Abstract
Background:
KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A and SMAD4 are established driver genes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). We aimed to determine if the mutational status of driver genes, and those involved in DNA repair pathways, are associated with clinical outcomes in individuals who undergo resection.
Methods:
Eligible individuals were those who underwent resection of PDAC and consented to targeted sequencing of their primary tumor using MSK-IMPACT. Genomic alterations were determined based on MSK-IMPACT results from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples. Associations between genomic alterations and clinical outcomes were assessed.
Results:
Targeted sequencing was performed on N=283 primary tumors resected between 2004–2017. Median follow up was 23 months among survivors. Alterations in KRAS and TP53 were associated with worse overall survival (OS) as compared to wildtype (median[95%CI], 38.8[33.0–45.5] vs 91.0[34.8-NA] months, p=0.043; 37.4[32.1–42.8] vs 65.0[33.0-NA] months, p=0.035). KRAS G12D mutations were associated with worse OS (31.6[25.3–45.5] vs 39.2[37.4–75.2] months, p=0.012). TP53 truncating mutations (39.6[32.4–75.2] vs 33.9[24.0–39.0] months, p=0.020) and those associated with loss of heterozygosity (LOH) (26.6[21.6–44.2] vs 39.2[34.5–49.1] months, p=0.048) had decreased OS. TP53 alterations were independently associated with OS on multivariate analysis (HR[95% CI], 1.54[1.01–2.33], p=0.042). Individuals with germline alterations in homologous repair deficiency (HRD) genes had improved OS as compared to those without (median OS not reached vs 37.0[33.0–49.8] months, p=0.035).
Conclusion:
In patients with resected PDAC, genomic alterations in KRAS and TP53 are associated with worse outcomes, whereas alterations in HRD genes are associated with favorable prognosis. Further studies are needed to better define these alterations as biomarkers in resected PDAC.
Keywords: Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma, Driver Gene Alterations, Resection, Homologous Recombination, Survival Outcomes
Precis:
Results from a routinely used, clinically-actionable targeted sequencing panel demonstrate that alterations in KRAS and TP53 are associated with worse outcomes in patients undergoing resection for PDAC. Specifically, KRAS G12D mutations, and TP53 alterations resulting in truncations and those in areas with loss of heterozygosity (LOH), were associated with poorer prognosis; additionally, germline HRD mutations are associated with improved overall survival.
Introduction
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is predicted to be the second leading cause of cancer deaths by 2030.1 Over the past decade, the genomic landscape of pancreatic cancer has been well characterized.2–5 KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A and SMAD4 are the main genes that drive pancreatic tumorigenesis. Alterations in KRAS and CDKN2A are early events in tumorigenesis, whereas mutations in TP53 and SMAD4 occur at a later stage.6,7 Additionally, a subset of genes involved in multiple oncogenic pathways mutated at a lesser frequency have been identified.2–5
Previous data has demonstrated an association between alterations in driver genes and overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) following resection for PDAC.8 Alterations in KRAS, TP53 and CDKN2A were associated with worse RFS, and CDKN2A alterations with worse OS. Other studies have demonstrated that loss of SMAD4 is associated with worse disease-free survival,9 and wildtype KRAS and CDKN2A are associated with improved OS.10,11 Additionally, studies have demonstrated that increasing numbers of driver gene mutations are associated with worse outcomes.8,11,12
While there has been an increased understanding of the genomics of PDAC, relatively few clinically actionable mutations have been identified. Previous data from our institution using targeted genomic profiling identified potentially targetable alterations in a minority of individuals with PDAC and other groups have suggested a greater frequency of actionability.13,14 Many targeted therapies are under investigation, but few have been validated in the treatment of PDAC.14–18 Several studies suggest that patients with germline BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations have improved outcomes following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy and poly-ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors.5,19–22 No targeted agents against any of the four driver genes have been validated and there are no FDA approved drugs for use in this setting.
In this study, we evaluated the use of a targeted sequencing panel, MSK-IMPACT, in individuals with PDAC, and investigated the associations of the four driver genes, and other commonly altered genes, including those involved in DNA repair pathways, with clinical and pathologic outcomes in those who underwent surgical resection for PDAC at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK).
Methods
Patient cohort
A prospectively maintained database was queried for consecutive individuals who underwent resection for PDAC at MSK and had targeted next generation sequencing (NGS) performed on their primary tumor. This study was reviewed by the MSK Institutional Review Board (IRB). Individuals were consented under an institutional protocol to have their tumors sequenced with Memorial Sloan Kettering-Integrated Mutational Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets (MSK-IMPACT, NCT01775072) as part of clinical practice.23 Demographic, clinical, pathologic, and outcome data were abstracted from the database and electronic medical record.
Genetic analysis
Samples were obtained from the resection specimen or pre-treatment biopsy of the primary pancreatic tumor. All tumor samples were reviewed by a gastrointestinal pathologist and macrodissected from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded blocks to ensure adequate cellularity. DNA was extracted from blood for somatic mutation calling and for germline testing when consent was obtained for the latter. Tumors were sequenced using MSK-IMPACT, which consists of deep, targeted sequencing of all exons and selected introns of 351 (n=4), 410 (n=176) or 468 (n=103) cancer-related genes. Tumor purity was estimated based on pathologic review of samples. Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and insertions and deletions (Indels) were called using MuTect, Pindel, and Somatic Indel Detector, as previously described.24 MSISensor was used to determine microsatellite instability.25,26 FACETS was used for evaluation of copy number alterations (CNA), including loss of heterozygosity (LOH),27 and results were manually reviewed to identify the best fit. To characterize LOH, mutant allele frequency and overall coverage at that locus was assessed. A region of LOH was considered present if the lower copy number was 0 or the mutant allele frequency was consistent with the variant allele frequency (VAF) that would be expected from LOH favoring the mutant allele.28 Three individuals without clear CNA profiles were removed from TP53 LOH analysis, and one patient with two TP53 alterations was removed from LOH and truncation analyses. Mutations with OncoKB annotation of “Predicted Oncogenic,” “Likely Oncogenic,” or “Oncogenic” are considered putative drivers, while other mutations are labeled as unknown significance.29
Homologous recombination (HRD) genes were analyzed, and included ARID1A, ATM, BAP1, BARD1, BLM, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CHEK2, FAM175A, FANCA, FANCC, NBN, PALB2, RAD50, RAD51, RAD51C, and RTEL1. Mismatch repair (MMR) genes, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2, were also evaluated. Mutational frequencies seen in this cohort were compared to those of a larger population of both primary and metastatic PDAC tumors (n=1,702) sequenced with MSK-IMPACT.
Germline Sequencing
A subset of individuals in the cohort consented to germline testing with MSK-IMPACT (n=154; NCT01775072), and serves as the denometer for germline analyses. This platform consists of up to 88 genes associated with cancer predisposition. Blood was used to call all germline mutations.
