Abstract
Lipo-chitooligosaccharides (LCOs) are signaling molecules produced by rhizobial bacteria that trigger the nodulation process in legumes, and by some fungi that also establish symbiotic relationships with plants, notably the arbuscular and ecto mycorrhizal fungi. Here, we show that many other fungi also produce LCOs. We tested 59 species representing most fungal phyla, and found that 53 species produce LCOs that can be detected by functional assays and/or by mass spectroscopy. LCO treatment affects spore germination, branching of hyphae, pseudohyphal growth, and transcription in non-symbiotic fungi from the Ascomycete and Basidiomycete phyla. Our findings suggest that LCO production is common among fungi, and LCOs may function as signals regulating fungal growth and development.
Subject terms: Microbial ecology, Cellular microbiology, Fungal biology, Fungal ecology
Lipo-chitooligosaccharides (LCOs) are signaling molecules produced by certain bacteria and fungi that establish symbiotic relationships with plants. Here, the authors show that LCOs are produced also by many other, non-symbiotic fungi, and regulate fungal growth and development.
Introduction
A conceptual leap in our understanding of the mechanism of plant-microbe symbiosis came when, almost 30 years ago, nitrogen-fixing rhizobial bacteria were found to produce nodulation (Nod) factors that are required to induce the formation of nodules on legume roots1. These Nod factors are lipo-chitooligosaccharides (LCOs), which consist of a polymer of three to five N-acetyl glucosamine (GlcNAc) residues (the chitin backbone) with β-(1,4) linkages modified with a long-chain fatty acyl group and various other functional groups2. Most rhizobia rely on LCOs to associate with their legume hosts and legumes can perceive LCOs down to 10−14 M concentrations3. Substitutions on the chitinous backbone are largely responsible for the often high level of host specificity observed in the rhizobia-legume symbiosis2.
Nearly 20 years later, arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi (sub-phylum Glomeromycotina), which are another group of microorganisms that live symbiotically with plant roots, were also found to produce LCOs (Myc-LCOs)4. Additional studies have shown that these two dissimilar symbioses share a highly conserved Common Symbiosis Signaling Pathway (CSSP), which is activated in plants by Nod- or Myc-LCOs to allow root colonization (either Nod or mycorrhization, respectively5,6). In both symbioses, LCOs are perceived at the plasma membrane by receptor-like kinases with extracellular LysM domains7,8. The perception of short chitooligosaccharides (COs) is also required to initiate the AM association and is mediated by the same family of LysM-containing receptors7.
We recently reported that a representative from a third group of symbiotic microorganisms, the ectomycorrhizal (EM) fungus Laccaria bicolor (phylum Basidiomycetes), also synthesizes LCOs9. L. bicolor colonizes the roots of Populus, a host plant that contains the genetic components of the CSSP and can also be colonized by AM fungi9; however, another EM fungus that was suspected to produce LCOs, Hebeloma cylindrosporum, colonizes mostly pine, which does not contain the components for the CSSP10. This latter finding suggests that LCOs may have functional roles beyond symbiotic signaling.
In this study, we explored the possibility that the production of LCOs is a more common trait among fungi than was previously anticipated. We demonstrate that LCOs are not produced solely by symbiotic microorganisms but also by widely divergent members of the Kingdom Fungi. Moreover, we show that LCOs have regulatory functions in fungal development.
Results
LCOs are produced by a wide range of fungi in the Kingdom Fungi
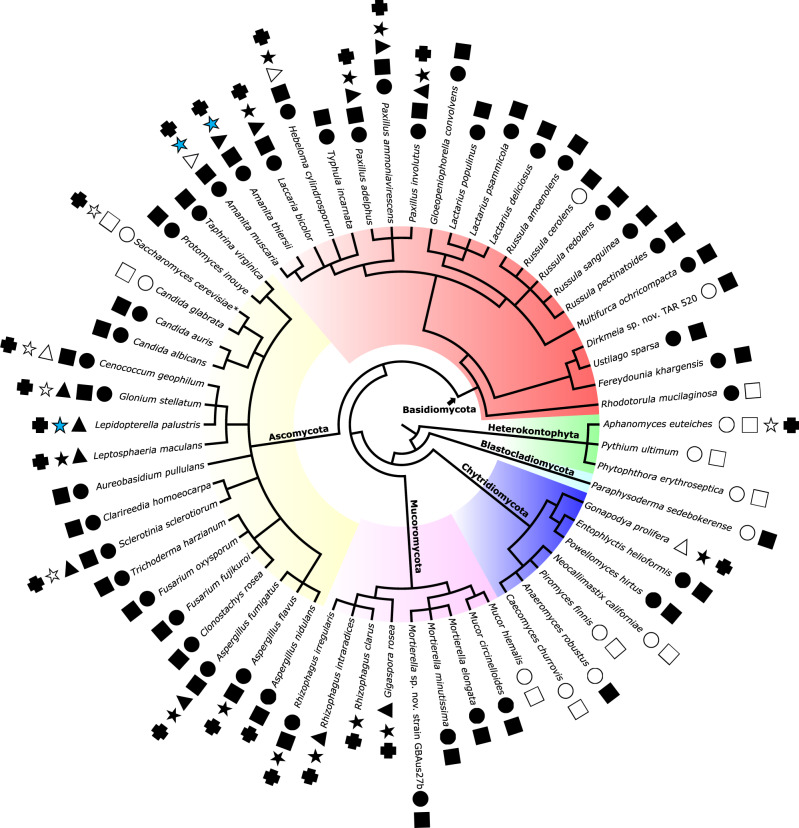
We tested 59 species of fungi belonging to most phyla within the kingdom for the presence of LCOs exuded into their culture media (Fig. 1 and Supplementary Data 1, 2, and 3). These exudates were assayed for LCO activity using the highly sensitive root hair deformation response triggered by LCOs in barrel medic (Medicago truncatula) and common vetch (Vicia sativa)1,2. As some of these root hair deformations, such as waving or bulb formation, are not specific responses to LCOs, our assay was scored strictly on root hair branching. In control experiments, as expected from their known Nod factor specificities, M. truncatula responded only to sulfated (s) LCOs, whereas V. sativa responded only to non-sulfated (ns) LCOs2 (Supplementary Fig. 1). To test the specificity of the root hair branching response to LCOs, we examined the effect of short COs, polymers of four to five GlcNAc residues (CO4 and CO5), which are precursors of LCOs and have been shown to also activate the CSSP11,12. We also tested long CO chains (CO8), which are not LCO precursors, but oligomers that activate symbiotic and defense-related responses7,13. Root hair branching was not triggered by the application of short (CO4 and CO5) or long (CO8) chain COs, fatty acids (palmitic or oleic), or by the fresh culture media in which the fungi grew (Supplementary Fig. 1 and Supplementary Data 4). Also, the absence in the fungal samples of bacteria that might produce LCOs was verified with specific PCR amplification (using fungus-specific and bacterium-specific primers) and light microscopy observation (Supplementary Fig. 2). When the exudates from 53 fungi were applied to the roots of M. truncatula or V. sativa, 47 of them triggered root hair branching in one or two legumes (Fig. 1, Supplementary Figs. 3–7, and Supplementary Data 4). We confirmed the presence of sLCOs in some butanol extracts of exudates by assaying for expression of the MtENOD11 gene in M. truncatula4 (Fig. 1 and Supplementary Fig. 8). Interestingly, the exudates of the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida glabrata did not induce root hair branching (Fig. 1). Compared with Candida albicans or Candida auris in which we detected LCO activity (Fig. 1), C. glabrata is more closely related to S. cerevisiae and reported to form pseudohyphae only under stress conditions or when genetically altered14,15.
Fig. 1. Production of lipo-chitooligosaccharides and chitooligosaccharides by fungi.
