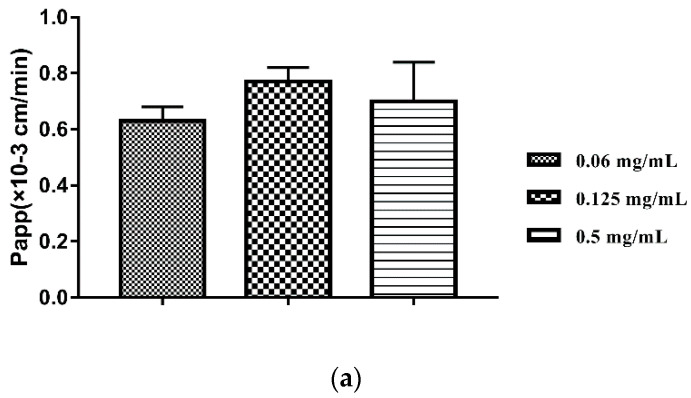
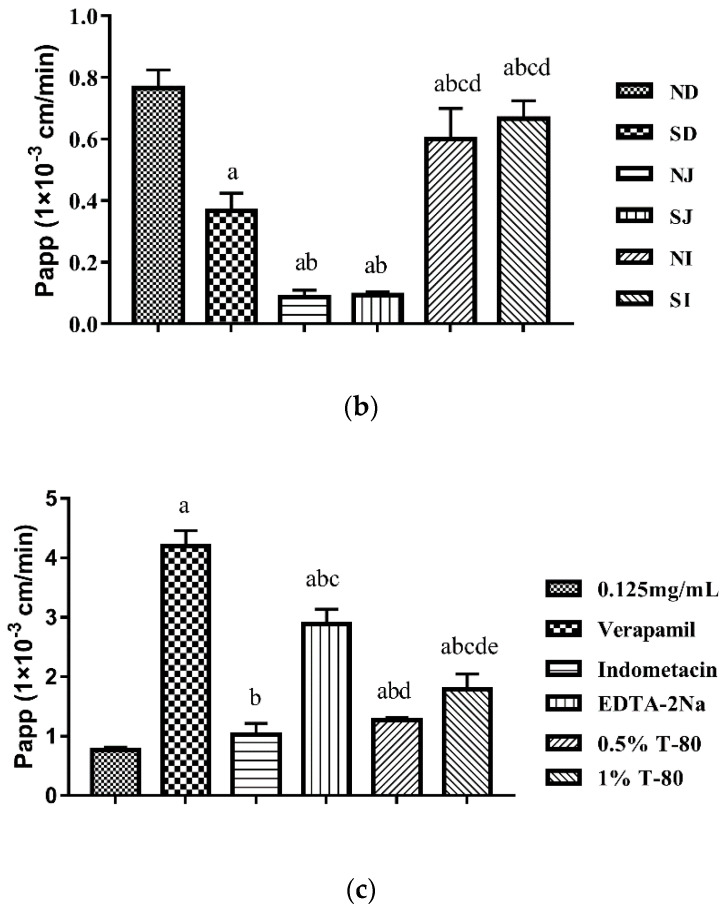
Figure 3.
The influences of concentration (a), intestinal sections (b), and inhibitors (c) on the Papp of TIL-SLNs or tilmicosin solution. The absorption site of tilmicosin was shifted from ileum to duodenum via TIL-SLNs. The absorption efficiency of TIL-SLNs was hindered by P-gp. Note: (a), the Papp of various concentration of TIL-SLNs; (b), the Papp of TIL-SLNs in various intestine sections; ND: TIL-SLNs duodenum; SD: solution duodenum; NJ: TIL-SLNs jejunum; SJ: solution jejunum; NI: TIL-SLNs ileum; SI: solution ileum. a Statistically significant from TIL-SLNs duodenum; b Statistically significant from solution duodenum; c Statistically significant from TIL-SLNs jejunum; d Statistically significant from solution jejunum; (c), T-80: polysorbate-80, a Statistically significant from TIL-SLNs (0.125 mg/mL); b Statistically significant from verapamil; c Statistically significant from indomethacin; d Statistically significant from EDTA-2Na; e Statistically significant from 0.5% T-80. The statistical difference was analyzed by one-way analysis of variance at p < 0.05.