Abstract
The most common cause of vision loss among the elderly is age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The aim of the present study was to investigate the potential cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs), and their ability to activate the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-related genes in human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells, as well as the inhibition of endothelial cell migration. It was first determined that CORM2 and CORM3 suppressed blue light-induced cell damage. In addition, a decrease in the level of cleaved poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 protein and dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential were considered to reflect the anti-apoptotic activity of CORMs. Furthermore, CORM2 induced Nrf-2 activation and the expression of the Nrf2-related genes heme oxygenase-1 and glutamate-cysteine ligase. Pretreatment with CORM2 abolished the blue light-induced increase in oxidative stress, suggesting that CORM2-induced antioxidant activity was involved in the cytoprotection against blue light. It was also demonstrated that CORMs markedly suppressed tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression. Moreover, it was further observed that CORMs exert their inhibitory effects through blocking nuclear factor-κB/p65 nuclear translocation and IκBα degradation in TNFα-treated RPE cells. It was observed that CORM2, but not CORM3, protected against oxidative stress-induced cell damage. CORMs abolished vascular endothelial growth factor-induced migration of endothelial cells. The findings of the present study demonstrated the cytoprotective, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of CORMs on RPE cells and anti-angiogenic effects on endothelial cells, suggesting the potential clinical application of CORMs as anti-AMD agents.
Keywords: carbon monoxide, blue light, nuclear factor-κB, glutathione, retinal pigment epithelial cells
Introduction
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of blindness in the elderly, which manifests by progressive loss of central vision through degeneration at the ocular interface between the retina and the underlying choroid (1). A typical characteristic non-neovascular (dry) form of AMD is the formation of drusen and geographic atrophy, whereas the exudative (wet) form involves blood vessel invasion. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is known to play a pivotal role in the growth of abnormal blood vessels that characterize the wet form of AMD (2).
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is firmly attached to the underlying choroid and is a monolayer of cells that plays critical roles in retinal homeostasis, eye development and vision. Dysfunction of RPE cells induces photoreceptor dystrophy, retinal diseases and blindness. It was previously demonstrated that the blue light-induced pathological changes of RPE cells resemble AMD (3). Since RPE cells are sensitive to blue light, which may trigger cellular apoptosis, blue light exposure is considered as a suitable model for AMD study.
Exacerbated oxidative stress and inflammation in the RPE contribute to the pathogenesis of AMD, eventually leading to RPE degeneration (4). The migration of macrophages and lymphocytes to the posterior compartment of the eye and the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines are characteristic during ocular inflammation (5). RPE cells are a component of the outer blood-retinal barrier and respond to the macrophage-secreted proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α (6). Leukocyte recruitment and adhesion to the retina are mediated by intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 (7). The inflammatory nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway plays a key role in TNFα-activated ICAM-1 expression (8).
The RPE is sensitive to blue light, which causes oxidative stress and RPE cell damage at certain doses (9). Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-derived heme oxygenase (HO)-1 and the synthesis of glutathione (GSH) have been found to act as critical antioxidants in vivo and in vitro (10-12). GSH maintains a reduced cellular environment and is part of a protective mechanism against numerous cellular stressors (13). Therefore, protecting RPE cells from blue light or oxidative stress through engendering a Nrf2-regulated cell redox state may provide a potential target for AMD treatment.
Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs) have been demonstrated to act pharmacologically by mimicking the bioactive effects of HO-1 and CO gas (14-16). Low concentrations of CO have been found to increase resistance to cell damage and apoptosis in various model systems (17). Since CO has exhibited the ability to mediate a number of biological functions, including anti-inflammation, cell cycle arrest and vasodilation, it has shown potential for use in various therapeutic applications (17,18). However, the cytoprotective mechanism of CO in RPE cells remains unclear. Thus, the present study was designed to determine the molecular mechanisms underlying the cytoprotective properties of CORMs in RPE cells. There are two widely used CORMs: The lipid-soluble CORM2 {[Ru(CO)3Cl2]2} and the water-soluble CORM3 [Ru(CO)3Cl2 (H2NCH2CO)2] (19). It was herein investigated whether these CORMs possess protective properties that may contribute to the CO-regulated cytoprotective effects.
Materials and methods
Materials
NF-κB/Luc vectors were constructed as described previously (20). ICAM-1/CD54 antibody (cat. no. 4915S; 1:1,000) was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. NF-κB/p65 antibody (cat. no. KAS-TF110; 1:1,000) was purchased from Stressgen Biotechnologies. Antibodies against IκBa (cat. no. sc-847; 1:1,000), poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) (cat. no. sc-136208; 1:200) and lamin (cat. no. sc-6217; 1:1,000) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. Tubulin antibody (cat. no. T568; 1:1,000) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA. Peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit (cat. no. G-21040; 1:1,000) and anti-mouse (cat. no. 31460; 1:2,500) antibodies were obtained from Invitrogen (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and nitrocellulose was obtained from Schleicher and Schuell. The luciferase assay kit (cat. no. E1500) was purchased from Promega Corporation. All other reagents, including TNF-α and VEGF-A proteins, were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA.
RPE cell culture and blue light exposure
The human RPE cell line ARPE-19 was obtained from ATCC and cultured in DMEM-Ham's F12 (1:1; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) containing 10% FBS (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The cells were grown for 3 days until reaching 90-100% confluence. The medium was replaced with fresh serum-free DMEM-Ham's F12, and the cells were grown for an additional 12 h prior to experimental treatment. ARPE-19 cells were cultured in the dark or irradiated with blue light (400 nm) at an intensity of 2,000±500 lux for 24 h to establish the light-induced injury model.
Endothelial cell and THP-1 cell cultures
The human umbilical vein cell line EA.hy926 (ATCC CRL-2922) was cultured in DMEM (Gibco-BRL; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) supplemented with 10% FBS at 37°C under 5% CO2. The THP-1 cells (ATCC® TIB202™) were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% FBS at 37°C under 5% CO2.
Cell viability assay
Cell viability was assayed using Alamar Blue (Serotec) according to the manufacturer's instructions. This assay identifies live cell metabolic activity by detecting redox activity in cells. The excitation/emission wavelength settings were adjusted to 530/590 nm.
Morphological analysis after DAPI staining
Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature and then stained with DAPI for 5 min in the dark at room temperature. After washing with PBS for 5 min, the cells were analyzed under a fluorescence microscope (Axiovert S100; Carl Zeiss AG) at a magnification of ×200. The normal cell nucleus is round, has clear borders and is uniformly stained, whereas apoptotic cells exhibit nuclear pyknosis, irregular edges and strong staining.