Statistical analysis
Continuous data are expressed as median and range, and categorical variables are expressed as frequency and percentage. Wilcoxon rank-sum and Fisher’s exact tests were used to compare pathological variables and binary gene mutation status. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the time from surgery to the date of death or date of last follow up. Postoperative imaging was reviewed for site of first recurrence. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was defined as the time between surgery and time of first recurrence or death, whichever occurred first; if the endpoint was not met, then patients were censored at the date of last imaging. Individuals were excluded from RFS analysis if they had metastatic disease at the time of operation (n=4) or incomplete follow up imaging (n=1). OS and RFS were estimated with Kaplan-Meier methods and compared using the log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were completed using a Cox proportional hazard model to evaluate the impact of genomic alterations on OS in the setting of potential cofounding variables (stage (AJCC 8th edition), LN status (positive or negative), lymphovascular invasion, perineural invasion, tumor size and neoadjuvant therapy. The multivariable model was constructed by including factors significantly associated with OS (p < 0.05) on univariate analysis.
Cumulative incidences of patterns of first recurrence (CIR; distant only, local only, local and distant) and death without evidence of recurrence, as well as specific site of distant recurrence, were estimated using competing risks methods from the date of operation. Associations between site of recurrence and gene mutation status were evaluated using Gray’s test and the Fine and Gray competing risks method. All tests were two-sided and p<0.05 was considered significant. The nominal p-value is shown unless otherwise noted. SAS (version 9.4, SAS institute Inc., Cary, NC) or R (Version 3.5.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) using ‘cmprsk’ were used for all analyses.
Results
Patient cohort
There were 283 individuals who underwent resection for PDAC at MSK between January 2004 and August 2017, and had targeted sequencing performed on the primary tumor (Table S1). All data was finalized in August 2018. Demographic and clinical characteristics are illustrated in Table 1. There were 58 patients (20%) who received neoadjuvant therapy, 72% (n=205) of the cohort underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy, and 77% (n=218) received adjuvant therapy. In total, 81% (n=229) had genomic sequencing of their tumors performed prior to receipt of systemic treatment.
Table 1.
Demographic, Clinical and Pathologic Data for Entire Cohort of Resected PDAC.
| n = 283 | |
|---|---|
| Epidemiology | |
| Age, years | 67 (59–73) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 137 (48) |
| Female | 146 (52) |
| Race/Ethnicityǂ | |
| White/Caucasian | 250 (88) |
| African American | 7 (2) |
| Asian | 10 (4) |
| Hispanic/Latino | 13 (5) |
| Ashkenazi Jewish Descent* | |
| Yes | 41 (15) |
| No | 224 (79) |
| Smoking History | |
| Yes | 158 (56) |
| No | 125 (44) |
| Diabetes | |
| Yes | 82 (29) |
| No | 201 (71) |
| Personal history of cancer | |
| Yes | 80 (28) |
| No | 203 (72) |
| Family history of pancreas cancer** | |
| Yes | 50 (18) |
| No | 226 (80) |
| Germline BRCA1/2 mutation | 7 (2) |
| Treatment | |
| Neoadjuvant Therapy | 58 (20) |
| Chemotherapy alone | 42 (72) |
| Chemotherapy + Radiation | 16 (28) |
| Platinum-based chemotherapy | 47 (81) |
| Procedure | |
| Pancreaticoduodenectomy | 205 (72) |
| Distal Pancreatectomy | 76 (27) |
| Central Pancreatectomy | 1 (0.5) |
| Total Pancreatectomy | 1 (0.5) |
| Adjuvant Therapy# | 220 (78) |
| Chemotherapy alone | 179 (81) |
| Chemotherapy + Radiation | 40 (18) |
| Platinum-based chemotherapy | 24 (11) |
| Pathology | |
| Tumor Diameter, cm | 2.8 (2.2–3.8) |
| Pathology | |
| Ductal adenocarcinoma | 265 (93) |
| IPMN/MCN-associated | 5 (2) |
| Adenosquamous | 13 (5) |
| Lymphovascular Invasion | |
| Yes | 194 (69) |
| No | 89 (31) |
| Perineural Invasion | |
| Yes | 253 (89) |
| No | 30 (11) |
| Tumor Stage (AJCC 8th Edition) | |
| T1 | 57 (20) |
| T2 | 171 (60) |
| T3 | 54 (19) |
| T4 | 1 (0.5) |
| Lymph Node Stage (AJCC 8th Edition) | |
| N0 | 90 (32) |
| N1 | 113 (40) |
| N2 | 20 (28) |
| Metastasis Stage | |
| M0 | 4 (1) |
| M1 | 279 (99) |
Variables expressed as n (%) or median (IQR).
unknown in 3 patients;
unknown in 18 patients;
unknown in 7 patients;
unknown in 20
The median OS of the entire cohort was 39.0 [95%CI: 33.3–46.3] months and median RFS was 12.8 [95%CI: 11.7–15.5] months, with a median follow up of 23 months among survivors. Sequencing with MSK-IMPACT was performed routinely beginning in 2014, and therefore a subset of individuals alive when MSK-IMPACT testing was initiated consented to have their primary tumor sequenced retrospectively (n=43), resulting in a survivor bias between those sequenced before and after 2014. The median OS for individuals resected after 2014 was 32.0 [95%CI: 27.2–37.6] months and RFS was 12.0 [95%CI: 10.1–13.9] months, as compared to 82.0 [95%CI: 51.6-NA] months and 28.0 [95%CI: 22.5–52.6] months for those resected before 2014. At the time of analysis, cumulative incidences of distant, isolated local, and simultaneous local and distant recurrences at 3-years postoperatively were 40.7% [95%CI: 34.3%−46.9%], 21.5% [16.3%−27.3%], and 15.0% [10.9%−19.8%], respectively (Figure S1a). The most common site of distant recurrence was the liver (n=75; 3-year CIR [95% CI], 27.9% [22.5–33.5%]; Figure S1b).
Genomic alterations in driver and HRD genes
The average sequencing depth of all variants was 722X and the median cellularity of all samples was 23%. An oncoprint demonstrating genetic alterations in the cohort is shown in Figure 1. KRAS was altered in 93% (n=262) of the cohort, of which, 42% (n=109) had G12D mutations. Alterations in TP53 occurred in 72% (n=203), and specifically, 27% (n=54) had truncating mutations and 29% (n=80) had alterations in the presence of LOH. Truncating mutations and LOH co-occurred in 10% (n=29) of patients. Mutations in CDKN2A were noted in 28% (n=79), and SMAD4 in 20% (n=57) of the cohort.
Figure 1.
