Abstract
Enzyme treatment and fermentation of cereals are known processes that enhance the release of bound bioactive compounds to make them available for bioactivity. In this study, we tested the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory ability of destarched rice, Prozyme 2000p treated destarched rice (DP), and fermented DP samples. Prozyme 2000p treatment increased the ACE inhibitory ability from 15 ± 5% to 45 ± 3%. Fermentation of the Prozyme 2000p treated samples with Enterococcus faecium EBD1 significantly increased the ACE inhibitory ability to 75 ± 5%, while captopril showed an ACE inhibition of 92 ± 4%. An untargeted metabolomics approach using Ultra-high-performance liquid tandem chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry revealed the abundance of vitamins, phenolic compounds, antioxidant peptides, DPP IV inhibitory peptides, and antihypertensive peptides in the fermented samples which may account for its strong ACE inhibition. Although fermented DP had decreased fatty acid levels, the amount of essential amino acid improved drastically compared to destarched rice. Our results show that fermenting Prozyme-treated destarched rice with Enterococcus faecium EBD1 generates abundant bioactive compounds necessary for developing antihypertensive functional foods.
Keywords: bioactive peptides, hypertension, phenolic compounds, functional food
1. Introduction
In recent years, cereal grains such as rice have attracted much scientific attention [1] because they contain phenolic compounds such as quercetin, ferulic acid, and salicylic acid [2] which have strong antioxidant abilities [3]. Over the years, oxidative stress has been shown to play a key role in the pathogenesis of hypertension [4,5] since reactive oxygen species can cause endothelial dysfunction [6] leading to arterial stiffness in humans [7,8]. One popular physiological mechanism of hypertension is the renin-aldosterone-angiotensin system (RAAS) [9]. In the RAAS, renin cleaves angiotensinogen to release angiotensin I which is then hydrolyzed by angiotensin 1-converting enzyme (ACE) to generate angiotensin II (a vasoconstrictor) [10]. Interestingly, phenolic compounds have been shown to strongly inhibit angiotensin 1-converting enzyme (ACE) [11,12] and the strength of inhibition is directly proportional to the number of hydroxyl groups they possess [13]. In addition to polyphenols, rice contains proteins which when hydrolyzed, generate bioactive peptides [10]. Many potent antihypertensive peptides such as IHRF [14], VNP, and VWP [15] have been identified in rice. These peptides may reduce hypertension by inhibiting ACE and/or renin activities [16], triggering nitric oxide production, or blocking angiotensin II receptors [17]. Antihypertensive peptides are usually generated in foods either by enzyme hydrolysis or fermentation of protein samples. Lactic acid bacteria have been effective in fermenting food materials to release polyphenols [18] and to generate antihypertensive peptides [19]. In recent years, metabolomic techniques such as 1H-NMR (1H-nuclear magnetic resonance), GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry), and LC-MS (liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry) have been used to identify metabolites in foods [20]. Among the techniques commonly used, LC-MS is the most used in metabolomic studies due to its detection sensitivity, high resolution, and nonderivatization of samples [21]. Ultra-high-performance liquid tandem chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QTOF/MS) is a new approach in chromatography and was developed based on LC-MS to determine and quantify more metabolites [22]. In this study, we determined the ACE inhibitory ability of destarched rice before and after Prozyme 2000p treatment and after fermentation. We then used UHPLC-QTOF/MS to analyze the metabolite changes that occurred after Prozyme 2000p treatment and after fermentation to identify bioactive compounds generated by the processing methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Cultures
All chemical reagents were of analytical grade. ACE-1 Assay Kit (Fluorometric) was purchased from Biovision (Milpitas, CA 95035, USA). All other reagents, unless specified, were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Seoul, Korea. Two rice powder samples (Oriza sativa L. variety Japonica) were received from Erom Company Limited (Chuncheon-si, Kangwon-do, Korea). One sample (destarched rice) was composed of rice powder treated with α-amylase to hydrolyze the starch present. The second sample (destarched rice + Prozyme (DP)) consisted of destarched rice treated with Prozyme 2000p.
