Abstract
Background
The gram-negative Coxiella burnetii bacterium is the pathogen that causes Q fever. The bacterium is transmitted to animals via ticks, and manure, air, dead infected animals, etc. and can cause infection in domestic animals, wild animals, and humans. Xinjiang, the provincial-level administrative region with the largest land area in China, has many endemic tick species. The infection rate of C. burnetii in ticks in Xinjiang border areas has not been studied in detail.
Results
For the current study, 1507 ticks were collected from livestock at 22 sampling sites in ten border regions of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous region from 2018 to 2019. C. burnetii was detected in 205/348 (58.91%) Dermacentor nuttalli; in 110/146 (75.34%) D. pavlovskyi; in 66/80 (82.50%) D. silvarum; in 15/32 (46.90%) D. niveus; in 28/132 (21.21%) Hyalomma rufipes; in 24/25 (96.00%) H. anatolicum; in 219/312 (70.19%) H. asiaticum; in 252/338 (74.56%) Rhipicephalus sanguineus; and in 54/92 (58.70%) Haemaphysalis punctata. Among these samples, C. burnetii was detected in D. pavlovskyi for the first time. The infection rate of Rhipicephalus was 74.56% (252/338), which was the highest among the four tick genera sampled, whereas the infection rate of H. anatolicum was 96% (24/25), which was the highest among the nine tick species sampled. A sequence analysis indicated that 63 16S rRNA sequences could be found in four newly established genotypes: MT498683.1 (n = 18), MT498684.1 (n = 33), MT498685.1 (n = 6), and MT498686.1 (n = 6).
Conclusions
This study indicates that MT498684.1 might represent the main C. burnetii genotype in the ticks in Xinjiang because it was detected in eight of the tick species studied. The high infection rate of C. burnetii detected in the ticks found in domestic animals may indicate a high likelihood of Q fever infection in both domestic animals and humans.
Keywords: Coxiella burnetii, Ticks, Ixodidae, Q fever
Background
Coxiella burnetii, an obligate gram-negative intracellular bacterium, can cause Q fever disease in humans, survive in the environment for long periods of time, and is often found in the phagolysosome of infected mammalian cells [1, 2]. Given its impact on global public health, it has attracted significant attention for research purposes [3]. In humans, infection with C. burnetii causes acute symptoms that include vomiting, headache, pneumonia, fever, and hepatitis, as well as chronic symptoms related to hepatitis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, and intravascular infection [4, 5]. In animals, infection with C. burnetii causes various reproductive problems, including delivery of weak offspring, infertility, postpartum metritis, stillbirth, and abortion [6].
Q fever was first detected in workers at a slaughterhouse in Brisbane, Australia, in 1935 by E.H. Derrick, who named the illness “question fever” [7]. It has also been reported in humans in other countries, including Great Britain, the Netherlands, Spain, Germany, and Switzerland [8–12]. It was first reported to be in China during the 1950s, with C. burnetii antibodies being reported in humans from 32 prefectures in 15 provinces of China [13]. Slaughterhouse workers, veterinarians, and farmers are currently at high risk of contracting this relatively rare zoonotic disease [14].
Ticks are widely distributed around the world and are among the most important vectors of human disease, second only to mosquitoes; they are also the main carrier of pathogens in wild animals and livestock [15]. Coxiella maintains a symbiotic relationship with ticks and can infect ticks at all tick life stages [16, 17]. It has been isolated from more than 40 species of hard ticks and at least 14 species of soft ticks, indicating the importance of ticks in its transmission [18]. Animals become infected with C. burnetii via tick bites, whereas humans become infected mainly via contact with tick excreta, manure, direct contact with birth products, and air [1, 19]. Although the direct transmission of C. burnetii to humans through tick bites has not been reported in detail [20], C. burnetii has been reported in the milk, birth products, faeces, and urine of the infected animals, to which humans can be exposed and thus become infected with C. burnetii by airborne transmission [1].
Xinjiang is the provincial-level administrative region with the largest land area in China. Its boundary is connected with many countries and there are endemic tick species. In the current study, molecular biological methods were used to detect Q fever in tick species collected from the border area of Xinjiang, China, to reveal the species and pathogen-carrying status of the ticks in this region, to analyse the cross-border spread of Q fever. Through this molecular epidemiological survey, the risk of cross-border transmission of tick-borne Q fever and its spread to mainland China was assessed, to provide basic information on the development of effective prevention and control measures for this important tick-borne disease.
Results
In total, 1507 tick samples were collected from livestock in different regions of the Xinjiang border (Table 1); the samples belonged to one family (Ixodidae), four genera (606 Dermacentor, 471 Hyalomma, 338 Rhipicephalus and 92 Haemaphysalis), and ten species (348 D. nuttalli, 146 D. pavlovskyi, 80 D. silvarum, 32 D. niveus, 132 Hy. rufipes, 2 Hy. scupense, 25 Hy. anatolicum, 312 Hy. asiaticum, 338 R. sanguineus, and 92 Ha. punctata).
Table 1.
