To the Editor:
An epidemic cluster of pneumonia cases caused by the novel coronavirus, SARS‐CoV‐2, first broke out in Wuhan City, China in December 2019. 1 This infection, named COVID‐19, then spread rapidly throughout continents and was declared pandemic on March 11, 2020. Currently, there are only anecdotal reports of COVID‐19 in immunosuppressed children 2 , 3 , 4 or in pediatric patients with cancer, and so far there is only one Chinese case report 5 of pediatric COVID‐19 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). No case reports describing ALL onset in patients with COVID‐19 have been published. Nonetheless, few data are available about the possible impact of the drugs currently being used for COVID‐19 on the clinical course of children with ALL.
We hospitalized a 3‐year‐old boy with fever, epistaxis, and weight loss. His mother, although asymptomatic, had already tested positive in a SARS‐CoV‐2 nasopharyngeal swab. She was tested again on arrival at hospital and resulted negative. At presentation, the patient had mild fever, bruises, hepatosplenomegaly, and multiple lymphadenopathy. He was neither coughing nor in respiratory distress. Blood tests showed hyperleukocytosis, anemia, and thrombocytopenia (white blood cells [WBC] 85.23 × 109/L, hemoglobin 5.7 g/dL and platelets 19 × 109/L); other results included normal C‐reactive protein, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and uric acid. A peripheral blood smear showed 80% lymphoid blasts. The chest X‐ray showed a mild diffuse bronchial wall thickening and the chest computed tomography scan was normal. His nasopharyngeal swab tested positive for SARS‐CoV‐2, so he was isolated in a COVID ward and started receiving antibiotic treatment and intravenous hydration. From the first day of his hospitalization, the patient started COVID‐19 treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir (140/35 mg BID) associated with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ; 5 mg/kg BID for the first day and then 2.5 mg/kg BID).
The bone marrow smear showed 90% lymphoid blasts FAB L2 on morphology; immunophenotype was compatible with “common” ALL (CD123+/CLL1−). The lumbar puncture was negative for blasts.
On day 4, a pruritic confluent maculopapular skin rash (Figure S1) developed on the trunk and upper arms, then faded spontaneously in around 24 h. SARS‐CoV‐2 nasopharyngeal swab testing resulted negative on days 4 and 6 of COVID‐19 treatment.
Following the first negative swab, steroid prephase of AIEOP‐BFM ALL 2017 protocol was started. WBC had already lowered (26.68 × 109/L) after hydration, blood transfusions, and 48 h after the start of the combination therapy with HCQ and lopinavir/ritonavir. A further drastic decrease in WBC (6.6 × 109/L) was observed during the steroid prephase (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
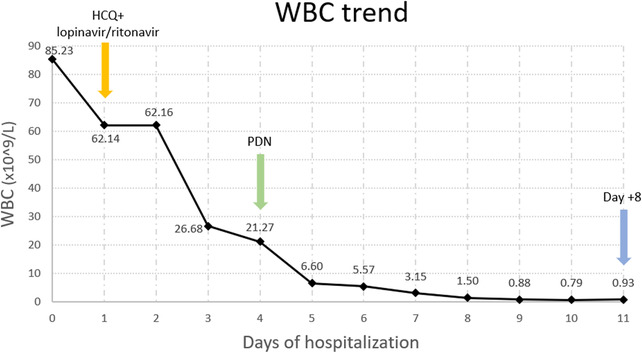
WBC trend in a 3‐year‐old child with SARS‐CoV‐2 infection at leukemia onset, and after hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) + lopinavir/ritonavir and prednisone (PDN) treatment. Prednisone good response (PGR) on day +8
The patient was a prednisone good responder on “day 8” of the steroid prephase (WBC 0.93 × 109/L, lymphoid blasts 6%) and received his first dose of vincristine‐daunorubicin without any relevant adverse effects. The good response to leukemia treatment was confirmed on day 15: WBC 0.94 × 109/L with lymphoid blasts 0.4%.
Treating a pediatric patient with a concurrent diagnosis of COVID‐19 and pediatric leukemia was a challenging situation and it was mandatory to proceed with caution. Since the neoplasm was not considered to be immediately life threatening, we decided to delay chemotherapy and prioritize the treatment of the viral infection. Our concern was that the viral infection could have rapidly worsened if we had started steroids and chemotherapy on day 1. The slight delay in the antineoplastic treatment and the concomitant administration of COVID‐19 drugs have not been detrimental to the child's clinical course and neither to his initial response to the leukemia treatment.
