Abstract
Background
We sought to determine whether COPD conferred a higher risk for healthcare utilization in terms of hospitalization and clinical outcomes due to COVID-19.
Methods
A cohort study with covariate adjustment using multivariate logistic regression was conducted at the Cleveland Clinic Health System in Ohio and Florida. Symptomatic patients aged 35 years and older who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 between March 8 and May 13, 2020 were included.
Findings
15,586 individuals tested for COVID-19 at the Cleveland Clinic between March 8, 2020 and May 13, 2020 met our inclusion criteria. 12.4% of COPD patients (164/1319) tested positive for COVID-19 compared to 16.6% (2363/14,267) of the non-COPD population. 48.2% (79/164) of COVID-19 positive COPD patients required hospitalization and 45.6% (36/79) required ICU admission. After adjustment for covariates, rates of COVID-19 infection were not significantly different than the non-COPD population (adj OR 0.97; CI: 0.89–1.05), but COPD patients had increased healthcare utilization as demonstrated by risk for hospitalization (adj OR 1.36; CI: 1.15–1.60), ICU admission (OR 1.20; CI: 1.02–1.40), and need for invasive mechanical ventilation (adj OR 1.49; CI: 1.28–1.73). Unadjusted risk for in-hospital mortality was higher in the COPD population (OR 1.51; CI: 1.14–1.96). After adjusting for covariates however, the risk for in-hospital mortality was not significantly different than the non-COPD population (adj OR 1.08: CI: 0.81–1.42).
Interpretation
Our analysis demonstrated that COPD patients with COVID-19 had a higher risk for healthcare utilization, although adjusted in-hospital mortality risk was not different than the non-COPD patients with COVID-19.
Key words: SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, COPD
Research in context.
Evidence before this study
Patients with advanced age or comorbidities like COPD are at increased risk for severe outcomes related to COVID-19. While COPD has been designated as a high risk condition, there is very limited data analyzing rates of healthcare utilization and clinical outcomes related to COVID-19 in the COPD population to date. We sought to determine whether COPD conferred a higher risk for healthcare utilization in terms of hospitalization and clinical outcomes due to COVID-19. We performed a cohort study with covariate adjustment using multivariate logistic regression of the Cleveland Clinic Health System in Ohio and Florida.
Added value of this study
This study is the largest and most comprehensive to date analyzing COPD outcomes in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Implications of all the available evidence
COPD patients with COVID-19 had a higher risk for healthcare utilization, although adjusted in-hospital mortality risk was not different than the non-COPD patients with COVID-19.
Alt-text: Unlabelled box
1. Introduction
The recent and ongoing outbreak of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has posed critical challenges for the research and medical communities. Patients with advanced age or comorbidities (including diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and obesity) are at increased risk for severe outcomes related to COVID-19 [1]. While chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) has been designated as a high risk condition, there is very limited data analyzing rates of healthcare utilization and clinical outcomes related to COVID-19 in the COPD population to date [2, 3].
The impact of COVID-19 on COPD patients has been reported in a limited number of patients from single centers and case series with a wide range of clinical outcomes [4]. A recent meta-analysis noted that COPD patients were more likely to have severe disease, and were at a higher risk of mortality compared to the general population. This study also noted a higher mortality rate amongst current smokers with COPD [4]. However the highly heterogeneous and low prevalence of COPD in current observational studies has made firm conclusions difficult [1], [2], [3], [4]. There is significant concern that COPD patients are at a higher risk for severe disease due to COVID-19 for multiple reasons. First, COPD patients tend to be older and have more comorbidities which are risk factors for COVID-19 severity [1]. Second, COPD patients are often treated with inhaled or oral corticosteroids. Using corticosteroids may increase the risk for acquiring COVID-19 through immunosuppression and may worsen the severity of disease by promoting viral shedding, a phenomenon observed with related coronaviruses, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV [5, 6]. Third, there is evidence that active smokers and patients with COPD have increased upregulation of the ACE2 receptor in lung epithelial cells [7], which is the site where SARS-CoV-2 binds to gain entry into host cells and cause COVID-19 infection [8].
Given these distinct features of COVID-19, and the potential public health impact on COPD, we sought to determine whether COPD patients where at a higher risk for hospitalization and poor clinical outcomes compared to the non-COPD population. To answer these questions, we used the Cleveland Clinic COVID-19 registry which tracks symptomatic patients who are referred by their physicians for COVID-19 testing. The registry records clinical variables, laboratory testing, imaging data, healthcare utilization and clinical outcomes which we utilized to perform our analysis.
2. Methods
2.1. Cleveland clinic registry
Data on patients’ demographics, medications, comorbidities, history of COVID-19 exposure, disease manifestation upon presentation, disposition, and outcomes were extracted from electronic health records (EHR) for all patients from the Cleveland Clinic COVID-19 registry [9]. Patients were asked if they had a diagnosis of COPD, and the diagnosis was confirmed if it was also included in the patient's medical chart in the EHR (which requires physician confirmation). Registry characterization and data collection reflect the clinical characteristics recently published on COVID-19 [10], [11], [12], [13], [14]. Uniform clinical templates were implemented across the Cleveland Clinic Health System (CCHS) in Ohio and Florida using EHR to standardize the care of patients tested for COVID-19, and to facilitate data extraction. Data extraction from EHR (Epic®, Epic Systems Corporation, Wisconsin, USA) at the CCHS was performed manually by a trained research team and using predefined processes that have previously been published [15]. This study and the registry were both approved by the Cleveland Clinic Institutional Review Board.
