Abstract
Purpose:
To determine whether FDG PET can expand eligibility in biomarker-selected clinical trials by providing a means to quantitate response in patients with non-assessable disease by RECIST.
Experimental Design:
SUMMIT (NCT01953926) is a multicenter phase II “basket” trial of the Pan-HER kinase inhibitor, neratinib. Patients had advanced ERBB2 (HER2)-mutant solid tumors, ≥ 1 measurable lesion, preferably defined unidimensionally by RECIST v1.1, or alternatively metabolically by PET Response Criteria (PRC). The primary aim was to determine the proportion of additional breast cancer patients accrued using PRC who would have otherwise been ineligible based on RECIST criteria alone. The secondary aim was to determine the concordance of response versus non-response between RECIST and PRC.
Results:
Eighty-one patients with HER2-mutant metastatic breast cancer were accrued; 77 were evaluable for response by RECIST and/or PRC. 63 (82%) were RECIST-evaluable and 14 (18%) were accrued using PRC alone. Bone-only disease (n = 11; 79%) was the most common reason for classification as non-measurable by RECIST. Twenty-nine patients were accrued and followed using both criteria, of which 25 (86%; 95% confidence interval, 68%–96%) were concordant for response versus non-response as defined by RECIST and PRC.
Conclusions:
PRC allowed patients with non-RECIST measurable disease access to therapy and facilitated more rapid accrual of patients to this trial of a rare biomarker. PRC and RECIST both provided methods of response assessment and were generally concordant. Thus, PRC was useful as a supplement to RECIST criteria. This provides a rationale for including FDG PET measurements in future clinical trials involving rare tumors or rare genomically defined subpopulations of more common cancers.
Introduction
Defining tumor burden is an essential component of oncology clinical trials, both for determining trial eligibility and for measuring treatment response (1). Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) is a system for quantifying tumor burden that focuses primarily on tumor size (2, 3). RECIST has become the standard for oncology clinical trials because it is easily implemented, applicable in a wide array of solid tumors, and accepted as a surrogate endpoint for drug approval in rare patient populations (1).
Despite the utility of RECIST, it has several important limitations. Target lesions are often selected on the basis of being amenable to repeated unambiguous measurement rather than on a clinical determination of which are most likely to cause morbidity or mortality for the patient. Moreover, tumor size is recorded unidimensionally and may therefore imperfectly reflect therapy response (2–5). Additional, interrater reliability of RECIST assessment is highly dependent on selection of target lesions (6). Furthermore, patients with advanced cancers may never develop disease that is measurable by RECIST. Often, this is due to bone-predominant disease, as is common in prostate and breast cancers, as osseous lesions are not measurable using RECIST criteria. A significant subset of patients with these common cancers have historically been ineligible for enrollment into most clinical trials and consequently been denied access to potentially beneficial therapy. As the presence of osseous only disease may co-associate with molecular subtypes (7), trial populations defined by the presence of RECIST measurable disease may not be reflective of the genetic diversity of patients seen in the clinic. Overall, these limitations suggest that opportunities for alternative measures of tumor burden should be considered in specific situations.
Although RECIST focuses on tumor size, other tumor characteristics may be used to monitor treatment response.18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) Positron-emission tomography (PET) can be used to monitor response to cancer treatments by measuring changes in tumor metabolism (8, 9). Indeed, in patients with lymphoma, FDG-PET has become the standard method for measuring tumor burden in both routine clinical practice and clinical trials (10, 11). For solid tumors, although routine clinical use of FDG-PET has grown, it has not been widely used for response assessment in clinical trials.
SUMMIT (NCT01953926) is an international, multicenter “basket” study evaluating the efficacy of the pan-HER kinase inhibitor neratinib in multiple indications, including patients with HER2-mutant solid tumors (12). As HER2 mutations are rare in solid tumors, with an estimated incidence of 3% in breast cancers (13) and similar low rates in other malignancies, SUMMIT was designed from the outset to enable enrollment and response evaluation on the basis of PET scans. To date, breast cancer represents the tumor type with the largest number of patients enrolled into SUMMIT. Patients with metastatic breast cancer often have bone-predominant disease providing the unique opportunity to evaluate the impact of incorporating PRC into the core eligibility and design of a precision medicine study targeting a rare genomic population (14).
Here, we report the utility of using PET Response Criteria (PRC) to supplement RECIST in the identification of patients eligible for trial accrual, and the impact of PET on assessing treatment response in a clinical trial focused on a rare molecularly defined population.
Materials and Methods
Study design
The design of the neratinib basket study (SUMMIT) has been previously described in detail (12). Given that breast cancer accounted for the largest patient population on SUMMIT, and to help ensure homogeneity of patient characteristics with the goal of permitting meaningful analysis of the data obtained using RECIST and PRC, this analysis was limited to patients with breast cancer. The patients with HER2-mutant breast cancer analyzed here were accrued from 15 medical centers worldwide. Accrual began on September 30, 2013, and the data cutoff for the analysis was June 22, 2018. Eligibility criteria for the breast cancer cohorts included male and female patients ages ≥18 years, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0–2, adequate hepatic and kidney function, and left ventricular ejection fraction of ≥50%. Patients were eligible to enroll regardless of hormone receptor status.
