The structures of three closely related NTF2-like superfamily proteins that are involved in type II polyketide biosynthesis in as-yet-unknown ways were determined. The presence of a solvent-accessible cavity and the conservation of the His/Asp dyad suggest a potential enzymatic role for these enzymes in polyketide biosynthesis.
Keywords: NTF2-like superfamily, polyketide cyclases, actinorhodin, alnumycin, secondary metabolism
Abstract
Proteins belonging to the NTF2-like superfamily are present in the biosynthetic pathways of numerous polyketide natural products, such as anthracyclins and benzoisochromanequinones. Some have been found to be bona fide polyketide cyclases, but many of them have roles that are currently unknown. Here, the X-ray crystal structures of three NTF2-like proteins of unknown function are reported: those of ActVI-ORFA from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and its homologs Caci_6494, a protein from an uncharacterized biosynthetic cluster in Catenulispora acidiphila, and Aln2 from Streptomyces sp. CM020, a protein in the biosynthetic pathway of alnumycin. The presence of a solvent-accessible cavity and the conservation of the His/Asp dyad that is characteristic of many polyketide cyclases suggest a potential enzymatic role for these enzymes in polyketide biosynthesis.
1. Introduction
Proteins in the NTF2-like superfamily (SCOP 54427) possess a wide variety of both enzymatic and non-enzymatic functions, and this versatile fold occurs in many proteins involved in the production of biologically relevant molecules such as polyketides (Eberhardt et al., 2013 ▸). A significant number of genes present in polyketide biosynthetic clusters encode hypothetical NTF2-like proteins for which roles have not been determined. The actVI-orfA gene in the well characterized actinorhodin biosynthetic cluster of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) encodes just such a protein. In 1994, Fernández-Moreno and coworkers carried out experiments with an S. coelicolor mutant in which the actVI-orfA gene was insertionally inactivated and observed decreased production of actinorhodin (1 in Fig. 1 ▸). They hypothesized that although the enzyme ActVI-ORF1 reduces the bicyclic intermediate 2 to give 3, which can cyclize non-enzymatically to give the pyran-ring-containing intermediate 4 and ultimately the stable intermediate 4-dihydro-9-hydroxy-1-methyl-10-oxo-3-H-naphtho-[2,3-c]-pyran-3-(S)-acetic acid [(S)-DNPA; 5] (Ichinose et al., 2001 ▸), such a reaction might be assisted by the actVI-orfA gene product (Fernández-Moreno et al., 1994 ▸). In 2003, Ozawa and coworkers chemically characterized the products of an actVI-orfA disruptant in S. coelicolor and found that in addition to actinorhodin, this strain also accumulated 5 as well as a shunt product, 1,4-naphthoquinone-8-hydroxy-3-[3(S)-acetoxybutyric acid] [(S)-NHAB; 6]. Owing to the fact that genes encoding proteins similar to ActVI-ORFA were found in biosynthetic pathways for type II polyketides lacking pyran rings, they concluded that it was more likely that ActVI-ORFA is instead a scaffolding protein that promotes the formation of a multi-enzyme type II polyketide synthase complex (Ozawa et al., 2003 ▸). However, at the time of writing, we could find no examples in the literature of NTF2-like proteins that act as scaffolds in polyketide pathways. A number of NTF2-like proteins have been proposed to have non-enzymatic ligand-binding roles (Eberhardt et al., 2013 ▸). Subsequent work by Taguchi and coworkers suggested that ActVI-ORFA is a transcriptional regulator that promotes the expression of a key ketoreductase gene (Taguchi et al., 2007 ▸). In this study, Taguchi and coworkers disrupted the actVI-ORFA gene in S. coelicolor and observed lower levels of transcription of several act genes, including the ketoreductase ActVI-ORF1. This led to the hypothesis that ActVI-ORFA is a transcriptional regulator that controls multiple act genes. However, no evidence of any nucleic acid-binding domain is present in the ActVI-ORFA sequence, so it is unclear how it would execute this proposed regulatory activity. It is possible, although perhaps not probable, that ActVI-ORFA could mediate protein–protein interactions between DNA-binding proteins and thus modulate gene expression indirectly. The scaffolding hypothesis is more plausible solely upon consideration of the primary sequence, but a non-essential enzymatic role for ActVI-ORFA cannot be ruled out based on previous studies. In fact, numerous NTF2-like proteins have catalytic roles in the synthesis of natural products. For example, SnoaL (PDB entry 1sjw) from S. nogalater has been shown to catalyze the formation of the fourth ring of nogalamycin via an intramolecular aldol condensation (Sultana et al., 2004 ▸). Likewise, recent structural work by Huang and coworkers hypothesized that the NTF2-like protein SgcJ (PDB entry 4ovm) from S. carzinostaticus may play a catalytic role in tailoring steps in the production of the enediyne antitumor antibiotic C-1027 (Huang et al., 2016 ▸).
Figure 1.
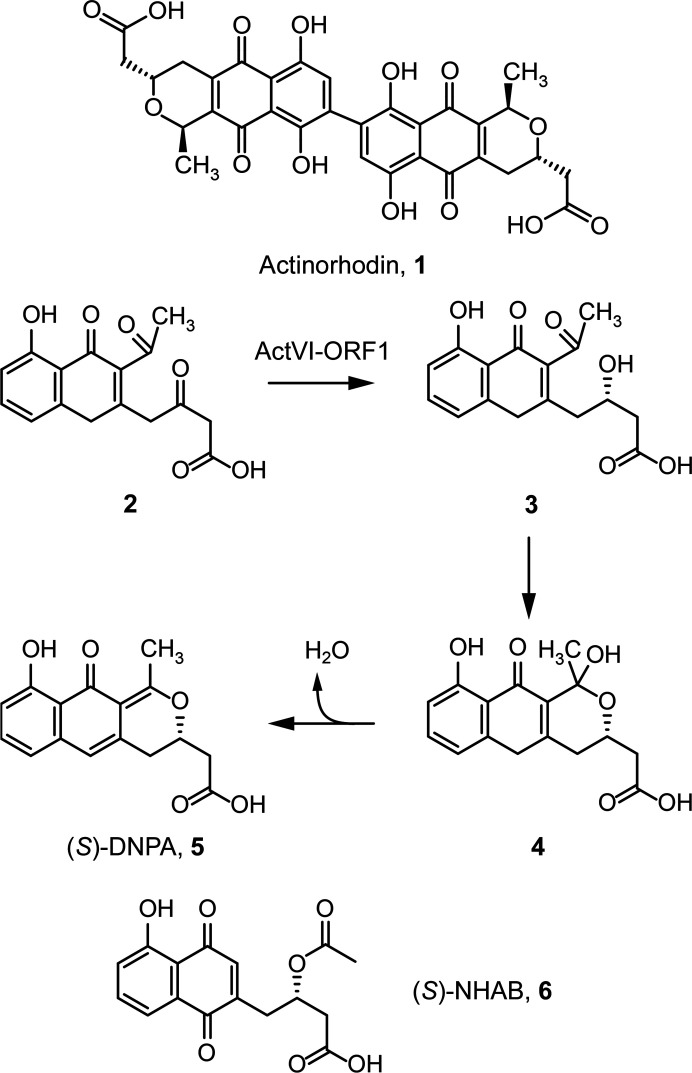
The structure of the benzoisochromanequinone antibiotic actinorhodin (1) and the series of enzymatic and non-enzymatic steps leading from the first bicyclic intermediate of actinorhodin biosynthesis (2) to the tricyclic intermediate (S)-DNPA (5). The structure of the off-pathway product (S)-NHAB (6) is also shown.
