This cohort study examines multiyear self-reported demographic, lifestyle choice, and medical history data to track weight changes, disease diagnoses, health outcomes, and other factors associated with pancreatic cancer risk among participants in 2 long-term national surveys.
Key Points
Question
Is there an association of diabetes duration and recent weight loss with subsequent risk of pancreatic cancer?
Findings
In this cohort study of 112 818 women and 46 207 men enrolled in 2 US cohort studies, participants with recent-onset diabetes accompanied by weight loss of 1 to 8 lb or more than 8 lb had a substantially increased risk for pancreatic cancer compared with participants with no such exposure.
Meaning
The findings from this study suggest that individuals with recent-onset diabetes accompanied by weight loss have a high risk for developing pancreatic cancer and may be a group for whom early detection strategies would be advantageous.
Abstract
Importance
Pancreatic cancer is the third-leading cause of cancer death in the United States; however, few high-risk groups have been identified to facilitate early diagnosis strategies.
Objective
To evaluate the association of diabetes duration and recent weight change with subsequent risk of pancreatic cancer in the general population.
Design, Setting, and Participants
This cohort study obtained data from female participants in the Nurses’ Health Study and male participants in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, with repeated exposure assessments over 30 years. Incident cases of pancreatic cancer were identified from self-report or during follow-up of participant deaths. Deaths were ascertained through reports from the next of kin, the US Postal Service, or the National Death Index. Data collection was conducted from October 1, 2018, to December 31, 2018. Data analysis was performed from January 1, 2019, to June 30, 2019.
Exposures
Duration of physician-diagnosed diabetes and recent weight change.
Main Outcome and Measures
Hazard ratios (HRs) for subsequent development of pancreatic cancer.
Results
Of the 112 818 women (with a mean [SD] age of 59.4 [11.7] years) and 46 207 men (with a mean [SD] age of 64.7 [10.8] years) included in the analysis, 1116 incident cases of pancreatic cancers were identified. Compared with participants with no diabetes, those with recent-onset diabetes had an age-adjusted HR for pancreatic cancer of 2.97 (95% CI, 2.31-3.82) and those with long-standing diabetes had an age-adjusted HR of 2.16 (95% CI, 1.78-2.60). Compared with those with no weight loss, participants who reported a 1- to 4-lb weight loss had an age-adjusted HR for pancreatic cancer of 1.25 (95% CI, 1.03-1.52), those with a 5- to 8-lb weight loss had an age-adjusted HR of 1.33 (95% CI, 1.06-1.66), and those with more than an 8-lb weight loss had an age-adjusted HR of 1.92 (95% CI, 1.58-2.32). Participants with recent-onset diabetes accompanied by weight loss of 1 to 8 lb (91 incident cases per 100 000 person-years [95% CI, 55-151]; HR, 3.61 [95% CI, 2.14-6.10]) or more than 8 lb (164 incident cases per 100 000 person-years [95% CI, 114-238]; HR, 6.75 [95% CI, 4.55-10.00]) had a substantially increased risk for pancreatic cancer compared with those with neither exposure (16 incident cases per 100 000 person-years; 95% CI, 14-17). Incidence rates were even higher among participants with recent-onset diabetes and weight loss with a body mass index of less than 25 before weight loss (400 incident cases per 100 000 person-years) or whose weight loss was not intentional judging from increased physical activity or healthier dietary choices (334 incident cases per 100 000 person-years).
Conclusions and Relevance
This study demonstrates that recent-onset diabetes accompanied by weight loss is associated with a substantially increased risk for developing pancreatic cancer. Older age, previous healthy weight, and no intentional weight loss further elevate this risk.
Introduction
Pancreatic cancer is the third-leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States, with a 5-year survival rate of less than 10%.1 This low survival rate is largely associated with the diagnosis occurring at an advanced stage when the cancer is no longer curable. To date, patients with a strong family history or genetic predisposition and those with pancreatic cystic lesions have been the primary focus of pancreatic cancer early detection programs, with initial evidence indicating a shift to earlier stage disease and longer survival among those who undergo surveillance imaging.2,3 Nevertheless, these patients represent only 15% to 20% of those presenting with pancreatic cancer,4 and the US Preventive Services Task Force recommends against pancreatic cancer screening for asymptomatic individuals with average risk.5 The identification of other high-risk groups is necessary to enhance screening efforts.
Multiple studies have identified type 2 diabetes as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer.6,7 However, a subset of patients with pancreatic cancer develop diabetes several months to years before their cancer diagnosis.8,9 Hyperglycemia in this setting is associated with an intact but not yet clinically diagnosed pancreatic tumor and has been classified as pancreatogenic or type 3c diabetes.10,11 Although type 2 diabetes is often accompanied by weight gain, pancreatogenic diabetes can paradoxically be accompanied by weight loss.12,13 Nonetheless, the risks for pancreatic cancer associated with different duration of diabetes and degree of weight loss have not been evaluated in the general population. Furthermore, whether metrics of weight loss intentionality are associated with the accuracy of pancreatic cancer risk prediction has not been assessed. Many patients with pancreatic cancer who present with pancreatogenic diabetes have a localized, surgically resectable tumor at the onset of hyperglycemia, providing a window of opportunity for earlier cancer detection and treatment.14
Methods
The protocol of this cohort study was approved by the institutional review boards of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and those of participating registries as required. All participants provided written informed consent for the researchers to access their medical records. Data collection was conducted from October 1, 2018, to December 31, 2018. Data analysis was performed from January 1, 2019, to June 30, 2019.
