Abstract
Background
Toxoplasma gondii is a major cause of abortion in small ruminants and presents a zoonotic risk when undercooked meat containing cysts is consumed. The aim of the present study was to investigate the genetic diversity among the T. gondii strains circulating in ovine livestock in Spain.
Methods
Selected samples collected from abortion outbreaks due to toxoplasmosis (n = 31) and from chronically infected adult sheep at slaughterhouses (n = 50) in different Spanish regions were bioassayed in mice, aiming at parasite isolation. In addition, all original clinical samples and the resulting isolates were genotyped by multi-nested PCR-RFLP analysis of 11 molecular markers and by PCR-DNA sequencing of portions of the SAG3, GRA6 and GRA7 genes.
Results
As a result, 30 isolates were obtained from 9 Spanish regions: 10 isolates from abortion-derived samples and 20 isolates from adult myocardial tissues. Overall, 3 genotypes were found: ToxoDB#3 (type II PRU variant) in 90% (27/30) of isolates, ToxoDB#2 (clonal type III) in 6.7% (2/30), and ToxoDB#1 (clonal type II) in 3.3% (1/30). When T. gondii-positive tissue samples (n = 151) were directly subjected to RFLP genotyping, complete restriction profiles were obtained for 33% of samples, and up to 98% of the specimens belonged to the type II PRU variant. A foetal brain showed a clonal type II pattern, and four specimens showed unexpected type I alleles at the SAG3 marker, including two foetal brains that showed I + II alleles as co-infection events. Amplicons of SAG3, GRA6 and GRA7 obtained from isolates and clinical samples were subjected to sequencing, allowing us to confirm RFLP results and to detect different single-nucleotide polymorphisms.
Conclusions
The present study informed the existence of a predominant type II PRU variant genotype (ToxoDB#3) infecting domestic sheep in Spain, in both abortion cases and chronic infections in adults, coexisting with other clonal (ToxoDB#1 and ToxoDB#2), much less frequent genotypes, as well as polymorphic strains as revealed by clinical sample genotyping. The use of multilocus sequence typing aided in accurately estimating T. gondii intragenotype diversity. 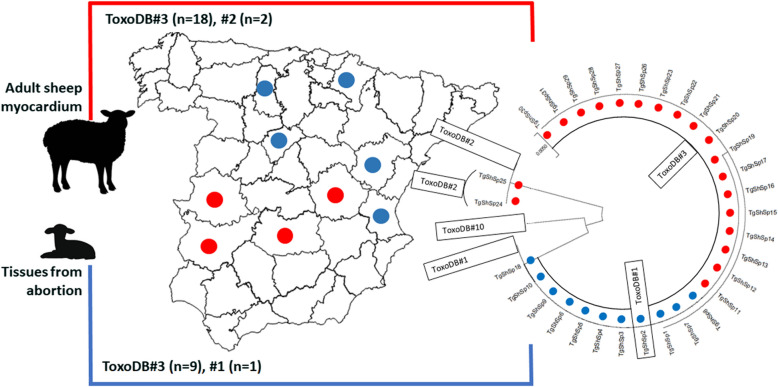
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii, Sheep, Abortion, Isolates, Genotyping, Sequencing, Population structure, Spain
Background
Toxoplasma gondii (Apicomplexa) is known as one of the main causes of ovine reproductive failure, causing significant economic losses to the sheep industry worldwide [1–3]. Among other factors, such as strain virulence and parasite stage at the time of infection [4, 5], clinical manifestations of ovine toxoplasmosis mostly depend on the pregnancy stage at which the primary infection occurs, ranging from early embryonic death with reabsorption to stillbirth or neonatal death, or even the birth of transplacentally infected lambs (congenital toxoplasmosis). In Europe, there is little information about T. gondii as the aetiological agent of ovine abortion outbreaks; nevertheless, similar rates of T. gondii-specific DNA have been detected in sheep abortion tissues submitted for diagnosis in distinct countries, i.e. in 10% of the ovine abortion-derived tissues from Ireland [6], 6–11% from UK [7], 11.1–18.1% from the Sardinia region, Italy [8, 9], 10.6% from Germany [10], and in 5.4–18.9% from Spain, as observed in previous reports [11–13].
The global seroprevalence of T. gondii in sheep flocks ranges between 3–98%, but the results are dependent on factors such as the age of the ewes or the management system [1]. In southern Spain, individual seroprevalence figures ranged between 41.2–49.3% in sheep flocks [14, 15], in agreement with rates found in other Mediterranean countries [3], giving the idea of a widespread prevalence.
Moreover, the role of T. gondii as a major pathogen in public health is well known, especially when raw or undercooked meat containing encysted bradyzoites is consumed [16, 17]. A risk assessment study estimated that the consumption of undercooked ovine meat is responsible for 14% of meat-related T. gondii infections in the Dutch population [18].
Vast research on T. gondii population structure, diversity, and geographical distribution is being conducted worldwide [19, 20]. Despite the importance of the ovine industry in Europe, information about T. gondii strains circulating in European ovine livestock is scarce (Table 1); while most ovine isolates and genotyping descriptions in Europe are clonal [21], some specific findings of novel genotypes [22] and non-clonal isolates [23], along with mixed infections [24], deserve attention. To date, no data are available from Spain.
Table 1.
Summary of studies reporting T. gondii genotypes circulating in ruminant livestock in Europe
| Country | Host species | n | Type (%) | Method | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | MRA | |||||
| Isolates | ||||||||
| France | Sheep | 8 | – | 100 | – | – | MS | [40] |
| Sheep | 46 | – | 97.8 | 2.2 | – | RFLP-ML + MS | [21] | |
| Cattle | 2 | – | 100 | – | – | MS | [68] | |
| Italy | Sheep | 5 | – | – | – | 100 | RFLP-ML | [23] |
| Portugal | Cattle | 1 | 100 | – | – | – | RFLP-ML + MS | [22] |
| Romania | Goat | 2 | – | 100 | – | – | MS | [69] |
| Serbia | Sheep | 1 | – | 100 | – | – | RFLP-ML | [70] |
| UK | Sheep | 2 | – | 100 | – | – | RFLP-SAG2 | [47] |
| Clinical samples | ||||||||
| Ireland | Sheep (foetal tissues) | 19 | – | 79 | 21 | – | RFLP-ML | [6] |
| Italy | Goat (milk) | 10 | 10 | – | 40 | 50 | RFLP-ML | [71] |
| Sheep (placental and foetal tissues) | 21 | – | 100 | – | – | RFLP-ML | [48] | |
| Sheep (milk) | 1 | 100 | – | – | – | RFLP-SAG3 | [72] | |
| Cattle (skeletal muscle) | 6 | 66.6 | 16.6 | 16.6 | – | RFLP-ML | [51] | |
| Sheep (meat) | 15 | – | 100 | – | – | B1-Seq | [77] | |
| Goat (meat) | 3 | – | 100 | – | – | |||
| Poland | Goat (milk) | 25 | – | – | 100 | – | RFLP-ML | [73] |
| Portugal | Sheep (myocardium) | 6 | – | 100 | – | 33.3 | RFLP-SAG2 | [74] |
| Goat (myocardium) | 3 | – | 100 | – | – | |||
| Cattle (myocardium) | 3 | – | 100 | – | – | |||
| The Netherlands | Sheep (myocardium) | 13 | – | 100 | – | – | MS + GRA6-Seq | [46] |
| Slovakia | Goat (milk) | 14 | – | 100 | – | – | RFLP-SAG2 | [75] |
| Switzerland | Sheep (diaphragm) | 5 | – | – | – | 100 | RFLP-ML | [24] |
| Cattle (diaphragm) | 9 | 100a | ||||||
| Sheep (diaphragm) | 5 | – | 40 | – | 60 | RFLP-ML | [76] | |
| Cattle (diaphragm) | 9 | – | – | – | 100a | |||
| UK | Sheep (placental tissues) | 13 | – | 100 | – | – | RFLP-SAG2 | [47] |
| Sheep (meat) | 6 | 60 | – | – | 40 | RFLP-SAG2 | [45] | |
| Cattle (meat) | 1 | – | – | – | 100 | |||
aIncomplete markers resembling atypical or recombinant patterns
MRA, patterns showing mixed infections; recombinants or atypical; MS, microsatellites; ML, multilocus; Seq, sequencing
This paper presents the genetic characterization of T. gondii ovine isolates and clinical samples obtained from abortion tissues and chronically infected adult animals, providing a picture of the genetic population of T. gondii infecting sheep in Spain.