Analysis of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS)
To detect intracellular ROS production, RPE cells were seeded into 96-well plates (2×104 cells/well) in DMEM–F12 for 24 h and incubated in serum-free DMEM-F12 for 12 h prior to experimental treatment. Next, the cells were incubated with 20 µM peroxide-sensitive fluorescent probe carboxy-H2DCFDA (Molecular Probes, LLC) for 30 min. After washing with PBS twice (5-10 min per wash), the cells were solubilized with 1% SDS and 5 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4). Fluorescence was measured with a spectrofluorophotometer (model Rf-5301PC; Shimadzu Corporation) with excitation and emission wavelengths of 450 and 520 nm, respectively. The cells were observed and images were captured with a fluorescence microscope (Axiovert S100; Carl Zeiss AG) at a magnification of ×200.
Determination of GSH and oxidized glutathione (GSSG) levels
The intracellular level of reduced GSH was determined as previously described (21). Briefly, cells were incubated with the fluorescent probe monochlorobimane (40 mM; cat. no. HY-101899; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 20 min at room temperature in the dark. After washing with PBS twice (5-10 min per wash), the cells were solubilized with 5 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) and 1% SDS. Fluorescence was measured using a spectrofluorophotometer (Rf-5301PC; Shimadzu Corporation) at an excitation wavelength of 390 nm and an emission wavelength of 520 nm. For GSSG analysis, the GSH scavenger 1-methyl-2-vinylpyridinium trifluoromethane sulfonate was added, and the GSSG levels were then determined spectrophotometrically using the GSH reductase-linked 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid).
Western blotting
Total protein was extracted from ARPE-19 cells using RIPA buffer (1% NP-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS) and a protease inhibitor mixture and separated by 10% SDS-PAGE. The nitrocellulose membrane (EMD Millipore) needed for the transfer was hydrated in cold Tris-glycine buffer (pH 8.3) at 10 V for 1.5 h. The membranes were blocked with TBS containing 5% non-fat milk and incubated for 2 h at room temperature, followed by incubation with primary antibodies against ICAM-1 (cat. no. 4915S; 1:1,000; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.), NF-κB/p65 (cat. no. KAS-TF110; 1:1,000; Stressgen Biotechnologies), IκBa (cat. no. sc-847; 1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.), PARP-1 (cat. no. sc-136208; 1:200; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.), lamin (cat. no. sc-6217; 1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) and tubulin (cat. no. T568; 1:1,000; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) overnight at 4°C with gentle shaking. After incubation with the primary antibodies, the membranes were washed with TBS with 5% non-fat milk and incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit (cat. no. G-21040; 1:1,000; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and anti-mouse (cat. no. 31460; 1:2,500; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) antibodies for 2 h at 4°C. Immunoreactive bands were visualized with enhanced chemiluminescence solution (EMD Millipore).
Mitochondrial membrane potential assay
ARPE-19 cells (1.5×104 cells/well) were cultured in a 12-well plate and exposed to blue light for 24 h. The measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential was performed using JC-1 dye (Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Probe; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The cells were washed with PBS for 5 min and incubated with 10 µg/ml JC-1 at 37°C for 15 min in the dark. Images were captured using a fluorescence microscope (Axiovert S100; Carl Zeiss AG; magnification, ×400), which detects healthy cells with JC-1 J-aggregates (excitation/emission, 540/605 nm) and unhealthy cells with mostly JC-1 monomers (excitation/emission, 480/510 nm). The quantification of the images was performed with ImageJ software, version 1.8.0 (National Institutes of Health).
Monocyte adhesion assay
Cells grown to 90-100% confluence in a 96-well plate were pretreated with CORMs and/or TNFα for 6 h to allow for the expression of ICAM-1. The cells were co-cultured with 5×105 calcein-labeled THP-1 cells for 30 min. After washing twice with RPMI-1640 medium, adherent cells were examined using an ELISA plate reader (FLx800, Bio-Tek Instruments, Inc.) at 485 nm excitation and 538 nm emission wavelengths (22).
Immunofluorescence staining
ARPE-19 cells were pretreated with the test compounds for 2 h at 37°C prior to exposure to TNFα. The cells were fixed in 80% ethanol at room temperature for 10 min and treated with 0.1% (v/v) Triton X-100 in PBS. After blocking with 3% BSA (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 1 h at room temperature, the cells were incubated with mouse monoclonal antibody (anti-NF-κB/p65 antibody diluted 1:100 in PBS) overnight at 4°C. Subsequently, the cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L; A28175; 1:1,000; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) for 1 h. Cell nuclei were stained with propidium iodide (10 ng/ml in PBS) at room temperature for 30 min in the dark and images were captured using a by Zeiss Axiovert S100 fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss AG).
Nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extraction
ARPE-19 cells were collected by scraping in cold PBS and pelleted by centrifugation at 1,000 × g for 5 min at 4°C. The cell pellet was resuspended in the cell lysis buffer (including 10 mM HEPES, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM KCl, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, 0.5 mM phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride and 0.3% Nonidet P-40) and then centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 5 min at 4°C. The collected supernatant was designated as the cytoplasmic fraction. Nuclear proteins were then extracted using a buffer containing 20 mM HEPES, 25% glycerol, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.6 M KCl and 0.2 mM EDTA.
RNA isolation and reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) analysis
Total RNA was isolated using the TRIzol reagent according to the manufacturer's instructions (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Equal quantities (5 µg) of RNA from the cells receiving various treatments were then reverse-transcribed using 50 units of Superscript II (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) for 50 min at 42°C. PCR was performed in a 25-µl reaction mixture containing 10 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.1% Triton X-100 (pH 9.0) and 0.6 U Taq DNA polymerase (Promega Corporation). The primers (30 pmol) used for the amplification of glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL) modifier subunit (GCLM), GCL catalytic subunit (GCLC), ICAM-1 and GAPDH were as follows: GCLM forward, 5′-CAG CGA GGA GCT TCA TGA TTG-3′ and reverse, 5′-TGA TCA CAG AAT CCA GCT GTG C-3′; GCLC forward, 5′-GTT CTT GAA ACT CTG CAA GAG AAG-3′ and reverse, 5′-ATG GAG ATG GTG TAT TCT TGT CC-3′; ICAM-1 forward, 5′-AGC AAT GTG CAA GAA GAT AGC CAA-3′ and reverse, 5′-GGT CCC CTG CGT GTT CCA CC-3′; GAPDH forward, 5′-TAT CGT GGA AGG ACT CAT GAC C-3′ and reverse, 5′-TAC ATG GCA ACTG TGA GGG G-3′. The thermocycling conditions were as follows: 1 cycle of 5 min at 95°C, followed by 30 cycles of 40 sec at 95°C, 30 sec at 59°C (62°C for GCLC), and 50 sec at 72°C, with a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. Reaction products were separated electrophoretically on a 2.5% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide.
