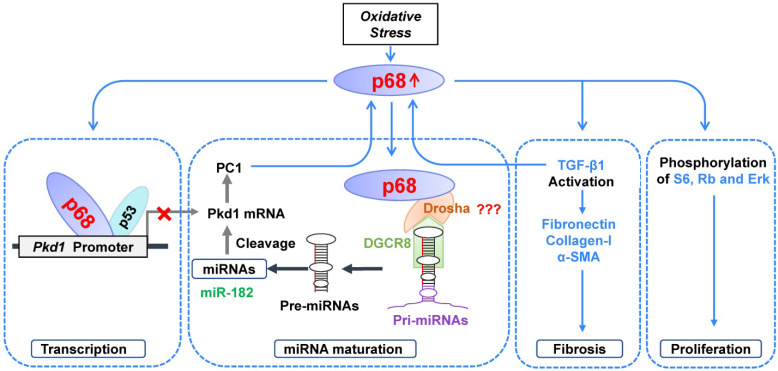
Figure 9.
Working model. In ADPKD, DNA damage and oxidative stress induce upregulation of p68, which 1) negatively regulates Pkd1 gene transcription by binding to the Pkd1 promoter together with p53, 2) positively regulates the expression and maturation of PKD-associated miRNAs leading to posttranscriptional cleavage and loss of Pkd1 mRNA, 3) positively regulates the expression of fibrotic markers, and 4) stimulates the phosphorylation and activation of PKD-associated signaling pathways, resulting in an increase of cystic renal epithelial cell proliferation and fibrosis in ADPKD kidneys.