Abstract
Doxorubicin (DOX) has been widely employed to treat cancer, particularly solid tumors and hematological malignancies, owing to its high efficacy; however, chemotherapy has been indicated to be cardiotoxic and induce adverse effects, including mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage, which limits its application. The mitochondria-associated protein leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat-containing (LRPPRC) has been reported to serve critical regulatory roles in physiological processes via regulating mitochondrial function. The aim of the present study was to investigate the possible protective effects of LRPPRC against DOX-induced cardiac injury. In a DOX-induced cardiotoxicity model in H9C2 cells, LRPPRC was indicated to be transcriptionally upregulated and stabilize Bcl-2 and Bax. LRPPRC overexpression exhibited protective effects against proliferation and both apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death following DOX treatment, but not under normal conditions. It was additionally observed that overexpressed LRPPRC reversed the decreases in ATP synthesis, mitochondrial mass and transcriptional activity, which were induced by DOX exposure. Overexpressed LRPPRC also decreased the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) under DOX treatment and inhibited cell death to a similar extent as N-acetyl-L-cysteine, which is a known ROS scavenger, indicating that LRPPRC potentially exerts protective effects via inhibiting ROS accumulation. Moreover, LRPPRC overexpression protected H9C2 cells against oxidative stress induced by H2O2, which also indicated its ROS-scavenging function. The present study demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that DOX-induced LRPPRC may exert cardioprotective effects via inhibiting ROS accumulation, thereby maintaining mitochondrial function.
Keywords: leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat-containing, H9C2 cells, cardiotoxicity, mitochondrial function, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress
Introduction
Doxorubicin (DOX), which is a member of the anthracycline family, has been widely used as a chemotherapeutic agent for solid tumors owing to its effective therapeutic outcomes (1). However, the administration of DOX is limited since anthracycline therapy has been indicated to be closely associated with dose-dependent cardiotoxicity (1). Although the exact molecular mechanism of cardiotoxicity induced by DOX treatment has not fully elucidated, DOX has been reported to promote mitochondrial dysfunction and alter the mitochondrial membrane by eliciting lipid peroxidation, generating free radicals, increasing the myocardial levels of sodium and calcium and inducing autophagy/mitophagy, thereby resulting in apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death in cardiomyocytes (2-5). DOX-induced toxicity has also been demonstrated to be primarily attributed to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS)/reactive nitrogen species (RNS) as a result of drug redox recycling (6). Therefore, decreasing or attenuating DOX-induced ROS accumulation has become a therapeutic strategy to reduce the risk of heart failure (6).
Leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat-containing (LRPPRC), which is also known as LRP130, is a well-known mitochondria-associated protein that has been indicated to serve critical roles in mitochondria by maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential and function (7). In the mitochondrial matrix, LRPPRC has been reported to bind stem-loop-interacting RNA-binding protein and subsequently regulate mRNA stability and polyadenylation and the coordination of translation (7-9). Mutations in LRPPRC have been indicated to result in cytochrome c oxidase deficiency, decreased mitochondrial mRNA levels and reduced mitochondrial translation in the liver and brain (7,10). Several reports have revealed that LRPPRC regulates mRNA transport from the cytoplasm to mitochondria (11) and RNA transport from the nucleus to mitochondria (12); however, LRPPRC has been indicated to be primarily localized in the mitochondria (13). Knockdown of LRPPRC in cells (13) and knockout of Lrpprc in mice (8) has been indicated to reduce mitochondrial membrane potential and homeostasis, and DNA mass and function. Therefore, LRPPRC regulates physiological processes both in vitro and in vivo via regulating mitochondrial function.
Numerous studies have been performed to investigate the effects and the mechanisms by which DOX targets mitochondrial energy metabolism and ROS production. Wang et al (14) reported that fibroblast growth factor 21, which is a well-known regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism, exerted cardioprotective effects against DOX-induced toxicity via the NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1/liver kinase B1/AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in H9C2 cells. Liu et al also reported that pterostilbene, which is a natural analogue of resveratrol and an antioxidant, exerted cardioprotective effects against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in H9C2 cells and injury in mouse cardiomyocytes by reducing oxidative stress, including ROS accumulation, which indicated that oxidative stress may be the principal cause of cardiotoxicity following DOX exposure (15). It has also been reported that salsolinol, a plant-based isoquinoline alkaloid, ameliorated cardiomyocyte function, promoting mitochondrial respiratory and energy metabolism (16). However, little is known of the effect of LRPPRC on oxidative stress induced by DOX exposure. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of LRPPRC on H9C2 cardiomyocytes under DOX-induced oxidative stress, and the regulatory roles of LRPPRC in mitochondrial function.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and treatment
H9C2 myoblast cells derived from the rat myocardium were obtained from the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Cells were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 10 ml/l 100X antibiotic-antimycotic solution containing 10,000 units of penicillin and 10 mg/ml streptomycin at 37 in a 5% CO2 humidified incubator. All reagents were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
For cell treatment, 30% inhibitory concentration (IC30, 4.75 µM) or 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50, 7.16 µM) of DOX was added into the culture medium for 24, 48, 72 and 96 h at 37˚C and cells were used for subsequent analysis.
