Abstract
Background
Breast cancer patients' self-understanding of their disease can impact their quality of life (QoL); the relationship between compliance and QoL is poorly understood.
Patients and Methods
The Patient's Anastrozole Compliance to Therapy (PACT) program, a prospective, randomized study, investigated the effect of additional patient information material (IM) packages on compliance with adjuvant aromatase inhibitor (AI) therapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer. The QoL subanalysis presented here examined the impact of IM packages on QoL and the association between QoL and compliance. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) QLQ-C30 and QLQ-BR23 questionnaires were completed at baseline, 12 and 24 months, or study termination to assess health-related QoL and disease-related symptoms.
Results
Of the 4,844 patients randomized to standard therapy or standard therapy + IM packages (1:1), 4,253 were available for QoL analysis. No difference in QoL was observed between groups at baseline. IM packages did not have a statistically significant impact on patient QoL at the 12- or 24-month follow-up. Compliant patients experienced improvement in multiple items across the QLQ-C30 and QLQ-BR23 scales at 12 months. However, those results should be interpreted carefully due to limitations in the statistical analyses.
Conclusions
Provision of IM packages did not influence patients' QoL or satisfaction with care during AI therapy. Compliant patients appear to experience improved QoL compared to noncompliant patients, perhaps indicating a more self-empowered perception of their condition.
Keywords: Aromatase inhibitors, Breast cancer, Compliance, Endocrine therapy, Intervention
Background
The evaluation of breast cancer patients' quality of life (QoL) is an important aspect of clinical trials [1]. The QoL of postmenopausal women receiving endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer has been found to depend on the prescribed treatment. Tamoxifen is associated with adverse events (AE) and side effects known to impact the QoL, including hot flushes, night sweats, and vaginal discharge [2, 3, 4, 5]. By contrast, joint symptoms and myalgia are frequently reported by patients undergoing treatment with aromatase inhibitors (AI) [6]. Although clinical trials with AI have garnered superior efficacy results compared to tamoxifen in this population [5, 7], no significant differences in terms of QoL have been observed [8, 9].
In addition, the reporting of QoL outcomes and the integration and consideration of these findings in routine clinical practice are inconsistent [1]. For example, physician- and patient-based reporting of AE has been shown to vary [10]. Life-threatening AE, or those for which there is an applicable intervention, tend to be monitored by physicians, but hormone-related AE are often underreported [2]. Nevertheless, hot flushes, night sweats, and fatigue can all impact the QoL, and it has been observed that AE affecting patients' QoL can influence patients' compliance with treatment [11, 12, 13]. Especially specific symptoms such as treatment-related pain have been associated with discontinuation and can seriously impact the QoL [9, 14, 15]. Therefore, information and management of hormone-related AE in order to sustain therapy adherence are of great importance. In fact, education of patients can significantly improve the patient QoL and in turn patient adherence [12]. By providing patient information material (IM), patients' knowledge about the medical condition through information about the diagnosis, risk factors, AE, and the prognosis is thought to be increased. [12]. As a result, a better understanding of the disease and in turn a diminished perception of powerlessness might affect different aspects of QoL.
There is a limited understanding of how QoL relates to compliance with medication and how it is influenced by the patient's self-understanding of their disease. Although it is often assumed that, due to the serious nature of their disease, patients with cancer will be compliant with their medication, this is often not the case [11, 16, 17]. In particular, adjuvant endocrine therapy is associated with poorer compliance rates than chemotherapy and radiotherapy [18]. The 1-year adherence rate ranges between 69 and 86% for AI [19, 20, 21]. Furthermore, the more prescription medications a patient receives, the poorer the level of compliance with medication is overall [22]. It is reasonable to assume that women with postmenopausal breast cancer will be taking additional treatments alongside their breast cancer medication, which could have a detrimental impact on compliance. Compliance with therapy maximizes the benefit (lower recurrence rate and improved overall survival) of the treatment and may subsequently increase the perceived QoL [12]. On the other hand, it has been shown that the presence of symptoms or a poor QoL at baseline can influence the occurrence of pain during therapy and in turn treatment continuation [9, 14, 15]. Moreover, changes in QoL influence a woman's decision to discontinue a therapy [23].
The Patient's Anastrozole Compliance to Therapy (PACT) program was designed to assess whether the provision of additional standardized patient IM packages throughout the first year of adjuvant therapy enhanced persistence and compliance in 4844 postmenopausal women with early breast cancer receiving anastrozole as the initial therapy in a real-life clinical setting [24, 25]. The term adherence is now commonly used to describe patient medication-taking behavior; however, in line with the predefined study endpoints, this paper will report on compliance and persistence.
The purpose of this PACT QoL explorative subanalysis was to examine the relationship between compliance with AI medication and perceived QoL. We also investigated whether the provision of IM packages was associated with changes in QoL. QoL over time was also assessed up to a 24-month follow-up.
Methods
Study Design
PACT was a prospective, multicenter, nationwide, randomized, open, parallel-group study (NCT00555867) [24]. Postmenopausal patients with early breast cancer were recruited at 109 certified breast cancer centers/clinics across Germany in cooperation with 1,361 office-based gynecologists and oncologists. Patients scheduled for adjuvant endocrine therapy were randomized 1:1 to receiving standard therapy (anastrozole 1 mg once daily) or standard therapy plus additional patient IM packages by post. Patients underwent all further investigations and treatments deemed necessary according to the current standards of care at that time.
