Abstract
Background
Subcutaneous cervical emphysema is a clinical sign associated with many conditions, including laryngotracheal trauma, pneumothorax and necrotizing deep tissue infections.
Case presentation
We discuss a case of a 76-year-old man presenting with extensive cervical emphysema a few hours after a minor dental filling procedure. The CT-scan revealed a significant amount of air within the cervical and mediastinal spaces, reaching lobar bronchi. Vitals were within normal values Bloodwork demonstrated an elevation of creatinine kinase (3718; normal < 150) and mild leukocytosis (WBC = 11.6). We decided to proceed to an urgent cervical exploration to exclude necrotizing fasciitis. This revealed air but no tissue necrosis nor abnormal fluid. The patient improved clinically and was discharged two days later with oral antibiotics. Although cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema following dental procedures has been reported, it is usually less extensive and involving more invasive procedures using air-driven handpieces.
Conclusion
As an otolaryngologist confronted with extensive subcutaneous emphysema following a potential entry route for an aggressive infection, given the seriousness of this diagnosis, the decision of whether or not to perform a diagnostic surgical exploration should remain.
Keywords: Pneumomediastinum, Subcutaneous emphysema, Dental restoration, Necrotizing fasciitis
Introduction
Subcutaneous cervicofacial emphysema is a relatively frequent clinical entity and has a large differential diagnosis including, among others: angioedema and/or anaphylactic reaction, deep neck space infections, necrotizing fasciitis, airway trauma, dental or surgical procedures, pneumothorax or pneumomediastinum. Iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema can be diagnosed through history and physical examination, combined with the right radiological and laboratory tests, after exclusion of life-threatening pathologies.
The first case of subcutaneous emphysema caused by a dental procedure has been reported in 1900 by Turnbull et al. [1] So far, two reviews have been published in dentistry journals, respectively in 1995 by Heyman et al. [2] and in 2006 by McKenzie et al. [3]. Our objective is to report a severe case of subcutaneous emphysema, to review the last 10 years of literature on the topic and to discuss the management of those patients from an otolaryngologist’s point of view.
Case report
A 76-year-old male presented to the emergency department in our tertiary care center with left-sided cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema. The questionnaire revealed he had sustained a routine dental filling of tooth #34 a few hours before. A small retraction cord (#00) was used without an air-driven high-speed hand piece. However, an air syringe was used to do the filling. In that case, a rubber dam could not be placed due to the presence of an old subgingival defective restauration in place. The procedure was done under local anesthesia without any ventilation, positive pressure event or CPAP use. About an hour after, cervical swelling and tenderness progressed. There were no other complaints. He had the same filing with the same procedure on the tooth #44 two weeks before.
He was otherwise known for hypertension, dyslipidemia and moderate chronic renal failure (baseline serum creatinine: 130 μmol/L). He had no history of head and neck pathologies or surgeries. He had known mild allergies to sulfamethoxzaole/Trimethoprime and to amoxicillin, but no to penicillin. The patient was on simvastatin and had no recent change to his medication.
Physical examination revealed extensive, mainly left sided cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema with associated erythema and tenderness on palpation. Vitals were: blood pressure 195 over 97 mmHg, heart rate 60 bpm and body temperature 37.5 °C.Oral cavity and teeth were unremarkable. There was no evidence of airway obstruction or respiratory distress. The remainder of the physical examination was within normal limits.
