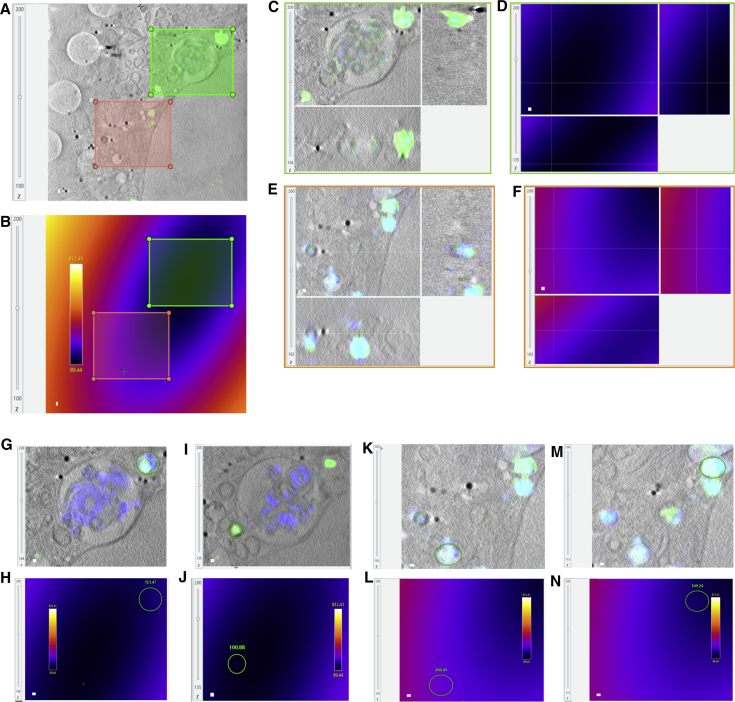
Figure S7.
Estimation of error on reovirus datasets, related to Figures 6, S3, and S5
(A and B) In (A) is an XY slice of the 3D X-ray tomogram (extracted from 4 h post-infection datasets) and in (B) is the corresponding slice of the 3D error map generated using the point-set used for registration. The color codes for predicted average error is in nm, ranging from 89 to 813 nm in the full volume (two sub regions are selected for best and possible worst accuracy in this view (green shaded and red shaded respectively). Best accuracy areas overall lie near the gravity center of the point-set used for registration, dark blue). The scale bar is 100 nm.
(C and D) In (C) are orthoviews of a crop of the merged dataset in the green sub region and in (D) is the corresponding crop in the error map. This area given the registration used, corresponds to the best accuracy we can obtain in this particular volume (89 to 150 nm). Scale bar is 100 nm.
(E and F) In (E) is an orthoview of a crop of the merged dataset in the red sub region of (A), and in (F) is the corresponding crop in the error map. This orthoview is centered in an area with a predicted accuracy of 300 nm, which can be seen in the discrepancy in Z on the focused endosome. Scale bar is 100 nm.
(G–N) Example of accuracy measured on finer areas within the error map for different endosomal arrangements. The circled areas indicate local 2D areas selected for which average predicted errors was measured, and their matching position on the merged dataset. The predicted error is displayed above these in the error map in nm. (G)–(J) and (K)–(N) are taken the green and red sub regions respectively. The scale bar is 100 nm.