Abstract
Background
Convalescent plasma administration may be of clinical benefit in patients with severe influenza, but reports on the efficacy of this therapy vary.
Methods
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis assessing randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving the administration of convalescent plasma to treat severe influenza. Healthcare databases were searched in February 2020. All records were screened against eligibility criteria, and the risks of bias were assessed. The primary outcome was the fatality rate.
Results
A total of 2861 studies were retrieved and screened. Five eligible RCTs were identified. Pooled analyses yielded no evidence that using convalescent plasma to treat severe influenza resulted in significant reductions in mortality (odds ratio, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.51–2·23; P = 0.87; I2 = 35%), number of days in the intensive care unit, or number of days on mechanical ventilation. This treatment may have the possible benefits of increasing hemagglutination inhibition titers and reducing influenza B viral loads and cytokine levels. No serious adverse events were reported. The included studies were generally of high quality with a low risk of bias.
Conclusions
The administration of convalescent plasma appears safe but may not reduce the mortality, number of days in the intensive care unit, or number of days on mechanical ventilation in patients with severe influenza.
Keywords: Efficacy, Convalescent plasma, Severe influenza, Meta-analysis
Introduction
Seasonal and pandemic influenza cause substantial disease and a high economic burden [1]. The main treatment for influenza is neuraminidase inhibitor administration [2]. Despite this therapy, pandemic influenza remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality globally [1, 3, 4]. Therefore, there is a need for effective therapy against influenza. Convalescent plasma therapy is a promising option that has been used experimentally for the last 100 years, since the Spanish flu of 1917–1918, and is currently being tested as a potential treatment for the novel coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) [5–7].
Preclinical animal studies have demonstrated the therapeutic efficacy of hyperimmune immunoglobulin and IgG antibody from convalescent plasma [8, 9]. It has been suggested that the administration of high-titer anti-influenza immune plasma derived from convalescent or immunized individuals may be clinically beneficial for the treatment of seasonal and pandemic influenza [10–12]. Additionally, treatment with convalescent plasma was reported to reduce hospital stays and mortality in patients with SARS-CoV infection [10] and in patients with severe influenza A (H1N1) [13]. Some systematic reviews of studies using convalescent plasma concluded that there is evidence of clinical benefits in such patients [10, 14, 15].
Until recently, the collective evidence based on previous studies has been of relatively poor quality because very few randomized trials had been conducted. However, two randomized, controlled, and multicenter trials were reported in 2019, and in both trials, convalescent plasma or hyperimmune intravenous immunoglobulin (H-IVIG) prepared from pooled plasma, obtained from convalescent patients, and conferred no significant benefit over placebo in patients with influenza infection [16, 17]. This is not concordant with previous studies [13, 18]. To investigate this discrepancy, the current study conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the clinical efficacy of either convalescent plasma or H-IVIG for the treatment of severe influenza.
Materials and methods
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
We conducted this study in compliance with the PRISMA guidelines [19]. Prospective randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving patients with influenza who were treated with convalescent plasma and/or H-IVIG were considered for inclusion in the analysis. The reports considered for inclusion were limited to those published in English. Crossover trials, before-after studies, conference presentations, abstract publications, case reports or case series, studies with no comparator, and editorials were excluded from consideration.
Search strategy
Two authors (ZH and JZ) performed the literature search during February 2020. To increase the sensitivity of the search, the search term “influenza” was used in conjunction with AND “convalescent plasma” OR “convalescent serum” OR “hyperimmune immunoglobulin” OR “immune plasma” OR “H-IVIG” as keywords or Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) search terms. The records of four electronic databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, and Web of Science), dating from their inception to February 10, 2020, were searched.
Definitions
The study population of interest included severe patients of any age or sex who were hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed influenza infection (as defined in the original trials). Severe influenza was defined of having either hypoxia (room air oxygen saturation of < 93%) or symptoms of respiratory distress or using the authors’ definitions, including a National Early Warning (NEW) score of > 2 points or a CURB-65 (severity score for community-acquired pneumonia) score of > 3 points. The interventions of interest were convalescent plasma, serum, or H-IVIG derived from convalescent or immunized individuals. Comparator treatments included placebo and low-titer plasma.