Depending on date of enrollment and hormone receptor status, patients received neratinib 240 mg daily on a continuous basis, either as monotherapy or in combination with fulvestrant (500 mg intramuscularly once every 2 weeks for 4 weeks, then once every 4 weeks). Patients were treated until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or withdrawal of consent.
The study complied with the International Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical Research Involving Human Subjects, Good Clinical Practice guidelines, the Declaration of Helsinki, and local laws and was approved by the institutional review boards of all institutions. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Determining trial eligibility and measurement of treatment response
Tumor measurements were performed every 8 weeks using computed tomography (CT), MRI, and/or FDG-PET/CT. The FDG PET/CT procedure was aligned across centers, following published uniform procedural guidelines (15), including quality control of FDG, instrumentation specifications, and patient preparation. Trial eligibility and subsequent measurement of treatment response was primarily performed according to RECIST version 1.1 (3). In patients whose disease was not measurable by RECIST, disease could be defined as trial eligible, and treatment response followed, using PRC, a modified version of PERCIST (8), as previously described (Supplementary Appendix Box SA1; ref. 16). Briefly, in PRC, the18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) avidity of each lesion is calculated as: Standardized uptake values (SUV) SUVcorrected for background = SUVmax lesion – SUVmax liver background. Values < 0 were treated as 0. This allows the FDG avidity of the lesion to be considered as the excess avidity above background. Complete metabolic response was defined as all lesions reduced to, at, or below SUVmax liver background. Partial metabolic response and progressive metabolic disease were defined as 30% decrease or increase in the sum of SUVs, respectively. This modification was utilized to deal with the issue of multi-scanner sites, where the PERCIST requirement of liver background reproducibility of 20% on all follow-up scans may cause scans to be deemed ineligible for analysis.
In Amendment 3 (finalized March 17, 2015) of the protocol, patients were optionally permitted, at their own and their treating physician’s discretion, to be followed by both RECIST and PRC; in such cases, RECIST was used as the primary criteria for determining response. In Protocol Amendment 4 (finalized May 20, 2016), PET assessment was mandatory for all patients with breast cancer. Patients with no baseline PET/CT scan were followed using RECIST only. Four patients had no liver background standard uptake values (SUV) reported and their responses were calculated without this information.
Statistical analysis
For patient demographics, medians and ranges were used to summarize continuous variables and percentages were used to summarize categorical variables.
The primary aim of this analysis was to determine the incremental number of patients eligible for accrual and measurement of treatment response as a result of the use of PET criteria when disease was not measurable using RECIST.
In patients followed by both RECIST and PRC, concordance in overall response was evaluated as a secondary aim. For this analysis, response was defined as a complete response (CR) or partial response (PR), and non-response as stable disease (SD) or progressive disease (PD). Overall response included patients with CR and PR. Patients non-evaluable for response were not included in the analysis. The 95% confidence interval for concordance of response (CR/PR) and non-response (SD/PD) was calculated using the Clopper exact method.
Results
Patients and measurability according to RECIST and PRC
A total of 81 patients with breast cancer and somatic HER2 mutations were enrolled in SUMMIT as of June 22, 2018. Age of patients ranged from 37 to 87 years (mean 60 years). All were metastatic with a median number of prior therapies in the metastatic setting of 3 (range 0 to11 therapies) and a median time from first metastasis of 2.3 years (range 0.1 to 11.5 years). Patient demographics are summarized in Table 1. Four of 81 patients (5%) did not have post-baseline RECIST or PRC assessments; thus 77 patients (95%) were evaluable for response using RECIST, PRC, or both (Fig. 1). Of the 77 efficacy evaluable patients, 63 (82%) were evaluable by RECIST and 43 (56%) were evaluable by PRC; 34 (44%) were followed using RECIST only, 14 (18%) were followed using PRC only, and 29 patients (38%) were followed using both RECIST and PRC.
Table 1.
Patient demographics
| Total | RECIST Only | RECIST and PET | PET Only | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 77) | (n = 34) | (n = 29) | (n = 14) | |
| Mean age, years (range) | 60 (37–87) | 59 (44–87) | 60 (37–79) | 62 (45–76) |
| Sex, n (%) | ||||
| Female | 75 (97) | 33 (97) | 29 (100) | 13 (93) |
| Male | 2 (3) | 1 (3) | 0 | 1 (7) |
| Race, n (%) | ||||
| White | 68 (88) | 29 (85) | 25 (86) | 14 (100) |
| Asian | 3 (4) | 1 (3) | 2 (7) | 0 |
| Black/African American | 3 (4) | 3 (9) | 0 | 0 |
| Other | 2 (3) | 0 | 2 (7) | 0 |
| Unknown | 1 (1) | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 |
| Disease location at enrollment, n (%) | ||||
| Visceral tumor | 57 (74) | 29 (85) | 26 (90) | 2 (14) |
| Bone metastasis | 24 (31) | 6 (18) | 11 (38) | 7 (50) |
| Median No. of prior therapies in metastatic setting (range) | 3 (0–11) | (0–9) | 2 (0–11) | 2 (0–7) |
| Median time from first metastasis to enrollment, years (range) | 2.3 (0.1–11.5) | 2.8 (0.3–11.5) | 2.0 (0.2–10.8) | 1.4 (0.1–3.6) |
Abbreviations: PRC, PET Response Criteria; RECIST, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors.