Blood tests showed a mild neutrophil-driven leucocytosis (white blood cells count of 11.6 × 106 (normal 3.8–10.6 × 106/mm3) with 7.8 × 106 neutrophils) along with a marked elevation of creatinine kinase at 3714 (normal < 185 units/L) and patient’s baseline at 216). C-reactive protein was within normal limits. A chest x-ray (CXR) confirmed diffuse cervical emphysema and pneumomediastinum (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
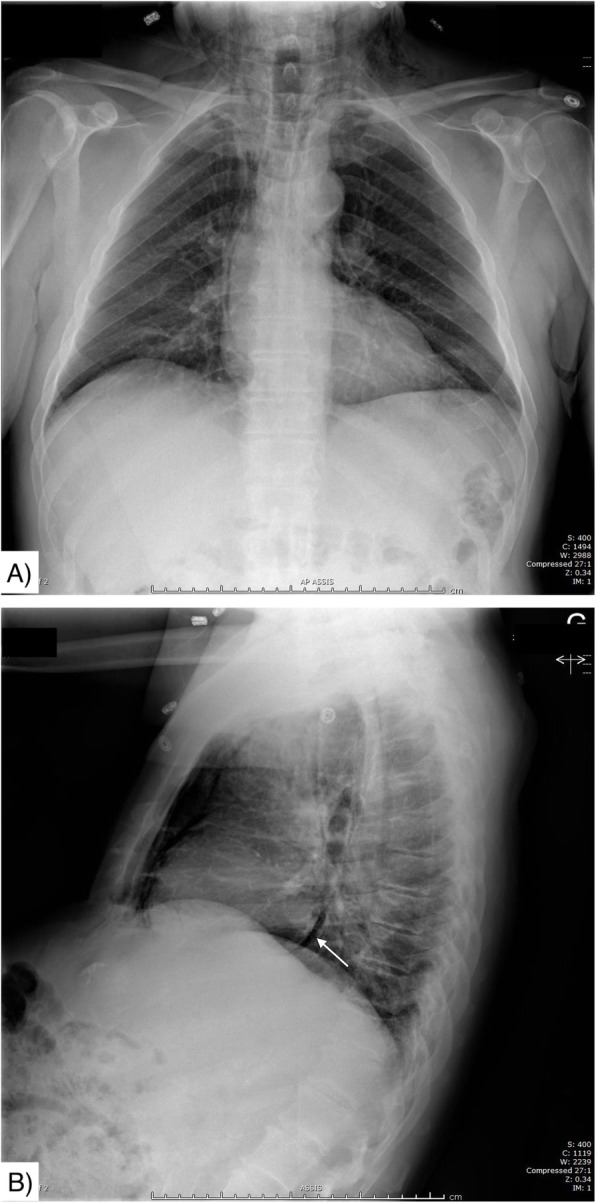
Initial CXR on arrival. a Antero-posterior view - important pneumomediastinum b) Lateral view - suspected pneumopericardium (white arrow). Both views show diffuse cervical emphysema
A cervicothoracic computed tomography (CT) was ordered and showed a significant quantity of air in the superficial and deep spaces of the neck and mediastinum reaching the lobar bronchi bilaterally, suspicious of an aggressive infectious process according to the radiologist report (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
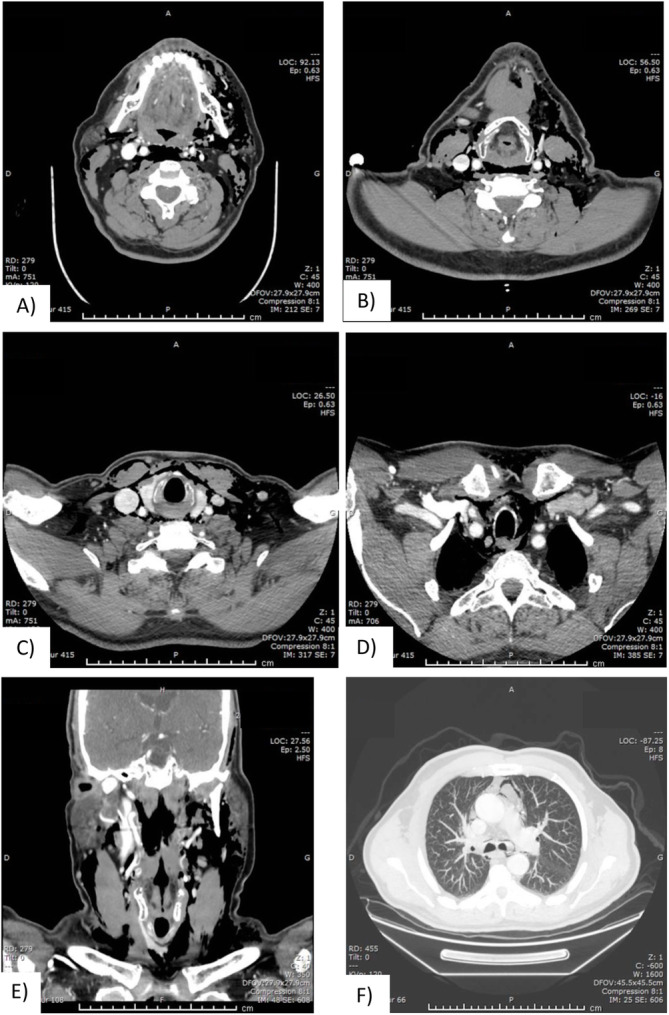
Cervicothoracic CT on arrival. a through f) Extensive emphysema, involving almost every deep neck and mediastinal spaces
A developing necrotizing fasciitis could not be ruled out considering the extensive clinical and radiological subcutaneous emphysema associated with the leukocytosis and the significant rise in CK levels. Antibiotic therapy consisting of piperacillin/tazobactam, vancomycin and clindamycin was administered and an urgent surgical cervical exploration was performed, revealing air bubbles that had dissected the involved deep spaces but no evidence of tissue necrosis nor exudative fluid. Hemocultures and surgical wound cultures eventually came back negative. A CXR on postoperative day 2 showed a marked decrease of the cervical subcutaneous emphysema (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