Fifty-nine fungi representing five of the eight phyla (indicated by colors) and three species of oomycetes (Heterokontophyta, green) were tested for the presence of lipo-chitooligosaccharide (LCO)s and chitooligosaccharide (CO)s in their culture supernatants. Black circle, detection of sulfated LCOs by the root hair branching assay with M. truncatula. Black square, detection of non-sulfated LCOs by the root hair branching assay with V. sativa. Black triangle, detection of sulfated LCOs in butanol extracts by MtENOD11 expression assay. Black star, detection of LCOs in butanol extracts by LC-MS/MS with high confidence (non-targeted mass spectrometry (MS) analysis or two to three MRM transitions per molecule). Blue star, detection of LCOs with lower confidence (MS signal at the expected retention time but with only one MRM transition). Black cross, detection of COs by HPLC/MS from water extracts. Clear symbols indicate no detection. Black asterisk indicates two or more strains were examined.
The structure of fungal LCOs
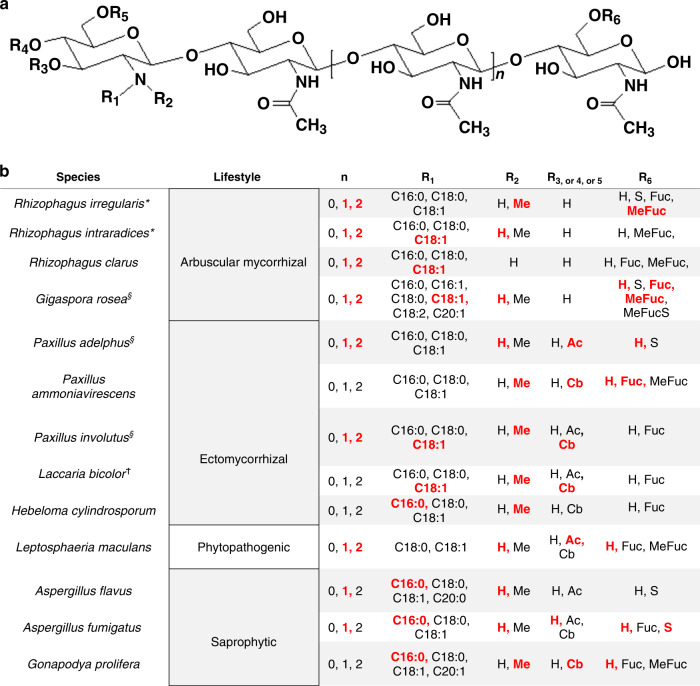
To confirm our findings with the root hair branching assay for LCOs and to determine the structure of LCOs produced by the various fungi, we used mass spectrometry (MS). The culture media were fractionated by butanol:water phase separation. The water phases were analyzed directly for COs and the butanol phases, in which LCOs were expected to fractionate, were either analyzed directly or were further purified by chromatography to minimize matrix effects on the MS analyses. Taking advantage of an in-house database (Supplementary Data 5) listing all possible mass-to-charge ratios (precursors/products ions) calculated from known Nod factors, and by using the very sensitive Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) MS approach, we found mass signals of LCOs in 16 of the 20 fungal exudates we analyzed (Fig. 1). The LCOs contained three to five GlcNAc residues bearing various fatty acyl chains and additional sulfate, methyl, carbamoyl, fucosyl, and methylfucosyl substitutions (Fig. 2). Exudates from three fungal species that were LCO positive—Gigaspora rosea, Paxillus adelphus, and Paxillus involutus—were concentrated enough for untargeted LCO detection by using enhanced MS-enhanced product ion (EMS–EPI), allowing a more exhaustive analysis of the different structures present. Examples of chromatograms and spectra of major LCO structures found in these three fungal exudates are given in Supplementary Figs. 9–11. LCOs were not detected in exudates from Cenococcum geophilum, Glonium stellatum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Fig. 1). Notably, the chemical structures of all detected LCOs were quite similar across the Kingdom Fungi, with the fucosyl and methylfucosyl functional groups as the most commonly found, even in species of AM fungi. In the water phases of the 20 analyzed fungal exudates, we found mass signals corresponding to COs containing three to five GlcNAc residues.
Fig. 2. Structures of LCOs found in fungi.
a The generic structure of LCOs. b LCO structures determined by LC-MS/MS analysis of the butanol phase extract of culture media from fungi with various lifestyles. Red indicates the most abundant LCO structures. (§) indicates when untargeted mass spectrometry (MS) analysis was used. The other structures were detected in targeted MS mode (MRM) (see “Methods” for details of various possible MRM transitions). (*) indicates when more than one strain was analyzed. (n) is the number of residues of chitin oligomers, (R1) is the type of fatty acid, identified as saturated or unsaturated fatty acids. (R2–R6) are chemical substitutions: hydrogen (H), acetyl (Ac), carbamoyl (Cb), fucosyl (Fuc), fucosyl sulfate (FucS), methylfucosyl (MeFuc) and sulfate (S). (ϯ) indicates data published previously9.
Given that the oomycete plant pathogen Aphanomyces euteiches produces COs16, we also analyzed exudates of this organism for the presence of chitinous molecules by MS and exudates of other Heterokontophyta/oomycete representatives Pythium ultimum and Phytophthora erythroseptica by using root hair branching assay. We confirmed the presence of short COs by MS but detected no LCOs either by MS or by the functional assays, suggesting that the ability to produce LCOs may be restricted to rhizobial bacteria and to the Kingdom Fungi (Fig. 1).
LCOs have regulatory functions in fungal development
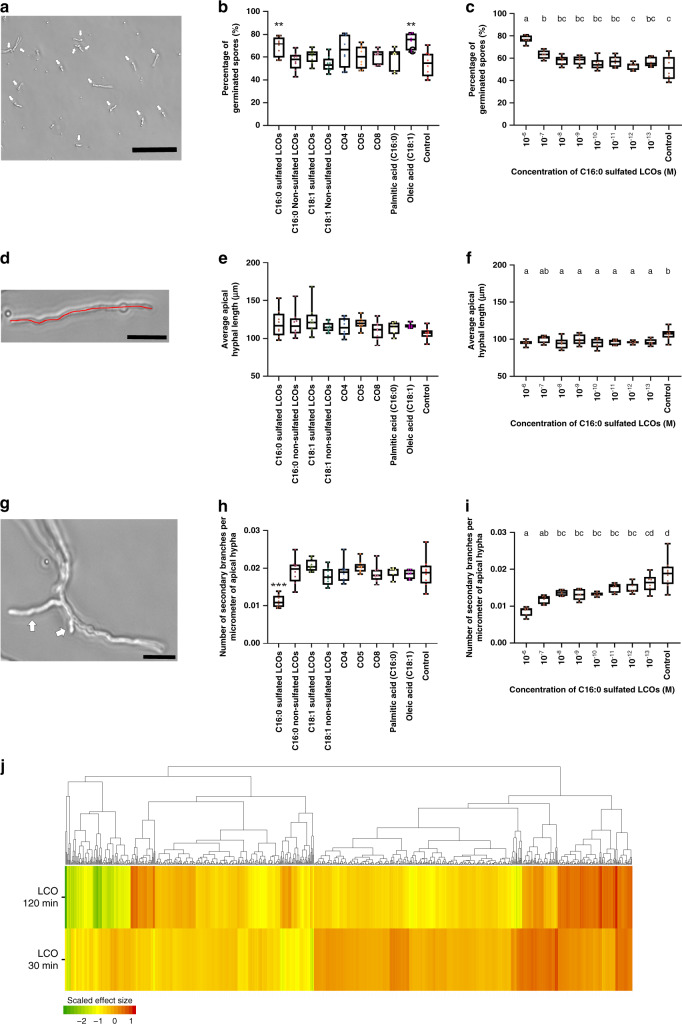
We found LCOs in fungi with various lifestyles and under different growth conditions (Figs. 1 and 2, and Supplementary Data 1, 2, and 3), including in non-symbiotic saprotrophic fungi that live and feed on dead organic matter, and in pathogenic fungi that grow on animals or plants, suggesting that their roles in fungal biology are not limited to symbioses with plants. To explore this hypothesis, we applied synthetic sLCOs or nsLCOs with various fatty acyl chains (C16:0—palmitic acid or C18:1—oleic acid), short (CO4 and CO5) and long (CO8) COs, and the C16:0 and C18:1 fatty acids to the saprotrophic and opportunistic human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus, which exhibits two easily scored developmental processes, germination, and hyphal branching. C16:0 sLCO (10−8 M) and oleic acid (10−8 M) increased spore germination by 28% and 36%, respectively, when compared with the control (Fig. 3a, b). The response to LCOs was dose dependent (Fig. 3c). Although the length of the primary apical hyphae was similar across the different treatments (Fig. 3d, e), not exceeding 11% difference among them (Fig. 3f), the branching of lateral hyphae, treated with the C16:0 sLCO, decreased by up to 41% (Fig. 3g, h) and in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 3i). The activity of C16:0 sLCO was detected at as little as 10−12 M. As the saccharidic (COs) and lipidic (oleic and palmitic acids) moieties of LCOs were not acting alone, we conclude that the observed biological activity of C16:0 sLCO is linked to its lipo-chitooligosaccharidic nature. As germination and branching are programmed developmental processes in fungi, we investigated the effect of these molecules on transcription activity in A. fumigatus. We found 91 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between control and LCO-treated cultures after only 30 min of treatment and 152 DEGs after 120 min (Fig. 3j, Supplementary Fig. 12, and Supplementary Data 6). Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) pathway analyses revealed that several DEGs encoding proteins associated with the cell membrane activities and cell wall processes were regulated at 30 min after treatment with LCOs. A much more diverse set of functions was represented at 120 min with a large number of proteins associated with responses to chemical stimuli and enzymes related to the tricarboxylic acid cycle (Supplementary Data 7 and 8). The vast majority of regulated genes in response to LCOs increased in expression and there was a significant overlap in these upregulated genes at 30 and 120 min, suggesting that some of these genes could be good reporters for the response to LCOs in A. fumigatus (Supplementary Fig. 13).