Filippova and coworkers also suggested that an NTF2-like protein from Catenulispora acidophila, Caci_0382 (PDB entry 4h3u), may have an enzymatic role based on structural study of its hydrophobic cavity (Filippova et al., 2014 ▸). In this work, we have determined the structures of three NTF2-like proteins: ActVI-ORFA (UniProt Q7AKI2), Caci_6494 (UniProt C7PWR4) from an uncharacterized gene cluster in C. acidophila and Aln2 (UniProt B6SEE8), a hypothetical protein from the alnumycin-biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces sp. CM020. Sequence alignment of these proteins shows that all three of them have a conserved His78/Asp26 dyad (Supplementary Fig. S1), which is a common acid/base catalyst pair that is found in numerous enzymes in the NTF2-like superfamily (InterPro accession ID IPR032710).
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Macromolecule production
The actVI-orfA gene from S. coelicolor A3(2) was synthesized using custom gBlocks (Integrated DNA Technologies; Section S1.1) and cloned into the pE-SUMOkan vector (LifeSensors) to give the plasmid pSUMO-actVI-orfA. The sequence was confirmed via Sanger sequencing by Genewiz.
The His6-tagged SUMO-ActVI-ORFA fusion protein was expressed from Escherichia coli BL21 Star (DE3) cells (Invitrogen) transformed with pSUMO-actVI-orfA and grown at 310 K in Luria–Bertani medium with 50 µM kanamycin. Protein expression was induced with 0.40 mM isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) at an OD600 nm of 1.0 and the cells were grown overnight in a shaking incubator at 298 K and 250 rev min−1. The cells were harvested via centrifugation and resuspended in 5 ml buffer A (25 mM Tris pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM imidazole) containing 0.1 mg ml−1 DNase I (Worthington Biochemical Corporation) per gram of cells. Cells were lysed using a Branson Sonifier S-450 cell disruptor (Branson Ultrasonics) for 10 min at 60% amplitude with 30 s pulses separated by 50 s rest periods. The temperature of the lysate was maintained below 277 K by keeping the steel container in a stirred ice bath. The lysate was clarified via centrifugation at 39 000g for 45 min before loading it onto a 5 ml HisTrap column (GE Life Sciences). The His6-tagged protein was purified using a four-step gradient increasing the proportion of buffer B (25 mM Tris pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole) from 0% to 5%, 15%, 50% and 100% using an ÄKTA purifier 10 FPLC (GE Life Sciences). The length of each step in the gradient was five column volumes. The purification was monitored spectrophotometrically at 280 nm. The peak fractions that eluted at 50% and 100% buffer B were collected and analysed by Coomassie-stained SDS–PAGE. Fractions containing ActVI-ORFA were pooled, SUMO protease was added to a final concentration of 10 µM and the material was dialyzed against 4 l dialysis buffer (25 mM Tris pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl) overnight at 277 K to remove the His6-SUMO tag. The cleaved tag and SUMO protease were removed by passing the dialysate through the same HisTrap column and collecting the flowthrough. The purity of the ActVI-ORFA samples was estimated to be >95% by Coomassie-stained SDS–PAGE. The protein was dialyzed against 4 l storage buffer (10 mM sodium succinate pH 5.7, 100 mM NaCl) overnight at 295 K. The finished protein was concentrated, aliquoted, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at 193 K.
Selenomethionine-labelled (SeMet) ActVI-ORFA was expressed using T7 Express Crystal cells (New England Biolabs) transformed with the pSUMO-actVI-orfA plasmid. The cells were grown in SelenoMethionine Medium Complete (Molecular Dimensions) with 50 µg ml−1 kanamycin. Protein expression and purification were carried out in the same manner as for the unlabeled protein.
C. acidophila (B-24433) was obtained from the Agricultural Research Service (NRRL) Culture Collection. To isolate genomic DNA from C. acidophila, the strain was grown in GYM medium at 301 K and 250 rev min−1 until the culture reached stationary phase. The genomic DNA was extracted from 2 ml saturated cell cultures using the UltraClean Microbial DNA Isolation Kit (MO BIO Laboratories). Using the primers listed in Table 1 ▸, the gene was cloned into the pE-SUMOkan vector to give the plasmid pSUMO-caci_6494.
Table 1. Macromolecule production of ActVI-ORFA, Caci_6494 and Aln2.
| Macromolecule | ActVI-ORFA | Caci_6494 | Aln2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source organism | S. coelicolor A3(2) | C. acidophila DSM 44928 | Streptomyces sp. CM020 |
| DNA source | Synthesized gBlocks | Genomic DNA | Synthesized gBlocks |
| Forward primer† | 5′-GGT CTC AAG GTA TGA CGA TTA CCG CG-3′ | 5′-GGT CTC AAG GTA TGG CCG ACC ACT GGT CGC AAG CCG CGC TGT-3′ | 5′-GGT CTC AAG GTA TGA CTA CCG ATG AAA CTA CCA C-3′ |
| Reverse primer‡ | 5′-GCT CTA GAT CAT CAG GCT GGG AAG ACA TG-3′ | 5′-GCT CTA GAT CAT CAT CGC GCG GCC GCG GTC CGC TCG GCC A-3′ | 5′-GCT CTA GAT CAT CAA CCT TGA GTC CGA GCA C-3′ |
| Cloning vector | pE-SUMOkan | pE-SUMOkan | pE-SUMOkan |
| Expression vector | pE-SUMOkan | pE-SUMOkan | pE-SUMOkan |
| Expression host | E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) | E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) | E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) |
| Complete amino-acid sequence of the construct produced | MTITALPTGLYAEVLSFYGHQMQKLDGRDFAGYAATFTEDGEFRHSPSLPAAHTRAGITAVLEDFHRKFDARKIQRRHWFDHTALSQASDGSITATSYCLVLTVHADVKAPEFGPSCLVHDVLVRGADGELLLRSRHVTHDHVFPA | MADHWSQAALYAEVQQHQARQMHALDEGKFEEYADTFTPDGVFRHTPGRDPAIGREAIVRELNEFHERYAEDPVQRRHMFTMLAIDELDELDDSAVQADFYTLVLTTRVDGLTVGPSCPVRDVLVRGADGRLLTASRWVEHDNRTVAERTAAAR | MTTDETTTTDATTITDATTIADATTRNAPKLPSPELYVEVTQFYARQMHRMDGDDFGGFAATFVAGAEFRLAGGTVLTGPEAIEAGARAAAGRFDGAQPRHWFDMMTVEEADDGTVSTSYYATVTVTSAQGAVLVEPTCFVRDTLVRVSGVLRSRSRVIERDDLVVRARTQG |
The BsaI site is underlined.
The XbaI site is underlined.
The His6-tagged Caci_6494 protein was expressed from E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) cells (Invitrogen) transformed with pSUMO-caci_6494 and the protein was expressed and purified in the same manner as ActVI-ORFA. The protein was desalted into 10 mM MOPS pH 6.5 by overnight dialysis at 295 K.