Plasmids, transfections, and measurement of luciferase activity
The ARPE-19 cells were transfected with 1 µg of NF-κB/Luc or p3xARE/Luc using Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, the reporter DNA (2 µg) and β-galactosidase DNA (0.5 µg) were mixed with 5 µl Lipofectamine 3000 for 10 min at room temperature. The mixture was added to ARPE-19 cells and, 4 h later, 10% FBS DMEM/F-12 was added for 24 h. For the luciferase assays, the cell lysate was mixed with luciferase substrate solution (Promega Corporation), and then the resultant luciferase activity was measured using the FB12 Tube Luminometer (Titertek-Berthold). The luciferase activities were standardized to β-galactosidase activity.
Scratch assay for endothelial cell (EC) migration
For the wound healing assay, 1.5×105 ECs per well were cultured for 24 h in a 12-well plate with serum-free DMEM. When the cells had grown to 90-100% confluence, the cell monolayer was scratched with a 200-µl pipette tip, washed twice with DMEM, and incubated in a serum-free medium with 10 ng/ml VEGF-A alone, or 10 ng/ml VEGF-A with CORMs. Cell migration and wound closure was monitored, and images were captured at 0, 12 and 24 h using a phase-contrast Axiovert S100 microscope (Carl Zeiss AG). Photographs were taken at 12 and 24 h after wounding. The distance migrated by the ECs to close the wounded area was measured. The quantification of the area was analyzed with ImageJ software, version 1.8.0 (National Institutes of Health). Results are expressed as a migration index calculated from the slope of the distance-time curve at 0, 6, 12, 18 and 24 h relative to the slope of the VEGF-treated cells.
Transwell migration assay
Cell migration assays were performed using Transwell plates with 8-µm pore filters (Corning, Inc.), following the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly, for the cell migration assay, cells (2×105) were suspended in 200 µl of serum-free medium and seeded into the upper chambers of the Transwell plates; serum-free medium supplemented with 10 ng/ml VEGF-A was applied to the lower chamber as a chemoattractant to induce migration. After incubation for 24 h at 37°C, cells were fixed with 4% cold paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature and stained with 0.1% crystal violet solution for 5 min at room temperature. Non-migrating cells remaining on the upper surface of the filter membrane were scraped off gently with a cotton swab. For quantification, the stained cells that had migrated to the other side of the membrane were extracted with 33% acetic acid. The absorbance of the eluted stain was determined at 570 nm.
Statistical analysis
Values are expressed as the mean ± standard error of at least three experiments. Statistical significance was assessed through one-way analysis of variance, followed by Tukey's post hoc test using SigmaPlot version 12 (Systat Software, Inc.). P<0.05 was considered to indicate statistically significant differences.
Results
CORMs reduce blue light-induced cytotoxicity in RPE cells
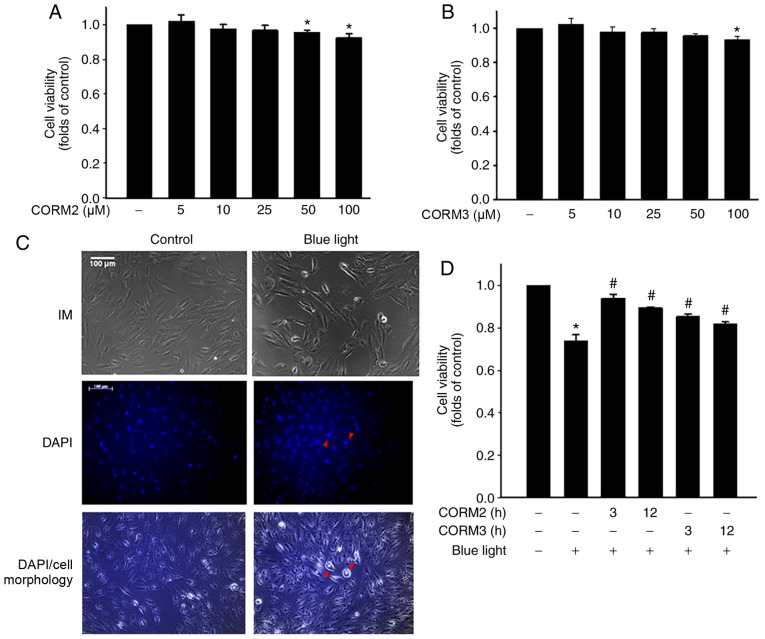
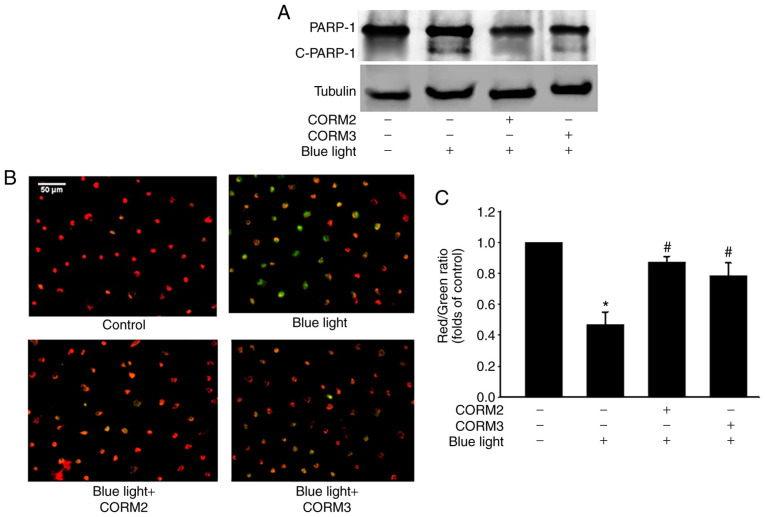
To determine whether CO could protect RPE cells from stress, the viability of ARPE-19 cells treated with CORM2 and CORM3 was first determined. As shown in Fig. 1A and B, CORM2 and CORM3 at 25 mM did not exert a cytotoxic effect on ARPE-19 cells. Subsequently, the protective effects of CORMs against blue light-induced cytotoxicity were examined in RPE cells. First, after exposure to blue light for 24 h, some RPE cells were shrunk and their nuclei were condensed, as detected by DAPI staining (Fig. 1C). Pretreating cells with 25 mM CORM2 or CORM3 for 3 or 12 h significantly prevented this blue light-induced cytotoxicity (Fig. 1D), with the protective effect of CORM2 being superior to that of CORM3. To elucidate whether CORM2 or CORM3 could attenuate blue light-induced cytotoxicity, the expression of cleaved PARP-1, which is one of the downstream effectors of caspase-3, was detected by immunoblotting. As shown in Fig. 2A, the blue light-induced cleaved PARP-1 expression was markedly suppressed by pre-incubation with CORM2 or CORM3. Subsequently, the protective mechanisms of CORM2 and CORM3 were compared to investigate the effect of blue light on mitochondrial activity using JC-1 fluorescence and the results are shown in Fig. 2B. As seen in the representative images, the red fluorescence intensity was increased by 25 mM CORM2 or CORM3 pretreatment compared to that of the blue light-treated cells (Fig. 2C). These results suggest that CORM2 and CORM3 effectively inhibited blue light-induced apoptosis by maintaining the mitochondrial membrane potential.
