Abstract
This review presents an overview of the impact of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy in papers published between January 2000 and February 2007. The results suggest that genetic counseling may have a positive impact on risk perception accuracy, though some studies observed no impact at all, or only for low-risk participants. Several implications for future research can be deduced. First, future researchers should link risk perception changes to objective risk estimates, define risk perception accuracy as the correct counseled risk estimate, and report both the proportion of individuals who correctly estimate their risk and the average overestimation of the risk. Second, as the descriptions of the counseling sessions were generally poor, future research should include more detailed description of these sessions and link their content to risk perception outcomes to allow interpretation of the results. Finally, the effect of genetic counseling should be examined for a wider variety of hereditary conditions. Genetic counselors should provide the necessary context in which counselees can understand risk information, use both verbal and numerical risk estimates to communicate personal risk information, and use visual aids when communicating numerical risk information.
Keywords: Genetic counseling, Risk perception, Systematic review
Introduction
Recent advances in genetic research have enabled us to identify individuals at risk for a wide variety of medical conditions due to their genetic makeup (Collins et al. 2003). At the same time, these advances have created the need to educate and guide these individuals (Lerman et al. 2002). Informing them of their hereditary risk and of the options for how to deal with this risk is the primary aim of genetic services (Wang et al. 2004). Genetic services involve both genetic counseling and genetic testing; of these, genetic counseling in particular aims to enable at-risk individuals to accurately identify, understand and adaptively cope with their genetic risk (Biesecker 2001; Pilnick & Dingwall 2001).
The National Society of Genetic Counselors’ (NSGC) Task Force defines genetic counseling as “the process of helping people understand and adapt to medical, psychological, and familial applications of genetic contributions to disease” (Resta et al. 2006, p. 79). As such, genetic counselors are faced with three important tasks: (1) to interpret family and medical histories to enable risk assessment, (2) to educate counselees about issues related to heredity, preventive options (e.g., genetic testing), and personal risk, and (3) to facilitate informed decisions and adaptation to personal risk (cf. Trepanier et al. 2004). The latter task may be considered the “core” (i.e., the desired outcome) of genetic counseling, with the former tasks in service of its fulfillment.
Informed decision making and adaptation to personal risk, however, are abstract concepts that cannot easily be assessed. As such, several measures have been developed to assess the efficacy of genetic counseling. Kasparian, Wakefield and Meiser (2007) summarized 23 available measurement scales which include satisfaction, knowledge, psychological adjustment, and risk perception measures. Although each of these measures significantly contributes to our understanding of the effect of genetic counseling, risk perception measures (and especially risk perception accuracy) may be regarded as one central concept. Indeed, several influential models of health behavior, such as the Health Belief Model (Janz & Becker 1984), the Protection Motivation Theory (Rogers 1983), and the Extended Parallel Process Model (Witte 1992), posit that adequate risk perception acts as a motivator to take (preventive) action and, as such, is a prerequisite of preventive behavior. Moreover, risk perception and risk perception accuracy have been shown to be related to several other important outcomes of genetic counseling, such as coping (Nordin et al. 2002), worry (Hopwood et al. 2001), and anxiety (Meiser et al. 2001).
The effect of genetic counseling on risk perception has been heavily examined during the past two decades, from early research into reproductive genetic counseling (e.g., Humphreys & Berkeley 1987) to recent studies into genetic predispositions to cancer (e.g., Bjorvatn et al. 2007). While these studies are valuable in their own right, few have investigated the effect of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy. Indeed, to facilitate informed decision making and adaptation to personal risk, counselees must have accurate risk perceptions.
In their 2002 meta-analysis, Meiser and Halliday (2002) identified only six studies that assessed the effects of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy. Their meta-analysis showed that individuals at risk for breast cancer significantly perceive their own risk more accurately after genetic counseling. In particular, they observed an average increase of 24.3% of the participants who accurately estimated their personal risk after counseling. A systematic review by Butow and colleagues (2003) 1 year later confirmed the positive impact of genetic counseling in breast cancer risk perception accuracy, although 22–50% continued to overestimate their risk even after counseling.
Research thus suggests that genetic counseling may indeed improve risk perception accuracy in some individuals. However, Meiser and Halliday (2002) and Butow et al. (2003) only included studies examining breast cancer risk. To date, there is no systematic review or meta-analysis which examines the effect of genetic counseling on perception of genetic risks in general. Thus, the purpose of the present review is twofold: (1) to provide an updated overview of the impact of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy in papers published between January 2000 and February 2007, and (2) to extend the results of Meiser and Halliday’s (2002) meta-analysis and Butow et al.’s (2003) systematic review to other genetic conditions.
Methods
Search Strategy
We searched the Pubmed, EMBASE, Web of Science, ERIC and PsycINFO databases. We also used the search engine Google Scholar to find papers and grey literature (literature not published in a journal—e.g., in press or under review—but nevertheless available on the internet) on risk perception accuracy and genetic counseling on the internet. To this end, we used the search term “(risk perception OR perceived risk OR perceived susceptibility OR susceptibility estimate OR risk estimate) AND (genetic counsel* OR genetic risk OR familial risk OR genetic predisposition).” If available in the databases, we used the standardized, subject-related indexing terms of the concepts in the search term. We also searched the following journals manually: Journal of Genetic Counseling, Patient Education and Counseling, Genetics in Medicine, Community Genetics, American Journal of Medical Genetics: Part A, Clinical Genetics, American Journal of Human Genetics, and Hereditary Cancer in Clinical Practice from January 2000 until February 2007. Additionally, we performed key-author and reference list searches.