Figure 1.
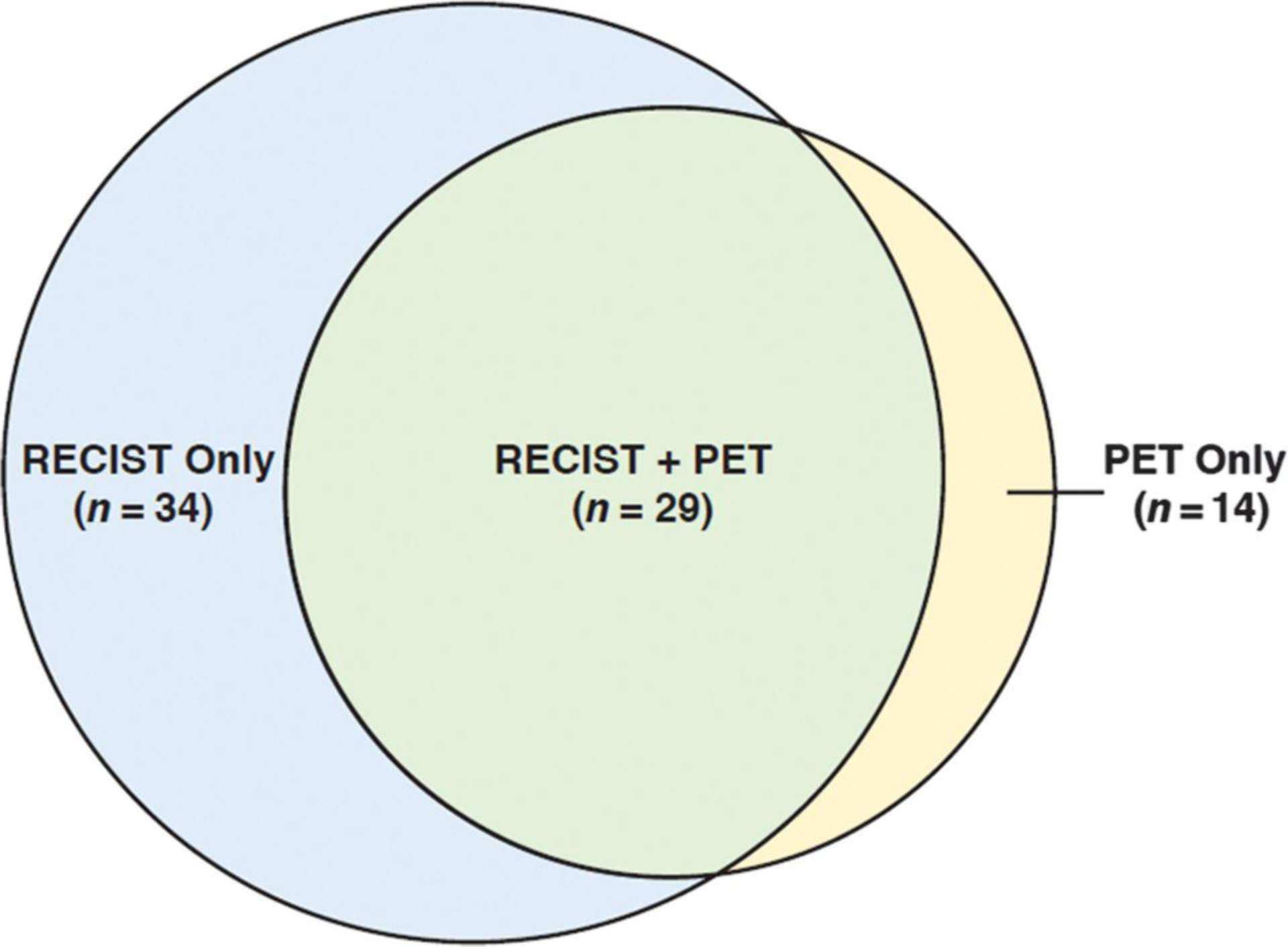
Use of RECIST, PRC, and both sets of criteria in assessing eligibility and measurability in patients in SUMMIT. Venn diagram. PRC, PET Response Criteria; RECIST, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors.
Responses according to RECIST and PRC are summarized in Table 2. At the data cutoff, 64 patients (83%) had discontinued treatment, 61 (79%) as a result of disease progression; 13 patients (17%) remained on therapy (Table 3).
Table 2.