Study Population
This study analyzed data from the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS), a study initiated in 1976 in which 121 700 US female nurses aged 30 to 55 years completed a mailed questionnaire on demographic characteristics, lifestyle choices, and medical history.15 Another source of data was the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study (HPFS), which was initiated in 1986 and involved 51 529 US male health professionals aged 40 to 75 years who responded to a similar mailed questionnaire.16 Since enrollment, participants in both the NHS and HPFS have updated their information through biennial follow-up questionnaires. In this study, we set the baseline as 1978 for the NHS and 1988 for the HPFS and excluded participants with prevalent diabetes or prior history of cancer at baseline. The study population comprised 112 818 women and 46 207 men.
Incident Cases of Pancreatic Cancer and Diabetes Duration
We identified incident cases of pancreatic cancer from self-report or during follow-up of participant deaths. Deaths were ascertained through reports from the next of kin, the US Postal Service, or the National Death Index.17 Among us, 2 physicians (K.N., B.M.W.) who were blinded to exposure status confirmed the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer by reviewing medical records, death certificates, or cancer registry data. Patients with nonadenocarcinoma type of pancreatic tumor were excluded.
The enrollment and biennial follow-up questionnaires asked participants if they had ever had a diabetes diagnosis by a physician. To verify the diagnosis, a supplementary questionnaire was sent to participants for details, such as the date of diagnosis, symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment. The validity of the supplementary questionnaire was established by medical record review.18,19 In the current study, we identified diabetes status from participant responses on biennial questionnaires and the supplementary questionnaire. For 2% of participants (n = 535) without a reported date of diabetes diagnosis on main or supplementary questionnaires, we used the return date of the biennial questionnaire on which they first reported being told by a physician that they had diabetes. Participants were categorized into 3 exposure groups: no diabetes, recent-onset diabetes (≤4 years), and long-standing diabetes (>4 years) (eFigure 1 in the Supplement). Participants with type 1 diabetes were excluded.
Weight Change Over 2-Year Intervals
Current weight was reported at enrollment and every 2 years thereafter. Recent change in body weight was calculated by subtracting the current weight (ie, weight from the most recent questionnaire) from the previous weight (ie, weight before the current weight). Therefore, for survey cycles in which pancreatic cancer was diagnosed, weight change was measured by comparing questionnaires returned at a median of 1 year (current weight) and 3 years (previous weight) before cancer diagnosis (eFigure 1 in the Supplement). We grouped those who lost no weight or gained weight into the no weight loss category, and we categorized those who lost weight into the following groups: 1- to 4-lb weight loss, 5- to 8-lb weight loss, and more than 8-lb weight loss (to convert lb to kg, multiply by 0.45).
Assessment of Covariates
In the NHS, height was included in the 1976 questionnaire, and weight at age 18 years was asked in the 1980 questionnaire. In the HPFS, height and weight at age 21 years were included in the 1986 questionnaire. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared and grouped as follows: healthy weight (<25.0 BMI), overweight (25.0-29.9 BMI), obese (30.0-34.9 BMI), or morbidly obese (≥35.0 BMI). Information on date of birth, race/ethnicity, physical activity, cigarette smoking, dietary intake, and multivitamin use was also obtained from questionnaires. Intentionality of weight loss (low, medium, or high) was ascertained by combining data on changes in physical activity and diet (a detailed description is provided in the eMethods in the Supplement).
Statistical Analysis
Person-years for participants were calculated from the return of the baseline questionnaire until the occurrence of pancreatic cancer, death from any cause, or the end of the follow-up period (June 2012 for the NHS, and January 2012 for the HPFS), whichever came first. We analyzed the risk of pancreatic cancer according to (1) diabetes duration, (2) recent weight change, and (3) combined status of diabetes and weight change (eMethods in the Supplement). Incidence rates were calculated by dividing the number of incident cases by the number of person-years in each category of exposure, with 95% CIs estimated by a Poisson distribution. Incidence ratios for each of the nonreference categories were computed by dividing the rates in these categories by the rate in the reference category, with 95% CIs estimated by the Mantel-Haenszel method. Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to compute adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs, with age and calendar year at the beginning of each survey cycle as stratification variables. We confirmed no violations of the proportional hazards assumption (eMethods in the Supplement). Cubic spline regression20 was used to delineate the association with the amount of weight loss. In multivariable analyses, we included a priori known or suspected factors for pancreatic cancer (eMethods in the Supplement). The likelihood ratio test was used to assess the potential interactions between diabetes duration and weight loss and by sex or cohort. For secondary analyses of the BMI trend, we matched each incident case of pancreatic cancer with 5 control participants who were free of pancreatic cancer at the time of the case diagnosis.
All analyses were performed with SAS, version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc). A 2-sided P < .05 indicated statistical significance.
Results
Participant Characteristics
During 4.5 million person-years of follow-up in a study population of 112 818 women (with a mean [SD] age of 59.4 [11.7] years) from the NHS and 46 207 men (with a mean [SD] age of 64.7 [10.8] years) from the HPFS, 1116 incident cases of pancreatic cancer (0.7%) were identified, for an incidence rate of 25 per 100 000 person-years. Age-specific incidence rates were somewhat lower than those in the US general population captured in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (eTable 1 in the Supplement).21 Among participants with a new diagnosis of diabetes, the 2-year cumulative incidence of pancreatic cancer after diabetes diagnosis was 0.18% (n = 41) and the 4-year rate was 0.29% (n = 67) (eFigure 2 in the Supplement). Among the 937 incident cases with known diabetes status, 135 participants (14.4%) reported long-standing (>4 years) diabetes and 67 participants (7.2%) reported recent-onset (≤4 years) diabetes. As expected, participants with diabetes vs those with no diabetes, were older (mean [SD] age: 68.6 [9.5] years vs 60.0 [11.6] years), had a higher mean (SD) BMI (29.7 [5.5] vs 24.9 [4.0]), and were less physically active (mean [SD]: 14.8 [14.5] hours per week vs 20.1 [20.2] hours per week) (Table 1).
