Abstract
SARS-CoV-2 has caused a severe, ongoing outbreak of COVID-19 in Massachusetts with 111,070 confirmed cases and 8,433 deaths as of August 1, 2020. To investigate the introduction, spread, and epidemiology of COVID-19 in the Boston area, we sequenced and analyzed 772 complete SARS-CoV-2 genomes from the region, including nearly all confirmed cases within the first week of the epidemic and hundreds of cases from major outbreaks at a conference, a nursing facility, and among homeless shelter guests and staff. The data reveal over 80 introductions into the Boston area, predominantly from elsewhere in the United States and Europe. We studied two superspreading events covered by the data, events that led to very different outcomes because of the timing and populations involved. One produced rapid spread in a vulnerable population but little onward transmission, while the other was a major contributor to sustained community transmission, including outbreaks in homeless populations, and was exported to several other domestic and international sites. The same two events differed significantly in the number of new mutations seen, raising the possibility that SARS-CoV-2 superspreading might encompass disparate transmission dynamics. Our results highlight the failure of measures to prevent importation into MA early in the outbreak, underscore the role of superspreading in amplifying an outbreak in a major urban area, and lay a foundation for contact tracing informed by genetic data.
SARS-CoV-2 has now caused over 22 million infections and over 775,000 deaths worldwide (1) in one of the worst public health crises of the past century. The early impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has been particularly severe in the state of Massachusetts (MA) in the northeastern United States (US). The first case in the state was confirmed on February 1, 2020 (2); case counts rapidly accelerated beginning in March and peaked in the third week in April. The Boston area, home to 70% of the population of MA, accounted for 79% of COVID-19 cases and 76% of COVID-19 deaths in the state to this point (3). COVID-19 has disproportionately affected vulnerable populations, particularly residents and staff in congregate living environments (4) and racial and ethnic minorities (5, 6). In MA, residents and healthcare workers in long-term care facilities accounted for 22% of all confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 64% of all reported deaths through August 1, 2020 (7).
COVID-19, like previous coronavirus outbreaks (8, 9), has been marked by the prominence of superspreading events (10, 11), in which one individual infects an unusually large number of secondary cases. (For this study, we define a superspreading event as the transmission of at least 8 secondary infections from a single source, corresponding to the 99th percentile (12) for an Reff of 2.5.) More broadly, a great deal of SARS-CoV-2 transmission has occurred in clusters of cases linked to events and gatherings, including on cruise ships (13), in churches (14), and especially in congregate settings such as care homes (15), homeless shelters (16), and prisons (17). However, the evidence indicating that these events drive transmission has been based largely on time-series data showing an increase in cases following them (18). Case counts alone have little ability to determine the contribution of any event to overall transmission or to distinguish superspreading from other forms of locally intense transmission. Yet understanding how the virus is actually spreading is critical for prioritizing public health interventions: cluster-based spread may be controlled with more limited restrictions than the population measures required to curb community-based transmission. Genomic data can reveal connections between cases that cannot be detected through conventional epidemiology alone, including direct evidence of superspreading based on shared viral sequences. To gain insight into the introduction and spread of SARS-CoV-2, and to examine the role of putative transmission linked to events and gatherings, we conducted a detailed genomic epidemiology study of the Boston area epidemic.
Genomic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 from the Boston Area
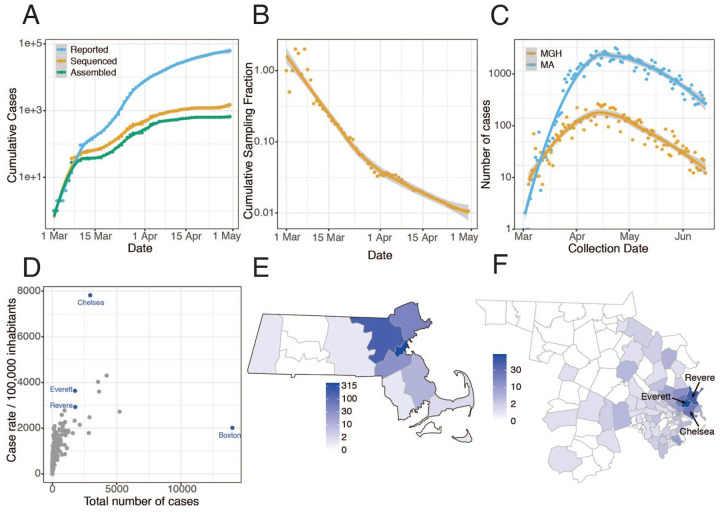
We performed viral genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of SARS-CoV-2-positive nasopharyngeal (NP) samples collected by the Massachusetts Department of Public Health (MADPH) between January 29, 2020, and April 18, 2020, and by the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) between March 4, 2020, and May 9, 2020. Our dataset includes nearly all confirmed early cases of the epidemic in MA through March 8, 2020 (Fig. 1A–B); samples from many of the highest-prevalence communities in and around Boston across the first wave (Fig. 1C), including Chelsea, Revere, and Everett (Fig. 1D–F, Fig. S1); and samples from putative superspreading events involving an international conference and congregate living environments, specifically among homeless shelter guests and staff and within a skilled nursing facility.
Fig 1. Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Massachusetts and of sequenced viral genomes.
A. Cumulative confirmed and presumed cases reported state-wide in MA (7) from March 1 through May 1, 2020, and the number of these cases that were processed (orange) and successfully yielded complete genomes with >98% coverage (green) in this study. B. Cumulative proportion of all MA confirmed positive cases with complete genome sequences from unique individuals that are part of this dataset over time. C. Daily reported cases across MA from March 1 through June 15 statewide (blue) and at MGH (orange). D. Total number of cases compared to cases per 100,000 people for cities across MA. Cities in blue are highly represented in the genome dataset. E. Distribution of MA cases with sequenced viral genomes by county. F. As in E but showing only Middlesex and Suffolk counties, the two counties with the highest number of sequenced samples, by zip code. Cases associated with congregate living environments were excluded from the maps in E and F.