Testing for COVID-19 at Cleveland Clinic facilities is currently indicated for symptomatic patients (presence of fever with cough or shortness of breath) and those with chronic medical conditions. After March 21 2020, diarrhea was added to the 3 qualifying symptoms [16]. Given previous beliefs that co-infection of SARS-CoV-2 with other respiratory viruses is rare [17], a reflex-testing algorithm was implemented to conserve resources. All patient specimens were first tested for the presence of influenza A/B and respiratory syncytial virus, and only those negative for influenza and respiratory syncytial virus were subsequently tested for SARS-CoV-2. After April 15th 2020, the registry stopped collecting data on control subjects that were COVID-19 negative. About 30% of all individuals in the registry had laboratory measurements done as an outpatient at the time of SARS-CoV-2 testing [16]. Monitoring from the COVID-19 home monitoring program consisted of telephone outreach by a registered nurse and self-monitoring through an app for patient-entry of COVID-19 symptoms. Patients were asked whether any of a list of symptoms (fever, cough, dyspnea, weakness, vomiting, diarrhea, and appetite) were present. Frequent comorbidities (ex. diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and others) and certain medications (corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs], ACE inhibitors, and angiotensin receptor blockers) were recorded in the database. Corticosteroids represented a combination of oral and inhaled medications. A random chart review of 10 subjects demonstrated that all of COPD patients documented as being on corticosteroids were on inhaled medication.
2.2. Subjects
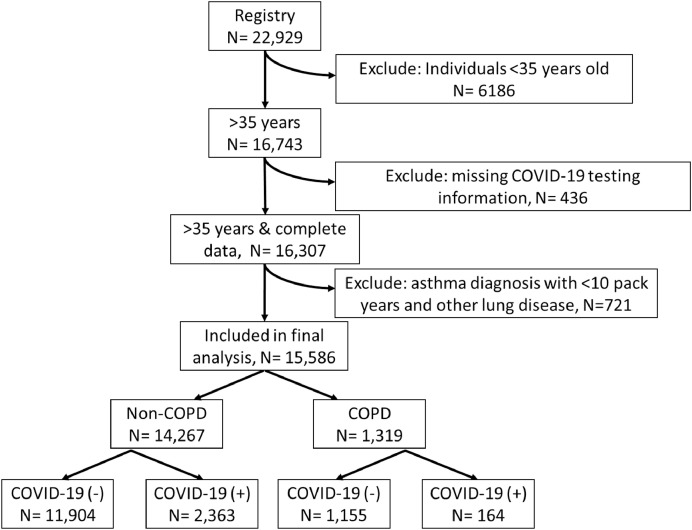
Data on 22,929 individuals tested for COVID-19 at the Cleveland Clinic between March 8, 2020 and May 13, 2020 was available. These dates represent the most recent data pull from our registry. We limited our analysis to individuals 35 years and older because the diagnosis of COPD is unlikely in those less than 35 years old [18]. We also excluded those less than 35 years old in the control population to reduce a significant age bias. Approximately 30% of subjects had labs drawn at the time of testing which were available for analysis. Additionally, to avoid having a biased sample we excluded those with concurrent diagnosis of asthma and less than a 10 pack year smoking history and also excluded those with other chronic lung conditions. Out of the initial sample size of 22,929, 15,586 met our inclusion criteria (see Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
flowchart of patients included in our analysis.
2.3. Laboratory confirmation
Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swab specimens were collected and pooled for testing by trained medical personnel as previously described [16]. Infection with SARS-CoV-2 was confirmed by laboratory testing using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction SARS-CoV-2 assay that was validated in the Cleveland Clinic Robert J. Tomsich Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Institute. This assay used an extraction kit (MagNA Pure;Roche) and 7500 DxReal-Time PCR System instruments (Applied Biosystems). All testing was authorized by the Food and Drug Administration under an Emergency Use Authorization and in accordance with the guidelines established by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [16]
2.4. Statistical analysis
Outcomes that were analyzed included COVID-19 infection in symptomatic COPD versus the non-COPD population as well as clinical outcomes and healthcare utilization of COVID-19 positive COPD patients in terms of risk for hospitalization, admission to the ICU, non-invasive ventilation and mechanical ventilation, and in-hospital mortality during the index hospitalization. Summary statistics included counts and percentages for categorical variables and means with standard deviations for continuous variables (which were all normally distributed). If the data was not normally distributed we would have provided medians with interquartile range, however this was not the case in our dataset. Data with missing dependent variables were excluded. All covariates included in the regression models were missing in fewer than 10% of subjects. Missing data were imputed using the mice package in R [19]. Mice replaces each missing value by a plausible value drawn from a distribution specifically designed for each missing datapoint. Sensitivity analysis was performed comparing imputed and non-imputed data. Categorical variables were analyzed with chi-square tests and normally distributed continuous variables were compared using t-tests. Models were constructed choosing covariates a priori known to be associated with COPD and identified from clinical experience and a review of the literature [20], [21], [22], [23], [24], [25], [26]. Binomial multivariate logistic regression was used to account for differences in clinical outcomes for COVID-19 infection, risk of hospitalization, risk of ICU admission, non-invasive ventilation, invasive mechanical ventilation, and in-hospital mortality, and included the following covariates for the model build: age, BMI, sex, race (African Americans vs Caucasian), smoking status (current versus former), comorbidities (hypertension, cancer, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, immunosuppressive therapy). We dichotomized our race variable due to the low number of other races (including Hispanic and Asian populations) in the dataset and in order to preserve degrees of freedom in our analysis of hospitalized patients, which had a lower number of observations. Model fit was assessed using R2 and C-index. All analyses were two-tailed, performed at a significance level of 0.05, and confidence intervals were 95%. R version 4.0.0 (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) were used for statistical analyses.
2.5. Role of funding
The funder had no role in data analysis or interpretation of results.