Response to treatment
| RECIST and PET | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RECIST Only | (n = 29) | PET Only | ||
| Response, n (%) | (n = 34) | RECIST | PRC | (n = 14) |
| Overall response rate (PR and CR) | 8 (24) | 16 (55) | 18 (62) | 9 (64) |
| Best overall response | ||||
| Complete response | 2 (6) | 2 (7) | 9 (31) | 5 (36) |
| Partial response | 6 (18) | 14 (48) | 9 (31) | 4 (29) |
| Stable disease | 12 (35) | 10 (35) | 8 (28) | 2 (14) |
| Progressive disease | 14 (41) | 3 (10) | 3 (10) | 3 (21) |
Abbreviations: PRC, PET Response Criteria; RECIST, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors.
Table 3.
Patient disposition
| Total | RECIST Only | RECIST and PET | PET Only | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, n (%) | (n = 77) | (n = 34) | (n = 29) | (n = 14) |
| Enrolled and received study drug | 77 (100) | 34 (100) | 29 (100) | 14 (100) |
| Received study drug and continuing on treatment | 13 (17) | 2 (6) | 7 (24) | 4 (29) |
| Ended treatment | 64 (83) | 32 (94) | 22 (76) | 10 (71) |
| Disease progression | 61 (79) | 29 (85) | 22 (76) | 10 (71) |
| Other reason | 3(4) | 3 (9) | 0 | 0 |
| Ended study | 41 (53) | 23 (68) | 13 (45) | 5 (36) |
| Death | 35 (45) | 17 (50) | 13 (45) | 5 (36) |
| Withdrawal of consent | 3 (4) | 3 (9) | 0 | 0 |
| Lost to follow-up | 2(3) | 2 (6) | 0 | 0 |
| Other | 1 (1) | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 |
Abbreviations: PRC, PET Response Criteria; RECIST, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors.
Patients evaluated by RECIST Only
Thirty-four of the 63 patients (54%) followed by RECIST did not have a PET/CT scan at baseline or follow-up and were followed using RECIST alone. The overall response rate (ORR) in these 34 patients was 24%. The best overall response (BOR) in these patients was CR in 2 patients, PR in 6, and SD in 12 patients; the remaining 14 patients had PD as best response.
Patients evaluated by both RECIST and PRC
Twenty-nine of the 63 patients with breast cancer (46%) with RECIST-measurable disease had a PET/CT scan at baseline and at least one follow-up PET/CT scan. All 29 patients had measurable disease by PRC, allowing secondary evaluation of treatment response by PRC and a comparison of the primary BOR determined by RECIST and by PRC. Responses in patients with disease that was measurable using RECIST and PRC are shown in Fig. 2. In total, 25 of 29 (86%; 95% CI, 68%–96%) of patients were concordant for response versus non-response as measured by RECIST and PRC at the individual patient level. This included 2 patients with CR, 6 with PR, 7 with SD, and 3 with PD using both RECIST and PRC criteria, as well as 7 patients with a PR by RECIST and a CR by PRC. The remaining four patients (14%) were discordant with regards to response versus non-response. In 3 patients, BOR was SD by RECIST but PR by PRC. Conversely, one patient had a BOR that was better by RECIST than by PRC (PR vs. SD; Fig. 3, patient 29). Of note, patients 2, 4, and 10 demonstrated progression in non-target lesions, and patient 23 demonstrated a RECIST PR due to a non-target lesion.
Figure 2.

Concordant and discordant best overall response measurements between RECIST and PRC. BOR, best overall response based on tumor measurements per RECIST v1.1 or PRC; CR, complete response; PD, progressive disease; PET, positron-emission tomography; PR, partial response; PRC, PET Response Criteria; RECIST, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors; SD, stable disease. Dotted line at −30% change distinguishes stable disease from response in target lesions.*, Change <2 SUV units. †, 0% change in target lesion measurement.
Figure 3.
