Extended Data Figure 4. RREB1 mediates KRAS-dependent TGF-β responses in PDA cells.
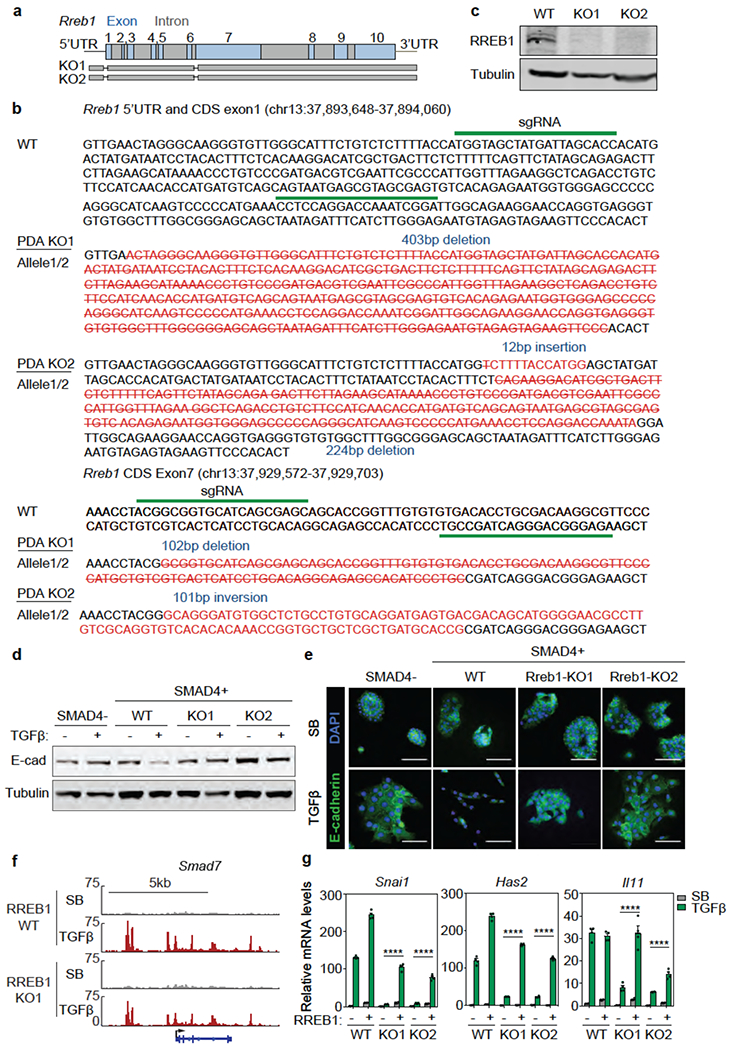
(a) Scheme of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutation of Rreb1 in mouse SMAD4-restored PDA cells. (b) sgRNA sequences and genomic sequences of Rreb1 coding region (CDS) exons 1 and 7 in mutant clones K01 and K02 derived from SMAD4-restored PDA cells, (c) Western immunoblot analysis of RREB1 levels in Rreb1 wild type (WT) and knockout (KO) cells. Anti-Tubulin immunoblotting was used as loading control. Data are representative of two independent experiments, (d) Western immunoblot analysis of E-cadherin in mouse KSIC PDA cells, SMAD4-restored PDA cells, and two RREB1 KO SMAD4-restored PDA clones, treated with SB or TGF-β for 24 h. Anti-Tubulin immunoblotting was used as loading control. Data are representative of two independent experiments, (e) Representative E-cadherin and DAPI immunofluorescence images of the same cells as in (f) treated with SB or TGF-β for 48 h. Scale bars, 100 pm. Data are representative of two independent experiments, (f) Gene track view of SMAD2/3 ChIP-seq tags in the Smad7 locus of the RREB1 WT and KO PDA cells. The gene body is schematically represented at the bottom. ChIP-seq was performed once and an independent ChIP was performed in which selective genomic regions were confirmed by qPCR. (g) mRNA levels of Snai1, Has2 and Il11 in WT and two RREB1 KO cells that were transduced with an RREB1 vector or empty vector and then treated with SB or TGF-β for 1.5 h. Mean ± s.e.m. n=4, two-way ANOVA analysis, ****, p<0.0001.