3. Results
A total of 15,586 symptomatic patients were tested for COVID-19, of which 1319 (9.2%) were positive (Table 1). The COPD population, which represented 8.5% of the total population tested, had a lower rate of COVID-19 positive test results compared to the non-COPD population (12.4% vs 16.6%, p = 0.001). Overall, the demographics varied considerably between the two populations, with the COPD population being almost ten years older (67.7 ± 12.1 vs 58.0 ± 14.8, p<0.001) and reported significantly more comorbidities, including diabetes mellitus (40.4% vs 23.4%, p<0.001), hypertension (76.9% vs 48.6%, p<0.001), and diagnosis of cancer (28.0% vs 17.4%, p<0.001). COPD patients also were less likely to be female (54.3% vs 59.6%, p<0.001), and had a higher proportion of African Americans (24.6% vs 19.3%, p<0.001). There were a higher proportion of current smokers (32.2% vs 11.8%, p<0.001), pack years of smoking (31.7 ± 32.9 vs 14.7 ± 25.1, p<0.001) and patients taking corticosteroids (41.5% vs 17.2%, p<0.001) in the COPD population.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of all patients tested for COVID-19 stratified by diagnosis of COPD.
| Non-COPD | COPD | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 14,267 | 1319 | |
| Demographics | |||
| Age (in years) (SD) | 58.0 (14.8) | 67.7 (12.1) | <0.001 |
| Female Sex (%) | 8500 (59.6) | 716 (54.3) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m^2) (SD) | 30.4 (7.8) | 29.9 (9.0) | 0.027 |
| Race (%) | |||
| Caucasian | 9747 (68.3) | 918 (69.6) | 0.331 |
| African American | 2760 (19.3) | 325 (24.6) | <0.001 |
| Other | 1760 (12.3) | 76 (5.8) | <0.001 |
| Hispanic Ethnicity (%) | 37 (2.6) | 5 (3.8) | 0.010 |
| Comorbidities (%) | |||
| Diabetes | 3333 (23.4) | 533 (40.4) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 6940 (48.6) | 1014 (76.9) | <0.001 |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 1883 (13.2) | 495 (37.5) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 1523 (10.7) | 454 (34.4) | <0.001 |
| Cancer status (current) | 552 (3.9) | 96 (7.3) | <0.001 |
| Cancer status (in remission) | 1193 (8.4) | 202 (15.3) | <0.001 |
| Immunosuppressive Therapy | 1628 (11.4) | 350 (26.5) | <0.001 |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | 795 (5.6) | 86 (6.5) | 0.177 |
| Smoking (pack years) (SD) | 14.68 (25.1) | 31.68 (32.9) | <0.001 |
| Current smokers | 1597 (11.8) | 413 (32.2) | <0.001 |
| Medications (%) | |||
| NSAIDS | 3232 (22.7) | 556 (42.2) | <0.001 |
| Corticosteroids# | 2456 (17.2) | 547 (41.5) | <0.001 |
| ACE Inhibitors | 1285 (9.0) | 181 (13.7) | <0.001 |
| Angiotensin Receptor Blockers | 956 (6.7) | 157 (11.9) | <0.001 |
| Laboratory Measurements (SD) | |||
| International Normalized Ratio | 1.4 (0.86) | 1.41 (0.9) | 0.109 |
| Platelet Count (x 109/L) | 244.9 (108.2) | 252.04 (109.1) | 0.022 |
| Eosinophil Count* (x 103/μL) | 0.1 (0.20) | 0.18 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte Count* (x 103/μL) | 1.5 (1.0) | 1.54 (1.0) | 0.070 |
| Neutrophil Count* (x 103/μL) | 6.8 (4.8) | 7.07 (4.7) | 0.029 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 (0.7) | 3.73 (0.6) | 0.964 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.4 (1.6) | 1.45 (1.7) | 0.282 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 39.8 (167.8) | 32.48 (88.7) | 0.117 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.7 (1.4) | 0.56 (0.6) | 0.001 |
| Outcomes (%) | |||
| COVID-19 positive | 2363 (16.6) | 164 (12.4) | 0.001 |
Peripheral blood Absolute count. Data are presented as n (%) for categorical variables and mean [SD] for continuous variables. CCCRR stands for Cleveland Clinic COVID-19 Research Registry; NSAIDS for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. #Corticosteroids represents inhaled and oral medications. P-values represent chi-square tests for categorical variables and t-tests for continuous variables.
Among the COPD patients who were tested, those who tested positive (n = 164, Table 2) were more likely to be older (72.5 ± 1.7 vs 67.1 + 11.9 years, p<0.001), and were less likely to report corticosteroid usage (18.3% vs 44.8%, p<0.001). They also had higher pack years of smoking history (38.1 ± 41.2 vs 30.9 ± 31.6, p = 0.009), although current smokers were less likely to be COVID-19 positive in the COPD cohort (19.5% vs 33.0%, p<0.001). Among the patients who were tested, symptomatic COPD patients that tested positive for COVID-19 were more likely to report flu-like symptoms (39.0% vs 27.0%, p = 0.003), loss of appetite (22.0% vs 7.4%, p<0.001), and diarrhea (19.5% vs 12.1%, p = 0.008) compared to symptomatic COPD patients that tested negative for COVID-19. When analyzing the 30% of subjects who had labs drawn at the time of testing, the COVID-19 positive cohort of COPD patients had lower absolute eosinophil (0.05±0.07 vs 0.19±0.19, p<0.001), lymphocyte (1.15±0.63 vs 1.59±1.05, p<0.001), and neutrophil counts (4.70±2.03 vs 7.31±4.83, p<0.001) compared to the COVID-19 negative COPD population. Those who tested positive were less likely to report corticosteroid usage (18.3% vs 44.8%, p<0.001) than those with COPD who tested negative for COVID-19.
Table 2.
Clinical characteristics of all patients tested for COVID-19 with a diagnosis of COPD.
