Abstract
Background
Laryngeal rhabdomyosarcomas (RMSs) mainly occurred in children, while were extremely rare in adults. Consequently, less information was available to guide clinicians to manage adult RMSs in larynx.
Case presentation
A 42-year-old man presented with a 2-year history of gradually worsening hoarseness. Then, he underwent a surgery with suspension laryngoscope with initially being diagnosed as vocal cord cyst. Unexpectedly, the lesion was proved to be embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS), pathologically. Next, he underwent chemoradiotherapy, while the tumor relapsed 18 months after the last treatment. Subsequently, a vertical hemilaryngectomy and a right selective neck dissection was performed, and the chemotherapy according to the anticancer drug sensitivity in vitro was arranged. Until the last check-up 18 months after chemotherapy, the patient did not display clinical or radiological signs of local recurrence and metastases.
Conclusions
Misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis of laryngeal RMSs might appear when tumors presented as smooth protuberance. We reported the first case of laryngeal RMSs in an adult with the multidisciplinary strategy based on the chemosensitivity assay in vitro. Furthermore, a systematic review of the literature was also discussed, highlighting the initial diagnostic pitfalls and subsequent management problems that may occur with this uncommon tumor.
Keywords: Rhabdomyosarcoma, Laryngeal rhabdomyosarcomas, Multidiscipline, Anticancer drug sensitivity
Background
Primary laryngeal sarcomas constitute less than 1% of all malignant laryngeal tumors [1], and more than 50% of these tumors are fibrosarcomas, followed by osteosarcomas, chondrosarcomas, liposarcomas, leiomyosarcomas, and rhabdomyosarcomas (RMSs) [2]. RMSs usually involve in skeletal muscle, and thus can be localized in almost any site [3]. Around 40% cases originate in the head and neck region, while RMSs arising in the larynx are extremely rare [4, 5]. Laryngeal RMSs, arising from undifferentiated mesodermal tissue, mainly occurred in children. To date, only 22 cases of laryngeal RMSs in adults have been reported (Table 1). As a result, less information was available to guide clinicians to manage adult RMSs in larynx. We reported the first case of laryngeal RMSs in an adult with the multidisciplinary strategy based on the chemosensitivity assay in vitro.
Table 1.
Reported cases of laryngeal rhabdomyosarcoma in adults
| Author/YR | Age/sex | Primary Location | Symptoms or signs | Histologic subtype | Treatment | Status by end of follow up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mungan S [1], 2016 | 64/M | Glottic | Hoarseness for 2 months | Pleomorphic | Total laryngectomy with left radical neck dissection and radiotherapy (6MV photons in an Elekta Synergy Platform linear accelerator) | Alive & disease-free, 24 months |
| Chiramel GK [6], 2015 | 70/M | Supraglottic | Hoarseness for 2 years | Pleomorphic | Chemotherapy (protocol was not provided) | Loss to follow-up |
| Li Y [7], 2015 | 22/F | Glottic | Hoarseness for 1 month | Embryonal | Right cordectomy and selective neck dissection | Alive & disease-free, 60 months |
| Russell JO [8], 2015 | 45/M | Glottic | Hoarseness for 11 months | Embryonal | Chemoradiation (vincristine, actinomycin, and cyclophosphamide combined with radiation dose of 50.4 Gy) | Alive, 34 months |
| Kukwa W [4], 2011 | 33/M | Supraglottic | Longstanding hoarseness | Embryonal | Hemilaryngectomy and chemotherapy | Alive & disease-free, 62 months |
| Leventhal DD [9], 2010 | 54/F | Glottic | Hoarseness for 9 months | Alveolar | Microsurgery by CO2 laser | Alive & disease-free, 12 months |
| Pittore B [3], 2010 | 75/M | Glottic | Dysphonia for 1 year | Pleomorphic | Partial left laryngectomy | Alive & disease-free, 9 months |
| Papacharalampous GX [10], 2009 | 83/F | Subglottic | Progressive dyspnoea for 3 months | Pleomorphic | Emergency tracheostomy and endoscopic tumour excision | dead (disease-free), 16 months |
| Schrock A [2], 2007 | 60/M | Glottic | Hoarseness for 1 months | Pleomorphic | Total laryngectomy with a bilateral selective neck dissection | Alive & disease-free, 20 months |
| 66/M | Glottic | Dyspnea for 6 weeks and hoarseness for 2 weeks | Pleomorphic | Microsurgery by CO2 laser | Alive & disease-free, 20 months | |
| Dikbas O [11], 2005 | 28/M | Glottic | Hoarseness for 15 days | Embryonal |