Detection of C. burnetii DNA in ticks according to tick species, origin of ticks
| Region | Location | Species | Adjacent farm animals | No. positive/No. examined |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kashgar Prefecture | Kashi | D. nuttalli | sheep | 97/120 (80.83%) |
| Hy. asiaticum | sheep | 9/40 (22.50%) | ||
| R. sanguineus | sheep | 65/70 (92.86%) | ||
| Ili Kazak Autonomous Prefecture | Gongliu | Hy. rufipes | cattle | 19/120 (63.33%) |
| Yining | R. sanguineus | sheep | 84/90 (93.33%) | |
| Xinyuan | D. silvarum | sheep | 66/80 (82.50%) | |
| Nilka | Hy. rufipes | cattle | 9/12 (75.00%) | |
| Qapqal Xibe | R. sanguineus | sheep | 35/100 (35.00%) | |
| Huocheng | Ha. punctata | cattle | 54/92 (58.70%) | |
| Kizilsu Kirghiz Autonomous Prefecture | Aheqi | D. pavlovskyi | sheep | 110/146 (75.34%) |
| Atushi | Hy. asiaticum | cattle | 24/25 (96.00%) | |
| Tarbagatay Prefecture | Hoboksar | D. nuttalli | sheep | 18/23 (78.26%) |
| Tacheng | D. nuttalli | cattle | 9/10 (90.00%) | |
| Yumin | D. niveus | cattle | 15/32 (46.88%) | |
| Altay Prefecture | Jeminay | D. nuttalli | sheep | 6/15 (40.00%) |
| Hy. scupense | cattle | 0/2 (0.00%) | ||
| Qinghe | D. nuttalli | sheep | 41/46 (89.13%) | |
| Habahe | D. nuttalli | cattle | 0/94 (0.00%) | |
| Akesu Prefecture | Akesu | D. nuttalli | sheep | 34/40 (85.00%) |
| Wushi | Hy. asiaticum | cattle | 28/30 (93.33%) | |
| R. sanguineus | sheep | 45/48 (93.75%) | ||
| Hotan Prefecture | Pishan | Hy. asiaticum | sheep | 20/30 (66.67%) |
| Karakax | R. sanguineus | sheep | 23/30 (76.67%) | |
| Hami Prefecture | Barkol Kazak | Hy. asiaticum | cattle | 0/48 (0.00%) |
| Changji hui autonomous prefecture | Qitai | Hy. asiaticum | cattle | 102/104 (98.08%) |
| BortalaMongolAutonomousPrefecture | Wenquan | Hy. asiaticum | cattle | 60/60 (100.00%) |
In this study, the tick samples were analysed to detect C. burnetii. The IS1111 DNA of C. burnetii was detected in 973 (973/1507) DNA samples in the following proportions: D. nuttalli, 205 (58.91%); D. pavlovskyi, 110 (75.34%); D. silvarum, 66 (82.50%); D. niveus, 15 (46.90%); H. scupense, 0 (0.00%); H. rufipes, 28 (21%); H. anatolicum, 24 (96.00%); H. asiaticum, 219 (70.19%); H. punctata, 54 (58.70%); and R. sanguineus 252 (74.56%). There were significant difference in the infection rate between different species and the reference group (P < 0.05) (Table 2). The infection rate of Dermacentor and Rhipicephalus had statistical significance with the reference group (P < 0.05), while the infection rate of Haemaphysalis had no statistical significance with the reference group (P > 0.05) (Table 2). Three IS1111 positive samples from each sampling site were randomly selected for sequencing the 16S PCR products. After multisequence alignment, the obtained 63 16S rRNA gene sequences formed four sequence clusters: MT498683.1 (n = 18) from R. sanguineus and H. asiaticum; MT498684.1 (n = 33) from D. nuttalli, D. pavlovskyi, D. silvarum, D. niveus, H. rufipes, H. anatolicum, H. asiaticum, and R. sanguineus; MT498685.1 (n = 6) from H. punctata; and MT498686.1 (n = 6) from D. nuttalli.
Table 2.
Tick species and the PCR results of C. burnetii from the Xinjiang samples
| Family | Genus | Species | No. examined | No. positive (%) | P | χ 2 | OR (95% CI) | No. examined | No. positive (%) | P | χ 2 | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ixodidae | Dermacentor | D. nuttalli | 348 | 205 (58.91) | < 0.05 | 54.44 | 0.19 (0.12–3.00) | 606 | 396 (65.35) | < 0.05 | 6.86 | 0.72 (0.56–0.92) |
| D. pavlovskyi | 146 | 110 (75.34) | < 0.05 | 81.25 | 0.09 (0.05–0.16) | |||||||
| D. silvarum | 80 | 66 (82.50) | < 0.05 | 75.81 | 0.06 (0.03–0.12) | |||||||
| D. niveus | 32 | 15 (46.90) | < 0.05 | 8.77 | 0.31 (0.14–0.69) | |||||||
| Hyalomma | H. scupense | 2 | 0 (0.00) | – | – | – | 471 | 271 (57.54) | Ref. group | |||
| H. rufipes | 132 | 28 (21.21) | Ref. group | |||||||||
| H. anatolicum | 25 | 24 (96.00) | < 0.05 | 53.07 | 0.01 (0.00–0.09) | |||||||
| H. asiaticum | 312 | 219 (70.19) | < 0.05 | 90.16 | 0.11 (0.71–0.19) | |||||||
| Haemaphysalis | H. punctata | 92 | 54 (58.70) | < 0.05 | 32.82 | 0.19 (0.11–0.34) | 92 | 54 (58.70) | > 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.95 (0.61–1.50) | |