| COVID-19 negative | COVID-19 positive | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 1155 | 164 | |
| Demographics | |||
| Age (in years) (SD) | 67.1 (11.9) | 72.5 (12.7) | <0.001 |
| Female Sex (%) | 635 (55.0) | 81 (49.4) | 0.178 |
| BMI (kg/m^2) (SD) | 29.8 (9.1) | 30.98 (8.0) | 0.102 |
| Race (%) | |||
| Caucasian | 807 (69.9) | 111 (67.7) | 0.567 |
| African American | 285 (24.7) | 40 (24.4) | 0.934 |
| Other | 63 (5.5) | 13 (7.9) | 0.219 |
| Hispanic Ethnicity (%) | 37 (3.2) | 5 (3.0) | 0.891 |
| Symptoms (%) | |||
| Cough | 773 (66.9) | 95 (57.9) | 0.023 |
| Sputum Production | 256 (22.2) | 34 (20.7) | 0.665 |
| Dyspnea | 793 (68.7) | 93 (56.7) | 0.002 |
| Fever | 276 (26.1) | 51 (31.1) | 0.176 |
| Fatigue | 302 (40.8) | 63 (38.4) | 0.558 |
| Flu Like Symptoms | 312 (27.0) | 64 (39.0) | 0.003 |
| Loss of Appetite | 86 (7.4) | 36 (22.0) | <0.001 |
| Diarrhea | 140 (12.1) | 32 (19.5) | 0.008 |
| Vomiting | 78 (6.8) | 6 (6.4) | 0.849 |
| Comorbidities (%) | |||
| Diabetes | 475 (41.1) | 58 (35.4) | 0.164 |
| Hypertension | 879 (76.1) | 135 (82.3) | 0.078 |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 424 (36.7) | 71 (43.3) | 0.103 |
| Heart Failure | 397 (34.4) | 57 (34.8) | 0.920 |
| Cancer (current) | 90 (7.8) | 6 (3.7) | 0.059 |
| Cancer (in remission) | 169 (14.6) | 33 (20.1) | 0.067 |
| Immunosuppressive Therapy | 329 (28.5) | 21 (12.8) | <0.001 |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | 311 (26.9) | 27 (16.5) | 0.004 |
| Smoking (pack years) (SD) | 30.9 (31.6) | 38.1 (41.2) | 0.009 |
| Current smokers | 381 (33.0) | 32 (19.5) | <0.001 |
| Medications (%) | |||
| NSAIDS | 506 (43.8) | 50 (30.5) | 0.001 |
| Corticosteroids | 517 (44.8) | 30 (18.3) | <0.001 |
| ACE Inhibitors | 160 (13.9) | 21 (12.8) | 0.702 |
| Angiotensin Receptor Blockers | 136 (11.8) | 21 (12.8) | 0.712 |
| Laboratory Measurements (SD) | |||
| C-reactive protein ( mg/L) | 6.6 (9.0) | 10.3 (9.2) | <0.001 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L) | 416.7 (736.0) | 323.9 (110.3) | 0.107 |
| D-Dimer (μg/L) | 286.6 (586.5) | 297.4 (432.6) | 0.820 |
| International Normalized Ratio | 1.4 (1.0) | 1.3 (0.6) | 0.041 |
| Platelet Count (x 109/L) | 254.8 (109.8) | 227.7 (99.6) | 0.003 |
| Eosinophil Count* (x 103/μL) | 0.2 (0.5) | 0.1 (0.1) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte Count* (x 103/μL) | 1.6 (1.1) | 1.2 (0.6) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil Count* (x 103/μL) | 7.3 (4.8) | 4.7 (2.0) | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.7 (0.6) | 3.6 (0.5) | 0.025 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.4 (1.6) | 1.6 (1.9) | 0.280 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 29.4 (54.7) | 59.8 (224.9) | <0.001 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.6 (0.6) | 0.5 (0.2) | 0.022 |
Peripheral blood Absolute count. Data are presented as n (%) for categorical variables and mean [SD] for continuous variables. NSAIDS for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. P-values represent chi-square tests for categorical variables and t-tests for continuous variables.
The proportion of patients that tested positive for COVID-19 and were hospitalized in the COPD cohort was significantly more than the non-COPD cohort (48.2% vs 26.5%, p<0.001), and COPD patients had a higher mortality rate (20.3% vs 14.5%, p = 0.044) (see Table 3). Of the 164 COPD patients who tested positive for COVID-19, 79 (48.2%) required hospitalization; of the 79 hospitalized, 36 (45.6%) required ICU admission. Compared to the non-COPD patients, COPD patients had higher rates of ICU admission (45.6% vs 34.2%, p = 0.003), need for non-invasive (69.4% vs 65.9%, p = 0.360) and invasive mechanical ventilation (63.9% vs 63.1%, p = 0.837).
Table 3.
Clinical characteristics of all patients positive for COVID-19 stratified by diagnosis of COPD.
| Non-COPD | COPD | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 2363 | 164 | |
| Demographics | |||
| Age (in years) (SD) | 60.2 (15.4) | 72.5 (12.7) | <0.001 |
| Female Sex (%) | 1237 (52.3) | 81 (49.4) | 0.472 |
| BMI (kg/m^2) (SD) | 31.0 (7.7) | 31.0 (8.0) | 0.974 |
| Race (%) | |||
| Caucasian | 1438 (60.9) | 111 (67.7) | 0.084 |
| African American | 616 (26.1) | 40 (24.4) | 0.631 |
| Other | 309 (13.1) | 13 (7.9) | 0.054 |
| Hispanic Ethnicity (%) | 281 (11.9) | 5 (3.0) | <0.001 |
| Symptoms (%) | |||
| Cough | 1738 (73.6) | 95 (57.9) | <0.001 |
| Sputum Production | 257 (10.9) | 34 (20.7) | <0.001 |
| Dyspnea | 948 (40.1) | 93 (56.7) | <0.001 |
| Fever | 1204 (51.0) | 51 (31.1) | <0.001 |
| Fatigue | 852 (36.1) | 63 (38.4) | 0.554 |
| Flu Like Symptoms | 1248 (52.8) | 64 (39.0) | <0.001 |
| Loss of Appetite | 505 (21.4) | 36 (22.0) | 0.856 |
| Diarrhea | 525 (22.2) | 32 (19.5) | 0.420 |
| Vomiting | 143 (6.1) | 6 (3.7) | 0.210 |
| Comorbidities (%) | |||
| Diabetes | 575 (24.3) | 58 (35.4) | 0.002 |
| Hypertension | 1169 (49.5) | 135 (82.3) | <0.001 |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 277 (11.7) | 71 (43.3) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 205 (8.7) | 57 (34.8) | <0.001 |