Figure 1.
Cytoprotective activity of CORMs in RPE cells. (A and B) RPE cells were incubated with CORM2 or CORM3 at the indicated concentrations for 24 h and cell viability was measured. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error. *P<0.05 compared with the untreated cells. (C) RPE cells were stimulated with blue light for 24 h, the morphological changes were observed under an inverted microscope (IM) and pyknotic nuclei were detected by DAPI staining. Red arrowheads indicate the nuclei with apoptotic-like morphological changes. Scale bar, 100 µm. (D) RPE cells were preincubated with or without 25 mM CORM2 and CORM3 for the indicated times, stimulated with blue light for 24 h, and cell viability was measured. *P<0.05 compared with the untreated cells, #P<0.05 compared with blue light alone. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; CORM, carbon monoxide-releasing molecule.
Figure 2.
CORMs reduce blue light-induced cytotoxicity in RPE cells. (A) RPE cells were preincubated with or without 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for 3 h and stimulated with blue light for 24 h. Cell lysates were detected by western blotting with anti-PARP-1. (B) Mitochondrial membrane potential was evaluated using JC-1 dye. Red fluorescence indicates healthy mitochondria and green fluorescence indicates mitochondria in injured cells with low membrane potential. Scale bar, 50 µm. (C) The fluorescent images of mitochondrial membrane potential of RPE cells were determined by the fluorescent dye JC-1 under a fluorescence microscope and expressed as red/green fluorescence intensity ratios. *P<0.05 compared with the untreated cells, #P<0.05 compared with blue light alone. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; CORM, carbon monoxide-releasing molecule; PARP-1, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; c-PARP-1, cleaved PARP-1.
The antioxidant activity of CORM2 is mediated through an increase in the GSH level
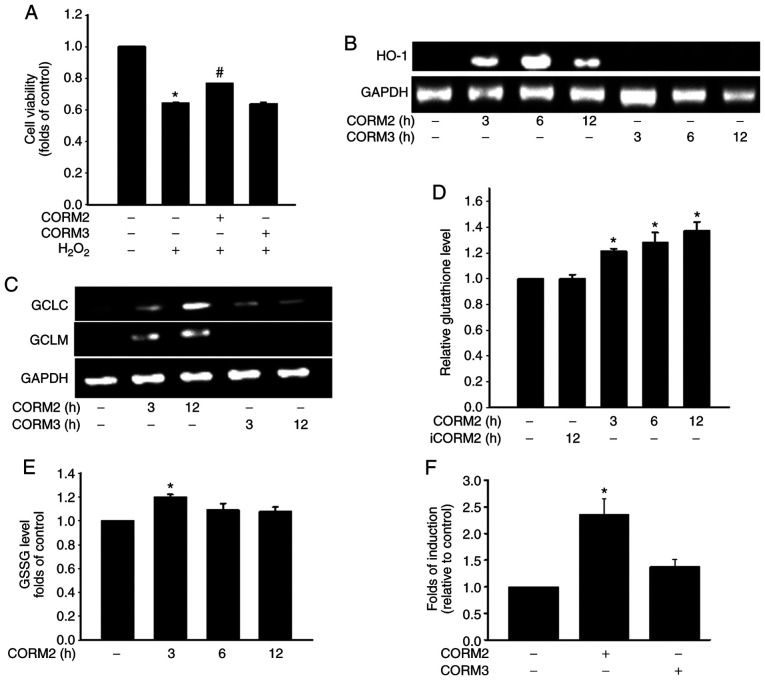
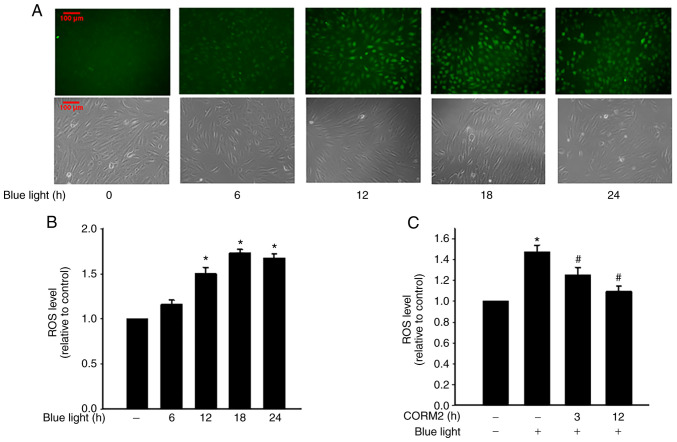
A Previous study demonstrated that inflammatory cytokines increase the production of ROS through mitochondria and NADPH oxidases in cultured RPE cells (23). To determine the antioxidant properties of CORMs, the protective effects of CORM2 and CORM3 against oxidative stress were first examined by subjecting the cells to 1 mM H2O2 for 1 h. Pretreating cells with 25 mM CORM2 for 12 h significantly prevented oxidative stress-induced cell death (Fig. 3A). As shown in Fig. 3B, CORM2 treatment for 3 h increased the HO-1 level. GSH is the most abundant antioxidant n maintaining cellular redox status (12). The enzyme involved in the de novo synthesis of GSH is GCL, which comprises GCLC and GCLM subunits. Treatment with CORM2 increased the GCLC and GCLM expression levels over the course of the incubation period (Fig. 3C). As indicated in Fig. 3D, the reduced GSH levels were increased after 3 h of CORM2 treatment. However, the GSSG levels were found to have increased slightly at 3 h of CORM2 treatment (Fig. 3E). CORM2, but not CORM3, caused an increase in Nrf2 transcriptional activity with ARE-luciferase reporter construct in RPE cells (Fig. 3F). These findings suggested that CORM2 pretreatment exerted a stronger antioxidant effect compared with CORM3. As shown in Fig. 4A and B, blue light exposure induced ROS generation in RPE cells and increased intracellular ROS levels in a time-dependent manner. In addition, CORM2 inhibited blue light-induced oxidative stress (Fig. 4C). Taken together, these results demonstrated that CORM2 exerted an antioxidant effect and abolished blue light-increased oxidative stress in RPE cells.
Figure 3.