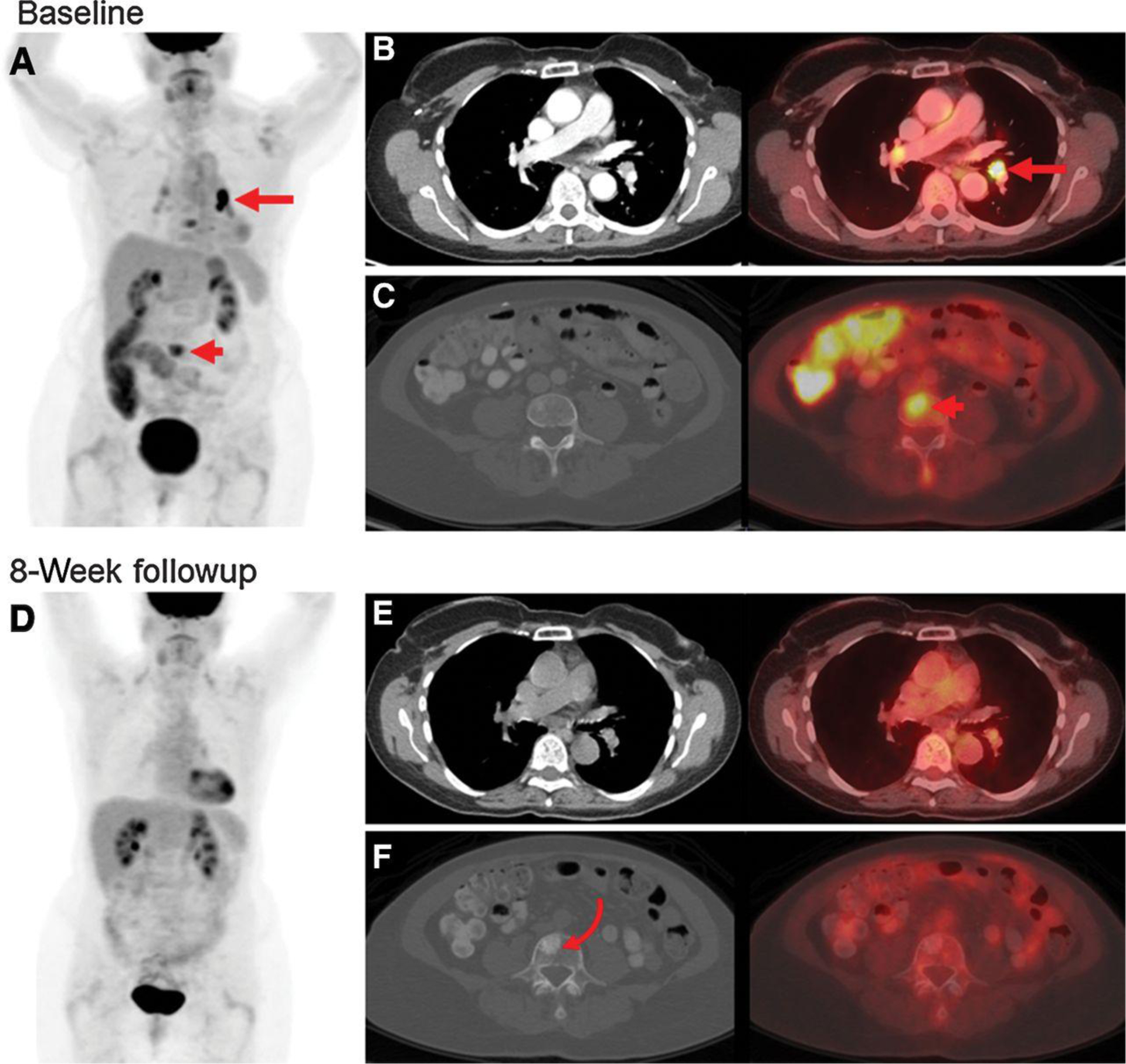
Measurable disease by PRC but not RECIST in a 70-year-old woman with HER2-mutant breast cancer. A, PET MIP image at baseline demonstrates FDG-avid lesions in the chest (arrow) and abdomen (arrowhead). B, Corresponding axial contrast-enhanced CT and fused PET/CT images of the chest demonstrate a thoracic FDG focus localized to a left hilar node (arrow) 8 mm in short axis on CT. This node was measurable by PRC but not by RECIST. C, Corresponding axial CT and fused PET/CT images of the abdomen demonstrate an abdominal FDG focus localized to a vertebral body (arrowhead) without clear correlate on CT. This osseous lesion was measurable by PRC but not by RECIST. D, PET MIP at 8-week follow-up demonstrates decrease of all FDG foci to background, representing a complete metabolic response. Corresponding axial images in the chest (E) and abdomen (F) confirm decrease to background FDG avidity. There was a sclerotic lesion at the prior FDG-avid osseous metastasis (curved arrow), which could have been mistaken for a new osseous metastasis without the corresponding PET. CT, computed tomography; FDG, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose; MIP, maximum intensity projection; PET, positron-emission tomography; PRC, PET Response Criteria; RECIST, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors.
Patients evaluated by PRC Only
An additional 14 patients were eligible for the SUMMIT trial due to the use of PRC to measure response, a 22% (14/63) increase over the 63 patients evaluable by RECIST. Of the 14 patients whose treatment response could be assessed by PRC alone, 11 had FDG-avid bone-only disease that was not apparent on CT, two had FDG-avid bone and liver disease that was not apparent on CT, and one had FDG-avid bone and nodal disease that was not apparent on CT (Fig. 3). PRC allowed effective measurement of tumor response in the absence of RECIST-measurable disease in all 14 patients. The ORR in these 14 patients was 64%, with 5 achieving a CR, 4 PR, 2 SD, and 3 with PD as BOR.
Discussion
HER2 mutations have been identified in the tumors of 3% to 6% of patients with breast cancer (13, 17, 18), making it challenging to accrue to clinical trials targeting this rare molecularly defined patient population. Here, we leveraged an ongoing multicenter basket trial of the HER kinase inhibitor neratinib (SUMMIT) to determine the clinical utility of using PRC to expand the population of eligible patients. RECIST was the primary method used to quantitate measurable disease and define trial eligibility; however, utilization of PRC as a secondary determinant of measurable disease for study eligibility led to a 22% increase in accrual of patients with HER2-mutant breast cancer. Any response criteria under consideration as a supplement to RECIST must provide a clear advantage over this established and widely used response criteria (2). Our data suggest that PRC can help accelerate accrual of a rare genetically defined patient population such as those with HER2-mutant breast cancer. In addition, use of PRC can allow patients with non-RECIST measurable disease access to therapy on clinical trials that otherwise would have been denied. These data provide strong rationale for including PRC in future clinical trials involving rare tumors or rare genomically defined subpopulations of more common cancers.
