Highlights
-
•
COVID-19 quarantine is associated with mild-severe psychological distress and a high prevalence of mental health symptoms such as Phobic-Anxiety, Anxiety, Depression, Obsession-Compulsion, Distress, and hostility.
-
•
Our study contributed to better understand: different populations at risk (women, young individuals, students, psychiatric/neurological patients, etc.). possible mechanisms associated with mental health outcomes during quarantine as COVID-19 related fear and coping-skills.
-
•
These findings suggest that quarantined people may require attention in the long-term. In addition, policy makers, clinicians and media, could implement communication strategies and mental health recommendations/programs, to reduce fear on the population, develop better coping strategies and improve general well-being.
Keywords: COVID-19, Quarantine, Psychological distress, Latent profile analysis, Mental Health
Abstract
Background
Mental health of the population during COVID-19 quarantine could be at risk. Previous studies in short quarantines, found mood-related and anxiety symptomatology. Here we aimed to characterize the subtypes of psychological distress associated with quarantine, assess its prevalence, explore risk/protective factors, and possible mechanisms.
Methods
Online cross-sectional data (n = 4408) was collected during the Argentine quarantine, between 1st-17th April 2020 along a small replication study (n = 644). Psychological distress clusters were determined using latent profile analysis on a wide-range of symptoms using the complete Brief-Symptom Inventory-53. Multinomial and Elastic-net regression were performed to identify risk/protective factors among trait-measures (Personality and Resilience) and state-measures (COVID-19 related fear and coping-skills).
Results
Three latent-classes defined by symptom severity level were identified. The majority of individuals were classified in the mild (40.9%) and severe classes (41.0%). Participants reported elevated symptoms of Phobic-Anxiety (41.3%), Anxiety (31.8%), Depression (27.5%), General-Distress (27.1%), Obsession-Compulsion (25.1%) and Hostility (13.7%). Logistic-regressions analyses mainly revealed that women, young individuals, having a previous psychiatric diagnosis or trauma, having high levels of trait-neuroticism and COVID-related fear, were those at greater risk of psychological distress. In contrast, adults, being married, exercising, having upper-class income, having high levels of trait-resilience and coping-skills, were the most protected. Mediation analysis, showed that state-measures mediated the association between trait-measures and class-membership.
Conclusions
Quarantine was associated intense psychological distress. Attention should be given to COVID-19-related fear and coping-skills as they act as potential mediators in emotional suffering during quarantine.
1. Introduction
Since December 2019, the novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) rapidly spread around the globe. Three months later, the World Health Organization declared the COVID-19 outbreak a global pandemic. The emergency became an unprecedented situation to general and mental-health services (Chen et al., 2020; Wu and McGoogan, 2020). As a consequence, several governments adopted partial or complete quarantine measures. Particularly in Argentina, complete mandatory quarantine was declared 17 days after the first case was confirmed. Thus, mandatory quarantine began before the situation became problematic. Only essential service workers (i.e., medical staff, security forces, etc.) were excepted. Little is known about the effects of quarantine on mental health of the general population (Ben-Ezra et al., 2020). Previous studies found significant levels of psychological distress, anger, hopelessness, depression, fear of contagion and, anxiety in quarantined persons (Blendon et al., 2004; Brooks et al., 2020; Desclaux et al., 2017; Marjanovic et al., 2007; Rogers et al., 2020; Rubin and Wessely, 2020). Moreover, the long-term effects of quarantine on mental-health were also reported three years after SARS outbreak (Wu et al., 2009). Similar results were found in hospital staff during the 2003 SARS outbreak and the current COVID-19 (Bai et al., 2004; Lai et al., 2020).
Quarantine and social isolation represent a challenge to general wellbeing (Brooks et al., 2020; Shankar et al., 2013) and may become a source of distress for many people. In everyday life, humans are exposed to a variety of stressors which may have different sources, duration and intensity. In the face of threats, stress promotes environmental adaptation through an orchestrated neuro-hormonal and sympathetic response (De Kloet et al., 2005; Ellis and Del Giudice, 2019). Psychological distress exists on a continuum in the population, from a transient and adaptive response to stressors, to those at the extreme end which may be at higher risk for mental disorders (Kessler et al., 2010; Tomitaka et al., 2019). Intense psychological distress is a hallmark of mental disorders associated with poorer health outcomes and increased mortality risk (Barry et al., 2020; Phillips, 2009). In this regard, it refers to a heterogeneous negative experience composed of a variety of symptoms of depression, anxiety, anger, functional impairment, and behavioral difficulties (Drapeau et al., 2012; Holden et al., 2010). Evidence from studies in the general population, suggests that sociodemographic factors (i.e., gender, age, immigration, unemployment, marital status, etc.), stressor characteristics (i.e., duration, intensity, natural catastrophe, etc.) and personal resources (i.e., personality, income, perceived control, etc.) modulate individuals´ level of psychological distress (Byles et al., 2014; Drapeau et al., 2012; Tomitaka et al., 2019). Considering such factors from a diathesis-stress perspective, individuals’ response to stressors may be mediated by perceived threat intensity and the ability to cope with such external demands (Beck and Dozois, 2011; Lazarus, 1966).
Most previous studies on quarantine focused predominantly on mood and fear-related symptoms during social isolation (Rogers et al., 2020). However, little research has examined the psychological effects of the quarantine experience as a whole (Ben-Ezra et al., 2020). In this sense, psychological distress associated with the quarantine experience may be composed either by different symptom clusters (i.e., > mood-related / > anxiety-related / < anger) or similar symptoms may be clustered according to different severity levels. The primary aim of the present study was to assess and identify possible clusters (classes) of psychological distress associated with the Argentine quarantine, across a wide range of symptom dimensions (Somatization, Anxiety, Phobic Anxiety, Obsession-Compulsion, Interpersonal Sensitivity, Depression, Hostility, Paranoid Ideation and Psychoticism). Additionally, we analyzed potential risk and protective factors associated with these psychological distress clusters, including trait-measures (personality and resilience). Finally, we developed two short scales to assess COVID-19-related fear and coping skills related to the quarantine, to examine their relationship with psychological distress and risk/protective factors. Following classical theories of stress-response (Beck and Dozois, 2011; Lazarus, 1966), we hypothesized that COVID-19-related fear and coping skills during quarantine, may be critical mediators between psychological distress and risk/protective factors.
2. Method
2.1. Participants
Data on a sample of 4408 Argentine volunteers ranging from 18 to 92 years (see Table 1 , for full description) was collected using an online questionnaire. Participants were recruited using social media, institutional emails, and announcements. Only 102 individuals (2.3%) from the sample tested positive for COVID-19 or knew someone with the disease, and 4328 (98.2%) reported complete quarantine obedience. The number of COVID-19 positive individuals were similar by gender (Percentage of Men COVID-19 positive = 2.7% and Women = 2.7%; χ2 (1) = 0.273, p> 0.05) but different according to their age range (Percentage of COVID-19 positive, 18–29 years old = 1.6%, 30–44 years old = 2.7%, 45–64 years old = 2.8%, 65–100 years old = 1.0%; χ2 (3) = 11.939, p< 0.05). Data collection started on April 1st 2020, 11 days after the beginning of mandatory quarantine, and was completed on April 17th 2020. Participants were on average on 20 days (SE = 0.06) in quarantine. Participants did not receive any compensation for their participation. The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional committees on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. All procedures involving human subjects were approved the FLENI ethical's committee. Online informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Table 1.