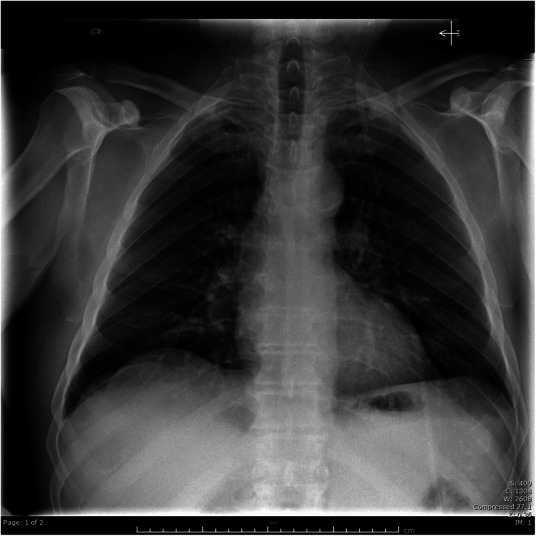
Postoperative day 2 CXR.Postero-anterior view showing significant improvement of subcutaneous emphysem
The patient was discharged two days later with moxifloxacin for a total of 7 days. Under infectious disease specialist’s advice, moxifloxacin was chosen because of the patient’s allergy to amoxicillin and of its daily dosage. The patient was seen for follow-up at 3 months and was doing well without any sequelae except the well-healed scar.
Literature review
A comprehensive review of the English and French literature from 2009 to 2018 was conducted through the PubMed database, using the research terms “dental”, “cervical emphysema” and “dental procedure”, in January 2020. Thirty-eight articles were selected based on their abstract and full text and were analyzed by 2 separate authors (AB and MP). The articles are summarized in Table 1. All patients presented with fascial and/or cervical swelling, and 37 (90.2%) presented within 24 h of the dental procedure. Thirty patients (73.2%) had a procedure involving molar teeth, of which twenty-two (73.3%) were mandibular. Twenty-eight patients (68.3%) had their procedure performed with a dental high-speed handpiece and five (12.2%) with an air-syringe. Thirty-eight patients (92.6%) had thoracic imaging (CXR or CT-scan), of which 27 (65.6%) had intrathoracic air or pneumomediastinum. Thirty-eight (92.6%) also received prophylactic antibiotics. Antibiotic regimen was heterogenous and was not detailed in 25 cases (61%). No complications were noted. No surgeries were performed, and all patients evolved well with resolution of the subcutaneous emphysema.
Table 1.