Viral genomes were sequenced using Illumina-based unbiased metagenomic short-read sequencing, followed by reference-guided assembly using viral-ngs 2.0.21 software (19) with the Wuhan-Hu-1 sequence (NC_045512.2) as the reference (Materials and Methods). We generated 778 high-quality SARS-CoV-2 assemblies (>98% complete) from 772 individuals, and an additional 72 high-quality partial genomes (>80% complete) (Fig. 1A). Genome recovery and coverage were strongly correlated with viral abundance and clinical diagnostic test results (Fig. S2 and S3). Genomes were separated from one another by a median of 6 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (interquartile range 4–9 SNPs; range 0–85 SNPs) (Fig. S4A–B). As expected during rapid population expansion, most alleles were rare, as assessed by a strongly negative Tajima’s D statistic throughout the genome (Fig. S4C).
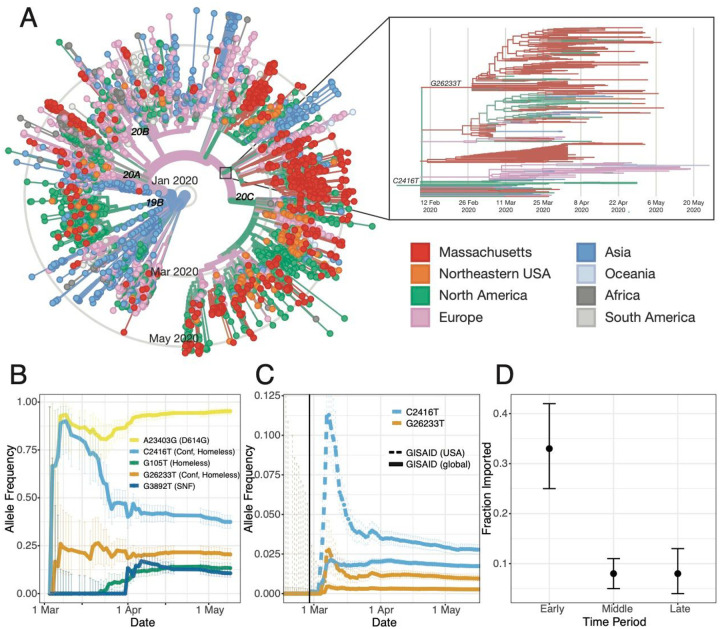
We constructed a phylogenetic tree from this dataset in the context of a global set of 4,011 high-quality genomes (Fig. 2A) drawn from the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID) (Materials and Methods). Root-to-tip regression showed a clear, albeit noisy, temporal signal in our dataset, with the fitted regression model accounting for 17% of the variance in the root-to-tip distance (Fig. S5). The presence of a temporal signal means that a molecular clock can be fitted to infer the timing of ancestral branching based on SARS-CoV-2 genomes. These trees form the basis of our analysis of the Boston area epidemic.
Fig 2. A.
A. Time tree of 772 MA genomes and a global set of 4,011 high-quality genomes from GISAID. The embedded panel shows the C2416T clade in detail (outlined in gray on the main tree). To view an interactive version of this tree and for more information on specific sub-groupings within the MA dataset see auspice.broadinstitute.org. B. Estimated allele frequency in sequenced genomes over time for major Boston-area lineages. C. Frequency of the C2416T allele in 58,043 GISAID samples reported through July 14, 2020. D. Proportion of genomes that were inferred as imported (ancestral state as not from MA) in the early (prior to March 28, 2020), middle (March 28 - April 14, 2020) and late (after April 15, 2020) time periods of the MA epidemic.
Introduction of SARS-CoV-2 into Massachusetts
We identified putative introductions into MA through phylogenetic analysis using an ancestral inference model (Materials and Methods). Most introductions of SARS-CoV-2 into MA occurred early in the pandemic, in March and early April, primarily from elsewhere in North America and from Europe (Table 1, Fig. 2D, and Fig. S6). We observed close connectivity between genome sequences from MA and genome sequences from elsewhere in the Northeastern USA, in particular New York (Fig. 2k). Close interstate connectivity is consistent with frequent domestic travel, which continued even after international routes were closed. The fraction of cases that were imported decreased over time (Fig. 2D), with the steepest decline during March (Fig. S6). By April 2020, the vast majority of cases resulted from local transmission rather than importation (Table 1, Fig. 2D, and Fig. S6). In total, we identified more than 80 likely introductions into MA through May 9, representing sources on four continents (Table 1).
Table 1.
Ancestral trait inference. Results of discrete trait inference using a binary model (MA vs non-MA) and regional model (regional geographic categories) are shown, divided into date ranges representing the early, middle, and late period of the first wave of the MA epidemic.
| Region | Before March 28 | March 28 - April IB | After April 15 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binary model | |||
| Imported (Non-MA) | 44 | 24 | 14 |
| Not imported (MA) | 90 | 289 | 172 |
| Regional model | |||
| North America | 18 | 17 | 5 |
| Europe | 18 | 3 | 4 |
| Oceania | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Asia | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Early diagnosed cases in MA cluster in a way consistent with their known travel and exposure history. This includes the first known COVID-19 case in MA, a traveler returning from Wuhan, China (2). Phylogenetic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from this case (named MA-1 by the CDC), based on a sample collected January 29, 2020, revealed that it clustered with others from China (Fig. S7), confirming its likely origin. Similarly, the viral sequence of the second known MA case (MA_DPH_00002), collected on March 3 from a patient who had recently traveled to Italy and Switzerland (21) clustered with European sequences (Fig. S8) and is descended from the SARS-CoV-2 genome seen in a third MA case (MA_DPH_00003), a patient who had been on the same trip. No other viral genomes in our dataset appeared to descend from these 3 cases. Thus, quarantine and contact tracing efforts appear to have prevented spread from the first known introductions into MA.