Sociodemographic characteristics, Covariates, Psychological Distress, Personality and Resilience scores by Class.
| No.(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic / Outcome | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Total | P value |
| Overall | 792 (17.9) | 1806 (40.9) | 1810 (41.0) | 4408 (100) | |
| Age Range | < 0.001 | ||||
| 18–29 | 62 (7.8) | 157 (8.7) | 336 (18.6) | 555 (12.6) | |
| 30–44 | 220 (27.8) | 540 (29.9) | 613 (33.9) | 1373 (31.1) | |
| 45–64 | 339 (42.8) | 732 (40.5) | 632 (34.9) | 1703 (38.6) | |
| >65 | 171 (21.6) | 377 (20.9) | 229 (12.7) | 777 (17.6) | |
| Gender | < 0.001 | ||||
| Men | 228 (28.8) | 429 (23.8) | 295 (16.3) | 952 (21.6) | |
| Women | 564 (71.2) | 1377 (76.2) | 1515 (83.7) | 3456 (78.4) | |
| Essential Service Workera | 0.079 | ||||
| No | 623 (78.7) | 1451 (80.3) | 1489 (82.3) | 3563 (80.8) | |
| Yes | 169 (21.3) | 355 (19.7) | 321 (17.7) | 845 (19.2) | |
| Education Level | < 0.001 | ||||
| High | 677 (85.5) | 1522 (84.3) | 1430 (79.0) | 3629 (82.3) | |
| Middle | 103 (13.0) | 251 (13.9) | 323 (17.8) | 677 (15.4) | |
| Low | 12 (1.5) | 33 (1.8) | 57 (3.1) | 102 (2.3) | |
| Marital Status | < 0.001 | ||||
| Divorced | 100 (12.6) | 306 (16.9) | 229 (12.7) | 635 (14.4) | |
| Married | 450 (56.8) | 886 (49.1) | 766 (42.3) | 2102 (47.7) | |
| Unmarried | 210 (26.5) | 518 (28.7) | 746 (41.2) | 1474 (33.4) | |
| Widow/er | 32 (4.0) | 96 (5.3) | 69 (3.8) | 197 (4.5) | |
| Income Stability | < 0.001 | ||||
| Fixed | 569 (71.8) | 1304 (72.2) | 1190 (65.7) | 3063 (69.5) | |
| Variable | 223 (28.2) | 502 (27.8) | 620 (34.3) | 1345 (30.5) | |
| Income Level | < 0.001 | ||||
| Upper | 175 (22.1) | 381 (21.1) | 234 (12.9) | 790 (17.9) | |
| Upper-Middle | 255 (32.2) | 512 (28.3) | 458 (25.3) | 1225 (27.8) | |
| Middle | 262 (33.1) | 640 (35.4) | 735 (40.6) | 1637 (37.1) | |
| Lower | 100 (12.6) | 273 (15.1) | 383 (21.2) | 756 (17.2) | |
| Ocuppation | < 0.001 | ||||
| Employed | 356 (44.9) | 813 (45.0) | 813 (44.9) | 1982 (45.0) | |
| House Wife | 32 (4.0) | 85 (4.7) | 108 (6.0) | 225 (5.1) | |
| Retiree | 181 (22.9) | 406 (22.5) | 269 (14.9) | 856 (19.4) | |
| Self Employed | 184 (23.2) | 384 (21.3) | 344 (19.0) | 912 (20.7) | |
| Student | 21 (2.7) | 57 (3.2) | 168 (9.3) | 246 (5.6) | |
| Unemployed | 18 (2.3) | 61 (3.4) | 108 (6.0) | 187 (4.2) | |
| Pertains to risk group | 0.002 | ||||
| No | 486 (61.4) | 1069 (59.2) | 1173 (64.8) | 2728 (61.9) | |
| Yes | 306 (38.6) | 737 (40.8) | 637 (35.2) | 1680 (38.1) | |
| Lives with a person of risk | 0.458 | ||||
| No | 449 (56.7) | 1011 (56.0) | 984 (54.4) | 2444 (55.4) | |
| Yes | 343 (43.3) | 795 (44.0) | 826 (45.6) | 1964 (44.6) | |
| Exercise | < 0.001 | ||||
| No | 293 (37.0) | 765 (42.4) | 949 (52.4) | 2007 (45.5) | |
| Yes | 499 (63.0) | 1041 (57.6) | 861 (47.6) | 2401 (54.5) | |
| Religious | 0.468 | ||||
| No | 303 (38.3) | 655 (36.3) | 688 (38.0) | 1646 (37.3) | |
| Yes | 489 (61.7) | 1151 (63.7) | 1122 (62.0) | 2762 (62.7) | |
| Spiritual | 0.02 | ||||
| No | 167 (21.1) | 371 (20.5) | 439 (24.3) | 977 (22.2) | |
| Yes | 625 (78.9) | 1435 (79.5) | 1371 (75.7) | 3431 (77.8) | |
| Previous Trauma | < 0.001 | ||||
| No | 626 (79.0) | 1317 (72.9) | 1191 (65.8) | 3134 (71.1) | |
| Yes | 166 (21.0) | 489 (27.1) | 619 (34.2) | 1274 (28.9) | |
| Diagnosed | < 0.001 | ||||
| No | 697 (88.0) | 1495 (82.8) | 1231 (68.0) | 3423 (77.7) | |
| Yes | 95 (12.0) | 311 (17.2) | 579 (32.0) | 985 (22.3) | |
| Tobacco use | < 0.001 | ||||
| No | 691 (87.2) | 1473 (81.6) | 1422 (78.6) | 3586 (81.4) | |
| Yes | 101 (12.8) | 333 (18.4) | 388 (21.4) | 822 (18.6) | |
| Alcohol use | 0.541 | ||||
| No | 345 (43.6) | 816 (45.2) | 831 (45.9) | 1992 (45.2) | |
| Yes | 447 (56.4) | 990 (54.8) | 979 (54.1) | 2416 (54.8) | |
| Marijuana use | < 0.001 | ||||
| No | 749 (94.6) | 1648 (91.3) | 1617 (89.3) | 4014 (91.1) | |
| Yes | 43 (5.4) | 158 (8.7) | 193 (10.7) | 394 (8.9) | |
| Economic Concern | 0.673 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 4.208 (0.933) | 4.243 (0.889) | 4.227 (0.955) | 4.230 (0.924) | |
| Number of people quarantined | 0.095 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 2.003 (1.412) | 1.917 (1.502) | 2.018 (1.441) | 1.974 (1.462) | |
| Days in Quarantine | 0.637 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 21.045 (3.991) | 21.166 (3.454) | 21.281 (3.512) | 21.191 (3.003) | |
| Hygiene Measures | 0.089 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 4.495 (0.669) | 4.436 (0.706) | 4.433 (0.714) | 4.445 (0.703) | |
| Media Exposure | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 3.676 (0.895) | 3.800 (0.867) | 3.836 (0.888) | 3.792 (0.882) | |
| Media Valuation | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 3.395 (0.875) | 3.528 (0.842) | 3.597 (0.878) | 3.532 (0.866) | |
| COVID-19 related Optimism | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 3.840 (0.910) | 3.616 (0.897) | 3.417 (1.001) | 3.575 (0.955) | |
| COVID-19 related Fear | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 16.769 (6.120) | 20.114 (6.023) | 23.541 (5.919) | 20.920 (6.492) | |
| Coping Skills | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 14.827 (2.612) | 13.715 (2.812) | 12.555 (3.059) | 13.438 (3.000) | |
| Extroversion | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 2.683 (0.725) | 2.728 (0.747) | 2.828 (0.822) | 2.761 (0.777) | |
| Agreeableness | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 2.703 (0.646) | 2.894 (0.677) | 3.062 (0.755) | 2.928 (0.716) | |
| Conscientiousness | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.694 (0.663) | 1.888 (0.756) | 2.105 (0.875) | 1.942 (0.806) | |
| Neuroticism | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 3.378 (0.518) | 3.533 (0.520) | 3.783 (0.592) | 3.608 (0.572) | |
| Openness | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 2.152 (0.810) | 2.290 (0.861) | 2.348 (0.909) | 2.289 (0.875) | |
| Resilience | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 41.085 (6.554) | 39.537 (6.334) | 36.352 (7.100) | 38.507 (6.955) | |
| Global Severity Index (GSI) | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.116 (0.077) | 0.511 (0.945) | 4.378 (1.903) | 1.731 (1.156) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 0 (0) | 29 (1.6) | 1166 (64.4) | 1195 (27.1) | |
| Somatization | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.037 (0.083) | 0.235 (0.271) | 1.034 (0.808) | 0.527 (0.695) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 0 (0) | 25 (1.4) | 748 (41.3) | 773 (17.5) | |
| Obsession-Compulsion | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.127 (0.187) | 0.538 (0.441) | 1.511 (0.898) | 0.864 (0.854) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 1 (0.1) | 133 (7.4) | 973 (53.8) | 1107 (25.1) | |
