Abstract
For pediatric flexible flatfoot, the subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis (SESA) and endosinotarsal device are the most popular techniques in current practice. Nevertheless, scarce literature is available comparing the outcomes between these two techniques. Thus, we aimed to provide a meta-analysis for the radiographic and clinical outcomes, respectively. A systemic search for correction of pediatric flexible flatfoot using subtalar arthroereisis was conducted mainly in Pubmed and Scopus, and the search was completed on 31 Dec., 2019. The standardized mean differences (SMD) of postoperative versus preoperative calcaneal pitch and Meary’s angle were defined as the primary outcomes, whereas the preoperative versus posteoperative AOFAS (American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society) as the secondary outcome. The meta-analysis included 12 comparative studies comprising 2063 feet in total. The quantitative analysis showed a marked improvement in Meary’s angle of endosinotarsal cone implant group (SMD: 4.298; 95% CI 2.706–5.889) than exosinotarsal screw group (SMD: 1.264; 95% CI 0.650–1.877). But no significant difference was noted between both groups in calcaneal pitch and AOFAS. The exosinotarsal screw and endosinotarsal device are both effective arthroereisis implant for pediatric flexible flatfoot. While considering the correction of Meary’s angle, the endosinotarsal device is better than exosinotarsal screw.
Subject terms: Bone, Musculoskeletal abnormalities, Bone
Introduction
For pediatric flexible flatfoot, the subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis (SESA) and endosinotarsal device are the most popular techniques in current practice. Nevertheless, we found that there were limited studies to compare the outcomes between these two techniques. Traditionally, exosinotarsal screw is thought as inexpensive, while endosinotarsal implant is thought to preserve more soft tissue. However, none of the study has provided the difference between the two procedures1. Although we further went through the literature focusing on outcomes of exosinotarsal screw and endosinotarsal device for subtalar arthroereisis procedure, the comparison study is still lacking2. Furthermore, there was no multi-center, multi-surgeon study to compare these two techniques in the previous research. Thus, we aimed to provide a meta-analysis for radiographic and clinical outcomes, respectively.
Material and methods
Search strategy and inclusion criteria
Pubmed, Scopus, Cochrane Collaboration Central Register of Controlled Clinical Trials, Cochrane Systemic Review, and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched for studies concerning the use of extraosseous subtalar arthroereisis for pediatric flexible flatfoot from the earliest record (September 1974, till 31 Dec., 2019). The bibliography of included trials and related review articles were manually reviewed for relevant reference. Literature not written in English, not available in full text, adult patients, focus on gait analysis, review articles, patients with neuromuscular diseases, case reports, or techniques except exosinotarsal subtalar screw in calcaneus or endosinotarsal cone-shaped implant were excluded. We investigated studies using endosinotarsal tunnel subtalar arthroereisis for pediatric flexible flatfoot treatment.
The search strategy comprised the following keywords combined with subtalar arthroereisis: flexible flatfoot and pes planus. Regarding the types of included studies, we enrolled randomized controlled trials (RCTs), comparative experimental trials, or single-armed follow up studies. We excluded case series and case reports. The target population comprised pediatric patients who suffered from painful flexible flatfoot.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two reviewers examined all of the retrieved articles and extracted data using a predetermined form. We recorded the first author, year, sample size, implant choice, combination of soft tissue procedure, radiographic outcome, and clinical outcome. The methodological quality of enrolled studies was independently evaluated by two reviewers using Jadad scoring for the RCTs and the Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale for the comparative experimental trials.
The Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale contains 9 items in 3 categories: participant selection (4 items), comparability (4 items), and exposure (3 items)3 A study can be scored a maximum of one point for each item in the Selection and Exposure domains and a maximum of 2 points for each item in the Comparability domain. Between-reviewer discrepancies were solved through discussions under the supervision of the corresponding author.
Data synthesis and analysis
The standardized mean differences (SMDs) of calcaneal pitch and Meary’s angle between the SESA group and endosinotarsal device group comprised the primary outcomes. Data extracted from the radiographic outcome parameters were evaluated during outpatient department follow up postoperatively. A negative SMD value indicated receiving arthroereisis surgery was a worse option. AOFAS (American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society) score was also retracted, and a negative SMD value of AOFAS indicated receiving arthroereisis surgery was a worse option.
A random effects model was employed to pool individual SMDs. All analyses were performed using CMA software V3. Between-trial heterogeneity was determined by using I2 tests; values > 50% were regarded as considerable heterogeneity4.
