Key Points
Question
Is magnetic resonance imaging screening cost-effective for women with a 20% or more familial risk of breast cancer without a known BRCA1/2 or TP53 variant, and what is the optimal screening strategy?
Findings
This economic evaluation found that magnetic resonance imaging every 18 months between ages of 35 and 60 years followed by the national screening program until age 75 years was cost-effective and considered optimal within the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence threshold for all densities. Higher thresholds would favor annual magnetic resonance imaging screening.
Meaning
These outcomes support a change of current screening guidelines for this specific risk group and support magnetic resonance imaging screening; the decision on which strategy to choose will also depend on the willingness to pay.
Abstract
Importance
For women with a 20% or more familial risk of breast cancer without a known BRCA1/2 (BRCA1, OMIM 113705; and BRCA2, OMIM 114480) or TP53 (OMIM 151623) variant, screening guidelines vary substantially, and cost-effectiveness analyses are scarce.
Objective
To assess the cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) screening strategies for women with a 20% or more familial risk for breast cancer without a known BRCA1/2 or TP53 variant.
Design, Setting, and Participants
In this economic evaluation, conducted from February 1, 2019, to May 25, 2020, microsimulation modeling was used to estimate costs and effectiveness on a lifetime horizon from age 25 years until death of MRI screening among a cohort of 10 million Dutch women with a 20% or more familial risk for breast cancer without a known BRCA1/2 or TP53 variant. A Dutch screening setting was modeled. Most data were obtained from the randomized Familial MRI Screening (FaMRIsc) trial, which included Dutch women aged 30 to 55 years. A health care payer perspective was applied.
Interventions
Several screening protocols with varying ages and intervals including those of the randomized FaMRIsc trial, consisting of the mammography (Mx) protocol (annual mammography and clinical breast examination) and the MRI protocol (annual MRI and clinical breast examination plus biennial mammography).
Main Outcomes and Measures
Costs, life-years, quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) were calculated and discounted by 3%. A threshold of €22 000 (US $24 795.87) per QALY was applied.
Results
This economic evaluation modeling study estimated that, on a lifetime horizon per 1000 women with the Mx protocol of the FaMRIsc trial, 346 breast cancers would be detected, and 49 women were estimated to die from breast cancer, resulting in 22 885 QALYs and total costs of €7 084 767 (US $7 985 134.61). The MRI protocol resulted in 79 additional QALYs and additional €2 657 266 (US $2 994 964.65). Magnetic resonance imaging performed only every 18 months between the ages of 35 and 60 years followed by the national screening program was considered optimal, with an ICER of €21 380 (US $24 097.08) compared with the previous nondominated strategy in the ranking, when applying the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence threshold. Annual screening alternating MRI and mammography between the ages of 35 and 60 years, followed by the national screening program, gave similar outcomes. Higher thresholds would favor annual MRI screening. The ICER was most sensitive to the unit cost of MRI and the utility value for ductal carcinoma in situ and localized breast cancer.
Conclusions and Relevance
This study suggests that MRI screening every 18 months between the ages of 35 and 60 years for women with a family history of breast cancer is cost-effective within the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence threshold for all densities. Higher thresholds would favor annual MRI screening. These outcomes support a change of current screening guidelines for this specific risk group and support MRI screening.
This economic evaluation uses data from the Familial MRI Screening Study to assess the cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging screening strategies for women with a 20% or more familial risk for breast cancer without a known BRCA1/2 or TP53 variant.
Introduction
Women with a family history of breast cancer have an increased risk of developing breast cancer, and an increased risk of developing it at a relatively young age.1 In approximately 64% to 87% of these women, no causative hereditary gene variant has been found.2 Because tumor stage at diagnosis is of importance for survival,3 screening is advised, but guidelines differ substantially.
The American Cancer Society advises additional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for women with a lifetime risk of 20% or more of developing breast cancer,4 whereas in the Netherlands and the UK, only mammography screening is advised for women at familial risk without a BRCA1/2 (BRCA1, OMIM 113705; and BRCA2, OMIM 114480) variant.4,5 All guidelines recommend to start screening among women with a familial risk of breast cancer at a younger age than women at average risk.4,5,6 However, younger women often have dense breast tissue,7 which is associated with decreased mammographic sensitivity.8 Magnetic resonance imaging screening has a high sensitivity, not affected by breast density.9,10 However, MRI leads to more false-positive results and is associated with higher costs.9,10,11 To our knowledge, little is known about the cost-effectiveness of MRI screening for women with a familial risk of breast cancer; one previous study evaluated the cost-effectiveness of MRI screening in women at familial risk of breast cancer without a known gene variant, showing by microsimulation modeling that MRI screening was very costly.11 The model was based on data from a nonrandomized study.
Recently, the randomized Familial MRI Screening (FaMRIsc) trial showed higher breast cancer detection rates and detection of breast cancer at, on average, an earlier stage when screening with MRI in comparison with mammography in women at increased familial risk without a known BRCA or TP53 (OMIM 151623) gene variant.9 In this study, we calculate real-life costs of MRI and mammography in the FaMRIsc trial. We estimate the cost-effectiveness by microsimulation modeling, and compare different screening scenarios by varying starting and stopping ages, screening intervals, and combinations of MRI and mammography.
