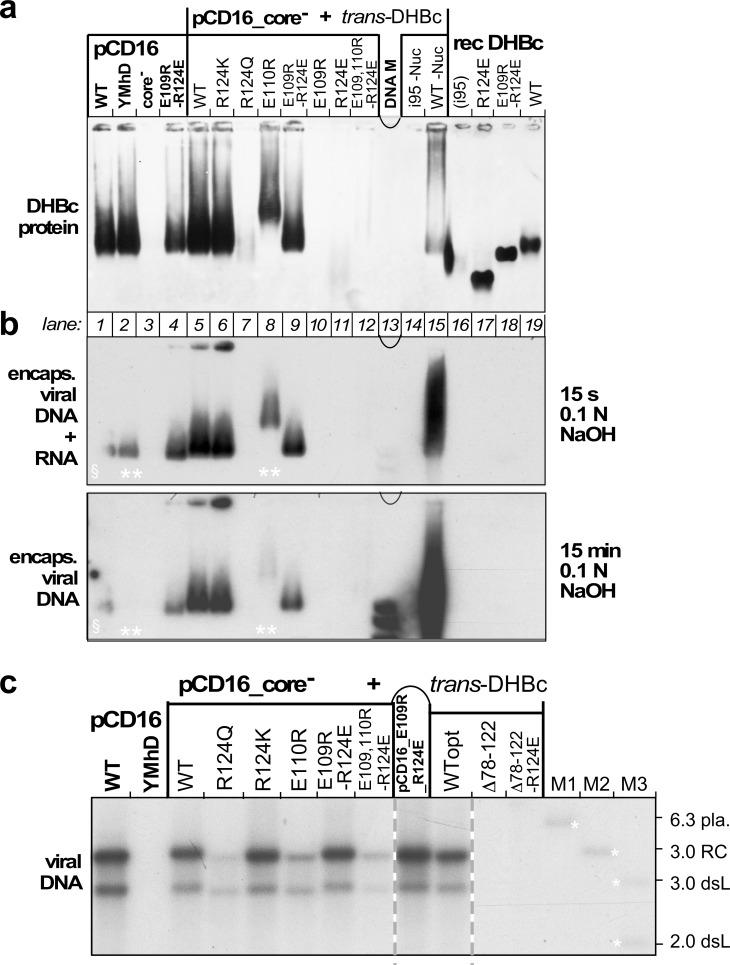
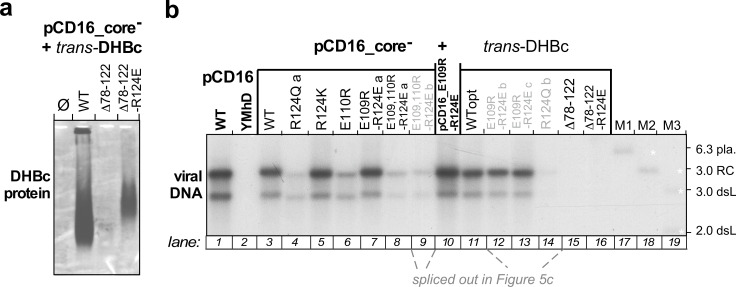
Figure 5. Opposite charges at DHBc positions 109 and 124 warrant stable capsid formation in hepatoma cells.
(a) Capsid formation. Cytoplasmic lysates from LMH cells transfected with the indicated constructs (pCD16: mutations present in cis; pCD16_core- + trans-DHBc: core-deficient DHBV genome co-transfected with DHBc vectors) were analyzed for capsid formation by NAGE and anti-DHBc immunoblot; recDHBc, E. coli derived CLPs. All samples except i95 -Nuc and WT -Nuc (lanes 14, 15) were treated with micrococcal nuclease to destroy non-packaged nucleic acids prior to NAGE. (b) Viral nucleic acid encapsidation. Cytoplasmic lysates separated as in (a) were examined by hybridization with a 32P-labeled DHBV probe after opening the blotted capsids via alkali treatment for 15 s (leaving RNA and DNA intact) and, thereafter, for 15 min (hydrolyzing RNA but not DNA). Signals from pCD16_YMhD (encoding a reverse transcription-deficient polymerase) and trans-DHBc E110R (lanes 2, 10; marked by **) showed strong and moderate, respectively, reductions upon longer treatment. § in lane one indicates poor transfer of the left part of the main band. (c) Absence of grossly aberrant reverse transcription products. DNAs from cytoplasmic capsids were analyzed by Southern blotting using the same probe as in (b). Labels WT vs. WTopt refer to the DHBc nucleotide sequence from DHBV16 vs. that from the E. coli optimized vectors. The presence of signals for DHBc_R124Q and E109,110R_R124E likely relates to the larger input of capsids for Southern blotting than for NAGE. M1-M3, marker DNAs; pla., pCD16 plasmid. The complete blot is shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 1.