Summary of the literature review
| Reference | Age (years) / Sex | Procedure / tooth (#) | Suspected cause | Timing of SC emphysema | Imaging modality/ air in mediastinum or intrathoracic | Labs | Hospitalization (#days)/Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arai & al. (2009) [4] | 40/F | Extraction/ 48 | HS | 1 day | CT / - | N | 5 days / Ampicillin |
| Parkar & al. (2009) [5] | 55/F | Endodontic treatment/ left upper molar | HS | 1 h | XR/ - | N | 1 day / corticosteroids + anti-histaminic + antibiotics |
| Samuels (2009) [6] | 20/F | Extraction/ left lower molar | HS | Immediate | XR/ + | N | admitted / corticosteroids + analgesia + antibiotics |
| Kim & al. (2010) [7] | 40/M | Endodontic treatment / 36 | HS | Immediate | CT / + | N | 5 days / O2 + antibiotics |
| Kim & al. (2010) [7] | 52/F | Endodontic treatment / 16 | HS | Per-procedure | CT /+ | N | 8 days / antibiotics |
| Sainsbury & Jaiganesh (2010) [8] | 40/M | Endodontic treatment / 27 | HS | Per-procedure | XR / - | N | < 1 day (14 h) / O2 + AmoxiClav |
| Afzali & al. (2010) [9] | 16/M | Extraction / 37 | HS | 1 day | XR + CT / + | WBC 21000 | 5 days / IV Clinda and ceftazidime |
| Hsu (2010) [10] | 59/F | Endodontic treatment / 38 + 48 | HS | 1 h | CT /− | N | Antibiotics |
| Bilecenoglu & al. (2012) [11] | 39/F | Extraction / 46 | HS | 1 day | – | N | N/A / analgesia + antibiotics |
| Durukan & al. (2012) [12] | 45/F | Endodontic treatment / 16 | AS + HS | Immediate | XR+ CT/ + | N | 3 days/ O2 + metronidazole+ ampicillin |
| Bergen (2013) [13] | 72/F | RDP / molar | HS | Per-procedure | XR / - | N | N/A / Amoxi Clav |
| Elia & al.(2013) [14] | 41/F | Extraction/ 47 | HS | Per-procedure | CT/ + | N | 7 days/ analgesia + antibiotics |
| Khandelwal & al. (2013) [15] | 4,5/F | Crown preparation / 16 | AS + HS | 1 h | – | – | - / Amoxicillin |
| Mitsunaga & al.(2013) [16] | 76/F | Laser treatment / 26 | Laser | Immediate | CT / + | – | 5 days / antibiotics |
| Olate & al. (2013) [17] | 23/F | Extraction / 48 | HS | 4 h | CT/ - | – | admitted / analgesia + chlorexidine mouth wash + Cefazolin |
| An & al. (2014) [18] | 33/F | Endodontic treatment/ 44 | AS | Per-procedure | CT/+ | N | 5 days / steroids + IV fluids + O2 + clindamycin and switch to ampicillin + metronidazole |
| Fleischman & al. (2014) [19] | 15/F | Extraction / 28 | ? | Immediate | CT/ - | – | N/A / attempt to decompress the eyelid (30G needle) + antibiotics |
| Kün-Darbois & al. (2014) [20] | 41/F | Extraction / 38 | HS | Per-procedure | CT / + | WBC 10370 | 2 days / - |
| Paik & al. (2014) [21] | 13/M | RDP / 36 | HS | Immediate | CT /+ | – | 1 day / - |
| Nishimura & al. (2015) [22] | 68/M | RDP /? | HS | 1 day | XR + CT / + | N | N/A / antibiotics |
| Picard & al. (2015) [23] | 27/M | Extraction / 48 | HS | 4 days | CT / + | – | 4 days / antibiotics |
| Ocakcioglu & al. (2015) [24] | 23/M | Extraction / 48 | HS | 7 days | CT / + | – | 4 days / O2 + antibiotics |
| Alonso & al.(2017) [25] | 73/F | Peri-implant cleaning / 4? | AP | Immediate | CT / - | – | N/A / corticosteroids + antibiotics |
| Alonso & al.(2017) [25] | 43/M | Dental cleaning / 42–43 | AP | Immediate | XR / + | – | < 1 day (12 h) / - |
| Alonso & al.(2017) [25] | 62/F | Dental cleaning / 47 | AP | Immediate | CT / - | – | N/A / Ibuprofen + antibiotics |