Methods
The FaMRIsc Trial
In the multicenter randomized clinical FaMRIsc trial, Dutch women aged 30 to 55 years with a cumulative lifetime breast cancer risk of 20% or more due to a family history of breast cancer without a known BRCA1/2 or TP53 variant were randomly assigned into 2 screening groups after providing written informed consent (trial protocol in Supplement 1). The MRI group received annual MRI plus clinical breast examination (CBE), and mammography every 2 years. The mammography (Mx) group received annual mammography and CBE, in accordance with the Dutch screening protocol.5 Women refusing randomization could participate in a registration group (Reg-MRI group or Reg-Mx group) by providing consent for registration of their screening results. More details have been described elsewhere.9,12 The FaMRIsc Study follows the Declaration of Helsinki13 and was approved by the Erasmus University Medical Center Institutional Review Board (Rotterdam, the Netherlands; reference MEC-2010-292). The FaMRIsc trial is registered with the Netherlands Trial Register NL2661.
The Microsimulation Screening Analysis Model
In this economic evaluation, conducted from February 1, 2019, to May 25, 2020, we used the Microsimulation Screening Analysis (MISCAN) model, which simulates individual natural histories from birth to death and the natural history of breast cancer. We adjusted the version by Sankatsing et al14 to extrapolate the findings of the FaMRIsc trial. To be able to model the difference in the numbers of detected ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and T1a and T1b tumors between the 2 study groups,9 2 additional preclinical states were added to the original MISCAN model: DCIS_MRI and T1a/T1b_MRI (eFigure 1 in Supplement 2). We assumed that DCIS and T1a and T1b tumors could for some time be detected only by MRI before they could also be detected by mammography or before they become clinically detectable. During all other preclinical states, the tumor could be detected with MRI as well as mammography or clinically diagnosed. Progression through the health states was modeled as a semi-Markov process. The model only takes into account first breast cancers and no contralateral breast cancers.
We assumed the mammographic sensitivity to be 15% lower than previously used in the model owing to the younger population we modeled.15 We assumed that CBE would not lead to additional cancer detection.16 Incidence, dwelling times, stage-specific sensitivities of MRI, and transition probabilities of the additional health state DCIS_MRI to DCIS and to T1a/T1b_MRI were estimated by calibration using the Nelder-Mead simplex optimization method.17 We used data from all trial groups (Mx group + Reg-Mx group and MRI group + Reg-MRI group) to increase the amount of data for calibration. Model predictions were calibrated to the number of screening-detected breast cancers per T stage, the number of interval cancers, the number of detected cancers per 10-year age groups, and the number of screening-detected tumors during incident and prevalent rounds, all stratified by screening protocol as observed during the FaMRIsc trial. We aimed for all predicted numbers to fall within 95% Poisson CIs of the observed numbers of tumors.
Probabilities of (false) positive results and diagnostic procedures were obtained from the FaMRIsc trial, stratified by screening modality and by age (<50 and ≥50 years). Both true-positive and false-positive results were associated with diagnostic follow-up and associated costs. For the screening period within the national breast cancer screening program, we applied the same probabilities as for the Mx protocol.
For the situation without screening, we assumed all women with a diagnosed breast cancer would undergo a diagnostic mammogram, CBE, biopsy, or fine needle aspiration, and all women with a diagnosed T2 or higher tumor would undergo an MRI. The percentage of ultrasonographic evaluations performed in diagnosed cases in a situation without screening was assumed to be equal to the percentage of those performed among women with a diagnosed breast cancer within the Mx protocol.
Screening Strategies
After calibration, we applied several screening strategies, varying in starting and stopping ages, intervals, and screening modalities. With stopping ages below the age of 75 years, we modeled the women to continue screening within the national screening program until the age of 75 years, consisting of biennial mammography at a local screening unit. Attendance rates were set at 100%.
Costs
We applied a health care perspective and considered only direct medical costs (converted to 2018 amounts; eTable 1 in Supplement 2) and costs related to other causes of death. Costs of MRI, mammography in a hospital setting, and ultrasonography were derived from the tariff tool from an insurance company by calculating the mean of all published prices.18 The price of mammography in a local screening unit was obtained from the Netherlands Comprehensive Cancer Organisation.19 All other costs were obtained from a study by Saadatmand et al.11 Costs of fine needle aspiration and biopsy were updated and adjusted by adding costs of pathologic examination of the specimen, obtained from the tariff tool.18 Costs of breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy were adjusted assuming 1.5 consecutive hospital days with its price obtained from the Dutch costing manual.20 Costs associated with breast cancer death were assumed to be €19 679 (US $22 179.91) and death due to other causes were assumed to be €15 044 (US $16 955.87).21
We multiplied costs with the resource use during the trial to calculate real-life costs. Mean treatment costs per TN stage were calculated by dividing total treatment costs per TN stage by the number of cancers. Model outcomes were multiplied with aforementioned prices to calculate costs per screening protocol.
