Abstract
Pancreatic cancer is associated with a poor prognosis due to challenges in early detection, severe progression of the primary tumor, metastatic lesions, and resistance to antitumor agents. However, previous studies have indicated a relationship between the microbiome and pancreatic cancer outcomes. Our previous study demonstrated that ferrichrome derived from Lactobacillus casei, a probiotic bacteria, exhibited tumor-suppressive effects in colorectal and gastric cancer, and that the suppressive effects were stronger than conventional antitumor agents, such as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and cisplatin, suggesting that certain probiotics exert antitumorigenic effects. However, whether or not probiotic-derived molecules, including ferrichrome, exert a tumor-suppressive effect in other gastrointestinal tumors, such as pancreatic cancer, remains unclear. In the present study, it was demonstrated that probiotic-derived ferrichrome inhibited the growth of pancreatic cancer cells, and its tumor-suppressive effects were further revealed in 5-FU-resistant pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo in a mouse xenograft model. Ferrichrome inhibited the progression of cancer cells via dysregulation of the cell cycle by activating p53. DNA fragmentation and cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase were induced by ferrichrome treatment, suggesting that ferrichrome induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. A transcriptome analysis revealed that the expression p53-associated mRNAs was significantly altered by ferrichrome treatment. Thus, the tumor-suppressive effects of probiotics may mediated by probiotic-derived molecules, such as ferrichrome, which may have applications as an antitumor drug, even in refractory and 5-FU-resistant pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: 5-FU, cancer, ferrichrome, pancreatic, probiotics
Introduction
Treatment options for pancreatic cancer have improved in past decades with the development of molecular targeted therapies and chemotherapy (1,2); however, most pancreatic cancers remain unresectable when detected, and the 5-year survival rate is <10% due to difficulties in early detection (3), rapid progression of the primary tumor and metastatic lesions, resistance to and/or the requirement for discontinuation of antitumor drugs such as 5 fluorouracil (5-FU), cisplatin and molecular targeted therapy due to insufficient efficacy (4), and strong side effects, including myelosuppression and gastrointestinal disorders (5). It is important to develop novel antitumor drugs that possess sufficient efficacy and safety, particularly for elderly patients and patients with comorbidities.
Recent studies have proposed that intestinal and oral microbiomes are potential factors that influence the outcome of patients with pancreatic cancer, despite most intestinal bacteria not making direct contact with pancreatic tissues under normal conditions (6,7); how the intestinal bacteria influence the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer is unclear. Probiotics are live microorganisms that confer a health benefit on consumers when they are administered in adequate quantities (8). Probiotics are associated with various health benefits, including the conditioning of the intestinal microflora, suppression of excess allergic responses and tumor-suppressive effects (9-11). Previous reports have suggested that certain probiotics exhibit tumor-suppressive effects in colorectal cancer (12), breast cancer (13) and pancreatic cancer (14) in vitro and in vivo in animal models, indicating that probiotic bacteria may be used safely and effectively for cancer therapy. However, the tumor-suppressive effects of probiotics are influenced by the bacterial culture condition (15) and the various individual intestinal conditions shaped by food particles and medicines (16), resulting in difficulties in achieving stable treatment effects.
Conversely, certain reports have indicated that the molecules derived from probiotics have tumor-suppressive effects. Antimicrobial peptides m2163 and m2386, identified from Lactobacillus casei (L. casei), induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells (17). Our previous study reported that inorganic polyphosphate exhibited tumor-suppressive effects via the activation of ERK (18). Our previous studies also revealed that ferrichrome, identified from L. casei ATCC334, exhibited tumor-suppressive effects in colorectal cancer cells and gastric cancer cells through the induction of DNA damage inducible transcript 3 (DDIT3)-mediated apoptosis (19,20). Ferrichrome was identified as a bacterial iron-chelating agent, as bacteria acquire Fe3+ from the external environment (21). These studies demonstrated the antitumor functions of ferrichrome for the first time in host mammal cells. Notably, the antitumor activity of ferrichrome was demonstrated to be stronger than that of conventional antitumor drugs, including 5-FU and cisplatin, in colorectal cancer cells. Thus, probiotic-derived ferrichrome may exhibit antitumor effects in refractory gastrointestinal cancers, including pancreatic cancer.
In the present study, it was revealed that ferrichrome exhibited an antitumor effect in pancreatic cancer in vitro and in a mouse xenograft model in vivo, through modulation of the cell cycle and apoptosis, even in 5-FU-resistant (FUR) cells, with no significant adverse events, indicating that probiotic-derived ferrichrome is an attractive candidate antitumor agent that may be applied in the treatment of refractory pancreatic cancer.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Human cancer cell lines were cultured in RPMI-1640 (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation) [PANC-1 (American Type Culture Collection), PK-1 (Cell Resource Center for Biomedical Research) and PCI-43 (provided by Dr Hiroshi Ishikura at Hokkaido University) (22)] or high-glucose Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation) [SUIT-2 (Health Science Research Resources Bank) and MIA PaCa-II (JCRB Cell Bank)] supplemented with 10% (vol/vol) FBS (Biosera), 2 mM L-glutamine, 50 U/ml penicillin and 50 µg/ml streptomycin in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 37°C.
Animal experiments
The animal experimental procedures performed were approved by the Animal Experiments Committee of Asahikawa Medical University based on guidelines for the protection of animals published by The Japanese Association of Laboratory Animal Facilities of National University Corporations.
Reagents
Ferrichrome (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) was dissolved in distilled water to a concentration of 5 mg/ml, which was used as a stock solution. It was stored at 4°C and used for assays within 6 months. 5-FU (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) was dissolved in DMSO to a concentration of 10 mg/ml, which was used as a stock solution. It was stored at -20°C and = used for assays within 6 months. Pifithrin-µ (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) was dissolved by DMSO to a concentration of 10 mg/ml, which was used as a stock solution. It was stored at 4°C and used for assays within 6 months. Each reagent was diluted in DMEM and the cells were treated.
Sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay
The cells were seeded on 96-well microplates at 0.25-1.0×104 cells/well at 24 h prior treatment with the test reagents. An equivalent volume of solvent (distilled water or DMSO) was used to treat control cells. The growth inhibition effects of ferrichrome and 5-FU were evaluated in the range of 1-1,000 µg/ml and 1-10 µg/ml, respectively. Cells were treated with ferrichrome (0.2 µg/ml) and 5-FU (0.2 µg/ml) in a combination study. Then, the cells were fixed in 5% trichloroacetic acid for 1 h at 4°C and washed 4 times in distilled water. The microplates were then dehydrated at room temperature, stained with 0.057% (wt/vol) SRB powder/distilled water (100 µl/well) at room temperature for 30 min, washed 4 times in 0.1% acetic acid and re-dehydrated at room temperature. The stained cells were lysed in 10 mM Tris-buffer and the optical density was measured at 510 nm.
Flow cytometry
The cells were seeded in 60-mm dishes at 0.5×106 cells/dish. After incubation in ferrichrome (1 µg/ml)-containing medium for 2 days at 37°C, the cells were trypsinized, washed twice with PBS, and fixed in a mixture of 0.5 ml PBS and 2 ml ethanol (100%) at 4°C (the final concentration of ethanol was 80%) overnight. The fixed cells were incubated with 25 U/ml RNase (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation) at room temperature for 20 min, and propidium iodide solution was added at a final concentration of 50 µg/ml at room temperature for 10 min. The cell cycle was assessed via flow cytometry using a BD FACSCalibur™ (BD Biosciences); 20,000 events were obtained from each sample. The acquired data were analyzed using CELLQuest Pro™ (v5.2.1; BS Biosciences) and ModFitLT™ (v3.0; Verity Software House, Inc.) software.