Funnel plots and Egger’s test were used to examine potential publication bias5. Statistical significance was defined as p-values < 0.05.
Results
We retrieved 101 non-duplicated citations for reviewing their titles and abstracts and other 4 articles using manual extraction. We finally included 12 articles for meticulous evaluation after eliminating references violating inclusion criteria (Fig. 1).
Figure 1.
Systematic reviews and flow diagram for the searching and identification of included studies.
We divided the study groups from Memeo in JFAS into endosinotarsal group and exosinotarsal group1. Thus, we have 12 groups in total.
After writing emails to corresponding authors, there had been no response until 31 Dec., 2019. We excluded 1 study for screw inserted in talus6; 7 studies for lack of calcaneal pitch angle, Meary’s angle, and AOFAS7–13 and 6 studies for lack of standard deviation or raw data14–19.
In terms of the patient population, 6 studies performed with endosinotarsal cone shaped implant20–23, 5 studies performed with exosinotarsal screw24–29, while one study performed with both surgeries were divided into two groups1.
The final quantitative analysis included 2063 feet. Ten studies were one-armed retrospective studies and the other one was two-armed retrospective study1. Patient age was 4 to 17 years in endosinotarsal cone-shaped implant group and 4 to 16 years in exosinotarsal group. The pediatric flexible flatfoot was the only diagnosis. Patient characteristics, study methodology, and quality assessment of included trials were listed in Table 1. The collected data of each article were listed in Table 2.
Table 1.
Summary of patient characteristics, study methodology, implant and quality assessment of trials for pediatric flexible flatfoot diagnosis retrieving from each article.
| Implant | Author, year, journal | Study Design | Arthroereisis implant | Age at op | Male/female (Feet) | Viladot classification | Implant (± soft tissue) | Quality Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCT vs. quasi-E | Extraosseous vs intraosseous | Newcastle–Ottawa quality assessment scale | ||||||
| Endosino tarsal device | Bernasconi A (2019) Orthop Traumatol Surg Res | Quasi-E | Endosinotarsal device | 10.5 ± 1.6 | 45M/17F | Not mention | Expanding non-reabsorbable Giannini implant | 7 |
| Endosino tarsal device | Megremis P (2019) J Foot Ankle Surg | Quasi-E | Endosinotarsal device | 10.71 ± 1.58 | 10M/4F (20:8) | Not mention | Intergra + Hoke | 7 |
| Endosino tarsal device | Hsieh CH (2019) JCM | Quasi-E | Endosinotarsal device | 9 ± 2 | 59M/43F (118:86) | 3–4 | Bioarch + Vulpius | 7 |
| Endosino tarsal device group solely | Memeo A (2019) J Foot Ankle Surg (endosinotarsal group) | Quasi-E | (Endosinotarsal device group) | 12.8 ± 4 | 61M/39F (122:78) | 3–4 | Endosinotarsal cone + two level Achilles lengthen | 7 |
| Endosino tarsal device | Cao L (2017) Orthop Surg | Quasi-E | Endosinotarsal device | 12.1 ± 5 | 12M/8F (not mention) | Not mention | Kalix II | 6 |
| Endosino tarsal device | Jay RM (2013) Foot Ankle Spec | Quasi-E | Endosinotarsal device | 10.6 ± 6 | 13M/7F (not mention) | Not mention | Endosinotarsal cone + gastrocnemius recession | 5 |
| Intra-osseous screw | Kubo H (2019) J Orthop Sci | Quasi-E | Intra-osseous screw | 10 ± 5 | Not mention | Not mention | Exosinotarsal screw + Baumann, Strayer, or Z lengthening of Achilles tendon | 7 |
| Exosino tarsal screw group solely | Memeo A (2019) J Foot Ankle Surg (exosinotarsal group) | Quasi-E | (Exosinotarsal screw group) | 13.6 ± 3 | 50M/51F (100:102) | Not mention | Exosinotarsal screw + percutaneous Achilles lengthen | 7 |
| Intraossoeus screw | Giannini S (2017) J Foot Ankle Surg | Quasi-E | Intraossoeus screw | 6 ± 2 | 31M/1 F (62:26) | 2–4 | Cannulated RSB + percutaneous Achilles lengthening | 6 |
| Intraosseous screw | De Pellegrin M (2014) J Child Orthop | Quasi-E | Intraosseous screw | 11.5 ± 1.81 | 267M/218F (not mention) | Not mention | Metallic screw | 7 |
| Intraosseous screw | Jerosch J (2009) Foot Ankle Surg | Quasi-E | Intraosseous screw | 11.9 ± 3 | 13M/5F (not mention) | Not mention | Metallic screw + Baumann | 6 |
| Intraosseous screw | V. Pavone (2018) J Child Orthop | Quasi-E | Intraosseous screw | 12.7 ± 3 | 38M/30F (76:60) | Not mention | Calcaneal stop screw (Synthes) | 7 |
| Intraosseous screw | Pavone V (2013) J Foot Ankle Surg | Quasi-E | Intraosseous screw | 11 ± 3 | 157M/85F (not mention) | Not mention | Calcaneal stop screw (Synthes) + Achilles tendon lengthening | 7 |
Table 2.