Health State Utilities
Utility values were obtained from the literature (eTable 2 in Supplement 2). The utility value for the healthy state was based on a study by Versteegh et al.22 Early-stage cancer was associated with disutility of 10%, regional cancer was associated with disutility of 25%, and metastasis was associated with disutility of 40%.23 A disutility of 0.105 was applied for a positive screening result with a duration of 5 weeks.24 We did not apply a disutility for screening visits.25
Statistical Analysis
We simulated the number of invitations, screening visits, screening-detected cancers, interval cancers, life-years, quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), deaths from breast cancer, and deaths from other causes, all on a lifetime horizon from age 25 years for a cohort of 10 million Dutch women born in 1980. All results were scaled to 1000 women. Overdiagnosis was defined as detected cancers that would not have been diagnosed in a woman’s lifetime in a situation without screening. Incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) were calculated by dividing incremental costs by incremental QALYs. We plotted an efficiency frontier representing efficient strategies that are either less costly and more effective, or more costly but more cost-effective than those below the frontier. A cost-effectiveness threshold was based on the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) threshold of £20 000 (€22 000 [US $24 795.87]). Average cost-effectiveness ratios were calculated by dividing additional costs by additional QALYs compared with a situation without screening. Costs and effects were discounted by 3%.26
One-way sensitivity analyses were performed for utility values, the price of MRI, and false-positive rates to analyze the association of these parameters with the ICER of the MRI protocol vs the Mx protocol. Utility values were varied ±10% of the base case values and the other parameters were varied ±20% of the base case values. Sensitivity analyses were discounted by 3%.
Five scenario analyses were performed to quantify methodological uncertainty. First, we applied discount rates of 4.0% for costs and 1.5% for effects, according to Dutch guidelines.20 Second, we calculated the ICER without discounting. Third, we applied utility values based on a study by Lidgren et al27 (eTable 3 in Supplement 2). Fourth, we calculated the ICER without costs related to death from other causes. Fifth, we applied a disutility of 0.006 for 1 week for screening participation.24 Scenario analyses were performed for the comparison of the 2 screening protocols of the FaMRIsc trial.
We calculated the risk of radiation-induced breast cancers for an optimal screening strategy with mammography compared with a strategy without mammography. We used the excess absolute risk model28,29 with a glandular dose of a 2-view mammogram of 4.4 mGy.
Results
Real-Life Results During the FaMRIsc Trial
After a mean follow-up of 4.3 years, 41 tumors were detected in the MRI group, whereas 15 tumors were detected in the Mx group.9 Table 19 shows the number of detected tumors, woman-years at risk, and real-life screening costs according to group, age, and density during the FaMRIsc trial. The MRI protocol resulted in approximately 2 times higher costs of screening and additional investigation. Mean treatment costs are shown in eTable 4 in Supplement 2.
Table 1. Real-Life Costs During the FaMRIsc Trial by Group, Age, and Density.
| Characteristic | No. of breast cancersa | Life-years at risk | Costs, € (US $) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screening | Additional investigation | |||
| MRI group by age | ||||
| <50 y | 18 | 2106 | 740 188 (834 254.79) | 171 054 (192 792.40) |
| ≥50 y | 23 | 1112 | 357 578 (403 020.80) | 59 281 (66 814.73) |
| Total | 41b | 3218 | 1 097 766 (1 237 275.59) | 230 335 (259 607.12) |
| Mx group by age | ||||
| <50 y | 8 | 2099 | 341 568 (384 976.17) | 87 576 (98 705.60) |
| ≥50 y | 7 | 1215 | 178 692 (201 401.07) | 31 266 (35 239.44) |
| Total | 15 | 3314 | 520 260 (586 377.24) | 118 842 (133 945.04) |
| MRI group and registration MRI protocol by density category | ||||
| BI-RADS density A-C (0%-75%) | 38 | 2743 | 939 818 (1 059 254.77) | 184 004 (207 388.15) |
| BI-RADS density D (>75%) | 5 | 507 | 176 580 (199 020.67) | 52 750 (59 453.73) |
| Total | 43b | 3249 | 1 116 397 (1 258 274.31) | 236 754 (266 841.88) |
| Mx group and registration Mx protocol by density category | ||||
| BI-RADS A-C | 17 | 3648 | 567 145 (639 220.62) | 120 408 (135 710.05) |
| BI-RADS D | 6 | 659 | 105 386 (118 778.98) | 42 227 (47 593.42) |
| Total | 23 | 4308 | 672 531 (757 999.60) | 162 635 (183 303.47) |
Abbreviations: BI-RADS, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System Atlas; FaMRIsc, Familial MRI Screening; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; Mx, mammography.
Breast cancers include invasive breast cancers and ductal carcinoma in situ.
One additional cancer was added in this article, which was excluded in the previous article.9 This was an interval cancer between a mammogram and MRI in the first screening round in the MRI group.
Model Calibration Results
eFigure 2 in Supplement 2 shows the number of observed breast cancers during the FaMRIsc trial according to T stage and the number of predicted cancers by our calibrated model. All predicted numbers were within the 95% CIs of the observed numbers.