To induce oxidative stress, 200 mM H2O2 was added into the culture medium for 24 h at 37˚C and cells were used for subsequent analysis.
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay
H9C2 cells were collected and resuspended in serum-free DMEM at a final concentration of 1x106 cells/ml. A total of 6x103 cells/well were seeded into a 96-well plate and cultured overnight. The cells were subsequently treated with various concentrations of DOX (1.0, 2.5, 5.0, 7.5, 10.0, 12.5, 15.0 and 17.5 µM) for 24 h at 37˚C and CCK-8 solution (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) was added to the cells and incubated for between 30 min and 2 h at 37˚C in the dark according to the manufacturer's protocol. The absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a microplate reader (Synergy 2 Multi-Mode Microplate Reader; BioTek Instruments, Inc.) to determine cell viability.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
A total of 1x106 H9C2 cells were employed for RNA extraction using TRIzol® (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) following the manufacturer's instructions. Complementary DNA was obtained via reverse transcription using the RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (Fermentas; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The reactions were performed according to the following temperature protocol: 65˚C for 5 min, ice bath for 2 min, 37˚C for 45 min and 85˚C for 10 min. qPCR was performed using the SYBR Green Real-Time PCR Master Mixes (Fermentas; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the following thermocycling conditions: 95˚C for 2 min; 35 cycles of 95˚C for 30 sec and 60˚C for 1 min. The primer sequences used are as follows: LRPPRC forward, 5'-CTGCACTGTGCTCTTCAAGC-3' and reverse, 5'-GACTGCACACTACCGAAGCA-3'; Bcl-2 forward, 5'-CGACTTTGCAGAGATGTCCA-3' and reverse, 5'-ATGCCGGTTCAGGTACTCAG-3'; Bax forward, 5'-CGAGCTGATCAGAACCATCA-3' and reverse, 5'-CTCAGCCCATCTTCTTCCAG-3'; β-actin forward, 5'-AGCCATGTACGTAGCCATCC-3' and reverse, 5'-CTCTCAGCTGTGGTGGTGAA-3'; cytochrome c oxidase subunit (COX) 1 forward, 5'-GGAGCAGTATTCGCCATCAT-3' and reverse, 5'-CGACGAGGTATCCCTGCTAA-3'; COX 3 forward, 5'-GAACATACCAAGGCCACCAC-3' and reverse, 5'-TAATTCCTGTTGGGGGTCAG-3'; NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 forward, 5'-CTCCCTATTCGGAGCCCTAC-3' and reverse, 5'-GGAGCTCGATTTGTTTCTGC-3'; and cytochrome b forward, 5'-GTCGGCGAAGAAAAATGTGT-3' and reverse, 5'-AAGCTGCTCACAGAGGGGTA-3'. β-actin was employed as an internal standard. Gene expression was calculated using the 2-ΔΔCq method (17). Each experiment was repeated three times.
MitoTracker Green and MitoTracker Red staining
A total of 1x106 H9C2 cells were loaded with 100 nM green-fluorescing MitoTracker Green (MitoGreen, YEASEN Technology Company, Shanghai) for 30 min at 37˚C to measure mitochondrial content, and 500 nM MitoTracker Red (MitoRed, YEASEN Technology Company, Shanghai) for 30 min at 37˚C. Images were taken using a X71 (U-RFL-T) fluorescence microscope (Olympus Corporation). All data were obtained from experiments with at least three replicates.
Western blot analysis
H9C2 cells were washed 3 times with ice-cold PBS and lysed in RIPA total protein lysis buffer (Guangzhou RiboBio Co., Ltd.) using the SoniConvert® sonicator (DocSense, Chengdu, China) according to the manufacturer's instructions for 3 sec(s) at room temperature. Concentration of protein in the lysate was measured using BCA kit (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) and protein was mixed with 5X SDS loading buffer (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) and incubated for 10 min at 100˚C to denature. Subsequently, 30 µg of each proteins was separated on a 6-15% gradient SDS-PAGE gels and transferred on to a PVDF membrane. Then membrane was blocked in blocking buffer containing 5% BSA (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) in PBS at room temperature for 1 h. Western blotting was performed using the primary antibodies anti-β-actin (1:5,000; cat. no. ab8226), mouse monoclonal anti-LRPPRC (1:500; cat. no. ab21864), rabbit polyclonal anti-Bcl-2 (1:2,000; cat. no. ab196495) and rabbit monoclonal anti-Bax (1:1,000; cat. no. ab32503; all from Abcam). Membranes were incubated with primary antibodies at room temperature for 1 h. Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit (cat. no. ab79080) or anti-mouse IgG secondary antibodies (cat. no. ab47827; both 1:20,000; both from Abcam) were then incubated with the membrane at room temperature for a further 1 h. Signals were detected using ECL reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and Image J software (version 2.0; National Institutes of Health) was used for densitometry. β-actin was used as the internal reference.