Enterococcus faecium EBD1 was obtained from the Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Kangwon National University, Korea to be used for fermentation. This bacterium was used in the current study because it demonstrated strong proteolytic ability in our previous study (data not shown). The bacteria stock culture was stored at −80 °C in de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) broth (Difco), containing 20% glycerol (v/v). The bacterium was spread on MRS agar and incubated at 37 °C overnight to obtain single colonies. MRS broth (10 mL) was then inoculated with a single bacteria colony and incubated at 37 °C. The cells were harvested at the exponential phase of growth. The number of viable bacterial cells was determined by the plate count on MRS agar.
2.2. Rice Fermentation
The bacteria growth medium for the lactic acid bacteria consisted of 10% (w/v) Prozyme 2000p treated destarched rice powder in distilled water. The growth media was sterilized by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 min before inoculating with lactic acid bacteria. E. faecium EBD1 (2 × 108 cfu/mL) was transferred from an overnight culture to a 200 mL of autoclaved growth media (pH 6). The media was incubated at 37 °C with 150 rpm agitation for 48 h. The media was then centrifuged at 10,000× g for 10 min and the supernatant was freeze-dried using TFD5505 table top freeze dryer (ilshinBioBase Co. Ltd., Gyeonggi-do, Korea) and the dried samples were stored at −20 °C for further analysis. The final fermented product was labelled as Fermented DP.
2.3. Determination of Angiotensin 1-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Ability
ACE inhibitory activities of destarched rice, Prozyme treated distarched rice (DP), and fermented Prozyme-treated rice (fermented DP) powder were measured using an ACE-1 Assay Kit according to the manufacture’s instructing with some modifications (Table S1). Briefly, 10 µL of diluted ACE-1 solution was transferred to a 96 well plate and the volume was adjusted to 50 µL/well with ACE-1 assay buffer. An aliquot of the rice samples (20 µL, 5 mg/mL) was added to the wells and mixed thoroughly. Captopril (20 µL, 5 mg/mL) was used as a positive control. ACE-1 substrate (50 µL) was added to the wells and mixed. Fluorescence (Ex/Em = 330/430 nm) was measured in a kinetic mode for 2 h at 37 °C. A standard curve was prepared using the Abz-standard solution. The ACE1 activity was calculated as:
| ACE1 activity = B×D/(ΔT×P) = pmol/minute/mg, |
where:
| B = Abz in sample based on standard curve slope (pmol), |
| ΔT = reaction time (minutes), |
| P = sample used into the reaction well (in mg), |
| D = sample dilution factor. |
One unit of ACE-1 activity is the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the release of 1 nmol of Abz per min from the substrate under the assay conditions at 37 °C. The extent of inhibition was calculated as 100% × [(B − A)/B] where A is the ACE-1 activity in the presence of ACE and ACE inhibitor, B is the ACE-1 activity without ACE inhibitory component.