Selecting Relevant Studies
The selection procedure was performed independently by two reviewers. The review process then consisted of three phases. During the first phase, papers were reviewed based on title only. In the second phase, the reviewers examined the abstracts of papers that could not be definitively included or excluded based on their title. Papers thought to be relevant to the review based on their abstracts were included; those judged irrelevant were excluded. In the third phase, the reviewers examined the papers included during the previous two phases for content. As recommended by the Cochrane guidelines (Higgins & Green 2006), we erred on the safe side during the whole selection process; if in doubt, we included the paper for more extensive review in the subsequent phase.
The following inclusion and exclusion criteria were used to determine whether papers were eligible for the review.
Studies should be published after 2000 (i.e., upper limit of the 2002 Meiser and Halliday meta-analysis, since one goal of this review was to provide an update of that analysis); studies published before 2000 were excluded (n = 8; e.g., Evans et al. 1994).
Studies should focus on genetic risk perception; studies which did not (n = 9; e.g., Clementi et al. 2006) or which discussed the effect of genetic mutations, prevalence, incidence, morbidity, or mortality only were excluded (n = 0).
Studies should examine the effect of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy; that is, should explicitly link perceived risk to objective risk estimates to examine whether they more closely align after (rather than before) counseling. Studies were excluded if they examined changes in risk perception without linking them to some objective risk estimate (n = 19; e.g., Burke et al. 2000), if they investigated risk perception as a determinant of genetic counseling participation (n = 6; e.g., Collins et al. 2000), or if they focused on the effectiveness of decision aids as compared to standard genetic counseling (n = 3; e.g., Warner et al. 2003).
To accurately assess whether genetic counseling affected risk perception accuracy, studies should employ either a prospective or a randomized control trial design. Studies using other designs were excluded (n = 12; e.g., Cull et al. 2001).
Risk perception accuracy should be assessed as a quantitative outcome measure; studies were excluded if they assessed risk perception as a qualitative outcome measure (n = 0).
Studies should focus on at-risk individuals; those focusing on intermediaries (e.g., genetic counselors, nurses) would be excluded (n = 0).
Studies should describe original research published in peer-reviewed journal in English. Studies describing secondary data or reviewing other studies, editorials, commentaries, book reviews, bibliographies, resources or policy documents were excluded (n = 5; e.g., Palmero et al. 2004) as they provided too little detail.
Data Abstraction
Risk perception outcomes were abstracted by two authors independently, using standardized extraction forms. In the event of disagreement, the authors discussed the particular paper until they reached consensus. We abstracted the characteristics of the study, the participants and the genetic counseling session, as well as the results and quality of the study (cf. Higgins & Green 2006).
Results
Selecting Relevant Studies
Figure 1 presents the flowchart of the study selection process. From the initial sample of 3,798 eligible papers from the database searches and the 62 unique papers from the Google Scholar, journal, reference list and key author searches, a total of 82 papers were eligible for extensive review. Of these, 19 papers were included in the review. Table 1 lists the included papers and information about the study design, genetic counseling session content, criteria for risk perception accuracy, measurement time points, and finally the risk perception outcomes. Given the heterogeneity in the studies, we decided against pooling the studies in a meta-analysis.
Fig. 1.
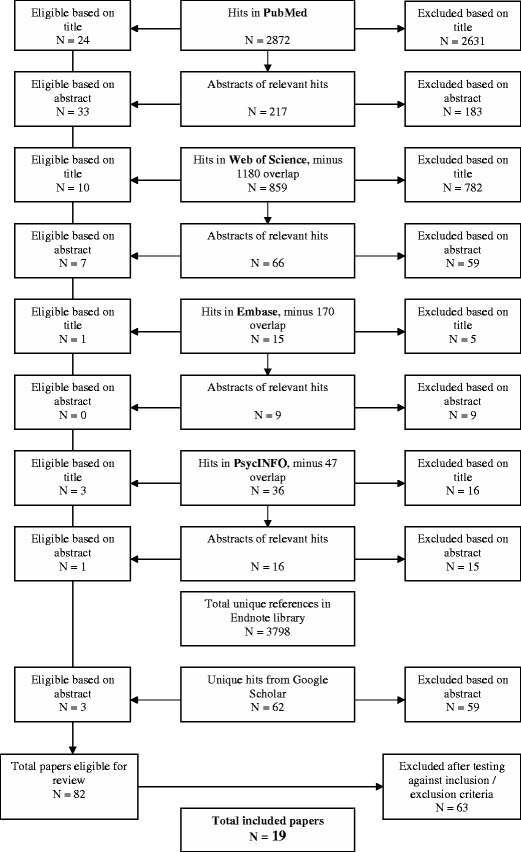
Flowchart of the Study Selection Process.
Table 1.