Fig. 3. Effects of LCOs, COs, and fatty acids on A. fumigatus.
a Germinated spores are indicated by white arrows. The scale bar is 100 µm. b Percentage of germinated spores 10 h after treatment with various molecules at 10−8 M. (**) indicates a significant difference between C16:0 sulfated LCO or oleic acid treatments and the control according to Dunnett’s multiple comparison procedure, the p-value is 7.21 × 10−4. Each treatment was analyzed in eight independent wells, except the palmitic and oleic acid treatments that were analyzed in six of them. c Effect of a range of C16:0 sulfated LCO concentrations on the percentage of germinated spores; one-way ANOVA p-value of 6.32 × 10−8. Each LCO concentration was analyzed in six wells, except for the control treatments that were analyzed in eight of them. d An example of an apical hypha germinated from both sides of a spore whose length measured is indicated in red. Scale bar is 25 µm. e Length of apical hyphae after 12 h treatment with various molecules at 10−8 M. There were no significant differences between treatments. Each treatment was analyzed in eight independent wells, except palmitic and oleic acid treatments that were analyzed in six of them. f Effect of a range of C16:0 sulfated LCO concentrations on the apical hyphae length; one-way ANOVA p-value is 3.91 × 10−3. Each LCO concentration was analyzed in six independent wells, except the control which was analyzed in eight of them. g Germination of a control spore showing two secondary branches (arrows) on a germinating apical hypha. Scale bar is 25 µm. h The ratio of secondary branches per micrometer of apical hypha after 12 h treatment with various molecules at 10−8 M. (***) indicates a significant difference between C16:0 sulfated LCO treatments and the control according to Dunnett’s multiple comparison procedure, p-value is 5.89 × 10−9. Each treatment was analyzed in eight independent wells, except palmitic and oleic acid treatments, which were analyzed in six of them. The ratio was determined by calculating the number of secondary branches for that specific apical hyphal branch length. i Effect of a range of C16:0 sulfated LCO concentrations on the ratio of secondary branches; one-way ANOVA p-value is 1.54 × 10−9. Each LCO concentration was analyzed in six independent wells, except the control which was analyzed in eight of them. The ratio was determined by calculating the number of secondary branches for that specific apical hyphal branch length. In box plots (c, f, i), different letters indicate significant differences and similar letters indicate no difference according to Tukey’s single-step multiple comparison procedure. In the box plots (b, c, e, f, h, i), the bars represent the minimum value, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum value such that 25% of the data are in each section. j Heatmap showing the scaled effect size of differentially expressed genes 30 and 120 min after C16:0 sulfated LCO treatment at a concentration of 10−8 M compared with the control solution. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
We also tested the effect of 10−8 M LCOs, COs, oleic, and palmitic acids on the growth of C. glabrata, a yeast in which we did not detect the synthesis of LCOs. All the molecules tested stimulated the formation of pseudohyphae (Fig. 4a, b and Supplementary Movies 1, 2, and 3), but the greatest activity was observed with the C16:0 sLCO after 12 h of exposure. This effect was dose dependent and detected at as little as 10−13 M (Fig. 4c and Supplementary Movie 1).
Fig. 4. Effect of LCOs, COs, and fatty acids on C. glabrata.
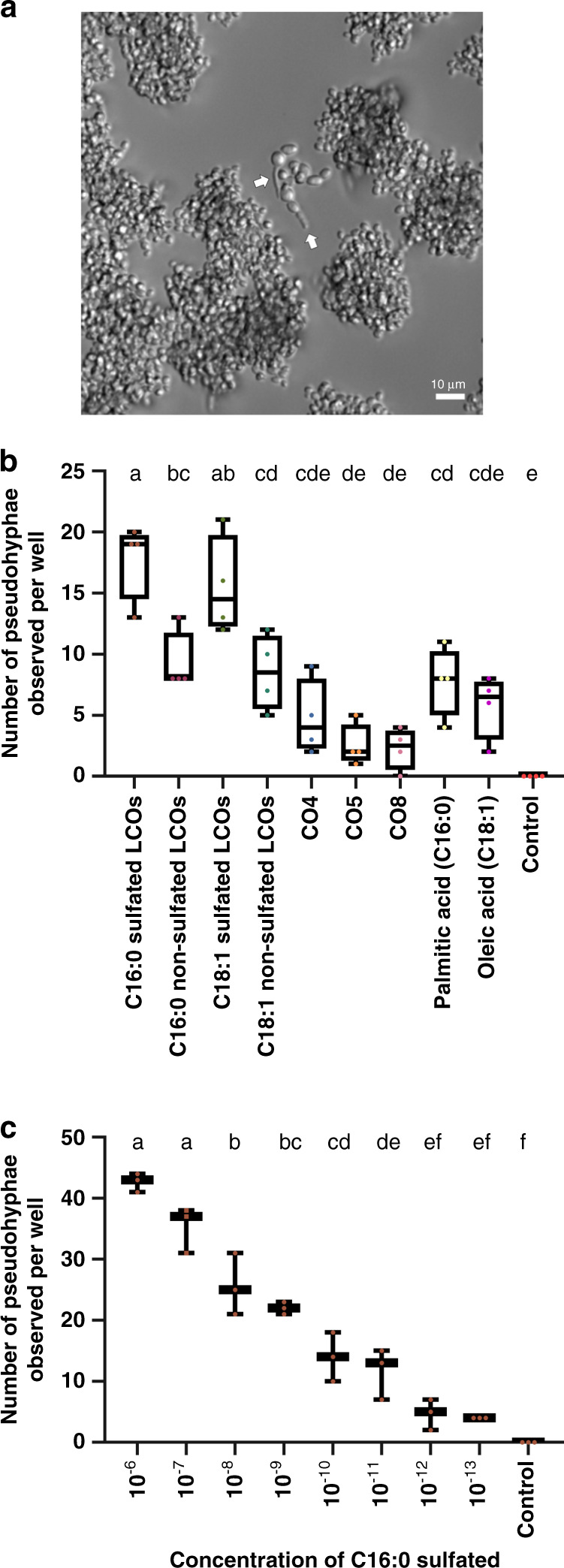
a White arrows show pseudohyphae of C. glabrata (see also Supplementary Movies 1, 2, and 3). Scale bar is 10 µm. b The number of pseudohyphae observed per well after treatment for 12 h with various LCOs, COs, and fatty acids at 10−8 M. Different letters indicate significant differences and similar letters indicate no difference according to Tukey’s single-step multiple comparison procedure; one-way ANOVA p-value is 9.90 × 10−10. Each treatment was analyzed in four independent wells. c Effect of a range of C16:0 sulfated LCO concentrations on pseudohyphae formation; one-way ANOVA p-value is 4.67 × 10−12. Different letters indicate significant differences and similar letters indicate no difference according to Tukey’s single-step multiple comparison procedure. Each LCO concentration was analyzed in three independent wells. In the box plots (b, c), the bars represent the minimum value, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum value such that 25% of the data are in each section. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
To evaluate whether fungi outside the phylum Ascomycota respond to LCOs, we tested a Basidiomycete that is a common allergen in humans, the yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa. Treatment with 10−8 M C16:0 sLCOs led to a 25% increase in the proliferation of R. mucilaginosa cells (Supplementary Fig. 14).