The potential utility of using PRC in clinical trials is not limited to accelerating patient accrual or broadening patient eligibility. Patients with RECIST non-measurable disease, such as those with metastatic breast cancer and bone-only metastases, are frequently seen in the clinic yet have been historically excluded from enrollment and/or efficacy assessment in clinical trials. In a pooled analysis of data from 13 prospective clinical trials of patients with metastatic breast cancer (n = 10,521), 12.5% of patients in these trials had bone-only metastases (19), and thus were non-measurable by RECIST. A quantitative criterion that uses PET to assess metabolic response may allow recruitment into clinical trials of patients more representative of those seen in the clinic. This could be particularly applicable to estrogen receptor positive cancers, which demonstrate a tendency to metastasize to bone. In addition, tumor response in bone has been shown to be better monitored by FDG PET/CT than CT and MR (20, 21). The use of PRC in this respect in similar to prior attempts to quantify disease in bone-predominant breast cancer with circulating tumor cells (CTC; refs. 22–25). Of note, CTCs are known to correlate with FDG PET (23, 25).
Successful accrual of patients into a trial is not sufficient to warrant usage of a method to measure disease status in trials of novel therapeutics; effectiveness in measuring tumor response is also critical. In this limited series of patients, PRC identified responders and non-responders to treatment with neratinib and was able to categorize patients for CR, PR, SD, and PD, analogous to RECIST. Considering all responses (CR + PR), concordance in the 29 patients evaluated by both criteria was 86%. Although additional studies will be needed to further support the utilization of FDG-PET to measure tumor response, an area of continued research and refinement, these preliminary results are promising and suggest efficacy data generated using PRC in patients with RECIST non-measurable disease can be useful in guiding drug development decisions (8, 11).
We did note that BOR was more favorable when measured by PRC as compared with RECIST in a subset of patients. As demonstrated in Fig. 2, 3 patients with a BOR of SD by RECIST had a PR by PRC. In addition, 7 patients with a BOR of PR by RECIST had a CR by PRC. Several of the discordant results were a result of a greater percentage decrease in FDG-PET measurements of target lesions compared with the percentage of change in the size of lesions. Furthermore, residual lesions on CT that would preclude a RECIST CR may decrease to background on FDG-PET, resulting in an apparently better response according to PRC than by RECIST. Although this difference is noteworthy and should be recognized when comparing RECIST and PRC results, delineating between partial versus complete response has generally not been considered clinically meaningful in studies evaluating agents used in the advanced/metastatic solid tumors where cure is not currently achievable.
PRC was used as a modification of the well-known PERCIST criteria (8). Several other response criteria using FDG PET have been utilized, including EORTC, iPERCIST, and others (26, 27). We used this modification due to the issue of multi-scanner sites where patients may not be scanned on the same scanner at all time points, which could cause to PERCIST requirement of liver backgrounds within 20% on all scans to cause patients and scans to become ineligible for analysis.
Some limitations of this analysis warrant consideration. It was not possible to formally assess differences in time to progression (TTP) in patients followed using both RECIST and PRC because not all patients with PD according to RECIST at a specific time point underwent PET/CT at that time. Consequently, RECIST- and PRC-determined TTP could not be calculated for all patients. Performing RECIST and PRC evaluations at all time points would have allowed a comparison of TTP according to RECIST and PRC. Inclusion of only patients with breast cancer, a disease where bone predominant disease is relatively common, was another limitation of this analysis; the incremental utility of PRC may be attenuated in studies enriched for patients with other tumor types. All methods of measuring tumor response have limitations. For PRC and other methods based on FDG PET, low grade malignancies may not express sufficient FDG-avidity to be appreciated on FDG PET, although for this trial HER2-mutant breast cancers are normally FDG-avid. Biologic and technical factors of FDG PET are known to affect SUV values (8, 15).
Although RECIST has become the standard for defining response in clinical trials of solid tumors, it has important and well-recognized limitations. Many patients with advanced cancers, including those with breast, prostate and ovarian cancer, often spend the entire course of their illness and eventually die of their disease, without ever developing RECIST measurable lesions. As such, clinical trial populations defined by a requirement for RECIST measurable disease may not be entirely reflective of the broader population of patients. Moreover, genome-driven studies are increasing targeting rare genomic subpopulations in oncology. The ability to accrue and learn from all patients harboring these rare and highly relevant genomic biomarkers, without artificially limiting enrollment to patients with RECIST measurable disease, will be increasingly critical to the success of these studies and the field in general. Using PRC to supplement RECIST in the SUMMIT trial provided an advantage in assessing patient eligibility and measuring treatment response in patients in rare HER2-mutant breast cancers. Use of PRC can allow patients with non-RECIST measurable disease access to therapy on clinical trials that otherwise would have been denied. Responses were concordant between PRC and RECIST in 86% of patients. The ability to offer trial assess for patients with RECIST non-measurable disease, as well as the ability to facilitate more rapid accrual of patients with a rare biomarker, suggest PRC could be used as a supplement to RECIST in clinical trials of rare tumors, a proposal which should be evaluated in further studies.