Results of the reviewed studies
| Study | N | Design | Content of the genetic counseling session | Criteria for risk perception accuracy | Measurement moments | Risk perception accuracy outcomes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage participants within each category | Degree of overestimation of objective risk estimate | |||||||||
| Accurate | Under estimation | Over estimation | Perceived Estimate (SD)* | Average overestimation (SD)* | ||||||
| I. Studies examining percentage of patients within accuracy category | ||||||||||
| Bjorvatn et al.(2007) | 213 | Prospective | - Family history | Within two categories of counseled risk (on a six point scale) | Pre-counseling | 81 | 9 | 10 | ||
| - Emotion | Immediately post-counseling | 86 | 9 | 5 | ||||||
| - Heredity | ||||||||||
| - Personal risk estimate | p < .001 | |||||||||
| - Incidence | ||||||||||
| - Disease development | ||||||||||
| - Surveillance | ||||||||||
| Hopwood et al. (2003) | 158 | Prospective | - Family history | Correct counseled risk estimate (odds) | Pre-counseling | 7 | 52 | 38 | ||
| - Personal risk estimate | 3 months | 68 | 9 | 20 | ||||||
| - Disease development | 6 months | 63 | 9 | 25 | ||||||
| - Follow-up letter | 9 months | 63 | 9 | 25 | ||||||
| 12 months post counseling | 61 | 9 | 25 | |||||||
| p < .001 | ||||||||||
| Hopwood et al. (2004) | 256 | Prospective | NA | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 63 | 27 | 9 | ||
| 1 month | 71 | 21 | 8 | |||||||
| 12 months post counseling | 73 | 21 | 7 | |||||||
| p = ns | ||||||||||
| Huiart et al. (2002) | 397 | Prospective | NA | Correct counseled risk estimate | Low risk: | p < .001 | ||||
| Pre-counseling | 6.3 | 0 | 93.7 | |||||||
| 1-7 days post counseling | 23.8 | 0 | 76.3 | |||||||
| High risk: | p = ns | |||||||||
| Pre-counseling | 87.7 | 12.3 | 0 | |||||||
| 1-7 days post counseling | 89.5 | 10.5 | 0 | |||||||
| Lidén et al. (2003) | 86 | Prospective | NA | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 17 | 36 | 47 | ||
| Post-counseling | 54 | 18 | 28 | |||||||
| 1 year follow-up | 28 | 33 | 39 | |||||||
| p < .01 | ||||||||||
| Lobb et al. (2004) | 89 | Prospective RCT | -Genetics | Within category of counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 50 | 27 | 23 | ||
| - Genetic testing | Post-counseling | 70 | 20 | 10 | ||||||
| - Family history | ||||||||||
| - Personal risk estimate | ||||||||||
| - Surveillance | ||||||||||
| Meiser et al. (2001) | 218 | Prospective | - Personal risk estimate | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 54 | 12 | 34 | ||
| - Genetic testing | 12 months | 54 | 14 | 31 | ||||||
| - Advice on early detection and surgery | p = ns | |||||||||
| Nordin et al. (2002) | 63 | Prospective | NA | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 18 | 38 | 44 | ||
| Post-counseling | 57 | 18 | 25 | |||||||
| Pieterse et al. (2006) | 51 | Prospective | - Personal risk estimate | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 48 | NA | NA | ||
| Post-counseling | 51 | NA | NA | |||||||
| p = ns | ||||||||||
| Rimes et al. (2006) | 150 | Prospective | - Personal risk estimate | Within 10% of counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 12.6 | 3.3 | 84.1 | 41.2 | |
| - Genetics and cancer | 6 months | 18 | 4.00 | 78.0 | 34.3 | |||||
| - Population rates cancer | p = ns | P < .0005 | ||||||||
| - Recommendations | ||||||||||
| - Surveillance | ||||||||||
| Rothemund et al. (2001) | 44 | Prospective RCT | -Psychological counseling | Within 50% of counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 47 | 18.8 | |||
| Post-counseling | 42 | 17.5 | ||||||||
| -Risk assessment | Counselees | 39 | 0 | 48 | ||||||
| - Information on menopause | Controls | 38 | 14 | 48, p = ns | p = ns | |||||
| - Personal risk estimate | ||||||||||
| - Genetic testing | ||||||||||
| II. Studies examining the degree of overestimation | ||||||||||
| Bowen et al. (2006) | 211 | RCT | - Family history | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 31(24) | 19 | |||
| - Personal risk estimate | 6 months postcounseling | 18(16) | 6 | |||||||
| - Incidence | p < .001 | |||||||||
| - Other risk factors | ||||||||||
| - Breast screening | ||||||||||
| Codori et al. (2005) | 101 | Prospective | -Heredity | Correct risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 52.47(21.3) | 30 | |||
| - Genetic testing | Immediately post-counseling | 52.17(21.1) | 30 | |||||||
| - Meaning of possible test results p = ns | ||||||||||
| - NO personal risk estimate | ||||||||||
| Gurmankin et al. (2005) | 108 | Prospective | NA | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 61%(26) | 42% | |||
| 1-7 days follow up | 44% (24) | 19 | ||||||||
| p < .001 | ||||||||||
| Kaiser et al. (2004) | 123 | Prospective | -Screening | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 15.5 (14.28) | 14.94 | |||
| -Description condition | Post-counseling | 8.34 (9.34) | 7.8 | |||||||
| - Personal risk estimate | p < .0005 | |||||||||
| - Implications | ||||||||||
| - Decisional support | ||||||||||
| Kelly et al. (2003) | 99 | Prospective | - Family and personal history | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 72.6 (29.2) | 23 | |||
| - Heredity | 1-2 days post-counseling | 66.2 (30.7) | 16.6 | |||||||
| - Risks /benefits testing p < .01 | ||||||||||
| - Efficacy health | ||||||||||
| - Personal risk estimate | ||||||||||
| Kent et al. (2000) | 90 | Prospective | - Personal risk estimate | - Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 55 | ||||
| - Translation to lay terms | 3 months | 52 | ||||||||
| - Coping/Prevention strategies | 6 months | 51 | ||||||||
| p = ns | ||||||||||
| Tercyak et al. (2001) | 129 | Prospective | - Personal and family history | Correct counseled risk estimate | Pre-counseling | 12.6(18.9) | 11.5 | |||
| - Genetic testing | Immediately post-counseling | 8.9(16.7) | 7.8 | |||||||
| - Patient education | p < .001 | |||||||||
| - Personal risk estimate | ||||||||||
| Van Dijk et al. (2003) | 241 | Prospective | - Heredity | Correct counseled risk estimate | Low risk: | 54.93 | ||||
| -Surveillance | Pre-counseling | 83 | (21.31) | |||||||
| - Genetic testing | Immediately post-counseling | 56 | 43.86 | |||||||
| - Personal risk estimate | (21.03) | |||||||||
| High risk: | ||||||||||
| Pre-counseling | p = ns | |||||||||
| Immediately | 89 | |||||||||
| Post-counseling | 89 | |||||||||
RCT = Randomized controlled trial; NA = not assessed or reported in this study. Percentages may not add up to 100% due to missing values or rounding.