Outcomes
The primary outcome of interest in the current analysis was the influenza case-fatality rate. The secondary outcomes analyzed included antibody levels, cytokine levels, viral loads, incidences of serious adverse events, and numbers of days spent on mechanical ventilation, in the intensive care unit (ICU), and in the hospital.
Data extraction
Two authors (ZX and JZ) independently reviewed the articles retrieved via the above-described search protocol and extracted the relevant data from them. Discrepancies were resolved via discussion.
Quality assessment
The quality of each trial included in the analysis was assessed based on a thorough review of the details provided in the “Materials and Methods” section and any relevant supplementary materials. Trial quality was also assessed using the Cochrane collaboration tool for assessing the risk of bias [20], including assessment of random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding (of interventions and outcome measurement or assessment), incomplete outcome data, selective reporting bias, and other potential sources of bias (e.g., industry funding). For each criterion, the risk of bias was rated as low, high, or unclear in cases where there were insufficient details. Two authors (ZX and JZ) independently assessed the study quality, and disagreements were resolved via discussion.
Assessment of heterogeneity
The I2 statistic was used to evaluate the influence of heterogeneity on the pooled results, and an I2 value of > 50% was deemed to indicate substantial heterogeneity [20]. Fixed-effects models were used to pool data when the level of heterogeneity was insignificant, and random effects models were used to pool data when significant heterogeneity was identified.
Statistical analysis
Categorical data were pooled, and odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. We did not construct funnel plots, as fewer than 10 trials were identified for each comparison. Statistical analyses were conducted using Review Manager software (version 5.3; Nordic Cochrane Centre, Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark), and two-sided p values of < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Description of studies
The initial search identified 2861 potentially eligible reports. After the exclusion of duplicates and irrelevant articles, 29 trials were deemed to warrant further detailed review. Twenty-four of these reports were subsequently excluded because they did not meet the predefined eligibility criteria, ultimately resulting in the inclusion of five trials in the present analysis (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
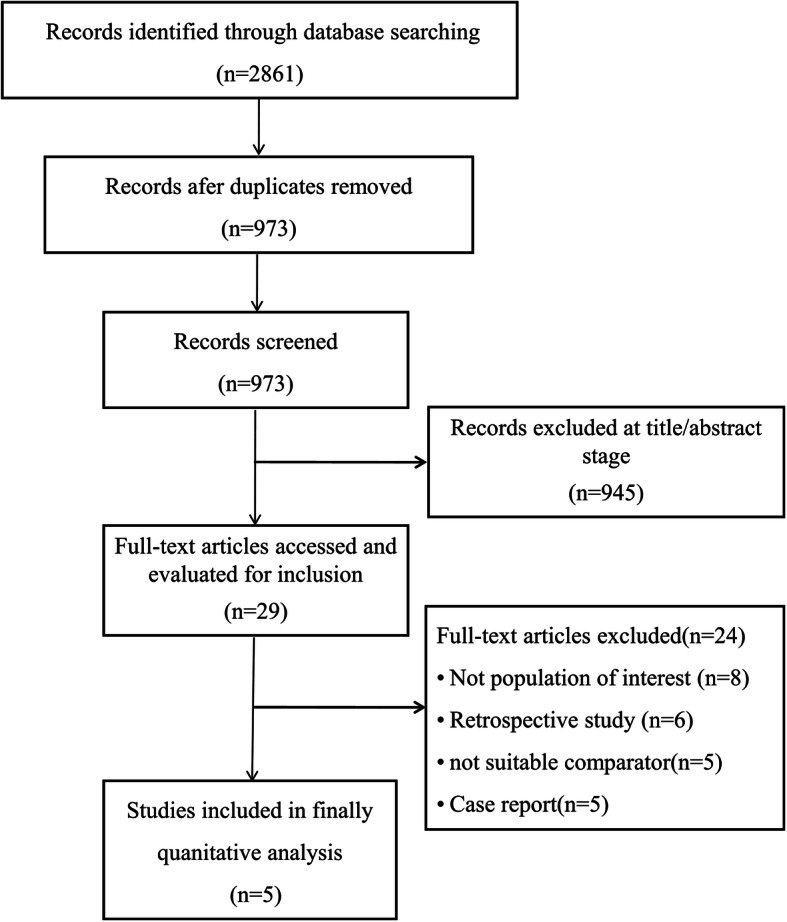
Search strategy used to identify reports for inclusion
All five studies included in the present analysis were randomized, controlled, and multicenter trials. Hung et al. [18] reported that H-IVIG administered within 5 days of symptom onset was associated with a lower viral load and less mortality in patients with severe H1N1 infection. In a pilot study reported by the INSIGHT FLU005 IVIG Pilot Study Group (Group IFIPS) [21], H-IVIG administration was associated with significantly higher hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titers in patients with