| Interpersonal Sensitivity | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.016 (0.063) | 0.256 (0.357) | 1.184 (1.023) | 0.594 (0.856) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 0 (0) | 31 (1.7) | 692 (38.2) | 723 (16.4) | |
| Depression | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.098 (0.140) | 0.507 (0.401) | 1.492 (0.864) | 0.838 (0.833) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 0 (0) | 172 (8.9) | 1071 (59.2) | 1213 (27.5) | |
| Anxiety | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.238 (0.213) | 0.639 (0.401) | 1.651 (0.874) | 0.982 (0.848) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 0 (0) | 188 (10.4) | 1212 (67.0) | 1400 (31.8) | |
| Hostility | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.127 (0.168) | 0.398 (0.345) | 1.029 (0.738) | 0.608 (0.640) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 0 (0) | 47 (2.6) | 556 (30.7) | 603 (13.7) | |
| Phobic Anxiety | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.298 (0.423) | 0.699 (0.706) | 1.395 (1.036) | 0.913 (0.927) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 97 (12.2) | 604 (33.4) | 1120 (61.9) | 1821 (41.3) | |
| Paranoid Ideation | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.047 (0.105) | 0.277 (0.322) | 0.981 (0.795) | 0.525 (0.675) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 0 (0) | 3 (0.2) | 345 (19.1) | 348 (7.9) | |
| Psychoticism | < 0.001 | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 0.043 (0.107) | 0.304 (0.307) | 1.098 (0.759) | 0.583 (0.686) | |
| Prevalence No.(%) | 0 (0) | 214 (11.8) | 1190 (65.7) | 1404 (31.9) |
Distribution by type of work: health services (608; 71.9%), food supply (112; 13.2%), food production (61; 7.2%), security services (43; 5.1%) and cleaning services (21; 2.5%).
2.2. Assessment
2.2.1. Psychological distress
The 53 items (range 0–4) and the derived 9 symptom dimensions (Somatization, Anxiety, Phobic Anxiety, Obsession-Compulsion, Interpersonal Sensitivity, Depression, Hostility, Paranoid Ideation, and Psychoticism) of the Brief Symptom Inventory-53 (BSI-53; Derogatis and Derogatis, 2001; Derogatis and Melisaratos, 1983), were used to examine psychological distress and psychopathology prevalence. Global Severity Index (GSI) was also calculated. The BSI-53 and its longer version (Symptom Checklist-90-Revised) have local community stratified norms (Casullo and Pérez, 2004). The BSI-53 has been used in a variety of psychiatric and natural settings (clinical patients, war, natural disasters; (Cook and Bickman, 1990; Derogatis and Melisaratos, 1983; Pereda et al., 2007). It has a 9-factor structure (Derogatis and Derogatis, 2001; Derogatis and Melisaratos, 1983; Pereda et al., 2007) with robust reliability (α = 0.88). To analyze the most frequent items, data was binarized (0 = symptom absent / 1, 2 and 3 = symptom present). Following the BSI-53 manual (Derogatis and Derogatis, 2001), clinically significant scores were set to be equivalent to T = 63 or higher, to characterize each symptom dimension prevalence.
2.2.2. Trait-Measures
Big Five Inventory-10 (BFI-10; Rammstedt and John, 2007) was used to assess the big five personality traits: Extroversion, Agreeableness, Openness, Neuroticism, and Conscientiousness. The BFI-10 has a comparable structure to those of the full BFI with acceptable psychometric properties (α = 0.85; Rammstedt, 2007). BFI-10 uses two items for each dimension on a 1–5 Likert scale. Trait-resilience was measured with the 10-item (range 0–4), self-rated Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (Connor and Davidson, 2003). This scale was demonstrated to have a one-factor structure, good reliability and validity in non-clinical and clinical samples (α = 0.90; Arias González et al., 2015; Cheng et al., 2020).
2.2.3. State-Measures
COVID-19 related fear (8-items) and coping skills during quarantine (5-items), were explored using two short-scales developed specifically for this study. The fear scale evaluated physical and cognitive anxiety in relation to COVID-19 (α = 0.89) and, the coping skills scale (α = 0.79) assessed perceived difficulties and life-changes caused by the quarantine (see Results in the Supplementary Material). Both scales consisted on a 0–4 Likert scale. Exploratory Factor Analysis and Confirmatory Factor Analysis of the scales showed an acceptable two-factor solution.
2.2.4. Sociodemographic data and covariates
Sociodemographic data was self-reported by all participants (Table 1), including age, gender, occupation, education level, marital status, and income stability (variable/fixed). Additional covariates were also examined: number of people quarantined with, belonging to a known risk group for COVID-19 (yes/no) or lives with one (yes/no), number of days in quarantine, economic concern derived from COVID-19 (range 1–5), overall number of hygiene measures against COVID-19 (range 1–5), time spent in COVID-19 related information and news (media exposure, range 1–5), importance given to COVID-19 related information and news (media valuation, range 1–5), exercise during quarantine (yes/no), overall optimism about the country COVID-19 situation (optimism, range 1–5), religiosity or spirituality (yes/no), tobacco (yes/no), alcohol (yes/no) or marijuana use (yes/no), being previously exposed to trauma (yes/no) or diagnosed with a neurological or psychiatric disorder (yes/no).
2.3. Statistical analysis
Data analysis was implemented in R, 3.6.3 (R Foundation). When appropriate, categorical and normally distributed variables were analyzed by means of chi-square tests and ANOVA. Non-normally distributed variables were analyzed with Mann-Whitney-U and Kruskal-Wallis test. The significance level was set at α = 0.05, and all tests were corrected for multiple comparisons using the Bonferroni correction.
2.3.1. Latent profile analysis (LPA)
LPA was performed on all participants with the 53 items of the BSI using Mclust R-package, to identify symptom classes. LPA is a robust mixture-model technique, commonly used to identify subtypes of homogeneous latent classes or subgroups within a large heterogeneous group (Garrett and Zeger, 2000; Hagenaars and McCutcheon, 2002). This iterative process, cluster together similar response profiles to generate subgroups/classes. We used maximum likelihood estimation procedure with 95% CI, calculated via 1000 non-parametric bootstrap. The optimal number of classes was determined by Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) and Integrated Complete-data Likelihood (ICL) values. Analysis started with 1 class, additional classes were added, and the model fit was assessed until the optimal number of classes was found. Bootstrap Likelihood Ratio Test (BLRT) was performed to compare model fit between the number of classes. Classification performance of the solution was estimated by discriminant analysis and k = 10-fold cross-validation based on Gaussian finite mixture modeling.