Tracheostomy with biopcy and chemoradiation (cisplatin, vincristine, doxorubicin, and Cyclophosphamide; protocol of radiotherapy was not provided) |
Alive & disease-free, 22 months |
| Libera DD [12], 1999 | 66/M | Supraglottic | Hoarseness and sense of throat fullness | Embryonal (botryoid) | Partial laryngectomy | Alive & disease-free, 10 years |
| Ruske DR [13], 1998 | 66/F | Supraglottic | Hoarseness and dyspnoea for 2 months | Pleomorphic | Total laryngectomy and radiotherapy (7040 cGys) | Alive & disease-free, 30 months |
| Akyol MU [14], 1998 | 63/M | Supraglottic | Hoarseness and increasing dyspnea for 3 months | Pleomorphic | Total laryngectomy with right modified radical neck dissection and radiotherapy (6000 cGy to the tumor bed and 5000 cGy to the neck was given with cobalt 60 at a dose of 200 cGy/day) | Died of extensive lung metastases, 8 months |
| Da Mosto MC [15], 1996 | 69/M | Glottic | Progrossive dysphonia for 7 months | Pleomorphic | Total laryngectomy and radiotherapy (6000 cGy over 6 weeks in 30 fractions) | Alive & disease-free, 24 months |
| Balázs M [16], 1989 | 40/M | Supraglottic | Hoarseness several years | Embryoid (Botryoid) | Microsurgery | Alive & disease-free, 36 months |
| Haerr RW [17], 1987 | 62/M | Supraglottic | Dysphagia several days | Alveolar | Total laryngectomy with left radical neck dissection and radiotherapy ((4000 cGy in 22 fractions) | Died of extensive distant metastases, 5 months |
| Srinivasan U [18], 1979 | 55/M | Supraglottic | Hoarseness, dysphagia and a burning sensation in the throat for two months | Pleomorphic | Laryngectomy planned | Died prior to surgery of acute laryngeal obstruction |
| Winter LK [19], 1978 | 72/M | Glottic | Hoarseness 2 months | Pleomorphic | Radical removal | Alive & disease-free, 9 months |
| Frugoni (Verona) [20] P, 1976 | 33/M | Supraglottic | Hoarseness 3 months | Pleomorphic | Partial laryngectomy and radiotherapy (protocol was not provided) | Alive & disease-free, 6 years |
| Hall-Jones J [21], 1975 | 54/M | Supraglottic | dramatically with a large tumour mass obstructing his laryngeal inlet | Embryonal | Total laryngectomy | Alive & disease-free, 15 months |
| Rodriguez LA [22], 1970 | 57/M | Glottic | Acute respiratory distress | Pleomorphic | Total laryngectomy | No follow-up reported |
Abbreviations: YR Year, F Female, M Male, Gy Gray, cGy Centigray
Case presentation
A 42-year-old man presented with a 2-year history of gradually worsening hoarseness without pain, dyspnoea or dysphagia. He had no history of alcohol or tobacco use. Flexible laryngoscopy in January 2016 showed a reddish, smooth and submucosal mass with protrusion medially in the anterior third of the right vocal cord, and glottic closure was incomplete posteriorly with normal mobility (Fig. 1a). Given the well-circumscribed and relatively benign appearance, the lesion was initially suspected to be vocal cord cyst. Then the patient was planned to undergo surgery with suspension laryngoscope. Unexpectedly, the tumor was found to be fleshy, crisp and easily bleeding without invading anterior commissure. Therefore, a frozen pathology was sent during the operation, and indicated malignancy (Fig. 1b). However, the definitive pathologic diagnosis could not be made in the operation. Besides, the scope of the lesion and the lymph nodes of the neck was not defined, due for the lack of preoperative computed tomography (CT) / the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Therefore, the combined therapy regimen (surgery, chemotherapy or radiotherapy) cannot be formulated. Ultimately, we performed a cordectomy with the visible lesion for the patient. The final diagnose was embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) with immunohistochemical staining positivity for myogenin, smooth muscle actin (EMA), desmin and myoD1 (Fig. 1c). In order to develop further therapeutic regime, the MRI was performed, and showed an asymmetric swelling of the right vocal cord with no lymphadenopathy being detected in the neck (Fig. 1d). After evaluation of the tumor size, grade, and lymph node involvement, we recommended extended resection or combined chemoradiotherapy, and the patient chose the latter. He underwent three cycles of induction chemotherapy with TDF regimen (paclitaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil) at 3-week intervals. In addition, he received a mean radiation dose of 70 Gray (Gy) to the laryngeal area. After treatment, the larynx presented with smooth appearance and good mobility of vocal cord.