influenza. The same group subsequently performed an international double-blind RCT in which H-IVIG administration was associated with similar safety outcomes regarding death and adverse events [17]. In 2017, Beigel et al. [22] reported a multicenter phase 2 trial in which immune plasma was associated with non-significant reductions in the number of days in hospital for patients with severe influenza. More recently, however, their phase 3 trial indicated that high-titer anti-influenza plasma conferred no significant benefit in patients with severe influenza A [16] (Table 1).
Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies
| NO. | Author | Journal, years | Study design | Multi-center | Population | Dose | Treatment (n) | Control (n) | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hung, et al. [18] | CHEST, 2013 | RCT, H-IVIG vs. normal IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) | Yes | Patients with severe H1N1 infection | 0.4 g/kg | 17 | 17 | H-IVIG was associated with a lower viral load and reduced mortality |
| 2 | Group IFIPS [21] | The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2016 | RCT, H-IVIG vs. placebo | Yes | Patients with influenza A or B | 0.25 g/kg | 16 | 15 | H-IVIG administration significantly increases HAI titer levels among patients with influenza |
| 3 | Davey Jr., et al. [17] | Lancet Respir Med, 2019 | RCT, H-IVIG vs. placebo | Yes | Patients with influenza A or B infection | 0.25 g/kg | 156 | 152 | H-IVIG was not superior to placebo for adults hospitalized with influenza infection |
| 4 | Beigel et al. [22] | Lancet Respir Med, 2017 | RCT, immune plasma vs. standard care | Yes | Patients with severe influenza A or B | HAI titers ≥ 1:80 | 42 | 45 | Immune plasma provided support for a possible benefit of severe influenza |
| 5 | Beigel et al. [16] | Lancet Respir Med, 2019 | RCT, high-titer anti-influenza plasma (≥ 1:80) vs. low-titer (≤ 1:10) | Yes | Patients with influenza A | HAI titers ≥ 1:80 | 91 | 47 | High-titer anti-influenza plasma conferred no significant benefit over non-immune plasma |
Risks of bias
The RCTs included in the current analysis [16–18, 21, 22] were all deemed to have low risks of attribution bias, reporting bias, and selection bias, with the exception of the Group IFIPS study [21] in which the details pertaining to random sequence generation were unclear. The phase 2 trial reported by Beigel et al. [22] was an open-label study; consequently, no allocation concealment and blinding were performed, so the study has high risks of performance bias and detection bias. The subsequent phase 3 trial by this group [16] was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind study with low risks of attribution bias, reporting bias, and selection bias (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
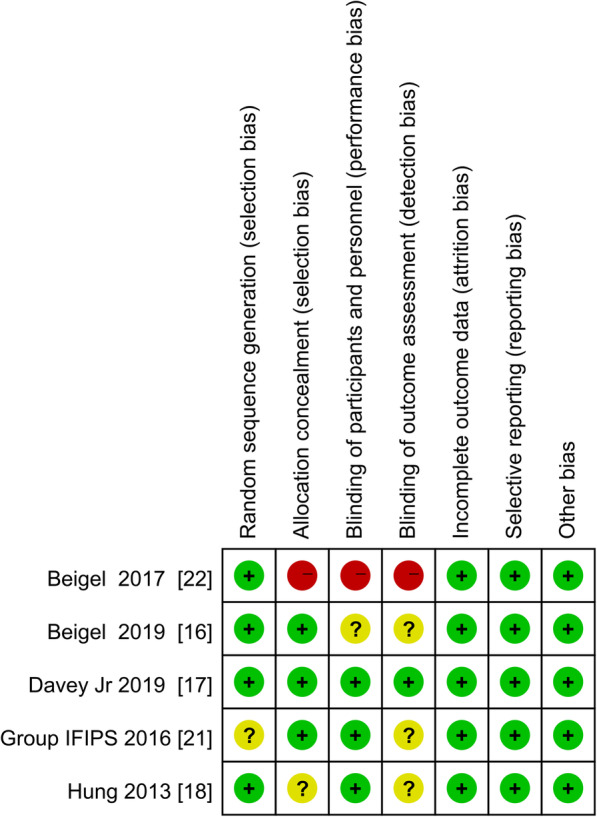
Diagram depicting the risks of bias in each study. Green represents low risk, yellow represents unclear risk, and red represents high risk
Mortality outcomes
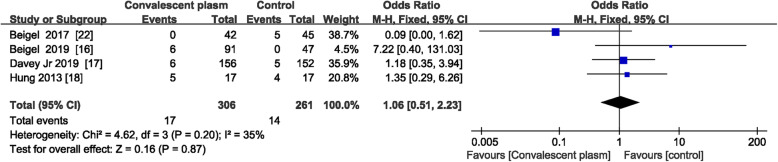