Fluorescence immunostaining
H9C2 (1x105) cells attached onto 18 mm coverslips were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature and permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 10 min at room temperature. To block unspecific staining, the cells were incubated with 5% normal goat serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) diluted in 1X PBS at room temperature for 30 min. Staining was performed using primary LRPPRC antibodies (1:200; cat. no. ab21864; Abcam) at room temperature for 2 h in the dark, followed by four washes with PBS-Tween 20 (0.5%) and incubation with rabbit Cy5®-conjugated secondary antibody (cat. no. ab6563, 1:2,000 in 0.5% normal goat serum) for 1 h at room temperature. Nuclei were subsequently stained with 5 µg/ml DAPI (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) at room temperature for 10 min. Images were captured with a X71 (U-RFL-T) fluorescence microscope (Olympus Corporation) at magnification, x100.
LRPPRC knockdown and overexpression
Knockdown of LRPPRC was achieved via transient transfection of H9C2 cells with small interfering RNA (siRNA) duplexes (cat. no. for si and NC sequence RSH045567; Guangzhou FulenGen Co., Ltd.) targeting LRPPRC mRNA, according to the manufacturer's instructions. A total of 1x106 cells in 2 ml serum-free DMEM were seeded per well of 6-well plates. Transfection complexes were formed via mixing 5 µl Lipofectamine® 2000 reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) with the siRNA oligomer (50 nM) in 0.5 ml OptiMEM medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at room temperature for 20 min. The complexes were subsequently added to the cells, which were cultured for 48 h at 37˚C and collected for subsequent analysis. Control cells were transfected with negative control siRNA.
For LRPPRC overexpression, the coding sequence of rat LRPPRC (accession no. NM_001008519.1) was provided by Guangzhou FulenGen Co. Ltd. and was inserted into the mammalian expressing vector pSG5L-Flag-HA (Addgene, Inc.). Overexpression of LRPPRC was achieved via transient transfection as aforementioned. Notably, for each transfection in 6-well plate, 1.6 µg of plasmid was used.
Cell cycle analysis
To analyze the distribution of the cell cycle phases via quantification of the DNA content, H9C2 cells (1x106/well) grown in 6-well plates were washed with ice-cold 1X PBS and fixed overnight at 4˚C with ice-cold 70% ethanol. Subsequently, fixed cells were washed 3 times with ice-cold 1X PBS, collected via centrifugation at 1,000 x g at 4˚C for 5 min and incubated with a final concentration of 100 µg/ml RNase A and 10 µg/ml propidium iodide (PI; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) for 15 min in the dark at room temperature. The cells were analyzed using a three laser Navios flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Inc.) and data was analyzed using FlowJo (FlowJo LLC; v9.7.4).
Apoptosis analysis
To detect apoptotic cell death, annexin V-FITC/PI double staining was performed using Annexin V FITC apoptosis detection kit (Becton, Dickinson and Company) following the manufacturer's instructions. H9C2 cells (1x106) were washed with ice-cold 1X PBS and pelleted by centrifugation at 400 x g at 4˚C for 10 min. Following removing of the supernatant, the pellet was resuspended in 1X binding buffer from the Annexin V FITC apoptosis detection kit and stained with 5 µl FITC-labeled annexin V at 4˚C for 15 min in the dark. Subsequently, 10 µl PI was added to the mixture and incubated at 4˚C for 5 min in the dark. The stained cells were analyzed via flow cytometry using a three lasers Navios flow cytometer within 1 h following staining (Beckman Coulter, Inc.) and data was analyzed using FlowJo.
ATP measurement
To measure total ATP content, 5x105 H9C2 cells were suspended and lysed in a buffer containing 0.22 M sucrose, 0.12 M mannitol, 40 mM tricine, pH 7.5 and 1 mM EDTA at 4˚C for 10 min. The total lysate was analyzed using ATP Bioluminescence Assay kit (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) according to the manufacturer's instructions and quantitatively measured using the Optocomp I BG-1 luminometer (GEM Biomedical, Inc.).
ROS staining
Subsequently, 2',7'-Dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFH-DA; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) was used for ROS staining following 4.75 µM of DOX exposure at 37˚C for 24 h. To scavenge induced ROS, 10 µM of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) was added to the culture for 24 h treatment. Briefly, 1x106 H9C2 cells/well cultured in a 6-well plate were incubated with 10 µM DCFH-DA in DMEM medium at 37˚C for 20 min. The plates were washed three times with ice-cold 1X PBS to remove excess DCFH-DA dye. Fluorescence was visualized immediately at 485 nm (excitation) and 530 nm (emission) using an inverted fluorescence microscope (Olympus Corporation) at magnification, x100.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using SPSS v13.0 (SPSS, Inc.). Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. The statistical significances of the differences between groups were assessed using unpaired Student's t-test or one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc analysis. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. All experiments were repeated three times independently.