In addition to standard therapy, patients randomized to the IM package arm received 9 letters and brochures developed in close collaboration with breast cancer survivors and advocates by mail during the first year of therapy, plus gift items of low monetary value (e.g., a 7-day tablet box). Details on the IM packages have been published elsewhere [25]. They were designed to deal with issues likely to be of relevance at specific points in time during therapy, such as side effects, sexuality, exercise, and diet, with the aim of motivating participants to take their medication regularly.
The study population and full inclusion and exclusion criteria have been described previously [24, 25].
Study Endpoints
The primary aim of the PACT study was to investigate whether the provision of IM packages in the first year of adjuvant endocrine therapy improved patient compliance and persistence versus standard treatment practices.
The present QoL exploratory analyses were performed to investigate whether the provision of IM packages impacted the patient health-related QoL and disease-related symptoms and whether QoL was associated with AI compliance.
Data Collection
Details on the collection of compliance data and AE reporting have been described elsewhere [24, 25].
Patients' self-reported health-related QoL and disease-related symptoms were assessed at baseline and after 12 and 24 months, or at treatment termination, using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) QLQ-C30 [26] and EORTC QLQ-BR23 [27] questionnaires. The EORTC QLQ-C30 comprises 6 functional scales assessing physical functioning, role functioning, emotional functioning, cognitive functioning, and social functioning, plus the global health status/QoL. In addition, single- and multi-item scales of the EORTC QLQ-C30 assessed the physical and financial impact of the disease and treatment, including measurements of fatigue, nausea and vomiting, pain, dyspnea, sleep disturbance, appetite loss, constipation, diarrhea, and financial impact. The 4 functional scales of the EORTC QLQ-BR23 assessed body image, sexual functioning, sexual enjoyment, and future perspectives. Single- and multi-item scales assessed patients' physical symptoms, including systemic therapy symptoms, breast symptoms, arm symptoms, and hair loss.
Data were collected over a 24-month period. This paper presents the QoL results for patients at baseline and 12 months, as well as at 24 months of follow-up.
Statistical Analysis
Compliance and persistence were evaluated via patient self-reporting. A patient could only be classified as compliant if she scored 80–100% when questioned about her daily intake of adjuvant endocrine therapy and when all prescription information (documented by the investigator) was consistently available for the treatment period. A patient was classified as persistent when case report form documentation, independently of the compliance evaluation, supported the intake of anastrozole during the full 12-month period. Full details of the statistical methodology have been reported previously [24, 25].
QoL was analyzed for all patients who were available for primary endpoint analysis and returned a QoL questionnaire at baseline, 12 months (defined as between 9 and 18 months), and 24 months (defined as between 21 and 30 months).
In accordance with the EORTC manual, if >50% of the questionnaire item responses were missing, all items for that respective patient were set to missing. If <50% of the questionnaire item responses were not available, only the single items not available were set to missing. For the QLQ-C30 and QLQ-BR23, raw scores from the individual items were summed and subsequently divided by the number of items within the scale. The resulting scores were linearly transformed to produce a scale range of 0–100. For the functional scales of QLQ-C30 and QLQ-BR23, a higher score represented a higher level of functioning. For the physical symptom single- and multi-item scales of the QLQ-C30 and QLQ-BR23, a higher score represented a higher level of symptomatology/problems.
The impact of patients receiving chemotherapy prior to inclusion in the study on QoL was analyzed using the Wilcoxon test. In addition, the impact of prior chemotherapy on the occurrence of fatigue and arthralgia was analyzed using the χ2 test.
Results
Patients
From October 2006 to November 2008, a total of 4,923 postmenopausal women who initiated adjuvant endocrine (anastrozole) therapy were enrolled into PACT. Of the 4,897 patients screened, 4,844 were randomized 1:1 to standard therapy (n = 2,402) or standard therapy plus IM packages (n = 2,442) and 2,740 patients were evaluable for primary endpoint analysis (compliance and persistence at the 12-month follow-up) [25]. In total, 4,253 patients completed at least 1 QoL questionnaire (online suppl. Fig. 1; for all online suppl. material, see www.karger.com/doi/10.1159/000500771). The baseline demographics and tumor characteristics for these patients are presented in Table 1. Full patient demographics as well as the primary endpoint analysis have been described previously [24, 25].
Table 1.