TUNEL staining
The SUIT-2 cells were plated on 3.5-cm dishes (2×105 cells/plate) and incubated in 1 µg/ml of ferri-chrome or 3 µg/ml of 5-FU-containing medium for 3 days at 37°C. Control cells were treated with an equal volume of solvent (distilled water or DMSO). The dishes were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 1 h and washed extensively with PBS. The dishes were stained using an in situ Cell Death Detection kit with TMR red (Roche Diagnostics) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The DNA end labelling reaction was performed at 37°C for 1 h. The cells were mounted with an anti-fade mounting medium (Vector Laboratories, Inc.), and the TUNEL-positive cells were visualized via fluorescence microscopy (Keyence Corporation). The TUNEL-positive cells were counted in 6-8 random fields (magnification, ×200).
Western blotting
Total protein (TP) was extracted from samples using a mammalian cell extraction kit (BioVision, Inc.). The protein concentration was determined using a Bradford protein assay according to the manufacturer's instructions (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). Equal quantities of protein (10-30 µg/lane) were resolved via 12.5% SDS-PAGE, blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane and then blocked in SuperBlock™ T20 (PBS or TBS) Blocking Buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at room temperature for 1 h. The blots were incubated overnight at 4°C with the following primary antibodies: Phosphorylated (p)-p53 (1:1,000; cat. no. ab1431; Abcam), p53 (1:500; cat. no. 506135; Calbiochem; Merck KGaA), cyclin B1 (1:1,000; cat. no. ab32053; Abcam), securin (1:1,000; cat. no. ab79546; Abcam), cyclin D1 (1:500; cat. no. CC12; Calbiochem; Merck KGaA), cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B; 1:1,000; cat. no. PAB10300; Abnova) and cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP; 1:1,000; cat. no. 5625; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.). The blots were washed in PBS-0.5% Tween 20 (T-PBS) or TBS-0.5% Tween 20 (T-TBS), incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:1,000; cat. nos. HAF007 and HAF008; R&D Systems, Inc.) at room temperature for 1 h, washed in T-PBS or T-TBS, and then developed using a SuperSignal™ West Pico enhanced chemiluminescence system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Densitometry was performed using ImageJ v1.8.0 (National Institutes of Health). The averaged protein expression was normalized to actin expression (1:5,000; cat. no. 612656; BD Biosciences).
ELISA
Whole blood was collected from the inferior vena cava of ferrichrome-treated mice. After collection, 3.2% EDTA was added to the blood, and plasma was retrieved via centrifugation at 2,500 × g for 10 min at room temperature. The plasma ferritin levels were determined using a Mouse Ferritin ELISA kit (cat. no. 41-FERMS-E01; ALPCO) according to manufacturer's instructions.
Immunocytochemistry
Cells were plated on 4-well plastic chamber slides (2×105/well), which were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 1 h, washed extensively with PBS, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 and blocked in SuperBlock T20 (PBS) Blocking Buffer at room temperature for 1 h. The slides were then sequentially incubated with anti-α-tubulin antibody (1:100; cat. no. NB100-690; Novus Biologicals, LLC) at 4°C overnight, washed with PBS and incubated with Alexa Fluor® 594-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:100; cat. no. A11032; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at room temperature for 1 h. The nuclei were counter-stained with Hoechst 33342 (1:2,000; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at room temperature for 5 min. The cells were mounted with an anti-fade mounting medium, and the immunofluorescence was visualized using a fluorescence microscope (magnification, ×1,200; Keyence Corporation) in 11 (control) and 10 (ferrichrome) fields.
Animal experiments
The protocols of the animal experiments were approved by the Asahikawa Medical University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. All aspects of animal welfare were considered, including efforts to minimize suffering and distress, use of analgesics or anesthetics, and special housing conditions. The sacrifice of animals maintained for scientific research was determined according to the completion or discontinuation of the experimental plan. All animals were treated with the test reagents for 10-14 days and then euthanized. A total of 48 BALB/c nude mice and 15 BALB/c mice (male; age, 6-10 weeks; weight, 20-25 g) housed at 20-25°C with 30-60% humidity under a 12:12 h light/dark cyclewith ad libitum access to food and water were used for the xenograft experiment and safety test, respectively. Animal health and behavior were monitored on the drug treatment day. For sacrifice, 4-5% isoflurane was administered via inhalation to mice, and then cervical dislocation was performed under anesthesia. The death of mice was confirmed by monitoring respiratory and cardiac arrest. The maximum loss of body weight of mice observed during the study was 5.6%.
Xenografts
Pancreatic cancer cells (SUIT-2 cells, 1×106 cells; FUR SUIT-2 cells, 2×106 cells) were injected subcutaneously into the back of male BALB/c nude mice (6 weeks old). PBS (n=5, 6 and 8 for the studies evaluating the effects of ferrichrome compared with PBS, the effects of ferrichrome compared with 5-FU and the effects of ferrichrome on FUR SUIT-2 cells, respectively), ferrichrome (10 mg/kg; n=5, 6 and 6, respectively) or 5-FU (10 mg/kg; n=6) treatments were intraperitoneally administered after the injection of SUIT-2 cells. The administration of each drug was started on the day after transplantation, and the durations of treatment with each drug were 12 days (every 2 days), 8 days (daily) and 10 days (daily) for the studies evaluating the effects of ferrichrome compared with PBS, the effects of ferrichrome compared with 5-FU and the effects of ferrichrome on FUR SUIT-2 cells, respectively. The tumor volume was calculated by the following formula: Tumor volume (mm3) = 0.5 × (major diameter) x (minor diameter)2.
Transcriptome analysis
Total RNA from SUIT-2 cells was extracted using an RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's protocols. RNA libraries were generated using an Ion Total RNA-Seq kit v2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The RNA libraries were then processed for emulsion PCR using an Ion OneTouch™ system and an Ion OneTouch 200 Template kit v3 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Template-positive Ion Sphere™ particles were enriched and purified for the sequencing reaction with an Ion OneTouch ES system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The template-positive Ion Sphere Particles were then applied on Ion PI™ Chips (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), and a high throughput sequencing reaction was performed using an Ion Proton™ Semiconductor sequencer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). All of the sequencing data were mapped on a human reference genome sequence (GRCh38/hg38), the expression analysis and gene functional annotation analysis for each sample was imported into CLC Genomics Workbench software v9.0.1 (CLC bio; Qiagen Digital Insights), and significant differences between the samples were determined using unpaired Student's t-tests.
Construction of FUR SUIT-2 cells
FUR SUIT-2 cells were obtained by the repeated treatment of non-FUR SUIT-2 cells with 5-FU as previously described (23). The acquisition of 5-FU resistance was confirmed by an SRB assay.
Histopathology
BALB/c mice (PBS, n=5; ferrichrome, n=5) were treated with PBS or ferrichrome (10 mg/kg) administered daily via tail vein injection for 14 days. The mice were sacrificed after the administration of ferrichrome, their organs were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature overnight. The fixed tissue was embedded in paraffin and cut into 4-µm thick sections, stained with hematoxylin at room temperature for 15 min and eosin at room temperature for 30 sec, and then assessed under a light microscope (magnification, ×200 or ×400). The histological changes were assessed in 3 fields of view.