Selenomethionine-labelled Caci_6494 was expressed using T7 Express Crystal cells transformed with the pSUMO-caci_6494 plasmid. The cells were grown in SelenoMethionine Medium Complete (Molecular Dimensions) with 50 µg ml−1 kanamycin. Protein expression and purification were carried out in the same manner as for the unlabeled protein.
The aln2 gene from Streptomyces sp. CM020 was synthesized using custom gBlocks (Section S1.1) and cloned into the pE-SUMOkan vector to give the plasmid pSUMO-aln2. The sequence was confirmed via Sanger sequencing by Genewiz. The His6-tagged SUMO-Aln2 fusion protein was expressed using E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) cells transformed with pSUMO-aln2 and the protein was expressed and purified in the same manner as ActVI-ORFA. The protein was desalted into 10 mM citrate pH 4.4 by overnight dialysis at 295 K.
2.2. Crystallization
2.2.1. SeMet ActVI-ORFA
Initial crystallization conditions were identified by screening 20 mg ml−1 ActVI-ORFA against the Index HT screen (Hampton Research). Diffraction-quality crystals were obtained after one day (Table 2 ▸). The crystals were large plates of varying thickness with approximate dimensions of 300 × 200 × 20 µm. The crystals were cryoprotected by quickly soaking them in a solution consisting of 20% glycerol, 25% PEG 3350, 0.1 M sodium citrate pH 4.5 before plunging them into liquid nitrogen.
Table 2. Crystallization.
| Protein | SeMet ActVI-ORFA | SeMet Caci_6494 | Caci_6494–DNPA | Aln2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Hanging-drop vapour diffusion | Hanging-drop vapour diffusion | Hanging-drop vapour diffusion | Sitting-drop vapour diffusion |
| Plate type | 24-well VDX | 24-well VDX | 24-well VDX | 96-well Swissci UV-transmissible MRC 2-drop |
| Temperature (K) | 295 | 295 | 295 | 295 |
| Protein concentration (mg ml−1) | 20 | 10 | 12 | 15 |
| Buffer composition of protein solution | 10 mM sodium succinate, 100 mM NaCl pH 5.7 | 10 mM MOPS pH 6.5 | 10 mM MOPS pH 6.5 | 10 mM sodium citrate pH 4.4 |
| Composition of reservoir solution | 20% PEG 3350, 0.1 M sodium citrate pH 4.5 | 1.47 M K2HPO4/0.07 M NaH2PO4, 5% PEG 400 pH 8.3 | 1.47 M K2HPO4/0.07 M NaH2PO4, 5% PEG 400, 2.5 mM (S)-DNPA pH 8.3 | 22% PEG 3350, 0.1 M bis-Tris, 3% ethylene glycol pH 5.5 |
| Volume and ratio of drop | 2 µl, 1:1 | 2 µl, 1:1 | 2 µl, 1:1 | 2 µl, 1:1 |
| Volume of reservoir (µl) | 500 | 500 | 500 | 50 |
2.2.2. SeMet Caci_6494
Initial crystallization conditions were identified by screening 10 mg ml−1 protein against the Index HT and SaltRX screens (Hampton Research). Crystals from Index HT condition B6 consisting of 1.4 M sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate/potassium phosphate dibasic pH 6.9 were further optimized by varying the pH and then running the optimized condition against Additive Screen HT (Hampton Research). Diffraction-quality crystals formed after two days (Table 2 ▸). The crystals were cube-shaped with dimensions of approximately 100 × 100 × 100 µm. The crystals were cryoprotected by soaking them in 20% glycerol, 1.4 M potassium phosphate dibasic, 0.07 M sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate pH 8.3, 10% PEG 400 before plunging them into liquid nitrogen.
2.2.3. Caci_6494 complexed with (S)-DNPA
To obtain crystals of the complex of Caci_6494 with (S)-DNPA, a 100 mM (S)-DNPA stock was prepared in DMSO and 2.5 µl of this stock solution was mixed with 97.5 µl 12 mg ml−1 Caci_6494. The solution was then incubated for 1 h at room temperature prior to the crystallization experiment. Diffraction-quality crystals were obtained and cryoprotected under the same condition as the SeMet Caci_6494 crystals, except that the cryoprotectant solution also contained 2.5 mM (S)-DNPA.
2.2.4. Aln2
Initial crystallization conditions were identified via the vapour-diffusion method using sitting-drop geometry by screening 15 mg ml−1 protein against the Index HT screen at 295 K. Further optimization of several conditions by altering the precipitant concentration and pH did not yield diffraction-quality crystals, so the most promising condition was optimized using Additive Screen HT. Diffraction-quality, rod-shaped crystals with dimensions of approximately 200 × 20 × 20 µm formed after six months (Table 2 ▸). The crystals were cryoprotected by a quick soak in a solution consisting of 80% crystallization solution and 20% glycerol before being plunged into liquid nitrogen.
2.3. Data collection and processing
All data were collected at the Advanced Photon Source (APS). Pertinent details of the data-collection strategies are given in Table 3 ▸. The SeMet ActVI-ORFA data set used an inverse-beam strategy, while the other data sets did not. The SeMet ActVI-ORFA data set was processed using HKL-3000 (Minor et al., 2006 ▸). The SeMet Caci_6494 and Aln2 data sets were processed using HKL-2000 (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▸). The Caci_6494–DNPA data set was processed with MOSFLM (Battye et al., 2011 ▸).
Table 3. Data collection and processing.
Values in parentheses are for the outer shell.
| Protein | SeMet ActVI-ORFA | SeMet Caci_6494 | Caci_6494–DNPA | Aln2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | APS beamline 23-ID-D | APS beamline 21-ID-F | APS beamline 21-ID-F | APS beamline 21-ID-D |
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.97934 | 0.97872 | 0.97872 | 0.97919 |
| Beam size (µm) | 5 × 5 | 50 × 50 | 50 × 50 | 50 × 50 |
| Temperature (K) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Detector | Dectris PILATUS 6M | MAR Mosaic 300 mm CCD | MAR Mosaic 300 mm CCD | Dectris EIGER X 9M |
| Crystal-to-detector distance (mm) | 200 | 250 | 215 | 200 |
| Rotation range per image (°) | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Total rotation range (°) | 180 | 183 | 180 | 180 |
| Exposure time per image (s) | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.1 |
| Space group | P2 | I23 | I23 | P21 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 82.3, 52.9, 98.9 | 159.3, 159.3, 159.3 | 161.2, 161.2, 161.2 | 50.2, 84.9, 104.6 |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 104.3, 90 | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 100.1, 90 |
| Mosaicity (°) | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 0.30 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 34.91–2.11 (2.19–2.11) | 45.97–2.50 (2.59–2.50) | 65.83–2.35 (2.43–2.35) | 39.27–1.80 (1.86–1.80) |
| Total No. of reflections | 157889 (15419) | 505643 (34478) | 182187 (17874) | 263499 (24641) |
| No. of unique reflections | 47889 (3195) | 23351 (2330) | 29103 (2846) | 78418 (7692) |
| Completeness (%) | 95.80 (67.80) | 99.97 (100.00) | 99.9 (100) | 97.92 (96.72) |
| Multiplicity | 3.3 (3.3) | 21.7 (14.8) | 6.3 (6.3) | 3.4 (3.2) |
| 〈I/σ(I)〉 | 8.30 (1.13)† | 28.48 (2.43) | 10.3 (2.20) | 10.14 (2.41) |
| R p.i.m. | 0.052 (0.46) | 0.042 (0.36) | 0.045 (0.038) | 0.056 (0.21) |
| Overall B factor from Wilson plot (Å2) | 26 | 48 | 44 | 19 |
The resolution at which I/σ(I) falls below 2.0 is 2.33 Å, but the overall completeness and CC1/2 suggested that a resolution of 2.11 Å is appropriate for this data set.