Methods
Study design and sample collection
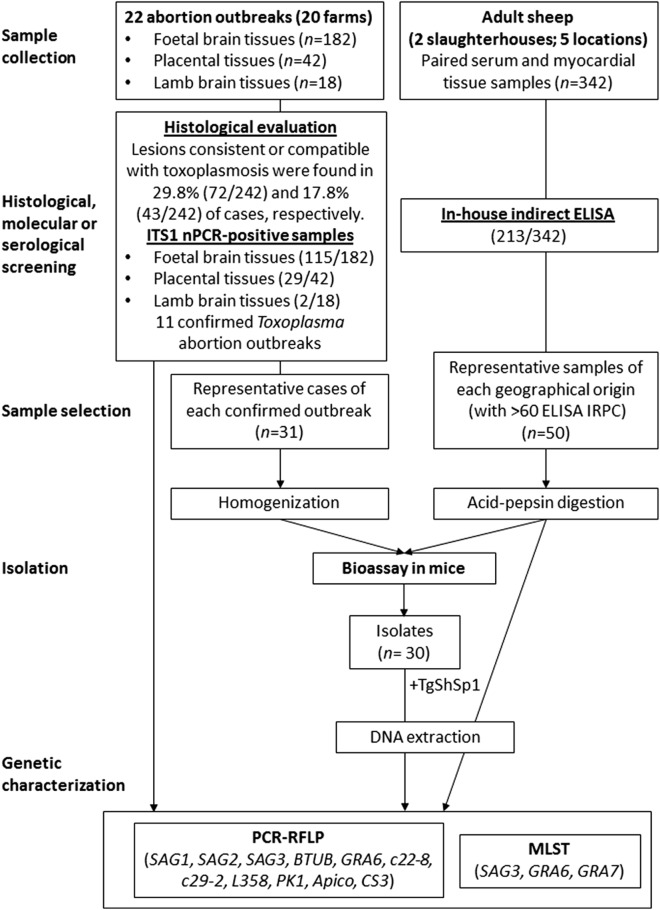
A workflow of the present study is shown in Fig. 1. Aiming to maximize the geographical extension covered within Spain and hypothesizing higher probabilities to describe genetic diversity among isolates, 2 types of tissue samples were collected for parasite isolation: (i) tissues derived from suspected Toxoplasma-related abortion outbreaks; and (ii) myocardial tissues from adult animals collected in authorized slaughterhouses. In this sense, between 2015 and 2018, foetal brains (n = 182), brains from weak lambs that died shortly after birth (n = 18), and placental/cotyledonary tissues (n = 42), were collected from 20 geographically distant farms of 22 different abortion cases (Table 2). Additionally, between February 2018 and July 2018, 342 paired serum and myocardial tissue samples were collected from adult animals slaughtered for human consumption at 2 different authorized slaughterhouses from Cáceres and Ciudad Real provinces (western and central Spain, respectively) (Table 3). The blood samples were collected with BD PLUS Serum tubes (Vacutainer; BD, Franklin Lakes, USA) at the bleeding step after the animals were euthanized, and half of the heart was taken during the evisceration process and individually stored refrigerated at 4 ℃ in labelled zip-lock plastic bags until analysis. Sampling covered a representative area within Spanish ovine farming, as samples were collected from 7 regions, representing 74.5% of the ovine census (16.6 million) in Spain [25].
Fig. 1.
Study design
Table 2.
Epidemiological data on toxoplasmosis-like abortion outbreaks in sheep flocks in Spain (2015–2018): etiology confirmation and T. gondii isolation
| Sample ID | T. gondii-associated abortion outbreak ID | Municipality (province) | Descriptiona | Period of time (lambing season) | Samples collectedb | Isolate designation (original sample) | RFLP genotype ID# (ToxoDB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foetal brain tissues | Placental tissues | Lamb brain tissues | |||||||
| 15/121 | 1 | Fuentes de Valdepero (Palencia, North) | Assaf, 1450, 20% | 2015/2016 | 3 (3, 2, 1) | 2 (2, 2, 0) | – | TgShSp1 (15/121.4)c | #3 |
| 15/141 | 2 | Artajona (Navarra, North) | Assaf, 3800, 10% | 2015/2016 | 2 (2, 1, 1) | – | – | TgShSp2 (15/141.2) | #1 |
| 17/4, 17, 18, 19, 21, 24, 28 | 3 | Autillo de Campos (Palencia, North) | Assaf, 2800, 4.3% | 2016/2017 | 24 (22, 6, 6) | 6 (6, 3, 1) | 7 (1, 1, 0) | TgShSp3 (17/4.1); TgShSp4 (17/21.2); TgShSp5 (17/28.1); TgShSp6 (17/19.3) | #3 |
| 17/61 | – | Villaconancio (Palencia, North) | Assaf, 600, 5%, Border disease virus | 2016/2017 | 2 (0, 0, 1) | – | – | – | |
| 17/5, 15 | 4d | Benavente (Zamora, North West) | Assaf, 500, 10% | 2016/2017 | 3 (2, 2, 1) | 3 (2, 0, 0) | – | – | |
| 17/6, 20, 22, 23, 25, 27, 41 | 5d | Mayorga (Valladolid, North) | Assaf, 1600, 10% | 2016/2017 | 11 (5, 2, 2) | 4 (2, 0, 2) | – | – | |
| 17/94, 17 2/7, 17 2/6, 17 2/8, 17/29, 17/32, 17/36, 17/52 17/62 | 6d | Villamañán (León, North-West) | Assaf, NA | 2016/2017 | 14 (6, 4, 2) | 7 (3, 0, 0) | 5 (0, 0, 0) | – | |
| 17/42 | – | Alcarraz (Lérida, North-East) | Lacaune, 800, 25% | 2016/2017 | 4 (0, 0, 0) | 1 (0, 0, 0) | – | – | |
| 17/49 | – | Fuentes de Valdepero (Palencia, North East) | Assaf, 1600, 5% | 2016/2017 | 2 (0, 0, 0) | 1 (0, 0) | – | – | |
| 17/220, 221, 222, 223, 224, 225, 18/1, 4, 10 | 7 | Navas de Oro (Segovia, Centre) | Merino, 900, 83% | 2017/2018 | 12 (10, 5, 2) | 6 (6, 1, 0) | 3 (1, 1, 0) | TgShSp7 (18/4.2) | #3 |
| 17/227 | – | Santa Cruz de Mudela (Ciudad Real, Centre) | Manchega, 1200, 5% | 2017/2018 | 3 (0,0,0) | – | – | – | |
| 18/3 | – | Benavente (Zamora, North–West) | Assaf, 500, 15%, Neospora caninum | 2017/2018 | 1 (0, 0, 0) | 1 (0, 0, 0) | – | – | |
| 18/12 | – | Benegiles (Zamora, North–West) | Assaf, 1049, 15.3%, Neospora caninum | 2017/2018 | 2 (0, 1, 0) | – | – | – | |
| 18/5, 17 | – | Casas de Juan Núñez (Albacete, East) | Manchega, 3000, 40% | 2017/2018 | 6 (0, 0, 0) | 1 (0, 0, 0) | – | – | |
| 18/6 | – | Ledesma (Salamanca, West) | Castellana, 20, 25%, Neospora caninum | 2017/2018 | 1(0, 1, 0) | 1 (0, 0, 0) | – | – | |
| 18/7 | 8 | Catadau (Valencia, East) | Lacaune, 2400, 21% | 2017/2018 | 2 (2, 2, 0) | – | TgShSp8 (18/7.2) | #3 | |
| 18/14, 15, 16, 18, 20 | 9 | Cuevas de Almudén (Teruel, East) | Lacaune, 700, 50% | 2017/2018 | 62 (50, 29, 18) | 6 (6, 5, 1) | 3 (0,0,0) | TgShSp9 (18/18.1); TgShSp10 (18/15.1); TgShSp18 (18/16.1) | #3 |
| 18/23 | – | Moral de la Reina (Valladolid, North) | Assaf, 3000, 15% | 2017/2018 | 5 (0, 0, 0) | 1 (0, 0, 0) | – | – | |
| 18/36, 38 | – | Valdetorres (Badajoz, West) | Merino, 450, 20%, Neospora caninum | 2017/2018 | 3 (0, 1, 1) | – | – | – | |
| 18/21 | – | Autillo de Campos (Palencia, North) | Assaf, 3000, > 1% | 2017/2018 | 5 (0, 0, 0) | – | – | – | |
| 18/219, 228 | 10d | Villafrechos (Valladolid, North) | Assaf, 1100, 12% | 2017/2018 | 4 (2, 2, 0) | – | – | – | |
| 18/222, 226 | 11d | Aguilar de Campos (Valladolid, North) | Lacaune, 2500, 25%, Coxiella burnetii | 2017/2018 | 11 (11, 2, 4) | 2 (2, 0, 0) | – | – | |
| Total | 11 | 182 (115, 59, 3, 9) | 42 (29, 11, 4) | 18 (2, 2, 0) | |||||
aBreed, flock size, % of abortion, other pathogens detected. Screening for common protozoal, bacterial and viral abortifacient agents was performed as reported in references [26] and [27]
bPCR-positive cases, cases with consistent lesions, cases with compatible lesions
cIsolation reported in reference [32]
dBioassay in mice was not successful or was not carried out due to previous tissue freezing
na, data not available
Table 3.