Complete blood count (CBC)
BALB/c mice (PBS, n=5; ferri-chrome, n=5; 5-FU, n=5) were treated with PBS, ferrichrome (10 mg/kg) or 5-FU (10 mg/kg) administered daily via tail vein injection for 14 days. The whole blood of mice was collected from the inferior vena cava. After collection, 3.2% EDTA was mixed with the whole blood to prevent coagulation. CBC was performed by the New Drug Research Center, Inc.
Serum biochemistry
Whole blood was collected from the inferior vena cava, subjected to centrifugation at 2,500 × g for 10 min at room temperature, and then the serum of PBS, ferrichrome or 5-FU-treated mice was obtained. The serum samples were kept at -80°C and biochemistry [creatinine (CRE), TP, albumin (ALB), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), iron, sodium, potassium, chlorine, calcium] was performed by Oriental Yeast Co., Ltd.
Statistical analysis
The assay data were analyzed using Student's unpaired t-test in two-group comparisons (control and ferrichrome) and Williams test (dose-dependent effects of ferrichrome). To analyze the effects of treatments (ferrichrome or 5-FU), one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test was performed. The datasets where measurements were collected at multiple time points, and the effects of single and combination treatment of ferrichrome and 5-FU were assessed using mixed or between-subjects two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's test and two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test, respectively. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Ferrichrome inhibits pancreatic cancer progression
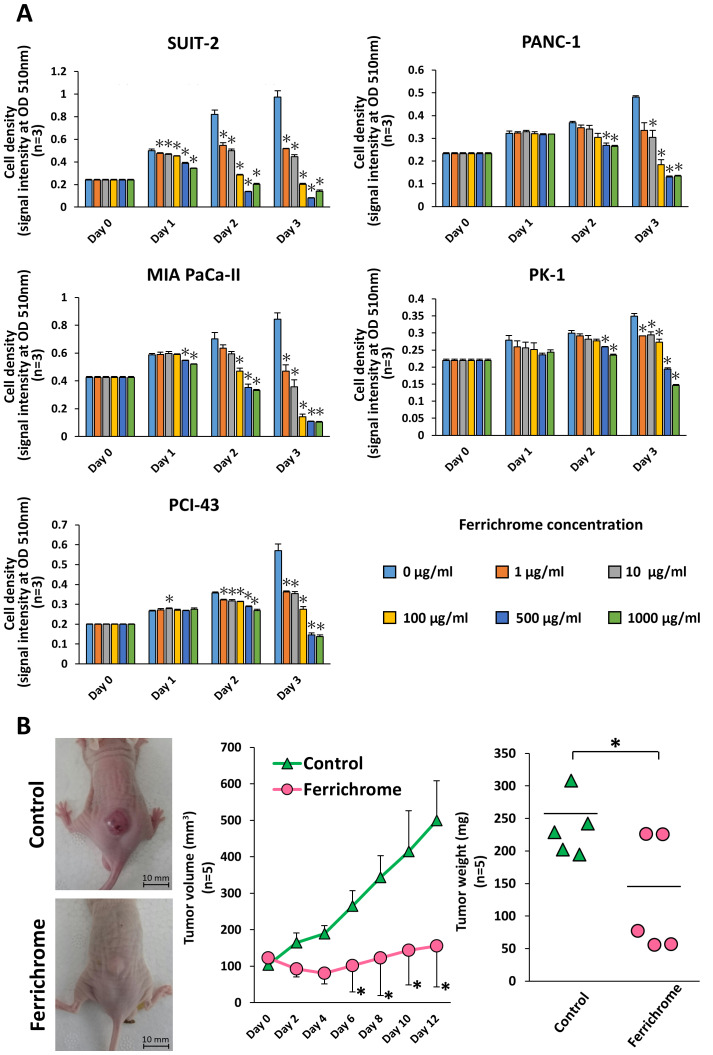
To investigate the tumor-suppressive effects of ferrichrome in pancreatic cancer cells, SUIT-2, PANC-1, MIA PaCa-II, PK-1 and PCI-43 cells were treated with ferrichrome (Fig. 1A). An SRB assay revealed that ferrichrome significantly inhibited cell growth in a dose-dependent manner in these pancreatic cancer cell lines, most notably in SUIT-2, MIA PaCa-II and PCI-43 cells. To assess the tumor-suppressive effects of ferrichrome in vivo, SUIT-2 cells were transplanted into nude mice, and ferrichrome was intraperitoneally administered. Tumor volume and weight were significantly decreased in animals treated with ferrichrome (Fig. 1B). These data indicated that ferrichrome exerted a tumor-suppressive effect in pancreatic cancer cells.
Figure 1.
Ferrichrome exhibits antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo. (A) Sulforhodamine B assay showing the growth suppression effects of ferrichrome in SUIT-2, PANC-1, MIA PaCa-II, PK-1 and PCI-43 cells (n=3). *P<0.05 vs. 0 µg/ml. (B) Ferrichrome exerted antitumor effects in a mouse xenograft model of pancreatic cancer cells. Ferrichrome was dissolved in PBS, and 10 mg/kg of ferrichrome or PBS was administered intraperitoneally to BALB/c nude mice transplanted with 1×106 SUIT-2 cells (n=5). The tumor volume and weight of the ferrichrome group were significantly decreased compared with the PBS group. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using Student's t-test, Williams test or two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test. *P<0.05 vs. Control or as indicated. OD, optical density.
Ferrichrome inhibits the progression of pancreatic cancer cells via p53-mediated cell cycle regulation
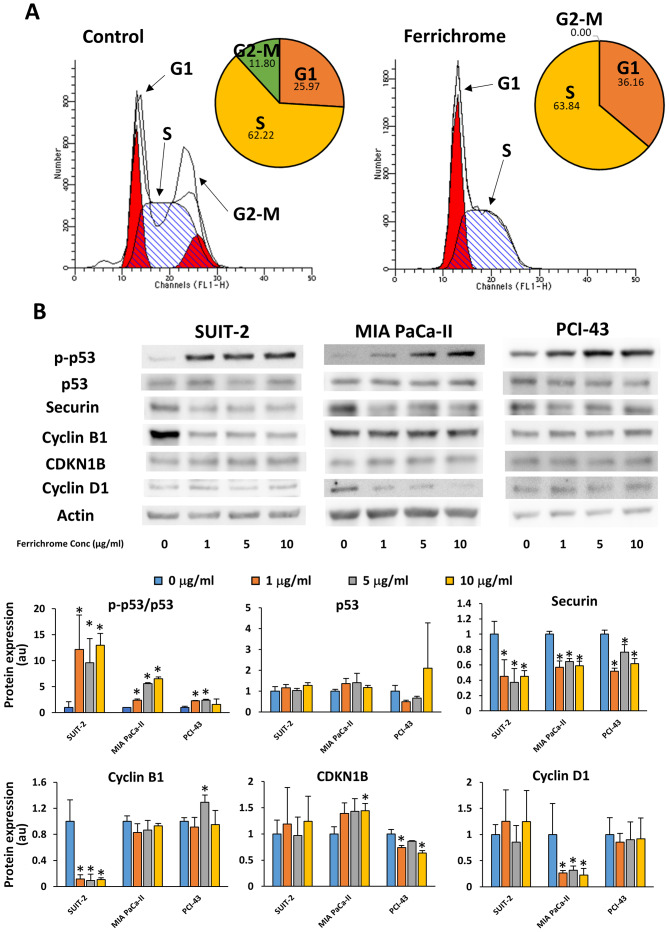
Flow cytometry and immunostaining were performed to analyze the effects of ferrichrome on cell cycle progression. These assays showed that the cell cycle was arrested in the S phase, without chromosome misalignment in 1 µg/ml ferrichrome-treated SUIT-2 cells (Figs. 2A and S1). Western blotting revealed that 1, 5 and 10 µg/ml ferrichrome significantly increased the phosphorylation of p53, and decreased the expression of securin and cyclin B1 in SUIT-2 cells (Fig. 2B). However, CDKN1B and cyclin D1, which are associated with the progression of cells from the G1 phase to the S phase (24), were not affected by ferrichrome treatment, suggesting that ferrichrome inhibited the progression of the cells to the G2-M phase but not DNA synthesis in SUIT-2 cells. To further determine whether the antitumor effects of ferrichrome were mediated by p53 activation in other ferrichrome-sensitive pancreatic cancer cells, phosphorylation of p53 was assessed in MIA PaCa-II and PCI-43 cells. Western blotting analysis indicated that p53 was activated in a dose-dependent manner without increasing total p53 levels, whereas the downregulation of cyclin D1 and CDKN1B was detected in MIA PaCa-II and PCI-43 cells, respectively (Fig. 2B). These findings indicated that p53 activation was required for ferrichrome to exert its antitumor effects, and the roles of other cell cycle-associated molecules were dependent upon the characteristics of the pancreatic cancer cells.