2.4. Structure solution and refinement
2.4.1. SeMet ActVI-ORFA
Phases were obtained using HKL-3000 (Minor et al., 2006 ▸) and the model was built by running 100 cycles of HKL Builder, which is integrated into the HKL-3000 package. The resulting model underwent iterative rounds of editing in Coot (Emsley & Cowtan, 2004 ▸; Emsley et al., 2010 ▸) and refinement using phenix.refine (Adams et al., 2010 ▸; Afonine et al., 2010 ▸). The structure was deposited in the Protein Data Bank with accession code 5bka.
2.4.2. SeMet Caci_6494
The experimental phases were obtained using the AutoSol package (Terwilliger et al., 2009 ▸) as implemented in the Phenix suite (Liebschner et al., 2019 ▸). Structure refinement was performed using phenix.refine and Coot. The final model-optimization and validation steps were performed using PDB-REDO (Joosten et al., 2014 ▸). The structure was deposited in the Protein Data Bank with accession code 6p77.
2.4.3. Caci_6494 complexed with (S)-DNPA
Molecular replacement was performed using chain A of the unliganded SeMet Caci_6494 structure as the search model in Phaser (McCoy et al., 2007 ▸). All solvent atoms were removed from the search model and all B factors were set to 20 Å2. The best solution had a TFZ of 51.1 and an LLG of 2580. The model was iteratively built and refined using Coot and phenix.refine, respectively. To confirm the presence of bound (S)-DNPA by removing model bias, a simulated-annealing composite OMIT map was generated using the tools implemented in Phenix (Terwilliger et al., 2008 ▸). The structure was deposited in the Protein Data Bank with accession code 6vw4.
2.4.4. Aln2
Molecular replacement was performed in MRage (Bunkóczi et al., 2013 ▸) using a single ensemble comprised of ActVI-ORFA chain A and Caci_6494 chain A, both of which were trimmed using Sculptor (Bunkóczi & Read, 2011 ▸), as the search model. The best solution had a TFZ of 18.5 and an LLG of 740.7. The model was then built in five iterative cycles of AutoBuild and refined using iterative rounds of refinement in phenix.refine and model building in Coot. The structure was deposited in the Protein Data Bank with accession code 6p7l.
The Ramachandran statistics reported in Table 4 ▸ were calculated by MolProbity (Chen et al., 2011 ▸; Williams et al., 2018 ▸). The buried surface areas between protomers were calculated by PDBePISA (Krissinel & Henrick, 2007 ▸) and cavity volumes were calculated by VOIDOO (Kleywegt & Jones, 1994 ▸; Kleywegt et al., 2001 ▸).
Table 4. Structure solution and refinement.
Values in parentheses are for the outer shell.
| Protein | SeMet ActVI-ORFA | SeMet Caci_6494 | Caci_6494–DNPA | Aln2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution range (Å) | 34.91–2.11 (2.19–2.11) | 45.97–2.50 (2.59–2.50) | 57.01–2.35 (2.44–2.35) | 39.27–1.80 (1.86–1.80) |
| Completeness (%) | 95.80 (67.73) | 99.97 (100.00) | 99.88 (100.00) | 97.92 (96.72) |
| σ Cutoff | 0 | 1.35 | 1.34 | 1.37 |
| No. of reflections, working set | 45936 (3195) | 23351 (2330) | 29054 (2881) | 78308 (7692) |
| No. of reflections, test set | 2168 (154) | 2004 (203) | 1444 (119) | 3947 (348) |
| Final R cryst | 0.224 (0.286) | 0.202 (0.293) | 0.198 (0.262) | 0.163 (0.208) |
| Final R free | 0.247 (0.309) | 0.225 (0.324) | 0.230 (0.356) | 0.205 (0.264) |
| Cruickshank DPI (R cryst) | 0.196 | 0.177 | 0.202 | 0.219 |
| No. of non-H atoms | ||||
| Protein | 6006 | 2228 | 2074 | 6287 |
| Ligand | 0 | 55 | 21 | 6 |
| Water | 331 | 27 | 85 | 557 |
| Total | 6337 | 2310 | 2180 | 6850 |
| R.m.s. deviations | ||||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.011 |
| Angles (°) | 0.82 | 1.55 | 1.29 | 1.12 |
| Average B factors (Å2) | ||||
| Protein | 39 | 39 | 53 | 28 |
| Ligand | n.a.† | 79.2 | 76.3 | 60.0 |
| Water | 38.7 | 48.0 | 50.7 | 38.6 |
| Total | 39.1 | 39.6 | 53.0 | 29.0 |
| Ramachandran plot | ||||
| Most favoured (%) | 98.9 | 98.5 | 99.2 | 99.6 |
| Allowed (%) | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| No. of TLS groups | 35 | 2 | 0 | 51 |
Not applicable.
2.5. Isolation and purification of (S)-DNPA
S-DNPA was produced by growing S. coelicolor M1152::pXZ11, a genetically engineered S. coelicolor strain (Gomez-Escribano & Bibb, 2011 ▸) harbouring plasmid pXZ11, in R4 medium in an incubator/shaker at 28°C and 180 rev min−1. The culture medium was clarified by centrifugation and vacuum filtration, acidified to pH 3.0 with 2 N HCl and extracted with one volume of ethyl acetate three times. The organic phase was collected, dehydrated with anhydrous ammonium sulfate and dried by rotary evaporation and overnight vacuum, resulting in the crude extract. The crude extract was dissolved in 50% acetonitrile. The solution was clarified by centrifugation and passage through a 0.20 µm PTFE filter. To isolate the compound, the clarified solution was injected into a reverse-phase high-performance liquid-chromatography (HPLC) column. The preparative HPLC separation was carried out using a Kromasil C-18 column (Kromasil octadecyl phase, 5 µm, 250 × 10 mm). For HPLC separation, ultrapure water containing 0.1% formic acid was used as solvent A and acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid was used as solvent B. The wavelength of the detector was set to 280 nm and the flow rate was set to 3.5 ml min−1. The HPLC program used was 40% solvent B for 4 min, 40–98% solvent B over 12 min and 98% solvent B for 3 min. The retention time of the peak for the target compound was 13.477 min. This peak was collected. The solvent was dried by rotary evaporation and overnight vacuum, giving a yellow solid. The structure of the compound was verified by high-resolution mass spectrometry (Supplementary Fig. S2) and by comparing the nuclear magnetic resonance data (Supplementary Fig. S2 and Table S1) with those reported for (S)-DNPA (Ichinose et al., 1999 ▸).