2.4. Metabolomics Analysis
Each rice sample (1 g) was extracted with 20 mL of 50% methanol and placed on a mini rocker (Clinical Diagnostics, Gangnam, Korea) overnight. The samples were mixed completely for 30 s using a vortex and subsequently centrifuged at 12,000× g for 12 min at 4 °C. Aliquots (1 mL) of the supernatants were filtered through 0.25 µm pore size Millex syringe filters (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and transferred into LC-MS vials. LC-MS/MS analysis was carried out using a UHPLC (SCIEX ExionLC AD system, Framingham, MA, USA) connected to a controller, a pump, a degasser, an autosampler, column oven, and a photodiode array detector (ExionLC) coupled to a quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer (Q-TOF-MS) (X500R QTOF). The analytical column used was a 100 × 3 mm, Accucore C18 column (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Solvent A consisted of water with 0.1% formic acid and solvent B was methanol. The chromatography was carried at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. A linear gradient was programmed for 25 min as follows: 0–3.81 min, 9% to 14% B; 3.81–4.85 min, 14% to 15% B; 4.85–5.89 min, 15% B; 5.89–8.32 min, 15% to 17% B; 8.32–9.71 min, 17% to 19% B; 9.71–10.40 min, 19% B; 10.40–12.48 min, 19% to 26% B; 12.48–13.17 min, 26% to 28% B; 13.17–14.21 min, 28% to 35% B; 14.21–15.95 min, 35% to 40% B; 15.95–16.64 min, 40% to 48% B; 16.64–18.37 min, 48% to 53% B; 18.37–22.53 min, 53% to 70% B; 22.53–22.88 min, 70% to 9% B; 22.88–25.00 min, 9% B. The injection volume was 5 μL. The Q-TOF-MS was set for the negative mode through a mass range of 100–1000 and a resolution of 5000. The capillary and cone voltages used to record full mass spectra were 1.45 kV and 30 V, respectively. The flow rate of Helium (the cone gas) was 45 L/h, while the flow rate of the desolvation gas (N2) was 900 L/h. The temperature of N2 was 250 °C, the ion source temperature was 120 °C, while the collision energies needed to obtain the MS/MS spectra were set at 15, 20, and 30 V.
2.5. Data Analysis
All data were obtained and processed using SCIEX OS 1.0 software. A non-target algorithm was used for peak finding. Matrix and sample specific signals were separated from true contaminations using an automatic sample-control comparison algorithm. Compound identification was done by using empirical formula finding, MS/MS library searching, and online database searching. Compound names, peak area, retention time, similarity to metabolites in the database, and mass (m/z) were ultimately imported into Microsoft Excel.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
For ACE inhibitory ability tests, all experiments were carried out in triplicates and the results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The statistical analysis of data was performed using GraphPad Prism 5.0 (2007) statistical software system (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA 92037 USA). p < 0.05 was considered significant as evaluated by Student’s t-test.
ClustVis software (http://biit.cs.ut.ee/clustvis/) was used in multivariate statistical analyses, including principal component analysis (PCA) and heat maps [23]. PCA was performed to visualize the changes in metabolite composition in destarched rice, Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP), and fermented DP. Heat maps and PCA plots were drawn by using identified compounds and their peak area. We used peak areas because it is widely accepted that the peak area of an analyte in a chromatograph is directly proportional to its concentration [24,25,26].
3. Results and Discussion
Rice consists of about 90% carbohydrate, up to 8% protein, and about 2% fat [27]. These major components are bound together in the food matrix and hence, hydrolyzing rice starch with α-amylase enables the release of bound proteins and other biomolecules from the food matrix, making them available for subsequent reactions.
3.1. ACE Inhibitory Activity of Rice Samples
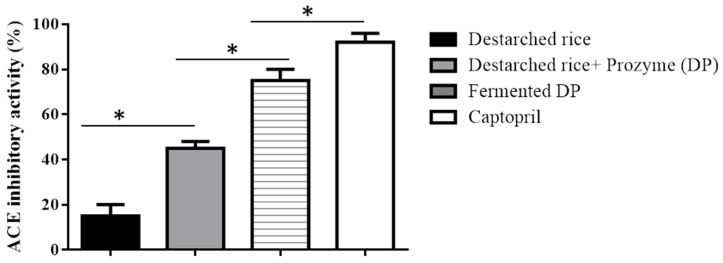
Prozyme treatment significantly (p < 0.05) increased the ACE inhibitory ability of destarched rice from 15 ± 5% to 45 ± 3% (Figure 1). This could be due to the release of ACE inhibitory compounds from the rice proteins during Prozyme proteolysis. Our observation agrees with earlier studies that showed that hydrolysis of rice proteins enhances the generation of ACE inhibitory hydrolysates [28]. Subsequent fermentation of the Prozyme hydrolysate with E. faecium EBD1 further increased the inhibitory effect up to 75 ± 5%, while Captopril (a standard ACE inhibitory peptide) demonstrated a 92 ± 4% inhibitory ability.