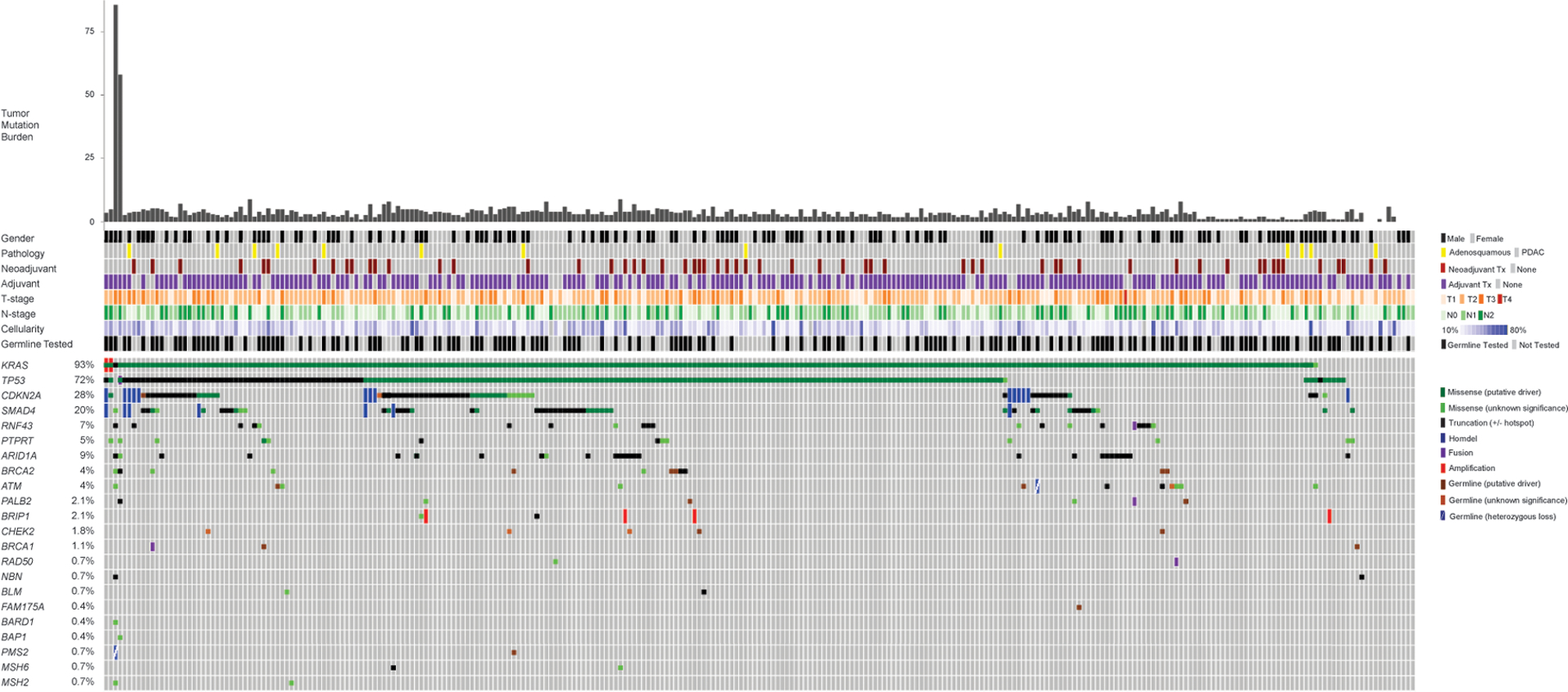
Oncoprint of Frequently Altered Genes and those Involved in DNA Repair Pathways.
ARID1A, RNF43, and PTPRT were altered in ≥5% of the cohort. There were 47 patients with somatic HRD mutations, and 4 patients had somatic alterations in MMR genes. There were 154 (54%) individuals who underwent germline testing with MSK-IMPACT, and of these, 29 (19%) had at least one germline mutation identified with 21 (14%) having a mutation predicted to be oncogenic. There were 18 patients with germline HRD (gHRD) mutations, of which 7 had germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations.
Following the implementation of routine genomic profiling with MSK-IMPACT, there have been a total of 1,702 PDAC tumors sequenced using this platform. We compared the alterations in our cohort of 283 resected tumors to all other primary and metastatic PDAC tumors sequenced at MSK. Mutational frequencies of the four driver genes, genes altered at a frequency of ≥5%, and both HRD and MMR genes were similar between the two cohorts (p>0.05).
Driver gene alterations and association with clinical and pathologic variables
Alterations in KRAS and TP53 were compared to pathologic variables associated with poor prognosis, including tumor diameter, lymphovascular invasion, perineural invasion and the presence of positive lymph nodes. The only positive association observed was between KRAS alterations and larger tumor size (median, 3.0 vs 2.2cm, p=0.009; Table S2). There were no significant associations between CDKN2A status, SMAD4 status, number of genes altered, and pathologic variables.
Driver gene alterations and association with survival
Gene-level alterations in both KRAS and TP53 demonstrated an association with OS on univariate analysis, but not RFS (Table 2). There was no association between alterations in CDKN2A, SMAD4, or the number of driver genes (0–4) and OS or RFS. Individuals with mutations in PTRPT had worse RFS than those with wildtype PTRPT (median [95%CI], 5.7 [3.2-NA] vs 14.0 [12.0–17.9] months, p=0.019).
Table 2.
Associations of Driver Genes, and Other Frequently Mutated Genes (> 5%), with Overall and Recurrence-Free Survival.
| Alteration n (%) | Overall Survival | Recurrence Free Survival | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (95% CI), months | 3-year (95% CI), % | Median (95% CI), months | 3-year (95% CI), % | ||||||||
| Wildtype | Altered | Wildtype | Altered | p-value | Wildtype | Altered | Wildtype | Altered | p-value | ||
| KRAS | 262 (93) | 91.0 (34.8–NA) | 38.8 (33.0–45.5) | 61.4 (38.9–96.8) | 53.5 (46.7–61.2) | 0.043 | 21.7 (14.2–76.5) | 12.9 (11.7–15.9) | 32.9 (16.5–65.5) | 19.8 (14.6–26.9) | 0.117 |
| TP53 | 203 (72) | 65.0 (33.0–NA) | 37.4 (32.1–42.8) | 59.0 (47.4–73.5) | 52.0 (44.3–61.0) | 0.035 | 15.1 (12.8–21.7) | 12.5 (10.9–18.1) | 21.2 (12.8–35.3) | 20.9 (15.0–29.1) | 0.352 |
| CDKN2A | 77 (27) | 39.0 (33.0–47.2) | 38.8 (29.1–NA) | 54.5 (47.2–63.0) | 51.7 (38.4–69.6) | 0.846 | 14.2 (12.3–18.6) | 11.7 (8.9–19.2) | 22.1 (16.3–30.1) | 17.8 (9.5–33.3) | 0.244 |
| SMAD4 | 57 (20) | 38.8 (32.4–47.2) | 39.2 (33.3–NA) | 53.8 (46.5–62.1) | 55.0 (41.1–73.6) | 0.375 | 13.2 (11.9–17.3) | 14.6 (10.3–23.6) | 19.9 (14.4–27.6) | 24.5 (14.3–42.1) | 0.594 |
| ARID1A | 26 (9) | 39.0 (33.9–46.3) | 33.3 (14.3–NA) | 54.6 (47.7–62.5) | 48.4 (30.9–75.8) | 0.722 | 14.0 (12.3–18.5) | 10.5 (7.2–24.5) | 22.1 (16.7–29.3) | 9.3 (1.8–48.7) | 0.119 |
| RNF43 | 20 (7) | 37.6 (33.2–45.5) | NR | 53.1 (46.2–61.0) | 61.7 (42.8–88.9) | 0.178 | 13.7 (12.0–17.6) | 15.5 (9.8–NA) | 21.5 (16.2–28.6) | 12.0 (2.4–60.5) | 0.708 |
| PTPRT | 13 (5) | 39.0 (33.3–47.2) | 34.8 (21.3–NA) | 54.9 (48.2–62.5) | 40.0 (17.8–89.6) | 0.428 | 14.0 (12.0–17.9) | 5.7 (3.2–NA) | 22.1 (16.8–29.1) | NA | 0.019 |
NR: median survival not reached
Median survival in individuals with KRAS alterations was 38.8 [95%CI: 33.0–45.5] months versus 91.0 [95%CI: 34.8-NA] months in those with wildtype KRAS (p=0.043, Figure 2a). Moreover, G12D mutations were associated with worse OS as compared to all other KRAS mutations (median [95% CI], 31.6 [25.3–45.5] vs 39.2 [37.4–75.2] months, p=0.012; Figure 2b), and specifically other G12 mutations (median [95%CI], 31.6 [25.3–45.5] vs 39.3 [37.2–51.6] months, p=0.027).