The antioxidant activity of CORM2 was mediated through an increase of the GSH level. (A) RPE cells were pretreated with 25 µM CORM2 or CORM3 for 12 h, then treated with 1 mM of H2O2 for 1 h, and cell viability was measured. The results shown are the mean ± standard error. *P<0.05 compared with untreated cells, #P<0.05 compared with H2O2 alone (mean ± standard error). (B) RPE cells were treated with 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for the indicated time periods and then subjected to RT-PCR analysis. (C) RPE cells were treated with 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for the indicated time periods and subjected to RT-PCR analysis. (D and E) RPE cells were exposed to 25 µM CORM2 or iCORM2 for the indicated time periods and the intracellular GSH and GSSG levels were then measured. The results shown are the mean ± standard error. *P<0.05 compared with untreated cells. (F) Cells were transfected with an ARE-luciferase construct. After 12 h, the cells were treated with 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3. All values are presented as mean ± standard error. *P<0.05. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; CORM, carbon monoxide-releasing molecule; iCORM2, inactive CORM2; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, oxidized GSH; HO-1, heme oxygenase 1; GCL, glutamate-cysteine ligase; GCLC, GCL catalytic subunit; GCLM, GCL modifier subunit; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-PCR.
Figure 4.
Antioxidant activity of CORM2 against blue light-induced oxidative stress. (A and B) RPE cells were stimulated with blue light for the indicated times and ROS production was measured using the DCFH-DA fluorogenic probe. The intracellular ROS levels were detected by fluorescence microscopy or spectrofluorophotometry. The results shown are the mean ± standard error. *P<0.05 compared with untreated cells. All values were normalized to the cell numbers. Scale bar, 100 µm. (C) RPE cells were pretreated with 25 µM CORM2 for 3 or 12 h and then exposed to blue light for 24 h and the ROS levels were detected. The results shown are the mean ± standard error. *P<0.05 compared with untreated cells, #P<0.05 compared with blue light alone (mean ± standard error). RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; CORM, carbon monoxide-releasing molecule; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
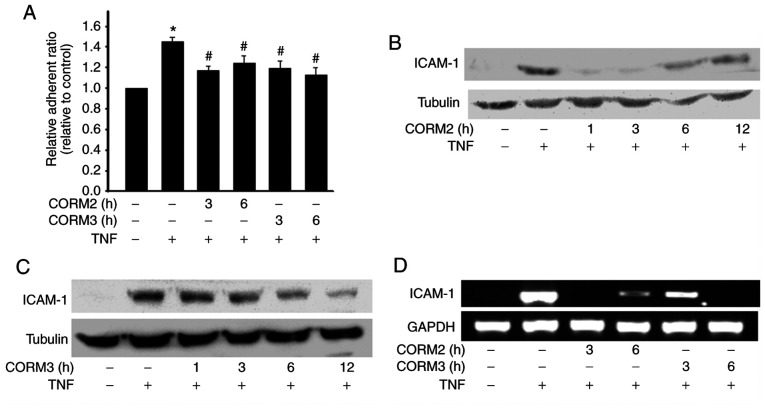
CORM2 and CORM3 inhibit monocyte adhesion and ICAM-1 expression
To detect the anti-inflammatory properties of CORMs in RPE cells, the effects of CORMs on monocyte adhesion to ARPE-19 were examined. We discovered that TNFα significantly increased monocyte adhesion, which was inhibited by pretreatment with 25 mM CORM2 and CORM3 for 3-6 h (Fig. 5A). ICAM-1 is a major component in leukocyte adhesion (5). Therefore, we next examined the effects of CORM2 and CORM3 on the expression of adhesion molecules in ARPE-19 cells. It was observed that pretreatment of ARPE-19 cells with CORM2 and CORM3 for 12 h significantly inhibited TNFα-induced ICAM-1 expression. Pretreatment of ARPE-19 cells with CORM2 was found to have inhibited TNFα-induced ICAM-1 expression after 1 h, but its effect became weaker over time (Fig. 5B). By contrast, the inhibitory effect of CORM3 did not begin until after 3 h of pretreatment, but its effect lasted for up to 12 h (Fig. 5C). In addition, the ICAM-1 mRNA levels were analyzed using RT-PCR. Pretreatments with CORM2 and CORM3 were conducted at 3 and 6 h, and it was observed that these treatments decreased the ICAM-1 mRNA levels consistently with the protein levels (Fig. 5D).
Figure 5.
CORM2 and CORM3 inhibit monocyte adhesion and ICAM-1 expression. (A) RPE cells were pretreated with or without 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for the indicated time periods and then stimulated with 100 U/ml TNFα for 4 h. The fluorescence-labeled THP-1 cells were added to the treated cells and incubated for 30 min. The data are presented as relative adherent ratio compared to the untreated control. *P<0.05 compared with the untreated cells, #P<0.05 compared with TNFa alone. (B and C) RPE cells were pretreated with 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for the indicated time periods, incubated with or without 100 U/ml TNFα for 4 h and analyzed by western blotting. (D) RPE cells were pretreated with 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for the indicated time periods, incubated with or without 100 U/ml TNFα for 4 h and analyzed by reverse transcription-PCR. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; CORM, carbon monoxide-releasing molecule; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
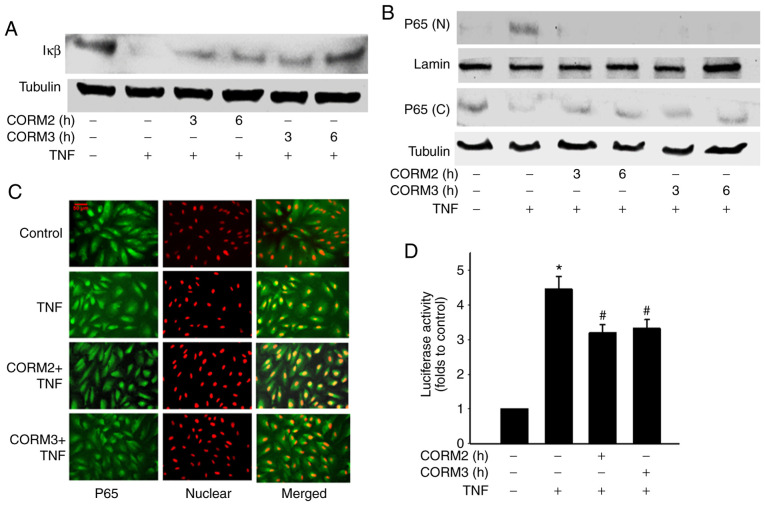
Effect of CORMs on TNFα-induced IκBα degradation and NF-κB nuclear translocation
A previous study demonstrated that TNFa induces the upregulation of ICAM-1 through an NF-κB activation pathway (7). In the present study, it was examined whether CORM2 and CORM3 regulate TNFα-induced NF-κB activation. Degradation of the inhibitory protein IκBα was blocked by CORM2 and CORM3 treatment (Fig. 6A). From 3 to 6 h after CORM2 and CORM3 pretreatment, TNFα-induced NF-κB/p65 nuclear translocation was decreased (Fig. 6B). The effect of CORM2 and CORM3 on nuclear translocation were further tested by immunostaining with a p65 antibody to determine NF-κB translocation, and an inhibitory effect was found to be associated with the 6-h pretreatment (Fig. 6C). In addition, we tested whether CORM2 and CORM3 inhibit TNFα-induced p65 activation at the transcriptional level by using an NF-κB reporter assay. After pretreatment and a subsequent delay of 12 h, a luciferase assay was employed (Fig. 6D) to confirm whether TNFα-induced NF-κB activation was inhibited. Collectively, our experiments demonstrated that CORM2 and CORM3 inhibited NF-κB nuclear translocation and activation.