Table 1. Age-Adjusted Characteristics of Participants by Diabetes Status.
| Characteristica | Nurses’ Health Study | Health Professionals Follow-Up Study | Combined cohorts | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No diabetes | With diabetes | No diabetes | With diabetes | No diabetes | With diabetes | |
| Person-years | 3 122 370 | 220 187 | 848 063 | 62 910 | 3 970 434 | 283 097 |
| Age, mean (SD), y | 58.8 (11.6) | 67.9 (9.5) | 64.2 (10.7) | 71.1 (9.4) | 60.0 (11.6) | 68.6 (9.5) |
| Race/ethnicity, %b | ||||||
| White | 97.2 | 94.5 | 91.2 | 87.5 | 95.9 | 93.3 |
| Black | 1.8 | 3.9 | 0.8 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 3.5 |
| Other | 1.0 | 1.7 | 3.1 | 5.5 | 1.5 | 2.4 |
| Unknown | 0 | 0 | 5.0 | 4.8 | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| BMI, %b | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 24.6 (4.2) | 29.9 (5.7) | 25.7 (3.2) | 28.8 (4.4) | 24.9 (4.0) | 29.7 (5.5) |
| <25.0 | 61.7 | 19.5 | 45.3 | 18.2 | 58.1 | 19.3 |
| 25.0-29.9 | 27.7 | 35.1 | 46.4 | 48.9 | 31.8 | 37.6 |
| 30.0-34.9 | 7.8 | 27.0 | 7.0 | 24.3 | 7.6 | 26.5 |
| ≥35.0 | 2.6 | 18.2 | 1.1 | 8.5 | 2.3 | 16.4 |
| Missing | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Physical activity, mean (SD), MET-h/wk | 17.1 (18.1) | 12.8 (12.7) | 27.3 (22.9) | 21.2 (18.6) | 20.1 (20.2) | 14.8 (14.5) |
| Tobacco smoking, pack-years, %b | ||||||
| Never | 44.1 | 44.3 | 47.3 | 42.4 | 44.8 | 44.0 |
| <5 | 9.5 | 9.1 | 4.4 | 3.8 | 8.4 | 8.1 |
| 5-19 | 18.5 | 18.0 | 18.0 | 17.6 | 18.4 | 17.9 |
| 20-39 | 15.8 | 15.3 | 16.0 | 19.1 | 15.9 | 16.0 |
| ≥40 | 10.8 | 11.9 | 8.8 | 11.6 | 10.3 | 11.9 |
| Missing | 1.4 | 1.4 | 5.6 | 5.4 | 2.3 | 2.1 |
| Alcohol use, mean (SD), g/d | 6.2 (9.4) | 3.2 (6.6) | 11.2 (13.7) | 8.7 (12.3) | 7.4 (10.8) | 4.4 (8.3) |
| Multivitamin use, %b | 48.1 | 45.9 | 48.5 | 45.5 | 48.2 | 46.0 |
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); MET, metabolic equivalent.
All values other than age have been directly standardized to the age distribution of the study population.
The percentages were standardized and thus were not consistent with the unstandardized numbers.
Association Between Diabetes and Pancreatic Cancer Risk
Participants with diabetes were at higher risk for pancreatic cancer (Table 2; eTable 2 in the Supplement). The age-adjusted HR was 2.97 (95% CI, 2.31-3.82) for those with recent-onset diabetes and 2.16 (95% CI, 1.78-2.60) for those with long-standing diabetes. When further stratified by duration of diabetes, a similarly elevated risk of pancreatic cancer was noted for participants with diabetes for more than 4 to 10 years (HR, 2.25; 95% CI, 1.74 -2.92) and for more than 10 years (HR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.61-2.66). The association of diabetes with risk of pancreatic cancer was noted for all BMI groups, including when BMI was considered from early adulthood (eg, <25.0 BMI: HR for long-standing diabetes, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.61-2.57) and middle to late adulthood (eg, <25.0 BMI: HR for long-standing diabetes, 2.19; 95% CI, 1.47-3.26) (eTable 3 in the Supplement). Among participants with a BMI lower than 25 throughout life, diabetes continued to be associated with elevated risk of pancreatic cancer (recent-onset diabetes: HR, 3.88 [95% CI, 2.39-6.29]; long-standing diabetes: HR, 2.29 [95% CI, 1.50-3.51]) (eTable 4 in the Supplement). Thus, recent-onset and long-standing diabetes were associated with future development of pancreatic cancer, and these elevated cancer risks were present for individuals regardless of their BMI.