2.3.2. Logistic regressions
To determine potential risk/protective factors associated with latent class membership and psychological distress, all covariates and trait/state measures were entered into two separate logistic regressions to facilitate coefficient interpretation: a multinomial-logistic regression (nnet R-package) and a penalized Elastic-net regression (glmnet R-package). Elastic-net regression is a well-suited technique dealing with multiple predictors and multicollinearity (Fig. 1 in the Supplementary Material; Zou, 2005). The optimal tuning parameter (Lambda) of the penalized regression was produced after 10-fold cross-validation. Both procedures were then 10-fold cross-validated, to evaluate model performance, and the AUC was estimated using the Hand and Till (Hand and Till, 2001) solution for multiclass models. Logistic regression coefficients are presented as odds ratios (ORs) and 95% Cis.
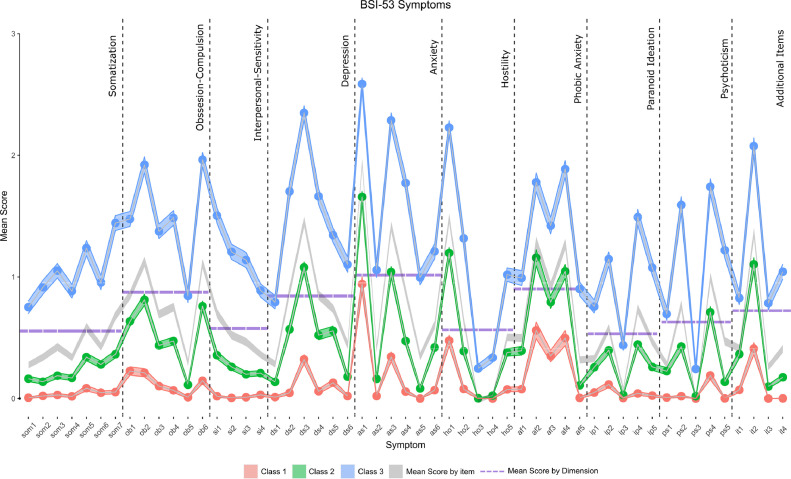
Fig. 1.
Mean Item Scores of the BSI-53 by Class. Width of the lines represents 95%CI. Vertical dotted lines stand for dimension separation and horizontal dotted lines represent the mean of that dimension.
Abbreviations: Som, Somatization items; Ob, Obsession-Compulsion items; Si, Interpersonal-Sensitivity items; Ds, Depression items; As, Anxiety items; Ho, Hostility items; af, Phobic Anxiety items; Ip, Paranoid Ideation items; Ps, Psychoticism items and It, Additional Items.
2.3.3. Mediation analysis
Based on previous work on the stress response and the significant correlation between state-measures and the variables of interest (trait-measures, and psychological distress; Fig. 1 Supplementary Material), we explored the possible mediating role of state-measures in the relationship between trait-measures and psychological distress severity associated with latent classes (outcome). First, we conducted a measurement model with all the state/trait measures indicators, and then we ran a parallel mediation analysis using Lavaan R-package. Loadings were fixed to be equal when the latent variable had two indicators to avoid instability. Model estimation was performed using the Diagonally Weighted Least Squares (DWLS) method and several model fit indices such as χ2/df, BIC, CFI, and RMSEA were computed. Mediation analysis was adjusted for all confounders, which were found to be predictors of psychological distress in the logistic-regression analysis. As the latent-classes were non-continuous, standardized probit coefficients are reported, such as that a probit-coefficient of 0.04 reveals that for each unit increase in the trait-measure predictor, there was an increment of 0.04 SDs in the expected Z-score of latent-classes (ordered outcome). Next, group comparison between variables of interest (gender and previous diagnosis) was performed using the same model in a group-mediation analysis, tested against a constrained model (regressions and intercepts were set to be equal across groups). Testing for group and path difference was estimated using the Wald test method. Finally, total, direct, and indirect (mediation) effects were analyzed using 1000 bootstraps with bias-corrected 95% CI. The magnitude of mediation was calculated by the proportion of the association mediated by the total indirect effect over the total direct effect.
2.4. Replication study
After data completion of the main study, we conducted a small replication study (n = 644), between April 20th 2020 and May 20th 2020, in order to test our original findings and evaluate the effects of prolonged exposure time in quarantine on psychological distress. The procedure and data analyses were exactly the same as in the main study.
3. Results
3.1. Subtypes and prevalence of psychological distress during quarantine
Data from the BSI-53 revealed a three-class solution for the LPA (Table 1 in the Supplementary Material). Classification performance of the model after cross-validation (k = 10 fold) yielded an 86.8% accuracy. As shown in Fig. 1, latent-class profiles were similar and defined by severity level across symptoms and dimensions: Class 1 (17.9% [95% CI, 17.2- 20.1]) exhibited low symptomatology, Class 2 (40.90% [95% CI, 37.0- 40.1]) mild symptomatology and Class 3 (41.06% [95% CI, 40.3- 44.0]) moderate/severe symptomatology. Thus, psychological distress during quarantine among participants was notably high in a wide range of symptoms and dimensions. Response probability of each symptom by latent-classes showed the same psychological distress profile (Figure 2 in the Supplementary Material). Class 1 and Class 2 scores across symptoms were mostly below the mean values of each dimension. Conversely, Class 3 was almost exclusively above the mean values of each dimension. Each symptom, dimension, and mean psychological distress (GSI) was significantly different between the three classes (Table 1; Figure 3 in Supplementary Material).
Overall, 60.1% of individuals was over the cutoff community-norms values, in at least one symptom dimension. More specifically, the prevalence of significant psychological distress associated with each symptom dimension, as measured by the BSI, was highest in individuals of Class 3, lower in individuals of Class 2, and almost null in individuals of Class 1 (Table 1). The overall composition and trends within latent-classes were similar: Anxiety, Phobic-Anxiety, Depression, Obsession-Compulsion, and Hostility were the dimensions with the highest scores (Figure 4 in Supplementary Material). The most frequent symptoms in all individuals showed that the majority of participants rate themselves as having some levels of Nervousness (86.1%), Irritation (73.9%), Sadness (70.1%), Being Fearful (67.8%), Sleep disturbances (61.2%), Concentration problems (58.3%), Fear of crowded places (56.5%), Feeling blocked (55.4%), Fear of traveling (50.6%), Feeling distant from people (50.2%), Memory difficulties (50%) and Tension/Agitation (49.6%).
Sociodemographic variables and covariates were mostly different based on class membership (Table 1). The proportion of women (78.4%), individuals with Higher education (82.3), married (47.7%), employees (45.0%), individuals with no known risk for COVID-19 (61.9%) or not belonging to the “essential workers” group (80.8%), was higher in the sample relative to the other categories. Women, younger individuals (18–29 years old) and individuals with previous neurological/psychiatric diagnosis or trauma reported experiencing more severe psychological distress and had a higher prevalence across symptom dimensions (Table 1; Figures 5, 6 and 7 in the Supplementary Material). Regarding state/trait measures, individuals in Class 3 had higher levels of COVID-19-related fear, extroversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness and neuroticism, and lower levels of coping skills during quarantine and resilience relative to Class 1 (Table 1, Figure 3 in Supplementary Material). Class 2 individuals showed intermediate scores of state/trait measures.