Figure 6.
CORMs inhibit TNFα-induced IκBα degradation and NF-κB nuclear translocation. (A) RPE cells were induced by 100 U/ml TNFα for 30 min, and a proportion of these cells was then pretreated with 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for the indicated time periods. Cell lysates were prepared and then subjected to western blotting. (B) RPE cells were preincubated with 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for the indicated time periods and then stimulated with TNFα. Cytosolic (C) and nuclear (N) extracts were prepared and subjected to western blotting. (C) RPE cells were pretreated with CORM2 and CORM3 for 6 h and treated with TNFα for 1 h. NF-κB/p65 was detected by an NF-κB/p65 antibody with an Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody (green). Propidium iodide was used to stain for DNA (red). The merged image displays yellow colored nuclei during NF-κB nuclear translocation. Scale bar, 50 µm. (D) RPE cells were cotransfected with the construct of NF-κB luciferase and β-galactosidase for 16 h. Cells were then treated to 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for 6 h and stimulated with TNFα for another 4 h. Luciferase activity was normalized against β-galactosidase activity. *P<0.05 compared with the untreated cells, #P<0.05 compared with TNFα alone. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; CORM, carbon monoxide-releasing molecule; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB.
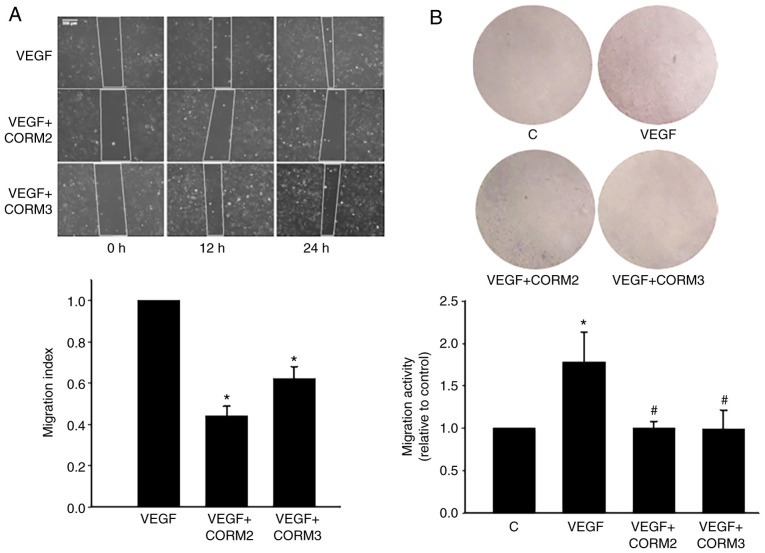
CORMs prevented the migration of ECs
VEGF-induced angiogenesis plays a pivotal role in the choroidal neovascularization that characterizes the wet form of AMD (2). To determine whether CO could inhibit EC migration, a scratch assay was used, and it demonstrated that VEGF induced the migratory capacity of ECs. VEGF-induced migration was decreased through treatment with 25 mM CORM2 and CORM3 (Fig. 7A). The results of Transwell assay revealed that CORMs considerably reduced the number of migrating cells on the membrane filter compared with the VEGF-containing medium (Fig. 7B). Collectively, these results suggest that CORM2 and CORM3 contribute to the inhibition of the migration capacity of ECs.
Figure 7.
CORMs prevent the migration of ECs. (A) ECs were treated in 10 ng/ml VEGF and incubated with or without 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 in serum-free medium for the indicated times. The image data were quantified to a migration index, as mentioned in Materials and methods. The data are expressed as means ± standard error from the results of three independent studies. Scale bar, 200 µm. (B) In the Transwell assay, ECs were preincubated with or without 25 µM CORM2 and CORM3 for 6 h, stimulated with VEGF (10 ng/ml) for 24 h and then the migrated stained cells were extracted and determined at 570 nm. The data are expressed as the relative ratio compared to untreated cells. *P<0.05 compared with the untreated cells, #P<0.05 compared with VEGF alone. ECs, endothelial cells; CORM, carbon monoxide-releasing molecule; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
Discussion
RPE cells are a component of the outer blood-retinal barrier located between the blood vessels of the choroid and the outer segments of the photoreceptors. They are vital for protecting the retina from excessive light exposure, oxidative stress and immune responses (24,25). In several retinal diseases, including AMD, the dysfunction of RPE cells is a crucial event in the disease process (4). How CORMs can cross the blood-retinal barrier is not fully understood, but released CO gas is considered to cross biological membranes (19). This suggests that CORMs may act as a therapeutic target to initiate protective mechanisms in the retina. The present study investigated the protective effects of CORMs against blue light-induced cell injury, TNF-α-induced inflammation and VEGF-induced cell migration.
RPE cells are sensitive to blue light
The present study demonstrated that blue light exposure induced cell injury and caused cell apoptosis (Fig. 1C). Our results also confirmed an increase in ROS levels in blue light-exposed RPE cells (Fig. 4A). A previous study demonstrated that blue light-induced mitochondrial ROS accumulation may lead to cell death (26), and oxidative stress may be responsible for the blue light-induced cell apoptosis. Consistently, we found that CORMs effectively reduced cleaved PARP-1 and maintained mitochondrial membrane potential in blue light-exposed RPE cells (Fig. 2). However, the protective mechanisms of CORM2 and CORM3 were compared with respect their effects of blue light-induced cytotoxicity. It was observed that CORM2 exerted a stronger protective effect compared with that of CORM3 in preventing blue light-induced cytotoxicity (Fig. 1D). A possible explanation is that the lipid-soluble CORM2 was more efficient than the water-soluble CORM3 in its antioxidant role (Fig. 3A).