We also investigated the first cases of community transmission in MA, which occurred in Berkshire County and included several patients who had attended the same public event. Analysis of 5 viral genomes (1 complete and 4 partial) from these cases indicated that the cluster involved at least 2 introductions (Fig. S9). Four of the genomes had the same consensus sequence, indicating a common source, most likely within the United States (Fig. S10); based on the presence of the C17747T variant (i.e. a T instead of a C at position 17747), it was probably from the West Coast. We are unable to assess subsequent community transmission in Western MA since our data does not include any later Western MA samples.
Investigation of Superspreading Events
Spread of SARS-CoV-2 in an International Business Conference
The first large cluster of cases in MA was recognized in the context of an international business conference held in Boston from February 26 – 27 (18). Ultimately, more than 90 cases were diagnosed in people associated with this conference or their contacts (22), raising suspicion that a superspreading event had occurred there. Our dataset contains SARS-CoV-2 genomes from 28 of these cases, allowing us to look for genetic evidence of superspreading. Genetic evidence of superspreading would take the form of phylogenetic clustering of identical or highly similar viruses occurring in a narrow time window.
The signature of superspreading can indeed be seen in the conference-associated cases. All 28 genomes form a well-supported monophyletic cluster (Fig. 3A, Fig. S11) marked by the presence of the SNP C2416T (Fig. 2B–C). The parent lineage of C2416T is defined by G25563T, a lineage that was widely distributed in Europe in January and February 2020. The estimated time to the most recent common ancestor (tMRCA) for C2416T-containing genomes is February 14 (95% highest posterior density (HPD) February 4 – February 20). The C2416T variant first appears in the GISAID database in 2 French patients, ages 87 and 88, on February 29, 2020, and is absent from the 1,312 genomes in the database sampled prior to February 29 (Fig. 2C). In our dataset, all 27 C2416T-containing viruses collected prior to March 10th were sampled from individuals with conference exposure, consistent with publicly available CDC genome data from MA cases from January 29 through March 7 (24). The rarity of C2416T in February (Fig. 2C) makes additional introductions of this allele unlikely. Taken together, this strongly suggests there was low-level community transmission of C2416T in Europe in February 2020 before the allele was introduced to Boston via a single introduction and amplified by superspreading at the conference.
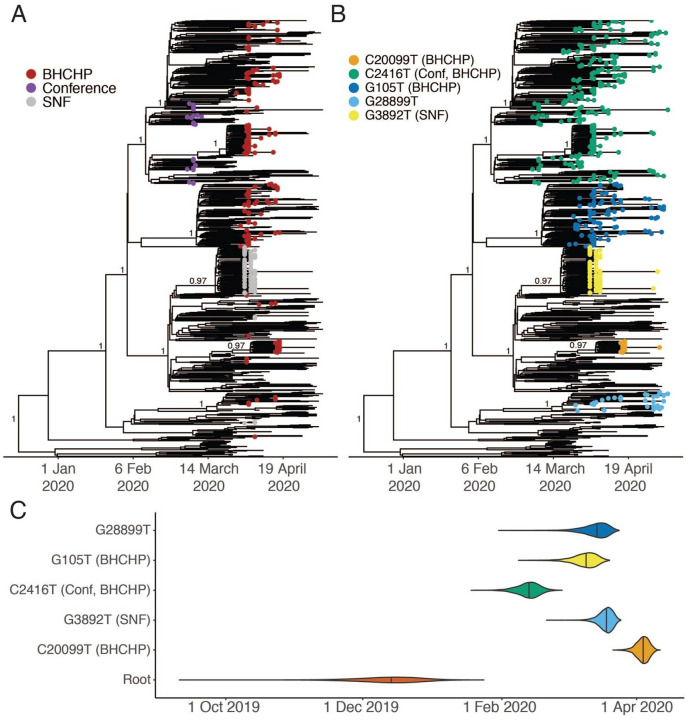
Fig 3. A.
A. Time-measured maximum-likelihood phylogeny of 772 MA genomes. B. Maximum clade credibility tree with tips labeled by clade. Nodes with posterior support > 0.8 are labeled. C. Violin plots of tMRCA for the major Boston-area clades.
SARS-CoV-2 containing the C2416T allele subsequently spread extensively in the Boston area, representing 261/744 or 35.1% of our dataset (exclusive of known-conference associated genomes) (Fig 2B, see Sustained Local Transmission below). Beginning in early March, C2416T also appeared in multiple other US states and other countries (Fig. 2A) and increased steeply in frequency, comprising 319/11,938 (2.7%) of domestic and 937/56,118 (1.7%) of global SARS-CoV-2 genomes in GISAID collected through June 28 (Fig. 2C). The superspreading event appears to have contributed to this rise in frequency, as observed in two ways. Firstly, we identified a second variant (G26233T) that shows strong evidence of emerging during or immediately after the conference as it was first seen in 7 of 28 individuals with known exposure to the conference, including in one sample from a conference attendee at intermediate frequency (26%). C2416T/G26233T was subsequently exported from Boston to several US states, including Virginia, North Carolina, and Texas, and to other countries, including Australia, Sweden, and Slovakia (Fig. 2A, Fig. S12A–B), with evidence of community spread in Virginia, Australia, and Michigan. Secondly, we assessed the extent to which US spread of C2416T could be due to additional importations from Europe. Two European sub-lineages (C2416T/G8371T and C2416T/G20578T) are extremely rare in the United States: 0/73 genomes and 1/228 genomes, respectively, compared with 24/197 genomes containing the C2416T/G26233T mutations (Fig. S12C–D). This, along with epidemiological data connecting multiple conference-linked cases to other US states (25–28), suggests that most C2416T viruses in the US likely derive from this initial introduction. However, we cannot estimate the absolute number of individuals involved as sequenced genomes are not a random sample of cases and US state-level data is highly incomplete at this time.