Key message
PET response criteria can facilitate more rapid accrual of patients to clinical trials of rare biomarkers and allows patients with non-RECIST measurable disease access to therapy on these trials. This provides a rationale for including FDG PET measurements in future clinical trials involving rare tumors or rare genomically defined subpopulations of more common cancers.
Translational Relevance.
Despite the utility of RECIST, it has limitations. Patients with advanced cancers may never develop disease that is measurable by RECIST. Often, this is due to bone-predominant disease, as seen in breast or prostate cancers, as osseous lesions are not measurable by RECIST. Here, we report the utility of using PET Response Criteria (PRC) to supplement RECIST in the identification of eligible patients in a multicenter phase II “basket” trial of neratinib for rare HER2-mutant malignancies (SUMMIT). PRC allowed recruitment of patients with RECIST non-measurable disease that otherwise would have been denied access to the trial, augmented patient enrollment, and provided response assessments analogous to REICST. These data provide strong rationale for including FDG PET measurements as a supplement to RECIST in future clinical trials of rare tumors or rare genomically defined subpopulations of more common cancers.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded in part through the NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30 CA008748 and Cycle for Survival. This work was supported by Puma Biotechnology. The authors thank the patients and families for participating in this study. Editorial support was provided by Lee Miller.
Footnotes
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
G.A. Ulaner is an employee/paid consultant for Sanofi, and reports receiving commercial research grants from Puma. C. Saura is an advisory board member/unpaid consultant for Puma Biotechnology. S.A. Piha-Paul reports receiving other commercial research support from Abbvie, Aminex Therapeutics, Bio-Marin Pharmaceutical, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Cerulean Pharma, Chugai, Curis, Five Prime Therapeutics, Genmab A/S, GlaxoSmithKline, Helix BioPharma, Incyte, Jacobi Pharmaceuticals, Medimmune, Medication, Merck Sharp and Dohme, NewLink Genetics Corp/Blue Link Pharmaceuticals, NewLink Genetics/Blue Link, Novartis, Pieris, Pfizer, Principia, Puma, Rapt, Seattle Genetics, Taiho, Tesaro, TransThera Bio, and XuanZhu Biopharma, I. Mayer is an employee/paid consultant for Eli-Lilly, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Immunomedics, Macrogenics, Seattle Genetics, AstraZeneca, and reports receiving commercial research grants from Genentech, Pfizer, and Novartis. D. Quinn is an employee/paid consultant for AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Pfizer, and Novartis. K. Jhaveri is an advisory board member/unpaid consultant for Novartis, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Taiho Oncology, Juno Therapeutics, SpecSpectrum Pharmaceuticals, ADC Therapeutics, and Synthon. M. Dujka and R. Bryce are employee/paid consultants for and hold ownership interest (including patents) in Puma Biotechnology. F. Meric-Bernstam is an employee/paid consultant for Genetech, Pieris Pharmaceuticals, Samsung Bioepis, Aduro, OrigMed, Debiopharm Group, Zencor, Jackson Laboratory, Zymeworks, Inflection Bioscience, Darwin Health, Spectrum, Mersana, and Seattle Genetics, reports receiving commercial research grants from Novartis; AstraZeneca; Taiho Pharmaceutical; Genentech; Calithera Biosciences; Debiopharm Group; Bayer; Aileron, reports receiving speakers bureau honoraria from Chugai, and is an advisory board member/unpaid consultant for Taiho, Genentech, Debiopharm Group, Pfizer. D. Solit is an employee/paid consultant for Pfizer, Loxo Oncology, Illumina, Vivideon Therapeutics, and Lilly Oncology. D.M. Hyman is an employee/paid consultant for Chugai, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Bayer, Genentech/Roche, Found, reports receiving commercial research grants from AstraZeneca, Puma, LOXO Oncology, and Bayer. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Prior Presentations: Data from some of the patients included in this analysis were presented in part in: HER kinase inhibition in patients with HER2- and HER3-mutant cancers (Hyman and colleagues, Nature 2018;554:189–194) and at the 2018 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (Smyth and colleagues, poster no. PD3–06).
Reprints and Subscriptions: To order reprints of this article or to subscribe to the journal, contact the AACR Publications Department at pubs@aacr.org.