3.2. Risk and protective factors associated with psychological distress severity
Multinomial logistic-regression showed that, after controlling for confounders and a k = 10 fold cross-validation, mild and severe psychological distress was predicted by being previously diagnosed with a psychiatric/neurological disorder, being previously exposed to trauma, being a women or tobacco user (Table 2 ). On the contrary, self-employed and married individuals, upper-class income, adults (45–64 years) and older adults (>65 years) were associated with lesser odds of intense psychological distress. Higher scores in state/trait measures predicted class membership such as those individuals with more COVID-19-related fear, agreeableness, conscientiousness, and neuroticism had a greater risk of more severe psychological distress. Coping skills during quarantine and trait-resilience were protective factors for intense psychological distress. Elastic-net regression yielded similar results (Table 2) and reinforced the features found in the multinomial logistic-regression, predicting psychological distress. Here, the only difference relied on the inclusion of students as a predictor of poorer mental health. Model performance estimated using k = 10 fold cross-validation and the mean Area Under the Curve (Hand and Till, 2001) was acceptable for both models, but slightly better for the Elastic-net model (Multinomial Logistic-regression RMSE = 0.59; AUC = 0.76 and Elastic-net: RMSE = 0.49; AUC = 0.80).
Table 2.
Risk and Protective Factors for Psychological Distress associated with Classes by Logistic and Elastic-net regression.
| Mulinomial Regression | Elastic-Net Regression | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Class 2a | P value | Class 3 | P value | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 |
| Age Range | |||||||
| 18–29 | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | nsb | ns | ns |
| 30–44 | 0.93 (0.60 – 1.43) | 0.73 | 0.58 (0.36 – 0.92) | 0.022 | ns | ns | ns |
| 45–64 | 0.77 (0.48 – 1.22) | 0.265 | 0.41 (0.25 – 0.68) | 0.001 | 0.0134 | 0.0117 | −0.0252 |
| >65 | 0.73 (0.41 – 1.28) | 0.27 | 0.32 (0.17 – 0.61) | 0.001 | 0.0504 | 0.0645 | −0.115 |
| Gender | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| Men | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Women | 1.33 (1.06 – 1.66) | 0.013 | 1.84 (1.41 – 2.40) | <0.001 | −0.0635 | −0.0189 | 0.0824 |
| Essential Service Worker | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 0.89 (0.71 – 1.13) | 0.354 | 0.74 (0.57 – 0.98) | 0.033 | ns | ns | ns |
| Education Level | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| High | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Middle | 1.16 (0.55 – 2.45) | 0.691 | 1.03 (0.75 – 1.40) | 0.866 | ns | ns | ns |
| Low | 0.98 (0.74 – 1.30) | 0.895 | 1.68 (0.75 – 3.76) | 0.204 | ns | ns | ns |
| Marital Status | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| Divorced | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Married | 0.62 (0.46 – 0.84) | 0.002 | 0.7 (0.50 – 0.99) | 0.043 | 0.0206 | −0.0072 | −0.0134 |
| Unmarried | 0.72 (0.51 – 1.00) | 0.049 | 0.9 (0.61 – 1.33) | 0.607 | −0.0759 | −0.0641 | 0.14 |
| Widow/er | 0.93 (0.56 – 1.55) | 0.784 | 1.02 (0.57 – 1.85) | 0.937 | ns | ns | ns |
| Income Stability | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| Fixed | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Variable | 1.08 (0.84 – 1.39) | 0.536 | 1.3 (1.00 – 1.70) | 0.054 | ns | ns | ns |
| Income Level | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| Upper | 0.98 (0.69 – 1.39) | 0.915 | 0.68 (0.45 – 0.98) | 0.047 | 0.0291 | 0.041 | −0.0701 |
| Upper-Middle | 0.91 (0.66 – 1.25) | 0.553 | 0.87 (0.61 – 1.24) | 0.436 | ns | ns | ns |
| Middle | 0.93 (0.69 – 1.26) | 0.651 | 0.94 (0.68 – 1.32) | 0.735 | ns | ns | ns |
| Lower | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | ns | ns | ns | |
| Ocuppation | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| Employed | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| House Wife | 1.16 (0.72 – 1.86) | 0.549 | 1.3 (0.77 – 2.20) | 0.33 | ns | ns | ns |
| Retiree | 0.93 (0.66 – 1.31) | 0.67 | 0.75 (0.50 – 1.12) | 0.156 | 0.0056 | 0.0096 | −0.0151 |
| Self Employed | 0.83 (0.63 – 1.08) | 0.165 | 0.65 (0.49 – 0.87) | 0.004 | ns | ns | ns |
| Student | 1.09 (0.67 – 1.77) | 0.738 | 1.6 (0.96 – 2.66) | 0.069 | −0.1473 | −0.1819 | 0.3292 |
| Unemployed | 1.2 (0.76 – 1.89) | 0.427 | 1.25 (0.77 – 2.02) | 0.37 | ns | ns | ns |
| Pertains to risk group | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 1.08 (0.85 – 1.39) | 0.517 | 1.08 (0.82 – 1.42) | 0.596 | ns | ns | ns |
| Lives with a person of risk | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 1.05 (0.86 – 1.28) | 0.623 | 1.02 (0.82 – 1.27) | 0.869 | ns | ns | ns |
| Exercise | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 0.96 (0.79 – 1.17) | 0.694 | 0.81 (0.65 – 1.00) | 0.05 | 0.0042 | 0.0032 | −0.0074 |
| Religious | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 1.09 (0.88 – 1.34) | 0.443 | 1.06 (0.84 – 1.35) | 0.611 | ns | ns | ns |
| Spiritual | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 1.19 (0.92 – 1.52) | 0.183 | 1.22 (0.92 – 1.62) | 0.166 | ns | ns | ns |
| Previous Trauma | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 1.46 (1.17 – 1.82) | 0.001 | 2.03 (1.59 – 2.60) | <0.001 | −0.0864 | −0.0168 | 0.1031 |
| Diagnosed | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 1.55 (1.18 – 2.03) | 0.002 | 3.01 (2.25 – 4.03) | <0.001 | −0.2398 | −0.1105 | 0.3502 |
| Tobacco use | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 1.35 (1.02 – 1.80) | 0.037 | 1.4 (1.02 – 1.93) | 0.035 | ns | ns | ns |
| Alcohol use | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 0.85 (0.70 – 1.03) | 0.103 | 0.97 (0.78 – 1.22) | 0.81 | ns | ns | ns |
| Marijuana use | ns | ns | ns | ||||
| No | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A | ns | ns | ns |
| Yes | 1.43 (0.94 – 2.16) | 0.094 | 1.31 (0.83 – 2.06) | 0.252 | ns | ns | ns |
| Economic Concern | 0.92(0.83 – 1.03) | 0.139 | 0.88 (0.78 – 0.99) | 0.035 | ns | ns | ns |
| Number of people quarantined | 0.97(0.90 – 1.04) | 0.4 | 0.98 (0.90 – 1.07) | 0.689 | ns | ns | ns |
| Days in Quarantine | 1.01 (0.99 – 1.02) | 0.429 | 1.01 (0.99 – 1.03) | 0.207 | ns | ns | ns |
| Hygiene Measures | 0.85 (0.74 – 0.98) | 0.027 | 0.82 (0.70 – 0.97) | 0.017 | ns | ns | ns |
| Media Exposure | 1.04 (0.92 – 1.16) | 0.556 | 1.04 (0.91 – 1.19) | 0.525 | ns | ns | ns |
| Media Valuation | 1.03 (0.91 – 1.16) | 0.62 | 1 (0.87 – 1.15) | 0.992 | ns | ns | ns |
| COVID-19 related optimism | 0.94 (0.84 – 1.04) | 0.217 | 0.93 (0.82 – 1.05) | 0.227 | ns | ns | ns |
| COVID-19 related Fear | 1.1 (1.08 – 1.12) | <0.001 | 1.23 (1.21 – 1.26) | <0.001 | −0.0699 | −0.0058 | 0.0757 |
| Coping Skills during quarantine | 0.87 (0.84 – 0.90) | <0.001 | 0.75 (0.73 – 0.79) | <0.001 | 0.0925 | 0.0037 | −0.0963 |
| Extroversion | 1.05 (0.92 – 1.19) | 0.494 | 1.17 (1.01 – 1.35) | 0.031 | ns | ns | ns |
| Agreeableness | 1.39 (1.21 – 1.59) | <0.001 | 1.66 (1.42 – 1.94) | <0.001 | −0.133 | 0.0102 | 0.1228 |
| Conscientiousness | 1.43 (1.24 – 1.64) | <0.001 | 1.72 (1.47 – 2.00) | <0.001 | −0.1741 | 0.0055 | 0.1686 |
| Neuroticism | 1.44 (1.21 – 1.71) | <0.001 | 2.41 (1.98 – 2.94) | <0.001 | −0.2671 | −0.0678 | 0.3348 |
| Opennes | 1.09 (0.97 – 1.22) | 0.166 | 1.02 (0.90 – 1.17) | 0.725 | ns | ns | ns |
| Resilience | 0.99 (0.97 – 1.00) | 0.079 | 0.95 (0.93 – 0.97) | <0.001 | 0.0154 | 0.0068 | −0.0222 |
Class 1 was used as reference.
ns are not significant coefficient which equal zero.
