Graphical Abstract
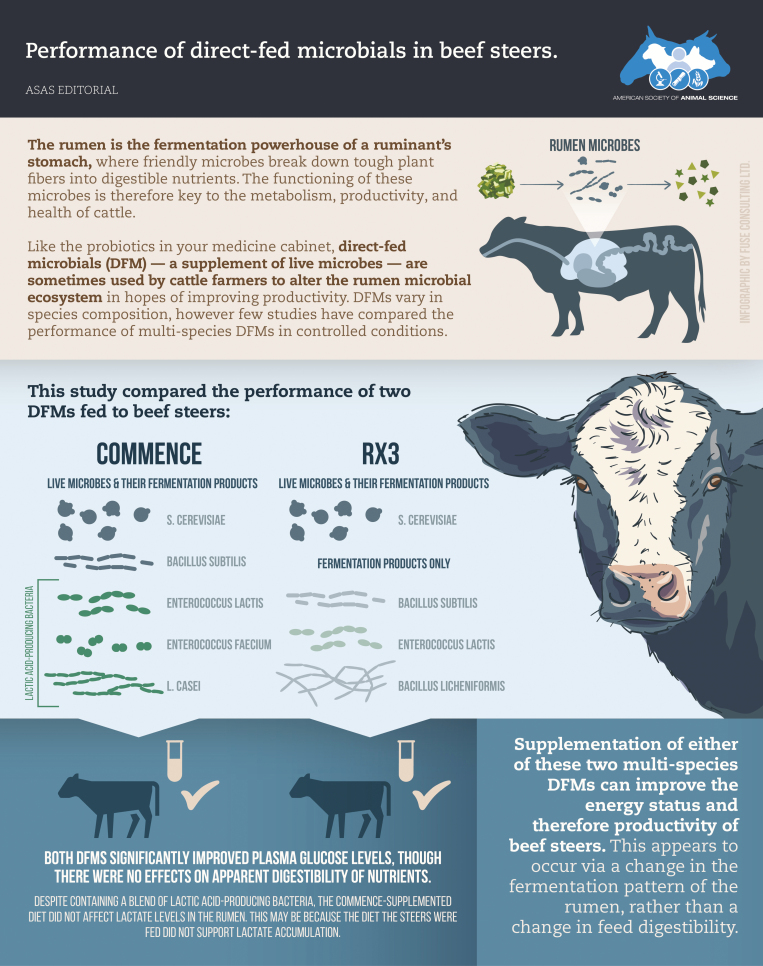
Direct-fed microbials (DFM) are probiotic supplements fed to cattle to alter the rumen microbiome and improve health and performance (Uyeno et al., 2015). Inclusion of DFMs in feedlot diets has variable effects ranging from no improvements in average daily gain to reduced performance in some feeding systems (Wilson et al., 2016; Swanson et al., 2018). In this issue, two DFMs were assessed for their ability to alter nutrient digestibility and blood parameters (Ugunade et al., 2020). Although no effects were evident on total tract digestibility, the DFMs increased blood glucose suggesting improved energy status.
References
- Swanson K C, Gaspers J J, Keomanivong F A, Gilbery T C, Lardy G P, Bauer M L, and Stokka G L. . 2018. Influence of feeding direct-fed microbial supplementation on growth performance and feeding behavior in naturally fed and conventionally fed finishing cattle with different dietary adaptation periods. J. Anim. Sci. 96:3370–3380. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugunade I M, McCoun M, Idowu M D, Peters S O, and Paulus Compart D M. . 2020. Comparative effects of two multi-species direct-fed microbial products on energy status, nutrient digestibility, and ruminal fermentation, bacterial community and metabolome of beef steers. J. Anim. Sci. 98:1–11. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeno Y, Shigemori S, and Shimosato T. . 2015. Effect of probiotics/prebiotics on cattle health and productivity. Microbes Environ. 30:126–132. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME14176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B K, Holland B P, Step D L, Jacob M E, VanOverbeke D L, Richards C J, Nagaraja T G, and Krehbiel C R. . 2016. Feeding wet distillers grains plus solubles with and without a direct-fed microbial to determine performance, carcass characteristics, and fecal shedding of O157:H7 in feedlot heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 94:297–305. doi: 10.2527/jas.2015-9601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]