Figure 2.
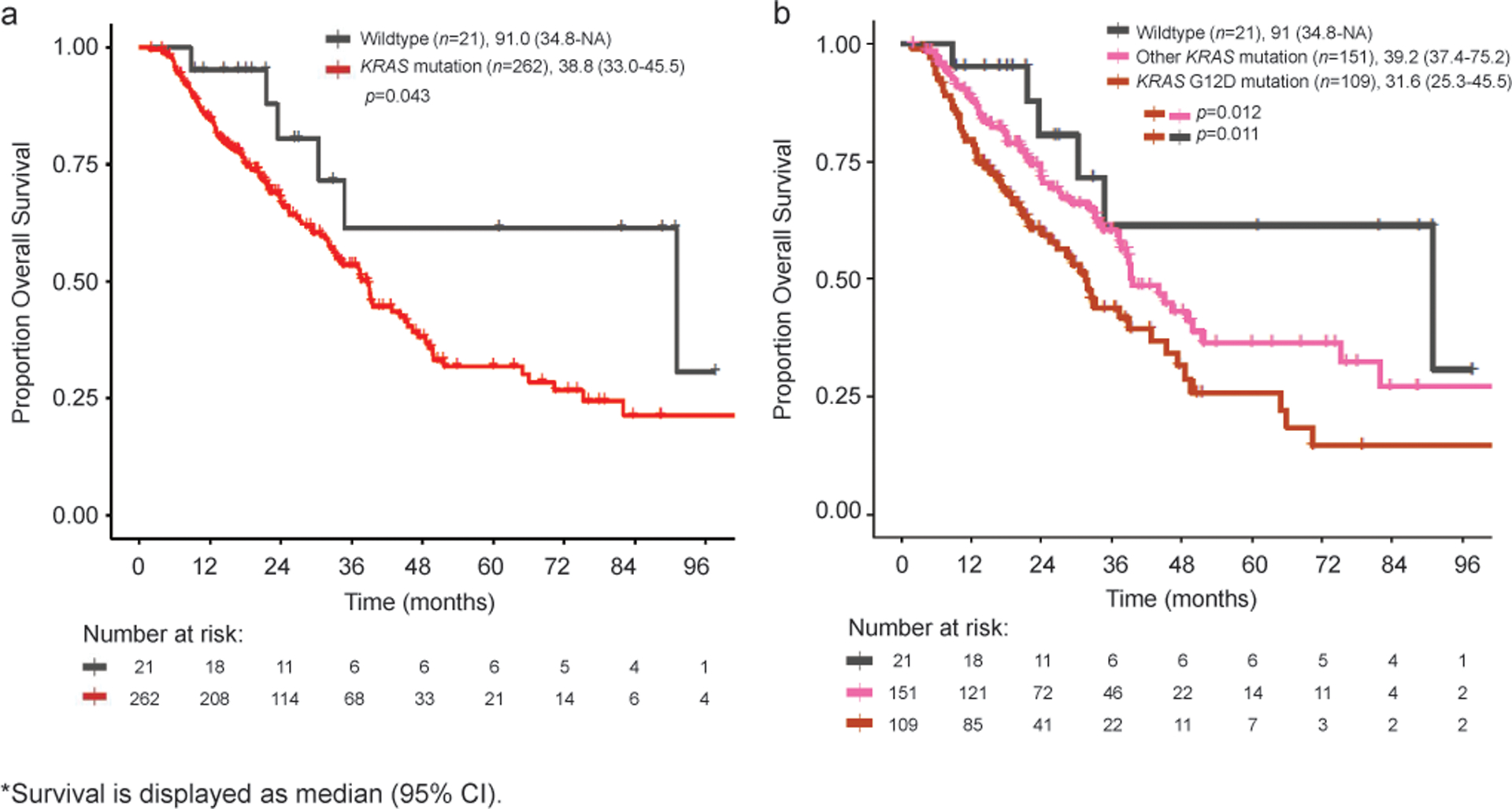
Kaplan-Meier Curves for Individuals with Gene-Level Alterations in KRAS (a) and KRAS G12D mutations (b).
There were 21 individuals (7.5%) with KRAS wildtype tumors (Figure S2). Of these, 5 patients had no other SNV or CNA identified while 16 individuals had other somatic alterations, 12 of which were exonic. The mean cellularity of all KRAS wildtype patients was 23.6%; it was 30.4% in patients with exonic somatic alterations, but only 16% in those without any identified alterations. One patient had a BRAF-KDM7A fusion, however, the breakpoint in KDM7A occurred 2Kb after the stop codon making the significance of this alteration unknown.
The median OS in patients with TP53 alterations was 37.4 [95%CI: 32.1–42.8] months and 65.0 [95%CI: 33.0-NA] months in those with wildtype TP53 (p=0.035, Figure 3a). TP53 mutations that resulted in truncations were associated with worse OS (median [95%CI], 33.9 [24.0–39.0] vs 39.6 [32.4–75.2] months, p=0.020, Figure 3b) and RFS (median [95%CI], 10.9 [8.5–13.7] vs 15.5 [11.4–21.6] months, p=0.014). TP53 mutations in regions with LOH were associated with worse OS compared to no LOH (median [95%CI], 26.6 [21.6–44.2] vs 39.2 [34.5–49.1] months, p=0.048, Figure 3c), although there was no significant difference in RFS (9.8 [6.8–15.5] vs 15.9 [12.3–21.8] months, p=0.079). Individuals who had truncating mutations in a region with LOH (n=29) had worse RFS than either truncating or LOH alone (median [95%CI], 8.7 [5.0–12.0] vs 12.7 [10.9–28.5] months, p=0.026 and 11.4 [6.8–35.9] months, p=0.019), however there was no significant difference in OS (Figure S3). Alterations in KRAS and TP53 co-occurred in 70% (n=197) of patients, and this was associated with worse OS than a single mutation alone (median [95% CI], 37.4 [32.0–42.8] vs 65.0 [33.0-NA] months, p=0.027).