Four of the trials in the current study included extractable data facilitating an assessment of the efficacy of immune plasma/H-IVIG administration for reducing mortality from severe influenza [16–18, 22]. Based on an analysis of the pooled data (n = 567), there was no significant difference in mortality between patients with severe influenza treated with immune plasma/H-IVIG and those who received a placebo (OR = 1.06; 95% CI = 0.51–2.23; P = 0.87; I2 = 35%) (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
Pooled estimates of case-fatality rates due to severe influenza in patients who were administered convalescent plasma and in control patients
Secondary outcomes
Antibody levels
It was reported that the HAI titers significantly increased in patients with influenza A or influenza B who received H-IVIG but that those increased titers gradually decreased after the first week of treatment [17, 21] (Table 2).
Table 2.
Secondary outcomes
| Secondary outcomes | Author | H-IVIG/immune plasma group | Control group | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody levels |
Davey Jr., et al., 2019 [17] Group IFIPS, 2016 [21] |
Significantly increases HAI titer levels among patients with influenza A and B | – | – |
| Viral loads | Hung et al., 2013 [18] | 3.3 log 10 copies/mL(H1N1) | 4.67 log 10 copies/mL | 0.04 |
| Davey Jr., et al., 2019 [17] | Mean log10 RNA − 1.95(Influenza A) | − 2.62 | 0.02 | |
| Davey Jr., et al., 2019 [17] | Mean log10 RNA − 2.09(influenza B) | − 1.54 | 0.005 | |
| Beigel et al., 2017 [22] | Median log 10 copies per mL 1.9 (1.9–1.9) day 7 (Nasal swab, Influenza A and B) | 1.9 (1.9–1.9) | NS | |
| Cytokines | Hung et al., 2013 [18] | TNF-a, IL-1ra, and IL-10 fell to a similar level as control 3 days after treatment | – | – |
| Mechanical ventilation, day | Beigel et al., 2017 [22] | 0 (0–6) (influenza A and B) | 3 (0–14) | 0.14 |
| Beigel et al., 2019 [16] | 9 (4–16) (influenza A) | 15.5 (7.0–29.0) | 0.22 | |
| Length of ICU stay, day | Hung et al., 2013 [18] | 11 (4–13.5) (H1N1) | 10 (4.5–13.5) | NS |
| Beigel et al., 2017 [22] | 2.5 (0.0–9.0) (influenza A and B) | 3 (0–13) | 0·37 | |
| Beigel et al., 2019 [16] | 5.0(3.0–12.5) (influenza A) | 8 (4–25) | 0.32 | |
| Length of hospital stay, day | Hung et al., 2013 [18] | 16 (11.5–13.5) (H1N1) | 16 (7–29) | NS |
| Beigel et al., 2017 [22] | 6 (4–16) (influenza A and B) | 11 (5–25) | 0·13 | |
| Beigel et al., 2019 [16] | 5 (3–12) (influenza A) | 6 (4–12) | 0.30 | |
| Serious adverse events | Beigel et al., 2017 [22] | 20% (influenza A and B) | 38% | 0·041 |
| Beigel et al., 2019 [16] | 35% (influenza A) | 32% | NS |
Viral loads and cytokines
Hung et al. [18] reported that the H1N1 viral loads were significantly lower in patients treated with a convalescent plasma infusion than in the control group subjects, as were the levels of cytokines interleukin-1ra, interleukin-10, and tumor necrosis factor alpha. However, in another large clinical trial, the reductions in overall viral load during the first 3 days did not differ significantly between the H-IVIG and placebo groups (P = 0.49) [17]. In that trial, 16% of the patients in the H-IVIG group and 20% of the patients in the placebo group had no detectable virus after infusion (P = 0.15). In the subgroup of patients with influenza B, the decline in viral loads appeared greater in the H-IVIG group than in the placebo group, but this difference did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.053) [17] (Table 2).