Summary of corrective figures of calcaneal pitch, Meary's angle and AOFAS under pre- and post-op status retrieving from each article.
| Implant | Author, year, journal | Preop Calcaneal pitch | Postop Calcaneal pitch | Preop AP Meary’s angle | Postop AP Meary’s angle | Preop lateral Meary’s angle | Postop lateral Meary’s angle | Pre op AOFAS | Post op AOFAS | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m1 | sd1 | n1(feet) | m2 | sd2 | n2 | m1 | sd1 | n1 | m2 | sd2 | n2 | m1 | sd1 | n1 | m2 | sd2 | n2 | m1 | sd1 | n1 | m2 | sd2 | n2 | ||
| Endosino tarsal device | Bernasconi A (2019) Orthop Traumatol Surg Res | 12 | 3.1 | 62 | 16.8 | 4.6 | 62 | Nil | 18.4 | 6 | 62 | 9.9 | 3.1 | 62 | nil | ||||||||||
| Endosino tarsal device | Megremis P (2019) J Foot Ankle Surg | 10.7 | 2.6 | 28 | 15.4 | 1.1 | 28 | 33.8 | 11.5 | 28 | 5.1 | 3 | 28 | 19 | 6.6 | 28 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 28 | 65.1 | 7.2 | 28 | 88.9 | 5.6 | 28 |
| Endosino tarsal device | Hsieh CH (2019) JCM | 15.3 | 2 | 118 | 16.8 | 1.3 | 118 | 11.1 | 6.4 | 118 | 5.2 | 0.7 | 118 | 12.4 | 3.2 | 118 | 4.8 | 2.2 | 118 | ||||||
| Endosino tarsal device group solely | Memeo A (2019) J Foot Ankle Surg (endosinotarsal group) | 12.9 | 1.4 | 186 | 16.4 | 2.3 | 186 | Nil | Nil | Nil | |||||||||||||||
| Endosino tarsal device | Cao L (2017) Orthop Surg | 9.4 | 1.3 | 27 | 11.5 | 1.4 | 27 | 19.1 | 2.2 | 27 | 6.3 | 1.2 | 27 | 19.6 | 1.7 | 27 | 4.2 | 0.9 | 27 | 71.1 | 6.1 | 27 | 88.1 | 6.3 | 6 |
| Endosino tarsal device | Jay RM (2013) Foot Ankle Spec | Nil | Nil | Nil | 67.7 | 7.9 | 34 | 89.0 | 5 | 34 | |||||||||||||||
| Intra-osseous screw | Kubo H (2019) J Orthop Sci | 10.6 | 3.7 | 95 | 11.9 | 3.9 | 95 | Nil | 19.1 | 9.1 | 95 | 13.2 | 6.7 | 95 | Nil | ||||||||||
| Exosino tarsal screw group solely | Memeo A (2019) J Foot Ankle Surg (exosinotarsal group) | 13 | 1.5 | 200 | 16.6 | 2.3 | 200 | Nil | Nil | Nil | |||||||||||||||
| Intra-ossoeus screw | Giannini S (2017) J Foot Ankle Surg | Nil | Nil | 20.4 | 7.7 | 88 | 9.4 | 6.5 | 88 | Nil | |||||||||||||||
| Intra-osseous screw | De Pellegrin M (2014) J Child Orthop | 11 | 6 | 732 | 14 | 5 | 732 | Nil | Nil | Nil | |||||||||||||||
| Intra-osseous screw | Jerosch J (2009) Foot Ankle Surg | Nil | Nil | 18 | 8.9 | 21 | 6 | 5.8 | 21 | Nil | |||||||||||||||
| Intra-osseous screw | V. Pavone (2018) J Child Orthop | 12.3 | 2.3 | 136 | 16.3 | 1.3 | 136 | Nil | Nil | 79.3 | 5.7 | 136 | 97.3 | 4.5 | 136 | ||||||||||
| Intra-osseous screw | Pavone V (2013) J Foot Ankle Surg | 12.5 | 1.4 | 410 | 16.7 | 1.2 | 410 | Nil | Nil | Nil | |||||||||||||||
SMD of postoperative radiographic alignment
The overall calcaneal pitch improvement was 1.594 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.915–2.273) (Fig. 2a).