Table 2. Observed Risk of Pancreatic Cancer by Diabetes Duration and Recent Weight Change.
| Exposure | Person-years | No. of cases | Incidence rate (95% CI)a | Incidence ratio (95% CI) | Hazard ratio (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age-adjustedb | Multivariablec | |||||
| Diabetes duration | ||||||
| No diabetes | 3 970 434 | 735 | 19 (17-20) | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| Recent-onset diabetes (≤4 y) | 86 715 | 67 | 77 (61-98) | 4.17 (3.25-5.36) | 2.97 (2.31-3.82) | 2.86 (2.21-3.69) |
| Long-standing diabetes (>4 y) | 196 382 | 135 | 69 (58-81) | 3.71 (3.09-4.46) | 2.16 (1.78-2.60) | 2.11 (1.73-2.57) |
| Recent weight change | ||||||
| No weight loss | 2 155 859 | 377 | 17 (16-19) | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| 1-4–lb weight loss | 490 957 | 137 | 28 (24-33) | 1.60 (1.31-1.94) | 1.25 (1.03-1.52) | 1.26 (1.04-1.54) |
| 5-8–lb weight loss | 334 566 | 99 | 30 (24-36) | 1.69 (1.36-2.11) | 1.33 (1.06-1.66) | 1.29 (1.03-1.62) |
| >8-lb weight loss | 351 653 | 153 | 44 (37-51) | 2.49 (2.06-3.00) | 1.92 (1.58-2.32) | 1.69 (1.38-2.05) |
SI conversion factors: To convert weight to kg, multiply by 0.45.
Incidence rates are presented as cases per 100 000 person-years.
Conditioned on age (continuous) and calendar year of the survey cycle.
Conditioned on age (continuous) and calendar year of the survey cycle and adjusted for sex/cohort, race/ethnicity (White, Black, other, or unknown), body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared; <25.0, 25.0-29.9, 30.0-34.9, ≥35.0, or missing), physical activity (quintiles by sex), smoking in pack-years (never, <5, 5-19, 20-39, ≥40, or missing), alcohol intake in grams per day (0, 0.1-4.9, 5.0-14.9, 15.0-29.9, ≥30.0, or missing), and multivitamin use (yes or no). In the analyses of weight change, the hazard ratios were also adjusted for previous weight (continuous) and diabetes duration (no diabetes, ≤4 years, or >4 years).
Association Between Recent Weight Change and Pancreatic Cancer Risk
We found a stepwise increase in risk for pancreatic cancer with absolute amount and percentage of recent weight loss (eFigure 3 in the Supplement). Compared with participants in the no weight loss group, participants who reported a 1- to 4-lb weight loss had an age-adjusted HR for pancreatic cancer of 1.25 (95% CI, 1.03-1.52), those with a 5- to 8-lb weight loss had an age-adjusted HR of 1.33 (95% CI, 1.06-1.66), and those with a weight loss of more than 8 lb had an age-adjusted HR of 1.92 (95% CI, 1.58-2.32) (Table 2). The HRs were similar after adjustment for previous weight and diabetes duration.
Incidence of Pancreatic Cancer by Combined Status of Diabetes and Weight Change
We analyzed the risk for pancreatic cancer by both diabetes duration and recent weight change (Table 3). Recent-onset diabetes accompanied by weight loss was associated with a forthcoming diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. A substantially higher incidence of pancreatic cancer was noted for participants with recent-onset diabetes accompanied by a 1- to 8-lb weight loss (91 incident cases per 100 000 person-years [95% CI, 55-151]; age-adjusted HR, 3.61 [95% CI, 2.14-6.10]) or by a weight loss of more than 8 lb (164 incident cases per 100 000 person-years [95% CI, 114-238]; age-adjusted HR, 6.75 [95% CI, 4.55-10.00]) compared with participants with neither exposure (16 incident cases per 100 000 person-years [95% CI, 14-17]). In contrast, the HRs for participants who developed weight loss in the setting of long-standing diabetes were less pronounced (1-8–lb weight loss: HR, 2.90 [95% CI, 2.00-4.22]; >8-lb weight loss: HR, 2.80 [95% CI, 1.81-4.34]) (Table 3). These findings were similar in the 2 independent prospective cohorts: the HRs for participants with recent-onset diabetes and weight loss were 6.89 (95% CI, 4.32-10.99) in the NHS and 5.81 (95% CI, 2.73-12.38) in the HPFS (eTable 5 in the Supplement). The secondary analyses that used recent change in BMI instead of weight detected a similar HR of 7.22 (95% CI, 4.90-10.64) for participants with recent-onset diabetes accompanied by a BMI decline of 1.5 or more (eTable 6 in the Supplement). Consistently, in the stratified analyses without joint effects, the association between weight change and pancreatic cancer risk was greater among participants with recent-onset diabetes (>8 lb weight loss: HR, 2.93; 95% CI, 1.49-5.77) vs those with no diabetes (HR, 1.72; 95% CI, 1.37-2.15) or with long-standing diabetes (HR, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.70-2.04) (eTable 7 in the Supplement).
Table 3. Observed Risk of Pancreatic Cancer by Combined Status of Diabetes and Recent Weight Change.
