Abstract
This cadaver study examines the prevalence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 colonization of the middle ear and mastoid in a sample of 3 patients.
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus and associated coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) disease pandemic have rapidly spread around the world since December 2019. The high rate of droplet spread can endanger health care workers during procedures of the aerodigestive tract,1 particularly affecting otolaryngologists. Although there are no human data relating to the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the middle ear, the recommendations to mitigate these risks include precautions for middle ear and mastoid surgery1,2 because middle ear effusions have been shown to contain some non–SARS-CoV-2 coronaviruses.3 We present confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 colonization of the middle ear and mastoid in 2 of 3 patients.
Methods
The Johns Hopkins Hospital research autopsy program4 includes institutional review board-approved autopsy of COVID-19–positive (nasal swab, Cepheid GeneXpert SARS-CoV-2 assay) decedents, subject to safety limitations including avoidance of powered instrumentation. Three decedents were selected, and each underwent bilateral cortical mastoidectomy and exposure of the aditus using osteotomes and curettes. Mastoid specimens included the bone and mucosa were obtained by curettage. The middle ear specimens were obtained using 3 cytobrush swabs (Cobas polymerase chain reaction [PCR] medial dual swab, Roche). Specimens were stored in RNA media (RNAlater, Invitrogen). Nucleic acid extraction and amplification was performed per protocol. Specimens were vortexed vigorously for 30 seconds with 500 uL extracted using the BioMerieux easyMAG platform,5 and specimens were eluted in 50 uL volume. Real-time reverse transcriptase-PCR was performed using the US Centers for Disease Control panel assay.5
Results
All 3 patients were COVID-19 positive and met SARS criteria (Table). Each sample was assayed for the N1, N2, and internal control target genes (Figure). For case 3, all samples were positive with cycle thresholds ranging from 24 to 36. Two of the 3 patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 virus in the mastoid or middle ear, with viral isolation from 2 of 6 mastoids and 3 of 6 middle ears. Results for case 1 were positive for the right middle ear only. Case 2 had negative results for all samples.
Table. Patient Demographics and Corresponding Pathology Specimen CT Values.
| Patient no. | Sex/age (by decade) | Postmortem interval, h | SARS criteria | Mastoid | Middle ear | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Left | Right | ||||||||||||||||
| CT values | N1 | N2 | RP | CT values | N1 | N2 | RP | CT values | N1 | N2 | RP | CT values | N1 | N2 | RP | ||||
| 1 | F/80s | 48 | Yes | Negative | … | … | 25 | Negative | … | … | 26 | Negative | … | … | 24 | Positive | … | 32 | 26 (Effusion present) |
| 2 | F/60s | 44 | Yes | Negative | … | … | 25 | Negative | … | … | 27 | Negative | … | … | 26 | Negative | … | … | 23 |
| 3 | M/60s | 16 | Yes | Positive | 36 | 36 | 26 | Positive | 31 | 31 | 25 | Positive | 25 | 25 | 24 | Positive | 26 | 26 | 24 |
Abbreviations: CT, cycle threshold; elipses, negative gene amplication; SARS, severe acute respiratory syndrome.
Figure. Amplification Plot of Patient 3.
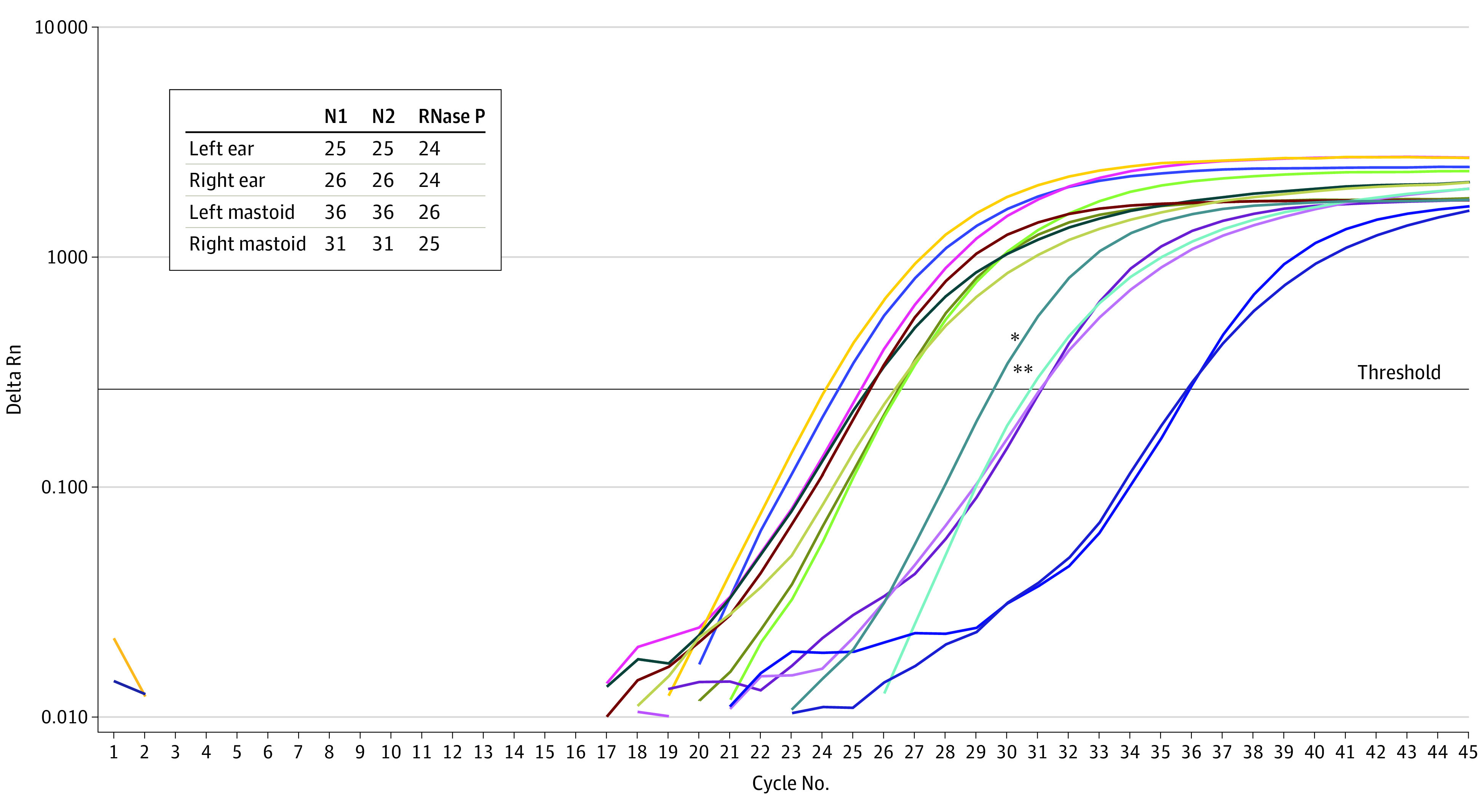
* Indicates N1-positive control; **, N2-positive control. The amplification of the N1, N2, and the internal control (RNase P) target genes is shown for specimens: left ear, right ear, left mastoid, and right mastoid. The cycle threshold values of the 3 genes for the 4 patient’s specimens are shown.
Discussion