Figure 3.
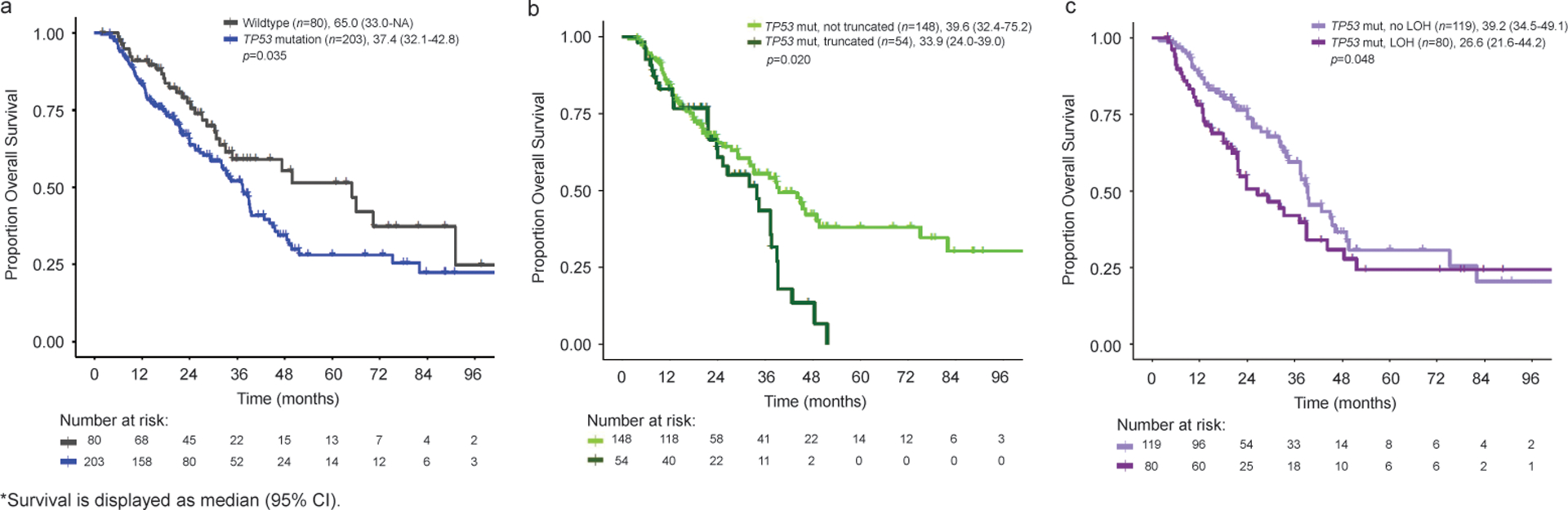
Kaplan-Meier Curves for OS Individuals with Gene-Level Alterations in TP53 (a), Truncating TP53 Mutations (b), and TP53 Mutations Associated with LOH (c).
We then conducted univariate and multivariate analyses looking at the association of KRAS and TP53 status with OS in the setting of other potential confounding variables. Results of univariate analysis demonstrated that KRAS alterations, TP53 alterations, Stage III/IV tumors, lymphovascular invasion and neoadjuvant therapy were associated with OS (Table 3). When adjusting for other variables, KRAS was no longer associated with OS (HR [95%CI], 1.74 [0.75–4.01], yet TP53 alterations remained significantly associated with a worse prognosis (HR [95% CI], 1.54 [1.01–2.33], p=0.042).
Table 3.
Univariate and Multivariate Analyses of Association between Genomic Alterations and Pathologic Variables with OS.
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-value | HR (95% CI) | p-value | |
| KRAS Alteration | 2.29 (1.00–5.22) | 0.049 | 1.74 (0.75–4.01) | 0.2 |
| TP53 Alteration | 1.54 (1.03–2.31) | 0.037 | 1.54 (1.02–2.33) | 0.042 |
| AJCC Stage (8th Edition) | <0.001 | 0.002 | ||
| I–II | Ref | Ref | ||
| III–IV | 1.89 (1.33–2.69) | 1.78 (1.23–2.57) | ||
| Lymphovascular Invasion | 1.73 (1.16–2.59) | 0.007 | 1.96 (1.26–3.04) | 0.003 |
| Perineural Invasion | 1.33 (0.68–2.63) | 0.41 | ||
| Tumor Size | 1.06 (0.94–1.20) | 0.36 | ||
| Neoadjuvant therapy | 1.96 (1.33–2.87) | <0.001 | 2.66 (1.77–4.01) | <0.001 |
| Lymph Nodes | 1.20 (0.82–1.75) | 0.34 | ||
Time to site of first recurrence and association with genomic alterations
Associations between genotype and cumulative incidence of site of first recurrence was evaluated for all patients. TP53 truncations and mutations associated with LOH were associated with simultaneous local and distant recurrences (3-year CIR [95%CI], 25.6% [14.3–38.5%] vs 10.4% [5.9–16.5%], p=0.009; 22.2% [13.2–32.7%] vs 9.1% [4.6–15.6%], p=0.030; Table 4). KRAS alterations were associated with an increased incidence of distant recurrences although not statistically significant (3-year CIR [95%CI], 14.2% [10.1–19.0%] vs 23.1% [6.4–45.9%], p=0.056).
Table 4.
Cumulative Incidence of Site of First Recurrences for KRAS and TP53 Alterations.