Spread of SARS-CoV-2 In Homeless Shelter Guests and Staff
To support public health investigations of transmission in high priority populations, we analyzed the introduction and spread of SARS-CoV-2 in homeless shelter guests and staff served by the Boston Health Care for the Homeless Program (BHCHP). Samples were collected in March and April 2020 and included those collected during universal screening at Boston’s largest homeless shelter(16). From these samples, we assembled and inferred a phylogeny from 193 SARS-CoV-2 genomes (Fig. 2A, Fig. 3A and Fig. 3B). We identified at least 7 introductions into the BHCHP population, including 4 that resulted in clusters containing 20 or more highly similar viral genomes (Fig. 4A and Fig. 4C); a phylogenetic signature consistent with superspreading. Two of the clusters were of genomes descended from the C2416T lineage: of the 193 genomes, 105 (54.4%) contained C2416T, and 54 of these 105 (51.4%) additionally contained G26233T, demonstrating that BHCHP guests and staff were affected by community transmission resulting from conference-associated amplification and spread of SARS-CoV-2.
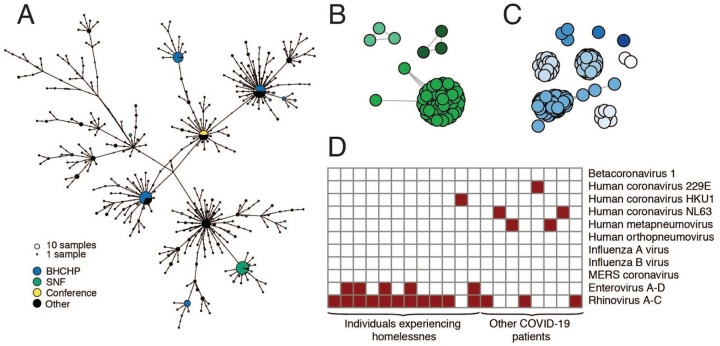
Fig 4. SARS-CoV-2 superspreading events.
A. Haplotype network of SARS-CoV-2 haplotypes in the MA dataset with major known superspreading events highlighted. B, C. Gene graphs showing clusters of highly similar sequences among viral genomes from the SNF (B) and BHCHP (C) cohorts. Sequences are clustered when they are separated by < 4 SNPs, and the lengths of lines between points reflect genetic distance. D. Detection of common respiratory viruses from metagenomic sequencing data. Samples with >10 reads mapped to at least 1 of these viruses using Kraken2 are shown in red. Enterovirus and Rhinovirus species have been grouped due to difficulty in discriminating at the sequence level.
Spread of SARS-CoV-2 In a Skilled Nursing Facility
We also investigated cases in another vulnerable population, cases that were involved in a superspreading event at a skilled nursing facility (SNF) in the Boston area. Prior to a planned relocation of residents in early April, universal screening detected SARS-CoV-2 in 82/97 (85%) of the residents and 36/97 (37%) of the staff by RT-qPCR (29). We assembled 83 SARS-CoV-2 genomes from these individuals, 75 of which comprised a single cluster of closely related genomes (59 identical), all containing a G3892T mutation (posterior support of 1 in maximum clade credibility tree, Fig. 3A and Fig. 3B). The paucity of genetic variation within the cluster implies that introduction into the facility had been recent and from a single predominant source (Fig. 4A). Consistent with this, the median tMRCA for sequences in the cluster was March 20 (Fig. 3C, 95 % HPD: March 13 - March 24, 2020). The estimated tMRCA along with the high proportion (30/45) of residents who tested negative on April 1, 2020, but were found to be positive 5 days later (29) suggests rapid spread within the facility in late March and early April 2020.
The genetic diversity in the SNF cluster is strikingly low even under the assumption of recent transmission from a single source. The 18 mutations seen in the cluster is significantly lower than what we would expect based on the conference cluster (p = 0.019), which occurred over a similarly short time window, and much lower than the 30 mutations expected under a simple model of SARS-CoV-2 substitution (p = 0.011, Materials and Methods). The low genetic diversity in this cluster might simply result from low diversity in the index patient, but could also reflect differences in the transmission process at work. For example, if more virions than usual were transmitted to each SNF case, then the resulting infections would more often have the same consensus genome as the index case.
In addition to the major SNF cluster, two other introductions, each containing three genomes, can also be seen among the patients and staff in the SNF (Fig. 3A and Fig. 4B). There is strong phylogenetic support for each of these two separate introductions (Fig 3A). The observation that one introduction led to massive spread, while the other two did not, is consistent with reported overdispersion of secondary infections in several coronaviruses (8, 12, 30, 31); that is, there is more variance in the number of secondary infections caused by each case than expected from a random Poisson process. Although one clade predominated within this SNF, the occurrence of at least three independent introductions underscores the high risk of introduction into a single facility (32). These introductions occurred despite strict infection control policies—including a restriction on visitors (33), universal masking for all staff, masking for all residents when leaving their rooms, and vigilance with hand hygiene—in place for at least two weeks before the first detected infection (29).
Investigation of potential nosocomial outbreaks
We investigated two case clusters at MGH for which the Infection Control Unit raised suspicions of a nosocomial outbreak. In the first cluster, two patients in the same hospital ward tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 during their hospital stay after testing negative at the time of admission. In the second cluster, five patients who received care in a speciality ward were diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infections over a period of several days. For each cluster, complete genomes (2 of 2 from the first cluster and 4 of 5 from the second cluster) were inconsistent with a common ancestor during the period of hospitalization (Fig. S13). We therefore rejected the hypothesis that the individuals in each cluster were part of the same transmission chain, although we cannot exclude the possibility of nosocomial transmission per se because independent introductions from multiple asymptomatic staff could theoretically have occurred.