| Lee & al. (2017) [26] | 59/F | RDP / 44 | HS | Immediate | XR + CT/ + | N | 8 days / O2 + ampicillin + TMP SMX |
| Ramnarine & Dubin (2017) [27] | 28/F | RDP / 14 + 20 + 21 | HS | Immediate | XR + CT/+ | N | < 1 day (12 h) / antibiotics |
| Tan & Nikolarakos (2017) [28] | 33/F | Extraction / 46 | HS | 1 day | XR / - | WBC 10000 | 2 days / analgesia + antibiotics |
| Thompson & Gohil (2017) [29] | 50/M | Extraction / 38 | ? | 4–6 h | XR / + | N | Admitted/ saline nebulisers + antibiotics |
| Chien (2018) [30] | 59/F | RDP / 44 + 46 | HS | Immediate | – | – | N/A / antibiotics |
| Jeong & al. (2018) [31] | 60/F | Crown preparation / 15 | HS | 1 h | XR + CT/ + | N | 4 days / O2 + antibiotics |
| Lee & al.(2018) [32] | 51/F | Peri-implant cleaning / 12 | AS | Per-procedure | XR + CT/ + | N | 13 days / O2 + analgesia + antibiotics |
| Liu & Lin (2018) [33] | 22/M | Extraction / 38 | ? | 1 week | XR + CT/ + | Elevated CRP + WBC | Admitted /Amoxi-Clav |
| Tay & Loh(2018) [34] | 18/M | Extraction / 18 + 28 + 38 + 48 | HS | 1 day | XR + CT/ + | – | 5 days/ O2 + antibiotics |
| Tenore & al. (2017) [35] | 60/F | Endodontic treatment / 22 | AS | Per-procedure | CT / - | – | Admitted / corticosteroid + analgesia + antibiotics |
| Cuccia & al [36]. | 30/F | Extraction / 37 | HS | Immediate | CT / + | N | 7 days / corticosteroids + tazocin/cubicin + bed rest |
| Fehrle & al [37]. | 32/M | Extraction / 48 | ? | Weeks | CT / + | CRP 75 | Admitted / antibiotics |
| Mascarenhas & al [38]. | 43/M | RDP / 47 | HS | Immediate | XR / - | – | N/A / Amoxicilin |
| Paschos & al [39]. | 17/F | Extraction / 38 | HS | 30 min | CT / + | N | 3 days / antibiotics |
| Rad et & [40]. | 36/M | Extraction / 37 | HS | Immediate | XR / + | N | N/A / antibiotics |
| Rawlinson & al [41]. | 40/F | RDP / upper and lower molar | ? | 1 day | CT / + | WBC 12500 | 1 day / antibiotics |
F Female, M Male, RDP restorative dental procedure, HS High speed handpiece, AP Air polishing, AS air syringe, XR X-Ray, CT computed tomography scan, WBC white blood cell count, CRP C-Reactive protein, HBP High blood pressure, SC subcutaneous, N normal
Discussion
The association between dental procedures and cervicofacial emphysema has been described in the dental literature. Even though every tooth may be implicated, mandibular molars are more frequently involved, for they have a closer relationship with head and neck deep spaces. The buccal, sublingual and submandibular spaces are intimately connected with the roots of these molars. The supra-hyoid spaces are contiguous with infra-hyoid spaces, notably the parapharyngeal and retropharyngeal spaces, which can lead to the mediastinal compartment. Different procedures have been associated with cervicofacial emphysema, ranging from endodental treatment to teeth extractions, even hygiene procedures [42]. Use of air syringes, or more frequently air-driven dental handpieces, which inject air at high pressure, are prominent risk factors [3]. With their use, air can dissect in the soft tissues exposed around the tooth and spread through the deep neck spaces. Dentists can use special equipment, like rubber dams, to isolate the tooth in order to prevent such complications.