Demographic and tumor characteristics at baseline for patients who completed at least 1 QoL questionnaire
| Standard arm (n = 2,114) | IM package arm (n = 2,139) | Total (n = 4,253) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristic | |||
| Age | |||
| ≤65 years | 1,035 (49.0) | 1,000 (46.8) | 2,035 (47.8) |
| >65 years | 1,079 (51.0) | 1,139 (53.2) | 2,218 (52.2) |
| ECOG PS (Karnofsky scale) | |||
| 0 (100%) | 1,190 (56.29) | 1,196 (55.91) | 2,386 (56.1) |
| 1 (80–90%) | 825 (39.03) | 838 (39.18) | 1,663 (39.1) |
| ≥2 (10–70%) | 82 (3.88) | 94 (4.39) | 176 (4.13) |
| Not disclosed | 17 (0.8) | 11 (0.51) | 28 (0.66) |
| BMI | |||
| <25 | 774 (36.6) | 776 (36.3) | 1,550 (36.4) |
| 25–30 | 803 (38.0) | 801 (37.5) | 1,604 (37.7) |
| >30 | 526 (24.9) | 545 (25.5) | 1,071 (25.2) |
| Not disclosed | 11 (0.5) | 17 (0.8) | 28 (0.7) |
| Additional tablets | |||
| 0 (n/day) | 52 (2.5) | 43 (2.0) | 95 (2.2) |
| 1–2 (n/day) | 582 (27.5) | 623 (29.1) | 1,205 (28.3) |
| 3–5 (n/day) | 404 (19.1) | 402 (18.8) | 806 (19.0) |
| 6–10 (n/day) | 174 (8.2) | 197 (9.2) | 371 (8.7) |
| >10 (n/day) | 40 (1.9) | 37 (1.7) | 77 (1.8) |
| Not disclosed | 862 (40.8) | 837 (39.1) | 1,699 (40.0) |
| Concomitant conditions (in >5% of the total patientsa) | |||
| Cardiovascular system | 949 (24.2) | 1,016 (25.0) | 1,965 (24.6) |
| Thyroid disorder | 447 (11.4) | 431 (10.6) | 878 (11.0) |
| Other (undisclosed) | 370 (9.4) | 368 (9.1) | 738 (9.2) |
| Joint pain | 240 (6.1) | 272 (6.7) | 512 (6.4) |
| Back pain | 242 (6.2) | 251 (6.2) | 493 (6.2) |
| Other types of angiopathy | 218 (5.6) | 231 (5.7) | 449 (5.6) |
| Diabetes | 199 (5.1) | 223 (5.5) | 422 (5.3) |
| Tumor characteristicb | |||
| Tumor grade | n = 2,193 | n = 2,194 | n = 4,387 |
| estimable tumors | estimable tumors | estimable tumors | |
| G1 | 298 (13.6) | 304 (13.9) | 602 (13.7) |
| G2 | 1,467 (66.9) | 1,457 (66.4) | 2,924 (66.7) |
| G3 | 406 (18.5) | 414 (18.9) | 820 (18.7) |
| Not determined | 22 (1.0) | 19 (0.9) | 41 (0.9) |
| T stage | n = 2,193 | n = 2194 | n = 4,387 |
| estimable tumors | estimable tumors | estimable tumors | |
| pT0 | 15 (0.7) | 14 (0.6) | 29 (0.7) |
| pT1 | 1,250 (57.0) | 1,250 (57.0) | 2,500 (57.0) |
| pT2 | 784 (35.8) | 784 (35.7) | 1,568 (35.7) |
| ≥pT3 | 123 (5.6) | 124 (5.6) | 247 (5.6) |
| Other/not determined | 21 (1.0) | 22 (1.0) | 43 (1.0) |
| Nodal status | n = 2,193 | n = 2,194 | n = 4,387 |
| estimable tumors | estimable tumors | estimable tumors | |
| pN0 | 1,379 (62.9) | 1,400 (63.8) | 2,779 (63.4) |
| pN1 | 511 (23.3) | 494 (22.5) | 1,005 (22.9) |
| ≥ pN2 | 263 (12.0) | 244 (11.1) | 507 (11.6) |
| Other/not determined | 40 (1.8) | 56 (2.6) | 96 (2.2) |
| ER status | n = 2,190 | n = 2194 | n = 4,348 |
| estimable tumors | estimable tumors | estimable tumors | |
| ER+ | 2,145 (98.0) | 2,153 (98.1) | 4,298 (98.9) |
| PgR status | n = 2,189 | n = 2189 | n = 4,378 |
| estimable tumors | estimable tumors | estimable tumors | |
| PgR+ | 1,942 (88.7) | 1,954 (89.3) | 3,896 (89.0) |
| HER2 status by ICH | n = 2,058 | n = 2,061 | n = 4,119 |
| estimable tumors | estimable tumors | estimable tumors | |
| 2+ | 188 (9.1) | 166 (8.1) | 351 (8.5) |
| 3+ | 175 (8.5) | 184 (8.9) | 359 (8.7) |
| HER2 status by FISH/CISH |
n = 435 estimable tumors |
n = 416 estimable tumors |
n = 851 estimable tumors |
| HER2 positive | 60 (13.8) | 48 (11.5) | 108 (12.7) |
Values are presented as numbers (%). ER, PgR, and HER2 status were not assessed for all tumor localizations. CISH, chromogenic in situ hybridization; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; ER, estrogen receptor; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IHC, immunohistochemistry; PgR, progesterone receptor.
Reported as a proportion of the total concomitant conditions (n = 7,991); multiple answers are possible.
A total of 134 of 4,253 patients had bilateral disease; therefore, tumor characteristics were assessed for 4,387 tumors.
Patient QoL Analysis According to Provision of IM Packages
EORTC QLQ-C30 Scales
At baseline, patients in the IM package arm reported a higher level of financial problems than patients in the standard arm (23.14 vs. 26.18; p =0.01; Table 2). Across all other items of the QLQ-C30 symptom scales, no statistically significant differences in baseline scores were observed between arms. Furthermore, no statistically significant differences were observed at the 12- and 24-month follow-ups.
Table 2.