Sustained Local Transmission
Our dataset covers March 3 through May 9, an interval that spans the beginning, peak, and initial decline of the first wave of the epidemic in MA (Fig. 1C). Several clades established early in the Boston-area outbreak showed continued community transmission throughout that period (Table 2, Fig. 3A–B), with the lineage containing C2416T, associated with the conference, being the largest. The C2416T lineage was likely the first of these clades imported into Boston (median estimated tMRCA, February 14, 2020; 95% HPD February 4 – 20, 2020) (Fig. 3C). The other four major lineages (G3892T, G105T, G28899T, and C20099T) appeared to enter the region between March and early April 2020. Consistent with a larger global trend (34, 35), we observed a rise in frequency of viruses harboring the D614G amino acid polymorphism, conferred by a SNP at nucleotide 23,403 in the Wuhan reference strain, which rose to near-fixation in MA by the end of the study period (Fig. 2B) and is present in all of the dominant lineages.
Table 2:
Major Boston-area lineages identified by lineage-defining mutation.
| Lineage | Root | C20099T | G3892T | C2416T | G105T | G28899T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Genomes | 772 | 21 | 77 | 288 | 98 | 34 |
| Epidemiology | BHCHP | SNF | Conference, BHCHP | BHCHP | ||
| Amino Acid substitution | ORF1b: A2211V; NSP15: A160V | ORF1a: E1209D; NSP3: E391D | N: R56I, ORF14: E56* | |||
| Median tMRCA (95% HPD) | 2019-12-15 (2019-11-20 – 2019-01-04) | 2020-04-04 (2020-03-30 – 2020-04-08) | 2020-03-19 (2020-03-13 – 2020-03-23) | 2020-02-14 (2020-02-04 – 2020-02-20) | 2020-03-10 (2020-03-01 – 2020-03-16) | 2020-03-15 (2020-03-04 – 2020-03-21) |
Based on tMRCA estimates for major Boston-area clades, we do not find evidence of undetected, or “cryptic,” transmission before mid-February, although small outbreaks may have gone undetected. In addition to the lineages reported here, none of the importation events we inferred (Table 1) occurred prior to known cases, although testing for SARS-CoV-2 in MA was restricted to a narrow definition prior to established community spread (36). In particular, additional isolated events similar to the MA-1 importation may have occurred and escaped detection with the current resolution of sampling.
Phylogenetic data, when labeled by patient zip code (Fig. S14), reveal that all major lineages, including conference-associated viruses, were circulating in the Boston-area communities of Chelsea, Revere, and Everett, which were among the most heavily affected communities in the state (Fig. 1D). Thus, while viral lineages entered and were amplified by distinct mechanisms, cases rapidly spread between communities (Fig. S15). C2416T was the most common lineage in the Boston area throughout the study period and across sampling sites (Fig. S16). By the end of that period, the cumulative allele frequency of C2416T in our dataset, exclusive of conference- and SNF-associated samples, was 46.4% (194/418) in Suffolk, 30.1% (31/103) in Middlesex, 30.0% in Essex (12/40), and 40.9% (9/22) in Norfolk counties. The conference superspreading event likely had an outsized effect because it occurred early in the pandemic (Fig. S17). Extensive spread within the Boston area likely then contributed to the rise in frequency of C2416T and C26233T in the United States and worldwide (Fig. 2B–C).
Respiratory Viral Coinfections
The metagenomic approach we used for sequencing SARS-CoV-2 enabled us to screen for respiratory viral co-infections in patients with COVID-19. We found other respiratory viruses in 20/1431 (1.4%) of COVID-19 cases (Fig. 4D) and confirmed these results using the BioFire FilmArray Respiratory Panel (Fig. S18). The most common co-infecting viruses were Rhinovirus/Enterovirus. The rarity of co-infections (lower than reported in an early dataset from California (37)) likely reflects the timing of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in MA, which began near the end of the influenza season; weekly data from MADPH show rapidly declining influenza activity in March and April 2020 (38). We observed a higher rate of co-infection with other respiratory pathogens among BHCHP clients and staff (12/314) than in the other samples in our dataset (8/1117) (p = 0.0002, Fisher’s exact test), consistent with an increased epidemiological risk in this population.
Conclusions
We present here an analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomic epidemiology primarily in the Boston area, which was severely affected early in the US COVID-19 epidemic. Through dense sampling of the early phase of the epidemic we show the frequency of importation events—over 80 independent introductions—and the impact of early superspreading events in driving amplification and community transmission, likely accelerating the transition from containment to mitigation strategies.
Besides better understanding of outbreak dynamics, viral sequencing and phylogenetic analysis can also provide immediately actionable insights. In the current study, we were able to rule out linked nosocomial spread in two episodes, reassuring hospital management that a failure of infection control practice in these wards had not led to a nosocomial cluster, and showed that despite multiple introductions of SARS-CoV-2 into a SNF, one introduction was responsible for 90% of cases. Real-time genomic epidemiology may be increasingly valuable as schools and workplaces navigate the challenges of reopening, as it can help distinguish between local outbreaks within institutions and introductions from outside.
The relatively narrow surveillance definition for SARS-CoV-2 in MA until March 4 may have limited identification of other early introductions or delayed detection of some individuals who did not meet testing criteria. Similarly, the dataset is not a random sample overtime, comprised instead largely of cases that fell in the MGH catchment area or that were sampled from particular subpopulations to gain insight into local epidemiology.
Our findings repeatedly highlight the close relationships between seemingly disconnected groups and populations: viruses from international business travel seeded major outbreaks among individuals experiencing homelessness, spread throughout the Boston area, and were exported to other domestic and international sites. It also illustrates the role of chance in the trajectory of an epidemic: a single introduction had an outsize effect on subsequent transmission because it was unfortunately amplified by superspreading in a highly mobile population very early in the outbreak, before many precautions were put in place and when its effects would be further amplified by exponential growth. By contrast, other early introductions led to very little onward transmission, and another superspreading event in a SNF, while devastating to the residents, had little large-scale effect because it occurred later and in a more isolated population. This study provides direct evidence that superspreading events may profoundly alter the course of an epidemic and implies that prevention, detection, and mitigation of such events should be a priority for public health efforts.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements:
We gratefully acknowledge the microbiology lab staff at MGH and DPH and all members of the COVID-19 emergency response efforts at MGH, BHCHP, and MADPH. We also thank Hayden C. Metsky for valuable feedback.
