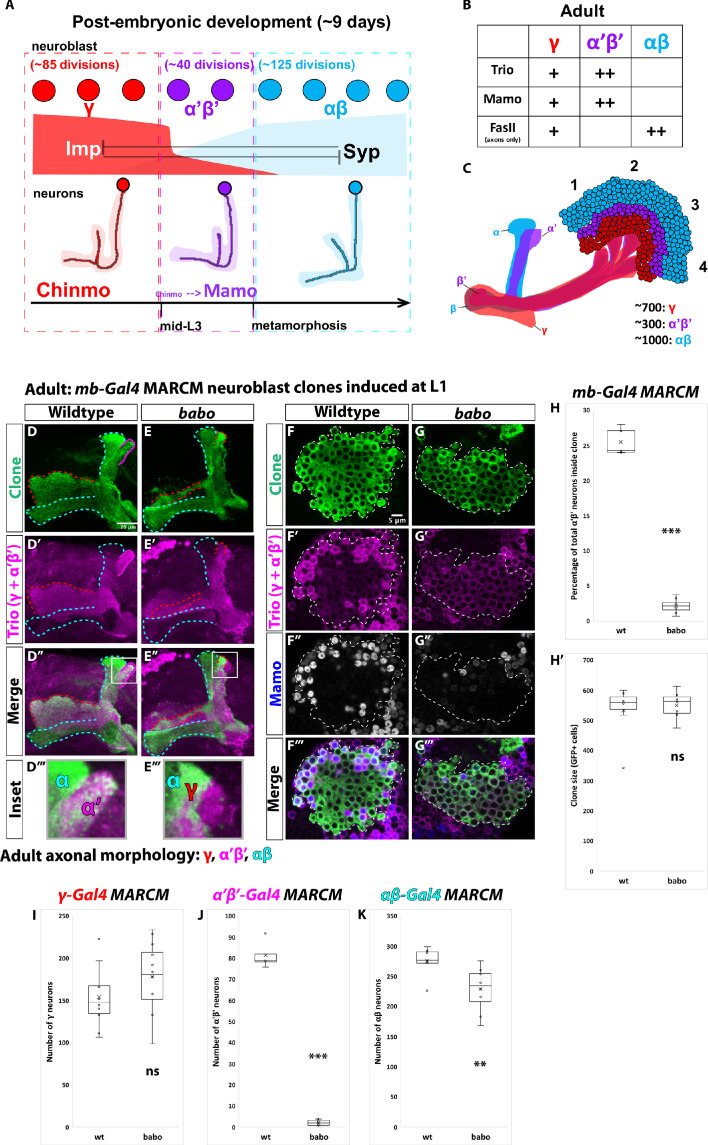
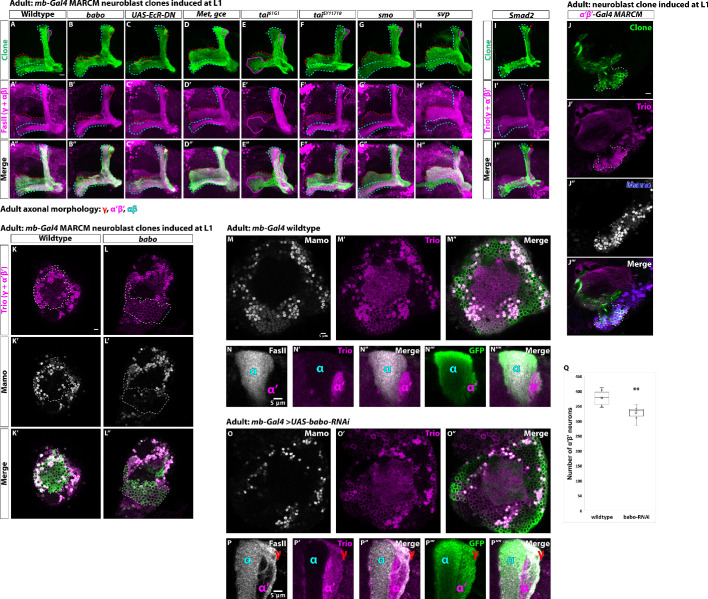
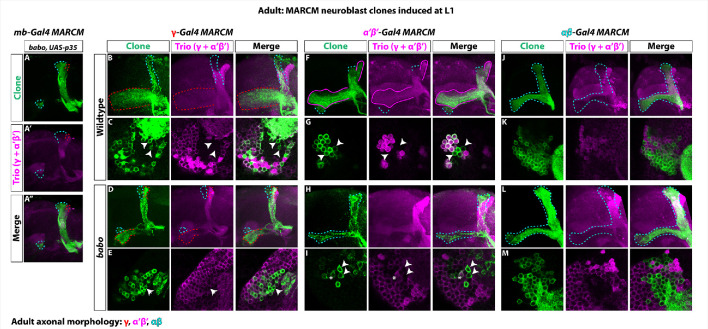
Figure 1. α’β’ neurons are not generated from babo mutant neuroblasts.