Figure 2.
(a) overall calcaneal pitch improvement of pre-op vs post-op; (b) subgroup improvement of endosinotarsal cone-shaped group vs exosinotarsal screw group.
The subgroup analysis showed both improvement in endosinotarsal cone-shaped group (SMD: 1.515; 95% CI 1.042–1.988) and exosinotarsal screw group (SMD: 1.639; 95% CI 0.482–2.797) (Fig. 2b).
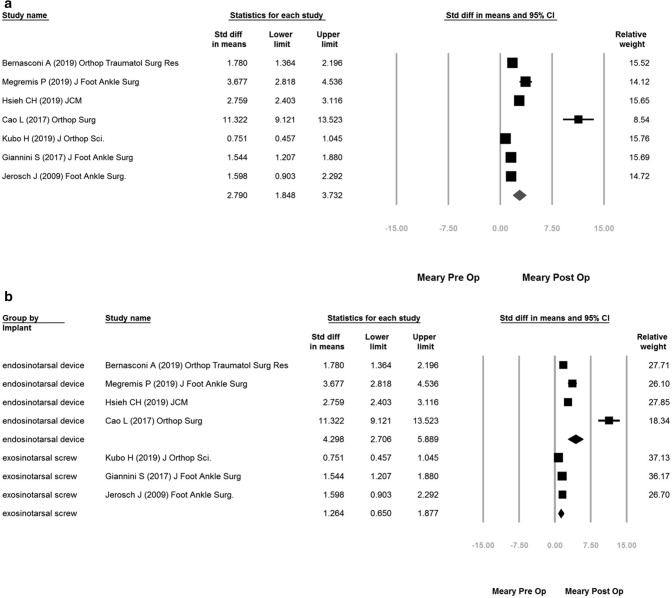
The overall Meary’s angle improvement was 2.790 (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.848–3.732) (Fig. 3a).
Figure 3.
(a): overall Meary’s improvement of pre-op vs post-op; (b) subgroup improvement of endosinotarsal cone-shaped group vs exosinotarsal screw group.
The subgroup analysis showed a more significant improvement in endosinotarsal cone-shaped group (SMD: 4.298; 95% CI 2.706–5.889) than exosinotarsal screw group (SMD: 1.264; 95% CI 0.650–1.877) (Fig. 3b).
SMD of postoperative clinical outcome score
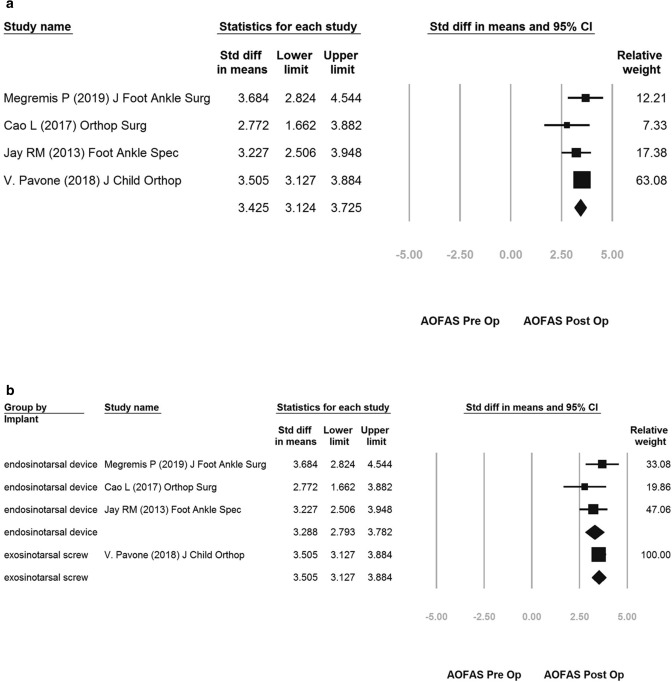
The overall AOFAS score improvement was 3.425 (95% confidence interval [CI] 3.124–3.725) (Fig. 4a).