Results
Low-dose DOX upregulates the expression of LRPPRC
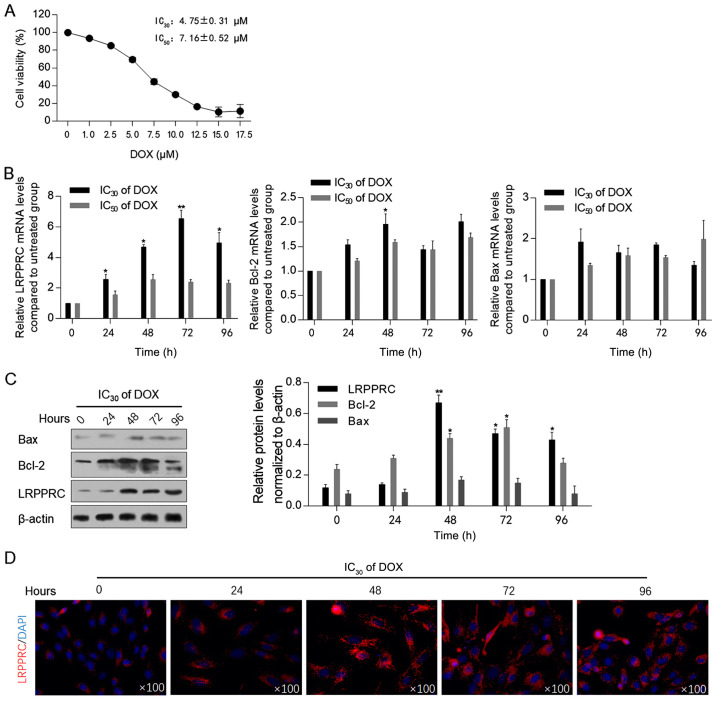
Prior to assessing the effect of DOX exposure on the expression levels of LRPPRC, the cytotoxic effect of DOX on H9C2 cells was measured using the CCK-8 assay. As illustrated in Fig. 1A, the IC30 (4.75±0.31 µM) and IC50 (7.16±0.52 µM) of DOX were employed for subsequent analysis. Following 0, 24, 48, 72 and 96 h of DOX exposure at IC30 or IC50, the mRNA and protein levels of LRPPRC were detected. The levels of Bcl-2 and Bax, which have been indicated to be regulated by LRPPRC (13), and therefore may be associated with mitochondrial homeostasis, were also examined. Following 24-96 h of DOX exposure at the IC30, LRPPRC mRNA levels were significantly upregulated compared with control cells. By contrast, DOX at the IC50 did not affect LRPPRC, Bcl-2 and Bax mRNA levels, indicating that a low dose of DOX may regulate LRPPRC, and thus modulate mitochondrial function (Fig. 1B). After 48-h treatment under IC30 of DOX, Bcl-2 mRNA was upregulated significantly. Subsequently, western blotting was performed to detect the effect of DOX at IC30 on the protein levels of LRPPRC, Bcl-2 and Bax. In consistence with the alterations at the mRNA level, an increase in the LRPPRC protein expression level was observed following DOX exposure. Notably, the protein levels of Bcl-2 and Bax were increased with no evident increase observed at their mRNA levels, which may be attributed to their possible stabilization by LRPPRC at the protein level (Fig. 1C). A significant increase in Bcl-2 mRNA and protein levels was observed at 48-h exposure, which suggested that Bcl-2 was potentially involved in LRPPRC regulation. The upregulation of LRPPRC following DOX exposure was additionally verified via immunofluorescence staining. As anticipated, the expression of LRPPRC was increased following 24-96 h of IC30 of DOX exposure compared with control cells (Fig. 1D).
Figure 1.
DOX treatment upregulates LRPPRC at the transcriptional level. (A) Cell Counting Kit-8 assay was performed to detect DOX cytotoxicity in H9C2 cells. (B) Following DOX treatment at IC30 or IC50 for 0, 24, 48, 72 and 96 h, the mRNA levels of LRPPRC, Bcl-2 and Bax were detected via reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. (C) Protein levels of LRPPRC, Bcl-2 and Bax were detected via western blot (left panel), and quantitatively analyzed via ImageJ software (right panel). (D) Via immunofluorescence staining, the expression and localization of LRPPRC (red) and nucleus (blue) were visualized. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. 0 h DOX exposure group. LRPPRC, leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat-containing; DOX, doxorubicin.