Summarized data on adult sheep myocardial tissue sample collection in authorized slaughterhouses in central and western Spain (2018)
| Animal origin (province) | Breeding area | Age | Breed | No. of serum samples | ELISA IRPC | Isolate ID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples analysed | ELISA-positive (%) | ||||||
| Plasencia (Cáceres) | West | Adult (4–5 years-old) | Merino | 100 | 39.0 (39/100) | 85.0 | TgShSp11 |
| 76.9 | TgShSp12 | ||||||
| 81.1 | TgShSp13 | ||||||
| 81.6 | TgShSp14 | ||||||
| 66.3 | TgShSp15 | ||||||
| 88.1 | TgShSp19 | ||||||
| 85.1 | TgShSp20 | ||||||
| 92.0 | TgShSp21 | ||||||
| 66.0 | TgShSp22 | ||||||
| 74.7 | TgShSp28 | ||||||
| Alburquerque (Badajoz) | South–West | Adult (4–5 years-old) | Merino | 100 | 95.0 (95/100) | 107.2 | TgShSp16 |
| 115.2 | TgShSp17 | ||||||
| 113.6 | TgShSp23 | ||||||
| 86.7 | TgShSp27 | ||||||
| 122.6 | TgShSp31 | ||||||
| Sisante (Cuenca) | Centre | Adult (4–5 years-old) | Manchega × Lacaune | 42 | 47.6 (20/42) | 75.1 | TgShSp26 |
| 115.5 | TgShSp30 | ||||||
| Valdepeñas (Ciudad Real) | Centre | Adult (4–5 years-old) | Manchega × Lacaune | 50 | 40.0 (20/50) | 89.0 | TgShSp24 |
| 82.5 | TgShSp25 | ||||||
| Puertollano (Ciudad Real) | Centre | Adult (4–5 years-old) | Manchega × Lacaune | 50 | 78.0 (39/50) | 107.4 | TgShSp29 |
| Total | – | – | – | 342 | 62.3 (213/342) | – | – |
Histological, molecular and serological diagnosis for sample selection
In abortion cases, brains from foetuses or dead lambs, and placental samples when available, were collected for histological, molecular, and mouse bioassay analyses. Initial screening for common protozoan, bacterial, and viral abortifacient agents was performed as reported elsewhere [26, 27]. Histological processing and evaluation were carried out following previous descriptions [12]. The cases were classified according to observed lesions as follows: (i) no significant lesions; (ii) lesions suggesting conditions other than toxoplasmosis; (iii) lesions compatible with toxoplasmosis (diffuse congestion and/or multifocal leukomalacia); and (iv) lesions consistent with toxoplasmosis (multifocal areas of necrosis at the placenta or glial foci with a central area of necrosis in the brain). Due to the low sensitivity and specificity of histological diagnosis, the selection of tissue samples for parasite isolation was carried out by T. gondii DNA detection by PCR. Genomic DNA was extracted from three different 50-mg pieces of each tissue using the Maxwell® 16 Mouse Tail DNA Purification Kit (Promega, Alcobendas, Spain), and T. gondii DNA detection was carried out by single-tube nested PCR amplification of the specific ITS1 region as previously described [28]. Within PCR-positive tissues, only representative cases with a lesser degree of autolysis of each confirmed outbreak were selected for the isolation assay (n = 31) to maximize the isolation success and geographic coverage of the study.
Regarding adult animals, T. gondii-specific IgG antibody levels in ovine serum samples were measured using an in-house indirect ELISA as previously described [28], considering the cut-off at 20 for ELISA IRPC (relative index per cent). Likewise, only those myocardial tissues associated with the highest antibody titres (> 60 ELISA IRPC) were selected for the mouse bioassay (n = 50) (Table 3).
Bioassay in mice
Five to 15 g of brain tissue from abortion cases was suspended in a proportional volume (w/v) of PBS supplemented with penicillin (1000 IU/ml; Sigma-Aldrich, Madrid, Spain) and streptomycin (100 μg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich) [1], homogenized in a paddle blender (IUL-Maxicator, Masticator Classic 400 ml; Geneq, Quebec, Canada), centrifuged (1200×g, 10 min, 4 ℃), and then passed through a 20 G needle prior to subcutaneous inoculation into 2 or 3 female Swiss/CD1 mice (Janvier Labs, Laval, France) per tissue sample [29]. Additionally, hearts (portions of 50 g/each) from selected seropositive adult animals were subjected to acid-pepsin artificial digestion [1] prior to bioassay in 3 female Swiss/CD1 mice. The resulting inocula were also subjected to ITS1 nested PCR [28] to discern whether further genotyping analysis could be possible directly on these samples.
Mice were observed daily, and clinical signs were scored [30]. Tissue imprints of brains and lungs from mice that died were examined for tachyzoite or tissue cyst presence. At 30 dpi (days post-inoculation), surviving mice were bled, and serum samples were collected for anti-T. gondii IgG antibodies detection by an indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFAT) [31], using an anti-mouse IgG conjugated to FITC (Sigma-Aldrich) diluted 1:64 in Evans Blue (Sigma-Aldrich) and considering the cut-off at 1:25. Seropositive mice were sacrificed at 42 dpi, and a fraction of freshly recovered brain tissue was homogenized in PBS supplemented with antibiotics by passing through tapered cross-section needles (20–25 G) to be intraperitoneally (IP) inoculated into two additional female Swiss/CD1 mice. At 7 dpi, peritoneal cavity flushes were aseptically collected from mice and used for in vitro culture.
In vitro cultivation
Peritoneal exudates of infected Swiss/CD1 mice were seeded into African green monkey kidney-derived cells (MARC-145 line) and maintained by serial passages. Cells were cultured in DMEM (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with foetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco), penicillin (100 U/ml), streptomycin (100 μg/ml) and amphotericin B (0.25 μg/ml) (Lonza Group, Basel, Switzerland) at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2 in 75 or 25 cm2 tissue culture flasks. Tachyzoites from successfully grown cultures were harvested from the medium for DNA isolation, and infected cells were suspended in FBS supplemented with 10% of DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide; Sigma-Aldrich) and cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen for further studies as described previously [1].
Genetic characterization of T. gondii
Toxoplasma gondii DNA was extracted from cell-culture-derived tachyzoites of all 30 isolates obtained, along with the isolate TgShSp1 [32]. Strain typing was performed by the widely used PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method based on SAG1, SAG2 (5’-3’ SAG2, and alt. SAG2), SAG3, BTUB, GRA6, c22-8, c29-2, L358, PK1 and Apico markers [33]. An additional RFLP marker, CS3, was included in the present study due to its proven link with the virulence of T. gondii strains in mice [34]. Reference strains of T. gondii were also incorporated in genotyping, including clonal type I (TgRH), clonal type II (TgMe49) and clonal type III (TgNED). Genotyping was also directly applied to DNA extracted from all brain and placental tissues in which T. gondii had been previously detected (n = 133) and from the T. gondii PCR-positive digests of sheep myocardial tissues inoculated into mice (n = 18). RFLP genotype numbers were assigned according to the ToxoDB database (https://toxodb.org/toxo/).
Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) analysis
We conducted PCR sequencing of 3 polymorphic genes, SAG3, GRA6 and GRA7, on all 31 isolates and clinical samples with previous successful nested PCR amplification of each marker (SAG3, n = 123; GRA6, n = 108; GRA7, n = 99) to provide sequence-based genotyping. Gene amplification of SAG3 and GRA6 resulted from the above-described Mn-PCR-RFLP method, and GRA7 amplifications were obtained by nested PCR using specific primer pairs [35]. PCR products were sent to the Center for Genomic Technologies of the Complutense University of Madrid (Spain) for direct sequencing. Briefly, amplicons were sequenced in both directions with the same internal primer pair used for amplification employing a BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and a 3730 × l DNA Sequence Analyser (Applied Biosystems). Sequencing was successful for 121 out of 123 SAG3-PCR positives, 77 out of 108 GRA6-PCR positives, and all 99 GRA7-PCR positives. The resulting sequences were imported, read, edited manually if necessary, and analysed using BioEdit software, version 7.0.5.3 [36]. Generated DNA consensus sequences were aligned to appropriate reference sequences using MEGA X software (http://www.megasoftware.net/) [37], and compared with sequences retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database through the BLAST tool (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
Phylogenetic analyses
By using DNA sequence-based phylogenetic analyses, we evaluated the population structure of T. gondii isolates obtained; clonal reference strains (TgRH, TgMe49 and TgNED) were included for comparison. Consensus SAG3, GRA6 and GRA7 sequences from isolates and reference strains were concatenated and aligned using MEGA X software [37] to generate an unrooted phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method [38]. The evolutionary distances were computed using the maximum composite likelihood method [39].
Results
Parasite detection and isolation
Two hundred forty-two tissue samples (182 foetal brains, 42 placentae and 18 lamb brains) from 22 suspected Toxoplasma-related abortion outbreaks among 20 farms distributed all over Spain were analysed by histological evaluation and nested PCR assay (Table 2). Histological lesions consistent or compatible with toxoplasmosis were found in 29.8% (72/242) and 17.8% (43/242), respectively, of the studied cases. No lesions suggesting other conditions were found, although multifocal necrotic glial foci and protozoan tissue cysts, lesions classified as characteristic of Toxoplasma infection, in two cases these were later confirmed to be caused by Neospora caninum. Toxoplasma gondii-specific DNA was detected in 60.3% (146/242) of samples; indeed, 63.2% (115/182) of foetal brains, 69.0% (29/42) of placental samples, and 11.1% (2/18) of lamb brains were positive for T. gondii DNA. Such findings allowed us to confirm T. gondii as the aetiological agent in 11 out of 22 abortion outbreaks in sheep farms (description is summarized in Table 2). Ten isolates (TgShSp2 to TgShSp10 and TgShSp18) were obtained from 31 bioassayed foetal brains (representing 5 different abortion outbreaks, Table 2).
Furthermore, T. gondii-specific IgG antibodies were detected in 62.3% (213/342) of adult sheep serum samples collected in slaughterhouses; 50 selected samples with the highest ELISA IRPC titres (ranging from 60.5 to 122.6; Table 3) were subjected to bioassay, and 20 isolates (TgShSp11 to 17, TgShSp19 to 31) were obtained (Table 3).
The bioassay success rate was established in 32.3% (10/31) of abortion cases and in 40% (20/50) of chronically infected adult tissues. Regarding samples from abortion outbreaks that occurred in Zamora (#4), Valladolid (# 5, #10 and #11) and León (# 6) provinces, bioassays in mice were not successful or were not carried out due to previous freezing of the tissues (Table 2).
PCR-RFLP genotyping
Cell-culture-derived tachyzoites from all 31 isolates (including TgShSp1) were successfully typed, revealing 3 different genotypes: ToxoDB#3 (90.3%; 28/31 isolates); ToxoDB#2 (6.5%; 2/31); and ToxoDB#1 (3.2%; 1/31). Although ToxoDB#3 was the most frequently found genotype, and ToxoDB#2 was detected only in chronically infected adult animals, no specific dominance of any RFLP genotype appears to be involved in abortion cases or chronic infections (Additional file 1: Table S1). The CS3 marker, a gene with a suggested high predictive value for virulence in mice [34], resulted in the type II allele in all isolates but 2 (TgShSp24 and 25), exhibiting a type III allele.
When PCR-RFLP assays were applied to T. gondii DNA-positive brain (n = 108) and placental tissues (n = 25) obtained from abortion outbreaks (Additional file 2: Table S2), and to myocardial sample digests (n = 18) (Additional file 3: Table S3), more complexity was observed, revealing co-infection events and suggesting the possible selection of certain strains during bioassay experiments. Amplifications yielded complete RFLP profiles for approximately 33% of specimens, with up to 98% belonging to the type II PRU variant (ToxoDB#3). Although incomplete RFLP profiles were obtained in some samples, allelic variations were detected in the SAG3 marker (Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Table S3). Infection with multiple T. gondii strains in the same foetus was detected in 2 brain tissues collected in outbreak #3 (Table 2), which occurred in 2017 in Palencia Province (North Spain) (ID#17/21.1 and #17/21.2), due to the coexistence of type II and type I SAG3 alleles in the same tissue. Apart from that, a type I allele was also detected in another foetal brain tissue from the same outbreak (ID#17/28.1) and in a myocardial sample (digest) from an adult sheep from Badajoz Province (Southwest Spain) (ID: BA18 G#34).
MLST genotyping
PCR-DNA sequencing-based genotyping considering 3 polymorphic genes, SAG3, GRA6 and GRA7, revealed that most isolates and samples showed complete sequence homology with either TgMe49 (clonal type II) or TgNED sequences (clonal type III), supporting the RFLP results in the case of the SAG3 and GRA6 markers (Additional file 1: Table S1, Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Table S3).
The SAG3 sequence alignment of the samples (and isolates) that showed a type II allele identified a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), G1691T, that divides our clonal type II (ToxoDB#1) and type II PRU variant (ToxoDB#3) isolates and samples into two well-defined groups. The first group had 100% homology with the TgMe49 reference sequence included and others deposited in GenBank, such as JX218226 (IIa SAG3 allele, MT361125), and the other group (G1691T) showed 100% identity with ovine (KU599412; KU599407) or caprine (KU599396) isolate sequences deposited (IIb SAG3 allele, MT361126) and leads to an amino acid change at codon 368 from Met to Ile. Concerning the incidence of each SAG3 type II allele, all outbreaks described were homogeneous, presenting one allele spread over all specimens; of note, only outbreak #6 occurring in León Province during 2017 presented foetuses infected by parasites showing alleles IIa and IIb. There appears to be a higher incidence of the SAG3 IIa allele in those outbreaks occurring in 2017, while the IIb allele seems to be more frequent in outbreaks during 2018. Regarding sample ID#17/28.1, which showed a type I allele by PCR-RFLP confirmed by PCR sequencing, a double peak was detected at position 1113 of the gene sequence, indicating a co-infection event. Between both alleles detected, one of them showed 100% homology with the TgRH reference strain sequence included and others deposited in GenBank (JX218225; AF340227) (Ia SAG3 allele, MT358429), but the other presented a SNP (T1113C) not shared by any other sequence reported previously (Ib SAG3 allele, MT361124) and resulted in a silent mutation. When using the BLAST tool to compare resulting consensus SAG3 sequences with those publicly available in the GenBank database obtained from sheep or goats, it was noted that the IIb SAG3 allele detected along part of our samples is also present in some French ovine isolates (GenBank: KU599412, KU599411 and KU599407) coexisting with IIa SAG3 alleles (GenBank: KU599409, KU599410). The same occurred with some Ethiopian ovine and caprine isolates deposited (GenBank: KU599394, KU599396, KU599399 and KU599400), showing one allele or the other. This fact also illustrated other instances of type I and III alleles present in sheep and lamb meat samples analysed in Iraq (GenBank: MK801822- MK801830).