This study confirms the presence of SARS-CoV-2 virus in the middle ear and mastoid, with significant implications for otolaryngology procedures. Similar to procedures of the nose, mouth, and airway, droplet precautions during ear surgery are warranted for patients with COVID-19 owing to risk of infection to health care personnel.1 Droplet precautions (including eye protection and proper N95 level mask) are warranted for outpatient procedures involving the middle ear due to proximity to these potentially infectious spaces. Given the high asymptomatic rate of COVID-19 cases, caution is warranted for all elective ear surgery, and negative status by testing is indicated.
Limitations of this study methodology include the postmortem interval prior to autopsy. We suspect the partial positive results of case 1 and negative results of case 2 are related to the much longer postmortem intervals. Increased intervals decrease tissue stability and affect viral stability and isolation at autopsy, and rapid autopsy protocols may provide tissue more comparable to fresh surgical biopsy.4 Additional conclusions are limited, particularly regarding asymptomatic carriers. There may be many other factors and comorbidities that affect the colonization of the mastoid and middle ear with SARS-CoV-2, and these may differ in the living host. There may be significant differences between dying from COVID-19 vs dying with COVID-19.
We recommend the implementation of COVID-19 screening and droplet precautions for middle ear procedures when aerosol and droplet generation is reasonably expected,6 as well as additional studies with in vivo samples during routine ear surgery to ascertain the incidence of viral colonization in living COVID-19–positive and COVID-19–negative patients. Identification of live virus from middle ear effusions would have implications for surgeons and staff who handle equipment such as instruments, suction tubing, and suction canisters due to current CDC biosafety recommendations. Finally, mastoid and middle ear colonization with SARS-CoV-2 does not necessarily imply current or future otologic symptomatology, and known living patients with SARS-CoV-2 ear colonization may benefit from screening for otologic manifestations.
References
- 1.Givi B, Schiff BA, Chinn SB, et al. . Safety recommendations for evaluation and surgery of the head and neck during the COVID-19 pandemic. [published online ahead of print, 2020 Mar 31]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2020.0780 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carron JD, Buck LS, Harbarger CF, Eby TL. A simple technique for droplet control during mastoid surgery. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;e201064. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1064 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Seppanen EJ, Thornton RB, Corscadden KJ, et al. . High concentrations of middle ear antimicrobial peptides and proteins and proinflammatory cytokines are associated with detection of middle ear pathogens in children with recurrent acute otitis media. PLoS One. 2019;14(12):e0227080. Published online December 26, 2019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227080 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Duregon E, Schneider J, DeMarzo AM, Hooper JE. Rapid research autopsy is a stealthy but growing contributor to cancer research. Cancer. 2019;125(17):2915-2919. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Uhteg K, Jarrett J, Richards M, et al. . Comparing the analytical performance of three SARS-CoV-2 molecular diagnostic assays. [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 26]. J Clin Virol. 2020;127:104384. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104384 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sharma D, Rubel KE, Ye MJ, et al. . Cadaveric simulation of otologic procedures: an analysis of droplet splatter patterns during the COVID-19 pandemic. [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 19]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;194599820930245:194599820930245. Accessed May 28, 2020. doi: 10.1177/0194599820930245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


