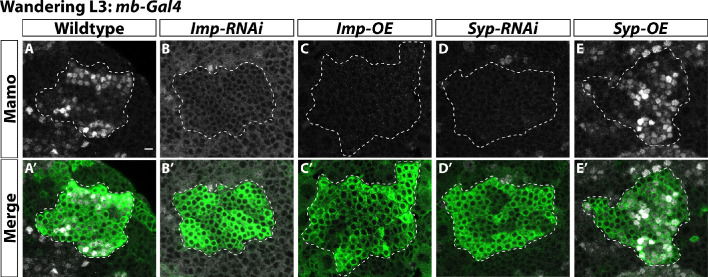
(
A-E) Representative images of adult mushroom body lobes labeled by
mb-Gal4 driving
UAS-CD8::GFP (green) in wildtype (
A),
UAS-Imp-RNAi (
B),
UAS-Imp-OE (
C),
UAS-Syp-RNAi (
D) or
UAS-Syp-OE (
E). When visible, γ axons are outlined in red, α’β’ axons are outlined in magenta, and αβ axons are outlined in cyan. Trio (magenta) labels γ and α’β’ axons. (
A) In wildtype, all three axonal types are present. (
B) With
Imp-RNAi, the majority of γ axons (red outline) are lost and α’β’ axons are completely missing. (
C)
Imp-OE leads to mushroom body axons projecting almost entirely into the γ lobe (red outline). Some αβ axons (cyan outline) are present but are missing the vertical α projection. α’β’ axons are completely lost. (
D)
Syp-RNAi is similar but more severe than
Imp-OE as mushroom body axons project entirely into the γ lobe (red outline). (
E)
Syp-OE does not abolish α’β’ axons (magenta outline). αβ axons (cyan outline) are also present. However, the vertical α’ and α lobes are both missing. (
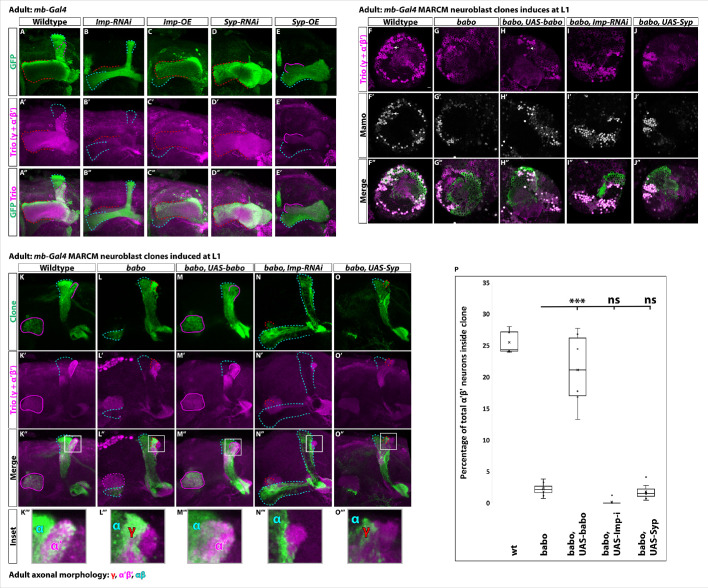
F-J) Representative images of single z slices. Strong Trio (magenta) labels α’β’ neurons while weak Trio labels γ neurons. Strong Mamo (gray) also labels α’β’ neurons while weak Mamo labels γ neurons. Arrows points to α’β’ neurons inside the clone. F. In wildtype clones driven by
mb-Gal4, GFP
+ cells (green) contain strong Trio
+ and Mamo
+ cells. (
G-H) These cells are lost in
babo clones (G) but rescued in clones expressing
UAS-babo (H). (
I-J) Expressing
UAS-Imp-RNAi (I) or
UAS-Syp (J) does not rescue the loss of α’β’ neurons. (
K-O). Representative maximum-projection images of adult mushroom body lobes from
mb-Gal4 MARCM clones induced at L1, focused on the α’ and β’ lobes. Clonally related neurons are GFP
+ (green). All mushroom body axons, both clonal and non-clonal, are marked by Trio (magenta). Outlines mark GFP
+ axons, where γ axons are outlined in red, α’β’ axons are outlined in magenta, and αβ axons are outlined in cyan. A gray box outlines the Inset panel. (
K) In wildtype, GFP
+ axons are observed in the α’β’ lobes (magenta outline). (
L) In
babo mutant clones, γ neurons do not remodel (red outline) and α’β’ neurons are missing. (
M) These phenotypes are rescued by expressing
UAS-babo inside mutant clones, as GFP
+ axons colocalize within the Trio labeled α’β’ lobes (magenta outline). (
N-O) Neither reducing Imp with
UAS-Imp-RNAi or decreasing the Imp to Syp ratio by expressing
UAS-Syp rescues the loss of α’β’ neurons. (
P) Quantification of MARCM clones represented in
K-O. Plotted is the percentage of strong Mamo
+ and GFP
+ cells (clonal cells) versus all Mamo
+ cells (clonal and non-clonal cells) within a single mushroom body. The number of α’β’ neurons is quantified in wildtype (n = 7, replotted from data in
Figure 1H),
babo (n = 8, replotted from data in
Figure 1H),
babo,
UAS-babo (n = 6),
babo,
UAS-imp-RNAi (n = 7), and
babo, UAS-Syp (n = 7), In wildtype, 25.5 ± 0.7% of the total strong Mamo expressing cells (α’β’ neurons) are within a clone while they only represent 2.2 ± 0.4% in
babo clones. Expressing
UAS-babo rescues to 21.1 ± 2.4%. In contrast, expression of
UAS-Imp-RNAi (0.17 ± 0.17%) or
UAS-Syp (1.8 ± 0.5%) is not statistically different from
babo. Significance values were determined using a Tukey test. ***p<0.001, ns: not significant.