| Exposure | Person-years | No. of cases | Incidence rate (95% CI)a | Incidence ratio (95% CI) | Hazard ratio (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age-adjustedb | Multivariablec | |||||
| No diabetes | ||||||
| + No weight loss | 2 043 907 | 318 | 16 (14-17) | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| + 1-8–lb weight loss | 772 054 | 190 | 25 (21-28) | 1.58 (1.32-1.89) | 1.24 (1.04-1.49) | 1.24 (1.04-1.49) |
| + >8-lb weight loss | 307 034 | 103 | 34 (28-41) | 2.16 (1.73-2.69) | 1.70 (1.36-2.13) | 1.67 (1.33-2.10) |
| Recent-onset diabetes (≤4 y)d | ||||||
| + No weight loss | 33 480 | 16 | 48 (29-78) | 3.07 (1.86-5.08) | 2.29 (1.38-3.79) | 2.15 (1.29-3.57) |
| + 1-8–lb weight loss | 16 448 | 15 | 91 (55-151) | 5.86 (3.49-9.84) | 3.61 (2.14-6.10) | 3.47 (2.05-5.87) |
| + >8-lb weight loss | 17 021 | 28 | 164 (114-238) | 10.57 (7.18-15.56) | 6.75 (4.55-10.00) | 6.44 (4.31-9.62) |
| Long-standing diabetes (>4 y)e | ||||||
| + No weight loss | 78 472 | 43 | 55 (41-74) | 3.52 (2.56-4.84) | 2.10 (1.52-2.90) | 2.01 (1.44-2.80) |
| + 1-8–lb weight loss | 37 021 | 31 | 84 (59-119) | 5.38 (3.72-7.78) | 2.90 (2.00-4.22) | 2.82 (1.93-4.13) |
| + >8-lb weight loss | 27 597 | 22 | 80 (52-121) | 5.12 (3.33-7.89) | 2.80 (1.81-4.34) | 2.64 (1.68-4.13) |
SI conversion factors: To convert weight to kg, multiply by 0.45.
Incidence rates are presented as cases per 100 000 person-years.
Conditioned on age (continuous) and calendar year of the survey cycle.
Conditioned on age (continuous) and calendar year of the survey cycle and adjusted for sex/cohort, race/ethnicity (White, Black, other, or unknown), body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared; <25.0, 25.0-29.9, 30.0-34.9, ≥35.0, or missing), physical activity (quintiles by sex), smoking in pack-years (never, <5, 5-19, 20-39, ≥40, or missing), alcohol intake in grams per day (0, 0.1-4.9, 5.0-14.9, 15.0-29.9, ≥30.0, or missing), and multivitamin use (yes or no).
P for interaction = .05 between recent-onset diabetes and recent weight change.
P for interaction = .35 between long-standing diabetes and recent weight change.
To further define groups with a high risk for pancreatic cancer, we conducted stratified analyses by the following covariates: current age, previous BMI, and change in physical activity and diet. We hypothesized that a particularly high-risk group would be older individuals given that pancreatic cancer is a disease of older age. We also investigated participants who initially had healthy weight or who did not increase physical activity or pursue a healthier diet because intentional weight loss was less likely in these individuals. Among participants with recent-onset diabetes and weight loss, we noted particularly high incidence rates of pancreatic cancer in those 70 years or older (234 incident cases per 100 000 person-years), those with a BMI of less than 25 before weight loss (400 incident cases per 100 000 person-years), and those with a low likelihood of intentional weight loss judging by changes in physical activity and diet (334 incident cases per 100 000 person-years) (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Pancreatic Cancer Incidence by Combined Status of Diabetes and Recent Weight Change .

Incidence rates are presented as cases per 100 000 person-years for participants in 4 groups of exposure: no diabetes and no weight loss, no diabetes and weight loss greater than 8 lb (to convert weight to kg, multiply by 0.45), recent-onset diabetes (≤4 years) and no weight loss, and recent-onset diabetes (≤4 years) and weight loss greater than 8 lb. Incidence rates were calculated by dividing the number of cases by the number of person-years in each group of exposure, with 95% CIs estimated by a Poisson distribution (only lower limits are shown). BMI indicates body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared).
Four-Year Pancreatic Cancer Risk by Combined Status of Diabetes and Weight Change
Among cohort participants with recent-onset diabetes and weight loss of more than 8 lb, the 4-year risk of pancreatic cancer was 0.66% (eTable 8 in the Supplement). This risk was higher in participants 70 years or older (0.94%) or in those who had healthy weight before weight loss or a low likelihood of intentional weight loss (1.45%). If participants with recent-onset diabetes and weight loss were both 70 years or older and had these BMI or weight loss characteristics, they carried a 4-year risk of 2.01% for pancreatic cancer. The absolute risks for pancreatic cancer by age and sex were 20% to 30% lower in the NHS and HPFS cohorts than in the general US population (eTable 1 in the Supplement) such that the identified 4-year risk estimates likely underestimated what would be identified in the US population as a whole.
Secondary Analyses
We examined the association between diabetes duration and weight loss among cases of pancreatic cancer (eTable 9 in the Supplement). Participants with recent-onset diabetes lost substantially more weight (median [interquartile range {IQR}], 7 [0-15] lb) than those with no diabetes (median [IQR], 0 [–4 to 5] lb) or with long-standing diabetes (median [IQR], 1 [–2 to 8] lb) (P < .001), and nearly half of patients with recent-onset diabetes (n = 28 [47.5%]) lost more than 8 lb. Similar weight loss was not seen for matched control participants with recent-onset diabetes (median [IQR], 0 [–5 to 10] lb), suggesting that the weight loss was specific to participants who developed pancreatic cancer.
