Recently, calpain (CAPN) 14 was identified by a genome-wide genetic association study to play a role in eosinophilic oesophagitis [1]. CAPN14 expression is also linked with asthma and allergy sensitivity [2]. The overexpression of CAPN14 impairs epithelial barrier function and CAPN14 expression is triggered by Th2-associated signalling, such as interleukin (IL)-13 and IL-4 [3]. CAPNs are intracellular regulatory proteases, and there are 16 members of the human CAPN family. CAPNs perform a number of functions, including cytoskeletal and membrane proteins restructuring, signal transduction and inactivating enzymes involved in cell cycle progression, gene expression and apoptosis [4]. Therefore, our group performed a small pilot study to investigate CAPN gene expression profiles in tissue from another disease associated with eosinophilia and epithelial barrier function, chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) [5]. Sinusitis is a condition associated with inflammation in the paranasal sinuses and contiguous nasal mucosa and ∼30 million adults report sinusitis symptoms annually in the United States [6]. Sinusitis is deemed chronic if symptoms persist more than 3 months, with most episodes of sinusitis associated with viral upper respiratory tract infections, asthma, allergic rhinitis and exposure to environmental factors, such as cigarette smoke [7]. Steroids are effective in treating sinusitis, thereby underlining the importance of inflammation in disease pathophysiology, with inflammatory cells such as eosinophils linked to nasal polyps formation that contribute to nasal obstruction [8].
Short abstract
Sinusitis is a common condition associated with inflammation in the sinuses and nasal mucosa. Calpain 14 is highly expressed in the nasal tissues of sinusitis subjects. Calpain 14 is associated with epithelial barrier disruption. https://bit.ly/3fyAwVO
To the Editor:
Recently, calpain (CAPN) 14 was identified by a genome-wide genetic association study to play a role in eosinophilic oesophagitis [1]. CAPN14 expression is also linked with asthma and allergy sensitivity [2]. The overexpression of CAPN14 impairs epithelial barrier function and CAPN14 expression is triggered by Th2-associated signalling, such as interleukin (IL)-13 and IL-4 [3]. CAPNs are intracellular regulatory proteases, and there are 16 members of the human CAPN family. CAPNs perform a number of functions, including cytoskeletal and membrane proteins restructuring, signal transduction and inactivating enzymes involved in cell cycle progression, gene expression and apoptosis [4]. Therefore, our group performed a small pilot study to investigate CAPN gene expression profiles in tissue from another disease associated with eosinophilia and epithelial barrier function, chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) [5]. Sinusitis is a condition associated with inflammation in the paranasal sinuses and contiguous nasal mucosa and ∼30 million adults report sinusitis symptoms annually in the United States [6]. Sinusitis is deemed chronic if symptoms persist more than 3 months, with most episodes of sinusitis associated with viral upper respiratory tract infections, asthma, allergic rhinitis and exposure to environmental factors, such as cigarette smoke [7]. Steroids are effective in treating sinusitis, thereby underlining the importance of inflammation in disease pathophysiology, with inflammatory cells such as eosinophils linked to nasal polyps formation that contribute to nasal obstruction [8].
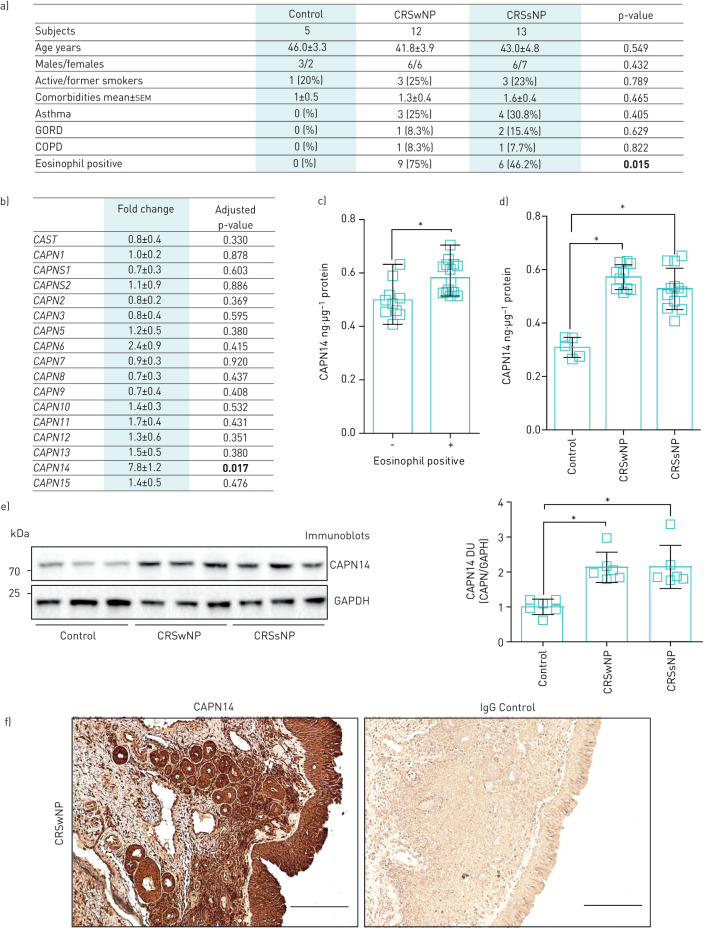
Here, we investigated nasal tissue samples collected from patients with documented CRS, who met diagnostic criteria set forth by the Adult Sinusitis Clinical Practice Guideline [9]. Subjects were prospectively recruited from a subspecialty, referral-based rhinology practice affiliated with SUNY Downstate Medical Center from January 2018 to September 2018. Diagnosis of CRS was made by a senior rhinologist based on a combination of clinical history and objective findings of mucosal inflammation, purulence or polyposis on either nasal endoscopy or radiographic imaging. Both polyposis phenotype-positive (CRSwNP) and -negative (CRSsNP) patients were recruited. All patients had previously failed maximal medical