LRPPRC overexpression exerts protective effects against DOX treatment
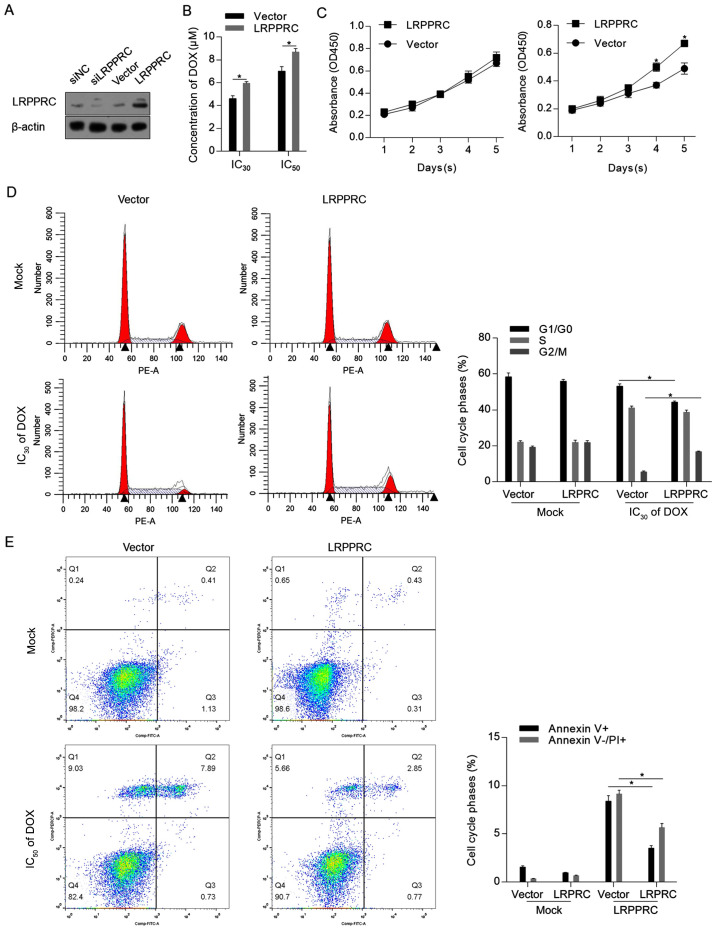
To assess the effect of LRPPRC under normal conditions and DOX treatment, LRPPRC expression level was firstly modulated via knockdown or overexpression. As demonstrated in Fig. 2A, the LRPPRC expression vector substantially increased the LRPPRC protein level. As knockdown of LRPPRC slightly affected the protein level compared with control cells, which may be attributed to the low endogenous level of LRPPRC, overexpression of LRPPRC was employed for subsequent functional analysis. The CCK-8 assay indicated that overexpression of LRPPRC sensitized H9C2 cells to DOX (Fig. 2B). Under normal conditions, overexpression of LRPPRC did not affect cell proliferation, while cell proliferation was induced by LRPPRC overexpression following DOX exposure compared with control cells (Fig. 2C). The protective effect of LRPPRC overexpression was additionally verified by detecting the distribution of the cell cycle phases and the apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death. As illustrated in Fig. 2D and E, although no detectable effects were observed on proliferation and cell death under normal conditions, overexpression of LRPPRC significantly reversed the DOX-induced G1/G0 arrest, increased the cell population in the G2/M phase and significantly reversed Dox-induced apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death. Taken together, these results indicated that LRPPRC overexpression exerts protective effects against DOX-induced cytotoxicity of H9C2 cardiomyocytes, while slightly affecting the cells under normal conditions.
Figure 2.
LRPPRC overexpression exerts protective effects against DOX-induced cell injury. (A) A total of 48 h post-transfection with siLRPPRC and the coding sequence of LRPPRC, the protein levels of LRPPRC were detected via western blotting. (B) Following LRPPRC overexpression, the cytotoxicity of DOX in H9C2 cells was measured. (C) Cell Counting Kit-8 assay was performed to detect the effect of LRPRC overexpression on cell proliferation under DOX treatment. (D) DOX at IC30 was utilized for cell treatment for 24 h, followed by PI staining and flow cytometric analysis to detect the cell cycle phases. (E) DOX at IC50 was employed for cell treatment for 24 h, followed by Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining and flow cytometric analysis to detect apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death. *P<0.05 vs. vector group. LRPPRC, leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat-containing; DOX, doxorubicin; si, small interfering; PI, propidium iodide; OD, optical density.
LRPPRC overexpression maintains mitochondrial function potentially via scavenging ROS induced by DOX
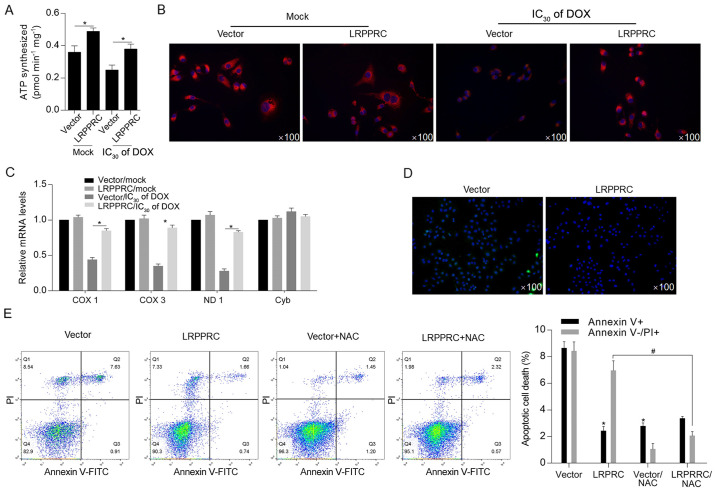
Considering the critical regulatory roles of LRPPRC on mitochondrial function (7), cellular ATP synthesis was detected following DOX exposure. The results indicated that LRPPRC overexpression significantly increased ATP synthesis both under normal conditions and following DOX exposure (Fig. 3A). Subsequently, mitochondrial function was examined via detecting the mitochondrial mass and transcriptional activity. As illustrated in Fig. 3B and C, the DOX treatment decreased mitochondrial mass and transcriptional activity compared with Mock/vector group, and overexpression of LRPPRC reversed the decrease in mitochondrial mass and transcriptional activity.. Moreover, ROS accumulation was decreased in LRPPRC-overexpressing cells after DOX treatment, which additionally indicated that LRPPRC may exert protective effects via scavenging ROS (Fig. 3D). Following DOX treatment at IC50 for 24 h, DOX-induced cell death was significantly attenuated by overexpression of LRPPRC or ROS scavenger NAC, indicating that LRPPRC potentially regulates ROS accumulation (Fig. 3E).