GRA6 marker sequencing also sustained RFLP findings; nevertheless, a double peak at position 1013 of the gene was detected in a foetal brain tissue collected in an abortion outbreak (#9, Table 2) that occurred in 2018 in Teruel Province (East Spain) (ID#18/14.5; PCR-RFLP type II allele), indicating co-infection by two strains. Between both alleles detected, one of them presented 100% homology with the TgMe49 sequence included and others deposited in GenBank (AF239285) (IIa GRA6 allele, MT370491), but the other one showed a SNP (C1013T) not shared by any other sequence deposited previously in that database (IIb GRA6 allele, MT370489) and was located at the 5’ UTR fragment.
Finally, GRA7 gene sequencing enabled us to test the sequence homology of our isolates and original clinical samples with the clonal reference strains included. Concerning the isolates obtained, the analysis showed 100% homology with the TgMe49 (clonal type II) sequence included in all cases except for the TgShSp24 and TgShSp25 sequences, which were found to be identical to the TgNED (clonal type III) sequence included. Besides, the GRA7 sequence obtained from DNA amplified from a foetal brain collected in the above-mentioned outbreak (#9, Table 2) that occurred in Teruel Province (East Spain) (ID#18/15.21), possessed a double peak at position 2688 of the gene sequence, indicating that a co-infection was also present in this tissue. Between both alleles detected, one of them presented 100% homology with the TgMe49 sequence included and others deposited in GenBank (DQ459445) (IIa GRA7 allele, MT361127), but the other carried a SNP (C2688T) not shared by any other sequence available (IIb GRA7 allele, MT361128), causing an amino acid change at codon 188 from Ala to Val.
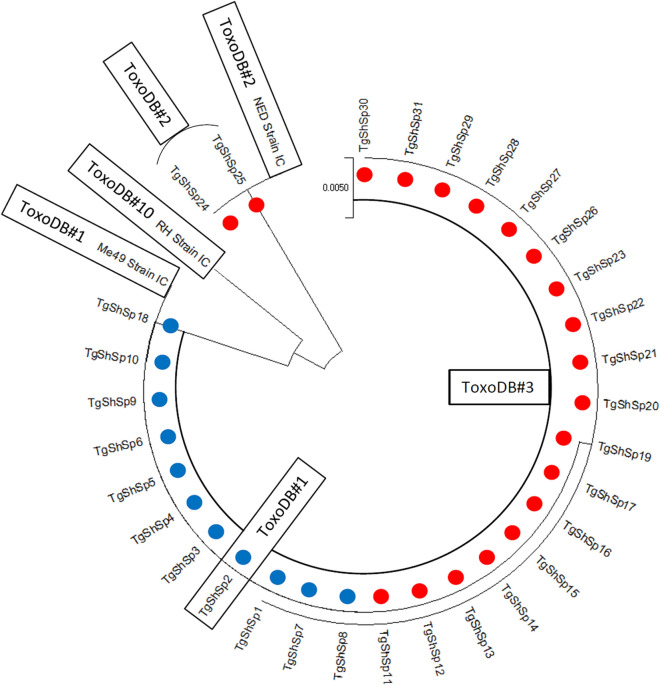
Phylogenetic analyses
The population structure of T. gondii isolates obtained was evaluated by DNA sequence-based phylogenetic analyses. A phylogenetic tree was constructed based on concatenated SAG3, GRA6 and GRA7 sequences from isolates obtained, in addition to those from the clonal reference strains included (TgRH, TgMe49 and TgNED) (Fig. 2). Predictably, TgShSp24 and TgShSp25 isolates (type III alleles for the three markers studied) were situated next to the TgNED strain. On the other hand, the rest of the isolates (type II alleles for the three markers) formed two well-defined clusters obeying the presence of the SNP (G1691T) described previously at the SAG3 locus.
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic tree constructed using concatenated consensus SAG3, GRA6 and GRA7 sequences of Toxoplasma gondii isolates obtained from abortion-derived tissues (blue dots) and myocardium from adult sheep (red dots) in Spain and T. gondii reference strains used along genotyping methods as internal controls (IC) (RH strain IC, Me49 strain IC and NED strain IC)
Discussion
Toxoplasma gondii has been recognized as a major cause of reproductive failure. Here, 11 toxoplasmosis-related ovine abortion outbreaks occurring in the 2015, 2016 and 2017 lambing seasons are reported. In addition to the clinical and economic interest derived from abortion outbreaks, the high seroprevalence in sheep highlights the potential public health risk posed by the consumption of lamb meat containing viable tissue cysts. In the present study, 62.3% (213/342) of blood samples collected from sheep slaughterhouses in western and central Spain were positive for T. gondii IgG antibodies, in agreement with the values in other European reports [3].
To the best of our knowledge, the present survey, along with two previous French investigations [21, 40], might be the only European studies comprehensive enough to analyse T. gondii population genetic diversity circulating through sheep flocks, and this is the first Spanish report of this nature. There is scarce knowledge regarding the genetic diversity of the T. gondii population in Spain. Pioneering studies were focused on genotyping human clinical samples [41] and positive tissues from wild big game species [42]; both studies corroborated a predominance of genotype II but also presented a significant prevalence of other clonal and recombinant types. To date, only two reports of T. gondii parasite isolation have been carried out in Spain. The first one was focused on stray cats, and typing based only on the SAG2 locus [43] showed that 26% (n = 12) of isolates were type I and 74% (n = 34) of isolates were type II, with an absence of type III. In a second report [32], the isolate TgShSp1 (ToxoDB#3) was obtained from an ovine abortion case and was also included in the present study for further in-depth genetic analysis. We were able to isolate T. gondii from five additional ovine abortion outbreaks that occurred among widely geographically distributed Spanish farms during 2015–2018, as well as from chronically infected adult sheep. Overall, 30 isolates were obtained that, along with the isolate TgShSp1 [32], represented a significant cross-section of the T. gondii Spanish population infecting sheep, covering a wide part of the country’s territory.
Genetic characterization based on PCR-RFLP classified most isolates (90.3%; 28/31) as the type II PRU variant (ToxoDB#3). This fact is consistent with traditional literature referring to the predominance of T. gondii type II alleles among European sheep flocks [44] (summarized in Table 1). As observed in the present study, no specific genotypes have been reported in the literature in association with chronically infected adult animals (e.g. commercial meat products) [21, 40, 45, 46] or causing abortion [47, 48]. Until recently, most T. gondii clonal types had been recognized as infecting livestock, pets and wild animals in Europe [43, 49], but this might be biased due to the use of only SAG2 genetic markers or a few of them for typing assays; currently, more comprehensive studies in terms of the sample size, number of molecular markers, and interactions between livestock and wildlife species have revealed an unexpectedly higher presence of polymorphic strains [50, 51], similar to direct genotyping from clinical samples.
As previously stated, in a context in which a high occurrence of Toxoplasma would suggest multiple exposures to the parasite during the life time of the animal [52], bioassay experiments might induce a selection of certain strains at the expense of others, resulting in an underestimation of co-infection events and, as a consequence, intraspecific diversity. Co-infection events were observed in our study in two abortion outbreaks (#3 and #9) that occurred in 2017 in Palencia Province (North Spain) and 2018 in Teruel Province (East Spain), with not only type II but also type I alleles at the SAG3 marker detected in different foetal brain tissues (samples #17/21.1 and #17/21.2). Mixed infections have been described previously not only in ovine and porcine livestock [24, 45, 53] but also in European wildlife species [42, 54]. The type I allele at the SAG3 marker was also detected alone in another foetal brain tissue (ID#17/28.1) from outbreak #3 and in the myocardium from an adult animal (BA18 G#34) bred in Badajoz Province (Southwest Spain), calling attention to the extension of this type I allele through livestock, as in other European studies [23, 45, 51]. Considering that the bioassay of samples #17/21.2 (Ia and IIa alleles detected) and #17/28.1 (Ia and Ib alleles present) resulted in TgShSp4 and TgShSp5 isolation (only IIa allele found), a selection of certain strains is evident during isolation experiments. It should be noted that the greatest genetic variability was detected in abortion outbreaks #3 and #9, coinciding with those from which more samples were collected, demonstrating that sampling effort is an important factor.