Cost-effectiveness Results
Table 2 and eTable 5 in Supplement 2 display the outcomes of all modeled strategies per 1000 women. With the Mx protocol of the FaMRIsc trial (strategy M), 346 breast cancers would be detected, and 49 women would die from breast cancer, resulting in 22 885 QALYs (discounted by 3%) and total costs of €7 084 767 (US $7 985 134.61) (discounted by 3%) and total costs of €23 497 356 (US $26 483 517.49) (undiscounted). With the MRI protocol of the FaMRIsc trial (strategy V), 377 breast cancers would be detected and 30 breast cancer deaths would occur, resulting in 79 additional QALYs (discounted by 3%) and additional costs of €2 657 266 (US $2 994 964.65) (discounted by 3%) and total costs of €28 024 674 (US $31 586 189.70) (undiscounted). Comparing these 2 protocols resulted in an ICER of €33 277 (US $37 506.01) per QALY gained (discounted).
Table 2. Modeled Effects and Costs per 1000 Women of Efficient Strategies With an ICER Below €100 000 (US $112 708.50), and the FaMRIsc Trial Strategiesa.
| Characteristic | No screening | Model Ab | Model Bc | Model Cd | Model De | Model Mf | Model Eg | Model Fh | Model Vi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screening rounds | NA | 22 296 | 27 136 | 18 895 | 18 706 | 27 136 | 26 196 | 25 939 | 25 924 |
| Breast cancers | 306 | 346 | 346 | 365 | 370 | 346 | 372 | 377 | 377 |
| Screening detected | NA | 288 | 297 | 319 | 332 | 297 | 337 | 348 | 349 |
| Clinically diagnosed | 306 | 58 | 49 | 46 | 38 | 49 | 35 | 29 | 28 |
| Breast cancer deaths | 136 | 53 | 49 | 44 | 38 | 49 | 37 | 31 | 30 |
| Reduction in breast cancer deaths compared with no screening, % | NA | −61 | −64 | −68 | −72 | −64 | −73 | −77 | −78 |
| False-positive results | NA | 1331 | 1578 | 1514 | 1885 | 2436 | 2086 | 2629 | 3825 |
| Overdiagnosis, No. (% of screening-detected cancers) | NA | 40 (14) | 40 (13) | 59 (18) | 65 (19) | 40 (13) | 66 (20) | 71 (20) | 71 (20) |
| LYs | 55 936 | 57 289 | 57 404 | 57 508 | 57 632 | 57 404 | 57 642 | 57 757 | 57 774 |
| QALYs | 47 450 | 48 774 | 48 885 | 48 992 | 49 113 | 48 876 | 49 122 | 49 236 | 49 242 |
| Costs, € (US $) | |||||||||
| Screening tests | NA | 1 937 798 (2 184 063.06) | 2 382 952 (2 685 789.45) | 2 980 816 (3 359 633.00) | 4 274 868 (4 818 139.60) | 3 994 553 (4 502 200.77) | 4 251 282 (4 772 722.99) | 6 141 510 (6 922 003.80) | 8 677 921 (9 780 754.59) |
| Diagnosis | 296 869 (334 596.60) | 608 169 (685 458.16) | 738 054 (831 849.59) | 917 523 (1 034 126.41) | 1 031 319 (1 162 384.18) | 1 138 243 (1 282 896.61) | 1 305 090 (1 470 947.36) | 1 451 048 (1 635 454.44) | 2 129 114 (2 399 692.45) |
| Treatment | 4 329 646 (4 879 879.06) | 3 367 954 (3 795 970.43) | 3 295 594 (3 714 414.56) | 2 798 040 (3 153 628.91) | 2 512 550 (2 831 857.42) | 3 295 594 (3 714 414.56) | 2 514 195 (2 833 711.47) | 2 268 554 (2 556 853.19) | 2 242 559 (2 527 554.61) |
| Breast cancer death | 2 684 157 (3 025 273.09) | 1 046 478 (1 179 469.66) | 972 526 (1 096 119.47) | 866 085 (976 151.41) | 744 323 (838 915.29) | 972 526 (1 096 119.47) | 723 739 (815 715.37) | 615 290 (693 484.13) | 598 822 (674 923.29) |
| Death from other causes | 12 816 630 (14 445 431.42) | 14 040 806 (15 825 181.83) | 14 096 439 (15 887 884.95) | 14 176 051 (15 977 614.44) | 14 267 489 (16 080 672.84) | 14 096 439 (15 887 884.95) | 14 282 608 (16 097 713.24) | 14 364 011 (16 189 461.34) | 14 376 257 (16 203 263.62) |
| Total | 20 127 302 (22 685 180.17) | 21 001 204 (23 670 142.01) | 21 485 565 (24 216 058.03) | 21 738 516 (24 501 155.31) | 22 830 549 (25 731 969.32) | 23 497 356 (26 483 517.49) | 23 076 913 (26 009 642.49) | 24 840 412 (27 997 255.76) | 28 024 674 (31 586 189.70) |
| QALYs gainedj,k | NA | 283 | 315 | 338 | 365 | 311 | 366 | 393 | 390 |
| Total costs, € (US $)k | 5 019 633 (5 657 553.06) | 5 653 893 (6 372 417.99) | 5 996 015 (6 758 018.57) | 6 306 999 (7 108 523.97) | 6 896 883 (7 773 373.38) | 7 084 767 (7 985 134.61) | 7 085 452 (7 985 906.67) | 8 009 853 (9 027 785.17) | 9 742 033 (10 980 099.26) |
| QALY, € (US $)k | |||||||||
| ACER | NA | 2241 (2525.80) | 3097 (3490.58) | 3811 (4295.32) | 5138 (5790.96) | 6648 (7492.86) | 5641 (6357.89) | 7617 (8585.01) | 12 094 (13 630.97) |
| ICER | NA | 2241 (2525.80) | 10 588 (11 933.58) | 13 812 (15 567.30) | 21 380 (24 097.08) | Strongly dominatedl | Weakly dominatedl | 40 919 (46 119.19) | Strongly dominatedl |
Abbreviations: ACER, average cost-effectiveness ratio (comparison of a strategy with a situation without screening); FaMRIsc, Familial MRI Screening; ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (comparison of a strategy to the previous nondominated strategy in the ranking); LYs, life-years; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; Mx, mammography; NA, not applicable; QALYs, quality-adjusted life-years.