Figure 3.
DOX-induced LRPPRC exerts protective effects against DOX exposure potentially via scavenging ROS. (A) Following DOX exposure, the effect of LRPPRC overexpression on ATP synthesis was examined. (B) Mitochondrial mass was measured using MitoTracker Red staining. (C) To evaluate the effect of LRPPRC on mitochondrial transcriptional activity, the expression levels of COX 1, COX 3, ND1 and Cyb were detected via reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. (D) ROS accumulation was detected following DOX exposure at IC30 for 24 h. (E) Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining followed by flow cytometric analysis was performed to detect apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death. *P<0.05 vs. vector group; #P<0.05 vs. LRPPRC group. LRPPRC, leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat-containing; DOX, doxorubicin; PI, propidium iodide; COX, cytochrome c oxidase subunit; ND1, NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1; Cyb, cytochrome b; NAC, N-acetyl-L-cysteine; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
Accumulated ROS is essential for LRPPRC upregulation
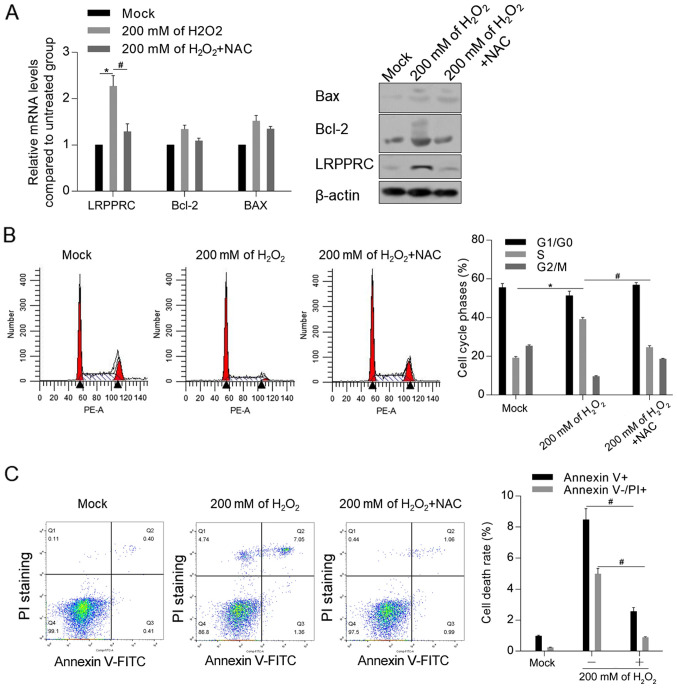
To investigate the mechanism of LRPPRC induction by DOX, it was examined whether accumulated ROS induced by H2O2 was associated with the upregulation of LRPPRC. As demonstrated in Fig. 4A, treatment with 200 mM H2O2 for 24 h significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein level of LRPPRC compared with control cells, which was reversed by co-treatment with ROS scavenger NAC. Moreover, NAC attenuated the H2O2-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis (Fig. 4B and C).
Figure 4.
LRPPRC exerts protective effects against reactive oxygen species-induced cell injury in H9C2 cells. (A) Following treatment with 200 mM H2O2, the mRNA and protein expression levels of LRPPRC, Bcl-2 and Bax were detected. *P<0.05 vs. Mock group; #P<0.05 vs. 200 mM H2O2 group. Following H2O2 exposure with or without NAC treatment, the (B) cell cycle phase distribution and (C) cell death rate were measured. *P<0.05 vs. Mock group; #P<0.05 vs. 200 mM H2O2 group. LRPPRC, leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat-containing; DOX, doxorubicin; NAC, N-acetyl-L-cysteine; PI, propidium iodide.