Figure 2.
Ferrichrome inhibits the initiation of the G2-M phase in pancreatic cancer cells. (A) Flow cytometry showing that after SUIT-2 cells were accumulated in the G1 and S phase of the cell cycle by the ferrichrome treatment. (B) Western blot analysis of p-p53, securin, cyclin B1, CDKN1B and cyclin D1 after 48 h of ferrichrome treatment in pancreatic cancer cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Data were analyzed via Williams test. *P<0.05 vs. 0 µg/ml. CDKN1B, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B; p, phosphorylated.
Ferrichrome induces cancer cell apoptosis via upregulation of the p53 pathway
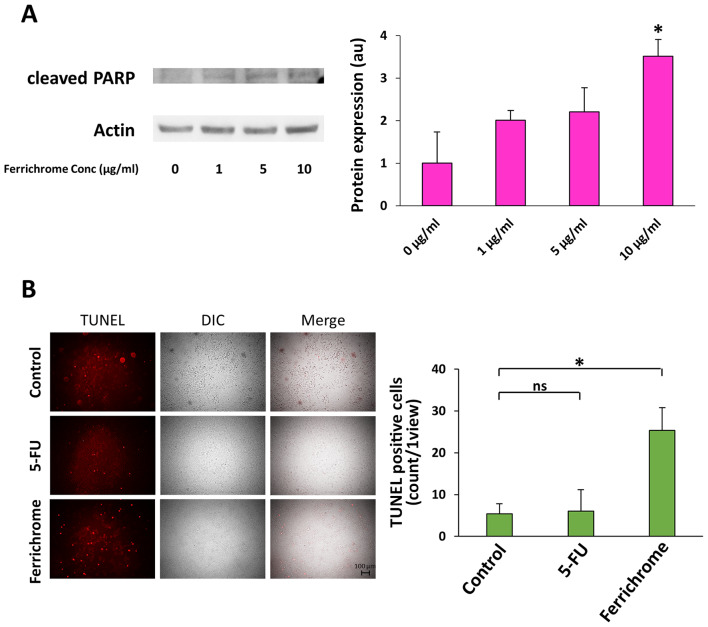
Western blotting showed that cleaved PARP levels in 10 µg/ml ferrichrome-treated SUIT-2 cells were significantly increased compared with control cells (Fig. 3A). TUNEL staining indicated that DNA fragmentation was induced by 1 µg/ml ferrichrome to a much greater extent than by 3 µg/ml 5-FU treatment (Fig. 3B). To clarify whether the growth suppression induced by ferrichrome treatment was mediated by p53 activation, SUIT-2 cells were treated with pifithrin-µ, which inhibits p53 function by directly binding to the DNA-binding domain of p53 (25). The growth suppression induced by 5 µg/ml ferrichrome treatment was reduced from 72 to 35% by treatment with 1 µg/ml pifithrin-µ (Table I), suggesting that ferrichrome suppressed pancreatic cancer cell progression via the upregulation of p53-mediated transcription of mRNAs. A transcriptome analysis was performed to further investigate the induction of p53-related mRNAs by ferrichrome treatment in pancreatic cancer cells. A total of 30 mRNAs that are directly regulated by activated p53 were significantly (>2-fold) induced in 10 µg/ml ferrichrome-treated SUIT-2 cells in comparison to control cells (Table II), as well as 48 apoptosis-inducible factors (Table SI) and 10 iron-related genes (Table III). These findings suggested that ferrichrome exhibited antitumor effects via the upregulation of p53-mediated mRNA transcription.
Figure 3.
Ferrichrome induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. (A) Western blotting revealing that cleaved PARP was significantly increased after 48 h of 10 µg/ml ferrichrome treatment. (B) TUNEL staining indicated the that 1 µg/ml ferrichrome induced apoptosis more strongly than 3 µg/ml 5-FU. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments or fields. Data were analyzed via Williams test or one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test. *P<0.05 vs. 0 µg/ml or as indicated. PARP, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; DIC, digital image correlation; ns, not significant.
Table I.
Growth-inhibiting effect of 5 µg/ml ferrichrome.
| Ferrichrome (µg/ml) | Pifithrin-µ (µg/ml) | Growth inhibition effect (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 100±3.2 |
| 5 | 0 | 72±3.4 |
| 5 | 0.1 | 60±4.2a |
| 5 | 0.5 | 57±1.4a |
| 5 | 1 | 35±9.4a |
P<0.05 vs. 0 µg/ml.
Table II.
List of mRNAs with significantly altered expression in ferrichrome-treated SUIT−2 cells.
| Gene | Fold change | P-value |
|---|---|---|
| ITGAM | 2.29 | 1.99×10−2 |
| ISG20 | 2.21 | 6.10×10−3 |
| DUSP5 | 2.04 | 8.34×10−4 |
| KLF7 | 2.03 | 4.51×10−3 |
| TMEM29 | 2.31 | 2.88×10−2 |
| JDP2 | 3.69 | 4.32×10−3 |
| PDGF-R-β | 2.41 | 1.12×10−3 |
| G6PE | 2.03 | 2.62×10−2 |
| ARTN | 2.09 | 4.00×10−2 |
| LIPIN1 | 2.04 | 8.54×10−5 |
| TEL2 | 3.24 | 8.59×10−4 |
| Syntaxin 11 | 3.51 | 6.04×10−3 |
| SLC7A11 | 2.75 | 1.59×10−4 |
| Syk | 2.05 | 2.90×10−2 |
| ABCC11 | 2.56 | 2.82×10−2 |
| DENND2C | 2.20 | 5.02×10−4 |
| FGF18 | 2.58 | 4.50×10−2 |
| DAB1 | 2.21 | 5.14×10−3 |
| CYP3A7 | 6.20 | 3.17×10−2 |
| iASPP | 2.06 | 6.93×10−3 |
| BNIPL | 2.07 | 4.71×10−2 |
| FLJ11259 | 2.94 | 6.66×10−4 |
| Gdap1 | 2.48 | 9.30×10−3 |
| NF-κB2 (p100) | 2.05 | 2.55×10−3 |
| TRUNDD(TNFRSF10D) | 3.10 | 1.47×10−4 |
| VEGF-A | 2.57 | 4.17×10−3 |
| SORBS1 | 2.07 | 3.71×10−6 |
| Keratin 15 | 3.93 | 2.98×10−4 |
| ATF-3 | 2.36 | 9.41×10−3 |
| REDD1 | 5.10 | 6.19×10−4 |
Table III.