Phylogenetic analyses of strongly variable loci coding for virulence factors such as surface and secretory antigens, often under significant selective pressure, have been widely used to infer possible genetic population structure models, evolutionary relationships between T. gondii populations, reservoirs, and transmission patterns, among other factors [20, 55, 56]. Our results suggest that Spanish and French T. gondii populations could be genetically related based on limited SAG3 sequences of sheep origin deposited in the GenBank database. Both sets of sequences clustered in two groups determined by the specific SNP (G1691T) described here. This may suggest common evolutionary forces or most likely common origins in livestock from both countries [56] due to a historical and intense trade exchange of sheep from Spain to France and vice versa. Sequences from two Ethiopian goat isolates deposited in GenBank also presented such dichotomy, possibly implying a further extension of the mutation.
The CS3 gene has been described previously as a marker highly predictive of T. gondii isolates mortality in mice [34]. Bioassay results suggest a low degree of virulence for isolates obtained here, since none of the mice infected during the isolation process presented acute symptoms or died of toxoplasmosis. Our CS3 typing results disagree with those of previous studies carried out with Brazilian and Chinese isolates of different host origins that report high mortality rates (normally above 80%) associated with type I or II alleles for the CS3 gene and low (3.7–9.3%) or null rates with type III alleles [34, 57–60]. Contradictory results were already exposed within avirulent Brazilian isolates presenting type I [61] or type II [62] alleles for the CS3 locus. Thus, the fact that all strains included in the studies mentioned above are polymorphic, none of them with a European or North American origin (“clonal” regions), suggests the need for further investigations to unravel the role of the gene in Toxoplasma virulence and clear differences between distant biogeographical global areas. Considering the known proximity of the CS3 gene to demonstrated virulence factors such as ROP18 and ROP5 in the Toxoplasma genome (chromosome VIIa) [63–67], a linked expression with still unknown implications might be possible; therefore, research on the expression of both factors would be relevant in future studies of isolates characterization.
In conclusion, our results show that a large majority of isolates circulating around sheep farms fall within three genotypes (ToxoDB#3, 2 and 1), with some infrequent SNPs, in agreement with low genetic variability in Europe. The differential clinical outcomes observed in abortion cases draw attention to the necessity of analysing the genetic and phenotypic diversity among Toxoplasma parasites in Europe, especially aiming to (i) predict epidemiological changes, (ii) identify virulence factors, and (iii) design effective vaccines against field strains. Thus, increasing the effort in isolation and genotyping will provide interesting information on the epidemiology of T. gondii and the paradigm of One Health parasites infecting humans, livestock, and wildlife in Europe.
Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, the present survey constitutes the first study aiming to describe the genetic population of T. gondii circulating in sheep flocks in Spain. Genetic characterization of 31 strains isolated from abortion cases and chronically infected adult animals showed low genetic variability, with a predominant type II PRU variant genotype (ToxoDB#3) coexisting with other clonal (ToxoDB#2 and #1), much less frequent genotypes. Furthermore, when directly examining the clinical samples and inocula, the genetic richness increases, allowing the identification of other genetic variants. The present results support the hypothesis of the existence of polymorphic and overlapping strains within ovine livestock in Spain and point out the necessity of increased genotyping and sampling efforts to accurately estimate T. gondii intraspecific genetic diversity.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Genotyping allele profile obtained by PCR-RFLP and PCR-sequencing on T. gondii isolates.
Additional file 2: Table S2. Genotyping allele profile obtained by PCR-RFLP and PCR-sequencing on T. gondii DNA-positive clinical samples collected from abortion outbreaks.
Additional file 3: Table S3. Genotyping allele profile obtained by PCR-RFLP and PCR-sequencing on T. gondii DNA-positive adult sheep myocardium digests.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the veterinary surgeons that provided abortion specimens, and to the staff of the Center for Genomic Technologies of the Complutense University of Madrid, Spain, for excellent technical assistance. Also, authors thank Dr Gereon Schares (Friedrich Loeffler Institut, Germany) for providing us with DNA samples of Toxoplasma gondii reference strains.
Abbreviations
- DMEM
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- DMSO
dimethyl sulfoxide
- dpi
days post-inoculation
- ELISA
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- FBS
fetal bovine serum
- FITC
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- IFAT
indirect fluorescent antibody test
- IP
intraperitoneally
- IRPC
relative index per cent
- MLST
multilocus sequence typing
- PBS
phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR-RFLP
polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism
- SNP
single nucleotide polymorphisms
Authors’ contributions
MF, RC, EC and LMO conceived and designed the laboratory tests, MF, RC, MCG, JR, DG, and JB performed experiments, MF, RC, DG, JR, and EC analysed the data and LO, EC and JB contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. MF, RC, JR, JB, EC and LMO drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by projects funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (AGL2016-75935-C2-R) and the Community of Madrid (PLATESA2-CM-P2018/BAA-4370). MF and RC were funded by UCM-Santander/2017 pre-doctoral grants, and PLATESA2 post-doctoral grants, respectively. CG was funded by DGAPA, National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM). RC, EC and LO are part of the TOXOSOURCES consortium, supported by funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation programme under grant agreement No. 773830: One Health European Joint Programme.
Availability of data and materials
Data supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its Additional files 1, 2, 3. The sequences generated in the present study were submitted to the GenBank database under the following accession numbers: SAG3 sequences (MT358429, MT361124-MT361126); GRA6 sequences (MT370489, MT370491); and GRA7 sequences (MT361127, MT361128). Histological samples are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Animal procedures for the bioassay in mice were approved by the Animal Welfare Committee of the Community of Madrid, Spain (PROEX 274/16, section 2.1.3), following proceedings described in Spanish and EU legislation (Law 32/2007, R.D. 53/2013, and Council Directive 2010/63/EU). All animals used in this study were handled in strict accordance with good clinical practices, and all efforts were made to minimize suffering. As a humane endpoint, mice exhibiting significant weight loss or nervous clinical signs were culled to limit unnecessary suffering.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Mercedes Fernández-Escobar, Email: merfer02@ucm.es.
Rafael Calero-Bernal, Email: r.calero@ucm.es.
Julio Benavides, Email: julio.benavides@csic.es.
Javier Regidor-Cerrillo, Email: jregidor@ucm.es.
María Cristina Guerrero-Molina, Email: mcgromo@hotmail.com.
Daniel Gutiérrez-Expósito, Email: dgute@unileon.es.
Esther Collantes-Fernández, Email: esthercf@ucm.es.
Luis Miguel Ortega-Mora, Email: luis.ortega@ucm.es.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s13071-020-04275-z.