| Rhipicephalus | R. sanguineus | 338 | 252 (74.56) | < 0.05 | 112.16 | 0.09 (0.06–0.15) | 338 | 252 (74.56) | < 0.05 | 24.94 | 0.46 (0.34–0.63) | |
| Total | 1507 | 973 (64.57) | 1507 | 973 (64.57) | ||||||||
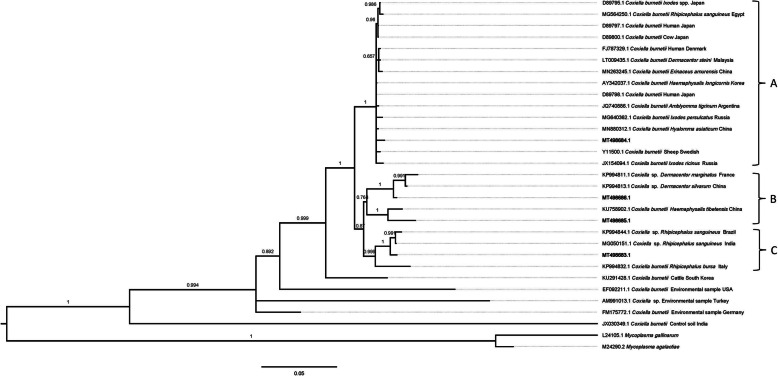
Based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, the MT498683.1 (n = 18) genotype shared 99.3 and 98.5% sequence identity with the Coxiella sp. in R. sanguineus from India (MG050151.1) and the C. burnetii in Ixodes persulcatus from the Russia (MG640362.1), respectively; the MT498684.1 (n = 33) genotype shared 99.5 and 99.3% sequence identity with the C. burnetii in H. asiaticum from China (MN880312.1) and the C. burnetii in a human (a patient with Q fever endocarditis) from Denmark (FJ787329.1). Respectively, the MT498685.1 (n = 6) genotype shared 99.3 and 96.6% sequence identity with the C. burnetii in I. persulcatus from the Russia (MG640362.1) and the C. burnetii in H. tibetensis from China (KU758902.1). Finally, the MT498686.1 (n = 6) genotype shared 98.4 and 96.6% sequence identity with the C. burnetii in I. ricinus from Russia (JX154094.1) and the C. burnetii in sheep from Swedish (Y11500.1), respectively. As shown by the phylogenetic analysis, the MT498684.1 genotypes belonged to group A, whereas the MT498686.1 and MT498685.1 genotypes belonged to group B, MT498683.1 genotypes belonged to group C (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic relationships of the MT498683.1, MT498684.1, MT498685.1, and MT498686.1 genotypes identified in the current study with other Coxiella samples by Bayesian inference. Each sequence consists of accession number, host source, and country. The numbers in node represent statistically significant posterior probabilities. The genotypes detected in this study are shown as bold. Mycoplasma gallinarum (L24105.1) and Mycoplasma agalactiae (M24290.2) were used as the outgroups. The scale bar (0.05) indicating nucleotide substitutions per site
Discussion
As the second largest group of vectors in the world, ticks are hosts to pathogens of a variety of important zoonoses [21–23], such as Forest encephalitis, Q fever, Lyme disease, Spot fever, tularemia, and babesiosis [24, 25]. In recent years, new tick-borne diseases, such as human granulocytic anaplasmosis (HGA), severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS), and Guertu virus (GTV), have been reported [26, 27]. Ticks transmit pathogens primarily by biting the host [28, 29], but also by aerosol transmission (C. burnetii) [5]. Previous reports indicated that ticks are widely distributed in China, with 42 species of ticks from nine genera reported in Xinjiang alone, accounting for more than one-third of the total tick species in China [30–32]. I. persulcatus, D. nuttalli, H. asiaticum, D. marginatus, and D. niveus are the dominant tick species in Xinjiang [33], and their wide distribution has a significant impact on the development of animal husbandry and public health.
Of the 1507 tick samples collected for the current study, 64.57% (973/1507) contained C. burnetii IS1111 DNA. Similarly, previous studies have found a high prevalence of C. burnetii in ticks (55.66%) [34] (However, the sample size is too small to accurately reflect the specific infection situation in these areas.); the R. sanguineus (60.00%, 3/5) in PTiB, northeastern Spain [35]; the R. sanguineus (60.00%, 9/15) in Cyprus [36]. While a lower rate was detected in D. nuttalli (12.50%, 7/56) in Gansu, China; the D. silvarum (2.79%, 11/394), D. niveus (14.75%, 9/61), H. asiaticum (22.65%, 41/181) in Xinjiang, China [37–39]; the H. rufipes (10.52%, 2/19), R. sanguineus (3.44%, 4/116) in Mali [40]; the H. anatolicum (13.33%, 2/15) in Cyprus [34]. The differences in infection rate between this study and others may be related to the number of samples, collection location, detection method, and ecological environment. The temperate continental climate provides a good habitat for a wide variety of ticks in Xinjiang. Xinjiang has a great variety of mammalian and avian species, which could serve as hosts of diverse tick species. Therefore, we speculate that climate and invertebrate vector abundance factors may be related to infection.