Figure 1.
ACE inhibitory activities of destarched rice, Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP), and fermented DP. Data show mean SD (n = 3). Each bar represents the means of three replicates ± S.D. * denotes a significant difference between the ACE inhibitory ability of the samples.
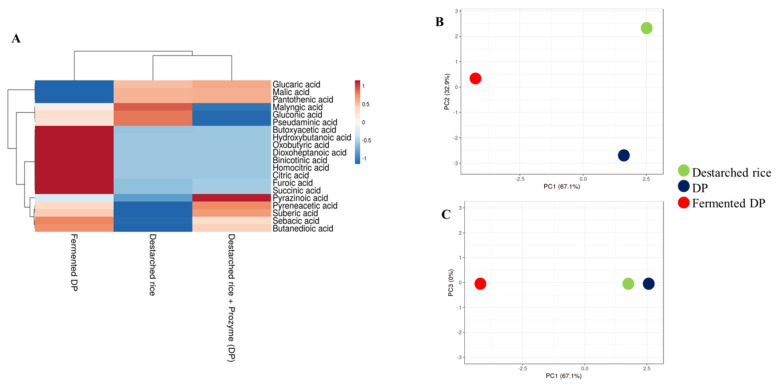
During lactic acid bacteria fermentation, a number of organic acids are generated from the sugars and lipids available in the growth media and this affects the flavor and pH of the final product [29]. ACE activity is best at a pH of ~8.3 [11] and hence, the increased acidity of fermented food may contribute to inhibition of the enzyme. In this study, a total of twenty organic acids were detected in all the rice samples (Figure 2A). Ten organic acids were detected in destarched rice, 14 in DP, and 19 in fermented DP (Table S2). Only the fermented samples contained homocitric acid, citric acid, binicotinic acid, dioxoheptanoic acid, oxobutyric acid, and hydroxybutanoic acid. Meanwhile, butyric acid [30], nicotinic acid [31], and citric acid are known antihypertensive compounds and hence, their enrichment in the fermentate makes it a potential antihypertensive functional food. Although the types and levels of organic acids in the three samples were different (Figure 2B), organic acid profiles of destarched rice and DP were similar (Figure 2C).
Figure 2.
Relative levels of organic acids and volatile compounds in destarched rice, Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP), and fermented DP. (A) Heat map shows the different levels of organic acids present in the three samples. The color range from red to blue represents higher to lower levels of organic acids. (B,C) are principal component analysis (PCA) plots. (B) consists of PC1 and PC2, while (C) consists of PC1 and PC3. Red circles represent fermented DP, black represents Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP), and green represents destarched rice samples.