Figure 4.
(a): overall AOFAS improvement of pre-op vs post-op; (b) subgroup improvement of endosinotarsal cone-shaped group vs exosinotarsal screw group.
The subgroup analysis showed more significant improvement in endosinotarsal cone-shaped group (SMD: 3.288; 95% CI 2.793–3.782) and exosinotarsal screw group (SMD: 3.505; 95% CI 3.127–3.884) (Fig. 4b).
The Egger’s test revealed no significant publication bias regarding the overall calcaneal pitch SMD (p = 0.22146), Meary’s SMD (p = 0.05507), and AOFAS SMD (p = 0.41738). The funnel plot is as shown in Fig. 5a–c for calcaneal pitch, Meary’s angle, and AOFAS score accordingly.
Figure 5.
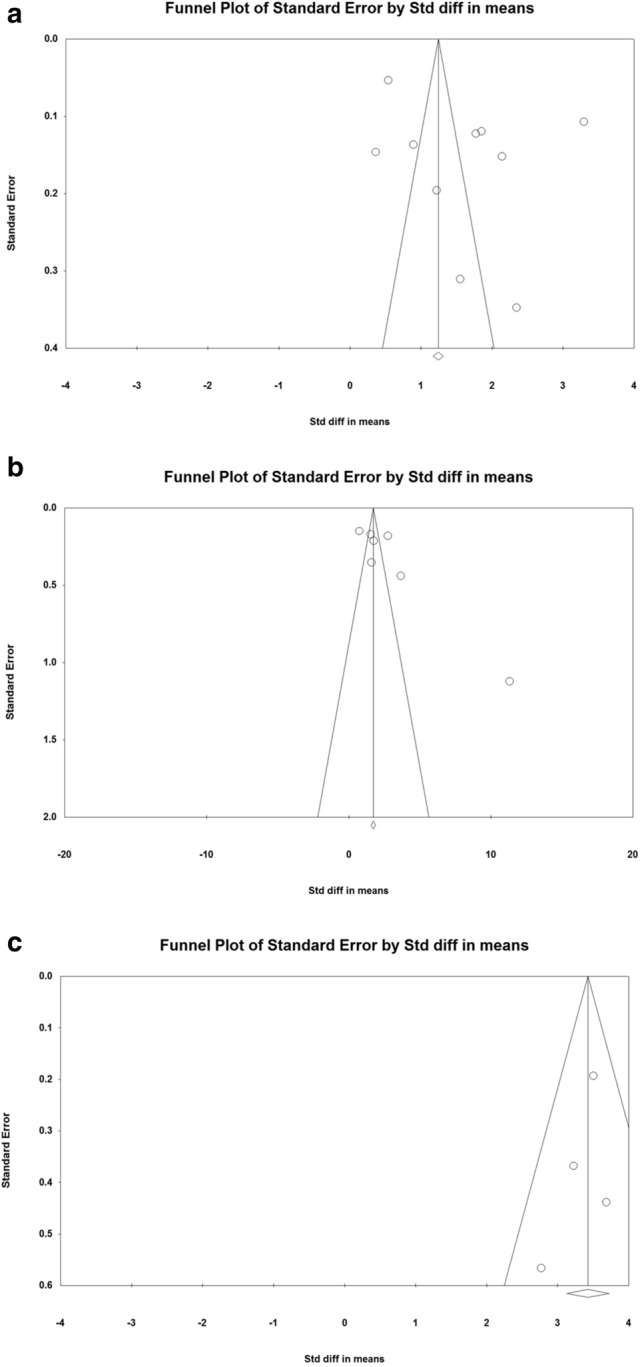
Funnel plots: (a) for calcaneal pitch, (b) for Meary’s angle, and (c) for AOFAS score.
Discussion
According to Memeo et al., the most common two techniques for subtalar arthroereisis were exosinotarsal metalic screw (SESA) technique and endosinotarsal cone shaped implant. However, previous studies failed to reveal significant difference between the two techniques. Our study thus pooled 12 articles and collected 2063 feet to compare the radiographic and clinical outcomes between the two surgical techniques1,2.
Our result revealed both techniques improved in both radiographic parameters. In Meary’s angle, the group of using endosinotarsal cone shaped implant technique improves more than the group using exosinotarsal metallic screw.