| KRAS Alteration | KRAS Wildtype | p-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-year | 3-year | 1-year | 3-year | ||
| Distant only | 28.8 (23.4–34.5) | 42.4 (35.7–48.9) | 10.0 (1.6–27.8) | 22.0 (6.3–43.0) | 0.056 |
| Liver only | 23.3 (18.3–28.7) | 29.7 (23.9–35.6) | 0 (0–0) | 5.8 (0.3–24.5) | 0.013 |
| Local only | 7.2 (4.4–10.8) | 21.6 (16.2–27.7) | 5.0 (0.3–21.2) | 22.3 (6.3–44.3) | 0.356 |
| Local + Distant | 9.9 (6.6–14.0) | 14.2 (10.1–19.0) | 10.0 (1.6–27.8) | 23.1 (6.4–45.9) | 0.669 |
| KRAS G12D | Other KRAS mutation | p-value | |||
| 1-year | 3-year | 1-year | 3-year | ||
| Distant only | 37.1 (27.9–46.3) | 49.9 (38.7–60.1) | 23.2 (16.7–30.4) | 37.0 (28.5–45.6) | 0.039 |
| Liver only | 26.7 (18.6–35.4) | 32.8 (23.9–42.0) | 21.2 (14.9–28.1) | 27.7 (20.2–35.6) | 0.268 |
| Local only | 5.7 (2.3–11.3) | 16.0 (8.8–25.0) | 8.3 (4.5–13.5) | 25.3 (17.6–33.7) | 0.089 |
| Local + Distant | 8.6 (4.2–14.9) | 13.7 (7.8–21.2) | 11.0 (6.5–16.7) | 14.6 (9.2–21.3) | 0.906 |
| TP53 Alteration | TP53 Wildtype | p-value | |||
| 1-year | 3-year | 1-year | 3-year | ||
| Distant only | 28.9 (22.7–35.3) | 39.7 (32.3–47.0) | 23.8 (14.8–33.9) | 43.0 (30.6–54.8) | 0.751 |
| Liver only | 25.8 (19.9–32.1) | 30.7 (24.1–37.5) | 10.5 (4.9–18.7) | 20.6 (12.1–30.7) | 0.084 |
| Local only | 8.7 (5.2–13.1) | 22.4 (16.1–29.3) | 2.7 (0.5–8.4) | 19.7 (10.9–30.4) | 0.875 |
| Local + Distant | 10.7 (6.8–15.5) | 14.6 (9.9–20.2) | 7.9 (3.2–15.4) | 16.1 (8.3–26.2) | 0.862 |
| TP53 Truncation | TP53 Mut, No Truncation | p-value | |||
| 1-year | 3-year | 1-year | 3-year | ||
| Distant only | 26.6 (15.4–39.1) | 37.5 (22.7–52.2) | 29.2 (22.0–36.8) | 40.4 (31.6–48.9) | 0.505 |
| Liver only | 25.8 (18.9–33.1) | 31.2 (23.5–39.3) | 26.6 (15.4–39.1) | 30.5 (17.2–44.9) | 0.831 |
| Local only | 13.3 (5.8–24.1) | 27.3 (15.1–41.0) | 7.0 (3.6–12.0) | 20.5 (13.4–28.7) | 0.173 |
| Local + Distant | 19.1 (9.7–30.8) | 25.6 (14.3–38.5) | 7.7 (4.1–12.8) | 10.4 (5.9–16.5) | 0.009 |
| TP53 LOH | TP53 Mutation, No LOH | p-value | |||
| 1-year | 3-year | 1-year | 3-year | ||
| Distant only | 34.2 (23.7–44.9) | 41.8 (29.6–53.5) | 24.8 (17.3–32.9) | 38.4 (28.8–48.0) | 0.257 |
| Liver only | 35.5 (24.9–46.3) | 40.5 (29.0–51.7) | 19.6 (13.0–27.3) | 24.5 (16.6–33.1) | 0.017 |
| Local only | 7.9 (3.2–15.4) | 15.1 (7.5–25.2) | 9.4 (5.0–15.6) | 28.1 (19.0–38.0) | 0.079 |
| Local + Distant | 17.1 (9.6–26.4) | 22.2 (13.2–32.7) | 6.0 (2.6–11.4) | 9.1 (4.6–15.6) | 0.030 |
| KRAS/TP53 Co-mutation | KRAS/TP53 Wildtype | p-value | |||
| 1-year | 3-year | 1-year | 3-year | ||
| Distant only | 29.8 (23.4–36.3) | 41.0 (33.4–48.5) | 14.3 (2.1–37.5) | 30.4 (8.4–56.3) | 0.255 |
| Liver only | 26.6 (20.6–33.0) | 31.6 (24.8–38.6) | 0 (0–0) | 8.0 (0.4–32.3) | 0.054 |
| Local only | 8.4 (5.0–12.9) | 21.9 (15.5–28.9) | 0 (0–0) | 14.3 (2.0–37.8) | 0.742 |
| Local + Distant | 10.5 (6.6–15.3) | 14.5 (9.7–20.2) | 7.1 (0.4–28.7) | 26.4 (5.1–55.2) | 0.976 |
Displayed as % CIR (95% CI)
KRAS alterations were associated with liver recurrences (Table 4, 3-year CIR [95%CI], 29.7% [23.9–35.6%] vs 5.8% [0.3–24.5%], p=0.013), as was TP53 LOH (40.5% [29.0–51.7%] vs 24.5% [16.6–33.1%], p=0.017). Additionally, co-occurrence KRAS/TP53 alterations trended towards significance in patients with liver metastases (3-year CIR [95%CI], 31.6 [24.8–38.6%] vs 8.0% [0.4–32.2%], p=0.054). No genomic alterations were associated with lung metastases as the first site of recurrence.
Alterations in HRD and association with clinical outcomes
Associations between somatic and germline mutations in genes involved in DNA repair pathways and survival outcomes were examined. There were 47 individuals with somatic HRD alterations, and there was no difference in OS or RFS in patients with somatic HRD mutations and those without (median [95%CI], 39.3 [24.3-NA] vs 39.0 [33.2–47.2] months, p=0.705; 11.3 [8.2–21.2] vs 14.2 [12.4–18.6] months, p=0.120). In this group, there were 11 patients who received platinum-based therapy perioperatively and 31 who received chemotherapy without platinum. There was no difference in survival outcomes in individuals with somatic HRD gene alterations who received or did not receive platinum-based chemotherapy (OS: 18.0 [14.0-NA] vs 51.6 [33.3-NA] months, p=0.114; RFS: 10.9 [6.7-NA] vs 11.9 [9.7–24.5] months, p=0.420). There were 18 individuals with mutations in gHRD genes, and these patients had significantly improved OS as compared to wildtype (median OS not reached vs 37.4 [33.0–49.8] months, p=0.035), but there was no difference in RFS (median [95%CI], 14.5 [9.4-NA] vs 13.9 [12–18.6] months, p=0.259). There were 7 individuals (2.5%) with a germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, and 3 patients demonstrated evidence of biallelic loss through LOH. Of these, one received neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX and two received adjuvant gemcitabine and cisplatin. Two of these patients subsequently developed metastatic disease and are maintained on olaparib with ongoing disease control at the time of data analysis.
There were two individuals in this cohort with MSI high tumors, and both patients had MMR germline alterations. One individual had PDAC arising within an IPMN and developed metastatic disease to retroperitoneal lymph nodes following resection. This patient was subsequently diagnosed with Lynch Syndrome based on outside genetic testing, and later developed urothelial, gastric, and prostate cancers. This patient was treated with pembrolizumab, to which his prostate and PDAC had a favorable response during two years of treatment, however ultimately died of progressive urothelial cancer (with controlled small volume metastatic PDAC). The other individual was diagnosed with PDAC arising in association with an IPMN, subsequently metastasized to retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Upon testing with MSK-IMPACT, they were noted to have a germline PMS2 heterozygous loss of exons 11–14. To date, this individual has not developed any other malignancy.
Discussion
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is associated with a poor prognosis, with an overall five-year survival rate of less than 10%.30 Only 15–20% of patients have resectable disease at diagnosis while most present with locally advanced or metastatic disease.31 Biomarkers are expanding, and recently several actionable targets have been identified in PDAC. The most promising of these have been the use of platinum agents and PARP-inhibitors in patients with germline BRCA mutations.19–22 Prior studies have evaluated targeting driver genes, yet results have thus far not demonstrated any clinical benefit.16 Therefore, there exists a need for novel predictive and prognostic biomarkers to improve outcome and refine therapeutic options.