Altered expression of iron-related genes in ferrichrome-treated SUIT-2 cells.
| Gene | Fold change | P-value |
|---|---|---|
| CYP7A1 | 14.78 | 6.40×10−3 |
| MIOX | 7.97 | 1.11×10−2 |
| CYP3A7-CYP3A51P | 6.20 | 3.17×10−2 |
| RHAG | 2.67 | 1.54×10−2 |
| RFESD | 2.16 | 3.53×10−2 |
| CYP2C18 | -2.04 | 4.86×10−3 |
| MUTYH | -2.12 | 4.50×10−3 |
| NOS3 | -2.53 | 4.29×10−2 |
| SLC40A1 | -3.61 | 7.75×10−3 |
| EXO5 | -3.78 | 1.91×10−4 |
Ferrichrome inhibits tumor progression of 5-FU-resistant SUIT-2 cells as well as 5-FU-non-resistant SUIT-2 cells
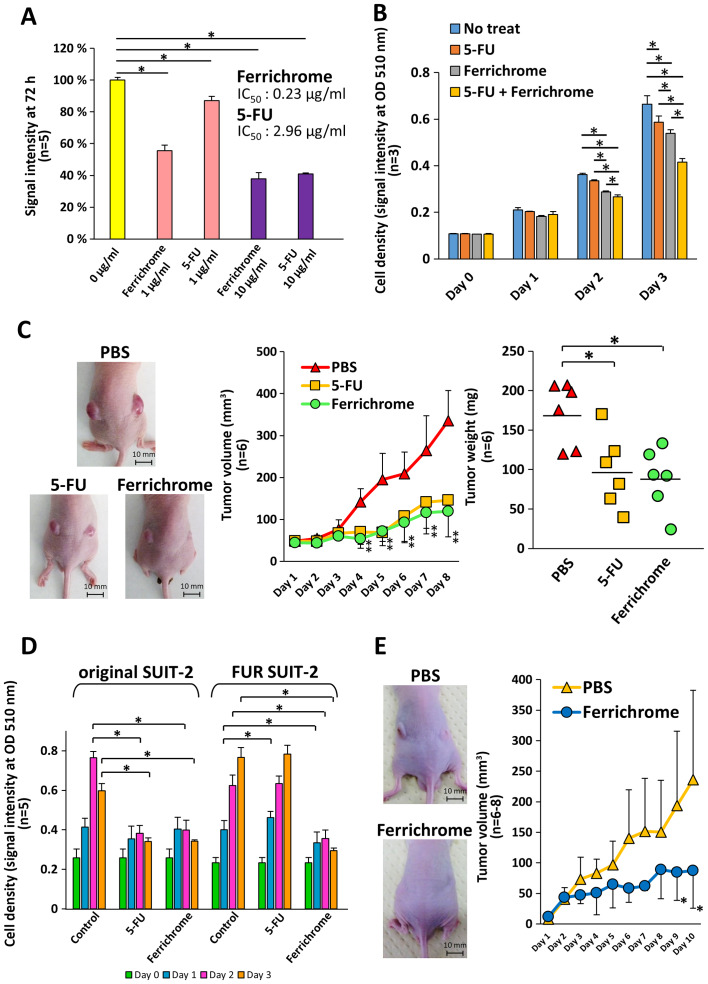
To compare the tumor-suppressive effects of ferrichrome and 5-FU, SUIT-2 cells were treated with ferrichrome or 5-FU. Growth inhibition was detected following 2 days treatment with ferrichrome (IC50: 0.23 µg/ml) or 5-FU (IC50: 2.96 µg/ml), and the tumor-suppressive effects of the molecules were not significantly different (Fig. 4A). The therapeutic effects of the combined treatment of 0.2 µg/ml of ferrichrome and 0.2 µg/ml of 5-FU were also assessed. Low-dose ferrichrome or 5-FU mildly suppressed tumor cell growth, whereas the combination of these agents synergistically exerted an antitumor effect in SUIT-2 cells (Fig. 4B). To determine the tumor-suppressive effects in vivo, a mouse xenograft model was generated via the transplantation of 1×106 of SUIT-2 cells, and ferrichrome (10 mg/kg) or 5-FU (10 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally administered. The tumor volumes of the ferrichrome- and 5-FU-treated groups were significantly reduced in comparison to the PBS-treated group from 4 days after treatment onwards (Fig. 4C).
Figure 4.
Ferrichrome exhibits antitumor effects in FUR SUIT-2 cells. (A) SRB assay showing dose-dependent effects of ferrichrome (IC50: 0.23 µg/ml) and 5-FU (IC50: 2.96 µg/ml) on SUIT-2 cells (n=5). (B) Combination effect of ferrichrome and 5-FU in SUIT-2 cells (n=3). (C) Ferrichrome exerted anti-tumor effects equal to or stronger than 5-FU in a mouse xenograft model (n=6). Ferrichrome and 5-FU were dissolved in PBS, and 10 mg/kg of ferrichrome, PBS or 10 mg/kg of 5-FU was administered intraperitoneally every day for 8 days to BALB/c nude mice transplanted with 1×106 SUIT-2 cells. The maximum tumor volume and diameter of the transplanted tumor were 684 mm3 and 11.7 mm (PBS), 303 mm3 and 9.1 mm (5-FU), and 194 mm3 and 8.4 mm (ferrichrome), respectively. The maximum combined tumor diameters were 22.8 mm (PBS), 18.1 mm (5-FU) and 16.3 mm (ferrichrome). (D) SRB assay demonstrating that 1 µg/ml ferrichrome significantly reduced tumor cell growth in both 5-FU-sensitive and FUR SUIT-2 cells after 2 days of treatment (n=5). (E) Ferrichrome suppressed tumor progression in FUR SUIT-2 cell-transplanted mice (n=6-8). The maximum tumor volume and diameter of the transplanted tumors were 468 mm3 and 11.3 mm (PBS) and 213 mm3 and 8.2 mm (ferrichrome), respectively. The maximum combined tumor diameters were 17.6 mm (PBS) and 14.9 mm (ferrichrome). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed via one-way, two-way or mixed ANOVA followed by Tukey's or Bonferroni's post hoc tests. *P<0.05 vs. PBS or as indicated. 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; FUR, 5-FU-resistant; SRB, sulforhodamine B; OD, optical density.
Next, FUR SUIT-2 cells were constructed to determine the antitumor effects of ferrichrome in antitumor agent-resistant cells. An SRB assay showed that the growth of FUR SUIT-2 cells was not inhibited by treatment with 3 µg/ml 5-FU, while growth was significantly inhibited by treatment with 1 µg/ml ferrichrome, to the same extent as in the original SUIT-2 cells (Fig. 4D). To assess the tumor-suppressive effects of ferrichrome in FUR cells in vivo, 2×106 FUR SUIT-2 cells were transplanted into nude mice, and PBS or ferrichrome (10 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally administered daily. The tumor volume in the ferrichrome-treated mice was significantly reduced compared with the PBS-treated mice at 9 days after the start of treatment (Fig. 4E). These data indicated that ferrichrome exhibited tumor-suppressive effects in vitro and in vivo, even in FUR cells, and suggested that the mechanism of action differed from that of 5-FU.