Given the eventuality of a dental iatrogenic cause being most probable based on history, surveillance in the emergency department or admission can be considered based on the clinician’s judgment. However, invasive infections, such as necrotizing fasciitis or mediastinitis, should be considered as they are infrequent but potentially catastrophic if not diagnosed promptly. Both are also known complications of the dental procedure itself [26]. In our review, most but not all patients received prophylactic antibiotics. The choice of the antibiotic, the route of administration and the duration of the treatment were heterogenous. Because of its adequate coverage of the buccal flora, penicillin is an adequate first choice, and it is what was chosen in most of the reported cases [1]. We found no case of significant infection, as was the case for McKenzie et al. [3]
Among other treatment modalities that have been reported, steroids have been used empirically in 5 patients to decrease edema and inflammation. Antihistamines were used in only 1 patient to treat empirically for a local anesthetic allergic reaction. However, depending on the clinical context, if an anaphylactic reaction or angio-edema is suspected, epinephrine, steroids and antihistamines should be administered in a timely fashion [3] Oxygen supplementation was administered in 7 patients. Although no study was done to evaluate the efficacy of 100% O2 supplementation in case of subcutaneous emphysema, its use is extrapolated from pneumothorax cases: using 100% O2 accelerates the resorption of pneumothorax by reducing nitrogen gas pressure in pleural capillaries thus promoting resorption of air (mostly nitrogen) from the pleural space [8, 43, 44]. Despite the patient’s well-being and normal CRP, the choice of performing surgical exploration was not instinctive but made mainly because of the significant CK elevation and the radiologist’s report raising a high suspicion index of necrotizing fasciitis. The dental procedure could have been the entry route for an aggressive infection even if, in retrospect, this was not the case.
Conclusion
The use of high-speed dental handpieces and air-syringes during dental procedures can infrequently precipitate extensive subcutaneous emphysema. Clinical history and paraclinical investigation are keys to making the right diagnosis. In cases of iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema related to dental procedure, conservative treatment has shown to be a safe option. Nevertheless, high clinical suspicion is warranted for an invasive necrotizing infection, given the seriousness of this eventuality but the choice between close observation or surgical exploration should rely on the clinician’s judgement.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AP
Air-polishing
- CT
Computed tomography
- CXR
Chest x-ray
- F
Female
- HBP
High blood pressure
- HS
High-speed handpiece
- M
Male
- RDP
Restorative dental procedure
- WBC
White blood cell
Authors’ contributions
AB: data collection, interpretation of the results, redaction of the manuscript. MP: data collection, interpretation of the results, redaction of the manuscript. LF: original research idea, revision of the case, revision of the manuscript. VT: revision of manuscript. MB: interpretation of the results, revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
AB and MP are respectively PGY-3 and PGY-2 in otolaryngology at Université de Sherbrooke. LF is an otolaryngologist currently undergoing a fellowship in head and neck surgery. VT is a dentist at Clinique Dentaire du Carrefour in Sherbrooke, Qc. MB is an otolaryngologist specialized in rhinosinusology and skull base surgery at the CIUSSS de l’Estrie – CHUS.
Funding
No funding received.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this report and any accompanying images.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Adnan Busuladzic, Email: Adnan.busuladzic@usherbrooke.ca.
Melissa Patry, Email: Melissa.patry2@usherbrooke.ca.
Laurent Fradet, Email: Laurent.fradet@usherbrooke.ca.
Valérie Turgeon, Email: Valerie.turgeon.4@umontreal.ca.
Marie Bussieres, Email: Marie.bussieres@usherbrooke.ca.