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Structural characterization of ActVI-ORFA, Caci_6494 and Aln2
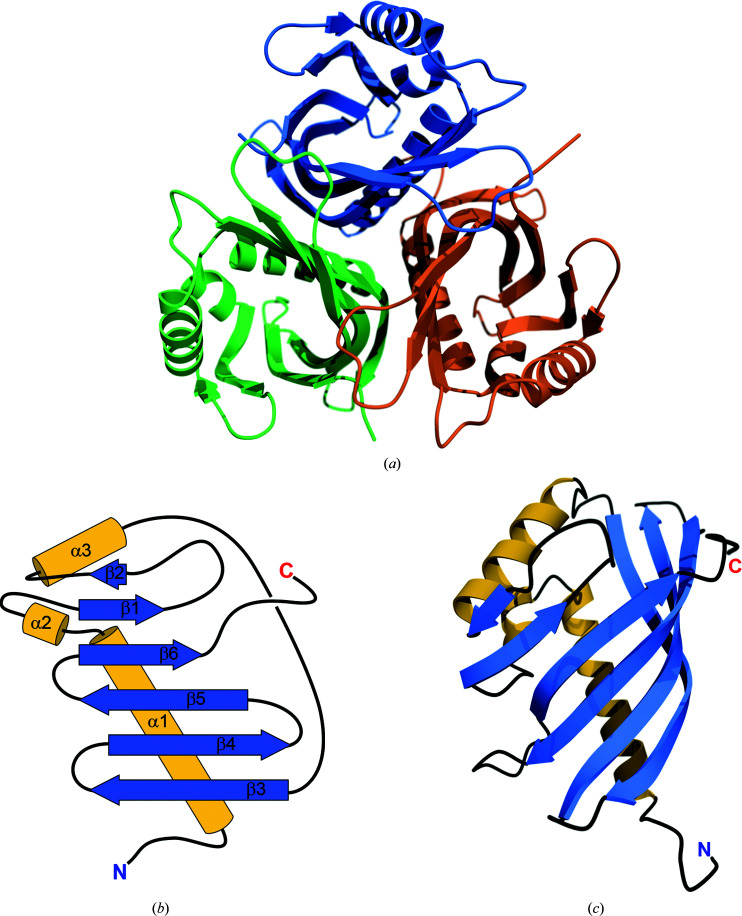
ActVI-ORFA crystallized in space group P2, with six molecules in the asymmetric unit arranged as two threefold-symmetrical trimers. Based on the results of size-exclusion chromatography and assembly calculations using PDBePISA, the trimers observed in the asymmetric unit appear to be physiological, and thus ActVI-ORFA is most likely to exist as a trimer in solution (Fig. 2 ▸ a). The average area buried at the monomer interface is 995 Å2. The model of the protein contains all 142 residues for each of the six chains, as well as 331 water molecules. The overall structure of the protein is very similar to others in the NFT2-like superfamily (see below). The fold consists of three helices and a partial β-barrel enclosing a solvent-accessible cavity (Fig. 2 ▸ b). The β-barrel consists of six antiparallel strands, with β2 being considerably shorter than the rest. The open side of the barrel is closed by helix α3 (Fig. 2 ▸ c). As in other members of the NTF2-like superfamily, the partial β-barrel encloses a cavity with a solvent-accessible volume of 160 Å3.
Figure 2.
(a) Quaternary structure of ActVI-ORFA. (b) A topology diagram of ActVI-ORFA showing the six β-strands (blue) and three α-helices (gold) that are characteristic of the NTF2-like fold. (c) Ribbon diagram showing the tertiary structure of the ActVI-ORFA protomer with secondary structures coloured as in (b). (a) and (c) were generated using the POVScript+ (Fenn et al., 2003 ▸) modification of MolScript (Kraulis, 1991 ▸) and POV-Ray. (b) was created using Adobe Illustrator 2020.
SeMet Caci_6494 crystallized in space group I23 with two molecules in the asymmetric unit and with a trimer assembly similar to that of ActVI-ORFA generated by crystallographic symmetry. The average area buried at the interfaces between the protomers is 960 Å2. The overall model contains two chains of 148 residues, with residues 4–70, 73–87 and 93–148 interpreted in chain A and residues 4–70, 73–88 and 93–148 interpreted in chain B. The model also contains 27 water molecules, two glycerol molecules, three polyethylene glycol fragments modelled as triethylene glycol and one modelled as tetraethylene glycol. The β-barrel encloses a cavity with a solvent-accessible volume of 180 Å3.
Aln2 crystallized in space group P21 with three molecules in the asymmetric unit in a trimeric arrangement similar to those of ActVI-ORFA and Caci_6494. The average area buried at the interfaces between the protomers in this trimer is 1065 Å2. The model contains six chains of 172 residues, with residues 30–169 interpreted in chains A–E and residues 30–167 in chain F. The model also contains 557 water molecules and a glycerol molecule. Owing to the conformation of the C-terminus of Aln2, the ‘cavity’ in this protein is so open to the solvent that it is more of a surface pocket. Presumably for this reason, VOIDOO did not recognize the cavity and was unable to calculate a volume.
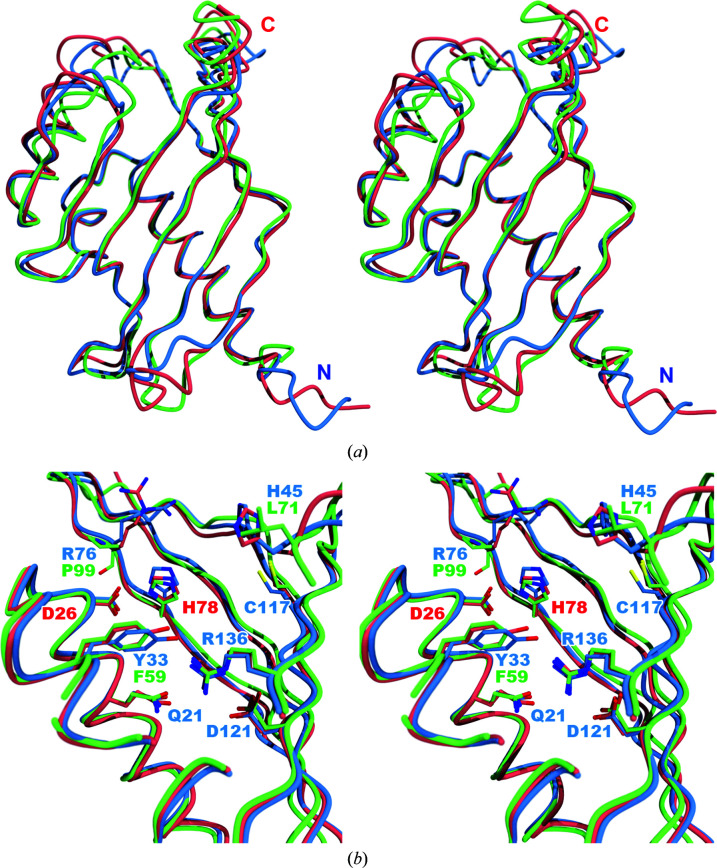
The superimposed structures of the three proteins show that Aln2 is missing 29 residues from the N-terminus (Fig. 3 ▸ a) relative to ActVI-ORFA and Caci_6494. The overlay also shows an internal cavity containing many polar residues, including the putative His/Asp dyad, and the His78/Asp26 dyad residues are oriented similarly in all three proteins (Fig. 3 ▸ b). Only three residues in the Aln2 cavity, Phe59, Leu71 and Pro99, do not align with the residues of the other two proteins. The corresponding residues in ActVI-ORFA and Caci_6494 are Tyr33, His45 and Arg76, respectively. In all three cases the change leads to a less polar cavity.