*Means and (standard deviations)
Content of the Counseling Session
Concerning the content and quality of the genetic counseling sessions, four studies mentioned using a genetic counseling protocol (Bjorvatn et al. 2007; Bowen et al. 2006; Kaiser et al. 2004; van Dijk et al. 2003). Two mentioned using a standardized counseling script (Codori et al. 2005; Tercyak et al. 2001). An additional three used audiotapes as a content check of the counseling session (Hopwood et al. 2003; Kelly et al. 2003; Lobb et al. 2004), while the remaining twelve did not mention the use of any protocol, standardized script or audio- or videotapes as a content check.
In-depth analyses of the content (see Table 1) revealed that a majority of the studies described counseling sessions with similar content. However, four studies did not provide a description of the counseling session at all (Hopwood et al. 2004; Huiart et al. 2002; Lidén et al. 2003; Nordin et al. 2002). Comparing the descriptions of the counseling sessions of the remaining fifteen studies to the recommendations of the NSGC Task Force, we observed that only six of these mentioned the first task, “interpretation of family and medical histories to enable risk assessment” (Bjorvatn et al. 2007; Bowen et al. 2006; Hopwood et al. 2003; Kelly et al. 2003; Pieterse et al. 2006; Tercyak et al. 2001; van Dijk et al. 2003).
Likewise, only five studies explicitly mentioned performing the second task, “educate counselees about issues related to heredity and treatment and preventive options” (Bjorvatn et al. 2007; Codori et al. 2005; Kelly et al. 2003; Meiser et al. 2001; van Dijk et al. 2003). Although judging whether counselors “facilitated decision making an adaptation to personal risk” is difficult, we did observe six studies claiming to advise counselees on surveillance (Bjorvatn et al. 2007; Kaiser et al. 2004; Meiser et al. 2001; Rimes et al. 2006; Rothemund et al. 2001; Tercyak et al. 2001), which may be regarded as facilitating informed decisions.
Risk Perception Accuracy
The included studies used two different types of measures to determine the effect of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy: several studies reported changes in the proportion of individuals who accurately perceive their risk, while others reported the degree of overestimation or underestimation as a measure of risk perception accuracy. Where available, we report both types of measures (see Table 1).
Overall, the studies indicate that genetic counseling has a positive impact on risk perception accuracy (cf. Table 1). However, some studies observed no effect on risk perception accuracy at all, or only for low-risk individuals (cf. Table 1).
The studies assessing the proportion of individuals who accurately estimated their risk (see Table 1, subsection I) showed an average increase of approximately 25% (range: 2–55%) of counselees who correctly estimated their risk after counseling; from an average of 42% pre-counseling to an average of 58% post-counseling. However, on average 25% (range: 5–76%) continued to overestimate and 19.5% (range: 7–55%) continued to underestimate their risk even after counseling.1 Other studies which assessed changes in the average overestimation of participants’ perceived risk (see Table 1, subsection II) still observed an average overestimation of approximately 18% (range: 6–40%) after counseling, in comparison with 25% (range: 11.5–42%) before counseling. Across the studies, the average decrease in overestimation was approximately 8%.2
Linking Content to Risk Perception Accuracy
Linking the outcome (i.e., risk perception accuracy) to the content of the counseling session (i.e., whether counselors performed the tasks as recommended by the NSGC Task Force), we observed that the studies in which the counselor gave information about family history and heredity as well as personal risk estimates positively influenced risk perception accuracy (Bjorvatn et al. 2007; Bowen et al. 2006; Hopwood et al. 2003; Kelly et al. 2003; Tercyak et al. 2001), although this improvement was not significant in two studies (Pieterse et al. 2006; van Dijk et al. 2003). In contrast, the studies that did not mention giving counselees this information observed no significant improvement of risk perception accuracy as a result of genetic counseling (Codori et al. 2005; Kent et al. 2000; Meiser et al. 2001; Rothemund et al. 2001), with the exception of one study (Kaiser et al. 2004).
The results for the other two tasks were mixed. While some studies that educated counselees about heredity observed a positive impact on risk perception accuracy (Bjorvatn et al. 2007; Kelly et al. 2003; van Dijk et al. 2003), others did not (Codori et al. 2005; Meiser et al. 2001). Similar results were observed for the third task of facilitating informed decision making and adaptation to personal risk. Three out of the six studies identified as performing this task observed a positive impact of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy (Bjorvatn et al. 2007; Rimes et al. 2006; Tercyak et al. 2001), while the other three did not (Kaiser et al. 2004; Meiser et al. 2001; Rothemund et al. 2001).