| Cancer (current) | 53 (2.2) | 6 (3.7) | 0.215 |
| Cancer (in remission) | 224 (9.5) | 33 (20.1) | <0.001 |
| Immunosuppressive Therapy | 209 (8.8) | 21 (12.8) | 0.085 |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | 227 (9.6) | 27 (16.5) | 0.005 |
| Smoking (pack years) (SD) | 16.4 (24.6) | 38.1 (41.2) | <0.001 |
| Current smokers | 126 (6.0) | 32 (20.8) | <0.001 |
| Medications (%) | |||
| NSAIDS | 462 (19.6) | 50 (30.5) | 0.001 |
| Corticosteroids | 227 (9.6) | 30 (18.3) | <0.001 |
| ACE Inhibitors | 55 (2.3) | 12 (7.3) | <0.001 |
| Angiotensin Receptor Blockers | 211 (8.9) | 21 (12.8) | 0.094 |
| Laboratory Measurements (SD) | |||
| Platelet Count (x 109/L) | 214.1 (86.3) | 225.1 (97.5) | 0.292 |
| Lymphocyte Count* (x 103/µL) | 1.2 (1.4) | 1.1 (0.5) | 0.402 |
| Neutrophil Count* (x 103/µL) | 5.3 (3.2) | 4.8 (2.2) | 0.256 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.7 (0.5) | 3.6 (0.5) | 0.377 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.6 (1.9) | 1.9 (2.5) | 0.236 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 12.4 (23.9) | 20.4 (27.1) | <0.001 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.6 (0.6) | 0.5 (0.2) | 0.108 |
| Outcomes (%) | |||
| Hospitalized | 626 (26.5) | 79 (48.2) | <0.001 |
| ICU admission# | 214 (34.2) | 36 (45.6) | 0.003 |
| Non-invasive ventilation* | 141 (65.9) | 25 (69.4) | 0.360 |
| Mechanical ventilation* | 135 (63.1) | 23 (63.9) | 0.837 |
| In-hospital mortality# | 91 (14.5) | 16 (20.3) | 0.044 |
Peripheral blood Absolute count. Data presented as n (%) for categorical variables and mean [SD] for continuous variables. NSAIDS for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; ICU for Intensive Care Unit. #Percentage denominator is in the hospitalized cohort. *Percent denominator is in the ICU cohort. P-values represent chi-square tests for categorical variables and t-tests for continuous variables.
Among the COPD patients who had COVID-19, there was no difference in age and sex when stratified by location of treatment, i.e. outpatient versus hospital ward versus ICU. However, African Americans had higher rates of hospitalization and ICU admission (30.6% hospitalized and 39.5% admitted to the ICU, p<0.001) in the COPD cohort. Subsequently, the inverse was true for Caucasians, where Caucasians represented 75.3% of those treated as an outpatient, 66.7% of those treated in the hospital and 55.8% of those treated in the ICU. Of patients with COPD admitted to the ICU, 25.6% (11/43) were on immunosuppressive therapy. (see Table 4).
Table 4.
Clinical characteristics of patients with COPD who tested positive for COVID-19 stratified by healthcare utilization.
| Outpatient | Hospital Ward | ICU | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 81 | 36 | 43 | |
| Demographics | ||||
| Age (in years) (SD) | 72.7 (13.3) | 72.1 (11.4) | 72.7 (13.1) | 0.968† |
| Female Sex (%) | 40 (49.4) | 17 (47.2) | 22 (51.2) | 0.941† |
| BMI (kg/m^2) (SD) | 30.1 (8.4) | 33.0 (8.6) | 30.5 (7.0) | 0.262† |
| Race (%) | <0.001† | |||
| Caucasian | 61 (75.3) | 24 (66.7) | 24 (55.8) | |
| African American | 11 (13.6) | 11 (30.6) | 17 (39.5) | |
| Other | 9 (11.1) | 1 (2.8) | 2 (4.7) | |
| Hispanic Ethnicity | 3 (3.7) | 1 (2.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0.431† |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Diabetes | 22 (27.2) | 17 (47.2) | 18 (41.9) | 0.068† |
| Hypertension | 62 (76.5) | 33 (91.7) | 38 (88.4) | 0.074† |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 36 (44.4) | 15 (41.7) | 18 (41.9) | 0.943† |
| Heart Failure | 25 (30.9) | 10 (27.8) | 20 (46.5) | 0.139† |
| Cancer (current) | 3 (3.7) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (7.0) | 0.417† |
| Cancer (in remission) | 18 (22.2) | 6 (16.7) | 8 (18.6) | 0.651† |
| Immunosuppressive Therapy | 7 (8.6) | 2 (5.6) | 11 (25.6) | 0.009† |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | 13 (16.0) | 6 (16.7) | 8 (18.6) | 0.936† |
Data are presented as n (%) for categorical variables and mean [SD] for continuous variables. †P-values represent ANOVA (analysis of variance).
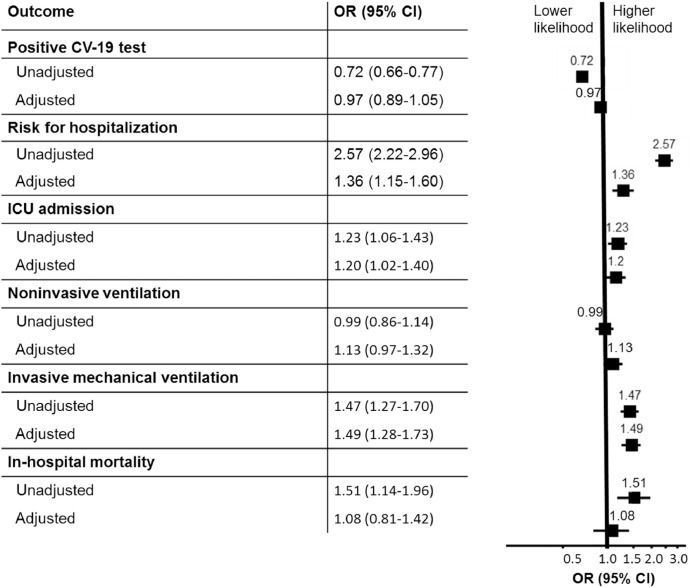
We then performed a multivariate regression model adjusting for age, race, sex, BMI, and comorbidities. We also performed a sensitivity analysis with the non-imputed data and found no significant difference in outcomes (see Methods). We found that after adjusting for covariates, COVID-19 prevalence was not significantly different between COPD and non-COPD patients (adj OR 0.97; CI: 0.89–1.05). However, COPD patients had an increased risk for hospitalization (adj OR 1.36; CI: 1.15–1.60), ICU admission (OR 1.20; CI: 1.02–1.40), need for invasive mechanical ventilation (adj OR 1.49; CI: 1.28–1.73), and a higher rate for non-invasive ventilation that was not statistically significant (adj OR 1.13; CI: 0.97–1.32). Unadjusted risk for in-hospital mortality was higher in the COPD population (OR 1.51; CI: 1.14–1.96), but after adjusting for covariates, the risk was not significantly different than the non-COPD population (adj OR 1.08: CI: 0.81–1.42). (Fig. 2)
Fig. 2.