Discussion
The present study investigated the effect of DOX on the expression of LRPPRC, which is a mitochondria-associated regulator, and subsequently evaluated the regulatory effects of DOX-induced LRPPRC on cultured H9C2 cardiomyocytes. DOX has been indicated to exhibit well-known side effects, including the induction of cardiotoxicity, by altering the mitochondrial membrane, which comprises lipid peroxidation, generation of free radicals, the increase in the myocardial levels of sodium and calcium and the induction of autophagy/mitophagy, thereby resulting in apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death in cardiomyocytes (2-5). The results of the present study demonstrated that DOX induced transcriptional upregulation of LRPPRC, which was followed by stabilization of Bcl-2 and Bax at the protein level. Antioxidants have been indicated to exert cardioprotective effects against DOX exposure via scavenging ROS (18,19). To the best of our knowledge, the current study indicated for the first time that the expression of LRPPRC, which exerted cardioprotective effects against DOX-induced injury, was increased following DOX exposure.
The results of the present study demonstrated that overexpressed LRPPRC exerted protective effects against DOX exposure. LRPPRC reversed the DOX-mediated inhibition of proliferation and cell cycle arrest and improved mitochondrial function. Under normal conditions, overexpressed LRPPRC increased ATP synthesis, mitochondrial DNA mass and transcriptional levels without affecting proliferation, which is consistent with previous findings (20,21). However, overexpressed LRPPRC did not affect cell proliferation and cell cycle distribution under normal conditions, indicating that LRPPRC primarily reversed DOX-induced oxidative stress. To further evaluate the cardioprotective effect of LRPPRC, DOX was administered to cells overexpressing LRPPRC. As anticipated, DOX exposure at a relatively high concentration (IC50 of DOX) induced cell death, which was significantly reversed following overexpression of LRPPRC. Consistently, overexpressed LRPPRC did not affect cell death under normal conditions. However, overexpressed LRPPRC significantly inhibited both apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death induced by DOX treatment, with apoptotic cell death being inhibited to a greater extent. Interestingly, LRPPRC-knockdown did not efficiently reduce LRPPRC levels, which may be attributed to the low levels of endogenous LRPPRC in H9C2 cells.
Mitochondria have been indicated to serve essential roles cardiac cell homeostasis and preventing cells from injury-induced death (22). Dysregulated mitochondrial homeostasis has been reported to induce mitochondrial dysfunction, including a decrease in ATP synthesis, the accumulation of mitochondrial and cytoplasmic ROS and alterations in redox balance in cardiomyocytes (23-25). ROS are considered to be the major mediators of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity (26,27). Excess ROS induced by DOX have been demonstrated to result in irreversible mitochondrial damage and exacerbate cardiac diseases (22). In the present study, DOX-induced LRPPRC and overexpressed LRPPRC were revealed to maintain mitochondrial homeostasis and function, as they increased ATP synthesis, mitochondrial mass and transcriptional activity compared with the mock group. Additionally, overexpression of LRPPRC in H9C2 cells reversed DOX-induced ROS accumulation and subsequent apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death. It was also revealed that accumulated ROS induced by H2O2 exposure increased LRPPRC protein levels, indicating that ROS may directly regulate LRPPRC. Notably, considering the low endogenous ROS level in the absence of H2O2, the effect of H2O2 was specifically detected with or without NAC treatment. Therefore, it was hypothesized that the ROS-LRPPRC axis may form a feedback loop, and it is worth investigating whether accumulated ROS regulates LRPPRC protein level in subsequent studies.
The current study aimed to evaluate the cardioprotective effects of LRPPRC and its function in energy metabolism in H9C2 rat cardiomyocytes. However, certain limitations exist in the present study. Firstly, the cardioprotective effects of LRPPRC were evaluated by introducing exogenous LRPPRC instead of using DOX-induced LRPPRC. Additional studies with DOX pretreatment are required to determine whether DOX-induced LRPPRC exhibits similar effects to those of exogenous LRPPRC. Secondly, although several mitochondrial functions were investigated in the current study (ATP synthesis, mitochondrial transcriptional activity and mass), mitochondria-associated autophagy and mitophagy in H9C2 cells under DOX treatment still require additional investigation. Taken together, these findings may provide evidence of the cardioprotective effects of LRPPRC against DOX treatment.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mrs. Yun Bai (Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, China) for language editing.