Discussion
The findings reported here impose a paradigm shift in our understanding of the biology of LCOs. Until now, these molecules were considered as exclusively produced by plant microbial symbionts, rhizobia, AM, and EM fungi. We now show that nearly all fungi—not only those that interact with plants—produce LCOs whose structures are very similar to those of Nod factors. As LCOs have been shown to suppress innate immunity in plants7,17,18, a function that may have predated the mycorrhizal symbiosis19, this discovery raises questions on how plants can distinguish symbiotic microbes from pathogenic fungi. Although it is indisputable that LCOs are symbiotic signals in the sense that they activate the CSSP pathway in plants, it remains to demonstrate that they are also used by rhizobia and mycorrhizal fungi to be distinguished from non-symbiotic microorganisms. Interestingly, the production of LCOs in rhizobia and of precursors of LCOs (short COs) in AM fungi are strongly stimulated by specific root signals2,12. This could ensure the production of the right LCO structures, in the right place, at the right time, and with adequate concentrations. If the existence of such a molecular dialogue also exists in non-symbiotic interactions, then additional symbiotic signals, other than LCOs, must provide specificity. AM fungi may produce more distinctive symbiotic signals, yet to be discovered, whereas pathogenic fungi are known to produce additional effectors recognized by the immune system of plants. In the former case, the ligand of the plant Dwarf14-Like (D14L) receptor that activates the D14L-dependent signaling mechanisms and the ensued removal of the negative regulator of mycorrhization SMAX1, could be a good candidate20,21. In the case of pathogenic fungi, the role that LCOs and COs could play in their virulence should be investigated. Indeed, these molecules, particularly when they are combined, can act synergistically to enhance symbiosis and suppress immunity7, i.e. can have an inverse role to that of the traditional pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecules also produced by the same organisms.
Given that we have detected LCOs in widely divergent lineages of fungi that diverged before the first land plants, we speculate that LCO production is an ancestral trait of fungi and that plants have acquired the ability to recognize these molecules first to detect the close presence of a fungus, then as symbiotic signals19. This hypothesis is in line with the recent reports that the same LysM-containing plant receptors are involved in both immunity and symbiosis signaling7,16,22. Our findings could also explain the surprising data showing that LCOs are active on mammalian cells23.
The effect of LCOs on A. fumigatus and C. glabrata development was observed at concentrations down to 10−12 M and 10−13 M, respectively. It seems unlikely that LCOs will have a nutritional effect at such low concentrations but we cannot exclude that building blocks or degradation products of LCOs (chitin oligomers and fatty acids) may also play a regulatory role. Indeed, we observed some effect of COs and fatty acids on fungal germination of A. fumigatus and on the formation of pseudohyphae in C. glabrata, but these effects were generally more limited than those of C16:0 sLCO.
Rather than nutrients, our work strongly supports LCOs as representing fungal autocrine and paracrine signals. We showed that A. fumigatus and C. glabrata responded to LCOs in a dose-dependent and structure-dependent manner. Furthermore, we find that cell membrane and perception genes are significantly upregulated within 30 min of A. fumigatus exposure to LCOs, processes associated with response to signal molecules. If the production of these molecules in the environment is proportional to fungal cell density, they could have a function similar to quorum-sensing molecules in bacteria or yeasts, but this concept is difficult to define with filamentous fungi24–26. It seems likely that LCO production will vary with life stages. Unfortunately, the detection techniques that we used (root hair deformation, gene expression, and MS analyses) are specific and sensitive but not quantitative enough to further investigate this quorum-sensing hypothesis.
Before this study, pseudohyphae in C. glabrata had only been observed under harsh conditions27,28. Interestingly, infections with C. glabrata have often been reported in the presence of C. albicans, a fungus that produces LCOs (Fig. 114,29). It would be interesting to examine if the production of pseudohyphae and the pathogenicity of C. glabrata may be regulated by the perception of LCOs produced by other fungi.
We cannot exclude, at this point, that LCOs may have some unspecific structural effect on the fungal cell wall but the timeframe of the transcriptional response to these molecules (<30 min) as well as the low concentration (10−8 M) sufficient to elicit their biological activities suggest that LCOs may be perceived by specific receptors. Given that LCOs are perceived by LysM receptor-like kinases in plants, it is tempting to speculate that LysM-containing proteins may also be involved in LCO perception in fungi8. As shown in Supplementary Table 1, fungi possess a significant number of LysM-containing proteins whose functions are largely unknown. It will also be interesting to decipher the signaling pathways in fungi controlling the transduction of the LCO signals. Investigating these questions will require new model organisms, such as A. fumigatus and C. glabrata, amenable to reverse genetics that may reveal new, perhaps essential, roles for LCOs in the biology of fungi.
Many questions remain such as how and where LCOs are synthesized in fungi. It will be interesting to determine if they are anabolically produced, like in rhizobia, or produced from the degradation and modification of longer chitin molecules. As a minimum, chitin synthases, chitin deacetylases, and N-acyltransferases are the enzymes required to produce the backbone of LCOs in fungi. An estimate for the number of genes encoding such proteins in Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes, and Zygomycetes is provided in Supplementary Table 1. Based on these numbers, chitin deacetylase and perhaps chitin synthases would be the most obvious targets to search for mutants unable to produce LCOs. Such an approach would obviously be essential to uncover the fundamental and probably conserved roles played by LCOs in the development of fungi and in their interaction with the biotic environment.
Methods
Analysis of COs and LCOs from fungal exudates
The list and sources of the 59 species of fungi and three species of oomycetes (Heterokontophyta) used in the study are presented in Supplementary Data 1–3. The fungal species examined are representatives of each sub-phyla within five phyla (out of eight phyla) of the Kingdom Fungi30. The absence of contaminants in the fungal and oomycete strains was systematically checked by PCR by using the specific primers ITS1F/ITS4 and fD1/rP231,32 (Supplementary Fig. 2). The inoculum type (cells, mycelium, spores, or zoospores), culture media and culture times used for each strain are indicated in Supplementary Data 1–3.
Fungi and oomycetes producing mycelia were pre-cultivated in Petri dishes on the solid media gelled with agar as indicated in Supplementary Data 233,34. Once the mycelium had covered the dish, plugs of the mycelium were transferred to Sylon-coated culture flasks35 or to 6.7 × 11.4 cm flat-bottom PYREX® flasks (Corning, Inc. Corning, NY), or for the Russulales to 25 × 95 mm flat-bottom culture tubes (PhytoTech), respectively, filled with 50 ml or 12 ml of the appropriate liquid medium to produce and collect exudates (Supplementary Data 2). In addition, using a separate experimental method, C. geophilum, G. stellatum, Lepidopterella palustris, Leptosphaeria maculans, S. sclerotiorum, and the species of Amanita, Hebeloma, and Paxillus were pre-cultivated as above but they were inoculated on a cellophane membrane laid on the solid medium. This membrane was used to transfer agar-free mycelium to Petri dishes filled with deionized sterile water or with liquid culture medium in order to produce and collect exudates (Supplementary Data 2).