Figure 3.
(a) Stereoview of the superimposed Cα traces of ActVI-ORFA (blue), Caci_6494 (salmon) and Aln2 (green). Least-squares fitting was performed using Secondary Structure Matching (SSM) as implemented in Coot. (b) Overlay of the putative active sites of ActVI-ORFA (blue), Caci_6494 (salmon) and Aln2 (green). Labels for the side chains of the putative active-site residues in ActVI-ORFA are displayed in blue; those residues that differ in Aln2 are shown in green. The His/Asp dyad is labelled in red. This figure was created using the POVScript+ modification of MolScript and POV-Ray.
3.2. Comparison of ActVI-ORFA with NTF2-like proteins of known catalytic activity
We compared the cavity of ActVI-ORFA with those of several other NTF2-like proteins using Secondary Structure Matching (SSM) as implemented in PDBeFold (Krissinel & Henrick, 2004 ▸). The list of structurally homologous proteins returned by PDBeFold contained three proteins for which functions have been fully characterized (Table 5 ▸). SnoaL (PDB entry 1sjw; Sultana et al., 2004 ▸) is a cyclase in the nogalamycin-biosynthetic pathway that converts methyl nogalonate to nogalaviketone. Scytalone dehydratase (ScyDH; PDB entry 1std; Lundqvist et al., 1994 ▸) is a lyase that catalyzes the conversion of scytalone to 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene (Basarab et al., 1999 ▸). LinA (PDB entry 3a76; Okai et al., 2010 ▸) is a γ-HCC dehydrochlorinase that is involved in the degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane by sphingomonads (Shrivastava et al., 2015 ▸). All three of these proteins of known function were compared with the three proteins under examination here. The structures of ActVI-ORFA, Caci_6494 and Aln2 are similar enough that for the sake of clarity we will confine our comparisons to ActVI-ORFA. It should be understood that everything that is said about ActVI-ORFA with respect to the known enzymes also applies to Caci_6494 and Aln2.
Table 5. 3D structural alignment of ActVI-ORFA with Caci_6494, Aln2 and selected NTF2-like homologs with confirmed enzymatic roles.
The alignment was performed using SSM as implemented in the PDBeFold server (Krissinel & Henrick, 2004 ▸).
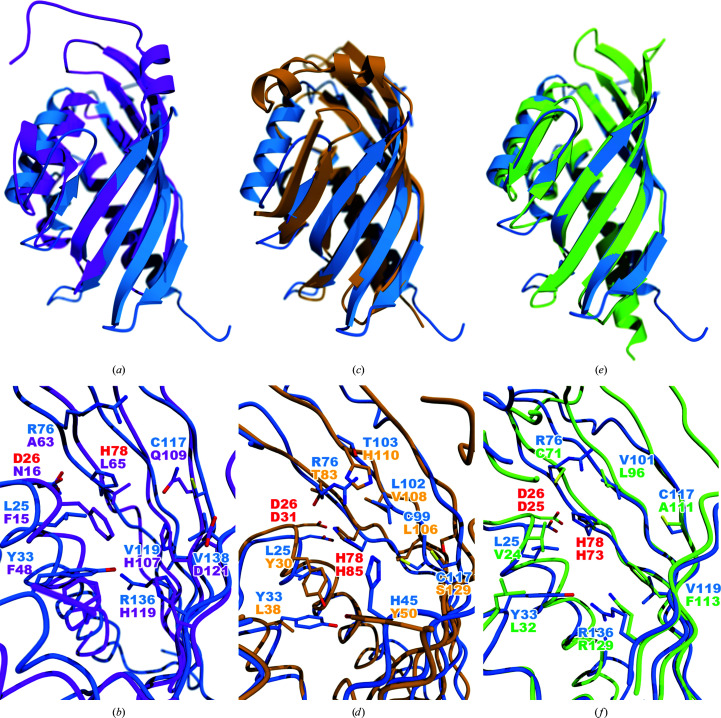
Although they share the NTF2-like fold, both the quaternary structures and interior cavities of ActVI-ORFA and SnoaL are very different. In the case of SnoaL, two loops cover the opening of the cavity (in this case a bona fide active site), making it inaccessible to solvent; this is not the case for ActVI-ORFA (Fig. 4 ▸ a). Additionally, SnoaL does not have a functional His/Asp dyad, since the catalytic Asp121 is more than 3.5 Å away from both of the conserved active-site histidine residues His107 and His119 (Sultana et al., 2004 ▸). The other active-site residues do not align well either (Fig. 4 ▸ b). This indicates that ActVI-ORFA, Caci_6494 and Aln2 are not SnoaL-type cyclases. Two other enzymes related to SnoaL, SnoaL2 and AclR, share the same fold and a similar active-site architecture with SnoaL (Beinker et al., 2006 ▸), but possess hydroxylase rather than cyclase activity (Siitonen et al., 2012 ▸). Comparison of SnoaL2 and AclR with ActVI-ORFA (not shown) shows that the active site of ActVI-ORFA bears little similarity to the cofactor-independent monooxygenase family active sites of SnoaL2 and AclR. Taken together, these comparisons make the hypothesis that ActVI-ORFA, Caci_6494 or Aln2 catalyse a pyran ring-closing reaction unlikely.
Figure 4.
Structural comparisons of functionally characterized NTF2-like proteins with ActVI-ORFA. (a) shows ribbon diagrams of ActVI-ORFA (blue) and SnoaL (magenta), while (b) shows a close-up view of the internal cavities of the two proteins. The His/Asp dyad residues are labelled in red; all other residue labels match the colouring of the structures. Least-squares fitting was performed using Secondary Structure Matching (SSM) as implemented in Coot. (c) and (d) show the analogous views for the comparison of ActVI-ORFA with ScyDH (orange). Likewise, (e) and (f) show the comparison of ActVI-ORFA with the dehydrochlorinase LinA (lime green). All images were rendered using POVScript+, MolScript and POV-Ray.
A comparison between ActVI-ORFA and scytalone dehydratase (ScyDH; PDB entry 1std; Lundqvist et al., 1994 ▸) shows that both proteins share a trimeric quaternary structure. The key tertiary-structure difference between them is that the C-terminus of ScyDH forms a pair of helices that cover the active site (Fig. 4 ▸ c), while the C-terminus of ActVI-ORFA is located far from the cavity opening. The His/Asp dyad is present in the ScyDH active site, but other residues are not well conserved (Fig. 4 ▸ d).
Lastly, we compared ActVI-ORFA with LinA (PDB entry 3a76; Okai et al., 2010 ▸). Again, both ActVI-ORFA and LinA share very similar trimeric quaternary structures. The chief difference in the tertiary structure of this pair of proteins is in the rim of the cavity formed by β4, β5 and β6, all of which are more extended in LinA (Fig. 4 ▸ e). The LinA enzyme uses a His/Asp dyad to abstract an axially oriented proton from a cyclohexane ring of its substrate (Okai et al., 2010 ▸), and these residues match the dyad of ActVI-ORFA well (Fig. 4 ▸ f). This suggests the possibility that ActVI-ORFA, Caci_6494 and Aln2 could be capable of abstracting a proton from an intermediate (for example, 3 or 4 in Fig. 1 ▸) or an off-pathway product such as 6 and returning it back to the productive biosynthetic pathway.