References
- 1.Mather AJ. Cervicofacial and Mediastinal Emphysema Complicating a Dental Procedure. J Can Dent Assoc. 2006;72(6)565–8. [PubMed]
- 2.Heyman SN, Babayofk I. Emphysematous complications in dentistry, 1960–1993: An illustrative case and review of the literature. Quintessence Int. 1995;26:535–43. [PubMed]
- 3.McKenzie WS, Rosenberg M. Iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema of dental and surgical origin: a literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67(6):1265–1268. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2008.12.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arai I, Aoki T, Yamazaki H, Ota Y, Kaneko A. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema after dental extraction detected incidentally by regular medical checkup: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontology. 2009;107(4):e33–e38. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Parkar A, Medhurst C, Irbash M, Philpott C. Periorbital oedema and surgical emphysema, an unusual complication of a dental procedure: a case report. Cases J. 2009;2(1):8108. doi: 10.4076/1757-1626-2-8108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Samuels TL. Rare complications of surgical emphysema and pneumomediastinum occurring post dental extraction. Postgrad Med J. 2009;85(1006):404. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.2009.079749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kim Y, Kim M-R, Kim S-J. Iatrogenic pneumomediastinum with extensive subcutaneous emphysema after endodontic treatment: report of 2 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontology. 2010;109(2):e114–e119. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sainsbury D, Jaiganesh T. Dentist’s drill allergy? Int J Emerg Med. 2010;3(4):427–429. doi: 10.1007/s12245-010-0189-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Afzali N, Malek A, Attar AHH. Cervicofacial Emphysema and Pneumomediastinum Following Dental Extraction: Case Report. Iran J Pediatr. 2011;21(2):253–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Hsu H-L, Chang C-C, Liu K-L. Subcutaneous emphysema after dental procedure. QJM. 2011;104(6):545. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcq085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bilecenoglu B, Onul M, Altay OT, Şakul BU. Cervicofacial Emphysema After Dental Treatment With Emphasis on the Anatomy of the Cervical Fascia. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23(6):e544–e548. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31825aef02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Durukan P, Salt O, Ozkan S, Durukan B, Kavalci C. Cervicofacial emphysema and pneumomediastinum after a high-speed air drill endodontic treatment procedure. Am J Emerg Med. 2012;30(9):2095. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2012.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bergen T. Unusual case of cervicofacial surgical emphysema. Emerg Med Australas. 2013;25(5):473. doi: 10.1111/1742-6723.12124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Elia F, Laface B, Pagnozzi F, Boccuzzi A, Ferrari G, Perna M, et al. Cervicofacial emphysema and Pneumomediastinum complicating a dental procedure. J Emerg Med. 2013;45(5):e179–e181. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2013.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Khandelwal V, Agrawal P, Agrawal D, Nayak PA. Subcutaneous emphysema of periorbital region after stainless steel crown preparation in a young child. Case Rep. 2013;2013(may22 1):bcr2013009952. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-009952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mitsunaga S, Iwai T, Aoki N, Yamashita Y, Omura S, Matsui Y, et al. Cervicofacial subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema caused by air cooling spray of dental laser. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013;115(6):e13–e16. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2011.10.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Olate S, Assis A, Freire S, de Moraes M, de Albergaria-Barbosa JR. Facial and cervical emphysema after oral surgery: a rare case. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2013;6(9):840–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.An GK, Zats B, Kunin M. Orbital, Mediastinal, and Cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema after endodontic retreatment of a mandibular premolar: a case report. J Endod. 2014;40(6):880–883. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.09.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fleischman D, Davis RM, Lee LB. Subcutaneous and Periorbital Emphysema Following Dental Procedure. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;30(2):e43–5. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 20.Kün-Darbois JD, Paré A, Chemli H, Daher G, Breheret R. Crépitations cervicales après avulsion dentaire. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillo-Faciale Chir Orale. 2014;115(2):e17–e18. doi: 10.1016/j.revsto.2013.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Paik YS, Lollar KW, Chang CWD. Iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema after dental treatment. Ear Nose Throat J. 2014;93(2):E14–6. [PubMed]