References
- 1.Dubey JP. Toxoplasmosis of animals and humans. 2. Boca Raton: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Katzer F, Brülisauer F, Collantes-Fernández E, Bartley PM, Burrells A, Gunn G, et al. Increased Toxoplasma gondii positivity relative to age in 125 Scottish sheep flocks; evidence of frequent acquired infection. Vet Res. 2011;42:121. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-42-121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stelzer S, Basso W, Benavides Silván J, Ortega-Mora LM, Maksimov P, Gethmann J, et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019;15:e00037. doi: 10.1016/j.fawpar.2019.e00037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dubremetz JF, Lebrun M. Virulence factors of Toxoplasma gondii. Microbes Infect. 2012;14:1403–1410. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2012.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Benavides J, Fernández M, Castaño P, Ferreras MC, Ortega-Mora L, Pérez V. Ovine toxoplasmosis: a new look at its pathogenesis. J Comp Pathol. 2017;157:34–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2017.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gutierrez J, O’Donovan J, Proctor A, Brady C, Marques PX, Worrall S, et al. Application of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis and enzootic abortion of ewes. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012;24:846–854. doi: 10.1177/1040638712452730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Carson A. Abortion in sheep: an update. Vet Rec. 2018;183:528–529. doi: 10.1136/vr.k4620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Masala G, Porcu R, Madau L, Tanda A, Ibba B, Satta G, et al. Survey of ovine and caprine toxoplasmosis by IFAT and PCR assays in Sardinia, Italy. Vet Parasitol. 2003;117:15–21. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2003.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Masala G, Porcu R, Daga C, Denti S, Canu G, Patta C, et al. Detection of pathogens in ovine and caprine abortion samples from Sardinia, Italy, by PCR. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2007;19:96–98. doi: 10.1177/104063870701900116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Steuber S, Niu A, Bauer C, Reetz J, Roth A, Janitschke K. The detection of Toxoplasma gondii in abortion tissues of sheep using the polymerase chain reaction. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1995;102:91–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hurtado A, Aduriz G, Moreno B, Barandika J, García-Pérez AL. Single tube nested PCR for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii in fetal tissues from naturally aborted ewes. Vet Parasitol. 2001;102:17–27. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4017(01)00526-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pereira-Bueno J, Quintanilla-Gozalo A, Pérez-Pérez V, Álvarez-García G, Collantes-Fernández E, Ortega-Mora LM. Evaluation of ovine abortion associated with Toxoplasma gondii in Spain by different diagnostic techniques. Vet Parasitol. 2004;121:33–43. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moreno B, Collantes-Fernández E, Villa A, Navarro A, Regidor-Cerrillo J, Ortega-Mora LM. Occurrence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii infections in ovine and caprine abortions. Vet Parasitol. 2012;187:312–318. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.12.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.García-Bocanegra I, Cabezón O, Hernández E, Martínez-Cruz MS, Martínez-Moreno Á, Martínez-Moreno J. Toxoplasma gondii in ruminant species (cattle, sheep, and goats) from southern Spain. J Parasitol. 2013;99:438–440. doi: 10.1645/12-27.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Almería S, Cabezón O, Paniagua J, Cano-Terriza D, Jiménez-Ruiz S, Arenas-Montes A, et al. Toxoplasma gondii in sympatric domestic and wild ungulates in the Mediterranean ecosystem. Parasitol Res. 2018;117:665–671. doi: 10.1007/s00436-017-5705-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cook AJ, Gilbert RE, Buffolano W, Zufferey J, Petersen E, Jenum PA, et al. Sources of toxoplasma infection in pregnant women: European multicentre case-control study. European Research Network on Congenital Toxoplasmosis. BMJ. 2000;321:142–147. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7254.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Belluco S, Simonato G, Mancin M, Pietrobelli M, Ricci A. Toxoplasma gondii infection and food consumption: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-controlled studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2018;58:3085–3096. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1352563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Opsteegh M, Prickaerts S, Frankena K, Evers EG. A quantitative microbial risk assessment for meatborne Toxoplasma gondii infection in The Netherlands. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011;150:103–114. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shwab EK, Zhu XQ, Majumdar D, Pena HF, Gennari SM, Dubey JP, et al. Geographical patterns of Toxoplasma gondii genetic diversity revealed by multilocus PCR-RFLP genotyping. Parasitology. 2014;141:453–461. doi: 10.1017/S0031182013001844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jiang T, Shwab EK, Martin RM, Gerhold RW, Rosenthal BM, Dubey JP, et al. A partition of Toxoplasma gondii genotypes across spatial gradients and among host species, and decreased parasite diversity towards areas of human settlement in North America. Int J Parasitol. 2018;48:611–619. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2018.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Halos L, Thébault A, Aubert D, Thomas M, Perret C, Geers R, et al. An innovative survey underlining the significant level of contamination by Toxoplasma gondii of ovine meat consumed in France. Int J Parasitol. 2010;40:193–200. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Verma SK, Ajzenberg D, Rivera-Sanchez A, Su C, Dubey JP. Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from Portugal, Austria and Israel reveals higher genetic variability within the type II lineage. Parasitology. 2015;142:948–957. doi: 10.1017/S0031182015000050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vismarra A, Barilli E, Miceli M, Mangia C, Genchi M, Brindani F, et al. Toxoplasma gondii in the Cornigliese sheep breed in Italy: meat juice serology, in vitro isolation and genotyping. Vet Parasitol. 2017;243:125–129. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Berger-Schoch AE, Herrmann DC, Schares G, Müller N, Bernet D, Gottstein B, et al. Prevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii in feline faeces (oocysts) and meat from sheep, cattle and pigs in Switzerland. Vet Parasitol. 2011;177:290–297. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.11.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.MAPA (Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food). El sector ovino y caprino de carne en cifras: Principales Indicadores Económicos, Subdirección General de Productos Ganaderos, Dirección General de Producciones y Mercados Agrarios. 2019. https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/ganaderia/temas/produccion-y-mercados-ganaderos/indicadoreseconomicosdelsectorovinoycaprino_carne_2018_tcm30-511496.pdf. Accessed 1 June 2020.
- 26.González-Warleta M, Castro-Hermida JA, Regidor-Cerrillo J, Benavides J, Álvarez-García G, Fuertes M, et al. Neospora caninum infection as a cause of reproductive failure in a sheep flock. Vet Res. 2014;45:88. doi: 10.1186/s13567-014-0088-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Elvira-Partida L, Fernández M, Gutiérrez J, Esnal A, Benavides J, Pérez V, et al. Detection of bovine viral diarrhoea virus 2 as the cause of abortion outbreaks on commercial sheep flocks. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2017;64:19–26. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Castaño P, Fuertes M, Ferre I, Fernández M, Ferreras Mdel C, Moreno-Gonzalo J, et al. Placental thrombosis in acute phase abortions during experimental Toxoplasma gondii infection in sheep. Vet Res. 2014;45:9. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-45-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Regidor-Cerrillo J, Gómez-Bautista M, Pereira-Bueno J, Aduriz G, Navarro-Lozano V, Risco-Castillo V, et al. Isolation and genetic characterization of Neospora caninum from asymptomatic calves in Spain. Parasitology. 2008;135:1651–1659. doi: 10.1017/S003118200800509X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Arranz-Solís D, Benavides J, Regidor-Cerrillo J, Fuertes M, Ferre I, del Ferreras MC, et al. Influence of the gestational stage on the clinical course, lesional development and parasite distribution in experimental ovine neosporosis. Vet Res. 2015;46:19. doi: 10.1186/s13567-014-0139-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Álvarez-García G, Collantes-Fernández E, Costas E, Rebordosa X, Ortega-Mora LM. Influence of age and purpose for testing on the cut-off selection of serological methods in bovine neosporosis. Vet Res. 2003;34:341–352. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2003009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sánchez-Sánchez R, Ferre I, Regidor-Cerrillo J, Gutiérrez-Expósito D, Ferrer LM, Arteche-Villasol N, et al. Virulence in mice of a Toxoplasma gondii Type II isolate does not correlate with the outcome of experimental infection in pregnant sheep. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019;8:436. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Su C, Shwab EK, Zhou P, Zhu XQ, Dubey JP. Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology. 2010;137:1–11. doi: 10.1017/S0031182009991065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pena HF, Gennari SM, Dubey JP, Su C. Population structure and mouse-virulence of Toxoplasma gondii in Brazil. Int J Parasitol. 2008;38:561–569. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bottós J, Miller RH, Belfort RN, Macedo AC, UNIFESP Toxoplasmosis Group. Belfort R, Jr, et al. Bilateral retinochoroiditis caused by an atypical strain of Toxoplasma gondii. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93:1546–1550. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2009.162412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser. 1999;41:95–98. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35:1547–1549. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987;4:406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tamura K, Nei M, Kumar S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:11030–11035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404206101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dumètre A, Ajzenberg D, Rozette L, Mercier A, Dardé ML. Toxoplasma gondii infection in sheep from Haute-Vienne, France: seroprevalence and isolate genotyping by microsatellite analysis. Vet Parasitol. 2006;142:376–379. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fuentes I, Rubio JM, Ramírez C, Alvar J. Genotypic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strains associated with human toxoplasmosis in Spain: direct analysis from clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:1566–1570. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.4.1566-1570.