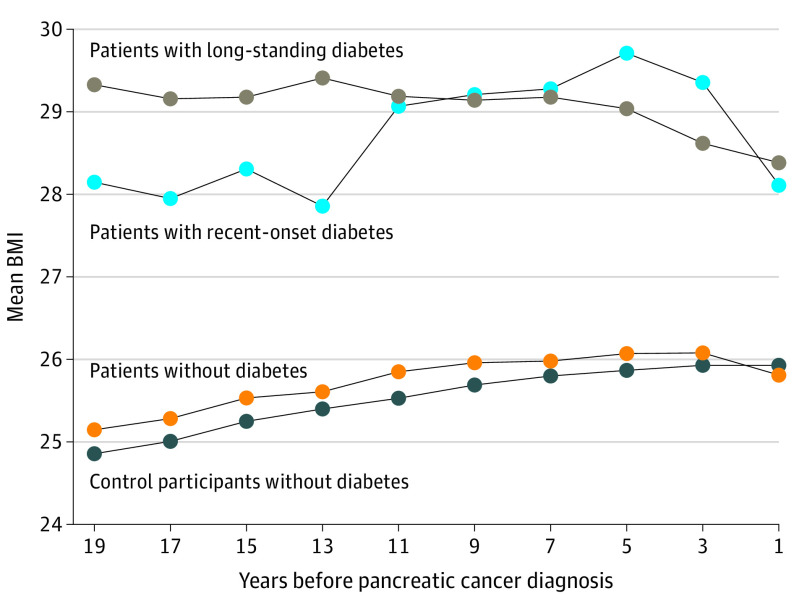
We examined the 20-year trend in BMI before cancer diagnosis (Figure 2). Participants with pancreatic cancer and long-standing diabetes (n = 96) typically started heavy (mean BMI, 29.3) and maintained weight, whereas those with recent-onset diabetes (n = 59) started less heavy (mean BMI, 28.2) and gained weight later in life before losing the weight as the pancreatic cancer diagnosis approached. In contrast, participants with no diabetes (n = 611) started lean (mean BMI, 25.2) and had modest weight gain as they advanced in age, which was similar to control participants with no diabetes (n = 3055).
Figure 2. Twenty-Year Trend in Body Mass Index (BMI) Before Diagnosis in Patients With Pancreatic Cancer and in Control Participants Without Pancreatic Cancer.
Each incident case was matched to 5 control participants who were free of pancreatic cancer at the time of the case diagnosis, based on age (within 12 months), sex/cohort, race/ethnicity (White, Black, other, or unknown), and diabetes duration (no diabetes, ≤4 years, or >4 years).
We performed multiple linear regression analysis to identify the factors associated with weight loss before pancreatic cancer diagnosis (eTable 10 in the Supplement). Older age (coefficient = 0.1442 per year), heavier previous weight (coefficient = 0.0519 per lb), greater weight gain in middle to late life (coefficient = 0.0627 per lb), and recent-onset diabetes (coefficient = 4.6575) were independently associated with greater weight loss before cancer diagnosis (all P ≤ .008). Long-standing diabetes was not associated with such weight loss (coefficient = 0.1530; P = .90). Weight loss before cancer diagnosis was not associated with a more advanced stage of disease at presentation (63.9% of patients with a weight loss of more than 8 lb had metastatic disease at presentation vs 62.2% of patients with no weight loss) (eTable 11 in the Supplement).
Discussion
In the NHS and HPFS cohorts of 112 818 women and 46 207 men with 4.5 million person-years of follow-up, diabetes and recent weight loss were each independently associated with a moderate increase in the risk for pancreatic cancer. However, when weight loss co-occurred with recent-onset diabetes, the subsequent risk of pancreatic cancer increased by more than 6-fold. In addition, the likelihood of a pancreatic cancer diagnosis was even further elevated among individuals with older age, healthy weight before weight loss, and unintentional weight loss.
The high mortality of pancreatic cancer has been associated with the presentation of more than 80% of patients with advanced, incurable disease.21 However, patients who are diagnosed with early-stage cancer can be cured with aggressive treatment, and such treatment has been improving with advancements in surgical procedures, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy.22,23,24 General population-based approaches to early detection for pancreatic cancer remain difficult, however, because of the overall low prevalence of the disease and the morbidity and cost of managing false-positive results.25 As mentioned, the US Preventive Services Task Force does not recommend screening for pancreatic cancer in individuals who are asymptomatic and have average risk.5 Identification and characterization of high-risk groups can potentially limit surveillance to individuals for whom the risk-to-benefit ratio of screening would be most favorable.26
Pancreatic cancer has been associated with the development of diabetes within 4 years before the cancer diagnosis in up to 20% of patients.8,9 In the present study, recent-onset diabetes was associated with a 3-fold higher adjusted risk of pancreatic cancer and a 0.29% pancreatic cancer risk at 4 years, which was consistent with findings in previous studies evaluating physician-diagnosed diabetes.6,7,27,28,29 In other studies, when diabetes was defined at hyperglycemic onset rather than by physician diagnosis, approximately 0.8% of patients were identified with pancreatic cancer in the ensuing 3 to 4 years given that hyperglycemia may occur months to years before a formal diabetes diagnosis is made.13,30 Another study found that most patients with recent-onset diabetes who developed pancreatic cancer had early-stage cancer at the time that they developed hyperglycemia, suggesting a window of opportunity for diagnosing and managing the cancer when it is still curable.14 Nevertheless, the risk associated with recent-onset diabetes alone may be insufficient to warrant risk stratification of the population to implement pancreatic cancer screening.13,27,28,29
In this cohort study, incidence rates for pancreatic cancer were 6-fold to 10-fold higher among participants with recent-onset diabetes and weight loss compared with participants without these exposure factors. Thus, the identified risks in this population were similar to those for families with a history of pancreatic cancer and inherited genetic mutations in pancreatic cancer predisposition genes, such as ATM (RefSeq NM_000051.4), BRCA2 (RefSeq NM_000059.4), and CDKN2A (RefSeq NM_000077.5).31 Members of such families undergo pancreatic cancer surveillance after age 50 to 55 years at specialized clinics,32 and data indicate a shift to earlier-stage disease diagnosis and longer patient survival with surveillance.2,3 The question of whether recent-onset diabetes after age 50 years in the context of weight loss should trigger pancreatic cancer surveillance should be evaluated in large prospective studies.33 Nevertheless, the coexistence of these symptoms should be recognized by clinicians given that both the relative and absolute risks for pancreatic cancer are high, particularly in individuals with healthy weight before weight loss or those who are not trying to lose weight through changes in physical activity or diet.