EORTC QLQ-C30 and QLQ-BR23 scores at baseline and the 12- and 24-month follow-ups by study arm
| Baseline, [n] Mean (SD) | 12 months, [n] Mean (SD) | 24 months, [n] Mean (SD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EORTC QLQ-C30 | |||
| Functional scale | |||
| Physical functioning | |||
| Standard arm | [1,990] 73.01 (21.55) | [1,299] 74.91 (21.61) | [724] 76.91 (19.94) |
| IM package arm | [2,010] 72.70 (22.11) | [1,362] 75.27 (75.27) | [705] 76.63 (21.02) |
| Role functioning | |||
| Standard arm | [1,974] 57.08 (31.45) | [1,288] 68.72 (29.28) | [722] 71.98 (28.52) |
| IM package arm | [1,993] 58.15 (31.88) | [1,353] 68.66 (29.65) | [701] 71.35 (28.64) |
| Emotional functioning | |||
| Standard arm | [1,986] 59.07 (26.68) | [1,287] 64.09 (27.00) | [723] 68.23 (25.84) |
| IM package arm | [2,004] 58.71 (26.61) | [1,357] 63.53 (27.07) | [702] 66.24 (25.73) |
| Cognitive functioning | |||
| Standard arm | [1,989] 77.76 (26.34) | [1,293] 75.42 (27.06) | [724] 76.36 (25.13) |
| IM package arm | [2,007] 77.41 (26.51) | [1,362] 74.47 (27.34) | [702] 77.71 (25.41) |
| Social functioning | |||
| Standard arm | [1,983] 67.61 (30.45) | [1,290] 73.93 (29.11) | [722] 78.51 (26.56) |
| IM package arm | [1,998] 67.49 (30.36) | [1,364] 74.74 (27.85) | [700] 78.31 (26.53) |
| Global health status/QoL | |||
| Standard arm | [1,966] 56.21 (21.58) | [1,279] 62.48 (21.78) | [707] 64.59 (21.58) |
| IM package arm | [1,985] 57.03 (20.55) | [1,346] 62.96 (21.42) | [692] 64.08 (22.31) |
| Symptom scale | |||
| Fatigue | |||
| Standard arm | [1,983] 45.62 (45.62) | [1,292] 41.31 (27.67) | [722] 37.47 (27.22) |
| IM package arm | [2,001] 45.26 (28.85) | [1,355] 41.48 (28.09) | [699] 37.70 (27.21) |
| Nausea and vomiting | |||
| Standard arm | [1,983] 9.62 (19.30) | [1,286] 6.16 (14.52) | [721] 5.59 (13.98) |
| IM package arm | [1,996] 10.50 (20.41) | [1,356] 6.21 (15.00) | [697] 5.09 (13.07) |
| Pain | |||
| Standard arm | [1,989] 33.32 (29.82) | [1,298] 34.53 (31.82) | [724] 30.71 (30.91) |
| IM package arm | [2,005] 32.04 (29.81) | [1,360] 34.13 (31.42) | [699] 31.33 (30.41) |
| Dyspnea | |||
| Standard arm | [1,962] 28.66 (32.47) | [1,283] 30.68 (33.02) | [716] 28.91 (31.69) |
| IM package arm | [1,973] 28.55 (32.84) | [1,341] 29.65 (32.40) | [691] 29.18 (31.68) |
| Sleep disturbance | |||
| Standard arm | [1,973] 43.76 (35.83) | [1,288] 48.50 (36.17) | [720] 46.81 (35.84) |
| IM package arm | [1,992] 44.81 (35.79) | [1,350] 49.95 (36.39) | [703] 47.32 (36.75) |
| Appetite loss | |||
| Standard arm | [1,986] 20.76 (30.16) | [1,292] 10.76 (23.00) | [723] 9.91 (21.38) |
| IM package arm | [2,002] 21.18 (30.83) | [1,357] 11.25 (23.73) | [701] 10.41 (21.48) |
| Constipation | |||
| Standard arm | [1,968] 17.90 (30.11) | [1,282] 14.72 (27.06) | [718] 13.97 (25.35) |
| IM package arm | [1,986] 18.18 (29.31) | [1,341] 15.71 (27.71) | [689] 14.61 (25.78) |
| Diarrhea | |||
| Standard arm | [1,969] 11.14 (23.52) | [1,273] 10.66 (22.91) | [719] 10.29 (22.51) |
| IM package arm | [1,981] 11.36 (23.68) | [1,347] 10.37 (22.27) | [696] 8.62 (20.05) |
| Financial impact | |||
| Standard arm | [1,896] 26.18 (32.39)* | [1,204) 22.56 (30.36) | [678] 18.63 (28.16) |
| IM package arm | [1,909] 23.14 (30.15)* | [1,283] 21.54 (29.43) | [654] 18.09 (28.05) |
| EORTC QLQ-BR23 | |||
| Functional scale | |||
| Body image | |||
| Standard arm | [1,968] 72.17 (29.96) | [1,276] 76.38 (27.76) | [703] 78.96 (26.01) |
| IM package arm | [1,979] 72.03 (29.65) | [1,332] 77.22 (27.90) | [686] 79.31 (26.14) |
| Sexual functioning | |||