treatment for more than 3 months, including topical nasal saline sprays, inhaled corticosteroids and oral antibiotics, to control their CRS. All patients received 3–5 days of preoperative oral corticosteroids (Prednisone 40 mg daily) prior to endoscopic surgery. The nasal tissue specimen was taken under topical anaesthesia. Control non-CRS patients (>18 years old) were recruited within the same clinic from patients without CRS. Twenty-five patients (12 males and 13 females) with documented CRS and five non-CRS patients (three males and two females) were prospectively recruited in the study. Twelve patients exhibited the phenotype CRSwNP and 13 CRSsNP. The mean age, smoking history, comorbidity index, asthma and gastrooesophageal reflux disease frequency was similar between the groups (figure 1a). Eosinophilia was noted in nine of the CRSwNP group, compared to six in CRSsNP and zero of the controls (p<0.001). Six patients had a history of prior sinonasal surgery related to their CRS. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants and approved by the institutional review board of the State University of New York Downstate Medical Center.
FIGURE 1.
Demographics, gene expression and protein levels of calpain (CAPN) 14 from controls and chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) patients. a) Patient demographics. b) Fold changes in gene expression of all human CAPN and CAST genes in nasal tissue of CRS with nasal polyps (wNP) compared to non-CRS controls (n=5 per group). CAPN14 protein concentration from nasal tissue determined by ELISA from c) eosinophil-positive and -negative CRS subjects and d) control, CRSwNP and CRS without nasal polyps (sNP) subjects. Data are presented as nanogram of CAPN14 per microgram of total nasal tissue protein. e) Immunoblots and densitometry analysis of CAPN14 and glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) from non-CRS controls, CRSwNP and CRSsNP nasal tissues. Data are represented as densitometry units (DU) of CAPN14 relative to GAPDH. a–e) Data are presented as n (%), median (range) (boxes and whiskers in c), mean±sd or mean±sem. Data were analysed by D'Agostino and Pearson omnibus normality test, t-tests, Mann–Whitney or by one-way ANOVA and a Dunn's multiple comparisons test. p-values from quantitative PCR data were adjusted with the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure to correct for multiple comparisons. p-values are shown here and significant differences in bold or highlighted by *. f) Immunohistochemistry was performed on CRSwNP tissue with anti-CAPN14 or control IgG. Scale bars=200 μm. GORD: gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.
We investigated the expression of all CAPN genes in control (n=5) and CRSwNP (n=5) subjects. Real-time PCR was performed on nasal tissue from controls and CRSwNP samples for all CAPN genes and the calpastatin gene (CAST) using Taqman probes (ThermoFisher). CAPN14 was the only CAPN gene to be significantly altered when comparing both groups (figure 1b). The endogenous CAPN inhibitor CAST was not altered between the groups. CAPN14 protein levels were measured by ELISA (MyBioSource.com) in all patients. Immunohistochemistry and immunoblots were performed with an anti-human CAPN14 polyclonal antibody (ThermoFisher). We observed elevated CAPN14 levels in eosinophil-positive CRS (figure 1c) samples, and CRSwNP and CRSsNP samples compared to non-CRS controls, when comparing total levels in tissue by ELISA and immunoblots (figure 1d and e). Here, the presence of nasal polyps had no impact on CAPN14 levels. However, with a 10% difference between CAPN14 levels observed between CRSwNP and CRSsNP by ELISA and power of 0.80 with an α=0.05, then a population size of at least 200 samples is required to confirm this negative finding. Finally, we performed immunohistochemistry on nasal tissues from CRSwNP for CAPN14 to determine the location of CAPN14 protein within the tissue. Positive CAPN14 staining is observed in epithelial cells, bowman's glands and throughout the lamina propria of CRSwNP nasal tissue (figure 1e). Therefore, CAPN14 is significantly expressed in the nasal tissue of CRS subjects and investigating its functional role in disease initiation and progression requires further investigation.