Funding: This work was sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (U19AI110818 to P.C.S; R37AI147868 to J.L.), the National Human Genome Research Institute (K99HG010669 to S.K.R.), the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (U54GM088558 W.P.H.), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U01CK000490; MGH), the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Broad Institute), and the US Food and Drug Administration (HHSF223201810172C), with in-kind support from Illumina, Inc., as well as support from the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation (J.E.L.), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (P.C.S.), the Herchel Smith Fellowship (K.A.L.), and the Evergrande COVID-19 Response Fund Award from the Massachusetts Consortium on Pathogen Readiness (J.L). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Footnotes
Competing interests: J.E.L. has received consulting fees from Sherlock Biosciences. J.B. has been a consultant for T2 Biosystems, DiaSorin, and Roche Diagnostics. A.P. is a Venture Partner at Google Ventures. P.C.S. is a co-founder and shareholder of Sherlock Biosciences, and a Board member and shareholder of Danaher Corporation.
Data and materials availability: Sequences and genome assembly data are publicly available in the Broad Institute’s Terra platform in a featured workspace for COVID-19. Researchers can use this workspace to reproduce analyses described here or perform similar analyses on their own viral sequence data. Assembled genomes and raw metagenomic reads from this dataset have been deposited at NCBI’s Genbank and SRA databases under BioProject PRJNA622837 in accordance with NIAID’s Data Sharing policy and will soon be available to visualize on nextstrain.org/ncov. Experimental protocols are publicly available on Benchling and can be accessed here: https://benchlina.com/sabetilab/f_/gaLGu5X9-sabeti_group_sars-cov-2_metaaenomic_seauencing_protocols/
References
- 1.Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU), COVID-19 Dashboard, (available at https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.MA Department of Public Health, Man returning from Wuhan, China is first case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus confirmed in Massachusetts (2020), (available at https://www.mass.gov/news/man-returning-from-wuhan-china-is-first-case-of-2019-novel-coronavirus-confirmed-in).
- 3.Coronavirus COVID-19 Cases in Massachusetts (2020), (available at http://boston.maps.arcgis.eom/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/a2f67ae8147948919ea2f99dd09d0955).
- 4.Arons M. M., Hatfield K. M., Reddy S. C., Kimball A., James A., Jacobs J. R., Taylor J., Spicer K., Bardossy A. C., Oakley L. P., Tanwar S., Dyal J. W., Harney J., Chisty Z., Bell J. M., Methner M., Paul P., Carlson C. M., McLaughlin H. P., Thornburg N., Tong S., Tamin A., Tao Y., Uehara A., Harcourt J., Clark S., Brostrom-Smith C., Page L. C., Kay M., Lewis J., Montgomery P., Stone N. D., Clark T. A., Honein M. A., Duchin J. S., Jernigan J. A., Public Health-Seattle and King County and CDC COVID-19 Investigation Team, Presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Transmission in a Skilled Nursing Facility. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 2081–2090 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Webb Hooper M., Nápoles A. M., Pérez-Stable E. J., COVID-19 and Racial/Ethnic Disparities. JAMA (2020), doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.8598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Williamson E. J., Walker A. J., Bhaskaran K., Bacon S., Bates C., Morton C. E., Curtis H. J., Mehrkar A., Evans D., Inglesby P., Cockburn J., McDonald H. I., MacKenna B., Tomlinson L., Douglas I. J., Rentsch C. T., Mathur R., Wong A. Y. S., Grieve R., Harrison D., Forbes H., Schultze A., Croker R., Parry J., Hester F., Harper S., Perera R., Evans S. J. W., Smeeth L., Goldacre B., OpenSAFELY: factors associated with COVID-19 death in 17 million patients. Nature (2020), doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.COVID-19 Response Reporting. Massachusetts Department of Public Health (2020), (available at https://www.mass.gov/info-details/covid-19-response-reporting).