Herein, we demonstrate that alterations in both KRAS and TP53 are associated with worse outcomes in patients who undergo resection for PDAC. Patients with KRAS alterations have decreased OS, and specifically, KRAS G12D mutations confer a worse prognosis as compared to other KRAS alterations. Furthermore, KRAS alterations are also associated with larger tumor size, and distant recurrences following resection, specifically liver metastases. TP53 alterations are associated with worse survival and time to concurrent local and distant metastases as first site of recurrence. In particular, truncating TP53 mutations and those associated with LOH were indicative of a poor prognosis. On multivariate OS analysis, alterations in TP53 were independently associated with OS after controlling for disease stage, vascular invasion, and exposure to neoadjuvant therapy.
KRAS and TP53 have been shown to be mutated in approximately 90% and 75% of PDAC, respectively.32–34 The results of the current study demonstrate that these two frequently altered genes are associated with poorer survival as well as recurrence patterns with higher rates of systemic failure. Previous data have demonstrated that alterations in driver genes are associated with worse outcomes in patients who underwent resection for PDAC.8–10 Using NGS and immunohistochemistry (IHC), Qian et al. demonstrated that KRAS, TP53 and CDKN2A alterations are associated with decreased RFS, and CDKN2A with worse OS.8 Specifically, patients with KRAS G12D mutations had worse RFS and OS.8 Additionally, NGS analysis of the CONKO-001 trial showed that p53 protein overexpression was associated with worse OS and RFS in the setting of adjuvant gemcitabine.35 Given the poor outcomes associated with KRAS and TP53 variants, these should be further evaluated for use as biomarkers to provide prognostic information and help guide treatment decisions. For example, adjuvant therapies could be intensified for patients with an unfavorable genomic profile.
Furthermore, such alterations could serve as therapeutic targets in the future, and several studies have demonstrated potential in targeting KRAS. KRAS is commonly altered in other solid tumors, and results of a recent phase I trial using AMG 510, a small molecule inhibitor of KRAS G12C, demonstrated a partial response or stable disease in KRAS G12C mutated colorectal and non-small cell lung cancers.36 In locally advanced pancreatic cancer, an initial phase 1/2a trial evaluating siG12D-LODER, a particle which releases small amounts of RNAi against KRAS G12D and to a lesser extent in KRAS G12V, in combination with gemcitabine, demonstrated stable disease or a partial response in all patients.37 Currently, there is an ongoing randomized phase 2 trial evaluating gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel with or without siG12D-LODER in locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients (NCT01676259).
Patients with wildtype KRAS have been shown to have improved OS as compared to KRAS-mutated individuals following resection for PDAC.11 Our results are consistent with these data. True wildtype KRAS should be confirmed by evaluation of CNA or the presence/absence of other mutations given the low cellularity of PDAC tumors. KRAS wildtype individuals have been shown to have other genomic alterations driving pancreatic tumorgenesis. In our cohort, two individuals had oncogenic BRAF mutations (as predicted by OncoKB24) and one was noted to have a BRAF-KDM7A of uncertain significance. Pishvaian et al. identified that 14 of 81 KRAS wildtype patients had alterations in BRAF.14 Additionally, ALK fusions have been shown to drive tumorgenesis in KRAS wildtype PDAC, and can be targeted with tyrosine kinase inhibitors.38,39 Although these alterations are noted in patients with metastatic disease, this demonstrates the importance of accurate identification of KRAS wildtype patients, as a subset of these patients may have other actionable targets.
Given recent data that has emerged with the use of platinum agents and PARP-inhibitors in PDAC, we evaluated the outcomes of individuals with both germline and somatic alterations in HRD genes. Preliminary data implies that some ARID1A alterations result in an HRD-like phenotype (unpublished data), and therefore we have included ARID1A mutations in this group, although we recognize this is not a point of consensus. Our results suggest that individuals with gHRD alterations have improved survival. Patients with gHRD mutations were diagnosed at a younger age (median, 59 vs 68 years), however given the heterogeneity of treatments received and small sample size, we are unable to accurately assess for confounding factors to account for this difference. No survival differences were observed in our cohort for individuals with and without somatic HRD alterations or with the use of platinum agents. However, the number of individuals with somatic HRD alterations in our cohort was small (17%), and likely underpowered to detect differences between groups. We had limited power to consider the effect of biallelic loss of HRD genes, given there were only 8 patients that had VAFs consistent with biallelic loss. This is important, as one wild-type copy of a gene is often sufficient for normal function. Additionally, only a small subset of these patients received platinum-based chemotherapy, as many patients underwent resection before this was routinely adopted in clinical practice.
In this study, we evaluated genomic alterations obtained from a routinely used, clinically-actionable targeted sequencing panel. This can be done using samples obtained from cytology or core needle biopsies of a tumor, whereas IHC often requires additional tissue. However, a limitation of this study is that we only evaluated genomic alterations, and did not account for downstream effects of gene products using IHC. Prior data has shown that CDKN2A is altered in up to 90% of tumors, either through genetic or epigenetic modifications;40,41 therefore, this could account for differences of association CDKN2A and SMAD4 status and outcome in this study as compared to prior studies.8–10 Additionally, the large stromal component in many PDAC tumors and use of bulk sequencing can lead to decreased mutation detection in some patients. There is an inherent selection bias in the subset of patients who underwent resection prior to 2014 for increased OS, as these patients were alive at the time that MSK-IMPACT was implemented. We included this subgroup of patients in our analysis as we evaluated all patients who had their primary tumor sequenced with MSK-IMPACT. Lastly, several of the subgroups analyzed are small in size and therefore limited in power.
In conclusion, our results demonstrate that alterations in KRAS and TP53, specifically KRAS G12D and TP53 truncations and LOH, are associated with a worse prognosis in patients who undergo surgical resection for PDAC. Patients with KRAS wildtype tumors and gHRD alterations have improved OS. Given the potential of KRAS, TP53, and HRD status as biomarkers for stratification of outcome or refinement of therapeutic choices, further studies are warranted.
Supplementary Material
Figure S1. Cumulative Incidence of Recurrence of Cohort Based on Local versus Distant Recurrence (a), and Site of Distant Recurrence (b).
Figure S3. Kaplan-Meier Curves for OS (a) and RFS (b) in Individuals with TP53 Mutations that Result in Truncations with and without LOH
Table S1. Patients resected and patients who had MSK-IMPACT on primary tumor.
Figure S2. Oncoprint of KRAS Wildtype Individuals (n = 21).
Table S2. Association of Pathologic Variables and Genome-Level Alterations in KRAS and TP53.