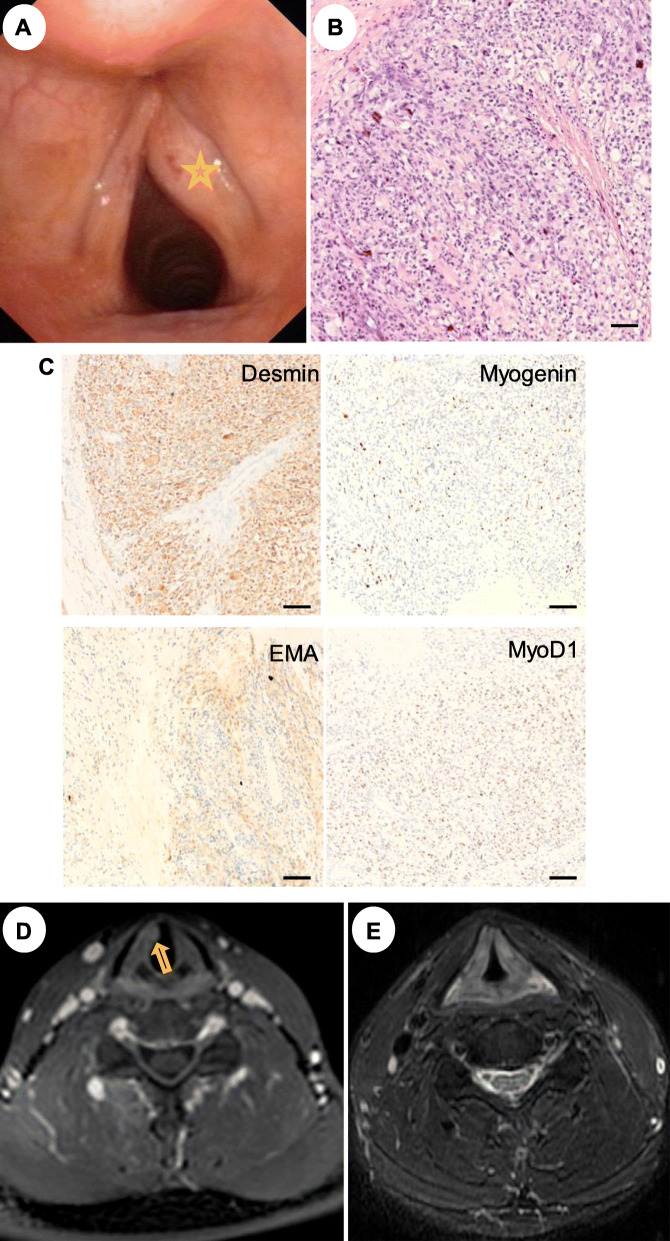
Fig. 1.
Imaging of initial treatment of this new reported case. a, The lesion (labeled with asterisk) was covered with normal mucosa without any ulcerations by flexible laryngoscopy. b, The majority of the tumor consisted of spindle-shaped cells with nucleus located centrally and eosinophilic-abundant cytoplasm (HE staining × 20). c, Immunohistochemistry was positive for myogenin, EMA, desmin and myoD1 (Original magnification for all slides is ×20.) d, MRI imaging showed the right vocal cord swelling several days after the first operation. e, On evaluations with MRI 1 year after the first multi-treatment, there was complete regression of the disease. Scale: 50um
The patient was followed up as scheduled with no recurrence (Fig. 1e). One year later, he lost follow-up until the presence of dyspnea 18 months after the last treatment. Flexible laryngoscopy (Fig. 2a), MRI imaging (Fig. 2b) and CT imaging (Fig. 2c) showed a submucosal mass of the right vocal cord. Intraoperative findings showed that the tan mass originated from the right vocal cord, invaded the anterior commissure and bulged into right perilaryngeal soft tissues without involving the laryngeal cartilage. Therefore, a vertical hemilaryngectomy and a right selective neck dissection was performed. No tumor cells were detected along the surgical margin and in the lymph nodes of the neck. Histological examination of the whole specimen postoperatively confirmed the diagnosis of ERMS. The tumor was clinically staged as T3N0M0 (stage III) glottic ERMS. Then the experiment of anticancer drug sensitivity of this tumor to eight chemotherapeutic regimens was determined in vitro, revealing that DCF regimen (docetaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil) was the most efficient (Fig. 2d). Finally, the patient underwent DCF regimen at 3-week intervals without radiotherapy. Until the last check-up 18 months after chemotherapy, the patient did not display clinical or radiological signs of local recurrence and metastases (Fig. 3).