- 8.Shen Z., Ning F., Zhou W., He X., Lin C., Chin D. P., Zhu Z., Schuchat A., Superspreading SARS events, Beijing, 2003. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 10, 256–260 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kupferschmidt K., “Superspreading event” triggers MERS explosion in South Korea. Science (2015), doi: 10.1126/science.aac4673. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hamner L., Dubbel P., Capron I., Ross A., Jordan A., Lee J., Lynn J., Ball A., Narwal S., Russell S., Patrick D., Leibrand H., High SARS-CoV-2 Attack Rate Following Exposure at a Choir Practice - Skagit County, Washington, March 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 69, 606–610 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.James A., Eagle L., Phillips C., Hedges D. S., Bodenhamer C., Brown R., Wheeler J. G., Kirking H., High COVID-19 Attack Rate Among Attendees at Events at a Church - Arkansas, March 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 69, 632–635 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lloyd-Smith J. O., Schreiber S. J., Kopp P. E., Getz W. M., Superspreading and the effect of individual variation on disease emergence. Nature. 438, 355–359 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tabata S., Imai K., Kawano S., Ikeda M., Kodama T., Miyoshi K., Obinata H., Mimura S., Kodera T., Kitagaki M., Sato M., Suzuki S., Ito T., Uwabe Y., Tamura K., Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in 104 people with SARS-CoV-2 infection on the Diamond Princess cruise ship: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. (2020), doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30482-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wei W. E., Li Z., Chiew C. J., Yong S. E., Toh M. P., Lee V. J., Presymptomatic Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 - Singapore, January 23-March 16, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 69, 411–415 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.McMichael T. M., Currie D. W., Clark S., Pogosjans S., Kay M., Schwartz N. G., Lewis J., Baer A., Kawakami V., Lukoff M. D., Ferro J., Brostrom-Smith C., Rea T. D., Sayre M. R., Riedo F. X., Russell D., Hiatt B., Montgomery P., Rao A. K., Chow E. J., Tobolowsky F., Hughes M. J., Bardossy A. C., Oakley L. P., Jacobs J. R., Stone N. D., Reddy S. C., Jernigan J. A., Honein M. A., Clark T. A., Duchin J. S., Public Health-Seattle and King County, EvergreenHealth, and CDC COVID-19 Investigation Team, Epidemiology of Covid-19 in a Long-Term Care Facility in King County, Washington. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 2005–2011 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Baggett T. P., Keyes H., Sporn N., Gaeta J. M., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Residents of a Large Homeless Shelter in Boston. JAMA (2020), doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Frieden T. R., Lee C. T., Identifying and Interrupting Superspreading Events-Implications for Control of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 26, 1059–1066 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schuchat A., CDC COVID-19 Response Team, Public Health Response to the Initiation and Spread of Pandemic COVID-19 in the United States, February 24–April 21, 2020. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 69 (2020), pp. 551–556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Park D. J., Dudas G., Wohl S., Goba A., Whitmer S. L. M., Andersen K. G., Sealfon R. S., Ladner J. T., Kugelman J. R., Matranga C. B., Winnicki S. M., Qu J., Gire S. K., Gladden-Young A., Jalloh S., Nosamiefan D., Yozwiak N. L., Moses L. M., Jiang P.-P., Lin A. E., Schaffner S. F., Bird B., Towner J., Mamoh M., Gbakie M., Kanneh L., Kargbo D., Massally J. L. B., Kamara F. K., Konuwa E., Sellu J., Jalloh A. A., Mustapha I., Foday M., Yillah M., Erickson B. R., Sealy T., Blau D., Paddock C., Brault A., Amman B., Basile J., Bearden S., Belser J., Bergeron E., Campbell S., Chakrabarti A., Dodd K., Flint M., Gibbons A., Goodman C., Klena J., McMullan L., Morgan L., Russell B., Salzer J., Sanchez A., Wang D., Jungreis I., Tomkins-Tinch C., Kislyuk A., Lin M. F., Chapman S., Maclnnis B., Matthews A., Bochicchio J., Hensley L. E., Kuhn J. H., Nusbaum C., Schieffelin J. S., Birren B. W., Forget M., Nichol S. T., Palacios G. F., Ndiaye D., Happi C., Gevao S. M., Vandi M. A., Kargbo B., Holmes E. C., Bedford T., Gnirke A., Ströher U., Rambaut A., Garry R. F., Sabeti P. C., Ebola Virus Epidemiology, Transmission, and Evolution during Seven Months in Sierra Leone. Cell. 161, 1516–1526 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.COVID-19 Investigation Team, Clinical and virologic characteristics of the first 12 patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the United States. Nat. Med. 26, 861–868 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Presumptive Positive COVID-19 Case Announced in Mass. has R.I. Connection. Rhode Island official government website (2020), (available at https://www.ri.gov/press/view/37835). [Google Scholar]
- 22.MA Department of Public Health, Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Cases in MA, March 15 2020 (2020).
- 23.Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 15 New Presumptive Positive Cases of COVID-19 Identified by Massachusetts State Public Health Laboratory (2020), (available at https://www.mass.gov/news/15-new-presumptive-positive-cases-of-covid-19-identified-by-massachusetts-state-public-health).
- 24.The CDC sequenced 19 MA genomes prior to March 8 2020. 17/19 cases (89%) contained C2416T. The CDC MA genomes are not annotated with exposure information, but given official MADPH data reporting that 23/28 cases as of March 8 2020 were linked to the conference (19), and the five non-conference associated cases include the travel-associated cases from this time period (MA-1, DPH_00002, and DPH_00003) and one from the Berkshire county cluster (all of which lack C2416), it can be inferred that a minimum of 16/17 C2416T-containing samples sequenced by the CDC were conference-associated.
- 25.Tennesse Department of Health, TDH Releases Further Information Regarding COVID-19 Case (2020), (available at https://www.tn.gOv/health/news/2020/3/5/tdh-releases-further-information-regarding-covid-19-case.html).
- 26.North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services, Five More People in North Carolina Test Positive for COVID-19 (2020), (available at https://www.ncdhhs.gov/news/press-releases/five-more-people-north-carolina-test-positive-covid-19).
- 27.Indiana State Department of Health, State Health Department Confirms 1st Case of COVID-19 in Hoosier with Recent Travel (2020).
- 28.Indiana State Department of Health, State Health Department Announces 2nd COVID-19 Case (2020), (available at https://calendar.in.gov/site/isdh/event/isdh-news-release-state-health-department-announces-2nd-covid-19-case/).
- 29.Goldberg S. A., Lennerz J., Klompas M., Mark E., Pierce V. M., Thompson R. W., Pu C. T., Ritterhouse L. L., Dighe A., Rosenberg E. S., Grabowski D. C., Presymptomatic Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Amongst Residents and Staff at a Skilled Nursing Facility: Results of Real-Time PCR and Serologic Testing. Clin. Infect. Dis. (2020), doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Endo A., Centre for the Mathematical Modelling of Infectious Diseases COVID-19 Working Group, Abbott S., Kucharski A. J., Funk S., Estimating the overdispersion in COVID-19 transmission using outbreak sizes outside China. Wellcome Open Res. 5, 67 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cho S. Y., Kang J.-M., Ha Y. E., Park G. E., Lee J. Y., Ko J.-H., Lee J. Y., Kim J. M., Kang C.-l., Jo I. J., Ryu J. G., Choi J. R., Kim S., Huh H. J., Ki C.-S., Kang E.-S., Peck K. R., Dhong H.-J., Song J.-H., Chung D. R., Kim Y.-J., MERS-CoV outbreak following a single patient exposure in an emergency room in South Korea: an epidemiological outbreak study. Lancet. 388, 994–1001 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Quicke K., Gallichote E., Sexton N., Young M., Janich A., Gahm G., Carlton E. J., Ehrhart N., Ebel G. D., Longitudinal Surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 RNA Among Asymptomatic Staff in Five Colorado Skilled Nursing Facilities: Epidemiologic, Virologie and Sequence Analysis. medRxiv (2020), doi: 10.1101/2020.06.08.20125989. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bharel M., Order of the Commisioner of Public Health (2020), (available at https://www.mass.gov/doc/march-15-2020-assisted-living-visitor-restrictions-order/download).