Length of ICU and overall hospital stay
Both Hung et al. [18] and Beigel et al. [16, 22] reported that there were no significant differences in the length of ICU stay or overall hospital stay between an H-IVIG/immune plasma treatment group and a control group. In the Beigel et al. study [16, 22], there was also no significant difference in the number of days on mechanical ventilation between an immune plasma treatment group and a standard care alone group. In the Davey et al. study [17], there were no significant differences in the proportions of patients alive and discharged at days 7 and 28 between an H-IVIG group and a control group (Table 2).
Serious adverse events
No adverse events related to treatment were reported by Hung et al. [18] or Davey et al. [17]. In the open-label RCT reported by Beigel et al. [22], there were fewer serious adverse events in the participants who were administered an immune plasma infusion than there were in the control group subjects; however, in the subsequent double-blind trial by the same group [16], there were similar numbers of serious adverse events in both groups, the most frequent of which was acute respiratory distress syndrome (Table 2).
Discussion
The current analyses suggest that convalescent plasma may not have clinically relevant effects on mortality in patients with influenza. Reductions in the number of days in the ICU, overall hospital stay lengths, and the number of days on mechanical ventilation following treatment with convalescent plasma were also not significant. Of interest, there was evidence of a possible benefit from this therapy by way of increased HAI titers and reduced influenza B viral loads and cytokine levels after convalescent plasma treatment. No serious adverse events were reported.
The use of immune plasma has been recommended as a primary therapy in patients with severe respiratory infectious diseases including influenza, severe acute respiratory syndrome, and Middle East respiratory syndrome [10, 14, 22]. However, until recently, relevant data pertaining to these recommendations were weak and limited to case reports and case series lacking controls. Compared with the previous meta-analyses [10, 14, 15], our meta-analysis differs in the inclusion criteria utilized, in the number of trials included, and in the summary estimates of treatment effect, which were strengthened by an extensive search, duplicate citation screening, and data abstraction. We focused on high-quality RCTs and estimated not only fatality rates but also both the biological effects (i.e., HAI titers, viral loads, cytokines) and clinical benefits (i.e., length of ICU/hospital stays, number of days on mechanical ventilation, and adverse events). The evidence for a reduction in mortality associated with convalescent plasma was strongest for influenza A (H1N1) [18], but this should be interpreted with an appropriate degree of caution because of the limited sample size (n = 17) and the early use of treatment (onset within 5 days) in that study. Additionally, in an analysis of pooled data derived from four trials (n = 567) in which deaths were reported, there was no significant association between the use of convalescent plasma and mortality in patients with severe influenza.