Discussion
The purposes of this review were (1) to provide an updated overview of the impact of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy from January 2000 until February 2007, and (2) to extend the Meiser and Halliday (2002) meta-analysis and the Butow et al. (2003) systematic review to other genetic conditions. Overall, the studies showed that an increased proportion of individuals correctly perceived their risk after counseling rather than before, and those who did not had smaller deviations from their objective risk than before counseling. These positive effects were sustained even at follow-up 1 year later. Some studies, however, observed no positive effect of genetic counseling, or only for low-risk individuals. These results are in line with those reported in the 2002 Meiser and Halliday meta-analysis and the 2003 systematic review conducted by Butow and colleagues.
The research in the present review may shed some light on why some studies observe positive effects of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy and others do not. First, one study (Codori et al. 2005) that observed no effect explicitly mentioned that personal risk information was not communicated during the relevant counseling session. Second, the provision of information about the role of family history, as recommended by the NSGC Task Force, may provide an appropriate context in which counselees can make sense of the risk information (cf. Codori et al. 2005), resulting in accurate risk perceptions. Third, some counselors may go to great lengths to explain risk information in terms the counselees can understand (cf. Kent et al. 2000). Unfortunately, research has shown that verbal and numerical risk estimates often do not coincide. That is, verbal risk information results in more variability in risk perception than does numerical information (Gurmankin et al. 2004b). Bjorvatn et al. (2007), for example, observed incongruence between numerical and verbal measures of risk perception. Similarly, Hopwood et al. (2003) observed that counselees included a wide range of numerical risk estimates within the same verbal category. The significance of this is discussed below, where we present the implications of our study for clinical practice. Finally, several studies (Pieterse et al. 2006; Rothemund et al. 2001) that observed no effect of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy had small sample sizes, and thus may not have observed a significant effect due to power limitations.
The present review has several important implications for future research. First, we selected a large number of studies assessing risk perception changes as a result of genetic counseling. However, we had to exclude 19 of these studies because they did not explicitly link risk perception to an objective risk figure. Assuming that researchers are aware of these objective risk figures, future studies should link risk perception changes to objective risk figures to assess changes in risk perception accuracy.
A second implication concerns the definition of risk perception accuracy, which differs between studies. For instance, in several studies accurate risk perception is defined as falling within a certain category (e.g., Bjorvatn et al. 2007; Kelly et al. 2003; Lidén et al. 2003) or within 50% of the counseled risk (e.g., Pieterse et al. 2006; Rothemund et al. 2001), while the majority define it as the correct counseled risk estimate (e.g., Bowen et al. 2006; Hopwood et al. 2003; Tercyak et al. 2001). Additionally, the reviewed studies based the counseled risk estimate on different methods, such as family history assessment (Huiart et al. 2002), Gail’s score (Bowen et al. 2006), or the BRCAPRO procedure (Kelly et al. 2003). These issues reduce our ability to compare the results of the studies, thereby lessening their value. Future researchers should define risk perception accuracy as correct counseled risk, and base their risk estimate on generally accepted and applied methods to allow for better interpretation of the results and comparison between studies.
A third, related issue concerns the type of outcome measure used: several studies report changes in the proportion of individuals who correctly perceive their risk, while others report the degree of overestimation or underestimation as a measure of risk perception accuracy. Researchers are advised to include both measures in their studies, as both provide valuable information about the effect of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy.
Further, we observed that the quality of the genetic counseling descriptions (in those descriptions that were present) was poor. Although the counseling sessions were labeled as standardized, they were described in general terms, such as “discussion about the risk” and “information was given about how hereditary factors contribute to disease.” These general descriptions leave room for substantial differences between counseling sessions. This is especially problematic given that perceptions of genetic risks before genetic counseling can determine the content of the counseling session (Julian Reynier et al. 1995), which tends to alter patient outcomes (Lobb et al. 2004).
Differences in the quality of the counseling session content may well explain the fact that not all studies in the present review observed a positive effect on risk perception accuracy. Future studies should therefore try to link the content of the counseling session to risk perception to determine which feature of the session actually contributes to improved risk perception accuracy (cf. Pieterse et al. 2006, or Shiloh et al. 2006). The present review provides some insight into how the content of the counseling session relates to risk perception accuracy. Indeed, the provision of information on the role of family history was observed to positively impact risk perception accuracy, perhaps because it creates a context in which the counselee can understand the information. Additionally, forcing numerical risk estimates to fit lay terms to aid counselees’ understanding may lead to inaccurate risk perceptions (Kent et al., 2000). A possible avenue for further research may be to link effectiveness to certain sociodemographic variables. We could then examine the influence of known psychological differences between certain groups, which is a more complex process and should thus occur later in time. By associating these psychological differences to the effectiveness of genetic counseling, we may be able to identify the processes responsible for the positive effect of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy. Knowledge of such processes will enable us to match the session’s content to these processes and thus to increase the session’s effectiveness.
Finally, we observed a relative lack of diversity in research on genetic counseling and genetic test result disclosure in terms of the genetic disorder under consideration. Although genetic counseling and testing can be effective for a variety of disorders (Biesecker 2001; Lerman et al. 2002; Pilnick & Dingwall 2001), most recent studies focus on their impact on cancer risk perception, particularly breast cancer. Although genetic counseling on cancer has been shown to positively affect risk perception accuracy, this does not guarantee it will do the same for other genetic conditions. Extensive research is needed to assess whether genetic counseling also effectively enhances risk perceptions for other genetic predispositions.