- 34.Yurkovetskiy L., Pascal K. E., Tompkins-Tinch C., Nyalile T., Wang Y., Baum A., Diehl W. E., Dauphin A., Carbone C., Veinotte K., Egri S. B., Schaffner S. F., Lemieux J. E., Munro J., Sabeti P. C., Kyratsous C., Shen K., Luban J., SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein variant D614G increases infectivity and retains sensitivity to antibodies that target the receptor binding domain. bioRxiv (2020), p. 2020.07.04.187757. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Korber B., Fischer W. M., Gnanakaran S., Yoon H., Theiler J., Abfalterer W., Hengartner N., Giorgi E. E., Bhattacharya T., Foley B., Hastie K. M., Parker, Partridge D. G., Evans C. M., Freeman T. M., de Silva T. I., McDanal C., Perez L. G., Tang H., Moon-Walker A., Whelan S. P., LaBranche C. C., Saphire E. O., Montefiori D. C., Angyal A., Brown R. L., Carrilero L., Green L. R., Groves D. C., Johnson K. J., Keeley A. J., Lindsey B. B., Parsons P. J., Raza M., Rowland-Jones S., Smith N., Tucker R. M., Wang D., Wyles M. D., Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus. Cell (2020), doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.MA Department of Public Health, Update and Interim Guidance on Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Wuhan, China (2020), (available at https://www.mass.gov/clinical-advisory/update-and-interim-guidance-on-outbreak-of-2019-novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov-in).
- 37.Kim D., Quinn J., Pinsky B., Shah N. H., Brown I., Rates of Co-infection Between SARS-CoV-2 and Other Respiratory Pathogens. JAMA (2020), doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Massachusetts Department of Public Health (MDPH) Weekly Influenza Update (2020), (available at https://www.mass.gov/doc/weekly-flu-report-may-22-2020/download).
- 39.Matranga C. B., Gladden-Young A., Qu J., Winnicki S., Nosamiefan D., Levin J. Z., Sabeti P. C., Unbiased Deep Sequencing of RNA Viruses from Clinical Samples. J. Vis. Exp. (2016), doi: 10.3791/54117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Matranga C. B., Andersen K. G., Winnicki S., Busby M., Gladden A. D., Tewhey R., Stremlau M., Berlin A., Gire S. K., England E., Moses L. M., Mikkelsen T. S., Odia I., Ehiane P. E., Folarin O., Goba A., Kahn S. H., Grant D. S., Honko A., Hensley L., Happi C., Garry R. F., Malboeuf C. M., Birren B. W., Gnirke A., Levin J. Z., Sabeti P. C., Enhanced methods for unbiased deep sequencing of Lassa and Ebola RNA viruses from clinical and biological samples. Genome Biol. 15, 519 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Katoh K., Standley D. M., MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 772–780 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ihaka R., Gentleman R., R: A Language for Data Analysis and Graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 5, 299–314 (1996). [Google Scholar]
- 43.Guindon S., Dufayard J. F., Hordijk W., Lefort V., Gascuel O., in Infection Genetics and Evolution (ELSEVIER SCIENCE BV PO BOX 211, 1000 AE AMSTERDAM, NETHERLANDS, 2009), vol. 9, pp. 384–385. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rambaut A., Lam T. T., Max Carvalho L., Pybus O. G., Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2, vew007 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nguyen L.-T., Schmidt H. A., von Haeseler A., Minh B. Q., IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 32, 268–274 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wood D. E., Lu J., Langmead B., Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 20, 257 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hadfield J., Megill C., Bell S. M., Huddleston J., Potter B., Callender C., Sagulenko P., Bedford T., Neher R. A., Nextstrain: real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics. 34, 4121–4123 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Leigh J. W., Bryant D., POPART: full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 6, 1110–1116 (2015). [Google Scholar]
- 49.Clement M., Posada D., Crandall K. A., TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 9, 1657–1659 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Jombart T., Ahmed I., adegenet 1.3–1: new tools for the analysis of genome-wide SNP data. Bioinformatics. 27, 3070–3071 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ferretti L., Wymant C., Kendall M., Zhao L., Nurtay A., Abeler-Dörner L., Parker M., Bonsall D., Fraser C., Quantifying SARS-CoV-2 transmission suggests epidemic control with digital contact tracing. Science. 368 (2020), doi: 10.1126/science.abb6936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gentleman R. C., Carey V. J., Bates D. M., Bolstad B., Dettling M., Dudoit S., Ellis B., Gautier L., Ge Y., Gentry J., Hornik K., Hothorn T., Huber W., lacus S., Irizarry R., Leisch F., Li C., Maechler M., Rossini A. J., Sawitzki G., Smith C., Smyth G., Tierney L., Yang J. Y. H., Zhang J., Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 5, R80 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wickham H., Averick M., Bryan J., Chang W., McGowan L. D., François R., Grolemund G., Hayes A., Henry L., Hester J., et al. , Welcome to the Tidyverse. Journal of Open Source Software. 4, 1686 (2019). [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yu G., Smith D. K., Zhu H., Guan Y., Lam T. T., ggtree : an r package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 8, 28–36 (2017). [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.