Previous research has demonstrated that adipose tissue and skeletal muscle wasting were early events in pancreatic cancer development.34,35,36 The present study found that weight loss before a pancreatic cancer diagnosis was associated with recent-onset diabetes, because individuals with long-standing diabetes or with no diabetes experienced substantially less prediagnostic weight loss. Overall, these changes suggest the potential for tumor-induced alterations in the metabolism of the host to indicate the presence of early-stage pancreatic cancer.37
Limitations
This study has limitations. Although the prospective design of the study was advantageous in many ways, it presented several limitations. First, a subset of participants with pancreatic cancer did not return a questionnaire close to the time of cancer diagnosis; therefore, we could not calculate weight change. Second, the use of biennial questionnaires could result in a lower proportion of participants with pancreatic cancer who were identified with recent-onset diabetes given that some patients may have developed diabetes after the last questionnaire was returned. Third, because weight measurements were reported every 2 years, we could not definitively identify whether weight loss had already begun before the development of hyperglycemia or occurred only afterward. Weight loss also may be attributed to other chronic conditions associated with diabetes. Fourth, the study participants were predominantly White health professionals; thus, a study of additional patient populations is warranted.
Conclusions
In this study, recent-onset diabetes accompanied by weight loss was associated with a substantial increase in risk for pancreatic cancer and may represent a high-risk group in the general population for whom early detection strategies would be advantageous. Further elevation of risk was seen in individuals with older age, previous healthy weight, and no intentional weight loss.
eMethods. Study Methods
eReferences
eFigure 1. Examples of Relationships in Time Between Diabetes, Weight Change, and Pancreatic Cancer
eFigure 2. Frequency and Cumulative Incidence of Pancreatic Cancer After Diabetes Diagnosis
eFigure 3. Relationship Between Recent Weight Change and Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer: (A) Absolute Amount; (B) Percentage
eTable 1. Age-Specific Incidence Rates of Pancreatic Cancer in the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, Compared to Incidence Rates in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database
eTable 2. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Diabetes Duration and Recent Weight Change Stratified by Cohort
eTable 3. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Diabetes Duration, Stratified by Body Mass Index in Early and Middle to Late Adulthood
eTable 4. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Diabetes Duration Among Participants With Body Mass Index <25 kg/m2 Throughout Life
eTable 5. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Combined Status of Diabetes and Recent Weight Change Stratified by Cohort
eTable 6. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Combined Status of Diabetes and Recent Change in Body Mass Index
eTable 7. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Recent Weight Change Stratified by Diabetes Duration
eTable 8. Absolute Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer by Diabetes Duration and Recent Weight Loss
eTable 9. Weight Loss Before Cancer Diagnosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cases According to Diabetes Duration
eTable 10. Factors Associated With Weight Loss Before Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis
eTable 11. Pancreatic Cancer Stage at Diagnosis According to Diabetes Duration and Weight Loss Before Cancer Diagnosis
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Canto MI, Almario JA, Schulick RD, et al. . Risk of neoplastic progression in individuals at high risk for pancreatic cancer undergoing long-term surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(3):740-751.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.05.035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vasen H, Ibrahim I, Ponce CG, et al. . Benefit of surveillance for pancreatic cancer in high-risk individuals: outcome of long-term prospective follow-up studies from three European expert centers. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(17):2010-2019. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.64.0730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kamisawa T, Wood LD, Itoi T, Takaori K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2016;388(10039):73-85. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00141-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al. ; US Preventive Services Task Force . Screening for pancreatic cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force reaffirmation recommendation statement. JAMA. 2019;322(5):438-444. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Huxley R, Ansary-Moghaddam A, Berrington de González A, Barzi F, Woodward M. Type-II diabetes and pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis of 36 studies. Br J Cancer. 2005;92(11):2076-2083. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602619 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ben Q, Xu M, Ning X, et al. . Diabetes mellitus and risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(13):1928-1937. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chari ST, Leibson CL, Rabe KG, et al. . Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus: prevalence and temporal association with diagnosis of cancer. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(1):95-101. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.10.040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pannala R, Leibson CL, Rabe KG, et al. . Temporal association of changes in fasting blood glucose and body mass index with diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(9):2318-2325. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.253 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Andersen DK, Andren-Sandberg Å, Duell EJ, et al. . Pancreatitis-diabetes-pancreatic cancer: summary of an NIDDK-NCI workshop. Pancreas. 2013;42(8):1227-1237. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182a9ad9d [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(suppl 1):S62-S69. doi: 10.2337/dc10-S062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hart PA, Kamada P, Rabe KG, et al. . Weight loss precedes cancer-specific symptoms in pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus. Pancreas. 2011;40(5):768-772. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318220816a [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sharma A, Kandlakunta H, Nagpal SJS, et al. . Model to determine risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with new-onset diabetes. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(3):730-739.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.05.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pelaez-Luna M, Takahashi N, Fletcher JG, Chari ST. Resectability of presymptomatic pancreatic cancer and its relationship to onset of diabetes: a retrospective review of CT scans and fasting glucose values prior to diagnosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102(10):2157-2163. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01480.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Colditz GA, Manson JE, Hankinson SE. The Nurses’ Health Study: 20-year contribution to the understanding of health among women. J Womens Health. 1997;6(1):49-62. doi: 10.1089/jwh.1997.6.49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Willett WC, et al. . Prospective study of alcohol consumption and risk of coronary disease in men. Lancet. 