Breast cancers include invasive breast cancers and ductal carcinoma in situ. Results are without discounting. Outcomes contain the effects of both the described strategy and the subsequent national breast cancer screening program.
Annual mammography between 40 and 60 years.
Annual mammography between 35 and 60 years.
Alternating MRI or mammography every 18 months between 35 and 60 years.
Magnetic resonance imaging every 18 months between 35 and 60 years.
Annual mammography and clinical breast examination between 35 and 60 years (Mx protocol in FaMRIsc trial).
Alternating annual MRI or mammography between 35 and 60 years.
Annual MRI between 35 and 60 years.
Annual MRI plus clinical breast examination, and biennial mammography between 35 and 60 years (MRI protocol in FaMRIsc trial).
Relative to a situation without screening.
Discounted by 3%.
Another strategy is more effective at the same or lower cost.
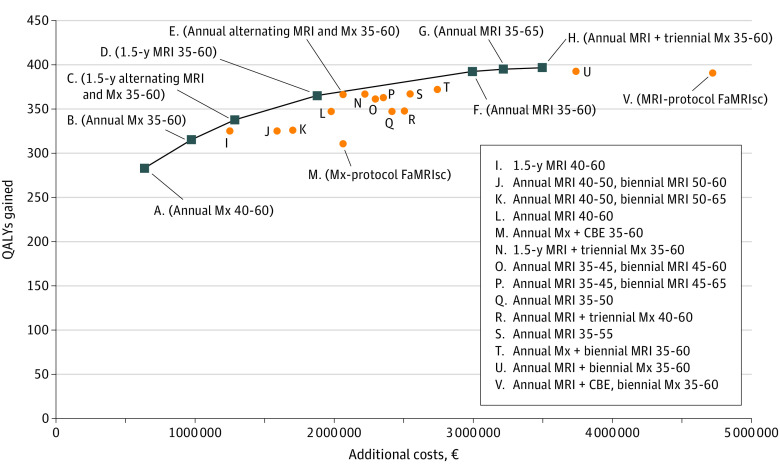
Both screening protocols of the FaMRIsc trial were dominated by similar screening strategies without CBE (strategy B and U) (Figure 1). Strategies involving MRI resulted in fewer breast cancer deaths, lower numbers of interval cancers, and lower total treatment costs but more overdiagnosed cancers, compared with screening without MRI. The 2 strategies with intervals of 18 months were both on the efficiency frontier (Figure 1). Most strategies on the efficiency frontier consisted of screening from age 35 until 60 years, continued within the national screening program. Switching to screening within the national screening program before age 60 years resulted in higher numbers of clinically diagnosed cancers and breast cancer deaths, and were therefore dominated (eTable 5 in Supplement 2).
Figure 1. Efficiency Frontier of Screening Strategies.
Number indicates interval, and ranges represent women’s ages reported in years; all results are discounted by 3%. CBE indicates clinical breast examination; FaMRIsc, Familial MRI Screening Study; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; Mx, mammography; and QALY, quality-adjusted life-year. Additional costs €1 = $1.13 on July 1, 2020.
Strategy D, consisting of MRI screening every 18 months between ages of 35 and 60 years followed by the national screening program had the highest acceptable ICER, €21 380 (US $24 002.36), when applying the NICE threshold of £20 000 (€22 000 [US $24 795.87]) and was considered optimal. Strategy E, consisting of alternating annual MRI or mammography between the ages of 35 and 60 years, was almost on the efficiency frontier. The effects of this strategy were similar to those of strategy D for somewhat higher cost. Strategies D and E, both followed by screening within the national breast cancer screening program, resulted in a reduction of 98 and 99 breast cancer deaths, respectively, and 65 or 66 overdiagnosed cases, respectively, when compared with a situation without screening.