For the anaerobic Neocallimastigomycetes, Neocallimastix californiae, Piromyces finnis, Anaeromyces robustus, and Caecomyces churrovis, 1 ml of fungal zoospores was used to inoculate 20 ml of modified minimal Medium C in a 60 ml borosilicate serum bottles containing 0.2 g switchgrass while sparging with CO236,37. Fungal cultures were incubated anaerobically 6 days before collecting the exudates.
For fungi (except AM fungi) producing cells, spores, or zoospores, 106 of these propagules were produced and collected according to published methods33,37–48. Propagules were inoculated directly in five independent Sylon-coated flasks with 50 ml liquid medium per species. AM cultures were propagated by in vitro mycorrhizal root organ cultures in solid M medium containing Phytagel (Sigma-Aldrich) and collected after solubilization of Phytagel39,49. Exudates from the AM fungal strains were collected from 10,000 spores germinating in 10 ml liquid medium for 10 days.
The various liquid media (broth or water), enriched with exudates, were filtered under sterile conditions through a 0.22 µm Millipore Express® PES membrane (MilliporeSigma, Darmstadt, Germany) prior to being analyzed in the bioassays.
One hundred to 400 ml of culture filtrates, depending on the fungal cultures, were extracted twice with butanol (1 : 1 v/v). The pooled butanol phases were washed with distilled water and evaporated under vacuum. The dry extract was re-dissolved in 4 ml water : acetonitrile (ACN) (1 : 1 v/v) and dried under nitrogen. This crude extract was resuspended in 1 ml of 20% ACN in water and separated on Hypersep C18 (500 mg, 3 ml, Thermo Fisher Scientific) by sequential elution with 3 ml each of 20%, 50%, and 100% ACN in water, respectively. The eluted samples were then dried under nitrogen. Occasionally, for further purification, the 50% eluate was resuspended in 75% ACN in water and separated on Chromabond HILIC (500 mg, 3 ml) by sequential elution with 3 ml each of 100%, 80 and 75% ACN in water. The eluates were then dried under nitrogen.
The presence of LCOs in filtered crude exudates (1× or 10×) or in the butanol fractions of media were assayed by root hair branching in V. sativa, which is induced by nsLCOs50, by root hair branching in M. truncatula accession Jemalong A17, which is induced by sLCOs, and by expression of MtENOD11 using the pENOD11:GUS transcriptional fusion in M. truncatula, which is also induced by (s)LCOs4,51.
The root hair branching assays in V. sativa and M. truncatula used the method of Cope et al.9. Eight young seedlings (3–7 days old) were treated with the fungal exudates, with the same concentration of solvent (negative controls), or with Nod factors purified from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae or Sinorhizobium meliloti supernatant at a concentration of 10−8 M (positive controls). One milliliter of fungal crude exudates or 40 µl of butanol fractions were applied on each seedling primary root.
The MtENOD11 gene expression assay was performed as in Maillet et al.4. Two kinds of samples were tested: butanol extracts diluted 100 times in water and HILIC column fractions diluted 10 times. Forty microliters of these solutions were applied to the primary root of each seedling for 16 hours. Seven to ten seedlings were tested by sample and compared to mock treatment (0.005% EtOH in water or 5% ACN in water). Plants were stained for 6 h. An arbitrary scale was used to quantify GUS (beta-glucuronidase)-staining (Supplementary Fig. 8).
Standard LCO compounds (non-sulfated C16:0 LCO IV, sulfated C16:0 LCO IV, non-sulfated C18:1 LCO IV, sulfated C18:1 LCO IV) were synthesized at CERMAV (Grenoble, France) and were used at 10−5 M in ACN/water (1/1, v/v) to determine retention times and to optimize HPLC/QTRAP tandem MS detection by MRM4,12. The UltiMate 3000 HPLC system (Dionex Corporation) was equipped with an Acquity C18 reversed-phase column (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 µm, Waters Corporation). Samples of 10 µl were injected. The elution was done at a constant flow rate of 450 µl min−1 using solvent A, water:acetic acid (1000 : 1, v-v) and solvent B, ACN, as follows: 30% B for 1 min, followed by a 30–100 % B during 8 min, followed by isocratic elution with 100% B for 2 min. A QTRAP 4500 mass spectrometer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA) equipped with an electrospray ionization source in the positive ion mode was used to analyze samples in the MRM mode or in the EMS–EPI mode (see below). For the MRM mode analyses, from the known substitutions and chitin lengths already described for Nod factor structures, we created a database of all possible combinations of structures, including new ones never described before, with their corresponding precursor proton adduct ion [M + H]+ and product B ions: in total, 76,386 precursor ions, 2,598,159 theoretical combined structures, and 358,473 MRM transitions (Supplementary Data 5). Given that the number of MRM transitions to be selected for each analysis must be reasonably low to ensure proper sensitivity, we have selected the most commonly described Nod-LCOs (corresponding to 990 MRM transitions). This highly sensitive, targeted, analytical approach was suitable for samples containing low concentrations of molecules. For samples with higher concentrations of molecules, full scan EMS–EPI analyses were performed. During EMS analysis, major precursor ions are selected automatically, and, after the collision, EPI analysis accumulates their product ions in the trapping module. From this data set, we selected only the precursor ions containing 3 to 6 GlcNAc. This more comprehensive mode could only be used with P. adelphus, P. involutus, and G. rosea LCO-rich samples.
Short COs were separated and analyzed using the same LC-MS system, equipped with an hypercarb column (5 μm, 2 × 100 mm; Hypercarb, Thermo). Samples of 10 µl were injected. The elution was done at a constant flow rate of 400 µl min−1 using solvent A, water : acetic acid (1000 : 1, v-v) and solvent B, ACN, as follows: 100% A for 1 min, then 100–50% A in 30 min then 50–0% A in 3 min. COs were identified in the MRM mode by monitoring the transitions from precursor proton adduct ion [M + H]+ m/z 628 (CO3), 831 (CO4), 1034 (CO5), or 1237 (CO6) generating after collision-induced dissociation (CID) the common product B ion m/z 204, comparatively to standard solutions (10−7 M in water). The capillary voltage was fixed at 4500 V and the source temperature at 400 °C. Fragmentation was performed by CID with nitrogen at a collision energy of 22–54 V; declustering potential was 90–130 V, optimized for each synthetic molecule available. Data processing was performed using Analyst 1.6.1 software (AB Sciex).
Experiments with A. fumigatus
A. fumigatus strain Af293 was grown in standard 90 mm Petri dishes on solid glucose minimal medium (GMM) and placed in the dark at 37 °C for 48 h52. Ten milliliters of 80% Tween 20 (Acros Organics, New Jersey) in sterile MiliQ water were added to the dishes and agitated with a sterile L-shaped cell spreader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) to collect spores. The spore suspension was sterilely transferred to a 50 ml polypropylene sterile Falcon® Centrifuge Tubes (Corning, Corning, NY). The spore suspension was homogenized by vortexing at maximum speed, and a 1 : 10 dilution was prepared with sterile MiliQ water, which was used to count spores using a hemocytometer. Afterward, spore suspension was adjusted to 106 spores with 80% Tween 20 in sterile MiliQ water44.