We did not detect C. burnetii in H. scupense (0/2; 0.00%), an outcome that may be related to the small sample size (2 samples of H. scupense). In addition, the presence of C. burnetii in D. pavlovskyi was first reported here. The high infection rate of C. burnetii in D. silvarum, H. asiaticum, and R. sanguineus seems to be related to the symbiosis and vertical transmission between them [41, 42]. Although there is no related article reporting the existence of symbiotic and vertical propagation of C. burnetii in D. nuttalli, D. pavlovskyi, D. niveus, H. rufipes, H. anatolicum, or H. punctata, the findings lead us to suspect that C. burnetii has these relationships to these ticks, particularly because some reports have shown that C. burnetii has a high infection rate and vertical transmission relationship among some ticks [43–46]. Confirmation of our hypothesis requires more literature support and research to prove; here we are merely stating the supposition. Overall, our results indicate that C. burnetii is widespread in the border areas of Xinjiang.
The presence of C. burnetii worldwide, including in the environment and in both vertebrate and invertebrate hosts. Phylogenetic analyses indicated that MT498684.1 (from D. nuttalli, D. pavlovskyi, D. silvarum, D. niveus, H. rufipes, H. anatolicum, H. asiaticum and R. sanguineus) belonged to group A, MT498686.1 (from D. nuttalli) and MT498685.1 (from H. punctata) belonged to group B, MT498683.1 (from R. sanguineus and H. asiaticum) belonged to group C (Fig. 1). MT498683.1, MT498686.1, and MT498685.1 genotypes and Coxiella sp. from ticks was clustered into a branch (A and B), whereas MT498684.1 genotypes forms a branch with C. burnetii from different sources (cows, human, sheep, and ticks) (Fig. 1). The results show that MT498684.1 genotypes have more hosts than MT498683.1, MT498686.1 and MT498685.1 genotypes. MT498684.1 genotypes may have low zoonotic risk, and the diversity of C. burnetii hosts indicates that ticks may play an important role in the transmission of C. burnetii.
In this study, 16S rRNA assays were used to detect previously unknown genotypes (MT498683.1, MT498684.1, MT498685.1, and MT498686.1) of C. burnetii from nine species of tick: D. nuttalli, D. pavlovskyi, D. silvarum, D. niveus, H. rufipes, H. anatolicum, H. asiaticum, R. sanguineus, and H. punctata. However, MT498683.1 was detected only in R. sanguineus and H. asiaticum, MT498685.1 was detected only in H. punctata and MT498686.1 was detected only in D. nuttalli, whereas MT498684.1 was detected in D. nuttalli, D. pavlovskyi, D. silvarum, D. niveus, H. rufipes, H. anatolicum, H. asiaticum, and R. sanguineus. Thus, these results suggest that MT498684.1 is the main genotype in ticks in Xinjiang. More importantly, MT498684.1 showed 99.3 and 99.5% identity with the C. burnetii in the human from Denmark (FJ787329.1) and Japan (D89797.1). There have been few reports of the direct transmission of C. burnetii to humans through ticks [20]. However, C. burnetii has been reported in the milk, birth products, faeces, and urine of infected animals, to which humans can be exposed and thus be infected [1]. At particularly high risk are veterinary personnel, stockyard workers, farmers, hide tannery workers and others who work closely with animals. Sporadic cases of C. burnetii in humans are reported each year, although occasionally there are large outbreaks in humans [16, 17]. For example, between 2007 and 2011, a Q fever epidemic occurred in the Netherlands, affecting 4107 people and causing the death of > 50,000 dairy goats. It was thought that most of these infected people developed Q fever by inhaling air in which C. burnetii had been released during the birthing season of both goats and sheep (February–May) (http://www.rivm.nl/Onderwerpen/Q/Q_koorts) [9, 47].
In the 1950s, Q fever was first reported in China [48, 49]. The first Chinese strain of C. burnetii (Qi Yi) was isolated from a confirmed Q fever patient in 1962 [50]. In the past few decades, C. burnetii DNA has been detected in blood samples of human (33.33%, 8/24), goats (25.00%, 4/16), horses (39.50%, 79/200; 22.22%, 4/18), cattle (20.51%, 40/195) from Xinjiang [51, 52], goats from Beijing (4.55%, 2/44) [53], spleen samples of mice in Yunnan (85.19%, 46/54) [54], in ticks from Gansu, Ningxia, Shanxi, Xinjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Heilongjiang [39, 55, 56].
In summary, this study reports, for the first time, the Q fever infection in ticks in the border areas of Xinjiang, China, indicated that the abundant tick species and high infection rates of C. burnetii in the border areas of Xinjiang pose potential threats to domestic animals and humans. Xinjiang, located in northwest China, is bordered by Pakistan, Tajikistan, Mongolia, Kyrgyzstan, India, Afghanistan, Russia and Kazakhstan. Ticks are widely distributed in wild animals and domestic animals across the region, providing increased opportunities for cross-border transmission of C. burnetii as global trade intensifies. Thus, there is a need for farmers to adhere to livestock testing and to implement tick control strategies. It is of great significance for public health and safety to reduce the risk of cross-border transmission of the pathogen and its spread to the mainland of China.
Conclusions
This study confirmed, for the first time, that C. burnetii is widely distributed in ticks in Xinjiang, China, indicating that domestic animals and humans in this region may be at risk of being infected with C. burnetii. Therefore, there is a need for further research on C. burnetii cross-border transmission via ticks. More importantly, there is a need to monitor domestic animals and humans in the region and in tick control in the region to the greatest extent possible to ensure animal and public health safety.