Association of COPD with results of COVID-19 testing, hospital admission, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, invasive and non-invasive ventilation, and in-hospital mortality. Adjusted analysis with multivariate logistic regression. Odds ratio for positive CV-19 test positivity represents the odds for the entire cohort. Odds ratio for hospitalization represents odds for the CV-19 positive cohort. Odds ratio for ICU admission, non-invasive and invasive mechanical ventilation, and in-hospital mortality represent the odds for the hospitalized cohort.
4. Discussion
In this registry based analysis, we found that COPD patients who tested positive for COVID-19 had higher overall healthcare utilization as they had increased risk for hospitalization, ICU admission, and invasive mechanical ventilation.
A potential risk factor for poor outcomes among patients with COPD who have COVID-19 is the use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) for the routine management of chronic stable disease. There has been concern that steroid usage increases the risk for contracting COVID-19 and developing severe disease due to immunosuppression and enhanced viral shedding [5, 6]. However our findings suggest that the usage of corticosteroids was associated with a lower rate of COVID-19 infection in the COPD population. While our registry does not differentiate oral versus ICS, a random audit of charts showed that 10/10 subjects were taking ICS which leads us to believe that the majority of subjects in our database were using ICS. In general, only a small proportion of COPD patients are maintained on oral corticosteroids due to the lack of efficacy and increased risk for side effects. [27, 28] Therefore, this finding is reassuring that COPD patients can be maintained on ICS during the COVID-19 pandemic. Interestingly, recent studies have shown that ICS is linked to down-regulation of the ACE2 receptor and potentially could impart a protective effect for COVID-19 infection which supports our findings [29]. A recently published large randomized control trial in the United Kingdom demonstrated that dexamethasone 6 mg daily given for 10 days reduced deaths by 1/3 in ventilated patients and by 1/5 in those receiving oxygen compared to standard care [30]. While these findings are encouraging and suggest the role for corticosteroids in the treatment of COVID-19, particularly in the setting of a hyperactive immune response, prospective studies of ICS use as a predictor of decreased susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection are needed.
Another concern has been that active smoking increases the risk for COVID-19 severity given that smoking upregulates the ACE2 receptor expression in lung epithelial cells [7] and increases the risk for SARs-CoV-2 entry into host cells [8]. We did not find an increased risk for COVID-19 infection in current smokers with COPD who tested positive for COVID-19 infection. However, our study was focused primarily on COPD patients and not current smokers alone. Therefore, future studies are needed to better assess whether current smoking status increases the risk for disease severity in COVID-19. Lymphopenia has been linked to an increased risk for COVID-19 severity [31] as well, and our study did find an increased rate of COVID-19 positivity in the COPD cohort with a lower absolute lymphocyte count.
In terms of healthcare utilization, we found that a significant proportion of patients with COPD required hospitalization, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation. While COVID-19 severity has been linked to age, male sex, race, and comorbidities [3], the age of COPD patients and rates of comorbidities was not significantly different when comparing outpatients to hospitalized patients (except for those on immunosuppressive therapy). We also did not find an increased risk in males versus females in terms of healthcare utilization. African American race has been linked to increased severity of COVID-19 [3]. Our study also demonstrates that African Americans with COPD were more likely to require hospitalization and ICU admission. There is an unmet need for targeted interventions for the African American population with COVID-19 due to their increased risk for healthcare utilization.
In addition to increased healthcare utilization, our study demonstrated that COPD patients had higher risk for mortality, which after adjustment with multivariate regression for age, race, BMI, and comorbidities (see Methods) was no longer statistically significant. This is an important finding of our study, which suggests that COPD does not confer mortality risk beyond its associated comorbidities. Greater outreach to the COPD community and coordinated care with other sectors of public health such as the Veterans Administration may be needed [32], given these facilities care for a significant number of COPD patients.
Our findings, while significant, may differ from other observational studies of COPD [4] due to the fact that Cleveland Clinic and its regional facilities did not experience a surge that overwhelmed hospitals during our study period [33]. It is also possible we may not have had enough power to detect a difference in mortality, although our study is the largest observational study to date on COVID-19 and concomitant COPD. It is well-known that survivors of critical illness are at risk for long-term morbidity, delayed mortality, cognitive impairment, and severe deconditioning known collectively as PICS (Post ICU syndrome) [34]. In-hospital mortality may not have afforded adequate time to ascertain this end point. Future long-term studies on the COPD population and the impact of COVID-19 are needed.