Spores were germinated in GMM liquid broth supplemented with various LCOs, COs, and fatty acids at a final concentration of 10−8 M. All LCOs and COs stock solutions were in 0.005% aqueous ethanol. The LCOs used were as follows: sulfated C16:0 LCO, non-sulfated C16:0 LCO, sulfated C18:1 LCO, and non-sulfated C18:1 LCO. The COs used were CO4, CO5, and CO8 (IsoSep, Tullinge, Sweden). The fatty acids used were palmitic and oleic acids. The negative control for these analyses was 0.005% aqueous ethanol, the solvent in which the LCO and CO stocks were prepared. The spore concentration was adjusted to 106 spores per ml of medium. One milliliter of spore suspension with the treatment of LCOs or COs were distributed into two replicate wells of a sterile Costar® 24 clear wells round, flat-bottom plate (Corning, Corning, New York) and the cells were incubated at 37 °C for 3 h. They were then observed at 1 h intervals over 21 h using a Nikon Ti inverted microscope with a ×40 objective and ten pictures were taken for each well every hour. Over 200 spores were scored for germination in each well. After 12 h of incubation, the length of the germinating apical hypha and the number of secondary branches per apical hypha were scored for over 200 germinated spores per well. Four independent experiments were performed. No differences between experiments were observed. Dose–response experiments were carried out in the same way, except that the spores were treated with a range of concentrations of sulfated C16:0 LCO(s) from 10−6 to 10−13 M.
Spores of A. fumigatus were grown in GMM supplemented with either 10−8 M sulfated C16:0 LCO or 0.005% ethanol as a negative control. The density was adjusted to 106 spores per ml of medium and the cultures were maintained at 37 °C on a New Brunswick Scientific Excella E25 incubator shaker (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) at 250 r.p.m. The spores were collected after 30 and 120 min by filtering the liquid broth through sterile cheesecloth. Spores were completely removed from the cheesecloth with a sterile spatula and placed into 1.5 ml FisherbrandTM Premium Microcentrifuge tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Four independent cultures were replicated per treatment and time point. Immediately after spore collection, tubes were placed in liquid nitrogen for 10 min. The spores were ground to a fine powder in liquid nitrogen and transferred into 50 ml centrifuge tubes. Total RNA was extracted by using QIAzol Lysis Reagent (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions but with an additional phenol : chloroform : isoamyl alcohol (24 : 1 : 1) extraction step before RNA precipitation. For RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq), total RNAs were further purified by using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). RNA samples were digested with DNase and stored at −80 °C for further use. A NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) was used to quantify and assess the purity of RNA. NanoDrop readings for samples were 112.24–491.44 ng µl−1.
Sixteen libraries of RNA-Seq single-end reads were prepared by using the TruSeq library preparation protocol and sequenced with an HiSeq 2500 sequencing system (Illumina, San Diego, CA). The 16 libraries corresponded to each of the four biological replicates for each of the four treatments. Read quality was assessed with FastQC 0.11.5. Read quality was excellent and adapter sequences were minimal, so reads were not trimmed. Paired-end reads were pseudo-aligned and quantified by using Kallisto 0.42.3 and the reference transcriptome of A. fumigatus Af293 (released 21 December 2012) downloaded from the Joint Genome Institute’s Genome Portal53,54. Bootstrap values were 100. Pairwise transcriptomic comparisons were made by using Sleuth version 0.30.055. We defined transcripts as differentially expressed if they had a false discovery rate (q-value) < 0.05, p-value < 0.01, and β-values < −0.4 or >0.4. GO-enrichment analysis for the A. fumigatus genome was carried by using the Gene ID. GO enrichment was performed using FungiDB56. Potentially regulated biochemical pathways were identified using the Search Pathway feature in KEGG Mapper57. The search mode was set to “Afm,” to specify A. fumigatus as our reference organisms. DEGs for the 30 and 120 mpi timepoints were entered as search objects. A list of objects was returned (Supplementary Data 8).
Experiments with C. glabrata
C. glabrata was grown overnight on yeast extract–peptone–dextrose medium (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% dextrose), supplemented with uridine (80 μg ml−1) on an orbital shaker at 200 r.p.m. and 30 °C. Ten microliters of the overnight culture were diluted 1 : 1000 in Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (without calcium or magnesium; HyClone Laboratories, Inc., Logan, UT) and counted by using a hemocytometer.
To initiate and develop biofilm production, RPMI 1640 medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific) is used for species of Candida58. Cells from an overnight culture were pelleted and resuspended (106 cells per ml) in RPMI 1640 medium, supplemented with various COs, LCOs and fatty acids at a final concentration of 10−8 M. The LCOs, COs, fatty acids, and negative controls used were the same as for the experiments with A. fumigatus. Three hundred microliters of cell suspension were distributed into each well of a sterile µ-Slide 8 Well chambered coverslip (Ibidi USA, Fitchburg, WI) and the cells were observed at 10-minute intervals over 12 hours at 37 °C with 5% CO2 in an INU series microscope incubator (Tokhi Hit, Shizuoka-ken Japan) attached to a Nikon TI2-E inverted microscope (Nikon, Louisville KY). Each well corresponded to one treatment and five pictures were taken for each well every 10 min. After 12 h, the total number of pseudohyphae per well was counted. Four independent experiments were performed. No differences between experiments were observed. Dose–response experiments were carried out in the same way, except that the cells were treated with a range of concentrations of sulfated C16:0 LCOs from 10−6 to 10−13 M.
Experiments with R. mucilaginosa
R. mucilaginosa strain was grown in 50 ml DifcoTM Dehydrated Culture Media: Potato Dextrose Broth (Thermo Fisher Scientific), in 125 ml flasks at 25 °C on an orbital shaker at 250 r.p.m. Cells were counted by using CountessTM Cell Counting Chamber slides and the Countess II Automated Cell Counter (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA).
The concentration of R. mucilaginosa cells was adjusted to 106 cells per ml of potato dextrose broth and various LCOs and COs were added to a final concentration of 10−8 M. The LCOs, COs and negative control were the same as for the experiments with A. fumigatus and C. glabrata above. Two hundred microliters of each mixture were distributed into the wells of a sterile Costar 96 Well flat-bottom plate (Corning, Corning, NY). The OD600 of each well was measured in 1 h intervals in a Cytation 5 Cell Imaging Multi-Mode Reader (BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT) over 24 h at 25 °C with shaking at 0.5 r.p.m. The outer wells of the plates were filled with sterile Milli-Q water to prevent evaporation of the samples. After 24 h, the maximum V was analyzed to determine the final OD600 nm reading per treatment. Six technical replicates were carried out for each treatment and three independent experiments were performed. No differences between experiments were observed.