3.3. State-measures mediating role between trait-measures and psychological distress severity
The initial measurement model encompassing all state/trait-measures indicators and the structural model for parallel mediation provided acceptable fit indices (Table 3 ). Table 3 shows that the indirect effect of trait-measures, gender, and age on psychological distress severity (latent classes) through the mediators were significant (simplified model in Figure 8 in the Supplementary Material). This result suggests that COVID-19-related fear and coping skills during quarantine partially mediated the association between gender, age, personality (Neuroticism, Openness, Agreeableness and Conscientiousness and trait-resilience) and psychological distress severity. This effect remained significant considering the mediators separately or together (total indirect effect) in most predictors.
Table 3.
Adjusted Direct Indirect and Total Associations of Trait-measures with Psychological Distress via State-measures.
| Trait | β (95% CI)a,b | P Value |
|---|---|---|
| Extroversion | ||
| Direct Effect | 0.106 (0.068 - 0.146) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Fear | −0.004 (−0.019 to −0.010) | 0.5828 |
| Indirect Effect - Coping Skills | 0.006 (−0.001 to 0.017) | 0.1927 |
| Total Indirect Effects | 0.002 (−0.015 to 0.021) | 0.8404 |
| Total Effect | 0.108 (0.068 −0.153) | <0.001 |
| Proportion Mediated (%) | 1.83 | |
| Agreeableness | ||
| Direct Effect | 0.224 (0.178 - 0.265) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Fear | 0.042 (0.025 - 0.059) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Coping Skills | 0.015 (0.006 - 0.026) | 0.0016 |
| Total Indirect Effects | 0.057 (0.03 - 0.079) | <0.001 |
| Total Effect | 0.281 (0.237 - 0.328) | <0.001 |
| Proportion Mediated (%) | 20.4 | |
| Conscientiousness | ||
| Direct Effect | 0.272 (0.233 - 0.309) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Fear | −0.026 (−0.042 to −0.009) | 0.0017 |
| Indirect Effect - Coping Skills | 0.014 (0.004 - 0.028) | 0.0154 |
| Total Indirect Effects | −0.011 (−0.032 - 0.010) | 0.2775 |
| Total Effect | 0.261 (0.222 - 0.300) | <0.001 |
| Proportion Mediated (%) | 5.6 | |
| Neuroticism | ||
| Direct Effect | 0.339 (0.284 - 0.400) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Fear | 0.142 (0.117 - 0.170) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Coping Skills | 0.032 (0.016 - 0.047) | <0.001 |
| Total Indirect Effects | 0.174 (0.147 - 0.201) | <0.001 |
| Total Effect | 0.514 (0.458 - 0.574) | <0.001 |
| Proportion Mediated (%) | 33.9 | |
| Openness | ||
| Direct Effect | 0.065 (0.028 - 0.103) | 0.0005 |
| Indirect Effect - Fear | 0.018 (0.005 - 0.033) | 0.0074 |
| Indirect Effect - Coping Skills | 0.022 (0.013 - 0.032) | <0.001 |
| Total Indirect Effects | 0.041 (0.025 - 0.060) | <0.001 |
| Total Effect | 0.107 (0.068 - 0.147) | <0.001 |
| Proportion Mediated (%) | 38.9 | |
| Resilience | ||
| Direct Effect | −0.323 (−0.378 to −0.268) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Fear | −0.080 (−0.100 to −0.061) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Coping Skills | −0.065 (−0.086 to −0.044) | <0.001 |
| Total Indirect Effects | −0.146 (−0.176 to −0.116) | <0.001 |
| Total Effect | −0.469 (−0.525 to −0.414) | <0.001 |
| Proportion Mediated (%) | 31.2 | |
| Age | ||
| Direct Effect | −0.014 (−0.016 to −0.012) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Fear | 0.002 (0.001 - 0.002) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Coping Skills | −0.0006 (−0.001 to −0.0002) | 0.0192 |
| Total Indirect Effects | 0.001 (0.0005 - 0.002) | 0.004 |
| Total Effect | −0.013 (−0.015 to −0.011) | <0.001 |
| Proportion Mediated (%) | 10.7 | |
| Genderc | ||
| Direct Effect | 0.081 (0.033 - 0.128) | 0.0005 |
| Indirect Effect - Fear | 0.091 (0.073 - 0.111) | <0.001 |
| Indirect Effect - Coping Skills | 0.0005 (−0.015 to 0.011) | 0.9376 |
| Total Indirect Effects | 0.091 (0.071 - 0.111) | <0.001 |
| Total Effect | 0.173 (0.124 - 0.219) | <0.001 |
| Proportion Mediated (%) | 52.9 |
Measurement Model Fit indices: χ2 = 7647.49, df = 223, P<0.0001, CFI = 0.95, TLI = 0.94, SRMR = 0.076, RMSEA = 0.076, 95% CI [0.075–0.078].
Mediation Model Fit Indices: χ2 = 17677.96, df = 569, P<0.0001, CFI = 0.94, TLI = 0.92, SRMR = 0.75, RMSEA = 0.073, 95% CI [0.071–0.073].
Gender coded as: 0 = Men; 1 = Women.
Next, we performed a multi-group mediation analysis by gender and found significant differences between Women and Men (unconstrained model: χ2 = 13,441, df = 1008; constrained model: χ2 = 13,704, df = 1008, P<0.0001; Table 2 and 3 in the Supplementary Material). The mediation of COVID-19-related fear for Conscientiousness on Classes was stronger for men (β = −0.03; 95% CI, −0.04- 0.01) than for women (β = −0.009; 95% CI, −0.01- 0.001; F(1) = 4.76, P < 0.001). Trait-resilience effect was more mediated by fear for women (β = −0.06; 95% CI, −0.07- 0.04) than for men (β = −0.06; 95% CI, −0.07- 0.04; F(1) = 21.68, P<0.001). Finally, individuals with previous diagnosis did not differ from undiagnosed individuals in a multi-group mediation model (unconstrained model: χ2 = 13,958, df = 928; constrained model: χ2 = 14,084, df = 1011, P = 0.22), suggesting that the state-measures mediation, may be independent from previous mental health conditions.
3.4. Replication study
Analysis of the independent sample (n = 644), yielded equivalent results to the main study (Results 2 in the Supplementary Material). That is, we found three-latent classes based on symptom severity, similar factor/protective factors, and a mediation effect of state-measures. Notably, here we found that mean number of days in quarantine (33.2 [SE = 6.4]), alcohol consumption, and belonging to a risk group, also predicted a more severe psychological distress (Results2 in the Supplementary Material).