Most of previous studies about subtalar arthroereisis did not specifically indicate if the procedure was performed with SESA or endosinotarsal device2. This appears that the outcomes in statistics of the studies may be mixed with diverse techniques. In addition, many reviewers could have unclear pictures to recognize which one of the techniques was better for rectifying the pediatric flexible flatfoot. In some articles, authors adopted the same term of “arthroereisis” with different types of implants, even data were from surgeons working in different affiliations. Memeo et al. indicated no statistical difference was found between the two techniques for Costa-Bertani angle, heel inclination, Kite angle and talar declination angle in 402 feet.
Apparently, the data from Memeo A et al. were collected for 10 years with quite complete records. However, with mono-clinical practical surgeries under one hospital, it seems that if we could take a further examination in the event of different hospitals, different surgeons, the result could be shared differently for its consequence.
We assumed the metallic screw had lesser contact area to bone than endosinotarsal implant, which may lead to screw head sinking into bone and thus less corrective effect. The other reason may be due to screw purchasing in cancellous bone with minor fixation effect. Based on above reasons, the results of corrective effect during follow-up did not meet the expectation. Furthermore, the favorite position and screw axis direction performed by surgeons in processing exosinotarsal screw were different. Thus, the screw position was difficult to change after insertion. On the contrary, surgeon can change varieties of endosinotarsal implant in size when the endosinotarsal implant stands at the improper position or appears a flaw of corrective effect. In light of this, the surgeons may change the endosinotarsal implant depending on personal preferences.
Our result revealed both techniques were effective regarding radiographic parameters. For Meary’s angle, the group with endosinotarsal cone shaped implant improved more than the group with exosinotarsal metallic screw. We suggest three possible explanations (there may be more). First, the exosinotarsal metallic screw implant had less contact area to bone than endosinotarsal implants, which may lead to bone erosion and consequent less corrective effect1,24. Second, the variable screw purchase to calcaneus may lead to screw loosening after repeated subtalar motion. Last but not least, the optimal position and trajectory for the screw has yet to be determined. Consequently, the stabilizing effect for exosinotarsal screw would be relatively unpredictable. On the contrary, surgeons can modify endosinotarsal implant size according to correcting effects.
There are some factors associated with the occurrence of complications. The type of implant chosen may result in different complication profiles. For example, sinus tarsi pain and implant migration were more frequently seen with endosinotarsal implants. Incomplete correction may be associated with the exosinotarsal implants30. Bioabsorbable material may be associated with regional inflammatory response1,30. Higher body mass index was found to be associate with higher complication rates and less deformity correction with endosinotarsal implants21. Careful selection of patients and techniques based on current evidence may be helpful to reduce the complication rate.
Generally speaking, there are four main types of complications: result of inappropriate indication, technical error, patient adaptation or irritation, and biomechanical failure of implant with incidence of 4.8–18.6%. Complications reported in endosinotarsal device included sinus tarsi pain, implant extrusion, local tissue reaction, and mechanical irritation. Complications reported in extrasinotarsal screw included sinus tarsi pain, subjective limitation, screw breakage, incorrected positioned screw, and local fracture of calcaneus or talus after fall/trauma. While the most common complication is unexpected sinus tarsi pain, the majority of symptoms could be adapted by patient or relieved after implant removal. It seemed to be more easily to handle complications in endosinotarsal device compared with exosinotarsal cases. Up to date, there has been no randomized controlled trial to compare advantages and disadvantages between the two techniques in the current literatures31–33.
There are several limitations in our study:
Most articles presented these 2 types techniques based on retrospective studies. The quality was limited due to retrospective articles in its nature. Newcastle score is between 5 and 7 with a limited number of extreme high-quality studies.
We approached some authors by emails for obtaining more detailed data of standard deviations and implant choices. However, there was no response till the end of our study.
The papers related to the outcomes of these two techniques are quite limited. AOFAS is widely used by most investigators. However, it is scattered on QxFAD-C (Oxford ankle foot questionnaire for children). Therefore, there is only one study on AOFAS for Exosinotarsal group.
The range of age distribution is relatively wide in both endosinotarsal cone group or exosinotarsal screw group. According to study of Kubo et al.24, the best time for the surgeries is 9–12 years old. According to Hsieh et al., most of their patients underwent endosinotarsal implants were before the age of 10, suggesting less bone remodeling in older children. More studies to support the best operation age are required in the future.