Methods
Sample collection and morphological identification of the ticks
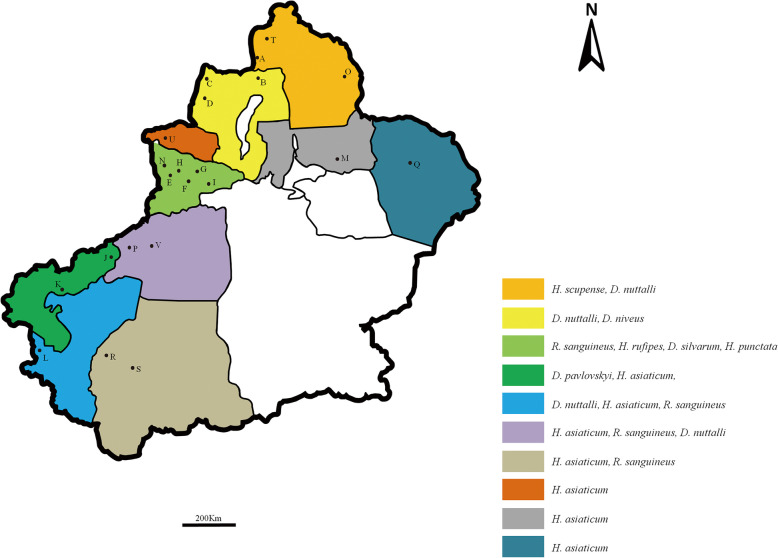
A total of 1507 ticks were collected from cattle and sheep at 22 sampling sites in ten border regions in the spring of Xinjiang, China from 2018 to 2019 (Fig. 2). The collected samples were stored in 50 mL centrifuge tubes and delivered to the laboratory. The ticks were identified based on morphological criteria following the descriptions provided by Deng GF (1991) [57]. Tick samples were collected with permission from the farmer.
Fig. 2.
Locations of the sample sites for tick collection in the border areas of Xinjiang (different locations are coded by colour; A–V indicate the sampling points). The map is made by ArcMap 10.2 (https://developers.arcgis.com/)
DNA extraction from tick samples
Tick samples were placed in 50 mL sterile centrifuge tubes and washed individually twice with 75% ethanol, followed by ddH2O rinsing until the liquid was clear. For each sample, DNA was extracted using a QIAamp DNA mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol, and the extracted DNA was stored at − 20 °C.
PCR amplification and sequencing
As described in previous studies [58–61], primers were designed with conserved regions of the C. burnetii IS1111 (This is a multi-copy gene encoding a transposase) and 16S rRNA gene sequences (Table 3); the expected product from the C. burnetii primers used for IS1111 amplification was 517 bp, and for the 16S rRNA primers, it was 592 bp. The 25 μL of PCR mixture comprised 2 μL of DNA sample, 12.5 μL of DreamTaq Green PCR Master Mix (2×) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Lithuania, MA, USA), 8.5 μL of ddH2O, and 1 μL of 10 μΜ forward primer and 10 μΜ reverse primer (TSINGKE Biotech, Xian, China). A negative control was prepared with double-distilled water, positive control for C. burnetii from H. asiaticum preserved by our laboratory. Finally, the 25 μL reaction mixture was subjected to PCR under the following conditions: denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, and 35 cycles of 72 °C for 1 min, and the final step at 72 °C for 5 min. Next, 5 μL of the PCR products were subjected to 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized after being stained with Goldview (Solarbio, Beijing, China); three positive samples (IS1111 gene) from each sampling site were selected for the amplification of C. burnetii 16S rRNA sequences. The nucleotide sequences were confirmed by bidirectional sequencing 16S rRNA PCR product in TSINGKE Biotech, China.
Table 3.
PCR primers used to detect DNA extracted from the ticks taken from Xinjiang
| Primers | Target gene | Primer sequence (5′ → 3′) | Annealing temp (°C) | Target fragment (bp) | Reference sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | IS1111 | GTGATCTACACGAGACGGGTT | 55 | 517 | M80806.1, KT391016.1, KT391020.1, KT391019.1, KT391018.1, KT391017.1, KT954146.1, KT391015.1, KT391014.1, KT391013.1, EU430257.1 |
| R | CGTAATCACCAATCGCTTCGT | ||||
| 16S-Fw | 16S rRNA | TCGGTGGHGAAGAAATTCTC | 55 | 592 | KP994776.1, GU797243.1, KP994812.1, KP994826.1, KP994854.1, D89792.1, NR_104916.1, FJ787329.1, HM208383.1, AY342037.1, MH769217.1, MK182891.1 |
| 16S-Rv | AGGCACCAARTCATYTCTGACAAG |
Phylogenetic analysis
Nucleotide sequences were aligned using MAFFT v7 (https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/), and use ModelFinder (ModelFinder is implemented in IQ-TREE version 1.6.1.2, http://www.iqtree.org) to calculate the best model (K2P + G4 model was selected based on Bayesian Information Criterion: BIC). Bayesian inference (BI) and Monte Carlo Markov Chain (MCMC) methods were used to construct the phylogenetic tree in PhyloSuite v1.2.2 (https://github.com/dongzhang0725/PhyloSuite/ releases), The number of substitutions (Nst) was set at two, and posterior probability values were calculated by running 2,000,000 generations with four simultaneous tree-building chains. A 50% majority-rule consensus tree was constructed from the final 75% of the trees generated by BI. Analyses were run three times to ensure convergence and insensitivity to priors. Phylogenetic tree were edited in Figtree v1.4.3 (https://github.com/rambaut/figtree/releases).