Based on the results, we have formulated some implications for practice. First, in accordance with the recommendations of the NSGC Task Force, we again strongly urge genetic counselors to discuss the role of family history and perform a family history assessment. We suggest that this information is an important factor in accurate risk perception because it may provide the necessary context in which counselees can understand the risk information. Indeed, the results seem to suggest that the provision of such information is positively related to risk perception accuracy. While this implication may seem redundant as it repeats the earlier recommendations by the NSGC Task Force, we nonetheless repeat it here since several studies in this review did not mention communicating this information to the counselee (Codori et al. 2005; Meiser et al., 2001; Kaiser et al. 2004; Kent et al. 2000; Rothemund et al. 2001).
Second, while explaining risk information in lay terms seems to be a useful strategy to help counselees to better understand their risk (cf. Trepanier et al. 2004), the one study that explicitly mentioned doing so did not observe a significant effect on risk perception accuracy (Kent et al. 2000). Moreover, there appears to be incongruency between verbal and numerical risk estimates (e.g., Bjorvatn et al. 2007; Hopwood et al. 2003). Both types of risk estimates, however, possess qualities that would make them especially suited for counseling. Compared to verbal risk estimates, numerical risk estimates have been shown to increase trust in (Gurmankin et al. 2004a) and satisfaction with (Berry et al. 2004) the information. On the other hand, individuals have been shown to more readily use verbal information when describing their risk to others (Erev & Cohen 1990) and when deciding on treatment (Teigen & Brun 2003). We therefore advise genetic counselors to present numerical risk estimates first, as they are accurate, objective information. The patient may then be asked what that risk estimate means to him or her. The patient’s verbal response will provide an opportunity for further discussion of the meaning and impact of the risk information. Genetic counselors should, however, be aware of the disadvantages of verbal information in accurately communicating risk information.
A third, related implication concerns the presentation of numerical risk information. Research has shown that visual presentation of risk information (e.g., odds or percentages) may be better understood than written presentation formats. Indeed, there seems to be general agreement that graphical formats, in comparison with textual information, are better able to accurately communicate risk information (Schapira et al. 2001; Timmermans et al. 2004) although contradictory evidence has also been published (Parrot et al. 2005). Furthermore, graphical information seems to have a larger impact on risk-avoiding behavior than textual information (Chua et al. 2006). We therefore advise genetic counselors to use visual aids when communicating numerical risk information (cf. Tercyak et al. 2001).
Conclusions
Overall, this review suggests that genetic counseling may have a positive impact on risk perception accuracy. It has also resulted in several implications for future research. First, future researchers should link risk perception changes to objective risk estimates to assess the effect of genetic counseling on risk perception accuracy. Researchers are advised to define risk perception accuracy as the correct counseled risk estimate instead of falling within a certain percentage of the counseled risk. Additionally, they should report both the proportion of individuals who correctly estimate their risk and the average overestimation of risk. Second, as the descriptions of the counseling sessions were generally poor, future research should include more detailed descriptions of these sessions, and link their content to risk perception outcomes to enable interpretation of the results. Finally, the effect of genetic counseling should be examined for a wider variety of hereditary conditions. Genetic counselors are advised to discuss the role of family history and perform a family history assessment to provide the necessary context in which counselees can understand the risk information. They should also use both verbal and numerical risk estimates to communicate personal risk information, and use visual aids when communicating numerical risk information.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Maastricht University and performed at the School for Public Health and Primary Care (Caphri). Caphri participates in the Netherlands School of Primary Care Research (CaRe), recognized by the Royal Dutch Academy of Science (KNAW) in 1995.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Footnotes
Note that the numbers reported here are not consistent; that is, 58% is not a 25% increase from 42%. This inconsistency is due to the fact that all three figures are means of the raw data, which do not have the property of consistency in such calculations.
Note that the numbers reported here are not consistent; that is, 18% is not an 8% decrease from 25%. This inconsistency is due to the fact that all three figures are means of the raw data, which do not have the property of consistency in such calculations.