Influence of ferrichrome on the biochemistry and pathological findings of organs in normal mice
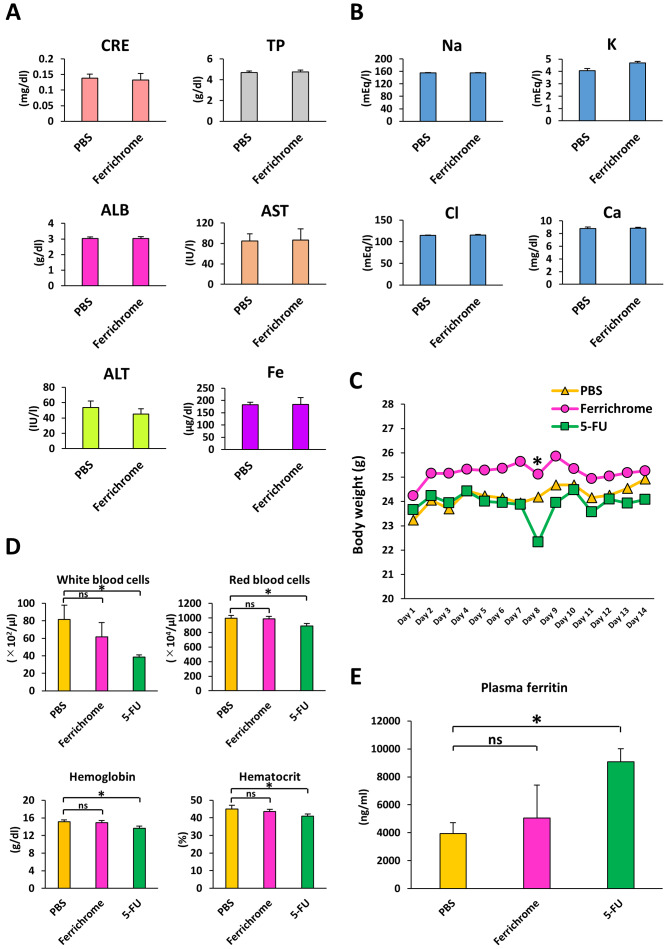
To investigated hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity and electrolyte imbalance induced by to ferrichrome treatment, PBS or ferrichrome (10 mg/kg) was administered daily via tail vein injection for 14 days. There were no changes in the test values of CRE, TP, ALB, AST, ALT, iron or electrolytes between the control and ferrichrome groups (Fig. 5A and B). Ferrichrome treatment was not associated with pathological changes of the organs, including the heart, kidney, small and large intestines, skin, liver, brain, and bone marrow (Fig. S2).
Figure 5.
Ferrichrome does not affect serum biochemistry. (A) Biochemical analysis of CRE, TP, ALB, AST, ALT and iron. (B) Biochemical analysis of serum electrolytes. (C) Body weights of ferrichrome (10 mg/kg)- or 5-FU (10 mg/kg)-treated mice were not significantly altered following an administration period of 14 days. (D) Complete blood count was not significantly altered in the ferrichrome group, but the white and red blood cell, hemoglobin and hematocrit values were significantly reduced in the 5-FU group. (E) Plasma ferritin levels were significantly increased in the 5-FU group but not in the ferrichrome group. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using Student's t-test, or one-way or mixed ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test. *P<0.05 vs. PBS or as indicated. CRE, creatinine; TP, total protein; ALB, albumin; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; ns, not significant.
To compare the safety of ferrichrome to 5-FU in vivo, body weight, survival rates and CBC were assessed in mice treated with PBS, ferrichrome (10 mg/kg) or 5-FU (10 mg/kg) via daily tail vein injection for 14 days. No cases of animal mortality were observed, and body weight was not markedly changed by ferrichrome or 5-FU treatment (Fig. 5C). The CBC was not significantly altered in the ferrichrome group compared with the PBS group, whereas the leukocyte, erythrocyte, hemoglobin and hematocrit counts were significantly reduced in the 5-FU group compared with the PBS group (Fig. 5D). To assess the presence of tissue injury and ferric abnormality, plasma ferritin was evaluated. Plasma ferritin levels were significantly increased in the 5-FU group compared with the PBS group, but not in the ferrichrome group (Fig. 5E). These data indicated that ferrichrome did not induce anemia, myelosuppression or tissue injury in the therapeutic range in mice. These findings suggested that ferrichrome exerted tumor-suppressive effects in pancreatic cancer cells with no notable adverse events.
Discussion
The present study revealed for the first time, to the best of the authors' knowledge, that probiotic-derived ferrichrome exhibited antitumor effects in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Notably, the tumor-suppressive effects of ferrichrome were equal to those of 5-FU in SUIT-2 cells and superior to those of 5-FU in FUR cells, indicating the strong efficacy of ferrichrome in the treatment of chemotherapy-naive as well as FUR pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, daily intravenous injection of ferrichrome was not associated with adverse events in the organs of mice. The results of the present study suggested that probiotic-derived ferrichrome may a useful and safe agent for the treatment of pancreatic cancer, which is frequently resistant to existing antitumor drugs.
A previous study indicated that microbiome diversity is strongly associated with the progression of gastrointestinal cancers, including pancreatic cancer (6,7). Michaud et al (26) and Fan et al (27), reported high levels of Porphyromonas gingi- valis in patients with pancreatic cancer. Pushalkar et al (28) found that Proteobacteria was the major genus of gut bacteria in patients with pancreatic cancer. Certain bacteria have recently been detected in pancreatic cyst fluids in intraductal papillary mucosal neoplasms, as well as non-neoplastic cysts (29). These microbial modifications are proposed to induce dysbiosis, thereby promoting tumor progression due to immunological abnormalities (30). In contrast, the present study using pancreatic cancer cells reported that probiotic-derived ferrichrome directly suppressed tumor progression, suggesting that probiotics stably exert an antitumor effect regardless of intestinal conditions or immunological status. Further analyses are required to identify other probiotic antitumor molecules and clarify the role of these molecules, thereby uncovering novel mechanisms underlying the antitumor functions of probiotics in pancreatic cancer, as well as other organ cancers.
Flow cytometry revealed that ferrichrome inhibited the entry of pancreatic cancer cells into the G2-M phase. Likewise, TUNEL staining and western blotting of cleaved PARP showed that ferrichrome induced apoptosis in SUIT-2 cells. Subsequently, the status of cell cycle-associated molecules, including p53, securin, CDKN1B, and cyclins B1 and D1, were examined, and ferrichrome treatment was determined to significantly induce the phosphorylation of p53, and downregulation of securin and cyclin B1, but not CDKN1B or cyclin D1, which are associated with progression to the G1 phase (24). p53 activation, but not reductions in cyclin B1, was observed in other pancreatic cancer cells (MIA PaCa-II and PCI-43), indicating that activation of p53 was a key mechanism via which ferrichrome exerted its antitumor effects, and that downstream events of p53 activation depended on the characteristics of pancreatic cancer cells. Notably, the p53 inhibitor pifithrin-µ repressed the antitumor effects of ferrichrome. Furthermore, transcriptome analysis showed that the expression of p53-associated mRNAs was altered by ferrichrome treatment. These data clearly indicated that p53 phosphorylation mediated the antitumor effects of ferrichrome in pancreatic cancer cells. It is widely reported that p53 is a pivotal gatekeeper molecule of the cell cycle in various types of mammalian cells, including pancreatic cells (31,32). It has also been reported that an ER-associated molecule, scotin, induced p53 activation under excessive endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, thereby inducing cell apoptosis (33). Our previous studies have reported that ferrichrome upregulated ER stress, leading to the activation of the JNK-DDIT3 pathway, and subsequent induction of apoptosis in colorectal and gastric cancer cells (19,20). Collectively, probiotic-derived ferrichrome is hypothesized to expose cancer cells to ER stress, and thereby induce apoptosis via the activation of ER stress-associated pathways, including JNK-DDIT3 and/or p53, which is a novel mechanism of the antitumor function of probiotic bacteria.