Statistical analysis
In this study, Analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics IBM 17 (© IBM Corporation, Somers, New York, USA). Chi-square (χ 2) test was used to conduct statistical analysis on different Genus and species with C. burnetii infection.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Figure S1. Specificity test results of IS1111 primer.
Additional file 2: Figure S2. Sensitivity test results of IS1111 primer.
Additional file 3: Figure S3. Specificity test results of 16S rRNA primer.
Additional file 4: Figure S4. Sensitivity test results of 16S rRNA primer.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- C. burnetii
Coxiella burnetii
- D. nuttalli
Dermacentor nuttalli
- D. pavlovskyi
Dermacentor pavlovskyi
- D. silvarum
Dermacentor silvarum
- D. niveus
Dermacentor niveus
- H. rufipes
Hyalomma rufipes
- H. anatolicum
Hyalomma anatolicum
- H. asiaticum
Hyalomma asiaticum
- R. sanguineus
Rhipicephalus sanguineus
- H. punctata
Haemaphysalis punctata
- H. scupense
Hyalomma scupense
Authors’ contributions
JN, XFX, and QYR performed experiments. HLL, MA, YL, and ZM participated in sample collection. GYL, ZC, JL, and QYR identification of tick samples. JN, JHG, WGL, ZQQ, ZGW, and YCT performed data analysis. JMW, YQL, GQG, JXL, HY, and GYL revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (Y2018PT76, Y2019YJ07–04) and NPRC-2019-194-30 supported the design of the study and sample collection, NSFC (1572511, 1702229, 1471967) supported the writing the manuscript, National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0501206, 2017YFD0501200, 2019YFC1200502, 2019YFC1200500) supported the analysis, ASTIP (CAAS-ASTIP-2016-LVRI), NBCIS (CARS-37) and Jiangsu Co-innovation Center programme for Prevention and Control of Important Animal Infectious Disease and Zoonose supported interpretation of data in this study.
Availability of data and materials
DNA sequences obtained in this study have been submitted to GenBank database (accession number: MT498683.1-MT498686.1).
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) (Permit No. LVRIAEC-2018-001). Tick samples were collected with permission from the farmer. Each of the farmer wrote consent and consented to this study. All the procedures were conducted according to the Animal Ethics Procedures and Guidelines of the People’s Republic of China.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Qiaoyun Ren, Email: renqiaoyun@gmail.com.
Guangyuan Liu, Email: liuguangyuan_lvri@163.com.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12917-020-02538-6.
References
- 1.Maurin M, Raoult D. Q fever. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12:518–553. doi: 10.1128/cmr.12.4.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Almeida AP, Marcili A, Leite RC, Nieri-Bastos FA, Domingues LN, Martins JR, et al. Coxiella symbiont in the tick Ornithodoros rostratus (Acari: Argasidae) Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012;3:203–206. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2012.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jado I, Carranza-Rodriguez C, Barandika JF, Toledo A, Garcia-Amil C, Serrano B, et al. Molecular method for the characterization of Coxiella burnetii from clinical and environmental samples: variability of genotypes in Spain. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12:91. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Porter SR, Czaplicki G, Mainil J, Guatteo R, Saegerman C. Q fever: current state of knowledge and perspectives of research of a neglected zoonosis. Int J Microbiol. 2011;2011:248418. doi: 10.1155/2011/248418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wildman MJ, Smith EG, Groves J, Beattie JM, Caul EO, Ayres JG. Chronic fatigue following infection by Coxiella burnetii (Q fever): ten-year follow-up of the 1989 UK outbreak cohort. QJM. 2002;95:527–538. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/95.8.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ristic M, Woldehiwet Z. Rickettsial and chlamydial diseases of domestic animals. 1. Oxford: Pergamon Press; 1993. p. 427. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Derrick EH. "Q" fever, a new fever entity: clinical features, diagnosis and laboratory investigation. Rev Infect Dis. 1983;5:790–800. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Guigno D, Coupland B, Smith EG, Farrell ID, Desselberger U, Caul EO. Primary humoral antibody response to Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of Q fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1992;30:1958–1967. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.1958-1967.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schimmer B, Dijkstra F, Vellema P, Schneeberger PM, Hackert V, ter Schegget R, et al. Sustained intensive transmission of Q fever in the south of the Netherlands, 2009. Euro Surveill. 2009;14. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 10.Aguirre EC, Montejo BM, Hernandez AJ, de la Hoz TC, Martinez GE, Villate NJ, et al. An outbreak of Q fever in the Basque country. Can Med Assoc J. 1984;131:48–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schneider T, Jahn HU, Steinhoff D, Guschoreck HM, Liesenfeld O, Mater-Bohm H, et al. A Q fever epidemic in Berlin. The epidemiological and clinical aspects. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1993;118:689–695. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dupuis G, Petite J, Peter O, Vouilloz M. An important outbreak of human Q fever in a Swiss Alpine valley. Int J Epidemiol. 1987;16:282–287. doi: 10.1093/ije/16.2.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yu S. Progress in the study of Q fever in China [in Chinese] Chin J Epidemiol. 2000;21:456–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Enserink M. Infectious diseases. Questions abound in Q-fever explosion in the Netherlands. Science. 2010;327:266–267. doi: 10.1126/science.327.5963.266-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mansfield KL, Jizhou L, Phipps LP, Johnson N. Emerging tick-borne viruses in the twenty-first century. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017;7:298. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Klyachko O, Stein BD, Grindle N, Clay K, Fuqua C. Localization and visualization of a coxiella-type symbiont within the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:6584–6594. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00537-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Machado-Ferreira E, Dietrich G, Hojgaard A, Levin M, Piesman J, Zeidner NS, et al. Coxiella symbionts in the Cayenne tick Amblyomma cajennense. Microb Ecol. 2011;62:134–142. doi: 10.1007/s00248-011-9868-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bolanos-Rivero M, Carranza-Rodriguez C, Rodriguez NF, Gutierrez C, Perez-Arellano JL. Detection of Coxiella burnetii DNA in Peridomestic and wild animals and ticks in an endemic region (Canary Islands, Spain) Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017;17:630–634. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2017.2120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Norlander L. Q fever epidemiology and pathogenesis. Microbes Infect. 2000;2:417–424. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(00)00325-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pacheco RC, Echaide IE, Alves RN, Beletti ME, Nava S, Labruna MB. Coxiella burnetii in ticks, Argentina. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:344–346. doi: 10.3201/eid1902.120362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cheng C, Fu W, Ju W, Yang L, Xu N, Wang YM, et al. Diversity of spotted fever group rickettsia infection in hard ticks from Suifenhe, Chinese-Russian border. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016;7:715–9. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 22.Diuk-Wasser MA, Vannier E, Krause PJ. Coinfection by Ixodes tick-borne pathogens: ecological, epidemiological, and clinical consequences. Trends Parasitol. 2016;32:30–42. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2015.09.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Firth C, Bhat M, Firth MA, Williams SH, Frye MJ, Simmonds P, et al. Detection of zoonotic pathogens and characterization of novel viruses carried by commensal Rattus norvegicus in New York City. Mbio. 2014;5:e1914–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Niu Q, Liu Z, Yang J, Gao S, Pan Y, Guan G, et al. Genetic characterization and molecular survey of Babesia sp. Xinjiang infection in small ruminants and ixodid ticks in China. Infect Genet Evol. 2017;49:330–5. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 25.Wu XB, Na RH, Wei SS, Zhu JS, Peng HJ. Distribution of tick-borne diseases in China. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Shen S, Duan X, Wang B, Zhu L, Zhang Y, Zhang J, et al. A novel tick-borne phlebovirus, closely related to severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus and heartland virus, is a potential pathogen. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018;7:95. doi: 10.1038/s41426-018-0093-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yu Z, Wang H, Wang T, Sun W, Yang X, Liu J. Tick-borne pathogens and the vector potential of ticks in China. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:24. doi: 10.1186/s13071-014-0628-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Abdullah S, Helps C, Tasker S, Newbury H, Wall R. Ticks infesting domestic dogs in the UK: a large-scale surveillance programme. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:391. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1673-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen M, Fan MY, Bi DZ, Zhang JZ, Huang YP. Detection of rickettsia sibirica in ticks and small mammals collected in three different regions of China. Acta Virol. 1998;42:61–4. [PubMed]
- 30.Chen Z, Yang X, Bu F, Yang X, Yang X, Liu J. Ticks (Acari: ixodoidea: argasidae, ixodidae) of China. Exp Appl Acarol. 2010;51:393–404. doi: 10.1007/s10493-010-9335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fan MY, Wang JG, Jiang YX, Zong DG, Lenz B, Walker DH. Isolation of a spotted fever group rickettsia from a patient and related ecologic investigations in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region of China. J Clin Microbiol. 1987;25:628–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Wang YZ, Mu LM, Zhang K, Yang MH, Zhang L, Du JY, et al. A broad-range survey of ticks from livestock in northern Xinjiang: changes in tick distribution and the isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Kong ZM. Investigations on ticks and tick-borne natural focal infections in xinjiang. Endemic Disease Bulletin. 1987. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gonzalez J, Gonzalez MG, Valcarcel F, Sanchez M, Martin-Hernandez R, Tercero JM, et al. Prevalence of Coxiella burnetii (Legionellales: Coxiellaceae) infection among wildlife species and the tick Hyalomma lusitanicum (Acari: Ixodidae) in a Meso-Mediterranean ecosystem. J Med Entomol. 2020;572:551–556. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjz169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Varela-Castro L, Zuddas C, Ortega N, Serrano E, Salinas J, Castella J, et al. On the possible role of ticks in the eco-epidemiology of Coxiella burnetii in a Mediterranean ecosystem. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018;93:687–694. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Psaroulaki A, Chochlakis D, Angelakis E, Ioannou I, Tselentis Y. Coxiella burnetii in wildlife and ticks in an endemic area. T Roy Soc Trop Med H. 2014;10810:625–631. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/tru134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Luo D, Yin X, Wang A, Tian Y, Liang Z, Ba T, et al. First detection of Q fever Rickettsia nucleic acid at Hyalomma asiaticum at the Alashankou port on the China-Kazakh border [in Chinese]. Disease Surveillance. 2016;3110:814–6.
- 38.Jiang L, Xu L, Zhu J, Chen M. First detection of Coxiella burnetii from Dermacentor nuttalli at erguna port [in Chinese]. Chin J Front Health Quarantine. 2017;4002:108–9.
