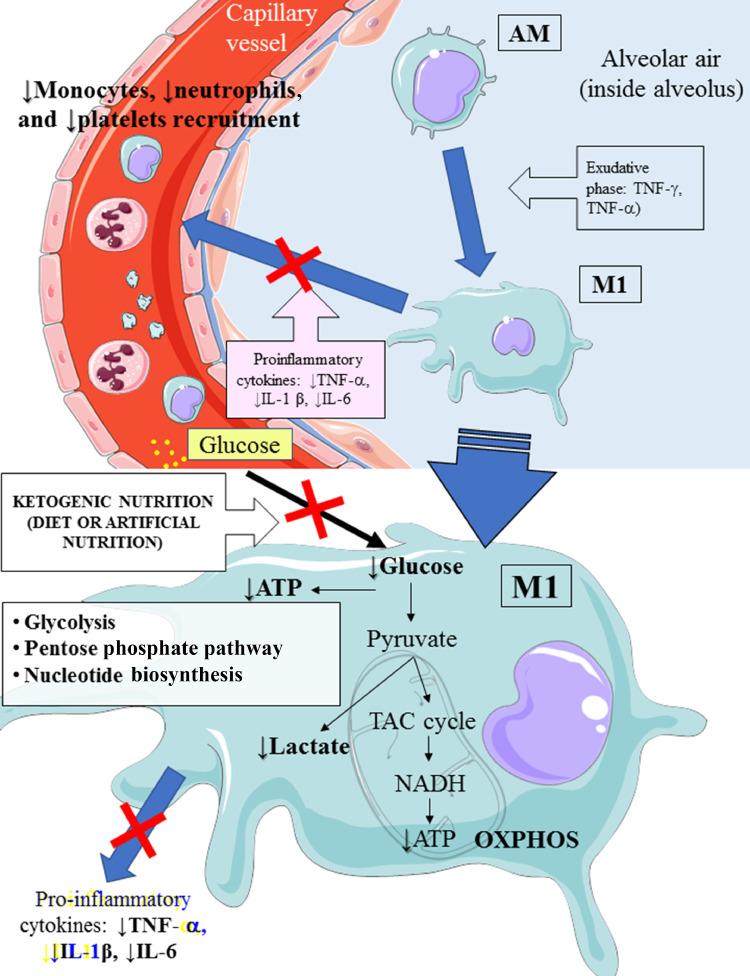
Fig. 2.
Hypothetical attenuation of phagocyte hyperactivation by means of an EKD. An EKD could reduce glucose availability for aerobic glycolysis (Warburg-like effect) in M1 macrophages. The main target of this approach is to inhibit M1 phagocyte hyperactivation, which provokes the overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-1 β), leading to excessive accrual of monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets from the blood. AM, alveolar quiescent macrophage; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; EKD, eucaloric ketogenic diet; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; M1, activated macrophage; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; TAC cycle,tricarboxylic acid cycle ; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. This figure was drawn adapting the vector image form the Servier Medical Art bank (http://smart.servier.com/). Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).