A 67-year-old man was admitted to the Emergency Department of our Hospital with fever and respiratory insufficience secondary to COVID-19 pneumonia, confirmed with RT-PCR test.
During the first hours of hospitalization the patient was intubated, due to early respiratory deterioration (needs of fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) up to 100%, with PaO2/FiO2 < 100).
Afterwards a right pneumothorax was detected as explanation for early respiratory deterioration. A right basal pleural drainage was placed with expansion of the right lung and progressive improvement of respiratory function.
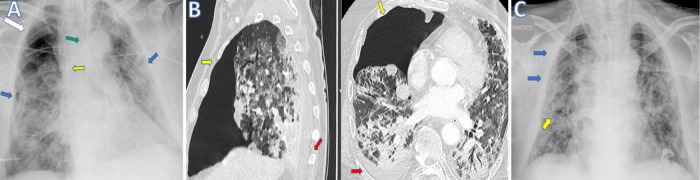
A chest X-ray (Fig. 1 A) and a CT Scan (Fig. 1B) illustrate a right pneumothorax resolved after positioning a right pleural drainage (Fig. 1C).
Fig. 1.
(A) Chest X-ray (anteroposterior projection) performed on day 24 from the admission showed bilateral peripheral opacities (blue arrow) and a right upper pneumothorax (white arrow). Endotracheal tube (green arrow) and left internal jugular central venous access with distal end at the level of the superior vena cava (SVC) (yellow arrow)are well placed. (B) CT scan on sagittal and trasverse planes images shows confirmed a right upper-anterior pneumothorax with partial collapse of the right upper lobe (yellow arrows) associated with mild right posterior pleural effusion (red arrows). (C) Chest X-ray with single anteroposterior projection scan obtained on day 26, after positioning of inferior right pleural drainage (yellow arrow), shows resolution of pneumothorax with riexpansion of the right lung (blue arrow).
In this case pneumothorax was caused by a barotrauma secondary to endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation.
Despite pneumothorax in this clnical scenario represents a frequent complication, only few papers focused on imaging findings related to mechanical ventilation complications in Covid-19 patients have been reported.
Salehi et al.1 and Yang et al.2 described just one case of pneumothorax in cohorts of 99 and 52 patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia respectively.2
Imaging techniques are key in the diagnosis and management of these complications.
References
- 1.Salehi S., Abedi A., Balakrishnan S., Gholamrezanezhad A. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review of imaging findings in 919 patients [published online ahead of print, 2020 Mar 14] Am J Roentgenol. 2020:1–7. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.23034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J, Liu H, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study [published online ahead of print, 2020 Feb 24] [published correction appears in Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Apr;8(4):e26]. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-522) Transl Pediatr. 2020;9:51–60. doi:10.21037/tp.2020.02.06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]