1991;338(8765):464-468. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90542-W [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rich-Edwards JW, Corsano KA, Stampfer MJ. Test of the National Death Index and Equifax Nationwide Death Search. Am J Epidemiol. 1994;140(11):1016-1019. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Manson JE, Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, et al. . Physical activity and incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in women. Lancet. 1991;338(8770):774-778. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90664-B [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hu FB, Leitzmann MF, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Willett WC, Rimm EB. Physical activity and television watching in relation to risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus in men. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(12):1542-1548. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.12.1542 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Harrell FE Jr, Lee KL, Pollock BG. Regression models in clinical studies: determining relationships between predictors and response. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988;80(15):1198-1202. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.15.1198 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975-2016. National Cancer Institute; 2019. Updated April 9, 2020. Accessed May 1, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2016/
- 22.Ryan DP, Hong TS, Bardeesy N. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(11):1039-1049. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1404198 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Conroy T, Hammel P, Hebbar M, et al. ; Canadian Cancer Trials Group and the Unicancer-GI–PRODIGE Group . FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine as adjuvant therapy for pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(25):2395-2406. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kindler HL. A glimmer of hope for pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(25):2463-2464. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1813684 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Singhi AD, Koay EJ, Chari ST, Maitra A. Early detection of pancreatic cancer: opportunities and challenges. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(7):2024-2040. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hart PA, Chari ST. Is screening for pancreatic cancer in high-risk individuals one step closer or a fool’s errand? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(1):36-38. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.09.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Munigala S, Singh A, Gelrud A, Agarwal B. Predictors for pancreatic cancer diagnosis following new-onset diabetes mellitus. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2015;6:e118. doi: 10.1038/ctg.2015.44 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gupta S, Vittinghoff E, Bertenthal D, et al. . New-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4(11):1366-1372. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2006.06.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Boursi B, Finkelman B, Giantonio BJ, et al. . A clinical prediction model to assess risk for pancreatic cancer among patients with new-onset diabetes. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(4):840-850.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chari ST, Leibson CL, Rabe KG, Ransom J, de Andrade M, Petersen GM. Probability of pancreatic cancer following diabetes: a population-based study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129(2):504-511. doi: 10.1016/j.gastro.2005.05.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hu C, Hart SN, Polley EC, et al. . Association between inherited germline mutations in cancer predisposition genes and risk of pancreatic cancer. JAMA. 2018;319(23):2401-2409. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.6228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Canto MI, Harinck F, Hruban RH, et al. ; International Cancer of Pancreas Screening (CAPS) Consortium . International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening (CAPS) Consortium summit on the management of patients with increased risk for familial pancreatic cancer. Gut. 2013;62(3):339-347. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Maitra A, Sharma A, Brand RE, et al. ; Consortium for the Study of Chronic Pancreatitis, Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer (CPDPC) . A prospective study to establish a new-onset diabetes cohort: from the Consortium for the Study of Chronic Pancreatitis, Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas. 2018;47(10):1244-1248. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sah RP, Sharma A, Nagpal S, et al. . Phases of metabolic and soft tissue changes in months preceding a diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(6):1742-1752. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mayers JR, Wu C, Clish CB, et al. . Elevation of circulating branched-chain amino acids is an early event in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma development. Nat Med. 2014;20(10):1193-1198. doi: 10.1038/nm.3686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Danai LV, Babic A, Rosenthal MH, et al. . Altered exocrine function can drive adipose wasting in early pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2018;558(7711):600-604. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0235-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Khalaf N, Wolpin BM. Metabolic alterations as a signpost to early pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(6):1560-1563. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eMethods. Study Methods
eReferences
eFigure 1. Examples of Relationships in Time Between Diabetes, Weight Change, and Pancreatic Cancer
eFigure 2. Frequency and Cumulative Incidence of Pancreatic Cancer After Diabetes Diagnosis
eFigure 3. Relationship Between Recent Weight Change and Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer: (A) Absolute Amount; (B) Percentage
eTable 1. Age-Specific Incidence Rates of Pancreatic Cancer in the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, Compared to Incidence Rates in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database
eTable 2. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Diabetes Duration and Recent Weight Change Stratified by Cohort
eTable 3. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Diabetes Duration, Stratified by Body Mass Index in Early and Middle to Late Adulthood
eTable 4. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Diabetes Duration Among Participants With Body Mass Index <25 kg/m2 Throughout Life
eTable 5. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Combined Status of Diabetes and Recent Weight Change Stratified by Cohort
eTable 6. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Combined Status of Diabetes and Recent Change in Body Mass Index
eTable 7. Observed Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer According to Recent Weight Change Stratified by Diabetes Duration
eTable 8. Absolute Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer by Diabetes Duration and Recent Weight Loss
eTable 9. Weight Loss Before Cancer Diagnosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cases According to Diabetes Duration
eTable 10. Factors Associated With Weight Loss Before Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis
eTable 11. Pancreatic Cancer Stage at Diagnosis According to Diabetes Duration and Weight Loss Before Cancer Diagnosis