The endosinotarsal group had a better corrective result in Meary’s angle compared with exosinotarsal group. For clinical AOFAS, exosinotarsal group also shows an improvement. We assumed that once the sample size was adequate enough, this outcome of clinical AOFAS would be better. Hence, investigators need to examine the outcome of AOFAS clinical scores.
For endosinotarsal device, some articles used bio-absorbable device1, while others applied metallic materials. We take conservative attitude to the rectification effectiveness on foot alignment while selecting different materials of endosinotarsal device. Considering the foot alignment needs to sustain a long period under same situation for different materials, age and body weight, future studies will be required for investigating the effectiveness.
Our study provided the evidence of comparing corrective effects of “subtalar arthroereisis” for pediatric flexible flatfoot using different techniques and implants. We suggest that the surgical types, implant selection, sources and costs should be well documented for a more specific statistics in the future.
Conclusion
The exosinotarsal screw and endosinotarsal device are both effective arthroereisis implants to treat pediatric flexible flatfoot. However, the endosinotarsal device shows a better improvement in Meary’s angle than exosinotarsal screw.
Author contributions
C.H. and T.M. conceived the experiment(s), C.H., C.C. and T.H. conducted the experiments, K.W., J.F. and T.M. analysed the results. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Data availability
All the data of the main text are available when Scientific Reports requires.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Memeo A, Verdoni F, Rossi L, Ferrari E, Panuccio E, Pedretti L. Flexible juvenile flat foot surgical correction: a comparison between two techniques after ten years' experience. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58(2):203–207. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2018.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Indino C, Villafañe JH, D’Ambrosi R, Manzi L, Maccario C, Berjano P, Usuelli FG. Effectiveness of subtalar arthroereisis with endorthesis for pediatric flexible flat foot: a retrospective cross-sectional study with final follow up at skeletal maturity. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020;26(1):98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2018.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chang KV, Hsiao MY, Chen WS, Wang TG, Chien KL. Effectiveness of intra-articular hyaluronic acid for ankle osteoarthritis treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013;94(5):951–960. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2012.10.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chang KV, Hung CY, Han DS, Chen WS, Wang TG, Chien KL. Early versus delayed passive range of motion exercise for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015;43(5):1265–1273. doi: 10.1177/0363546514544698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chang KV, Hung CY, Wu WT, Han DS, Yang RS, Lin CP. Comparison of the effectiveness of suprascapular nerve block with physical therapy, placebo, and intra-articular injection in management of chronic shoulder pain: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016;97(8):1366–1380. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2015.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Roth S, Sestan B, Tudor A, Ostojic Z, Sasso A, Durbesic A. Minimally invasive calcaneo-stop method for idiopathic, flexible pes planovalgus in children. Foot Ankle Int. 2007;28(9):991–995. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2007.0991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ruiz-Picazo D, et al. Radiographic and functional results following subtalar arthroereisis in pediatric flexible flatfoot. Adv. Orthop. 2019 doi: 10.1155/2019/5061934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hagen L, Pape JP, Kostakev M, Peterlein CD. Pedobarographic changes during first month after subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis (SESA) operation of juvenile flexible flatfoot. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2019;140(3):313–320. doi: 10.1007/s00402-019-03230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Faldini C, et al. Patient-perceived outcomes after subtalar arthroereisis with bioabsorbable implants for flexible flatfoot in growing age: a 4-year follow-up study. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2018;28(4):707–712. doi: 10.1007/s00590-017-2119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Baker JR, Klein EE, Weil L, Jr, Weil LS, Sr, Knight JM. Retrospective analysis of the survivability of absorbable versus nonabsorbable subtalar joint arthroereisis implants. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013;6(1):36–44. doi: 10.1177/1938640012470712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yen-Douangmala D, Vartivarian M, Choung JD. Subtalar arthroereisis and its role in pediatric and adult population. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2012;29(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2012.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Scharer BM, Black BE, Sockrider N. Treatment of painful pediatric flatfoot with Maxwell-Brancheau subtalar arthroereisis implant a retrospective radiographic review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2010;3(2):67–72. doi: 10.1177/1938640010362262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Costa FP, Costa FP, Costa G, Carvalho MS, Moura AM, Pinto R, Torres J. Long-term outcomes of the calcaneo-stop procedure in the treatment of flexible flatfoot in children: a retrospective study. Acta Med. Port. 2017;30(7–8):541–545. doi: 10.20344/amp.8137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Caravaggi P, Lullini G, Berti L, Giannini S, Leardini A. Functional evaluation of bilateral subtalar arthroereisis for the correction of flexible flatfoot in children: 1-year follow-up. Gait Posture. 