- 22.Nishimura T, Sawai T, Kadoi K, Yamada T, Yoshie N, Ueda T, et al. Iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum following a high-speed air drill dental treatment procedure: emphysema following dental treatment. Acute Med Surg. 2015;2(4):253–256. doi: 10.1002/ams2.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Picard M, Pham Dang N, Mondie JM, Barthelemy I. Cervicothoracic Subcutaneous Emphysema and Pneumomediastinum After Third Molar Extraction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;73(12):2286.e1–2286.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2015.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ocakcioglu I, Koyuncu S, Kupeli M, Bol O. Pneumomediastinum after tooth extraction. Case Rep Surg. 2016;2016:1–3. doi: 10.1155/2016/4769180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Alonso V, García-Caballero L, Couto I, Diniz M, Diz P, Limeres J. Subcutaneous emphysema related to air-powder tooth polishing: a report of three cases. Aust Dent J. 2017;62(4):510–515. doi: 10.1111/adj.12537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee S-W, Huh Y-H, Cha M-S. Iatrogenic subcutaneous cervicofacial emphysema with pneumomediastinum after class V restoration. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;43(1):49. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ramnarine M, Dubin Z. Cervicofacial and mediastinal emphysema due to a dental procedure. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2017;10(1):34. doi: 10.4103/0974-2700.199526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tan S, Nikolarakos D. Subcutaneous emphysema secondary to dental extraction: a case report. Aust Dent J. 2017;62(1):95–97. doi: 10.1111/adj.12464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Thompson C, Gohil R. Pneumatic dental extractions: an unusual cause of extensive cervical surgical emphysema. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;bcr-2016-218677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 30.Chien P-H. Iatrogenic subcutaneous facial emphysema secondary to a class V dental restoration: a case report. Aust Dent J. 2019;64(1):43–46. doi: 10.1111/adj.12657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jeong C-H, Yoon S, Chung S-W, Kim J-Y, Park K-H, Huh J-K. Subcutaneous emphysema related to dental procedures. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;44(5):212. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2018.44.5.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lee S-T, Subu MG, Kwon T-G. Emphysema following air-powder abrasive treatment for peri-implantitis. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018 40(1). doi: 10.1186/s40902-018-0151-7. [cited 2019 Mar 27]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Liu C-C, Lin M-Y. Diffuse soft tissue emphysema after dental procedure. CJEM. 20(S2):S38–39. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 34.Tay YBE, Loh WS. Extensive subcutaneous emphysema, pneumomediastinum, and pneumorrhachis following third molar surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;47(12):1609–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2018.04.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tenore G, Palaia G, Ciolfi C, Mohsen M, Battisti A, Romeo U. Subcutaneous emphysema during root canal therapy: endodontic accident by sodium hypoclorite. Ann Stomatol (Roma). 2017;7(3):117–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 36.Cuccia A, Geraci A. Cervicofacial and mediastinal emphysema after dental extraction. Dent Med Probl. 2019;56(2):203–207. doi: 10.17219/dmp/108615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fehrle C. Mediastinal and cutaneous emphysema following dental extraction. Dtsch Aerzteblatt Online. 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mascarenhas RJ. Management of subcutaneous facial emphysema secondary to a class V dental restoration. Clin Case Rep. 2019;7(5):1025–1030. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Paschos K, Chatzigeorgiadis A. Cervicofacial emphysema, Pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax caused by a dental procedure. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2019;29(2):191–192. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2019.02.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rad MV, Chan EKY, Ahmed IH. Cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum secondary to dental treatment in a young man. Respir Med Case Rep. 2019;28:100918. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2019.100918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rawlinson RD, Negmadjanov U, Rubay D, Ohanisian L, Waxman J. Pneumomediastinum After Dental Filling: A Rare Case Presentation. Cureus. 2019; Available from: https://www.cureus.com/articles/21620-pneumomediastinum-after-dental-filling-a-rare-case-presentation. [cited 2020 Mar 17]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 42.Bocchialini G, Ambrosi S, Castellani A. Massive Cervicothoracic subcutaneous emphysema and Pneumomediastinum developing during a dental hygiene procedure. Case Rep Dent. 2017;2017:1–4. doi: 10.1155/2017/7016467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ali A, Cunliffe DR, Watt-Smith SR. Surgical emphysema and pneumomediastinum complicating dental extraction. Br Dent J. 2000;188(11):589–90. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 44.Northfield TC. Oxygen therapy for spontaneous pneumothorax. BMJ. 1971;4(5779):86–88. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5779.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.