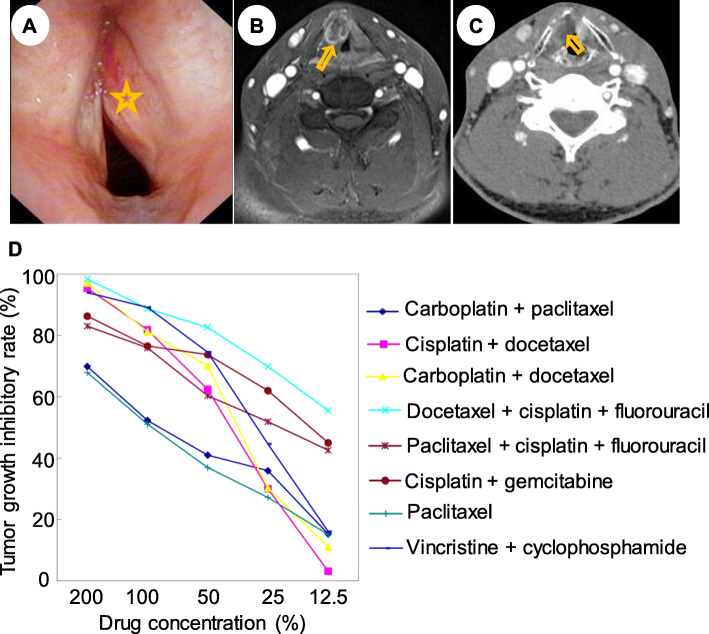
Fig. 2.
Imaging of second treatment of this new reported case. a, Flexible laryngoscopy revealed that a submucosal mass bulged the right true vocal cord medially and pressed the left true vocal fold with no restrictive mobility of bilateral vocal cords. b, MRI imaging showed that the lesion caused a partial obstruction at the level of the glottis with the size of 1.6 × 1.2 × 1.7 cm. c, No evidence of thyroid cartilage invasion was detected in the CT imaging. d, Anticancer drug sensitivity of this tumor to eight chemotherapeutic regimens was conducted, and revealed that docetaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil was the most efficient
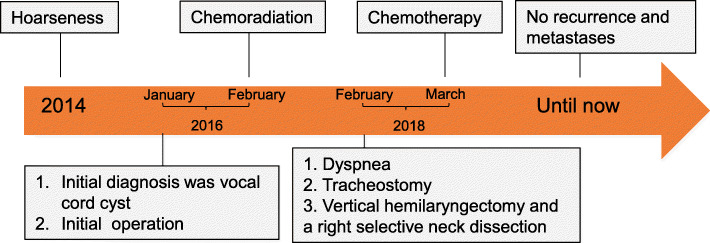
Fig. 3.
The timeline of medical record of the new reported case
Discussion and conclusions
The first case of laryngeal RMS was reported by Glick in 1944 [22]. Subsequently, most of these reported cases have occurred in children and more than 70% of RMSs were diagnosed younger than 10 years. In contrast, laryngeal RMSs occurred very infrequently in adults [13], and were more commonly found in males than females. Reviewing the 22 well-documented cases in the English-language literature, 18 cases were males (81.8%) versus 4 cases of female (18.2%). Meanwhile, laryngeal RMSs in adults were predominantly reported in the glottic and supraglottic region (Table 2). The clinical features of the case in this study were similar with previous cases.
Table 2.