- 39.Zhang F, Liu ZZ. Molecular epidemiological studies on Coxiella burnetii from northwestern China [in Chinese] J Pathogen Biol. 2011;66:183–185. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Diarra AZ, Almeras L, Laroche M, Berenger JM, Kone AK, Bocoum Z, et al. Molecular and MALDI-TOF identification of ticks and tick-associated bacteria in Mali. Plos Neglect Trop D. 2017;117:e5762. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang M, Zhu D, Dai J, Zhong Z, Zhang Y, Wang J. Tissue localization and variation of major Symbionts in Haemaphysalis longicornis, Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides, and Dermacentor silvarum in China. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018;84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 42.Zhang R, Yu G, Huang Z, Zhang Z. Microbiota assessment across different developmental stages of Dermacentor silvarum (Acari: Ixodidae) revealed stage-specific signatures. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019;101321. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Machado-Ferreira E, Vizzoni VF, Balsemao-Pires E, Moerbeck L, Gazeta GS, Piesman J, et al. Coxiella symbionts are widespread into hard ticks. Parasitol Res. 2016;115:4691–9. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 44.Khoo JJ, Lim FS, Chen F, Phoon WH, Khor CS, Pike BL, et al. Coxiella detection in ticks from wildlife and livestock in Malaysia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016;16:744–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 45.Seo MG, Lee SH, Ouh IO, Lee GH, Goo YK, Kim S, et al. Molecular detection and genotyping of Coxiella-like Endosymbionts in ticks that infest horses in South Korea. PLoS One. 2016;11:e165784. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Duron O, Noel V, McCoy KD, Bonazzi M, Sidi-Boumedine K, Morel O, et al. The recent evolution of a maternally-inherited Endosymbiont of ticks led to the emergence of the Q fever pathogen, Coxiella burnetii. Plos Pathog. 2015;11:e1004892. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schimmer B, Dijkstra F, Vellema P, Schneeberger PM, Hackert V, ter Schegget R, et al. Sustained intensive transmission of Q fever in the south of the Netherlands. Euro Surveill. 2009;14. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 48.Zhang NC. Preliminary study on the problem of Q fever in Beijing [in Chinese]. Chin Med J. 1951;23537.
- 49.Zhai SC, Liu SH. Q fever: report of a case [in Chinese]. Chi J Int Med. 1957;3165.
- 50.Yu SR. Isolation and identification of Q fever rickettsia in Sichuan in monograph on Rickettsiaceae and Chlamydiaceae infections [in Chinese]. Chin J Epidemiol Press Beijing. 1981;18.
- 51.Li J, Li Y, Moumouni P, Lee SH, Galon EM, Tumwebaze MA, et al. First description of Coxiella burnetii and Rickettsia spp. infection and molecular detection of piroplasma co-infecting horses in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region, China. Parasitol Int. 2019;76:102028. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2019.102028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Li Y, Li J, Chahan B, Guo Q, Zhang Y, Moumouni P, et al. Molecular investigation of tick-borne infections in cattle from Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. China Parasitol Int. 2020;74:101925. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2019.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pan L, Zhang L, Fan D, Zhang X, Liu H, Lu Q, et al. Rapid, simple and sensitive detection of Q fever by loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the htpAB gene. Plos Neglect Trop D. 2013;75:e2231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ya HX, Zhang L, Zhang LJ, Bai L. Establishment of real-time PCR in detecting of Coxiella burnetii and its application to testing mouse samples collected from Yunnan province [in Chinese] Infectious Disease Information. 2009;6:345–347. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Guo YW. Tick-borne disease Q fever in thermal detection methods to establish and north and Northeast Inner Mongolia disease investigation. Jilin: Jilin Agricultural University; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 56.El-Mahallawy HS, Lu G, Kelly P, Xu D, Li Y, Fan W, et al. Q fever in China: a systematic review, 1989-2013. Epidemiol Infect. 2015;143:673–681. doi: 10.1017/S0950268814002593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Deng GF, Jiang ZJ. Economic insect fauna of China. Fasc 39 Acari: Ixodidae. Thirty-nine volumes. [in Chinese] Beijing: Science Press; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Das DP, Malik SV, Rawool DB, Das S, Shoukat S, Gandham RK, et al. Isolation of Coxiella burnetii from bovines with history of reproductive disorders in India and phylogenetic inference based on the partial sequencing of IS1111 element. Infect Genet Evol. 2014;22:67–71. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Denison AM, Thompson HA, Massung RF. IS1111 insertion sequences of Coxiella burnetii: characterization and use for repetitive element PCR-based differentiation of Coxiella burnetii isolates. BMC Microbiol. 2007;7:91. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Marmion BP, Storm PA, Ayres JG, Semendric L, Mathews L, Winslow W, et al. Long-term persistence of Coxiella burnetii after acute primary Q fever. QJM. 2005;98:7–20. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hci009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.McLaughlin HP, Cherney B, Hakovirta JR, Priestley RA, Conley A, Carter A, et al. Phylogenetic inference of Coxiella burnetii by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. PLoS One. 2017;12:e189910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Figure S1. Specificity test results of IS1111 primer.
Additional file 2: Figure S2. Sensitivity test results of IS1111 primer.
Additional file 3: Figure S3. Specificity test results of 16S rRNA primer.
Additional file 4: Figure S4. Sensitivity test results of 16S rRNA primer.
Data Availability Statement
DNA sequences obtained in this study have been submitted to GenBank database (accession number: MT498683.1-MT498686.1).