Inflammation is a defense mechanism that is triggered by tissue damage due to various causes. Chronic inflammation is a prolonged condition in which damaged tissues attempt to self-repair, leading to tissue remodeling and possible dysfunction. Chronic inflammation is the common pathological basis for certain age-associated diseases, such as AMD. Local inflammation and immune-mediated processes play a key role in AMD pathogenesis (4,5). The results of the present study demonstrated that treatment with CORMs conferred anti-inflammatory protection on cytokine-treated RPE cells, and that CORM2 and CORM3 enhanced the inhibition of TNF-α-induced monocyte-RPE interaction by downregulating the expression of ICAM-1. It was demonstrated that CORM2 and CORM3 exerted an anti-inflammatory effect on RPE cells, and this effect was characterized by inhibition of TNF-α-induced expression of ICAM-1 with respect to the molecular mechanisms of NF-κB translocation and IκBa degradation. A particularly notable finding was that the lipid-soluble CORM2 and water-soluble CORM3 displayed different patterns in their anti-inflammatory effects by blocking ICAM-1 expression (Fig. 5) and degradation of the inhibitory protein IκBα (Fig. 6A). A shown in Fig. 5B and C, CORM2 pretreatment exert its inhibitory effect on ICAM-1 expression in 1 and 3 h, while the inhibitory effect of CORM3 is observed after 6 h of pretreatment. A possible explanation is the lipid solubility of CORM2, which enables it to exert its anti-inflammatory effects more quickly compared with the water-soluble CORM3. The lipid-soluble CORM2 may pass through cell membranes and more efficiently release CO at the targets, whereas CORM3 may release CO at a certain concentration outside the cells.
The effects of CORM2 are mediated through HO-1 induction in various systems (14,15,27). In the present analyses, a significant increase in HO-1 protein level was observed following treatment with CORM2, but not CORM3, for 3 h (Fig. 3B). This finding suggests the involvement of HO-1 in the CORM2-mediated antioxidant effect during long-term treatment. Although the half-life of CORM2 is short (~20 min), CORM2 triggers a positive feedback loop through increasing the HO-1 expression to maintain the antioxidant effect of CO for 12 h (Fig. 3A).
GSH plays numerous roles in protecting cells from oxidants and maintaining cellular thiol redox state. An imbalance in the cellular thiol redox state has been implicated in the progression of AMD (28). Our earlier study reported that lycopene, a natural carotenoid, can increase GSH, which further protects the RPE cells from oxidative stress-induced damage (29). Another study demonstrated that curcumin protects retinal cells from light-induced and oxidative stress-induced damage through Nrf2-dependent upregulation of antioxidative enzymes (30). Our previous studies demonstrated that the GSH-dependent redox state is a major modulator of the anti-inflammatory effects of cinnamaldehyde and CO in ECs (31,32). CO has been reported to generate mild oxidative stress by inhibition of the function of cytochrome c oxidase in the mitochondria; however, this mild stress may induce the Nrf2 pathway and, thus, increase GSH levels (32). The present study determined that CORM2 increased the gene expression of both GCLC and GCLM, which are the key rate-limiting enzyme in GSH synthesis (Fig. 3C). Additional experiments demonstrated that CORM2 increased the intracellular GSH level and Nrf-2 activity in RPE cells (Fig. 3D and E). There is a possibility that the lipid-soluble CORM2 can more efficiently reach an intracellular concentration to increase antioxidant activity. In the present study, it was demonstrated that CORM2 could abolish blue light-induced oxidative stress (Fig. 4C). Thus, the increased GSH level is a key contributor to the cytoprotective effect of CORM2.
AMD is a major cause of vision loss among elderly people. The neovascular form (wet AMD) is characterized by the growth of blood vessels from the choroid toward the retina (1). VEGF plays a critical role in the pathophysiological process of neovascular AMD (33). Anti-VEGF therapy is currently the standard of care for wet AMD (34). A previous study demonstrated that CO inhibits sprouting angiogenesis and VEGF receptor-2 phosphorylation (35). In addition, our previous study demonstrated that CORM2 induced nitric oxide (NO) production in ECs (36). NO acts as a potent vasodilator and plays a key role in the physiological regulation of ocular blood flow. The present study demonstrated that treatment with 25 mM CORM2 and CORM3 enhanced the suppression of VEGF-induced migration (Fig. 7A). In Transwell invasion assays, CORMs reduced cell migration toward the VEGF-containing medium (Fig. 7B). Collectively, these results suggest that CORM2 and CORM3 contribute to the inhibition of the migration and invasion capacity of ECs.
In conclusion, the present research demonstrated that CORM2 and CORM3 exhibited different patterns of anti-inflammatory effects and played pivotal roles in the anti-inflammatory process through the suppression of NF-κB activation in ARPE-19 cells. Compared with CORM3, CORM2 was more efficient in increasing antioxidant enzyme expression, resulting in more prominent cytoprotective effects. A better understanding of the functional mechanisms of CORMs may contribute to the development of an effective CO-releasing model for therapeutic application in pathological eye conditions.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Kai-Qin Yang, Yu-Zhang Chen, Jing-Yao Huang and Zi-Qiao Lan for their assistance with selected experiments.