Summary of reported cases of laryngeal rhabdomyosarcoma in adults
| Characteristic | Total (NO.) | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| M | 18 | 81.81 |
| F | 4 | 18.18 |
| Primary location | ||
| Supraglottic | 10 | 45.45 |
| Glottic | 11 | 50.00 |
| Subglottic | 2 | 4.55 |
| Histologic subtype | ||
| Embryonal | 7 | 31.82 |
| Pleomorphic | 13 | 59.09 |
| Alveolar | 2 | 9.09 |
Abbreviations: F Female, M Male
The clinical features and macroscopic appearances do not differ substantially from the other laryngeal tumors, therefore, the initial diagnosis of laryngeal RMS in adults may be difficult [13]. The most common symptoms and signs, including hoarseness, dyspnea, stridor, dysphagia and polypoid appearance, provided limited diagnostic information [11]. To review the literature, RMSs had been misdiagnosed as hemangioma [23] and laryngopharyngeal reflux [7]. Our case was initially diagnosed as the vocal cord cyst, due for the cystic appearance, and the overlying mucosa was smooth. Therefore, stroboscopy or narrow-band imaging was not performed. This was the main reason of misdiagnosis, which reminded us that for vocal cord tumor, diagnosis should be combined with stroboscopy, narrow band imaging and other comprehensive evaluations, instead of clinical experience or the appearance. CT was often preferred with the information of whether laryngeal cartilage or bone erosion [10]. MRI enabled us to perform a noninvasive assessment of tumor size, localization, nerve or vascular invasion. While CT/ MRI proved to be incapable of distinguishing RMSs from other laryngeal malignant tumors.
Therefore, the definite diagnosis is based on optical microscope and immunohistochemistry [2]. Positivity for vimentin indicates the mesenchymal origin, and the staining for actin, desmin, myogenin and myoglobin suggests muscular differentiation. The histological classification of RMS is controversial. Most authors accepted the system proposed by Horn and Enterline [24] that there were three principal histological varieties of RMS: embryonal, alveolar, pleomorphic according to their degree of cellular differentiation and maturity; both spindle cell RMSs and botryoid RMSs were considered to be subtypes of embryonal RMSs [25]. The embryonal subtype is the most frequent, accounting for 70–75% of all RMSs, followed by the alveolar (20–25%) and pleomorphic differentiation (5%) [2]. To date, there were 22 cases of laryngeal RMS in adults, including 13 (59.09%) pleomorphic RMS, 7 (31.82%) embryonal RMS and 2 (9.09%) alveolar RMS (Table 2). The case described here was an adult with the type of ERMS, which did not accord with this general pattern concerning the preponderance of age and pathological type. ERMS of the larynx must be differentiated from other common histological types in that it differs significantly with respect to its management [4].
The management of RMSs has evolved from radical surgery to less morbid regimen, which is now typically limited to organ-sparing procedures supplemented with chemoradiotherapy. This paradigm shift can be attributed to the multimodality protocols initiated by the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group (IRSG) over several decades [9, 26, 27]. Since RMSs are rare in the adult population, there is no standard adult-specific chemoradiation protocols, so far, most of the chemoradiation protocols refer to pediatric series. The treatment responses of radiotherapy were variable and difficult to interpret, as radiotherapy often followed radical excision of the tumor. Markedly, ERMS of the larynx appears to be highly responsive to chemotherapy. However, further studies are required in order to improve the comprehending of their biological behaviors and to draft the optimum therapeutic approach. Nowadays, the experiment of anticancer drug sensitivity in vitro is the evidence in the chemotherapy and has become a highlight for the realization of individual tumor treatment [28, 29]. In our case, the tumor relapsed via microlaryngoscopic surgery combined with initial chemoradiotherapy. Therefore, we adopted more aggressive surgical intervention, and adjusted chemotherapy regimen according to the chemosensitivity assay in vitro (Fig. 2d). Finally, the patient has been remaining disease-free until now. Totally, the optimal therapy for laryngeal RMSs in adults is a multimodal approach comprising surgery followed by chemo- (in line with the anticancer drug sensitivity) and/or radiotherapy.