Funding
The present study was funded by Starting Scientific Foundation of Zunyi Medical University (grant no. SS20180601ZF).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
QT and DL designed the investigation strategy. WX, XK and JZ participated in data collection, performed the statistical analysis and wrote the manuscript. WX and XK performed cell experiments. YX performed part of the molecular experiments, including transfection and RT-qPCR. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Minotti G. Doxorubicin degradation in cardiomyocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;322:408–419. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.122820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Umansky SR, Shapiro JP, Cuenco GM, Foehr MW, Bathurst IC, Tomei LD. Prevention of rat neonatal cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by simulated in vitro ischemia and reperfusion. Cell Death Differ. 1997;4:608–616. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Olson HM, Young DM, Prieur DJ, LeRoy AF, Reagan RL. Electrolyte and morphologic alterations of myocardium in adriamycin-treated rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1974;77:439–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Myers CE, Gianni L, Simone CB, Klecker R, Greene R. Oxidative destruction of erythrocyte ghost membranes catalyzed by the doxorubicin-iron complex. Biochemistry. 1982;21:1707–1712. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Olson RD, Mushlin PS. Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity: Analysis of prevailing hypotheses. FASEB J. 1990;4:3076–3086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Piasek A, Bartoszek A, Namiesnik J. Phytochemicals that counteract the cardiotoxic side effects of cancer chemotherapy. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 2009;63:142–158. (In Polish) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sasarman F, Brunel-Guitton C, Antonicka H, Wai T, Shoubridge EA. LRPPRC and SLIRP interact in a ribonucleoprotein complex that regulates posttranscriptional gene expression in mitochondria. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21:1315–1323. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e10-01-0047. LSFC Consortium. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ruzzenente B, Metodiev MD, Wredenberg A, Bratic A, Park CB, Cámara Y, Milenkovic D, Zickermann V, Wibom R, Hultenby K, et al. LRPPRC is necessary for polyadenylation and coordination of translation of mitochondrial mRNAs. EMBO J. 2012;31:443–456. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chujo T, Ohira T, Sakaguchi Y, Goshima N, Nomura N, Nagao A, Suzuki T. LRPPRC/SLIRP suppresses PNPase-mediated mRNA decay and promotes polyadenylation in human mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:8033–8047. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xu F, Morin C, Mitchell G, Ackerley C, Robinson BH. The role of the LRPPRC (leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat cassette) gene in cytochrome oxidase assembly: Mutation causes lowered levels of COX (cytochrome c oxidase) I and COX III mRNA. Biochem J. 2004;382:331–336. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mili S, Pinol-Roma S. LRP130, a pentatricopeptide motif protein with a noncanonical RNA-binding domain, is bound in vivo to mitochondrial and nuclear RNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:4972–4982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.23.14.4972-4982.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Topisirovic I, Siddiqui N, Orolicki S, Skrabanek LA, Tremblay M, Hoang T, Borden KLB. Stability of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E mRNA is regulated by HuR, and this activity is dysregulated in cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:1152–1162. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01532-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sterky FH, Ruzzenente B, Gustafsson CM, Samuelsson T, Larsson NG. LRPPRC is a mitochondrial matrix protein that is conserved in metazoans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;398:759–764. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang S, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Liu Q, Gu J. Cardioprotective effects of fibroblast growth factor 21 against doxorubicin-induced toxicity via the SIRT1/LKB1/AMPK pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(e3018) doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu D, Ma Z, Xu L, Zhang X, Qiao S, Yuan J. PGC1α activation by pterostilbene ameliorates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity by reducing oxidative stress via enhancing AMPK and SIRT1 cascades. Aging (Albany NY) 2019;11:10061–10073. doi: 10.18632/aging.102418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wen J, Zhang L, Liu H, Wang J, Li J, Yang Y, Wang Y, Cai H, Li R, Zhao Y. Salsolinol attenuates doxorubicin-induced chronic heart failure in rats and improves mitochondrial function in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10(1135) doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Errami M, Galindo CL, Tassa AT, Dimaio JM, Hill JA, Garner HR. Doxycycline attenuates isoproterenol- and transverse aortic banding-induced cardiac hypertrophy in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324:1196–1203. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.133975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hori Y, Kunihiro S, Sato S, Yoshioka K, Hara Y, Kanai K, Hoshi F, Itoh N, Higuchi S. Doxycycline attenuates isoproterenol-induced myocardial fibrosis and matrix metalloproteinase activity in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009;32:1678–1682. doi: 10.1248/bpb.32.1678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mourier A, Ruzzenente B, Brandt T, Kühlbrandt W, Larsson NG. Loss of LRPPRC causes ATP synthase deficiency. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:2580–2592. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cuillerier A, Honarmand S, Cadete V, Ruiz M, Forest A, Deschênes S, Beauchamp C, LSFC Consortium; Charron G, Rioux JD, et al. Loss of hepatic LRPPRC alters mitochondrial bioenergetics, regulation of permeability transition and trans-membrane ROS diffusion. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26:3186–3201. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sack MN, Fyhrquist FY, Saijonmaa OJ, Fuster V, Kovacic JC. Basic biology of oxidative stress and the cardiovascular system: Part 1 of a 3-part series. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:196–211. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.05.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liu D, Ma Z, Di S, Yang Y, Yang J, Xu L, Reiter RJ, Qiao S, Yuan J. AMPK/PGC1a activation by melatonin attenuates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity via alleviating mitochondrial oxidative damage and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;129:59–72. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ma Z, Xin Z, Di W, Yan X, Li X, Reiter RJ, Yang Y. Melatonin and mitochondrial function during ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74:3989–3998. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2618-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Galley HF, McCormick B, Wilson KL, Lowes DA, Colvin L, Torsney C. Melatonin limits paclitaxel-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in vitro and protects against paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain in the rat. J Pineal Res. 2017;63(e12444) doi: 10.1111/jpi.12444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Takemura G, Fujiwara H. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy from the cardiotoxic mechanisms to management. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2007;49:330–352. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2006.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Octavia Y, Tocchetti CG, Gabrielson KL, Janssens S, Crijns HJ, Moens AL. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;52:1213–1225. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.