With regard to secondary outcomes, including the number of days in the ICU, overall number of days in the hospital, and the number of days on mechanical ventilation, three RCTs reported relevant data, and the reductions in an H-IVIG/immune plasma group compared with a control group were not significant in any of them [16, 18, 22]. Despite robust increases in the HAI titers against influenza A and B [17, 21], reductions in the influenza B viral loads [17], and reductions in the cytokine levels in patients with H1N1 [18], no clinical benefit of receiving H-IVIG/immune plasma infusion was evident in influenza patients.
Our meta-analysis has some limitations. First, despite an extensive literature search, we identified only four trials with a primary outcome that could be pooled. Second, the severity of influenza may have been different between the evaluated RCTs. Third, we did not registering in PROSPERO, but we conducted this study in compliance with the PRISMA guidelines [19]. Finally, we were not able to pool all data reported for outcomes such as viral loads, cytokine levels, and ICU and hospital stay lengths, due to variability in the measuring and reporting of these outcomes.
Presently, many questions remain about the use of convalescent plasma for treating influenza. For example, it is still unknown how much of severe disease is due to virus replication versus inflammation. The composition of plasma is complex, and transfusion reactions can occur after the administration of blood products [23, 24]. Furthermore, titers of the relevant antibodies contained in convalescent serum preparations differ. The standardized extraction and purification of specific antibodies can be difficult and time-consuming. Lastly, viral shedding and the induced immune responses may be different between influenza A and B. Thus, more definitive animal and pilot studies should be conducted to identify the optimal timing, dosage, and indications for the use of H-IVIG/immune plasma in patients infected with different virus subtypes.
Conclusion
The available high-quality evidence suggests that convalescent plasma/H-IVIG is safe but unlikely to reduce mortality in patients with severe influenza. Further clinical trials with larger populations remain needed to evaluate the efficacy of convalescent plasma for the treatment of severe influenza.
Acknowledgements
None.
Abbreviations
- COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019
- CIs
Confidence intervals
- Group IFIPS
INSIGHT FLU005 IVIG Pilot Study Group
- H-IVIG
Hyperimmune intravenous immunoglobulin
- HAI
Hemagglutination inhibition
- ICU
Intensive care unit
- MeSH
Medical Subject Heading
- ORs
Odds ratios
- RCTs
Randomized controlled trials
- SARS-CoV
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
Authors’ contributions
ZX and JZ performed the literature review, acquired the data, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. YL and Xiaoqing Liu conceived the initial concept and interpreted the data. YH, Xuesong Liu, and YX analyzed the data and revised the manuscript. SC, DL, and ZL made substantial contributions to the conception and interpretation of the data. All authors contributed substantially the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The study was funded by the National Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2017ZX10204401), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81970071), National Key Research and Development Plan for the Emergency Management of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (2020YFC0845100), the Special Project of Guangdong Science and Technology Department (2020B111105001) and Guangzhou Science and Technology Program projects (202008040003).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the included randomized controlled trials.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Zhiheng Xu and Jianmeng Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Xiaoqing Liu, Email: lxq1118@126.com.
Yimin Li, Email: dryiminli@vip.163.com.