References
- 1.Litiere S, Collette S, de Vries EG, Seymour L, Bogaerts J. RECIST - learning from the past to build the future. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2017;14:187–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000;92:205–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 2009;45:228–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wolchok JD, Hoos A, O’Day S, Weber JS, Hamid O, Lebbé C, et al. Guidelines for the evaluation of immune therapy activity in solid tumors: immune-related response criteria. Clin Cancer Res 2009;15:7412–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hodi FS, Ballinger M, Lyons B, Soria JC, Nishino M, Tabernero J, et al. Immune-modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (imRECIST): refining guidelines to assess the clinical benefit of cancer immunotherapy. J Clin Oncol 2018;36:850–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kuhl CK, Alparslan Y, Schmoee J, Sequeira B, Keulers A, Brummendorf TH, et al. Validity of RECIST version 1.1 for response assessment in metastatic cancer: a prospective, multireader study. Radiology 2019;290:349–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Da Ros L, Moretti A, Querzoli P, Pedriali M, Lupini L, Bassi C, et al. HER2-positive lobular versus ductal carcinoma of the breast: pattern of first recurrence and molecular insights. Clin Breast Cancer 2018;18:e1133–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wahl RL, Jacene H, Kasamon Y, Lodge MA. From RECIST to PERCIST: evolving considerations for PET response criteria in solid tumors. J Nucl Med 2009;50Suppl 1:122S–150S. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.O JH, Lodge MA, Wahl RL. Practical PERCIST: a simplified guide to PET response criteria in solid tumors 1.0. Radiology 2016;280:576–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF, Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E, et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol 2014;32:3059–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Younes A, Hilden P, Coiffier B, Hagenbeek A, Salles G, Wilson W, et al. International Working Group consensus response evaluation criteria in lymphoma (RECIL 2017). Ann Oncol 2017;28:1436–47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hyman DM, Piha-Paul SA, Won H, Rodon J, Saura C, Shapiro GI, et al. HER kinase inhibition in patients with HER2- and HER3-mutant cancers. Nature 2018;554:189–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ma CX, Bose R, Gao F, Freedman RA, Telli ML, Kimmick G, et al. Neratinib efficacy and circulating tumor DNA detection of HER2 mutations in HER2 nonamplified metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:5687–95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wu Q, Li J, Zhu S, Wu J, Chen C, Liu Q, et al. Breast cancer subtypes predict the preferential site of distant metastases: a SEER based study. Oncotarget 2017;8:27990–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Delbeke D, Coleman RE, Guiberteau MJ, Brown ML, Royal HD, Siegel BA, et al. Procedure guideline for tumor imaging with 18F-FDG PET/CT 1.0. J Nucl Med 2006;47:885–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Diamond EL, Subbiah V, Lockhart AC, Blay JY, Puzanov I, Chau I, et al. Vemurafenib for BRAF V600-mutant Erdheim-Chester disease and Langerhans cell histiocytosis: analysis of data from the histology-independent, phase 2, open-label VE-BASKET study. JAMA Oncol 2018;4:384–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Desmedt C, Zoppoli G, Gundem G, Pruneri G, Larsimont D, Fornili M, et al. Genomic characterization of primary invasive lobular breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2016;34:1872–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Razavi P, Chang MT, Xu G, Bandlamudi C, Ross DS, Vasan N, et al. The genomic landscape of endocrine-resistant advanced breast cancers. Cancer Cell 2018;34:427–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wedam SB, Beaver JA, Amiri-Kordestani L, Bloomquist E, Tang S, Goldberg KB, et al. US Food and Drug Administration pooled analysis to assess the impact of bone-only metastatic breast cancer on clinical trial outcomes and radiographic assessments. J Clin Oncol 2018;36:1225–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Azad GK, Taylor BP, Green A, Sandri I, Swampillai A, Harries M, et al. Prediction of therapy response in bone-predominant metastatic breast cancer: comparison of [(18)F] fluorodeoxyglucose and [(18)F]-fluoride PET/CT with whole-body MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2019;46:821–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Peterson LM, O’Sullivan J, Wu QV, Novakova-Jiresova A, Jenkins I, Lee JH, et al. Prospective study of serial (18)F-FDG PET and (18)F-fluoride PET to predict time to skeletal-related events, time to progression, and survival in patients with bone-dominant metastatic breast cancer. J Nucl Med 2018; 59:1823–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bidard FC, Peeters DJ, Fehm T, Nolé F, Gisbert-Criado R, Mavroudis D, et al. Clinical validity of circulating tumour cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer: a pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol 2014;15:406–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.De Giorgi U, Valero V, Rohren E, Mego M, Doyle GV, Miller MC, et al. Circulating tumor cells and bone metastases as detected by FDG-PET/CT in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 2010;21:33–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pierga JY, Hajage D, Bachelot T, Delaloge S, Brain E, Campone M, et al. High independent prognostic and predictive value of circulating tumor cells compared with serum tumor markers in a large prospective trial in first-line chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol 2012;23: 618–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.De Giorgi U, Mego M, Rohren EM, Liu P, Handy BC, Reuben JM, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT findings and circulating tumor cell counts in the monitoring of systemic therapies for bone metastases from breast cancer. J Nucl Med 2010;51:1213–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Aide N, Hicks RJ, Le Tourneau C, Lheureux S, Fanti S, Lopci E. FDG PET/CT for assessing tumour response to immunotherapy: Report on the EANM symposium on immune modulation and recent review of the literature. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2019;46:238–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Goldfarb L, Duchemann B, Chouahnia K, Zelek L, Soussan M. Monitoring anti-PD-1-based immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer with FDG PET: introduction of iPERCIST. EJNMMI Res 2019;9:8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