4. Discussion
In the present cross-sectional study on 4408 participants, the quarantine experience was associated with mild-severe psychological distress and a high prevalence of mental health symptoms. More importantly, we found that the overall quarantine experience was similar for every individual, as symptoms were clustered by severity instead of types or subtypes. The more common classes (81.9% between Class 2 and Class 3) reported elevated levels of phobic anxiety, anxiety, depression, general distress (GSI), obsession-compulsion and hostility symptoms (overall prevalence: 41.3%, 31.8%, 27.5%, 27.1%, 25.1% and 13.7% respectively). Moreover, fear associated with outdoor activities (travel = 50.6%; crowded places = 56.5%), sleep disturbances (61.2%) and cognitive symptoms (concentration and memory difficulties; 58.3% and 50%) were within the most frequent symptoms.
Our study describes potential risk and protective factors associated with emotional suffering among quarantined people. First, individual characteristics such as being a woman, tobacco smoker or a student, having a previous neurological or psychiatric diagnosis or previous trauma, predicted more severe psychological distress, while being an adult or older adult, married, having upper-class income and exercising during quarantine, were associated with better mental health outcomes. Thus, our results are in line with previous studies on epidemics and psychological distress, which showed a greater risk for emotional suffering in populations with similar sociodemographic characteristics such as female gender, previous diagnosis or younger individuals (Drapeau et al., 2012; Iw et al., 2010; Lai et al., 2020; Su et al., 2007). In contrast to a previous report regarding medical staff in China (Lai et al., 2020), we did not find an effect in relation to essential service workers. Second, state/trait characteristics were differentially linked to class membership. Higher levels of neuroticism, agreeableness, conscientiousness, and COVID-19 related fear were associated with more intense psychological distress, while higher scores on resilience and coping skills during quarantine had the opposite effect. Current findings are consistent with the literature on traits characteristics and mental health outcomes, which found that personality traits such as neuroticism are positively associated with poorer mental health outcomes and, that elevated trait resilience has a protective effect (Hu et al., 2015; Kotov et al., 2010). Moreover, other studies also reported that state variables such as fear of infection during epidemic times are associated with elevated levels of psychological distress (Brooks et al., 2020).
Finally, our study contributed to better understand the mechanisms associated with mental health outcomes during the mandatory quarantine. We found that COVID-19 related fear and coping skills during quarantine partially mediated the effect of individuals’ trait characteristics on psychological distress. The proportion mediated by state-measures was notably high in openness (38.9%), neuroticism (33.9%), resilience (31.2%), and gender differences (52.9%). Importantly, this indirect effect was no different for individuals with or without previous psychiatric or neurological diagnosis. Notably, these results are congruent with the diathesis-stress model, and classical theories on stress response (Byles et al., 2014; Lazarus, 1966), which posit the relation between threat appraisal, personal resources, and mental health outcomes. In this sense, psychological distress severity during mandatory quarantine, could be mapped as a function of different sociodemographic factors, stable personality traits and state appraisals, which modulates the association between the quarantine experience and current mental health.
4.1. Implications
As psychological distress is partially mediated by COVID-19 related fear and coping skills during quarantine, policymakers and media could implement communication strategies and mental health recommendations/programs to reduce fear on the population, develop better-coping strategies and improve general wellbeing. Moreover, this study identified different populations at risk (women, young individuals, students, psychiatric/neurological patients, etc.) for specific psychological distress that should be carefully attended, as the pandemic is expected to have long-term consequences on mental health (Brooks et al., 2020; Holmes et al., 2020; Rogers et al., 2020).
4.2. Strengths and limitations
Overall, our results are in line with previous reports on the effects of social isolation and quarantine on mental health (Blendon et al., 2004; Cao et al., 2020; Lai et al., 2020; Marjanovic et al., 2007; Rubin and Wessely, 2020), which indicate that individuals suffer from significant levels of anxiety and depression. However, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to explore a wide range of symptoms using latent-class analysis and to evaluate risk/protective factors (individual characteristics, context, and state/trait measures) along with possible mechanisms on psychological distress. Moreover, we implemented a small replication study, with robust and cross-validated techniques to improve inference precision. However, the current study has several limitations. First, despite the large sample used (n = 4408), most of our respondents were women and highly educated individuals. Additionally, there were fewer lower-class and young individuals relative to the other categories. Second, psychological distress was not contrasted with related measures of interest, such as general wellbeing or level of functional impairment. Finally, there was no comparison group nor baseline measures. Future research should include more representative samples and track psychological distress in longitudinal studies, to analyze mental health trajectories in time. More importantly, it is unclear if individuals with high levels of psychological distress during quarantine could develop stable mental disorders or whether some of them will eventually return to their normal baseline. Finally, measures related to physical health such as blood pressure or weight, are also recommended as they could be associated with mental-health outcomes (Cappeliez et al., 2004; Ojike et al., 2016).
Conclusions
We demonstrated that psychological distress in quarantined people differs in terms of the degree of severity, instead of the type of symptomatology. However, most individuals experienced moderate-severe levels of psychological distress (more specifically anxiety, depression, hostility, phobic symptoms, sleep disturbances, etc.) which resembles some characteristics of stress-related disorders. Finally, we found risk and protective factors associated with mental health outcomes and showed the critical role of COVID-19-related fear and coping skills mediating between those factors and psychological distress levels.
Funding/Support
This work was supported by Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica PICT 2016–0243 (MEP) and Fleni, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Role of the funder/sponsor
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author´s contributions
Concept and design: RSF, LC, NMG; Acquisition and interpretation of the data: RSF, LC, NMG; Drafting the manuscript: RSF; Critical revision of the manuscript: RSF, LC, NMG, RFA, MEP; Statistical analysis: RSF, Supervision: MEP.
Data availability
The datasets obtained in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Declaration of Competing Interest
None reported.
Acknowledgment
We thank Mariano Boccia and Damian Testori for critical comments.
Footnotes
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.07.133.
Appendix. Supplementary materials
References
- Arias González V.B., Crespo Sierra M.T., Arias Martínez B., Martínez-Molina A., Ponce F.P. An in-depth psychometric analysis of the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale: calibration with Rasch-Andrich model. Health Qual. Life Outcomes. 2015;13:154. doi: 10.1186/s12955-015-0345-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai Y., Lin C.-.C., Lin C.-.Y., Chen J.-.Y., Chue C.-.M., Chou P. Survey of stress reactions among health care workers involved with the SARS outbreak. Psychiatr. Serv. Wash. DC. 2004;55:1055–1057. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.55.9.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry V., Stout M.E., Lynch M.E., Mattis S., Tran D.Q., Antun A., Ribeiro M.J., Stein S.F., Kempton C.L. The effect of psychological distress on health outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. J. Health Psychol. 2020;25:227–239. doi: 10.1177/1359105319842931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck A.T., Dozois D.J. Cognitive therapy: current status and future directions. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011;62:397–409. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-052209-100032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ezra M., Sun S., Hou W.K., Goodwin R. The association of being in quarantine and related COVID-19 recommended and non-recommended behaviors with psychological distress in Chinese population. J. Affect. Disord. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.06.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blendon R.J., Benson J.M., DesRoches C.M., Raleigh E., Taylor-Clark K. The public's response to severe acute respiratory syndrome in Toronto and the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2004;38:925–931. doi: 10.1086/382355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks S.K., Webster R.K., Smith L.E., Woodland L., Wessely S., Greenberg N., Rubin G.J. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence. Lancet. 2020;395:912–920. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30460-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byles J.E., Robinson I., Banks E., Gibson R., Leigh L., Rodgers B., Curryer C., Jorm L. Psychological Distress and Comorbid Physical Conditions: disease or Disability? Depress. Anxiety. 2014;31:524–532. doi: 10.1002/da.22162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao W., Fang Z., Hou G., Han M., Xu X., Dong J., Zheng J. The psychological impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on college students in China. Psychiatry Res. 2020;287 doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.112934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappeliez P., Sèvre-Rousseau S., Landreville P. Physical health, subjective health, and psychological distress in older adults: Reciprocal relationships concurrently and over time. Ageing Int. 2004;29:247–266. doi: 10.1007/s12126-996-1001-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Casullo M., Pérez M. El inventario de síntomas SCL-90-R de L. Derogatis. Univ. B. Aires. 2004 [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q., Liang M., Li Y., Guo J., Fei D., Wang L., He L., Sheng C., Cai Y., Li X. Mental health care for medical staff in China during the COVID-19 outbreak. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;7:e15–e16. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30078-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C., Dong D., He J., Zhong X., Yao S. Psychometric properties of the 10-item Connor–Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC-10) in Chinese undergraduates and depressive patients. J. Affect. Disord. 2020;261:211–220. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor K.M., Davidson J.R. Development of a new resilience scale: the Connor-Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC) Depress. Anxiety. 2003;18:76–82. doi: 10.1002/da.10113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J.D., Bickman L. Social support and psychological symptomatology following a natural disaster. J. Trauma. Stress. 1990;3:541–556. doi: 10.1002/jts.2490030406. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- De Kloet E.R., Joëls M., Holsboer F. Stress and the brain: from adaptation to disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005;6:463–475. doi: 10.1038/nrn1683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derogatis, L.R., Derogatis, L., 2001. Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI). Administration, scoring, and procedures manual.