| Standard arm | [1,784] 18.50 (24.75) | [1,129] 22.69 (26.35) | [622] 21.44 (25.76) |
| IM package arm | [1,822] 18.21 (24.05) | [1,182] 22.07 (25.73) | [600] 21.56 (25.28) |
| Sexual enjoyment | |||
| Standard arm | [500] 49.27 (34.76) | [370] 50.45 (33.40) | [189] 51.68 (33.40) |
| IM package arm | [499] 49.97 (33.82) | [389] 51.33 (32.23) | [196] 48.98 (31.91) |
| Future perspectives | |||
| Standard arm | [1,969] 35.80 (32.80) | [1,281] 48.58 (33.77) | [704] 55.16 (32.71) |
| IM package arm | [1,987] 35.06 (32.86) | [1,335] 48.64 (33.75) | [690] 54.40 (33.08) |
| Symptom scale | |||
| Systemic therapy symptoms | |||
| Standard arm | [1,973] 31.01 (23.19) | [1,287] 27.74 (18.76) | [709] 26.66 (19.53) |
| IM package arm | [1,993] 31.13 (23.21) | [1,345] 28.46 (19.82) | [692] 26.53 (19.25) |
| Breast symptoms | |||
| Standard arm | [1,952] 29.53 (24.20) | [1,267] 22.21 (20.78) | [687] 18.80 (19.13) |
| IM package arm | [1,967] 28.14 (23.82) | [1,326] 22.80 (21.19) | [681] 18.53 (19.77) |
| Arm symptoms | |||
| Standard arm | [1,947] 30.19 (26.18) | [1,264] 32.87 (27.51) | [689] 29.06 (27.56) |
| IM package arm | [1,966] 28.78 (25.43) | [1,325] 31.36 (27.71) | [680] 28.49 (26.84) |
| Hair loss | |||
| Standard arm | [884] 56.86 (39.40) | [511] 48.27 (38.50) | [330] 49.09 (39.68) |
| IM package arm | [882] 59.18 (59.18) | [549] 47.18 (38.56) | [312] 46.26 (37.90) |
For the functional scales, a higher score was representative of a higher level of functioning. For the physical symptom single- and multi-item scales, a higher score was representative of a higher level of symptomatology/problems. * Significant change (p = 0.0116).
EORTC QLQ-BR23 Scales
At baseline, no statistically significant differences in any items of the QLQ-BR23 symptom scales were observed between the standard and IM package arms (Table 2). Follow-up analysis at both 12 and 24 months demonstrated no statistically significant differences for any items of the functional scale between arms.
QoL According to Patient Compliance
Analysis of QoL between compliant and noncompliant patients was performed at the 12-month follow-up using the questionnaires returned by the 2,740 patients in whom the primary analysis was conducted.
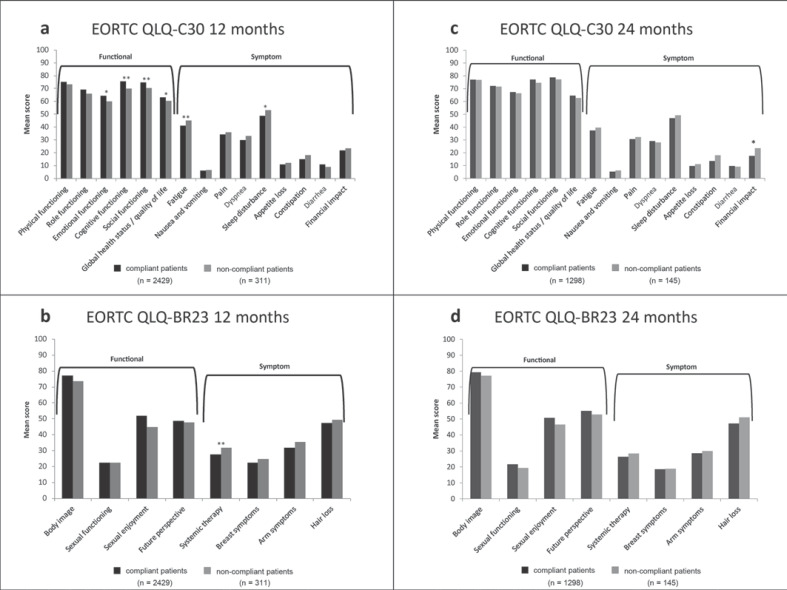
For the QLQ-C30 functional scales, compliant patients reported statistically significantly higher scores in emotional functioning (p = 0.03), cognitive functioning (p = 0.007), social functioning (p =0.009), and global health status/QoL (p =0.03) than noncompliant patients (Fig. 1a). Analysis of the QLQ-C30 symptom scale showed that compliant patients had statistically significantly lower scores for fatigue and sleep disturbance than noncompliant patients (fatigue: 40.92 vs. 45.17; p =0.01; sleep disturbance: 53.13 vs. 48.75; p =0.049; Fig. 1a), indicating a lower level of symptoms. No other symptoms were associated with compliance.
Fig. 1.
QoL according to patient compliance at 12 (a, b) and 24 months (c, d). QoL measured according to: the EORTC QLQ-C30 (a, c) and the EORTC QLQ-BR23 (b, d). Functional scales: a higher scale score represents a higher level of functioning. Symptom scales: a higher score represents a higher level of symptomatology/problems. * p < 0.05. ** p < 0.01.
Compliant patients reported statistically significantly lower scores for systemic therapy symptoms (p =0.001), as recorded via the QLQ-BR23 symptom scale, than noncompliant patients, indicating a lower level of symptoms (Fig. 1b). Analysis of the QLQ-BR23 functional scales did not show an association between symptoms and compliance.