2018;64:152–158. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2018.06.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kubo H, et al. Radiological outcome after treatment of juvenile flatfeet with subtalar arthroereisis: a matched pair analysis of 38 cases comparing neurogenic and non-neurogenic patients. J. Child Orthop. 2019;13(4):346–352. doi: 10.1302/1863-2548.13.190046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Koning PM, Heesterbeek PJ, de Visser E. Subtalar arthroereisis for pediatric flexible pes planovalgus: fifteen years experience with the cone-shaped implant. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2009;99(5):447–453. doi: 10.7547/0990447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nelson SC, Haycock DM, Little ER. Flexible flatfoot treatment with arthroereisis: radiographic improvement and child health survey analysis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2004;43(3):144–155. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2004.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.de Bot R, Stevens J, Hermus JPS, Staal HM, van Rhijn LW, Witlox AM. Clinical and radiological outcomes of subtalar kalix II arthroereisis for a symptomatic pediatric flexible flatfoot. Foot Ankle Spec. 2019 doi: 10.1177/1938640019892062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Forg P, Feldman K, Flake E, Green DR. Flake-austin modification of the STA-Peg arthroereisis: a retrospective study. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2001;91(8):394–405. doi: 10.7547/87507315-91-8-394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Megremis P, Megremis O. Arthroereisis for symptomatic flexible flatfoot deformity in young children: radiological assessment and short-term follow-up. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58(5):904–915. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2019.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hsieh CH, Lee CC, Tseng TH, Wu KW, Chang JF, Wang TM. Body weight effects on extra-osseous subtalar arthroereisis. J. Clin. Med. 2019 doi: 10.3390/jcm8091273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cao L, Miao XD, Wu YP, Zhang XF, Zhang Q. Therapeutic outcomes of kalix II in treating juvenile flexible flatfoot. Orthop. Surg. 2017;9(1):20–27. doi: 10.1111/os.12309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jay RM, Din N. Correcting pediatric flatfoot with subtalar arthroereisis and gastrocnemius recession: a retrospective study. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013;6(2):101–107. doi: 10.1177/1938640012470714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kubo H, et al. Outcome after subtalar screw arthroereisis in children with flexible flatfoot depends on time of treatment: midterm results of 95 cases. J. Orthop. Sci. 2020;25(3):497–502. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2019.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Giannini S, et al. Bioabsorbable calcaneo-stop implant for the treatment of flexible flatfoot: a retrospective cohort study at a minimum follow-up of 4 years. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(4):776–782. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2017.02.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jerosch J, Schunck J, Abdel-Aziz H. The stop screw technique: a simple and reliable method in treating flexible flatfoot in children. Foot Ankle Surg. 2009;15(4):174–178. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2009.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pavone V, Costarella L, Testa G, Conte G, Riccioli M, Sessa G. Calcaneo-stop procedure in the treatment of the juvenile symptomatic flatfoot. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2013;52(4):444–447. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2013.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pavone V, Vescio A, Di Silvestri CA, Andreacchio A, Sessa G, Testa G. Outcomes of the calcaneo-stop procedure for the treatment of juvenile flatfoot in young athletes. J. Child Orthop. 2018;12(6):582–589. doi: 10.1302/1863-2548.12.180032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.De Pellegrin M, Moharamzadeh D, Strobl WM, Biedermann R, Tschauner C, Wirth T. Subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis (SESA) for the treatment of flexible flatfoot in children. J. Child Orthop. 2014;8(6):479–487. doi: 10.1007/s11832-014-0619-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tan JHI, Tan SHS, Lim AKS, Hui JH. The outcomes of subtalar arthroereisis in pes planus: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s00402-020-03458-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bernasconi A, Lintz F, Sadile F. The role of arthroereisis of the subtalar joint for flatfoot in children and adults. EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(11):438–446. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.2.170009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Needleman RL. Current topic review: subtalar arthroereisis for the correction of flexible flatfoot. Foot Ankle Int. 2005;26(4):336–346. doi: 10.1177/107110070502600411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.van Ooij B, Vos CJ, Saouti R. Arthroereisis of the subtalar joint: an uncommon complication and literature review. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2012;51(1):114–117. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2011.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All the data of the main text are available when Scientific Reports requires.