- Derogatis L.R., Melisaratos N. The brief symptom inventory: an introductory report. Psychol. Med. 1983;13:595–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desclaux A., Badji D., Ndione A.G., Sow K. Accepted monitoring or endured quarantine? Ebola contacts’ perceptions in Senegal. Soc. Sci. Med. 2017;178:38–45. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.02.009. 1982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau A., Marchand A., Beaulieu-Prévost D. Epidemiology of psychological distress. Ment. Illnesses - Underst. Predict. Control. 2012 doi: 10.5772/30872. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis B.J., Del Giudice M. Developmental adaptation to stress: an evolutionary perspective. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019;70:111–139. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-122216-011732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett E.S., Zeger S.L. Latent class model diagnosis. Biometrics. 2000;56:1055–1067. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.01055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenaars J.A., McCutcheon A.L. Cambridge University Press; 2002. Applied Latent Class Analysis. [Google Scholar]
- Hand D.J., Till R.J. A simple generalisation of the area under the ROC curve for multiple class classification problems. Mach. Learn. 2001;45:171–186. [Google Scholar]
- Holden L., Scuffham P., Hilton M., Vecchio N., Whiteford H. Psychological distress is associated with a range of high-priority health conditions affecting working Australians. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health. 2010;34:304–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-6405.2010.00531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes E.A., O'Connor R.C., Perry V.H., Tracey I., Wessely S., Arseneault L., Ballard C., Christensen H., Silver R.C., Everall I., Ford T., John A., Kabir T., King K., Madan I., Michie S., Przybylski A.K., Shafran R., Sweeney A., Worthman C.M., Yardley L., Cowan K., Cope C., Hotopf M., Bullmore E. Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: a call for action for mental health science. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;7:547–560. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30168-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu T., Zhang D., Wang J. A meta-analysis of the trait resilience and mental health. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2015;76:18–27. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2014.11.039. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Iw M., Cm C., Pc P., Mg Y., Sc H., Vl C. Risk factors for chronic post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in SARS survivors. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry. 2010;32:590–598. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2010.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R.C., Green J.G., Gruber M.J., Sampson N.A., Bromet E., Cuitan M., Furukawa T.A., Gureje O., Hinkov H., Hu C.-.Y., Lara C., Lee S., Mneimneh Z., Myer L., Oakley-Browne M., Posada-Villa J., Sagar R., Viana M.C., Zaslavsky A.M. Screening for serious mental illness in the general population with the K6 screening scale: results from the WHO World Mental Health (WMH) survey initiative. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2010;19(Suppl 1):4–22. doi: 10.1002/mpr.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotov R., Gamez W., Schmidt F., Watson D. Linking “big” personality traits to anxiety, depressive, and substance use disorders: a meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2010;136:768–821. doi: 10.1037/a0020327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J., Ma S., Wang Y., Cai Z., Hu J., Wei N., Wu J., Du H., Chen T., Li R., Tan H., Kang L., Yao L., Huang M., Wang H., Wang G., Liu Z., Hu S. Factors Associated With Mental Health Outcomes Among Health Care Workers Exposed to Coronavirus Disease 2019. JAMA Netw. Open. 2020;3:e203976. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, R.S., 1966. Psychological stress and the coping process.
- Marjanovic Z., Greenglass E.R., Coffey S. The relevance of psychosocial variables and working conditions in predicting nurses’ coping strategies during the SARS crisis: an online questionnaire survey. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2007;44:991–998. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2006.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojike N., Sowers J.R., Seixas A., Ravenell J., Rodriguez-Figueroa G., Awadallah M., Zizi F., Jean-Louis G., Ogedegbe O., McFarlane S.I. Psychological Distress and hypertension: results from the national health interview survey for 2004–2013. Cardiorenal Med. 2016;6:198–208. doi: 10.1159/000443933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereda N., Forns M., Peró M. Dimensional structure of the brief symptom inventory with Spanish college students. Psicothema. 2007;19:634–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M.R. Is distress a symptom of mental disorders, a marker of impairment, both or neither? World Psychiatry Off. J. World Psychiatr. Assoc. WPA. 2009;8:91–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammstedt B. The 10-item Big Five Inventory: Norm values and investigation of sociodemographic effects based on a German population representative sample. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2007;23(3):193–201. doi: 10.1027/1015-5759.23.3.193. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rammstedt B., John O.P. Measuring personality in one minute or less: a 10-item short version of the Big Five Inventory in English and German. J. Res. Personal. 2007;41:203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J.P., Chesney E., Oliver D., Pollak T.A., McGuire P., Fusar-Poli P., Zandi M.S., Lewis G., David A.S. Psychiatric and neuropsychiatric presentations associated with severe coronavirus infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis with comparison to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;0 doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30203-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G.J., Wessely S. The psychological effects of quarantining a city. BMJ. 2020;368:m313. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar A., Hamer M., McMunn A., Steptoe A. Social isolation and loneliness: relationships with cognitive function during 4 years of follow-up in the english longitudinal study of ageing. Psychosom. Med. 2013;75:161–170. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e31827f09cd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T.-.P., Lien T.-.C., Yang C.-.Y., Su Y.L., Wang J.-.H., Tsai S.-.L., Yin J.-.C. Prevalence of psychiatric morbidity and psychological adaptation of the nurses in a structured SARS caring unit during outbreak: a prospective and periodic assessment study in Taiwan. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007;41:119–130. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2005.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomitaka S., Kawasaki Y., Ide K., Akutagawa M., Ono Y., Furukawa T.A. Distribution of psychological distress is stable in recent decades and follows an exponential pattern in the US population. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:11982. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47322-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu P., Fang Y., Guan Z., Fan B., Kong J., Yao Z., Liu X., Fuller C.J., Susser E., Lu J., Hoven C.W. The psychological impact of the SARS epidemic on hospital employees in China: exposure, risk perception, and altruistic acceptance of risk. Can. J. Psychiatry Rev. Can. Psychiatr. 2009;54:302–311. doi: 10.1177/070674370905400504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323:1239–1242. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou H., Hastie T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B. 2005;67:301–320. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets obtained in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request.