Recently in eosinophilic oesophagitis, CAPN14 was shown to be inducible by IL-13 [3] and the same research group has also demonstrated that the CAPN14 promotor possesses STAT6 binding sites [10]. High levels of IL-13 are observed in the nasal tissues of CRS patients with or without polyps [11], which could influence CAPN14 expression in the nasal tissue. Equally, IL-4 and IL-13 signalling are linked to STAT6 responses [12]. IL-13 also induces MUC5AC expression via STAT6/SAM domain-containing prostate-derived Ets factor (SPDEF) signalling in human airway epithelial cells [13]. This is important as overproduction of mucus is frequently observed in CRS. Increased gene expression of MUC5AC and eosinophilic infiltration into airways is observed in mice following the instillation of IL-13, mediated by the JAK/STAT6 pathway [14]. In nasal polyps, epithelium and gland cells are STAT6-positive and epithelial cell expression of STAT6 is significantly increased and is associated with the recruitment of eosinophils [15]. Therefore, CAPN14 changes in nasal tissue of CRS patients could be mediated by IL-13 and STAT6 and contribute to CRS disease progression.
In conclusion, we demonstrate significant CAPN14 levels in the nasal tissue of CRS patients, which could influence the impairment of epithelial barrier function. Further investigation into the impact of CAPN14 expression in nasal tissue is warranted in CRS pathology and other diseases associated with eosinophilia and epithelial barrier disruption.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the patients who participated in this study.
Footnotes
Support statement: This work was supported by a grant made available to P. Geraghty (Flight Attendant Medical Research Institute CIA160005) and R.F. Foronjy (Flight Attendant Medical Research Institute CIA160028). Funding information for this article has been deposited with theCrossref Funder Registry.
Conflict of interest: M. Boruk has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: A.J. Dabo has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: S. Nath has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: K. Zahid has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: M. Ploszaj has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: D. Wu has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: R. Rosenfeld has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: R.F. Foronjy has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: P. Geraghty has nothing to disclose.
References
- 1.Kottyan LC, Davis BP, Sherrill JD, et al. Genome-wide association analysis of eosinophilic esophagitis provides insight into the tissue specificity of this allergic disease. Nat Genet 2014; 46: 895–900. doi: 10.1038/ng.3033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yang IV, Pedersen BS, Liu AH, et al. The nasal methylome and childhood atopic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2017; 139: 1478–1488. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.07.036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Davis BP, Stucke EM, Khorki ME, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis-linked calpain 14 is an IL-13-induced protease that mediates esophageal epithelial barrier impairment. JCI Insight 2016; 1: e86355. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.86355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chakraborti S, Alam MN, Paik D, et al. Implications of calpains in health and diseases. Indian J Biochem Biophys 2012; 49: 316–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Soyka MB, Wawrzyniak P, Eiwegger T, et al. Defective epithelial barrier in chronic rhinosinusitis: the regulation of tight junctions by IFN-gamma and IL-4. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012; 130: 1087–1096 e1010. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Blackwell DL, Villarroel MA, Clarke TC. Tables of Summary Health Statistics for U.S. adults: 2013 National Health Interview Survey. 2015.
- 7.Tan RA, Corren J. The relationship of rhinitis and asthma, sinusitis, food allergy, and eczema. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 2011; 31: 481–491. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2011.05.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Caughey RJ, Jameson MJ, Gross CW, et al. Anatomic risk factors for sinus disease: fact or fiction? Am J Rhinol 2005; 19: 334–339. doi: 10.1177/194589240501900402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rosenfeld RM, Piccirillo JF, Chandrasekhar SS, et al. Clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2015; 152: Suppl., S1–S39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Miller DE, Forney C, Rochman M, et al. Genetic, inflammatory, and epithelial cell differentiation factors control expression of human calpain-14. G3 (Bethesda) 2019; 9: 729–736. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Milonski J, Zielinska-Blizniewska H, Majsterek I, et al. Expression of POSTN, IL-4, and IL-13 in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. DNA Cell Biol 2015; 34: 342–349. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2712 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nofziger C, Vezzoli V, Dossena S, et al. STAT6 links IL-4/IL-13 stimulation with pendrin expression in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2011; 90: 399–405. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2011.128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yu H, Li Q, Kolosov VP, et al. Interleukin-13 induces mucin 5AC production involving STAT6/SPDEF in human airway epithelial cells. Cell Commun Adhes 2010; 17: 83–92. doi: 10.3109/15419061.2010.551682 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nakano T, Inoue H, Fukuyama S, et al. Niflumic acid suppresses interleukin-13-induced asthma phenotypes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006; 173: 1216–1221. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200410-1420OC [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cao Q, Zhang T, Wang L, et al. [Expression of STAT6 in human nasal polyps and the relation between STAT6 and eosinophil infiltration]. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2009; 23: 917–919, 922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]