Sensitivity and Scenario Analyses
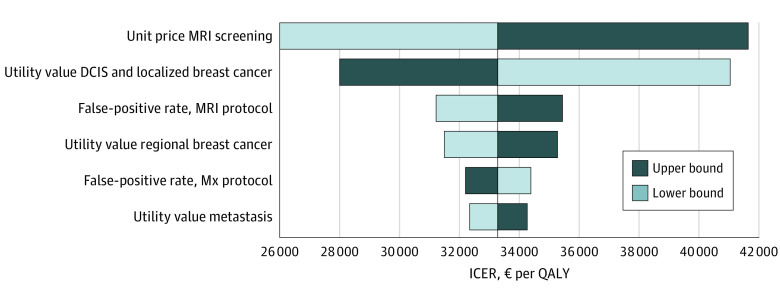
Results of the deterministic sensitivity analyses are shown in Figure 2. The ICER was most sensitive to the price of MRI screening and the utility value for DCIS or localized breast cancer.
Figure 2. Tornado Diagram of the 1-Way Sensitivity Analyses.
All results are discounted by 3%. DCIS indicates ductal carcinoma in situ; ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; Mx, mammography; and QALY, quality-adjusted life-year.
When applying Dutch discount rates, the ICER of the MRI protocol vs the Mx protocol became lower: €13 108 (US $14 773.83) per QALY gained. The difference in life-years and QALYs between the 2 protocols were 176 and 170, respectively, and the difference in costs was €2 234 665 (US $2 518 657.40). Without discounting, the ICER was €12 376 (US $13 948.80).
In the third scenario analysis, in which we applied a different set of utility values, the difference in QALYs between the MRI protocol and Mx protocol became 71, which was lower compared with the base case. Consequently, the ICER became larger: €37 489 (US $42 253.29) per QALY gained (discounted). When not applying costs related to death from other causes, the ICER became €32 712 (US $36 869.20) per QALY gained (discounted), which was similar to the ICER when including these costs. Applying a utility decrement for screening participation hardly affected the ICER, which became €33 534 (US $37 795.67) (discounted).
Radiation Risk
In a situation with additional mammography to the optimal screening strategy (D) consisting of MRI every 18 months between the ages of 35 and 60 years, radiation would induce 0.94 breast cancers and 0.12 breast cancer deaths per 1000 women. In this situation, 3 additional breast cancers would be detected by screening of which 1 would be overdiagnosed, and 2 breast cancer deaths would be prevented (undiscounted) compared with a strategy without additional mammography (strategy D).
Discussion
This economic modeling study of data on Dutch women showed that the detection of more tumors at an early stage and fewer at a late stage by MRI9 could be a cost-effective method to reduce breast cancer mortality despite more overdiagnosis and higher costs in comparison with mammography. Yearly MRI seems to bring the largest mortality reduction, but for an ICER higher than allowed by NICE guidelines.30 Neither protocol of the FaMRIsc trial was on the efficiency frontier, mainly owing to the addition of CBE that proved to be inefficient.9,16 Screening with MRI only every 18 months between the ages of 35 and 60 years and subsequent screening in the national screening program until age 75 years would be an efficient and cost-effective strategy, with an ICER just below the threshold of £20 000 (€22 000 [US $24 795.87]). We also found that the additional association of mammography with this strategy was limited. Screening consisting of alternating annual MRI and mammography between ages of 35 and 60 years, followed by screening within the national screening program until the age of 75 years was almost on the frontier, with similar effects and more costs as the previously mentioned strategy (MRI only every 18 months between the ages of 35 and 60 years). Most of the efficient strategies consisted of screening from 35 to 60 years of age, with continuation of screening within the national screening program. Furthermore, our results indicated that the switch to the national screening program should not take place before 60 years of age.
We modeled a Dutch health care setting but we expect the relative difference in health outcomes between our modeled strategies to be similar in other countries. In contrast, unit prices as well as cost-effectiveness thresholds vary substantially per country, which should be taken into account when generalizing our results to other countries.
We simulated one group of women with, on average, the same risk of breast cancer. However, starting screening at 35 years of age may not be beneficial for all women within this group, depending on the youngest age of breast cancer diagnosis of a family member and their individually calculated lifetime risk.31 Therefore, family history should be taken into account when choosing the starting age for screening.
To our knowledge, one previous study evaluated the cost-effectiveness of additional MRI screening for this group of women. Saadatmand et al11 calibrated the MISCAN model on data from the 1999-2006 MRI Screening (MRISC) study. The breast cancer incidence in the FaMRIsc Study was higher than that in the MRISC study, and the sensitivity of both MRI and mammography were also higher.
Strengths and Limitations
This study has some strengths, including the use of randomized clinical trial data for calibration, which has, to our knowledge, not been done before for this group of women. By using randomized clinical trial data, the model gets more information on the performance of MRI and mammography separately than when these screening modalities are performed simultaneously.