Analysis of QoL between compliant and noncompliant patients at the 24-month follow-up showed that compliant patients reported a statistically significantly lower financial impact (p =0.02) on the QLQ-C30 than noncompliant patients (Fig. 1c). No statistically significant differences between compliant and noncompliant patients were apparent for any other items on either scale (Fig. 1c, d).
Effect of Prior Chemotherapy
Statistically significant relationships were found between prior chemotherapy and occurrence of arthralgia (p =0.0097), occurrence of fatigue (p =0.0034), and QoL concerning fatigue (p =0.015). Patients who had received chemotherapy prior to inclusion in the study were more likely to report arthralgia symptoms, but less likely to report fatigue, and the impact of fatigue on QoL was lower compared with patients who had not received prior chemotherapy.
Discussion
In this prospective trial we analyzed the impact of the provision of patient IM packages on QoL in postmenopausal early breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant AI therapy. Our own previous data from the PACT trial showed that IM packages do not significantly influence patients' compliance [25]. Nonetheless, we assumed that they might influence QoL as they were designed specifically to cover many aspects of QoL affected by AI therapy, including fatigue, lymphedema, anxiety, depression, and sexuality. However, these did not seen to impact patients' QoL or satisfaction with care. Across both of the functional and symptom scales (QLQ-C30 and QLQ-BR23) used to evaluate QoL, similar scores for the standard and IM package arms were observed at baseline and both follow-up analyses. Therefore, no considerable influence of IM packages on QoL was observed. Patients who have a better understanding of their condition are expected to be more likely to report AE, due to an ability to connect symptoms with treatment. This enables physicians to respond more appropriately to their patients' needs [12]. However, IM packages were not seen to impact the QoL in the PACT trial. As the patients participating in PACT were a selected patient population actively participating in a study, they may have already had a good level of understanding of their disease, thereby minimizing the impact of the IM packages. Scores at baseline may also have impacted the result. While consistent with other clinical studies [28], the PACT QoL baseline scores may be better than those observed in daily clinical practice. It is also worth considering that the IM packages may not have adequately addressed the actual AE experienced, leaving patients unable to identify the AE as artefacts of their treatment.
A further exploratory analysis of the study aimed to investigate the relationship between compliance with AI medications and perceived QoL. Compliant patients may have a greater belief in the efficacy of their treatment and its ability to reduce the risk of disease recurrence, compared with noncompliant patients [11]. This perceived benefit of treatment should drive compliance with the medication and could lead to improvements in patients' perceived outcomes and QoL. This was observed in the PACT study, with compliant patients at 12-month follow-up reporting better outcomes in various symptoms versus non-compliant patients. As the data were not corrected for multiple testing, the statistically significant results might however have been observed by chance. Therefore, the data have to be interpreted carefully. Compliant patients could have a greater willingness to accept their disease and treatment-associated AEs compared with non-compliant patients. The QoL data from the ATAC trial suggest that there may be a relationship between compliance and QoL. At 2-year follow-up, patients reported improved QoL compared with baseline and were also shown to be compliant in completing their QoL questionnaires, with 85% of questionnaires completed at each follow-up visit [8]. The level of compliance for completing QoL questionnaires is mirrored in the overall compliance results for ATAC [29], which are similar to those reported in PACT. However, the 12-month results from our study were not mirrored in the 24-month analysis; a statistically significantly lower financial impact for compliant patients versus noncompliant patients was the only difference observed at that time point. Nonetheless, the evaluation of compliance to endocrine therapy is still complex as it depends on various factors, such as AE, polypharmacy, negative changes in menopause-specific QoL, disease-related knowledge, and symptoms before treatment start [9, 15, 23]. Due to this multiplicity and complexity of influencing factors, a more comprehensive investigation is needed.
Arthralgia and fatigue are recognized AE of AI therapy [30] and patients reporting these AE are expected to have a reduced QoL. In PACT, patients reported a worsening of arm symptoms at 12 months, followed by a slight improvement at 24 months regardless of whether IM packages were provided. Fatigue was seen to decrease between baseline and 24 months in both study arms. Patients who were considered compliant reported statistically significantly lower levels of arm symptoms and fatigue compared to noncompliant patients. Our findings confirm the data of Laroche et al. [14], who observed an association of prior taxanes with AI-induced arm symptoms. However, it should be noted that patients with prior chemotherapy were statistically more likely to report arthralgia symptoms than those without prior chemotherapy and statistically less likely to report fatigue than patients without prior chemotherapy.
Conclusions
PACT is the first prospective study to assess the influence of patient IM packages on compliance with adjuvant endocrine therapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer. This observational study design is likely to more accurately reflect a real-life clinical setting than clinical trials. Our data showed that IM packages provide no benefit on compliance with AI therapy and QoL and, therefore, the PACT trial has not met these endpoints. These findings suggest that IM packages do not sufficiently replace personal physician-patient interaction and care. The positive relationship between compliance and QoL is an interesting finding. However, it requires further characterization as a mutual influence cannot be excluded. Compliant patients might either experience an improved QoL, or have a greater acceptance of their disease and its associated AE, thereby minimizing their perceived impact on QoL. It indicates that these patients recognize the benefits and limitations of their medication. This result should be considered both by physicians in routine clinical practice and by investigators in the design of future clinical trials.