References
- Berry D. C., Raynor T., Knapp P., Bersellini E. Over the counter medicines and the need for immediate action: A further evaluation of European Commision recommended wordings for communicating risks. Patient Education and Counseling. 2004;53:129–134. doi: 10.1016/S0738-3991(03)00111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker B. B. Goals of genetic counseling. Clinical Genetics. 2001;60:323–330. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0004.2001.600501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorvatn C., Eide G. E., Hanestad B. R., Oyen N., Havik O. E., Carlsson A., et al. Risk perception, worry and satisfaction related to genetic counseling for hereditary cancer. Journal of Genetic Counseling. 2007;12:211–222. doi: 10.1007/s10897-006-9061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen D. J., Burke W., Culver J. O., Press N., Crystal S. Effects of counseling Ashkenazi Jewish women about breast cancer risk. Cultural Diversity & Ethnic Minority Psychology. 2006;12:45–56. doi: 10.1037/1099-9809.12.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke W., Culver J. O., Bowen D., Lowry D., Durfy S., McTiernan A., et al. Genetic counseling for women with an intermediate family history of breast cancer. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 2000;90:361–368. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(20000228)90:5<361::AID-AJMG4>3.0.CO;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butow P. N., Lobb E. A., Meiser B., Barratt A., Tucker K. M. Psychological outcomes and risk perception after genetic testing and counselling in breast cancer: a systematic review. The Medical Journal of Australia. 2003;178:77–81. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2003.tb05069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua H. F., Yates J. F., Priti S. Risk avoidance: Graphs versus numbers. Memory & Cognition. 2006;34:399–410. doi: 10.3758/BF03193417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementi M., Di Gianantonio E., Ponchia R., Petrella M., Andrisani A., Tenconi R. Pregnancy outcome after genetic counselling for prenatal diagnosis of unexpected chromosomal anomaly. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology. 2006;128:77–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2006.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codori A. M., Waldeck T., Petersen G. M., Miglioretti D., Trimbath J. D., Tillery M. A. Genetic counseling outcomes: perceived risk and distress after counseling for hereditary colorectal cancer. Journal of Genetic Counseling. 2005;14:119–132. doi: 10.1007/s10897-005-4062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Green E. D., Guttmacher A. E., Guyer M. S. A vision for the future of genomics research. Nature. 2003;422:835–847. doi: 10.1038/nature01626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins V., Halliday J., Warren R., Williamson R. Cancer worries, risk perceptions and associations with interest in DNA testing and clinic satisfaction in a familial colorectal cancer clinic. Clinical Genetics. 2000;58:460–468. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0004.2000.580606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull A., Fry A., Rush R., Steel C. M. Cancer risk perceptions and distress among women attending a familial ovarian cancer clinic. British Journal of Cancer. 2001;84:594–599. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erev I., Cohen B. L. Verbal versus numerical probabilities: Efficiency, biases, and the preference paradox. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes. 1990;45:1–18. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(90)90002-Q. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G. R., Blair V., Greenhalgh R., Hopwood P., Howell A. The impact of genetic-counseling on risk perception in women with a family history of breast-cancer. British Journal of Cancer. 1994;70:934–938. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurmankin A. D., Baron J., Armstrong K. The effect of numerical statements of risk on trust and comfort with hypothetical physician risk communication. Medical Decision Making. 2004;24:265–271. doi: 10.1177/0272989X04265482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurmankin A. D., Baron J., Armstrong K. Intended message versus message received in hypothetical physician risk communications: Exploring the gap. Risk Analysis. 2004;24:1337–1347. doi: 10.1111/j.0272-4332.2004.00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J. P. T., & Green, S. (Eds.).(2006). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions 4.2.6 [updated September 2006]. In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 4, 2006. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
- Hopwood P., Howell A., Lalloo F., Evans G. Do women understand the odds? Risk perceptions and recall of risk information in women with a family history of breast cancer. Community Genetics. 2003;6:214–223. doi: 10.1159/000079383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood P., Shenton A., Lalloo F., Evans D. G. R., Howell A. Risk perception and cancer worry: An exploratory study of the impact of genetic risk counselling in women with a family history of breast cancer. Journal of Medical Genetics. 2001;38:139–142. doi: 10.1136/jmg.38.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood P., Wonderling D., Watson M., Cull A., Douglas F., Cole T., et al. A randomised comparison of UK genetic risk counselling services for familial cancer: psychosocial outcomes. British Journal of Cancer. 2004;91:884–892. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huiart L., Eisinger F., Stoppa Lyonnet D., Lasset C., Nogues C., Vennin P., et al. Effects of genetic consultation on perception of a family risk of breast/ovarian cancer and determinants of inaccurate perception after the consultation. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2002;55:665–675. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(02)00401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys P., Berkeley D. Representing risks: supporting genetic counseling. Birth Defects Original Article Series. 1987;23:227–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janz N., Becker M. H. The health belief model: A decade later. Health Education Quarterly. 1984;11:1–47. doi: 10.1177/109019818401100101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian Reynier C., Chabal F., Sobol H., Aurran Y., Nogues C., Vennin P., et al. Risk perception, anxiety and attitudes towards predictive testing alter cancer genetic consultations. American Journal of Human Genetics. 1995;57:1722–1722. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser A. S., Ferris L. E., Katz R., Pastuszak A., Llewellyn Thomas H., Johnson J. A., et al. Psychological responses to prenatal NTS counseling and the uptake of invasive testing in women of advanced maternal age. Patient Education and Counseling. 2004;54:45–53. doi: 10.1016/S0738-3991(03)00190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasparian N. A., Wakefield C. E., Meiser B. Assessment of psychological outcomes in genetic counseling research. Journal of Genetic Counseling. 2007;16:693–712. doi: 10.1007/s10897-007-9111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Leventhal H., Toppmeyer D., Much J., Dermody J., Marvin M., et al. Subjective and objective risks of carrying a BRCA 1/2 mutation in individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. Journal of Genetic Counseling. 