Although the survival rate of RMSs has been improved from 25% in 1970 to approximately 75% today, local tumor recurrence and metastasis remained challenging. Some authors noted that micro-metastasis is presumed leading to the high rate of failure with surgery alone [30]. Prognostic indicators, including age, tumor location, histologic subtype and response to treatment, have been identified. Hawkins [31] reported that patients with age < 20 years and those with a tumor size < 5 cm had a better prognosis. Multi-institutional pediatric trials have showed a 70% cure rate in children without metastatic disease, whereas adults had a poor prognosis. This may be implicated in the discrepancy of histologic variation that unfavorable subtypes (such as the pleomorphic RMSs) are more common in adults [32]. The embryonal subtype has a better overall prognosis associated with earlier age of onset, and the alveolar subtype, which accounts for the least, tends to carry the worst prognosis. Notably, laryngeal RMSs are supposedly less aggressive than RMSs elsewhere, presumably due to the cartilaginous borders of the larynx restricting local tumor spread [13]. Reviewing the 22 cases in the English-language literature, there were 21 cases receiving treatment (surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy or combination therapy) with 2 cases being lost to follow-up. Among these 19 cases, 17 cases were alive and disease-free at the ending of follow-up; 2 patients died of extensive distant metastases, and the pathological type was alveolar RMS and pleomorphic, respectively. The present case here did neither show systemic metastasis and is alive with disease-free after more than 18 months of follow up. However, late relapses warrant long-term follow up.
This was an unusual occurrence of an ERMS in the larynx of a middle-aged man who was a non-smoker. Misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis of laryngeal RMSs might appear when tumors presented as smooth protuberance. Therefore, it is important for otolaryngologists to remain vigilant and to suspect, confirm, and localize these tumors. Presently, multidisciplinary treatment based on the anticancer drug sensitivity remains the mainstay of the management, and offers best results to the patients. This is ideal, but not represent the reality around the word.
Acknowledgements
None.
Abbreviations
- RMSs
Rhabdomyosarcomas
- ERMS
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
- EMA
Smooth muscle actin
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- CT
Computed tomography
- F
Female
- M
Male
- Gy
Gray
- cGy
Centigray
- YR
Year
- HE
Hematoxylin-eosin staining
Authors’ contributions
JH and DL drafted the manuscript. JZ and HY studied the concept and designed the report. JR, SL, and JL diagnosed and treated the patients. QW, JZ, and WG followed up the patients. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Major Subject of the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2017SZ0015) (to Hui Yang). Dr. Hui Yang studied the concept and designed the report. In this study, laboratory analyses and cover publication costs were supported by the funding.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal on request.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Mungan S, Arslan S, Küçüktülü E, Ersöz Ş, Çobanoğlu B. Pleomorphic Rhabdomyosarcoma arising from true vocal fold of larynx: report of a rare case and literature review. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2016;2016:8135967. doi: 10.1155/2016/8135967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schrock A, Jakob M, Zhou H, Bootz F. Laryngeal pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2007;34(4):553–556. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2007.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pittore B, Fancello G, Cossu Rocca P, Ledda GP, Tore G. Rhabdomyosarcoma: a rare laryngeal neoplastic entity. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2010;30(1):52–57. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kukwa W, Wojtowicz P, Jagielska B, Sobczyk G, Kukwa A, Czarnecka AM. Laryngeal embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma in an adult - a case presentation in the eyes of geneticists and clinicians. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:166. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Diehn KW, Hyams VJ, Harris AE. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the larynx: a case report and review of the literature. Laryngoscope. 1984;94(2 Pt 1):201–205. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198402000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chiramel GK, Chacko BR, Thomas R, Jebakumar D. A rare and unusual occurrence of rhabdomyosarcoma arising from the larynx. Indian J Cancer. 2015;52(1):125–126. doi: 10.4103/0019-509X.175575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li Y, Fu Z, Chen W, Yang L, Zhu W. Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Adult's vocal cord: a case report. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2015;17(8):e28876. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.28876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Russell JO, Revenaugh PC, Budd GT, Greskovich J, Scharpf J. Failed organ preservation strategy for adult laryngeal embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Otolaryngol. 2015;36(2):277–279. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2014.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Leventhal DD, Spiegel J, Keane W. Laryngeal alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma involving the true vocal fold in an adult: case report. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010;89(12):E8. doi: 10.1177/014556131008901203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Papacharalampous GX, Manolopoulos L, Korres S, Dicoglou C, Bibas A. Adult laryngeal rhabdomyosarcoma: is aggressive treatment justified in all cases? A case report and review of the literature. J Laryngol Otol. 2009;123(11):e21. doi: 10.1017/S0022215109990946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dikbas O, Altundag K, Abali H, Turker A, Engin H, Sungur A, et al. Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the larynx. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;133(1):160–162. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2004.09.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Libera DD, Falconieri G, Zanella M. Embryonal "Botryoid" rhabdomyosarcoma of the larynx: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of two cases. Ann Diagn Pathol. 1999;3(6):341–349. doi: 10.1016/S1092-9134(99)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ruske DR, Glassford N, Costello S, Stewart IA. Laryngeal rhabdomyosarcoma in adults. J Laryngol Otol. 1998;112(7):670–672. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100141416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Akyol MU, Sözeri B, Küçükali T, Oğretmenoğlu O. Laryngeal pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1998;255(6):307–310. doi: 10.1007/s004050050065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Da Mosto MC, Marchiori C, Rinaldo A, Ferlito A. Laryngeal pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma. A critical review of the literature. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1996;105(4):289–294. doi: 10.1177/000348949610500409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Balázs M, Egerszegi P. Laryngeal botryoid rhabdomyosarcoma in an adult. Report of a case with electron microscopic study. Pathol Res Pract. 1989;184(6):643–649. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(89)80174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Haerr RW, Turalba CI, el-Mahdi AM, Brown KL. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma of the larynx: case report and literature review. Laryngoscope. 1987;97(3 Pt 1):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Srinivasan U, Talvalkar GV. True carcinosarcoma of the larynx: a case report. J Laryngol Otol. 1979;93(10):1031–1035. doi: 10.1017/S002221510008806X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Winter LK, Lorentzen M. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the larynx. Report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Laryngol Otol. 1978;92(5):417–424. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100085546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Frugoni (Verona) P, Ferlito (Padua) A. Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma of the larynx. A case report and review of the literature. J Laryngol Otol. 1976;90(7):687–698. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100082578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hall-Jones J. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the larynx. J Laryngol Otol. 1975;89(9):969–976. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100081251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rodriguez LA, Ziskind J. Rhabdomyosarcoma of larynx. Laryngoscope. 1970;80(11):1733–1739. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197011000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cobanoglu B, Simsek M, Senol S. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the upper lip in an adult patient. Case Rep Med. 2015;2015:508051. doi: 10.1155/2015/508051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Newton WA, Jr, Gehan EA, Webber BL, Marsden HB, van Unnik AJ, Hamoudi AB, et al. Classification of rhabdomyosarcomas and related sarcomas. Pathologic aspects and proposal for a new classification--an intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma study. Cancer. 1995;76(6):1073–1085. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950915)76:6<1073::AID-CNCR2820760624>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Knipe TA, Chandra RK, Bugg MF. Sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma: a rare variant with predilection for the head and neck. Laryngoscope. 2005;115(1):48–50. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000150676.75978.3c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Crist WM, Anderson JR, Meza JL, Fryer C, Raney RB, Ruymann FB, et al. Intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study-IV: results for patients with nonmetastatic disease. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(12):3091–3102. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2001.19.12.3091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Crist W, Gehan EA, Ragab AH, Dickman PS, Donaldson SS, Fryer C, et al. The third intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma study. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13(3):610–630. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.3.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Unger FT, Klasen HA, Tchartchian G, de Wilde RL, Witte I. DNA damage induced by cis- and carboplatin as indicator for in vitro sensitivity of ovarian carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:359. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Isogai A, Nagaya M, Matsuoka H, Watanabe T, Tsukikawa S, Kubota S. An anticancer drug sensitivity test to determine the effectiveness of UFT as postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with stage III colorectal cancer. Surgery. 2007;142(5):741–748. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2007.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wagemans J, Beuselinck B, Nuyts S, Sciot R, Delaere P, Vander Poorten V, et al. A case series of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the head and neck in adults. Acta Clin Belg. 2010;65(6):404–410. doi: 10.1179/acb.2010.65.6.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hawkins WG, Hoos A, Antonescu CR, Urist MJ, Leung DH, Gold JS, et al. Clinicopathologic analysis of patients with adult rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer. 2001;91(4):794–803. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20010215)91:4<794::AID-CNCR1066>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sultan I, Qaddoumi I, Yaser S, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Ferrari A. Comparing adult and pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results program, 1973 to 2005: an analysis of 2,600 patients. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(20):3391–3397. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.7483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.