Statement of Ethics
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Ulm (reference No. 1033GR/0002/[PACT]) and all appropriate local ethics committees and it was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and International Committee on Harmonization Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice. Informed consent was obtained from all of the individual participants included in the study.
Availability of Data and Material
The data that support the findings of this study can be requested from the study sponsor, AstraZeneca, via the Data Request Portal (https://astrazenecagroup-dt.pharmacm.com/DT/Home). The request will be evaluated and reviewed by AstraZeneca on a case-by-case basis.
Disclosure Statement
C.J. has received advisory board fees, honoraria, and payment for the development of patient IM packages from AstraZeneca, Roche, Novartis, and Pfizer. R.K. has received advisory board fees from AstraZeneca. M.B. has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca. N.H. has received consultancy fees and payment for development of IM packages presentations. H.-J.L. has received advisory board fees from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Roche, Tesaro, and Pfizer and speaker's bureau fees from Roche, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Novartis. C.W.-K. has received clinical research organization fees from AstraZeneca. S.Z. is a former employee of AstraZeneca. P.H. has received advisory board fees, consultancy fees, lecture fees, travel reimbursements, and research grants from AstraZeneca. R.H., D.C.S., and H.S. declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding Source
This study was sponsored by AstraZeneca.
Author Contributions
C.J. participated in the conception and design of the study, development of methodology, acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data, writing, review, and revision of this paper, and the statistical analysis. R.K. participated in the conception and design of the study, development of methodology, acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data, writing, review, and revision of this paper, and study supervision. M.B. participated in the conception and design of the study, writing, review, and revision of this paper, and the statistical analysis. N.H. participated in the conception and design of the study, acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data, writing, review, and revision of this paper, and study supervision and was a member of the steering committee. H.-J.L. participated in acquisition of data and review and revision of this paper. R.H. participated in the conception and design of the study and writing, review, and revision of this paper and provided administrative, technical, or material support. D.C.S. and H.S. participated in writing, review and revision of this paper. C.W.-K. participated in analysis and interpretation of data, writing, review, and revision of this paper, and the statistical analysis. S.Z. participated in the conception and design of the study, analysis and interpretation of data, and writing, review, and revision of this paper and provided administrative, technical, or material support. P.H. participated in the conception and design of the study, development of methodology, acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data, writing, review, and revision of this paper, and study supervision. All of the authors read and approved the final version of this paper.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary data
Supplementary data
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the patients who participated in the study, their fellow investigators, and the patient advocates involved in developing the IM packages (Annette Rexrodt von Fircks, Doris C. Schmitt, Hilde Schulte, Rita-Rosa Martin, and Renate Haidinger).
Medical writing services were funded by AstraZeneca and were provided by Lucy Turner of iMed Comms, Macclesfield, UK, an Ashfield Company, part of UDG Healthcare plc, and by Sonja Hartmann, Alcedis GmbH, Giessen, Germany.
References
- 1.Lemieux J, Goodwin PJ, Bordeleau LJ, Lauzier S, Théberge V. Quality-of-life measurement in randomized clinical trials in breast cancer: an updated systematic review (2001-2009) J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 Feb;103((3)):178–231. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fallowfield L, Jenkins V. Quality of life issues during adjuvant endocrine therapy. Cancer Treat Res. 2009;151:353–65. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-75115-3_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hadji P. Menopausal symptoms and adjuvant therapy-associated adverse events. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008 Mar;15((1)):73–90. doi: 10.1677/ERC-07-0193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Howell A, Cuzick J, Baum M, Buzdar A, Dowsett M, Forbes JF, et al. ATAC Trialists' Group Results of the ATAC (Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination) trial after completion of 5 years' adjuvant treatment for breast cancer. Lancet. 2005 Jan;365((9453)):60–2. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17666-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Thürlimann B, Keshaviah A, Coates AS, Mouridsen H, Mauriac L, Forbes JF, et al. Breast International Group (BIG) 1-98 Collaborative Group A comparison of letrozole and tamoxifen in postmenopausal women with early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005 Dec;353((26)):2747–57. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sestak I, Cuzick J, Sapunar F, Eastell R, Forbes JF, Bianco AR, et al. ATAC Trialists' Group Risk factors for joint symptoms in patients enrolled in the ATAC trial: a retrospective, exploratory analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2008 Sep;9((9)):866–72. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cuzick J, Sestak I, Baum M, Buzdar A, Howell A, Dowsett M, et al. ATAC/LATTE investigators Effect of anastrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for early-stage breast cancer: 10-year analysis of the ATAC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010 Dec;11((12)):1135–41. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fallowfield L, Cella D, Cuzick J, Francis S, Locker G, Howell A. Quality of life of postmenopausal women in the Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination (ATAC) Adjuvant Breast Cancer Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2004 Nov;22((21)):4261–71. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.08.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wagner LI, Zhao F, Goss PE, Chapman JW, Shepherd LE, Whelan TJ, et al. Patient-reported predictors of early treatment discontinuation: treatment-related symptoms and health-related quality of life among postmenopausal women with primary breast cancer randomized to anastrozole or exemestane on NCIC Clinical Trials Group (CCTG) MA.27 (E1Z03) Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jun;169((3)):537–48. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4713-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fellowes D, Fallowfield LJ, Saunders CM, Houghton J. Tolerability of hormone therapies for breast cancer: how informative are documented symptom profiles in medical notes for ‘well-tolerated’ treatments? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2001 Mar;66((1)):73–81. doi: 10.1023/a:1010684903199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Grunfeld EA, Hunter MS, Sikka P, Mittal S. Adherence beliefs among breast cancer patients taking tamoxifen. Patient Educ Couns. 2005 Oct;59((1)):97–102. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2004.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hadji P. Improving compliance and persistence to adjuvant tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitor therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2010 Feb;73((2)):156–66. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2009.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lash TL, Fox MP, Westrup JL, Fink AK, Silliman RA. Adherence to tamoxifen over the five-year course. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006 Sep;99((2)):215–20. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Laroche F, Perrot S, Medkour T, Cottu PH, Pierga JY, Lotz JP, et al. Quality of life and impact of pain in women treated with aromatase inhibitors for breast cancer. A multicenter cohort study. PLoS One. 2017 Nov;12((11)):e0187165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kidwell KM, Harte SE, Hayes DF, Storniolo AM, Carpenter J, Flockhart DA, et al. Patient-reported symptoms and discontinuation of adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy. Cancer. 2014 Aug;120((16)):2403–11. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hershman DL, Shao T, Kushi LH, Buono D, Tsai WY, Fehrenbacher L, et al. Early discontinuation and non-adherence to adjuvant hormonal therapy are associated with increased mortality in women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Apr;126((2)):529–37. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1132-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ruddy K, Mayer E, Partridge A. Patient adherence and persistence with oral anticancer treatment. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009 Jan-Feb;59((1)):56–66. doi: 10.3322/caac.20004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ma AM, Barone J, Wallis AE, Wu NJ, Garcia LB, Estabrook A, et al. Noncompliance with adjuvant radiation, chemotherapy, or hormonal therapy in breast cancer patients. Am J Surg. 2008 Oct;196((4)):500–4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Partridge AH, LaFountain A, Mayer E, Taylor BS, Winer E, Asnis-Alibozek A. Adherence to initial adjuvant anastrozole therapy among women with early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008 Feb;26((4)):556–62. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.5451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sedjo RL, Devine S. Predictors of non-adherence to aromatase inhibitors among commercially insured women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Jan;125((1)):191–200. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-0952-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ziller V, Kalder M, Albert US, Holzhauer W, Ziller M, Wagner U, et al. Adherence to adjuvant endocrine therapy in postmenopausal women with breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009 Mar;20((3)):431–6. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gellad WF, Grenard JL, Marcum ZA. A systematic review of barriers to medication adherence in the elderly: looking beyond cost and regimen complexity. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2011 Feb;9((1)):11–23. doi: 10.1016/j.amjopharm.2011.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Meggetto O, Maunsell E, Chlebowski R, Goss P, Tu D, Richardson H. Factors Associated With Early Discontinuation of Study Treatment in the Mammary Prevention.3 Breast Cancer Chemoprevention Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017 Feb;35((6)):629–35. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.68.8895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Harbeck N, Blettner M, Hadji P, Jackisch C, Lück HJ, Windemuth-Kieselbach C, et al. Patient's Anastrozole Compliance to Therapy (PACT) Program: Baseline Data and Patient Characteristics from a Population-Based, Randomized Study Evaluating Compliance to Aromatase Inhibitor Therapy in Postmenopausal Women with Hormone-Sensitive Early Breast Cancer. Breast Care (Basel) 2013 May;8((2)):110–20. doi: 10.1159/000350777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hadji P, Blettner M, Harbeck N, Jackisch C, Lück HJ, Windemuth-Kieselbach C, et al. The Patient's Anastrozole Compliance to Therapy (PACT) Program: a randomized, in-practice study on the impact of a standardized information program on persistence and compliance to adjuvant endocrine therapy in postmenopausal women with early breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2013 Jun;24((6)):1505–12. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Mar;85((5)):365–76. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.5.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sprangers MA, Groenvold M, Arraras JI, Franklin J, te Velde A, Muller M, et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer breast cancer-specific quality-of-life questionnaire module: first results from a three-country field study. J Clin Oncol. 1996 Oct;14((10)):2756–68. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.10.2756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cella D, Fallowfield L, Barker P, Cuzick J, Locker G, Howell A, ATAC Trialistsa9 Group Quality of life of postmenopausal women in the ATAC (“Arimidex”, tamoxifen, alone or in combination) trial after completion of 5 years' adjuvant treatment for early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006 Dec;100((3)):273–84. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9260-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Forbes JF, Cuzick J, Buzdar A, Howell A, Tobias JS, Baum M, Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination (ATAC) Trialists' Group Effect of anastrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for early-stage breast cancer: 100-month analysis of the ATAC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008 Jan;9((1)):45–53. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cuzick J, Sestak I, Cella D, Fallowfield L, ATAC Trialists' Group Treatment-emergent endocrine symptoms and the risk of breast cancer recurrence: a retrospective analysis of the ATAC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008 Dec;9((12)):1143–8. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary data
Supplementary data
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study can be requested from the study sponsor, AstraZeneca, via the Data Request Portal (https://astrazenecagroup-dt.pharmacm.com/DT/Home). The request will be evaluated and reviewed by AstraZeneca on a case-by-case basis.