Prediction of proteins involved in LCO synthesis and LysM-containing proteins in fungi
The predicted number of genes encoding chitin synthases, chitin deacetylases, N-acyltransferases, and LysM-containing proteins was reported according to the respective references 59–70.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using RStudio (version 1.2.1335, RStudio Team 2015, Boston, MA) and GraphPad Prism software version 8.3.0 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA). One-way analysis of variance differences were considered significant when p < 0.05. For the A. fumigatus experiments, the Tukey’s single-step multiple comparison test was used to compare the different concentrations of C16:0 sLCOs and control, and the Dunnett’s pairwise test was used to compare the treatments (LCOs and COs) to the control. Statistically significant differences were based on p-values < 0.05. For the C. glabrata experiments, the Tukey’s single-step multiple comparison test was used to compare all treatments to each other, as the control had no pseudohyphae formation, and to compare the different concentrations of C16:0 sLCO and control. For the R. mucilaginosa experiment, Dunnett’s pairwise test was used to compare the treatments (LCOs and COs) to the control.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Supplementary information
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Hugues Driguez for providing some synthetic lipochitin standards for mass spectrometry. RNA-Seq data were based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Award Numbers DBI-0735191, DBI-1265383, and DBI-1743442 (URL: http://www.cyverse.org). Support for mass spectrometry analyses was provided by the ICT-Mass spectrometry and MetaToul-MetaboHUB Facilities, and by the MetaboHUB-ANR-11-INBS-0010 network. Support for synthesis and characterization of COs and LCOs was provided by Labex Arcane and CBH-EUR-GS (ANR-17-EURE-0003), CDP Glyco@alps (ANR-15-IDEX-02), PolyNat Carnot Institut (16-CARN-0025-01), and ICMG (FR 2607) mass spectrometry platform. We thank Dr. Gregory Bonito for the cultures of Mortierella elongata, M. minutissima, and Mortierella sp. nov. strain GBAus27b; Dr. Tony Goldberg, Dr. Jeffrey Lorch, and Karen Vanderwolf for cultures of Aureobasidium pullulans, Protomyces inouye, R. mucilaginosa, and Taphrina virginica; Dr. Chris Hittinger for a culture of S. cerevisiae; Dr. Brian Hudelson and Armila Francis for cultures of Fusarium oxysporum, Mucor circinelloides, P. erythroseptica, P. ultimum, and Trichoderma harizanum; Dr. Paul Koch for cultures of Clarireedia homoeocarpa, Fusarium fujikuroi, and Typhula incarnata; Drs. Timothy James and Rabern Simmons for cultures of Entophlyctis luteolus, Paraphysoderma sedebokerensis, and Powellomyces hirtus; Dr. Thierry Rouxel for a culture of L. maculans; Drs. Francis Martin and Annegret Kohler for their advice and for cultures of L. bicolor, C. geophilum, G. stellatum, and L. palutris; and Dr. Anne Pringle for cultures and samples of Amanita muscaria and A. thiersii. We also thank Marie Rodriguez, Juliette Teyssandier, Clément Bertrand, and Sandrine Paute for technical assistance, and Drs. Jacob Golan and Katie Morey Gold for statistical advice. This work was supported by the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche under contract ANR-14-CE18-0008-01, the research project Engineering Nitrogen Symbiosis for Africa (ENSA), which is funded through a grant to the University of Cambridge by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (OPP11772165), the Laboratoire d’Excellence entitled TULIP (ANR-10-LABX-41), the Plant-Microbe Interfaces Scientific Focus Area in the Genomic Science Program, the Office of Biological and Environmental Research in the US Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science (Oak Ridge National Laboratory is managed by UT-Battelle, LLC, the DOE (contract DE-AC05-00OR22725), the United States Department of Agriculture (WIS01695), and by the National Science Foundation (DGE-1256259, PGRP −1546742, and IOS-1331098). We thank the University of Wisconsin-Madison Advanced Opportunity Fellowship, Science, and Medicine Graduate Research Scholars program and the Ford Foundation Pre-Doctoral Scholarship for their support and funding of T.A. Rush.
Source data
Author contributions
J.M.A., G.B., N.P.K., M.R.S., and K.G. initiated and designed the project. S.F. and S.C. synthesized the LCO and CO molecules. T.A.R., J.T., C.J., J.N., J.W.B., N.P.K., and J.M.A. designed and implemented the experiments with Aspergillus fumigatus and C. glabrata. T.A.R., K.R.C., P.J., K.G., and F.M. maintained the fungal isolates, collected and filtered fungal exudates, and performed the biological assays on legumes. T.A.R. performed the RNA-Seq experiment and M.K.P. analyzed the data. T.A.R., P.J., and B.K. conducted DNA e811941xtractions and PCR of fungal and bacterial cultures. J.M. propagated M. truncatula seeds and purified LCOs. M.K.P. analyzed the RNA-Seq data. Q.J.C. and J.L. collected and provided DNA and filtered fungal exudates from species of the Populus mycobiome (e.g., Russulales). C.S. and M.A.O. provided DNA and fungal extracts for the Neocallimastigales samples. V.P., A.B., P.J., A.H., A.Q.M., V.P., C.L., and G.B. planned and executed the HPLC/MS experiments and analysis, as well as the experiments with the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. T.A.R., C.C.C., and D.K. predicted the chitin synthases, chitin deacetylases, acyltransferases, and LysM proteins. T.A.R., G.B., J.M.A., and N.P.K. wrote the manuscript with feedback from all the coauthors.
Data availability
The RNA-seq data presented in this article are accessible through the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) BioProject# PRJNA642658 [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA642658]. Source data are provided with this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks Nikolay Nifantiev, Giles Oldroyd and the other, anonymous, reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Tomás Allen Rush, Virginie Puech-Pagès.
Contributor Information
Guillaume Bécard, Email: becard@lrsv.ups-tlse.fr.
Jean-Michel Ané, Email: jeanmichel.ane@wisc.edu.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41467-020-17615-5.
References
- 1.Lerouge P, et al. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990;344:781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dénarié J, Debellé F, Promé J-C. Rhizobium lipo-chitooligosaccharide nodulation factors: signaling molecules mediating recognition and morphogenesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996;65:503–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sun J, et al. Activation of symbiosis signaling by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in legumes and rice. Plant Cell. 2015;27:823–838. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.131326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Maillet F, et al. Fungal lipochitooligosaccharide symbiotic signals in arbuscular mycorrhiza. Nature. 2011;469:58–63. doi: 10.1038/nature09622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Venkateshwaran M, Volkening JD, Sussman MR, Ané J-M. Symbiosis and the social network of higher plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013;16:118–127. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2012.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zipfel C, Oldroyd GEDD. Plant signalling in symbiosis and immunity. Nature. 2017;543:328–336. doi: 10.1038/nature22009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Feng F, et al. A combination of chitooligosaccharide and lipochitooligosaccharide recognition promotes arbuscular mycorrhizal associations in Medicago truncatula. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:5047. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12999-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kelly S, Radutoiu S, Stougaard J. Legume LysM receptors mediate symbiotic and pathogenic signalling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017;39:152–158. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2017.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cope KR, et al. The ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor produces lipochitooligosaccharides and uses the common symbiosis pathway to colonize Populus roots. Plant Cell. 2019;31:2386–2410. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Garcia K, Delaux P-M, Cope KR, Ané J-M. Molecular signals required for the establishment and maintenance of ectomycorrhizal symbioses. N. Phytol. 2015;208:79–87. doi: 10.1111/nph.13423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Despras G, Alix A, Urban D, Vauzeilles B, Beau J-M. From chitin to bioactive chitooligosaccharides and conjugates: access to lipochitooligosaccharides and the TMG-chitotriomycin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014;53:11912–11916. doi: 10.1002/anie.201406802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Genre A, et al. Short-chain chitin oligomers from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi trigger nuclear Ca2+ spiking in Medicago truncatula roots and their production is enhanced by strigolactone. N. Phytol. 2013;198:190–202. doi: 10.1111/nph.12146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Buendia L, Girardin A, Wang T, Cottret L, Lefebvre B. LysM receptor-like kinase and LysM receptor-like protein families: an update on phylogeny and functional characterization. Front. Plant Sci. 2018;9:1531. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brunke S, Hube B. Two unlike cousins: Candida albicans and C. glabrata infection strategies. Cell. Microbiol. 2013;15:701–708. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gimeno CJ, Ljungdahl PO, Styles CA, Fink GR. Unipolar cell divisions in the yeast S. cerevisiae lead to filamentous growth: regulation by starvation and RAS. Cell. 1992;68:1077–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90079-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gibelin-Viala C, et al. The Medicago truncatula LysM receptor-like kinase LYK9 plays a dual role in immunity and the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. N. Phytol. 2019;223:1516–1529. doi: 10.1111/nph.15891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Limpens E, van Zeijl A, Geurts R. Lipochitooligosaccharides modulate plant host immunity to enable endosymbioses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015;53:311–334. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080614-120149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liang Y, et al. Nonlegumes respond to rhizobial nod factors by suppressing the innate immune response. Science. 2013;341:1384–1387. doi: 10.1126/science.1242736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liang Y, et al. Lipochitooligosaccharide recognition: an ancient story. J. Physiol. 2014;204:289–296. doi: 10.1111/nph.12898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gutjahr C, et al. Rice perception of symbiotic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi requires the karrikin receptor complex. Science. 2015;350:1521–1524. doi: 10.1126/science.aac9715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Choi J, et al. The negative regulator SMAX1 controls mycorrhizal symbiosis and strigolactone biosynthesis in rice. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:2114. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16021-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang X, et al. The receptor kinase CERK1 has dual functions in symbiosis and immunity signalling. Plant J. 2015;81:258–267. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Djordjevic MA, et al. Lipo-chitin oligosaccharides, plant symbiosis signalling molecules that modulate mammalian angiogenesis in vitro. PLoS One. 2014;9:e112635. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mehmood, A. et al. Fungal Quorum-Sensing Molecules and Inhibitors with Potential Antifungal Activity: A Review. Molecules24, 1950 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Horowitz Brown S, Zarnowski R, Sharpee WC, Keller NP. Morphological transitions governed by density dependence and lipoxygenase activity in Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008;74:5674–5685. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00565-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Affeldt KJ, Brodhagen M, Keller NP. Aspergillus oxylipin signaling and quorum sensing pathways depend on g protein-coupled receptors. Toxins. 2012;4:695–717. doi: 10.3390/toxins4090695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Csank C, Haynes K. Candida glabrata displays pseudohyphal growth. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000;189:115–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lachke SA, Joly S, Daniels K, Soll DR. Phenotypic switching and filamentation in Candida glabrata. Microbiology. 2002;148:2661–2674. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-9-2661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tati S, et al. Candida glabrata binding to Candida albicans hyphae enables its development in oropharyngeal candidiasis. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:1–21. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Spatafora, J. W. et al. The fungal tree of life: from molecular systematics to genome-scale phylogenies. Microbiol. Spectr.5 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 31.Gardes M, Bruns TD. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes–application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993;2:113–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294x.1993.tb00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991;173:697–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Botha A, et al. An isolation procedure for arachidonic acid producing Mortierella species. Antonie Van. Leeuwenhoek. 1999;75:253–256. doi: 10.1023/a:1001848709005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jargeat, P., Chaumeton, J. -P., Navaud, O., Vizzini, A. & Gryta, H. The Paxillus involutus (Boletales, Paxillaceae) complex in Europe: Genetic diversity and morphological description of the new species Paxillus cuprinus, typification of P. involutus s.s., and synthesis of species boundaries. Fungal Biol.118, 12–31 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 35.Castro JF, et al. Identification and heterologous expression of the chaxamycin biosynthesis gene cluster from Streptomyces leeuwenhoekii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015;81:5820–5831. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01039-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Solomon KV, et al. Early-branching gut fungi possess a large, comprehensive array of biomass-degrading enzymes. Science. 2016;351:1192–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.aad1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Haitjema CH, et al. A parts list for fungal cellulosomes revealed by comparative genomics. Nat. Microbiol. 2017;2:17087. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hoffman Y, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel chytrid species (phylum Blastocladiomycota), parasitic on the green alga Haematococcus. Mycol. Res. 2008;112:70–81. doi: 10.1016/j.mycres.2007.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Doner LW, Bécard G. Solubilization of gellan gels by chelation of cations. Biotechnol. Tech. 1991;5:25–28. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kurtzman, C., Fell, J. W. & Boekhout, T. The Yeasts: A Taxonomic Study (Elsevier, 2011).
- 41.Longcore JE. Morphology and zoospore ultrastructure of Entophlyctis luteolus sp. nov. (Chytridiales): Implications for chytrid taxonomy. Mycologia. 1995;87:25–33. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Marx DH, Bryan WC. Growth and ectomycorrhizal development of loblolly pine seedlings in fumigated soil infested with the fungal symbiont Pisolithus tinctorius. Forest Sci. 1975;21:245–254. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Johnson CJ, Kernien JF, Hoyer AR, Nett JE. Mechanisms involved in the triggering of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) by Candida glabrata during planktonic and biofilm growth. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:13065. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13588-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pfannenstiel, B. T. et al. Revitalization of a forward genetic screen identifies three new regulators of fungal secondary metabolism in the genus Aspergillus. mBio8 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 45.Powell, M. J. In Handbook of the Protists (eds. Archibald, J. M., Simpson, A. G. B. & Slamovits, C. H.) 1523–1558 (Springer, 2017).
- 46.Simmons DR. Phylogeny of Powellomycetaceae fam. nov. and description of Geranomyces variabilis gen. et comb. nov. Mycologia. 2011;103:1411–1420. doi: 10.3852/11-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schloegel LM, et al. Novel, panzootic and hybrid genotypes of amphibian chytridiomycosis associated with the bullfrog trade. Mol. Ecol. 2012;21:5162–5177. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Singleton, L. L., Mihail, J. D. & Rush, C. M. Methods for Research on Soilborne Phytopathogenic Fungi (APS, 1992).
- 49.Bécard G, Fortin JA. Early events of vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhiza formation on Ri T-DNA transformed roots. N. Phytol. 1988;108:211–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1988.tb03698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Price NPJ, et al. Broad-host-range Rhizobium species strain NGR234 secretes a family of carbamoylated, and fucosylated, nodulation signals that are O-acetylated or sulphated. Mol. Microbiol. 1992;6:3575–3584. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Andriankaja A, et al. AP2-ERF transcription factors mediate Nod factor–dependent Mt ENOD11 activation in root hairs via a novel cis-regulatory motif. Plant Cell. 2007;19:2866–2885. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.052944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Brookman JL, Denning DW. Molecular genetics in Aspergillus fumigatus. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2000;3:468–474. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(00)00124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Nierman WC, et al. Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature. 2005;438:1151–1156. doi: 10.1038/nature04332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P, Pachter L. Erratum: near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016;34:888. doi: 10.1038/nbt0816-888d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Pimentel H, Bray NL, Puente S, Melsted P, Pachter L. Differential analysis of RNA-seq incorporating quantification uncertainty. Nat. Methods. 2017;14:687–690. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Stajich JE, et al. FungiDB: an integrated functional genomics database for fungi. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:D675–D681. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kanehisa M, Sato Y. KEGG Mapper for inferring cellular functions from protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2020;29:28–35. doi: 10.1002/pro.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Weerasekera MM, et al. Culture media profoundly affect Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis growth, adhesion and biofilm development. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2016;111:697–702. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760160294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gonçalves IR, et al. Genome-wide analyses of chitin synthases identify horizontal gene transfers towards bacteria and allow a robust and unifying classification into fungi. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016;16:252. doi: 10.1186/s12862-016-0815-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Liu R, Xu C, Zhang Q, Wang S, Fang W. Evolution of the chitin synthase gene family correlates with fungal morphogenesis and adaptation to ecological niches. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:44527. doi: 10.1038/srep44527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ma L-J, et al. Genomic analysis of the basal lineage fungus Rhizopus oryzae reveals a whole-genome duplication. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pacheco-Arjona JR, Ramirez-Prado JH. Large-scale phylogenetic classification of fungal chitin synthases and identification of a putative cell-wall metabolism gene cluster in Aspergillus genomes. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e104920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Mouyna I, et al. What are the functions of chitin deacetylases in Aspergillus fumigatus? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020;10:28. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Larriba E, et al. Sequencing and functional analysis of the genome of a nematode egg-parasitic fungus, Pochonia chlamydosporia. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014;65:69–80. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2014.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Petrasch S, et al. Infection strategies deployed by Botrytis cinerea, Fusarium acuminatum, and Rhizopus stolonifer as a function of tomato fruit ripening stage. Front. Plant Sci. 2019;10:223. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Chibucos MC, et al. An integrated genomic and transcriptomic survey of mucormycosis-causing fungi. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:12218. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Abramyan, J. & Stajich, J. E. Species-specific chitin-binding module 18 expansion in the amphibian pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. mBio3, e00150-12 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 68.de Jonge R, Thomma BPHJ. Fungal LysM effectors: extinguishers of host immunity? Trends Microbiol. 2009;17:151–157. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Nordberg H, et al. The genome portal of the Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute: 2014 updates. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D26–D31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sayers EW, et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:D9–D16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Data Availability Statement
The RNA-seq data presented in this article are accessible through the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) BioProject# PRJNA642658 [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA642658]. Source data are provided with this paper.