This study also has some limitations. First, the study sample of the FaMRIsc trial was still quite small for calibration. The numbers of observed cancers stratified by group and stage were small and therefore 95% CIs were large. Therefore, we added the data of the registration groups. However, there may have been a difference in population between women registered and those randomized. A second limitation is the assumption that there is no DCIS that is detectable only by mammography. Third, we were unable to model strategies by breast density categories as the numbers by breast density in the FaMRIsc trial were too small, albeit the associations of MRI with detection seem similar across density categories. A recent study showed the benefit of MRI screening in women with extremely dense breasts.32 Fourth, we did not measure utility values within our study population. Utility values related to breast cancer vary significantly in the literature33,34 and we are aware of the association of these values with the results, as shown in our analyses. Furthermore, we would like to point out the uncertainty of efficiency frontiers as such. Efficiency frontiers are sensitive to changes in underlying data and assumptions, and they do not display uncertainty.35
Downsides of MRI are its high costs, more false-positive results, and increased overdiagnosis. Overdiagnosis may be a result of excessive detection of low-grade tumors, but our model cannot distinguish between low-grade or high-grade tumors. Overdiagnosis is captured in our results and the same (dis)utility values were applied to all modeled breast cancer cases because one does not know whether a cancer is overdiagnosed or not.
Applying MRI screening may have some practical implications. Hospitals need to have enough capacity for the screening and for additional diagnostic testing due to more (false) positive results, to prevent waiting lists. In addition, radiologists may need additional training to guarantee good quality, as MRI screening requires expertise.
Currently, abbreviated MRI seems promising, which has shorter acquisition time and reading time while maintaining diagnostic accuracy.36 A less time-consuming MRI will decrease the price of the test, which has a favorable association with the ICER, as shown in our sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions
Based on this cost-effectiveness analysis, MRI screening every 18 months or alternating annual MRI and mammography between the ages of 35 and 60 years may be recommended for women at increased familial risk of breast cancer, both followed by screening within the national screening program, when applying the NICE threshold. Annual MRI was associated with the largest mortality reduction, but for an ICER higher than allowed by NICE guidelines.
Trial Protocol
eFigure 1. Model Structure
eFigure 2. Observed and Predicted Screen-Detected Cancers According to T-Stage
eTable 1. Unit Prices per Procedure Associated With Breast Cancer Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment
eTable 2. Utility Values and Durations
eTable 3. Alternative Utility Values and Durations Used in a Scenario Analysis
eTable 4. Mean Costs per Tumor Stage
eTable 5. Modelled Effects and Costs per 1000 Women of Dominated Screening Protocols and of Protocols With an ICER>100 000 Euro per QALY Gained
eReferences
References
- 1.Claus EB, Risch NJ, Thompson WD. Age at onset as an indicator of familial risk of breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1990;131(6):961-972. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115616 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hartmann LC, Lindor NM. The role of risk-reducing surgery in hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(5):454-468. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1503523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Saadatmand S, Bretveld R, Siesling S, Tilanus-Linthorst MMA. Influence of tumour stage at breast cancer detection on survival in modern times: population based study in 173,797 patients. BMJ. 2015;351:h4901. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h4901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al. ; American Cancer Society Breast Cancer Advisory Group . American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57(2):75-89. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.57.2.75 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.oncoline Richtlijn mammacarcinoom (breast cancer national guideline). Accessed January 15, 2019.https://www.oncoline.nl/borstkanker.
- 6.American College of Radiology American College of Radiology (ACR) Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System Atlas (BI-RADS Atlas). American College of Radiology, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Checka CM, Chun JE, Schnabel FR, Lee J, Toth H. The relationship of mammographic density and age: implications for breast cancer screening. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;198(3):W292-W295. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.6049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Boyd NF, Guo H, Martin LJ, et al. Mammographic density and the risk and detection of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(3):227-236. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa062790 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Saadatmand S, Geuzinge HA, Rutgers EJT, et al. ; FaMRIsc study group . MRI versus mammography for breast cancer screening in women with familial risk (FaMRIsc): a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(8):1136-1147. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30275-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Berg WA, Zhang Z, Lehrer D, et al. ; ACRIN 6666 Investigators . Detection of breast cancer with addition of annual screening ultrasound or a single screening MRI to mammography in women with elevated breast cancer risk. JAMA. 2012;307(13):1394-1404. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.388 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Saadatmand S, Tilanus-Linthorst MMA, Rutgers EJT, et al. Cost-effectiveness of screening women with familial risk for breast cancer with magnetic resonance imaging. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(17):1314-1321. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Saadatmand S, Rutgers EJ, Tollenaar RA, et al. Breast density as indicator for the use of mammography or MRI to screen women with familial risk for breast cancer (FaMRIsc): a multicentre randomized controlled trial. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:440. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.World Medical Association World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. 2013;310(20):2191-2194. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.281053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sankatsing VDV, Heijnsdijk EAM, van Luijt PA, van Ravesteyn NT, Fracheboud J, de Koning HJ. Cost-effectiveness of digital mammography screening before the age of 50 in the Netherlands. Int J Cancer. 2015;137(8):1990-1999. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29572 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kolb TM, Lichy J, Newhouse JH. Comparison of the performance of screening mammography, physical examination, and breast US and evaluation of factors that influence them: an analysis of 27,825 patient evaluations. Radiology. 2002;225(1):165-175. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2251011667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Roeke T, van Bommel AC, Gaillard-Hemmink MP, Hartgrink HH, Mesker WE, Tollenaar RA. The additional cancer yield of clinical breast examination in screening of women at hereditary increased risk of breast cancer: a systematic review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;147(1):15-23. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-3074-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Barton RR, Ivey JS. Nelder-Mead simplex modifications for simulation optimization. Manag Sci. 1996;42(7):954-973. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.42.7.954 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.CZ Healthcare Insurance Tarieventool. Accessed October 3, 2018. https://www.cz.nl/service-en-contact/zoek-tarieven
- 19.Netherlands Comprehensive Cancer Organisation (IKNL) Monitor bevolkingsonderzoek borstkanker 2016. Published June 2018. Accessed July 9, 2019. https://www.rivm.nl/sites/default/files/2018-11/Monitor%20bevolkingsonderzoek%20borstkanker%202016%20webversie.pdf
- 20.Hakkaart-van Roijen L, van der Linden N, Bouwmans C, Kanters T, Tan S. Kostenhandleiding: methodologie van kostenonderzoekIn: Referentieprijzen Voor Economische Evaluaties in de Gezondheidszorg. Diemen; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Polder JJ, Barendregt JJ, van Oers H. Health care costs in the last year of life—the Dutch experience. Soc Sci Med. 2006;63(7):1720-1731. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.04.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Versteegh MM, Vermeulen KM, Evers SMAA, de Wit GA, Prenger R, Stolk EA. Dutch tariff for the five-level version of EQ-5D. Value Health. 2016;19(4):343-352. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2016.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Stout NK, Rosenberg MA, Trentham-Dietz A, Smith MA, Robinson SM, Fryback DG. Retrospective cost-effectiveness analysis of screening mammography. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(11):774-782. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djj210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.de Haes JC, de Koning HJ, van Oortmarssen GJ, van Agt HM, de Bruyn AE, van Der Maas PJ. The impact of a breast cancer screening programme on quality-adjusted life-years. Int J Cancer. 1991;49(4):538-544. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490411 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rijnsburger AJ, Essink-Bot ML, van Dooren S, et al. Impact of screening for breast cancer in high-risk women on health-related quality of life. Br J Cancer. 2004;91(1):69-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601912 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gold M, Siegel J, Russel L, Weinstein M.. Cost-Effectiveness in Health and Medicine. Oxford University Press; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lidgren M, Wilking N, Jönsson B, Rehnberg C. Health related quality of life in different states of breast cancer. Qual Life Res. 2007;16(6):1073-1081. doi: 10.1007/s11136-007-9202-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Preston DL, Mattsson A, Holmberg E, Shore R, Hildreth NG, Boice JD Jr. Radiation effects on breast cancer risk: a pooled analysis of eight cohorts. Radiat Res. 2002;158(2):220-235. doi: 10.1667/0033-7587(2002)158[0220:REOBCR]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.de Gelder R, Draisma G, Heijnsdijk EA, de Koning HJ. Population-based mammography screening below age 50: balancing radiation-induced vs prevented breast cancer deaths. Br J Cancer. 2011;104(7):1214-1220. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.67 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Guide to the processes of technology appraisal. Published April 2019. Accessed June 25, 2020. https://www.nice.org.uk/Media/Default/About/what-we-do/NICE-guidance/NICE-technology-appraisals/technology-appraisal-processes-guide-apr-2018.pdf [PubMed]
- 31.Tilanus-Linthorst MM, Lingsma HF, Evans DG, et al. Optimal age to start preventive measures in women with BRCA1/2 mutations or high familial breast cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(1):156-163. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, et al. ; DENSE Trial Study Group . Supplemental MRI screening for women with extremely dense breast tissue. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(22):2091-2102. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903986 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bromley HL, Petrie D, Mann GB, Nickson C, Rea D, Roberts TE. Valuing the health states associated with breast cancer screening programmes: a systematic review of economic measures. Soc Sci Med. 2019;228:142-154. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.03.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Peasgood T, Ward SE, Brazier J. Health-state utility values in breast cancer. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2010;10(5):553-566. doi: 10.1586/erp.10.65 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stollenwerk B, Lhachimi SK, Briggs A, et al. Communicating the parameter uncertainty in the IQWiG efficiency frontier to decision-makers. Health Econ. 2015;24(4):481-490. doi: 10.1002/hec.3041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kuhl CK, Schrading S, Strobel K, Schild HH, Hilgers RD, Bieling HB. Abbreviated breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): first postcontrast subtracted images and maximum-intensity projection—a novel approach to breast cancer screening with MRI. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(22):2304-2310. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.52.5386 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Trial Protocol
eFigure 1. Model Structure
eFigure 2. Observed and Predicted Screen-Detected Cancers According to T-Stage
eTable 1. Unit Prices per Procedure Associated With Breast Cancer Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment
eTable 2. Utility Values and Durations
eTable 3. Alternative Utility Values and Durations Used in a Scenario Analysis
eTable 4. Mean Costs per Tumor Stage
eTable 5. Modelled Effects and Costs per 1000 Women of Dominated Screening Protocols and of Protocols With an ICER>100 000 Euro per QALY Gained
eReferences