An SRB assay indicated that the antitumor effects of ferri-chrome were not completely abolished by the p53 functional inhibitor pifithrin-µ. Pifithrin-µ was administered at 1 µg/ml as higher concentrations completely inhibited the growth of SUIT-2 cells. The p53-inhibitory effect of pifithrin-µ was observed to be partial at 1 µg/ml, and p53 with its original properties as a tumor suppressor gene was activated by ferrichrome treatment, resulting in the p53 pathway being partially functional during ferrichrome treatment. It was hypothesized that other pathways associated with cell growth may also continue to function under ferrichrome treatment. Transcriptome analysis also indicated that ferrichrome induced the expression of apoptosis-inducible factors, including CHAC1 and DDIT4, suggesting that other pathways in addition to the p53 pathway were activated and may induce tumor-suppressive effects following ferrichrome treatment of pancreatic cancer cells.
Transcriptome and gene functional annotation analysis of ferrichrome-treated SUIT-2 cells showed that 319 genes were iron-related, and that the expression of 10 iron-related genes was significantly altered by ferrichrome treatment. As ferrichrome interacts with iron ions, it is important to assess the relationship between the antitumor effects of ferrichrome and expression changes in these 10 genes. These molecules are classified by CLC Genomics Workbench software as 'drug-degrading enzymes containing iron ions' (CYP7A1, CYP3A7-CYP3A51P, CYP2C18, MIOX and RFESD), 'indicators of Rh blood type' (RHAG), 'iron transporters' (SLC40A1), 'nitric oxide synthases' (NOS3) and 'DNA damage repair molecules' (MUTYH and EXO5). Previous studies reported that the downregulation of SLC40A1, NOS3 and MUTYH (34-37) promoted tumor cell progression, suggesting that these genes worked as tumor-suppressor genes. In the present study, it was shown that ferrichrome induced antitumor effects in pancreatic cancer cells, whereas these tumor-suppressive genes were downregulated. Therefore, changes in these iron-associated genes are not essential for ferrichrome to function, suggesting that the contributions of iron-related genes are secondary in ferrichrome-treated cells.
It was shown in the present study that the antitumor effects of ferrichrome were equal to or greater than those of 5-FU via intraperitoneal injection. To assess the safety of ferrichrome in pancreatic cancer treatment, the CBC, plasma ferritin and serum biochemical test values (CRE, TP, ALB, AST, ALT, iron, electrolytes) of mice treated by ferrichrome or 5-FU via intravenous injection for 14 days were checked. The test values of ferrichrome-treated mice did not show any abnormal changes. Of note, the CBC was not markedly altered by the intravenous injection of ferrichrome; however, the leukocyte, erythrocyte, hemoglobin and hematocrit values of 5-FU-treated mice were significantly decreased. Plasma ferritin levels were significantly increased in the 5-FU group but not in the ferrichrome group, suggesting that ferrichrome did not influence ferritin production. Likewise, abnormal histological changes were not detected in the ferrichrome-treated mice. These data indicated that the safety and therapeutic efficacy of ferrichrome were superior to those of classical antitumor drugs, such as 5-FU.
In FUR SUIT-2 cells, ferrichrome inhibited growth to the same degree as was observed in 5-FU-sensitive SUIT-2 cells. In cancer cells, 5-FU is known to bind to thymidylate synthase, inhibit DNA synthesis and thereby inhibit progression to the S phase (38). The present study showed that ferrichrome inhibited the progression of cancer cells to the G2-M phase via the upregulation of p53, and downregulation of securin and cyclin B1. These data indicated that the mechanisms underlying the antitumor effects of ferrichrome differ from those of 5-FU, suggesting that ferrichrome could be used clinically as an anti-tumor drug for the treatment of pancreatic cancer that shows resistance to existing drugs.
In conclusion, it was revealed the antitumor effects of probiotic-derived ferrichrome in pancreatic cancer cells, including FUR cells. The mechanism via which ferrichrome suppressed cancer cells appeared to involve the induction of cancer cell apoptosis via p53 upregulation, which differs from the mechanisms of existing drugs. These findings indicated that probiotics are associated with pancreatic tumor progression, and probiotic-derived ferrichrome is expected to be a novel attractive ant-tumor agent for the treatment of refractory pancreatic cancer.
Supplementary Data
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Kotoe Shibusa (Division of Gastroenterology and Hematology/Oncology, Department of Medicine, Asahikawa Medical University) for technical assistance, and Mr. Hiroaki Akutsu and Mr. Shinichi Chiba (Center for Advanced Research and Education Asahikawa Medical University) for assistance with flow cytometric analysis and genetic analysis. CBC and serum biochemistry analyses were performed by New Drug Research Center, Inc. and Oriental Yeast Co., Ltd., respectively.
Abbreviations
- 5-FU
5-fluorouracil
- PARP
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- DDIT3
DNA damage inducible transcript 3
- DMEM
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- SRB
sulforhodamine B
- CDKN1B
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B
- FUR
5-FU-resistant
- CRE
creatinine
- TP
total protein
- ALB
albumin
- AST
aspartate aminotransferase
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- ER
endoplasmic reticulum
Funding
The present study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant nos. 18K07927, 19K16484, 18K15770, 18K08906, 17K15913, 19K17419 and 19K08410) and the Takeda Science Foundation. This study was also supported by research funds from Kamui Pharma, Inc., Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd., and EA Pharma Co., Ltd used to purchase experimental agents and mice.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
AK, MF and HK were substantially involved in the conception and design of the study, drafted the manuscript and supervised all experiments. AK and HK performed the biochemical experiments. HT performed histopathological assessments. SK, TI, MI, YM, ST, TG, AS, KA NU, NO and TO were involved in the design of the study, the interpretation of the data, and preparation and review of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal experiments were approved by the Asahikawa Medical University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Mikihiro Fujiya received research funds from Kamui Pharma, Inc., Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd., and EA Pharma Co., Ltd., to purchase experimental agents and mice.