It can be hypothesized that the presence of the SARS‐CoV‐2 infection (known to carry a high burden of systemic inflammation 6 ) could have pushed the patient's leukocyte count higher in the setting of a preexistent leukemic clone. However, we observed an interesting effect, likely HCQ‐related, in the significant reduction of the WBC after 48 h of administration of the drug and before starting the steroid prephase. In fact, such WBC reduction is improbably related only to IV hydration and blood transfusions.
Besides its recognized use in rheumatologic and infectious diseases, HCQ has been known to have an antineoplastic effect. 7 Many ongoing clinical trials are focusing on combining treatment of chloroquine‐HCQ with standard chemotherapies, demonstrating prolonged survival rates in certain types of cancer. 8 However, chloroquine therapy does not show significant benefits in vivo, possibly due to its inability to reach effective drug concentrations. 7
The use of lopinavir/ritonavir associated with HCQ in COVID‐19 pediatric patients was based on local guidelines supported by the current literature. 9 , 10 , 11 Additional evidence supports the potential use of human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors (HIV‐PI; eg, lopinavir) as antineoplastic drugs. 12 Furthermore, the preclinical study of Meier‐Stephenson et al 13 focused on the identification of HIV‐PI‐mediated cytotoxicity in pediatric leukemia cells.
On consulting these reported scientific data, we were confident in starting the concurrent COVID‐19 therapy, taking into consideration the possible impact on the patient's leukemic course.
Our report shows that treatment of childhood acute leukemia in the setting of a concomitant SARS‐CoV‐2 infection may be successful. The timing of chemotherapy and the antiviral treatment must be carefully weighed on a case‐by‐case basis. In our patient, a prompt initiation of anti‐COVID‐19 drugs and a rapid viral clearance allowed us to start leukemia treatment with just a slight delay and did not prevent a satisfactory tumor response.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Supporting information
Supporting information
Marta Marcia and Barbara Vania contributed equally as co‐first authors to this article.
REFERENCES
- 1. Shen K, Yang Y, Wang T, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in children: experts’ consensus statement. World J Pediatr. 2020. 10.1007/s12519-020-00343-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus‐infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061‐1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497‐506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. D'Antiga L. Coronaviruses and immunosuppressed patients: the facts during the third epidemic. Liver Transpl. 2020. 10.1002/lt.25756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Chen Z, Xiong H, Li JX, et al. [COVID‐19 with post‐chemotherapy agranulocytosis in childhood acute leukemia: a case report]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41(0):E004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, et al. COVID‐19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1033‐1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Chen X, Clark J, Wunderlich M, et al. Autophagy is dispensable for Kmt2a/Mll‐Mllt3/Af9 AML maintenance and anti‐leukemic effect of chloroquine. Autophagy. 2017;13(5):955‐966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Verbaanderd C, Maes H, Schaaf MB, et al. Repurposing Drugs in Oncology (ReDO)‐chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as anti‐cancer agents. Ecancermedicalscience. 2017;11:781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Chen Z‐M, Fu J‐F, Shu Q, et al. Diagnosis and treatment recommendations for pediatric respiratory infection caused by the 2019 novel coronavirus. World J Pediatr. 2020. 10.1007/s12519-020-00345-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Lu X, Zhang L, Du H, et al. SARS‐CoV‐2 infection in children. N Engl J Med. 2020:382(17):1663‐1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Gao J, Tian Z, Yang X. Breakthrough: chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID‐19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci Trends. 2020;14(1):72‐73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Maksimovic‐Ivanic D, Fagone P, McCubrey J, Bendtzen K, Mijatovic S, Nicoletti F. HIV‐protease inhibitors for the treatment of cancer: repositioning HIV protease inhibitors while developing more potent NO‐hybridized derivatives. Int J Cancer. 2017;140(8):1713‐1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Meier‐Stephenson V, Riemer J, Narendran A. The HIV protease inhibitor, nelfinavir, as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of refractory pediatric leukemia. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:2581‐2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting information