References
- 1.Iuliano AD, Roguski KM, Chang HH, Muscatello DJ, Palekar R, Tempia S, Cohen C, Gran JM, Schanzer D, Cowling BJ, et al. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: a modelling study. Lancet. 2018;391(10127):1285–1300. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33293-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dobson J, Whitley RJ, Pocock S, Monto AS. Oseltamivir treatment for influenza in adults: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 2015;385(9979):1729–1737. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ruuskanen O, Lahti E, Jennings LC, Murdoch DR. Viral pneumonia. Lancet. 2011;377(9773):1264–1275. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61459-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dandachi D, Rodriguez-Barradas MC. Viral pneumonia: etiologies and treatment. J Investig Med. 2018;66(6):957–965. doi: 10.1136/jim-2018-000712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Duan K, Liu B, Li C, Zhang H. Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shen C, Wang Z, Zhao F, Yang Y, Li J, Yuan J, Wang F, Li D, Yang M, Xing L, et al. Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma. JAMA. 2020;323(16):1582–89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Ye M, Fu D, Ren Y, Wang F, Wang D, Zhang F, Xia X, Lv T. Treatment with convalescent plasma for COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hohenadl C, Wodal W, Kerschbaum A, Fritz R, Howard MK, Farcet MR, Portsmouth D, McVey JK, Baker DA, Ehrlich HJ, et al. Hyperimmune intravenous immunoglobulin containing high titers of pandemic H1N1 hemagglutinin and neuraminidase antibodies provides dose-dependent protection against lethal virus challenge in SCID mice. Virol J. 2014;11:70. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-11-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Renegar KB, Small PA, Jr, Boykins LG, Wright PF. Role of IgA versus IgG in the control of influenza viral infection in the murine respiratory tract. J Immunol. 2004;173(3):1978–1986. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.3.1978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mair-Jenkins J, Saavedra-Campos M, Baillie JK, Cleary P, Khaw F-M, Lim WS, Makki S, Rooney KD, Nguyen-Van-Tam JS, Beck CR, et al. The effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral etiology: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 2015;211(1):80–90. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Simmons CP, Bernasconi NL, Suguitan AL, Mills K, Ward JM, Chau NVV, Hien TT, Sallusto F, Ha DQ, Farrar J, et al. Prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of human monoclonal antibodies against H5N1 influenza. PLoS Med. 2007;4(5):e178. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wu JT, Lee CK, Cowling BJ, Yuen KY. Logistical feasibility and potential benefits of a population-wide passive-immunotherapy program during an influenza pandemic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(7):3269–3274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911596107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hung IF, To KK. Lee C-K, Lee K-L, Chan K, Yan W-W, Liu R, Watt C-L, Chan W-M, Lai K-Y, et al. Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(4):447–456. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Luke TC, Kilbane EM, Jackson JL, Hoffman SL. Meta-analysis: convalescent blood products for Spanish influenza pneumonia: a future H5N1 treatment? Ann Intern Med. 2006;145(8):599–609. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-145-8-200610170-00139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lim VW, Tudor Car L, Leo Y-S, Chen MIC, Young B. Passive immune therapy and other immunomodulatory agents for the treatment of severe influenza: systematic review and meta-analysis. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2020;14(2):226–236. doi: 10.1111/irv.12699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Beigel JH, Aga E, Elie-Turenne M-C, Cho J, Tebas P, Clark CL, Metcalf JP, Ozment C, Raviprakash K, Beeler J, et al. Anti-influenza immune plasma for the treatment of patients with severe influenza A: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7(11):941–950. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30199-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Davey RT, Jr, Fernández-Cruz E, Markowitz N, Pett S, Babiker AG, Wentworth D, Khurana S, Engen N, Gordin F, Jain MK, et al. Anti-influenza hyperimmune intravenous immunoglobulin for adults with influenza A or B infection (FLU-IVIG): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7(11):951–963. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30253-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hung IFN, KKW T, Lee C-K, Lee K-L, Yan W-W, Chan K, Chan W-M, Ngai C-W, Law K-I, Chow F-L, et al. Hyperimmune IV immunoglobulin treatment: a multicenter double-blind randomized controlled trial for patients with severe 2009 influenza A(H1N1) infection. Chest. 2013;144(2):464–473. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JAC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Group IFIPS INSIGHT FLU005: an anti-influenza virus hyperimmune intravenous immunoglobulin pilot study. J Infect Dis. 2016;213(4):574–578. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Beigel JH, Tebas P, Elie-Turenne M-C, Bajwa E, Bell TE, Cairns CB, Shoham S, Deville JG, Feucht E, Feinberg J, et al. Immune plasma for the treatment of severe influenza: an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 randomised study. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5(6):500–511. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30174-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Delaney M, Wendel S, Bercovitz RS, Cid J, Cohn C, Dunbar NM, TO A, Popovsky M, Stanworth SJ, Tinmouth A, et al. Transfusion reactions: prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Lancet. 2016;388(10061):2825–2836. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Panch SR, Montemayor-Garcia C, Klein HG. Hemolytic transfusion reactions. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(2):150–162. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1802338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the included randomized controlled trials.