3.3. Structural characterization of the complex of Caci_6494 with (S)-DNPA
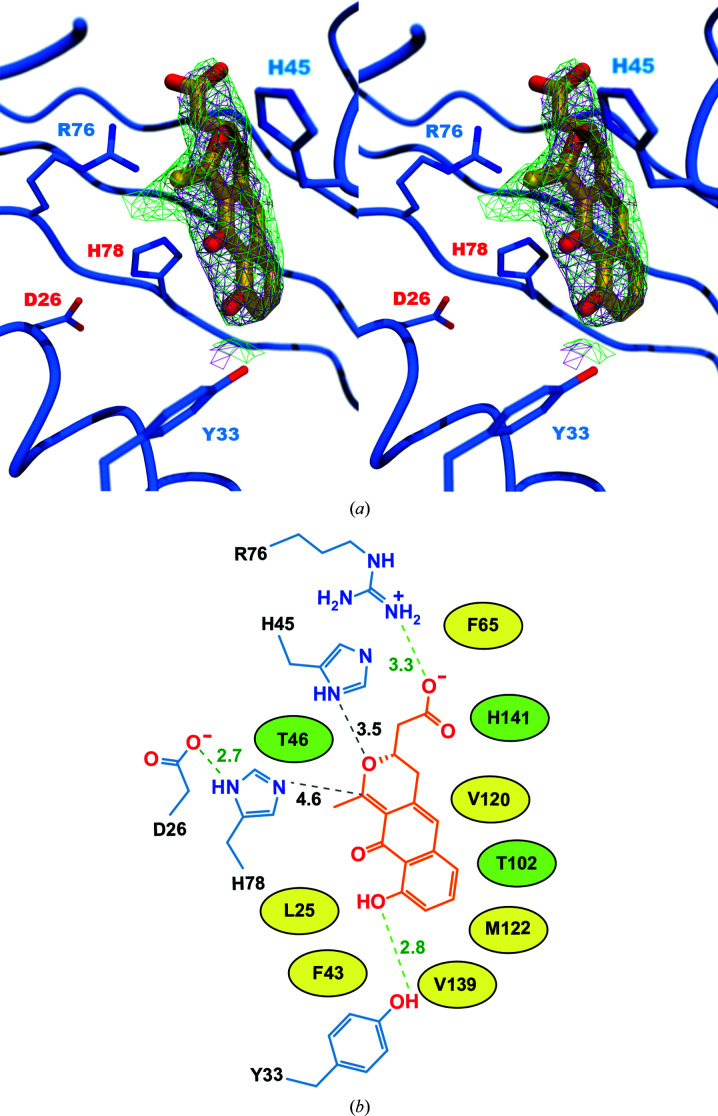
The reduction of a bicyclic intermediate by ActVI-ORF1 is followed by the pyran ring-closing formation of (S)-DNPA (Taguchi et al., 2007 ▸). Since ActVI-ORFA has been hypothesized to assist with pyran ring closure (Fernández-Moreno et al., 1994 ▸), we decided to use (S)-DNPA in co-crystallization experiments with ActVI-ORFA. We were unable to co-crystallize ActVI-ORFA in the presence of (S)-DNPA, and ActVI-ORFA crystals that were soaked with (S)-DNPA diffracted poorly. The resulting maps showed electron density in the interior cavity, but this was too poorly defined to allow the modelling of (S)-DNPA (data not shown). However, the closest homolog of ActVI-ORFA, Caci_6494, was successfully crystallized in the presence of (S)-DNPA. The resulting electron-density maps allowed (S)-DNPA to be modelled unambiguously in the putative active site of Caci_6494 (Fig. 5 ▸). The calculation of a simulated-annealing composite OMIT map confirmed the presence of the ligand in the cavity (Fig. 5 ▸ a). (S)-DNPA is held in the cavity by only a few hydrogen-bonding interactions (Fig. 5 ▸ b); the remainder of the contacts of the ligand with the protein are van der Waals interactions with hydrophobic residues lining the cavity. The guanidinium group of Arg36 is within hydrogen-bonding distance of the carboxylic acid group of the (S)-DNPA. His45 is almost within hydrogen-bonding distance of the pyran ring O atom of (S)-DNPA. At the other end of the ligand, Tyr33 participates in a hydrogen-bonding interaction with a hydroxyl group of the ligand. His78 of the His/Asp dyad is somewhat distant from the pyran ring, but it is not likely that (S)-DNPA would be the correct substrate should Caci_6494 prove to be an enzyme. His78 is close enough to (S)-DNPA that one could easily envision the correct ligand for Caci_6494 binding in such a way that His78 would be in position to participate in general acid/base chemistry.
Figure 5.
(a) Stereoview showing the orientation of (S)-DNPA inside the active site of Caci_6494. The magenta mesh shows the 2F o − F c map, while the green mesh shows the simulated-annealing composite OMIT 2F o − F c map; both are contoured at 1σ. (b) The orientation and distances of (S)-DNPA relative to the His78/Asp26 dyad and other active-site residues. Electrostatic interactions are shown as green dashed lines, while distances discussed in the text that are too long to be true electrostatic interactions are shown as black dashed lines. The distances in ångströms are given next to each line. Residues drawn as simple ovals make van der Waals contacts with (S)-DNPA; structures and distances are omitted for clarity. Hydrophobic side chains are coloured yellow and polar side chains are coloured green.
Although this work did not lead to a definitive answer regarding the roles of ActVI-ORFA and its homologs, we believe that the presence of a binding cavity that is lined with residues capable of participating in hydrogen-bonding interactions and containing a common acid/base catalysis motif (His/Asp dyad) justifies further investigation of these proteins as possible accessory enzymes. Future work supported by the organic synthesis of the actinorhodin metabolites 3 and 6 may be the most efficient route to ascertaining whether ActVI-ORFA possesses enzymatic activity.
4. Related literature
The following references are cited in the supporting information for this article: Robert & Gouet (2014 ▸) and Taguchi et al. (2001 ▸).
Supplementary Material
PDB reference: ActVI-ORFA from Streptomyces coelicolor, 5bka
PDB reference: Caci_6494 from Catenulispora acidiphila, 6p77
PDB reference: complex with S-DNPA, 6vw4
PDB reference: Aln2 from Streptomyces sp. CM020, 6p7l
Supporting information: additional methods and materials, supplementary figures and supplementary table. DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X20009814/rf5029sup1.pdf
Acknowledgments
This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a US Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. Use of the LS-CAT Sector 21 was supported by the Michigan Economic Development Corporation and the Michigan Technology Tri-Corridor (Grant 085P1000817). The authors also wish to thank the staff at the 2016 CCP4/APS School of Macromolecular Crystallography.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by National Science Foundation, Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences grant CHE-1606842. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences grant P20 GM103451. Jane ja Aatos Erkon Säätiö grant .