We recognize several limitations to our analysis. First, our study is a single study from a tertiary center where COVID-19 was diagnosed and treated according to prespecified pathways. Although patients were referred by physicians in the Cleveland Clinic Health System, some patients may have chosen to utilize other hospitals and therefore leading to incomplete outcome data. Nonetheless, we find that possibility to be low and unlikely to introduce an intergroup-bias. Another methodologic concern may be that our control population was from the months of March and April 2020, and after April 15th 2020 our registry no longer collected outcome data on controls but continued to collect information on COVID-19 positive patients. While this may have introduced a chronological bias, we have no reason to believe that outcomes would be different during these adjacent time intervals during which management algorithms did not change for the Cleveland Clinic Health System. We also found that the comorbidity profile of our dataset showed a relatively high rate of diabetes reported in our COPD population; while diabetes is more common in COPD, the proportion in our population was double the typical percentile [35]. Unfortunately, our questionnaire did not distinguish prediabetes versus diabetes which may account for this higher proportion of patients. Our data set also does not include variables associated with severity of COPD such as pulmonary function tests, long-acting bronchodilator usage, degree of emphysema on CT thorax imaging, or exacerbation frequency, and it is well known that mortality and healthcare utilization are increased among those patients with severe COPD and history of exacerbations [36, 37]. Given our dataset does not capture the severity of COPD, it is possible that only a specific cohort of COPD patients (i.e. severe patients) had an increased risk for healthcare utilization. While our registry included self-reported COPD (which required confirmation in the EHR by a physician), it is possible that patients may have been misclassified without spirometric data for diagnosis. However, previous analyses have shown that self-report, coupled with physician confirmation, has a high likelihood of yielding a positive diagnosis of COPD [38], [39], [40]. Finally, the clinicians may have referred patients with more severe symptoms or comorbid conditions for testing introducing a selection bias. Therefore, the findings may not be generalizable to the population at large.
In conclusion, our analysis of Cleveland Clinic COVID-19 registry demonstrates that COPD patients had increased risk for healthcare utilization in terms of hospital admission, ICU admission, and invasive mechanical ventilation. Future studies analyzing the long-term impact of COVID-19 on patients in the COPD population are needed.
Authors contributions
AA, JZ, and UH conceived and designed the study. AA and JZ were involved in data analysis. AA, JZ, and UH were involved in data analysis and interpretation, manuscript writing, and approved the final version for submission.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health – National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Grant: K08 HL133381 (JZ).
Data sharing statement
A data sharing statement provided by the authors is available upon request.
Declaration of Competing Interest
We declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Zhang J.J., Dong X., Cao Y.Y., Yuan Y.D., Yang Y.B., Yan Y.Q. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy. 2020;75:1730–1741. doi: 10.1111/all.14238. Epub 2020/02/23PubMed PMID: 32077115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Qingxian C., Fengjuan C., Fang L., Xiaohui L., Tao W., Qikai W., et al. Obesity and COVID-19 severity in a designated hospital in Shenzhen, China. Preprint at SSRN 2020. https://doiorg/102139/ssrn3556658. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3.Garg S., Kim L., Whitaker M., O'Halloran A., Cummings C., Holstein R. Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 - COVID-NET, 14 states, March 1-30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(15):458–464. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3. Epub 2020/04/17PubMed PMID: 32298251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alqahtani J.S., Oyelade T., Aldhahir A.M., Alghamdi S.M., Almehmadi M., Alqahtani A.S. Prevalence, severity and mortality associated with COPD and smoking in patients with COVID-19: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(5) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233147. Epub 2020/05/12PubMed PMID: 32392262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lee N., Allen Chan K.C., Hui D.S., Ng E.K., Wu A., Chiu R.W. Effects of early corticosteroid treatment on plasma SARS-associated Coronavirus RNA concentrations in adult patients. J Clin Virol. 2004;31(4):304–309. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2004.07.006. Epub 2004/10/21PubMed PMID: 15494274PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC7108318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Russell C.D., Millar J.E., Baillie J.K. Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):473–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30317-2. Epub 2020/02/12PubMed PMID: 32043983PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC7134694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Leung J.M., Yang C.X., Tam A., Shaipanich T., Hackett T.L., Singhera G.K. ACE-2 expression in the small airway epithelia of smokers and COPD patients: implications for COVID-19. Eur Respir J. 2020;55(5) doi: 10.1183/13993003.00688-2020. Epub 2020/04/10PubMed PMID: 32269089PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC7144263 C.X. Yang has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Tam has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: T. Shaipanich has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: T.L. Hackett has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: G.K. Singhera has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D.R. Dorschied has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D.D. Sin reports grants from Merck, personal fees for advisory board work from Sanofi-Aventis and Regeneron, grants and personal fees for research from Boehringer Ingelheim, grants and personal fees for advisory board work and lectures from AstraZeneca, personal fees for advisory board work and lectures from Novartis, outside the submitted work. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li W., Moore M.J., Vasilieva N., Sui J., Wong S.K., Berne M.A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. 2003;426(6965):450–454. doi: 10.1038/nature02145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Medina M, Babiuch C, Card M, Gavrilescu R, Zafirau W, Boose E, et al. Home monitoring for COVID-19. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020; doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc028. [published online ahead of print, 2020 Jun 11]. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 10.Arentz M., Yim E., Klaff L., Lokhandwala S., Riedo F.X., Chong M. Characteristics and outcomes of 21 critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Washington state. JAMA: J Am Med Assoc. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4326. Epub 2020/03/20PubMed PMID: 32191259PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC7082763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bhatraju P.K., Ghassemieh B.J., Nichols M., Kim R., Jerome K.R., Nalla A.K. Covid-19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle region - case series. N Engl J Med. 2020 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2004500. Epub 2020/04/01PubMed PMID: 32227758PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC7143164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guan W.J., Ni Z.Y., Hu Y., Liang W.H., Ou C.Q., He J.X. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. Epub 2020/02/29PubMed PMID: 32109013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lauer S.A., Grantz K.H., Bi Q., Jones F.K., Zheng Q., Meredith H.R. The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: estimation and application. Ann Intern Med. 2020 doi: 10.7326/M20-0504. Epub 2020/03/10PubMed PMID: 32150748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in china: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648. Epub 2020/02/25PubMed PMID: 32091533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Milinovich A., Kattan M.W. Extracting and utilizing electronic health data from fpic for research. Ann Transl Med. 2018;6(3):42. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.01.13. Epub 2018/04/04PubMed PMID: 29610734PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC5879514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mehta N., Kalra A., Nowacki A.S., Anjewierden S., Han Z., Bhat P. Association of use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with testing positive for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) JAMA Cardiol. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1855. Epub 2020/05/06PubMed PMID: 32369097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xing Q., Li G., Xing Y., Chen T., Li W., Ni W. Precautions are needed for covid-19 patients with coinfection of common respiratory pathogens. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.29.20027698. 2020.02.29.20027698. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Titmarsh S., Poliziani M., Russell R.E. Breathing new life into chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)" - results from an online survey of UK patients. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:2799–2807. doi: 10.2147/copd.S222139. Epub 2019/12/12PubMed PMID: 31824144PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC6900271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Buuren Sv, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K. Mice: multivariate Imputation by chained equations inR. J Stat Softw. 2011;45(3) doi: 10.18637/jss.v045.i03. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rycroft C.E., Heyes A., Lanza L., Becker K. Epidemiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a literature review. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2012;7:457–494. doi: 10.2147/copd.S32330. Epub 2012/08/29PubMed PMID: 22927753PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3422122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schols A.M., Broekhuizen R., Weling-Scheepers C.A., Wouters E.F. Body composition and mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;82(1):53–59. doi: 10.1093/ajcn.82.1.53. Epub 2005/07/09PubMed PMID: 16002800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jones S.E., Maddocks M., Kon S.S., Canavan J.L., Nolan C.M., Clark A.L. Sarcopenia in COPD: prevalence, clinical correlates and response to pulmonary rehabilitation. Thorax. 2015;70(3):213–218. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206440. Epub 2015/01/07PubMed PMID: 25561517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Swallow E.B., Reyes D., Hopkinson N.S., Man W.D., Porcher R., Cetti E.J. Quadriceps strength predicts mortality in patients with moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2007;62(2):115–120. doi: 10.1136/thx.2006.062026. Epub 2006/11/09PubMed PMID: 17090575PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2111256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Roig M., Eng J.J., MacIntyre D.L., Road J.D., Reid W.D. Deficits in muscle strength, mass, quality, and mobility in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2011;31(2):120–124. doi: 10.1097/HCR.0b013e3181f68ae4. Epub 2010/11/03PubMed PMID: 21037481PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3326068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.von Haehling S., Anker S.D. Prevalence, incidence and clinical impact of cachexia: facts and numbers-update 2014. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2014;5(4):261–263. doi: 10.1007/s13539-014-0164-8. Epub 2014/11/12PubMed PMID: 25384990PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4248411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Remels A.H., Gosker H.R., Langen R.C., Schols A.M. The mechanisms of cachexia underlying muscle dysfunction in COPD. J Appl Physiol. 2013;114(9):1253–1262. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00790.2012. (1985)Epub 2012/09/29PubMed PMID: 23019314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Walters J.A., Walters E.H., Wood-Baker R. Oral corticosteroids for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;3 doi: 10.1002/14651858.Cd005374. Epub 2005/07/22PubMed PMID: 16034972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Horita N., Miyazawa N., Morita S., Kojima R., Inoue M., Ishigatsubo Y. Evidence suggesting that oral corticosteroids increase mortality in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res. 2014;15(1):37. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-15-37. Epub 2014/04/09PubMed PMID: 24708443PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3976535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Peters M.C., Sajuthi S., Deford P., Christenson S., Rios C.L., Montgomery M.T. COVID-19 related genes in sputum cells in asthma: relationship to demographic features and corticosteroids. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 doi: 10.1164/rccm.202003-0821OC. Epub 2020/04/30PubMed PMID: 32348692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Group R.C., Horby P., Lim W.S., Emberson J.R., Mafham M., Bell J.L. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19 - preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 2020 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2021436. Epub 2020/07/18PubMed PMID: 32678530. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tan L., Wang Q., Zhang D., Ding J., Huang Q., Tang Y.-.Q. Lymphopenia predicts disease severity of COVID-19: a descriptive and predictive study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1) doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0148-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Reese R.L., Clement S.A., Syeda S., Hawley C.E., Gosian J.S., Cai S. Coordinated-transitional care for veterans with heart failure and chronic lung disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(7):1502–1507. doi: 10.1111/jgs.15978. Epub 2019/05/14PubMed PMID: 31081946PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC6612585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Richardson S., Hirsch J.S., Narasimhan M., Crawford J.M., McGinn T., Davidson K.W. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York city area. JAMA. 2020;323(20):2052–2059. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6775. Epub 2020/04/23PubMed PMID: 32320003PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC7177629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Colbenson G.A., Johnson A., Wilson M.E. Post-intensive care syndrome: impact, prevention, and management. Breathe (Sheff) 2019;15(2):98–101. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0013-2019. Epub 2019/06/14PubMed PMID: 31191717PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC6544795 interest: A. Johnson is co-chair of SCCMs Thrive Peer Support Collaborative. Conflict of interest: M.E. Wilson has nothing to disclose. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cazzola M., Bettoncelli G., Sessa E., Cricelli C., Biscione G. Prevalence of comorbidities in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respiration. 2010;80(2):112–119. doi: 10.1159/000281880. Epub 2010/02/06PubMed PMID: 20134148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Soler-Cataluña J.J., MÁ Martínez-García, Román Sánchez P., Salcedo E., Navarro M., Ochando R. Severe acute exacerbations and mortality in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2005;60(11):925–931. doi: 10.1136/thx.2005.040527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hurst J.R., Vestbo J., Anzueto A., Locantore N., Müllerova H., Tal-Singer R. Susceptibility to exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(12):1128–1138. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0909883. Epub 2010/09/17PubMed PMID: 20843247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Radeos M.S., Cydulka R.K., Rowe B.H., Barr R.G., Clark S., Camargo C.A., Jr. Validation of self-reported chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among patients in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2009;27(2):191–196. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2008.01.011. PubMed PMID: 19371527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Murgia N., Brisman J., Claesson A., Muzi G., Olin A.-.C., Torén K. Validity of a questionnaire-based diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a general population-based study. BMC Pulm Med. 2014;14:49. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-14-49. PubMed PMID: 24650114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Barr R.G., Herbstman J., Speizer F.E., Camargo C.A., Jr. Validation of self-reported chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a cohort study of nurses. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;155(10):965–971. doi: 10.1093/aje/155.10.965. Epub 2002/05/08PubMed PMID: 11994237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]