Funding
The present study was supported by grants from the National Science Council of Taiwan (no. 105-2320-B-415-007) and the Chiayi Christian Hospital (grant no. R107-20).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
PMY, KCC and BSW conceived and designed the experiments. PMY, KCC and SHY performed all experiments. PMY and BSW analyzed the data. BSW wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Kokotas H, Grigoriadou M, Petersen MB. Age-related macular degeneration: Genetic and clinical findings. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011;49:601–616. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kent D, Sheridan C. Choroidal neovascularization: A wound healing perspective. Mol Vis. 2003;9:747–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vicente-Tejedor J, Marchena M, Ramírez L, García-Ayuso D, Gómez-Vicente V, Sánchez-Ramos C, de la Villa P, Germain F. Removal of the blue component of light significantly decreases retinal damage after high intensity exposure. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0194218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Strauss O. The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:845–81. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cousins SW, Espinosa-Heidmann DG, Csaky KG. Monocyte activation in patients with age-related macular degeneration: A biomarker of risk for choroidal neovascularization? Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:1013–1018. doi: 10.1001/archopht.122.7.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yang L, Froio RM, Sciuto TE, Dvorak AM, Alon R, Luscinskas FW. ICAM-1 regulates neutrophil adhesion and transcellular migration of TNF-alpha-activated vascular endothelium under flow. Blood. 2005;106:584–592. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-12-4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ledebur HC, Parks TP. Transcriptional regulation of the inter-cellular adhesion molecule-1 gene by inflammatory cytokines in human endothelial cells. Essential roles of a variant NF-kappaB site and p65 homodimers. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:933–943. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tak PP, Firestein GS. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 2001;107:7–11. doi: 10.1172/JCI11830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nakanishi-Ueda T, Majima HJ, Watanabe K, Ueda T, Indo HP, Suenaga S, Hisamitsu T, Ozawa T, Yasuhara H, Koide R. Blue LED light exposure develops intracellular reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation, and subsequent cellular injuries in cultured bovine retinal pigment epithelial cells. Free Radic Res. 2013;47:774–780. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2013.829570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Katoh Y, Oyake T, Hayashi N, Satoh K, Hatayama I, et al. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;236:313–322. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.6943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Alam J, Stewart D, Touchard C, Boinapally S, Choi AM, Cook JL. Nrf2, a Cap'n'Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:26071–26078. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.37.26071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McMahon M, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Chanas SA, Henderson CJ, McLellan LI, Wolf CR, Cavin C, Hayes JD. The Cap'n'Collar basic leucine zipper transcription factor Nrf2 (NF-E2 p45-related factor 2) controls both constitutive and inducible expression of intestinal detoxification and glutathione biosynthetic enzymes. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3299–3307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Townsend DM, Tew KD, Tapiero H. The importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 2003;57:145–155. doi: 10.1016/S0753-3322(03)00043-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim KM, Pae HO, Zheng M, Park R, Kim YM, Chung HT. Carbon monoxide induces heme oxygenase-1 via activation of protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase and inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis triggered by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Circ Res. 2007;101:919–927. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.154781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schwer CI, Mutschler M, Stoll P, Goebel U, Humar M, Hoetzel A, Schmidt R. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-2 inhibits pancreatic stellate cell proliferation by activating p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/heme oxygenase-1 signaling. Mol Pharmacol. 2010;77:660–669. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.059519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shin DY, Chung J, Joe Y, Pae HO, Chang KC, Cho GJ, Wolf CR, Cavin C, Hayes JD. Pretreatment with CO-releasing molecules suppresses hepcidin expression during inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress through inhibition of the STAT3 and CREBH pathways. Blood. 2012;119:2523–2532. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-366690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ryter SW, Alam J, Choi AM. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: From basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:583–650. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00011.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bannenberg GL, Vieira HL. Therapeutic applications of the gaseous mediators carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2009;19:663–682. doi: 10.1517/13543770902858824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Queiroga CS, Vercelli A, Vieira HL. Carbon monoxide and the CNS: Challenges and achievements. Br J Pharmacol. 2015;172:1533–1545. doi: 10.1111/bph.12729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lian KC, Chuang JJ, Hsieh CW, Wung BS, Huang GD, Jian TY, Sun YW. Dual mechanisms of NF-kappaB inhibition in carnosol-treated endothelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;245:21–35. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kamencic H, Lyon A, Paterson P, Juurlink BH. Monochlorobimane fluorometric method to measure tissue glutathione. Anal Biochem. 2000;286:35–37. doi: 10.1006/abio.2000.4765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Braut-Boucher F, Pichon J, Rat P, Adolphe M, Aubery M, Font J. A non-isotopic, highly sensitive, fluorimetric, cell-cell adhesion microplate assay using calcein AM-labeled lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1995;178:41–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)00239-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yang D, Elner SG, Bian ZM, Till GO, Petty HR, Elner VM. Pro-inflammatory cytokines increase reactive oxygen species through mitochondria and NADPH oxidase in cultured RPE cells. Exp Eye Res. 2007;85:462–472. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.06.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sparrow JR, Hicks D, Hamel CP. The retinal pigment epithelium in health and disease. Curr Mol Med. 2010;10:802–823. doi: 10.2174/156652410793937813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pavan B, Dalpiaz A. Retinal pigment epithelial cells as a therapeutic tool and target against retinopathies. Drug Discov Today. 2018;23:1672–1679. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.King A, Gottlieb E, Brooks DG, Murphy MP, Dunaief JL. Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species mediate blue light-induced death of retinal pigment epithelial cells. Photochem Photobiol. 2004;79:470–475. doi: 10.1562/LE-03-17.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Choi YK, Kim CK, Lee H, Jeoung D, Ha KS, Kwon YG, Kim KW, Kim YM. Carbon monoxide promotes VEGF expression by increasing HIF-1alpha protein level via two distinct mechanisms, translational activation and stabilization of HIF-1alpha protein. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:32116–32125. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.131284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Samiec PS, Drews-Botsch C, Flagg EW, Kurtz JC, Sternberg P, Jr, Reed RL, Jones DP. Glutathione in human plasma: Decline in association with aging, age-related macular degeneration, and diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med. 1998;24:699–704. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(97)00286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yang PM, Wu ZZ, Zhang YQ, Wung BS. Lycopene inhibits ICAM-1 expression and NF-κB activation by Nrf2-regulated cell redox state in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Life Sci. 2016;155:94–101. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mandal MN, Patlolla JM, Zheng L, Agbaga MP, Tran JT, Wicker L, Kasus-Jacobi A, Elliott MH, Rao CV, Anderson RE. Curcumin protects retinal cells from light-and oxidant stress-induced cell death. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009;46:672–679. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Liao BC, Hsieh CW, Liu YC, Tzeng TT, Sun YW, Wung BS. Cinnamaldehyde inhibits the tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced expression of cell adhesion molecules in endothelial cells by suppressing NF-kappaB activation. Effects upon IkappaB and Nrf2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008;229:161–171. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yeh PY, Li CY, Hsieh CW, Yang YC, Yang PM, Wung BS. CO-releasing molecules and increased heme oxygenase-1 induce protein S-glutathionylation to modulate NF-kappaB activity in endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;70:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hernández-Zimbrón LF, Zamora-Alvarado R, Ochoa-De la Paz L, Velez-Montoya R, Zenteno E, Gulias-Cañizo R, Quiroz-Mercado H, Gonzalez-Salinas R. Age-related macular degeneration: New paradigms for treatment and management of AMD. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:8374647. doi: 10.1155/2018/8374647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Martin DF, Maguire MG, Ying GS, Grunwald JE, Fine SL, Jaffe GJ. Ranibizumab and bevacizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1897–1908. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1102673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ahmad S, Hewett PW, Fujisawa T, Sissaoui S, Cai M, Gueron G, Al-Ani B, Cudmore M, Ahmed SF, Wong MK, et al. Carbon monoxide inhibits sprouting angiogenesis and vascular endo-thelial growth factor receptor-2 phosphorylation. Thromb Haemost. 2015;113:329–337. doi: 10.1160/TH14-01-0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yang PM, Huang YT, Zhang YQ, Hsieh CW, Wung BS. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule induces endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation through a calcium and phosphati-dylinositol 3-kinase/Akt mechanism. Vascul Pharmacol. 2016;87:209–218. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2016.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.