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Calero-Bernal R, Saugar JM, Frontera E, Pérez-Martín JE, Habela MA, Serrano FJ, et al. Prevalence and genotype identification of Toxoplasma gondii in wild animals from southwestern Spain. J Wildl Dis. 2015;51:233–238. doi: 10.7589/2013-09-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Montoya A, Miró G, Mateo M, Ramírez C, Fuentes I. Molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from cats in Spain. J Parasitol. 2008;94:1044–1046. doi: 10.1645/GE-1403.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dubey JP. Toxoplasmosis in sheep - the last 20 years. Vet Parasitol. 2009;163:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.02.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Aspinall TV, Marlee D, Hyde JE, Sims PF. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in commercial meat products as monitored by polymerase chain reaction - food for thought? Int J Parasitol. 2002;32:1193–1199. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(02)00070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Opsteegh M, Langelaar M, Sprong H, den Hartog L, De Craeye S, Bokken G, et al. Direct detection and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii in meat samples using magnetic capture and PCR. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010;139:193–201. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.02.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Owen MR, Trees AJ. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii associated with abortion in sheep. J Parasitol. 1999;85:382–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chessa G, Chisu V, Porcu R, Masala G. Molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii type II in sheep abortion in Sardinia, Italy. Parasite. 2014;21:6. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2014007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Richomme C, Aubert D, Gilot-Fromont E, Ajzenberg D, Mercier A, Ducrot C, et al. Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from wild boar (Sus scrofa) in France. Vet Parasitol. 2009;164:296–300. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sharif M, Amouei A, Sarvi S, Mizani A, Aarabi M, Hosseini SA, et al. Genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from ruminants: a systematic review. Int J Food Microbiol. 2017;258:38–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Battisti E, Zanet S, Trisciuoglio A, Bruno S, Ferroglio E. Circulating genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii in northwestern Italy. Vet Parasitol. 2018;253:43–47. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.02.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Verma SK, Sweeny AR, Lovallo MJ, Calero-Bernal R, Kwok OC, Jiang T, et al. Seroprevalence, isolation and co-infection of multiple Toxoplasma gondii strains in individual bobcats (Lynx rufus) from Mississippi, USA. Int J Parasitol. 2017;47:297–303. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sroka J, Bilska-Zając E, Wójcik-Fatla A, Zając V, Dutkiewicz J, Karamon J, et al. Detection and molecular characteristics of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in retail raw meat products in Poland. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2019;16:195–204. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2018.2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Herrmann DC, Maksimov P, Maksimov A, Sutor A, Schwarz S, Jaschke W, et al. Toxoplasma gondii in foxes and rodents from the German Federal States of Brandenburg and Saxony-Anhalt: seroprevalence and genotypes. Vet Parasitol. 2012;185:78–85. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.10.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Dubey JP, Rajendran C, Ferreira LR, Martins J, Kwok OC, Hill DE, et al. High prevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from goats, from a retail meat store, destined for human consumption in the USA. Int J Parasitol. 2011;41:827–833. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2011.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bertranpetit E, Jombart T, Paradis E, Pena H, Dubey J, Su C, et al. Phylogeography of Toxoplasma gondii points to a South American origin. Infect Genet Evol. 2017;48:150–155. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.12.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yai LE, Ragozo AM, Soares RM, Pena HF, Su C, Gennari SM. Genetic diversity among capybara (Hydrochaeris hydrochaeris) isolates of Toxoplasma gondii from Brazil. Vet Parasitol. 2009;162:332–337. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wang L, Cheng HW, Huang KQ, Xu YH, Li YN, Du J, et al. Toxoplasma gondii prevalence in food animals and rodents in different regions of China: isolation, genotyping and mouse pathogenicity. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:273. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Silva LA, Andrade RO, Carneiro AC, Vitor RW. Overlapping Toxoplasma gondii genotypes circulating in domestic animals and humans in southeastern Brazil. PLoS One. 2014;9:e90237. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Rocha DS, Nilsson MG, Maciel BM, Pena HFJ, Alves BF, Silva AV, et al. Genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from free-range chickens in Bahia, Brazil. J Parasitol. 2018;104:377–382. doi: 10.1645/18-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Langoni H, Matteucci G, Medici B, Camossi LG, Richini-Pereira VB, Silva RC. Detection and molecular analysis of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum from dogs with neurological disorders. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2012;45:365–368. doi: 10.1590/s0037-86822012000300016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rêgo WMF, Costa JGL, Baraviera RCA, Pinto LV, Bessa GL, Lopes REN, et al. Association of ROP18 and ROP5 was efficient as a marker of virulence in atypical isolates of Toxoplasma gondii obtained from pigs and goats in Piauí, Brazil. Vet Parasitol. 2017;247:19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Khan A, Taylor S, Su C, Mackey AJ, Boyle J, Cole R, et al. Composite genome map and recombination parameters derived from three archetypal lineages of Toxoplasma gondii. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:2980–2992. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Taylor S, Barragan A, Su C, Fux B, Fentress SJ, Tang K, et al. A secreted serine-threonine kinase determines virulence in the eukaryotic pathogen Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 2006;314:1776–1780. doi: 10.1126/science.1133643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Khan A, Taylor S, Ajioka JW, Rosenthal BM, Sibley LD. Selection at a single locus leads to widespread expansion of Toxoplasma gondii lineages that are virulent in mice. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000404. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Behnke MS, Khan A, Lauron EJ, Jimah JR, Wang Q, Tolia NH, et al. Rhoptry proteins ROP5 and ROP18 are major murine virulence factors in genetically divergent south american strains of Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Genet. 2015;11:e1005434. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Shwab EK, Jiang T, Pena HF, Gennari SM, Dubey JP, Su C. The ROP18 and ROP5 gene allele types are highly predictive of virulence in mice across globally distributed strains of Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol. 2016;46:141–146. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2015.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Blaga R, Aubert D, Thébault A, Perret C, Geers R, Thomas M, et al. Toxoplasma gondii in beef consumed in France: regional variation in seroprevalence and parasite isolation. Parasite. 2019;26:77. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2019076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Paştiu AI, Ajzenberg D, Györke A, Şuteu O, Balea A, Rosenthal BM, et al. Traditional goat husbandry may substantially contribute to human toxoplasmosis exposure. J Parasitol. 2015;101:45–49. doi: 10.1645/13-483.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Marković M, Ivović V, Stajner T, Djokić V, Klun I, Bobić B, et al. Evidence for genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii in selected intermediate hosts in Serbia. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;37:173–179. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2014.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mancianti F, Nardoni S, D’Ascenzi C, Pedonese F, Mugnaini L, Franco F, et al. Seroprevalence, detection of DNA in blood and milk, and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii in a goat population in Italy. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:905326. doi: 10.1155/2013/905326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Vismarra A, Barilli E, Miceli M, Mangia C, Bacci C, Brindani F, et al. Toxoplasma gondii and pre-treatment protocols for polymerase chain reaction analysis of milk samples: a field trial in sheep from southern Italy. Ital J Food Saf. 2017;6:6501. doi: 10.4081/ijfs.2017.6501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Sroka J, Kusyk P, Bilska-Zajac E, Karamon J, Dutkiewicz J, Wojcik-Fatla A, et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in goats from the south-west region of Poland and the detection of T. gondii DNA in goat milk. Folia Parasitol (Praha). 2017;64:023. doi: 10.14411/fp.2017.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lopes AP, Vilares A, Neto F, Rodrigues A, Martins T, Ferreira I, et al. Genotyping characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in cattle, sheep, goats and swine from the North of Portugal. Iran J Parasitol. 2015;10:465–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Spišák F, Turčeková L, Reiterová K, Špilovská S, Dubinský P. Prevalence estimation and genotypization of Toxoplasma gondii in goats. Biologia. 2010;65:670–674. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Frey C, Berger-Schoch A, Herrmann D, Schares G, Müller N, Bernet D, et al. Incidence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii in the muscle of sheep, cattle, pigs as well as in cat feces in Switzerland. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2012;154:251–255. doi: 10.1024/0036-7281/a000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gazzonis AL, Zanzani SA, Villa L, Manfredi MT. Toxoplasma gondii infection in meat-producing small ruminants: meat juice serology and genotyping. Parasitol Int. 2020;76:102060. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2020.102060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Genotyping allele profile obtained by PCR-RFLP and PCR-sequencing on T. gondii isolates.
Additional file 2: Table S2. Genotyping allele profile obtained by PCR-RFLP and PCR-sequencing on T. gondii DNA-positive clinical samples collected from abortion outbreaks.
Additional file 3: Table S3. Genotyping allele profile obtained by PCR-RFLP and PCR-sequencing on T. gondii DNA-positive adult sheep myocardium digests.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its Additional files 1, 2, 3. The sequences generated in the present study were submitted to the GenBank database under the following accession numbers: SAG3 sequences (MT358429, MT361124-MT361126); GRA6 sequences (MT370489, MT370491); and GRA7 sequences (MT361127, MT361128). Histological samples are available from the authors upon reasonable request.