(A) Summary of intrinsic temporal patterning mechanism operating during mushroom body development. During early larval stages, mushroom body neuroblasts express high levels of Imp (red) and Chinmo (red) in neurons to specify γ identity for ~85 neuroblast divisions (red-dashed box). From mid-L3 to metamorphosis, when Imp and Syp (cyan) are both at low levels, the same neuroblast divides ~40 times to produce α’β’ neurons (magenta-dashed box). Low Chinmo regulates the expression Mamo, a terminal selector of α’β’ identity. From the beginning of metamorphosis throughout pupal development, high Syp leads to αβ neurons (cyan-dashed outline). (B) Known molecular markers can distinguish between the three mushroom body neuronal types in the adult. (C) Mushroom body projections originating from neurons born from four neuroblasts (numbered 1 to 4) per hemisphere fasciculate into a single bundle (peduncle) before branching into the five mushroom body lobes. The first-born γ neurons (red) remodel during development to project into a single, medial lobe in the adult. This lobe is the most anterior of the medial lobes. Axons from α’β’ neurons (magenta) bifurcate to project into the vertical and medial α’ and β’ lobes. The β’ lobe is posterior to the γ lobe. The last-born αβ neurons (cyan) also bifurcate their axons into the vertical projecting α lobe and medial projecting β lobe. The α lobe is positioned adjacent and medial to the α’ lobe. The β lobe is the most posterior medial lobe. (D-E) Representative max projections showing adult axons of clonally related neurons born from L1 stage in wildtype and babo conditions. UAS-CD8::GFP is driven by mb-Gal4 (OK107-Gal4). Outlines mark GFP+ axons, where γ axons are outlined in red, α’β’ axons are outlined in magenta, and αβ axons are outlined in cyan. A white box outlines the Inset panel. Trio (magenta) is used to label all γ and α’β’ axons for comparison to GFP+ axons. (D) In wildtype, GFP+ axons (green, outlined in red, magenta and cyan) are visible in all observable mushroom body lobes. (E) In babo mutant clones, γ neurons (red outline) remain unpruned. GFP+ axons are missing inside the Trio+ α’ lobe, indicating the absence of α’β’ neurons. (F-G) Representative, single z-slices from the adult cell body region of clones induced at L1 in wildtype and babo conditions. UAS-CD8::GFP is driven by mb-Gal4. (F) Wildtype clones show the presence of strongly expressing Trio (magenta) and Mamo (blue, gray in single channel) neurons, indicative of α’β’ identity. (G) In babo mutant clones, cells strongly expressing Trio and Mamo are not present. (H) Quantification of MARCM clones marked by mb-Gal4, which labels all mushroom body neuronal types. The number of α’β’ neurons are quantified in wildtype (n = 7) and babo (n = 8) conditions. Plotted is the percentage of strong Mamo+ and GFP+ cells (clonal cells) versus all Mamo+ cells (clonal and non-clonal cells) within a single mushroom body. In wildtype, 25.5 ± 0.7% of the total strong Mamo expressing cells (α’β’ neurons) are within clones, consistent with our expectation since each mushroom body is made from four neuroblasts. In babo clones, only 2.2 ± 0.4% of α’β’ neurons are within clones. (H’) There are no significant differences between the average clone sizes (wildtype:533.6 ± 33.3; babo:551.3 ± 17.6). (I) Quantification of γ neurons marked by γ-Gal4 (R71G10-Gal4) in MARCM clones. Plotted is the total number of γ neurons marked by GFP and Trio in wildtype (n = 10) and babo mutant (n = 12) clones. In wildtype, the average number of γ neurons is 154.3 ± 11.4. In babo mutants, the average is 178.4 ± 11.9. (J) Quantification of α’β’ neurons marked by α’β’-Gal4 (R41C07-Gal4) in MARCM clones. Plotted is the total number of α’β’ neurons marked by GFP and strong Trio in wildtype (n = 4) and babo mutant (n = 8) clones. In wildtype, the average number of α’β’ neurons is 81.5 ± 3.4. In babo mutants, the average is 2.1 ± 0.5. (K) Quantification of αβ neurons marked by αβ-Gal4 (R44E04-Gal4) in MARCM clones. Plotted is the total number of GFP+ cells in wildtype (n = 7) and babo mutant (n = 8) clones. In wildtype, the average number is 276 ± 9.1. In babo mutants, the average number is 228.9 ± 13.2. A two-sample, two-tailed t-test was performed. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, ns: not significant. Scale bars: D, 20 µm; F, 5 µm.