2003;12:351–371. doi: 10.1023/A:1023905106360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent G., Howie H., Fletcher M., Newbury-Ecob R., Hosie K. The relationship between perceived risk, thought intrusiveness and emotional well-being in women receiving counselling for breast cancer risk in a family history clinic. British Journal of Health Psychology. 2000;5:15–26. doi: 10.1348/135910700168739. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman C., Croyle R. T., Tercyak K. P., Hamann H. Genetic testing: psychological aspects and implications. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2002;70:784–797. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.70.3.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidén A., Berglund G., Hansson M. G., Rosenquist R., Sjödén P. O., Nordin K. Genetic counselling for cancer and risk perception. Acta Oncologica. 2003;42:726–734. doi: 10.1080/02841860310011023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb E. A., Butow P., Barratt A., Meiser B., Gaff C., Young M. A. Communication and information-giving in high-risk breast cancer consultations: influence on patient outcomes. British Journal of Cancer. 2004;90:321–327. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb E. A., Butow P. N., Barratt A., Meiser B., Gaff C., Young M. A., et al. Communication and information-giving in high-risk breast cancer consultations: influence on patient outcomes. British Journal of Cancer. 2004;90:321–327. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiser B., Butow P., Barratt A., Gattas M., Gaff C., Haan E., et al. Risk perceptions and knowledge of breast cancer genetics in women at increased risk of developing hereditary breast cancer. Psychology & Health. 2001;16:297–311. doi: 10.1080/08870440108405508. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Meiser B., Butow P. N., Barratt A. L., Schnieden V., Gattas M., Kirk J., et al. Long-term outcomes of genetic counseling in women at increased risk of developing hereditary breast cancer. Patient Education and Counseling. 2001;44:215–225. doi: 10.1016/S0738-3991(00)00191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiser B., Halliday J. L. What is the impact of genetic counseling in women at increased risk of developing hereditary breast cancer? A meta-analytic review. Social Science & Medicine. 2002;54:1463–1470. doi: 10.1016/S0277-9536(01)00133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordin K., Lidén A., Hansson M., Rosenquist R., Berglund G. Coping style, psychological distress, risk perception, and satisfaction in subjects attending genetic counselling for hereditary cancer. Journal of Medical Genetics. 2002;39:689–694. doi: 10.1136/jmg.39.9.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmero E. I., Caleffi M., Vargas F. R., Rocha J. C. C., Giugliani R., Kalakun L., et al. Genetic counseling and cancer risk perception in Brazilian patients at-risk for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2004;22:884–884. doi: 10.1200/jco.2004.22.90140.9698. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Parrot R., Silk K., Dorgan K., Condit C., Harris T. Risk comprehension and judgements of statisical evidentiary appeals. When a picture is not worth a thousand words. Human Communication Research. 2005;31:423–452. [Google Scholar]
- Pieterse A. H., van Dulmen S., van Dijk S., Bensing J. M., Ausems M. G. E. M. Risk communication in completed series of breast cancer genetic counseling visits. Genetics in Medicine. 2006;8:688–696. doi: 10.1097/01.gim.0000245579.79093.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilnick A., Dingwall R. Research directions in genetic counselling: a review of the literature. Patient Education and Counseling. 2001;44:95–105. doi: 10.1016/S0738-3991(00)00181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resta R., Biesecker B., Bennet R., Blum S., Estabrooks Hahn S., Strecker M., et al. A new definition of genetic counseling: Notional Society of Genetic Counselors’ Task Force report. Journal of Genetic Counseling. 2006;15:77–83. doi: 10.1007/s10897-005-9014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimes K. A., Salkovkis P. M., Jones L., Lucassen A. M. Applying cognitive-behavioral models of health anxiety in a cancer genetics service. Health Psychology. 2006;25:171–180. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.25.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers R. W. Cognitive and physiological processes in fear appeals and attitude change: A revised theory of protection motivation. In: Cacioppo T., Petty R. E., editors. Social psychophysiology: A sourcebook. New York: Guilford Press; 1983. pp. 153–176. [Google Scholar]
- Rothemund Y., Paepke S., Flor H. Perception of risk, anxiety, and health behaviors in women at high risk for breast cancer. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 2001;8:230–239. doi: 10.1207/S15327558IJBM0803_5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M. M., Nattinger A. B., McHorney C. A. Frequency or probability? A qualitative study of risk communication formats used in health care. Medical Decision Making. 2001;21:459–467. doi: 10.1177/0272989X0102100604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiloh S., Gerad L., Goldman B. The facilitating role of information provided in genetic counseling for counselees’ decisions. Genetics in Medicine. 2006;8:116–124. doi: 10.1097/01.gim.0000196823.50502.a4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teigen K. H., Brun W. Verbal probabilities: A question of frame? Journal of Behavioral Decision Making. 2003;16:53–72. doi: 10.1002/bdm.432. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tercyak K. P., Johnson S. B., Roberts S. F., Cruz A. C. Psychological response to prenatal genetic counseling and amniocentesis. Patient Education and Counseling. 2001;43:73–84. doi: 10.1016/S0738-3991(00)00146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans D., Molewijk B., Stiggelhout A., Kievit J. Different formats for communicating surgical risks to patients and the effect on choice of treatment. Patient Education and Counseling. 2004;54:255–263. doi: 10.1016/S0738-3991(03)00238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepanier A., Ahrens M., McKinnon W., Peters J., Stopfer J., Grumet S., et al. Genetic Cancer Risk Assessment and Counseling: Recommendations of the National Society of Genetic Counselors. Journal of Genetic Counseling. 2004;13:83–114. doi: 10.1023/B:JOGC.0000018821.48330.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk S., Otten W., Zoeteweij M. W., Timmermans D. R., van Asperen C. J., Breuning M. H., et al. Genetic counselling and the intention to undergo prophylactic mastectomy: effects of a breast cancer risk assessment. British Journal of Cancer. 2003;88:1675–1681. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Gonzalez R., Merajver S. D. Assessment of genetic testing and related counseling services: current research and future directions. Social Science & Medicine. 2004;58:1427–1442. doi: 10.1016/S0277-9536(03)00337-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner E., Carroll J. C., Heisey R. E., Goel V., Meschino W. S., Lickley H. L., et al. Educating women about breast cancer. An intervention for women with a family history of breast cancer. Canadian Family Physician Medecin de Famille Canadien. 2003;49:56–63. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte K. Putting the fear back into fear appeals: The extended parallel process model (EPPM) Communication Monographs. 1992;59:329–349. doi: 10.1080/03637759209376276. [DOI] [Google Scholar]