References
- Adams, P. D., Afonine, P. V., Bunkóczi, G., Chen, V. B., Davis, I. W., Echols, N., Headd, J. J., Hung, L.-W., Kapral, G. J., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., McCoy, A. J., Moriarty, N. W., Oeffner, R., Read, R. J., Richardson, D. C., Richardson, J. S., Terwilliger, T. C. & Zwart, P. H. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Afonine, P. V., Mustyakimov, M., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Moriarty, N. W., Langan, P. & Adams, P. D. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 1153–1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Basarab, G. S., Steffens, J. J., Wawrzak, Z., Schwartz, R. S., Lundqvist, T. & Jordan, D. B. (1999). Biochemistry, 38, 6012–6024. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Battye, T. G. G., Kontogiannis, L., Johnson, O., Powell, H. R. & Leslie, A. G. W. (2011). Acta Cryst. D67, 271–281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Beinker, P., Lohkamp, B., Peltonen, T., Niemi, J., Mäntsälä, P. & Schneider, G. (2006). J. Mol. Biol. 359, 728–740. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bunkóczi, G., Echols, N., McCoy, A. J., Oeffner, R. D., Adams, P. D. & Read, R. J. (2013). Acta Cryst. D69, 2276–2286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bunkóczi, G. & Read, R. J. (2011). Acta Cryst. D67, 303–312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Chen, V. B., Arendall, W. B., Headd, J. J., Keedy, D. A., Immormino, R. M., Kapral, G. J., Murray, L. W., Richardson, J. S. & Richardson, D. C. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 12–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, R. Y., Chang, Y., Bateman, A., Murzin, A. G., Axelrod, H. L., Hwang, W. C. & Aravind, L. (2013). BMC Bioinformatics, 14, 327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. (2004). Acta Cryst. D60, 2126–2132. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P., Lohkamp, B., Scott, W. G. & Cowtan, K. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 486–501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Fenn, T. D., Ringe, D. & Petsko, G. A. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst. 36, 944–947.
- Fernández-Moreno, M. A., Martínez, E., Caballero, J. L., Ichinose, K., Hopwood, D. A. & Malpartida, F. (1994). J. Biol. Chem. 269, 24854–24863. [PubMed]
- Filippova, E. V., Luan, C.-H., Dunne, S. F., Kiryukhina, O., Minasov, G., Shuvalova, L. & Anderson, W. F. (2014). J. Struct. Funct. Genomics, 15, 33–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Escribano, J. P. & Bibb, M. J. (2011). Microb. Biotechnol. 4, 207–215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Huang, T., Chang, C.-Y., Lohman, J. R., Rudolf, J. D., Kim, Y., Chang, C., Yang, D., Ma, M., Yan, X., Crnovcic, I., Bigelow, L., Clancy, S., Bingman, C. A., Yennamalli, R. M., Babnigg, G., Joachimiak, A., Phillips, G. N. & Shen, B. (2016). J. Antibiot. 69, 731–740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ichinose, K., Surti, C., Taguchi, T., Malpartida, F., Booker-Milburm, K. I., Stephenson, G. R., Ebizuka, Y. & Hopwood, D. A. (1999). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 9, 395–400. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ichinose, K., Taguchi, T., Bedford, D. J., Ebizuka, Y. & Hopwood, D. A. (2001). J. Bacteriol. 183, 3247–3250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Joosten, R. P., Long, F., Murshudov, G. N. & Perrakis, A. (2014). IUCrJ, 1, 213–220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kleywegt, G. J. & Jones, T. A. (1994). Acta Cryst. D50, 178–185. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kleywegt, G. J., Zou, J.-Y., Kjeldgaard, M. & Jones, T. A. (2001). International Tables for Crystallography, Vol. F, edited by M. G. Rossmann & E. Arnold, pp. 353–356. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
- Kraulis, P. J. (1991). J. Appl. Cryst. 24, 946–950.
- Krissinel, E. & Henrick, K. (2004). Acta Cryst. D60, 2256–2268. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Krissinel, E. & Henrick, K. (2007). J. Mol. Biol. 372, 774–797. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liebschner, D., Afonine, P. V., Baker, M. L., Bunkóczi, G., Chen, V. B., Croll, T. I., Hintze, B., Hung, L.-W., Jain, S., McCoy, A. J., Moriarty, N. W., Oeffner, R. D., Poon, B. K., Prisant, M. G., Read, R. J., Richardson, J. S., Richardson, D. C., Sammito, M. D., Sobolev, O. V., Stockwell, D. H., Terwilliger, T. C., Urzhumtsev, A. G., Videau, L. L., Williams, C. J. & Adams, P. D. (2019). Acta Cryst. D75, 861–877.
- Lundqvist, T., Rice, J., Hodge, C., Basarab, G. S., Pierce, J. & Lindqvist, Y. (1994). Structure, 2, 937–944. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A. J., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Adams, P. D., Winn, M. D., Storoni, L. C. & Read, R. J. (2007). J. Appl. Cryst. 40, 658–674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Minor, W., Cymborowski, M., Otwinowski, Z. & Chruszcz, M. (2006). Acta Cryst. D62, 859–866. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Okai, M., Kubota, K., Fukuda, M., Nagata, Y., Nagata, K. & Tanokura, M. (2010). J. Mol. Biol. 403, 260–269. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, M., Taguchi, T., Itoh, T., Ebizuka, Y., Booker-Milburn, K. I., Stephenson, G. & Ichinose, K. (2003). Tetrahedron, 59, 8793–8798.
- Robert, X. & Gouet, P. (2014). Nucleic Acids Res. 42, W320–W324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, N., Prokop, Z. & Kumar, A. (2015). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81, 7553–7559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Siitonen, V., Blauenburg, B., Kallio, P., Mäntsälä, P. & Metsä-Ketelä, M. (2012). Chem. Biol. 19, 638–646. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sultana, A., Kallio, P., Jansson, A., Wang, J.-S., Niemi, J., Mäntsälä, P. & Schneider, G. (2004). EMBO J. 23, 1911–1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, T., Ebizuka, Y., Hopwood, D. A. & Ichinose, K. (2001). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 11376–11380. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, T., Okamoto, S., Lezhava, A., Li, A., Ochi, K., Ebizuka, Y. & Ichinose, K. (2007). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 269, 234–239. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Terwilliger, T. C., Adams, P. D., Read, R. J., McCoy, A. J., Moriarty, N. W., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Afonine, P. V., Zwart, P. H. & Hung, L.-W. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 582–601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Terwilliger, T. C., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Afonine, P. V., Moriarty, N. W., Adams, P. D., Read, R. J., Zwart, P. H. & Hung, L.-W. (2008). Acta Cryst. D64, 515–524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Williams, C. J., Headd, J. J., Moriarty, N. W., Prisant, M. G., Videau, L. L., Deis, L. N., Verma, V., Keedy, D. A., Hintze, B. J., Chen, V. B., Jain, S., Lewis, S. M., Arendall, B. W., Snoeyink, J., Adams, P. D., Lovell, S. C., Richardson, J. S. & Richardson, D. C. (2018). Protein Sci. 27, 293–315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
PDB reference: ActVI-ORFA from Streptomyces coelicolor, 5bka
PDB reference: Caci_6494 from Catenulispora acidiphila, 6p77
PDB reference: complex with S-DNPA, 6vw4
PDB reference: Aln2 from Streptomyces sp. CM020, 6p7l
Supporting information: additional methods and materials, supplementary figures and supplementary table. DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X20009814/rf5029sup1.pdf