FUNDING:
P30 Cancer Center Support Grant CA0008748; David M. Rubenstein Center for Pancreatic Cancer Research; Reiss Family Foundation
DISCLOSURES:
EOR: Research funding to MSK: Genentech-Roche, BMS, Celgene, MabVax Therapeutics, ActaBiologica, AstraZenica, Silenseed; Consulting/Advisory: CytomX Therapeutics, BioLineRx, Targovax, Celgene, Bayer, Polaris, Sobi, Merck
WP: Research funding: SITC -Sparkathon TimIOs, Merck, Astellas, Gossamerbio; Consulting: Ipsen
References
- 1.Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74(11):2913–2921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bailey P, Chang DK, Nones K, et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2016;531(7592):47–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Biankin AV, Waddell N, Kassahn KS, et al. Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon guidance pathway genes. Nature. 2012;491(7424):399–405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jones S, Zhang X, Parsons DW, et al. Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses. Science. 2008;321(5897):1801–1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Waddell N, Pajic M, Patch AM, et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;518(7540):495–501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kanda M, Matthaei H, Wu J, et al. Presence of somatic mutations in most early-stage pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(4):730–733 e739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Maitra A, Adsay NV, Argani P, et al. Multicomponent analysis of the pancreatic adenocarcinoma progression model using a pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia tissue microarray. Mod Pathol. 2003;16(9):902–912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Qian ZR, Rubinson DA, Nowak JA, et al. Association of Alterations in Main Driver Genes With Outcomes of Patients With Resected Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(3):e173420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kang CM, Hwang HK, Park J, et al. Maximum Standard Uptake Value as a Clinical Biomarker for Detecting Loss of SMAD4 Expression and Early Systemic Tumor Recurrence in Resected Left-Sided Pancreatic Cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(17):e3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chang DT, Chapman CH, Norton JA, et al. Expression of p16(INK4A) but not hypoxia markers or poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase is associated with improved survival in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 2010;116(22):5179–5187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schlitter AM, Segler A, Steiger K, et al. Molecular, morphological and survival analysis of 177 resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs): Identification of prognostic subtypes. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hayashi H, Kohno T, Ueno H, et al. Utility of Assessing the Number of Mutated KRAS, CDKN2A, TP53, and SMAD4 Genes Using a Targeted Deep Sequencing Assay as a Prognostic Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas. 2017;46(3):335–340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lowery MA, Jordan EJ, Basturk O, et al. Real-Time Genomic Profiling of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Potential Actionability and Correlation with Clinical Phenotype. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(20):6094–6100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pishvaian MJ, Bender RJ, Halverson D, et al. Molecular Profiling of Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: Initial Results from the Know Your Tumor Initiative. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(20):5018–5027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Aguirre AJ, Nowak JA, Camarda ND, et al. Real-time Genomic Characterization of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer to Enable Precision Medicine. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(9):1096–1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Singh RR, Goldberg J, Varghese AM, Yu KH, Park W, O’Reilly EM. Genomic profiling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and a pathway towards therapy individualization: A scoping review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019;75:27–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Witkiewicz AK, McMillan EA, Balaji U, et al. Whole-exome sequencing of pancreatic cancer defines genetic diversity and therapeutic targets. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Electronic address aadhe, Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Integrated Genomic Characterization of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2017;32(2):185–203 e113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Golan T, Hammel P, Reni M, et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(4):317–327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Golan T, Kanji ZS, Epelbaum R, et al. Overall survival and clinical characteristics of pancreatic cancer in BRCA mutation carriers. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(6):1132–1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kaufman B, Shapira-Frommer R, Schmutzler RK, et al. Olaparib monotherapy in patients with advanced cancer and a germline BRCA1/2 mutation. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(3):244–250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.O’Reilly EM, Lee JW, Lowery MA, et al. Phase 1 trial evaluating cisplatin, gemcitabine, and veliparib in 2 patient cohorts: Germline BRCA mutation carriers and wild-type BRCA pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 2018;124(7):1374–1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cheng DT, Mitchell TN, Zehir A, et al. Memorial Sloan Kettering-Integrated Mutation Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets (MSK-IMPACT): A Hybridization Capture-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Clinical Assay for Solid Tumor Molecular Oncology. J Mol Diagn. 2015;17(3):251–264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zehir A, Benayed R, Shah RH, et al. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):703–713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Middha S, Zhang L, Nafa K, et al. Reliable Pan-Cancer Microsatellite Instability Assessment by Using Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Data. JCO Precis Oncol. 2017;2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Niu B, Ye K, Zhang Q, et al. MSIsensor: microsatellite instability detection using paired tumor-normal sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(7):1015–1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shen R, Seshan VE. FACETS: allele-specific copy number and clonal heterogeneity analysis tool for high-throughput DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(16):e131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jonsson P, Bandlamudi C, Cheng ML, et al. Tumour lineage shapes BRCA-mediated phenotypes. Nature. 2019;571(7766):576–579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chakravarty D, Gao J, Phillips SM, et al. OncoKB: A Precision Oncology Knowledge Base. JCO Precis Oncol. 2017;2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.American Cancer Society, Cancer Facts & Figures 2019. 2019.
- 31.Hidalgo M Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(17):1605–1617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wood LD, Hruban RH. Pathology and molecular genetics of pancreatic neoplasms. Cancer J. 2012;18(6):492–501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Almoguera C, Shibata D, Forrester K, Martin J, Arnheim N, Perucho M. Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell. 1988;53(4):549–554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Redston MS, Caldas C, Seymour AB, et al. p53 mutations in pancreatic carcinoma and evidence of common involvement of homocopolymer tracts in DNA microdeletions. Cancer Res. 1994;54(11):3025–3033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Striefler JK, Sinn M, Pelzer U, et al. P53 overexpression and Ki67-index are associated with outcome in ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma with adjuvant gemcitabine treatment. Pathol Res Pract. 2016;212(8):726–734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fakih M, ONeil B, Price TJ, et al. Phase 1 study evaluating the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and efficacy of AMG 510, a novel small molecule KRASG12C inhibitor, in advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Golan T, Khvalevsky EZ, Hubert A, et al. RNAi therapy targeting KRAS in combination with chemotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2015;6(27):24560–24570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Singhi AD, Ali SM, Lacy J, et al. Identification of Targetable ALK Rearrangements in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017;15(5):555–562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shimada Y, Kohno T, Ueno H, et al. An Oncogenic ALK Fusion and an RRAS Mutation in KRAS Mutation-Negative Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Oncologist. 2017;22(2):158–164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Schutte M, Hruban RH, Geradts J, et al. Abrogation of the Rb/p16 tumor-suppressive pathway in virtually all pancreatic carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1997;57(15):3126–3130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Caldas C, Hahn SA, da Costa LT, et al. Frequent somatic mutations and homozygous deletions of the p16 (MTS1) gene in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Nat Genet. 1994;8(1):27–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Cumulative Incidence of Recurrence of Cohort Based on Local versus Distant Recurrence (a), and Site of Distant Recurrence (b).
Figure S3. Kaplan-Meier Curves for OS (a) and RFS (b) in Individuals with TP53 Mutations that Result in Truncations with and without LOH
Table S1. Patients resected and patients who had MSK-IMPACT on primary tumor.
Figure S2. Oncoprint of KRAS Wildtype Individuals (n = 21).
Table S2. Association of Pathologic Variables and Genome-Level Alterations in KRAS and TP53.