References
- 1.Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O, Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de la Fouchardière C, et al. Groupe Tumeurs Digestives of Unicancer. PRODIGE Intergroup FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1817–1825. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1011923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Heinemann V, Boeck S, Hinke A, Labianca R, Louvet C. Meta-analysis of randomized trials: Evaluation of benefit from gemcitabine-based combination chemotherapy applied in advanced pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:82. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chand S, O'Hayer K, Blanco FF, Winter JM, Brody JR. The landscape of pancreatic cancer therapeutic resistance mechanisms. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12:273–282. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.14951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Loehrer PJ, Sr, Einhorn LH, Williams SD, Hui SL, Estes NC, Pennington K. Cisplatin plus 5-FU for the treatment of adeno-carcinoma of the colon. Cancer Treat Rep. 1985;69:1359–1363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gaiser RA, Halimi A, Alkharaan H, Lu L, Davanian H, Healy K, Hugerth LW, Ateeb Z, Valente R, Fernández Moro C, et al. Enrichment of oral microbiota in early cystic precursors to invasive pancreatic cancer. Gut. 2019;68:2186–2194. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Half E, Keren N, Reshef L, Dorfman T, Lachter I, Kluger Y, Reshef N, Knobler H, Maor Y, Stein A, et al. Fecal microbiome signatures of pancreatic cancer patients. Sci Rep. 2019;9:16801. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53041-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. World Health Organization . Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food. Ontario, Canada: 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gerritsen J, Smidt H, Rijkers GT, de Vos WM. Intestinal microbiota in human health and disease: The impact of probiotics. Genes Nutr. 2011;6:209–240. doi: 10.1007/s12263-011-0229-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kalliomäki M, Salminen S, Arvilommi H, Kero P, Koskinen P, Isolauri E. Probiotics in primary prevention of atopic disease: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2001;357:1076–1079. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gu Y-H, Choi H, Yamashita T, Kang KM, Iwasa M, Lee MJ, Lee KH, Kim CH. Pharmaceutical production of anti-tumor and immune-potentiating Enterococcus faecalis-2001 β-glucans: Enhanced activity of macrophage and lymphocytes in tumor-implanted mice. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2017;18:653–661. doi: 10.2174/1389201018666171002130428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rowland IR, Rumney CJ, Coutts JT, Lievense LC. Effect of Bifidobacterium longum and inulin on gut bacterial metabolism and carcinogen-induced aberrant crypt foci in rats. Carcinogenesis. 1998;19:281–285. doi: 10.1093/carcin/19.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Maroof H, Hassan ZM, Mobarez AM, Mohamadabadi MA. Lactobacillus acidophilus could modulate the immune response against breast cancer in murine model. J Clin Immunol. 2012;32:1353–1359. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9708-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Singhal B, Mukherjee A, Srivastav S. Role of probiotics in pancreatic cancer prevention: The prospects and challenges. Adv Biosci Biotechnol. 2016;07:468–500. doi: 10.4236/abb.2016.711045. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Segawa S, Fujiya M, Konishi H, Ueno N, Kobayashi N, Shigyo T, Kohgo Y. Probiotic-derived polyphosphate enhances the epithelial barrier function and maintains intestinal homeostasis through integrin-p38 MAPK pathway. PLoS One. 2011;6:e23278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hemarajata P, Versalovic J. Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: Mechanisms of intestinal immunomodulation and neuromodulation. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2013;6:39–51. doi: 10.1177/1756283X12459294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tsai TL, Li AC, Chen YC, Liao YS, Lin TH. Antimicrobial peptide m2163 or m2386 identified from Lactobacillus casei ATCC 334 can trigger apoptosis in the human colorectal cancer cell line SW480. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:3775–3789. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-3018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sakatani A, Fujiya M, Ueno N, Kashima S, Sasajima J, Moriichi K, Ikuta K, Tanabe H, Kohgo Y. Polyphosphate derived from lactobacillus brevis inhibits colon cancer progression through induction of cell apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:591–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Konishi H, Fujiya M, Tanaka H, Ueno N, Moriichi K, Sasajima J, Ikuta K, Akutsu H, Tanabe H, Kohgo Y. Probiotic-derived ferrichrome inhibits colon cancer progression via JNK-mediated apoptosis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12365. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ijiri M, Fujiya M, Konishi H, Tanaka H, Ueno N, Kashima S, Moriichi K, Sasajima J, Ikuta K, Okumura T. Ferrichrome identified from Lactobacillus casei ATCC334 induces apoptosis through its iron-binding site in gastric cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2017;39:1010428317711311. doi: 10.1177/1010428317711311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ecker DJ, Passavant CW, Emery T. Role of two siderophores in Ustilago sphaerogena. Regulation of biosynthesis and uptake mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982;720:242–249. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kato H, Ishikura H, Kawarada Y, Furuya M, Kondo S, Kato H, Yoshiki T. Anti-angiogenic treatment for peritoneal dissemination of pancreas adenocarcinoma: A study using TNP-470. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2001;92:67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2001.tb01049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li Z, Wang N, Huang C, Bao Y, Jiang Y, Zhu G. Downregulation of caveolin-1 increases the sensitivity of drug-resistant colorectal cancer HCT116 cells to 5-fluorouracil. Oncol Lett. 2017;13:483–487. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Moore JD. In the wrong place at the wrong time: Does cyclin mislocalization drive oncogenic transformation? Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:201–208. doi: 10.1038/nrc3468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Leu JIJ, Pimkina J, Frank A, Murphy ME, George DL. A small molecule inhibitor of inducible heat shock protein 70. Mol Cell. 2009;36:15–27. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.09.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Michaud DS, Izard J, Wilhelm-Benartzi CS, You DH, Grote VA, Tjønneland A, Dahm CC, Overvad K, Jenab M, Fedirko V, et al. Plasma antibodies to oral bacteria and risk of pancreatic cancer in a large European prospective cohort study. Gut. 2013;62:1764–1770. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fan X, Alekseyenko AV, Wu J, Peters BA, Jacobs EJ, Gapstur SM, Purdue MP, Abnet CC, Stolzenberg-Solomon R, Miller G, et al. Human oral microbiome and prospective risk for pancreatic cancer: A population-based nested case-control study. Gut. 2018;67:120–127. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pushalkar S, Hundeyin M, Daley D, Zambirinis CP, Kurz E, Mishra A, Mohan N, Aykut B, Usyk M, Torres LE, et al. The pancreatic cancer microbiome promotes oncogenesis by induction of innate and adaptive immune suppression. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:403–416. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Li S, Fuhler GM, Bn N, Jose T, Bruno MJ, Peppelenbosch MP, Konstantinov SR. Pancreatic cyst fluid harbors a unique microbiome. Microbiome. 2017;5:147. doi: 10.1186/s40168-017-0363-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sethi V, Kurtom S, Tarique M, Lavania S, Malchiodi Z, Hellmund L, Zhang L, Sharma U, Giri B, Garg B, et al. Gut microbiota promotes tumor growth in mice by modulating immune response. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:33–37.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kastan MB, Zhan Q, el-Deiry WS, Carrier F, Jacks T, Walsh WV, Plunkett BS, Vogelstein B, Fornace AJ., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992;71:587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kuerbitz SJ, Plunkett BS, Walsh WV, Kastan MB. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bourdon JC, Renzing J, Robertson PL, Fernandes KN, Lane DP. Scotin, a novel p53-inducible proapoptotic protein located in the ER and the nuclear membrane. J Cell Biol. 2002;158:235–246. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200203006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gu Z, Wang H, Xia J, Yang Y, Jin Z, Xu H, Shi J, De Domenico I, Tricot G, Zhan F. Decreased ferroportin promotes myeloma cell growth and osteoclast differentiation. Cancer Res. 2015;75:2211–2221. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Markkanen E, Dorn J, Hübscher U. MUTYH DNA glyco-sylase: The rationale for removing undamaged bases from the DNA. Front Genet. 2013;4:18. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Oka S, Leon J, Tsuchimoto D, Sakumi K, Nakabeppu Y. MUTYH, an adenine DNA glycosylase, mediates p53 tumor suppression via PARP-dependent cell death. Oncogenesis. 2014;3:e121–e121. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2014.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ali S, Zhang Y, Zhou M, Li H, Jin W, Zheng L, Yu X, Stark JM, Weitzel JN, Shen B. Functional deficiency of DNA repair gene EXO5 results in androgen-induced genomic instability and prostate tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2020;39:1246–1259. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1061-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Longley DB, Harkin DP, Johnston PG. 5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:330–338. doi: 10.1038/nrc1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.