3.2. Amino Acid Levels in the Rice Samples
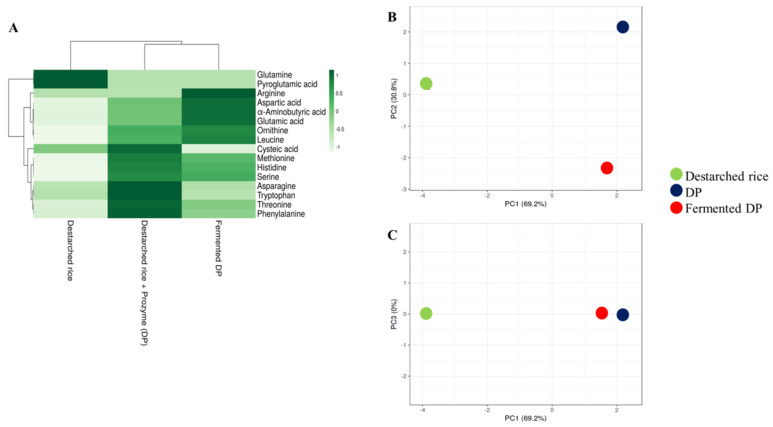
A total of sixteen amino acids were detected in the analyzed samples (Figure 3A, Table S3). In this study, destarched rice contained the least free amino acids contents since most of the amino acids might have remained bound to their parent proteins. Hydrolysis of rice proteins with Prozyme resulted in the cleavage and release of high amounts of essential amino acids such as phenylalanine, threonine, methionine, histidine, and tryptophan (Figure 3). The levels of these essential amino acids reduced drastically after fermentation except for histidine and methionine. Glutamine, cysteic acid, tryptophan, and pyroglutamic acid, though present in the Prozyme treated sample, were not detected in the fermented sample (Table S3) probably because they were consumed by the bacteria to meet their nitrogen requirements during the fermentation process. Meanwhile, the level of leucine (an essential amino acid) and some conditionally essential amino acids such as ornithine, arginine, and serine were increased after fermentation (Figure 3). As shown in the PCA plot (Figure 3B), the amino acid profiles of DP were similar to those of fermented DP but different from destarched rice (Figure 3C).
Figure 3.
Relative levels of amino acids in destarched rice, Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP), and fermented DP. (A) Heat map shows the different levels of organic acids present in the three samples. The color range from green to white represents higher to lower levels of amino acids. (B,C) are principal component analysis (PCA) plots. (B) consists of PC1 and PC2, while (C) consists of PC1 and PC3. Red circles represent fermented DP, black represents Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP), and green represents destarched rice samples.
3.3. E. faecium EBD1fermentation Increases the Amount of Phenolic Compounds in Rice
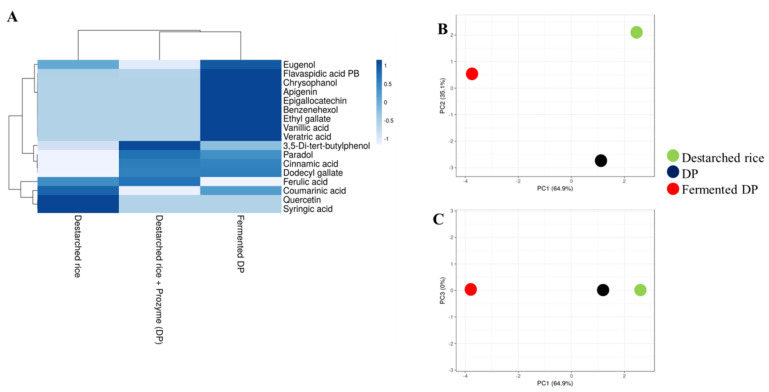
Recent studies have shown that a strong hydrophobic interaction exists between phenolic compounds and other rice components [32]. In this study, 10 out of the 17 detected phenolic compounds were present in destarched rice, while 9 were detected after Prozyme treatment (Figure 4, Table S4). In the fermented samples however, 16 phenolic compounds were present and this implies that the fermentation process effectively enhanced the liberation of phenolic compounds that remained bound to the rice matrix even after α-amylase and Prozyme treatments. Fermentation resulted in the enrichment of strong antioxidant and antihypertensive phenolic compounds such as vanillic acid [33], eugenol [34], veratric acid [35], ethyl gallate [36], epigallocatechin [37], apigenin [38], and chrysophanol [39]. Our observation agrees with an earlier study that demonstrated that microbial fermentation increases the polyphenol contents of cereals [40,41].
Figure 4.
Relative levels of phenolic compounds in destarched rice, Prozyme treated destarched (DP), and fermented DP. (A) Heat map shows the different levels of phenolic compounds present in the three samples. The color range from blue to white represents higher to lower levels of phenolic compounds. (B,C) are principal component analysis (PCA) plots. (B) consists of PC1 and PC2, while (C) consists of PC1 and PC3. Red circles represent fermented DP, black represents Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP), and green represents destarched rice samples.
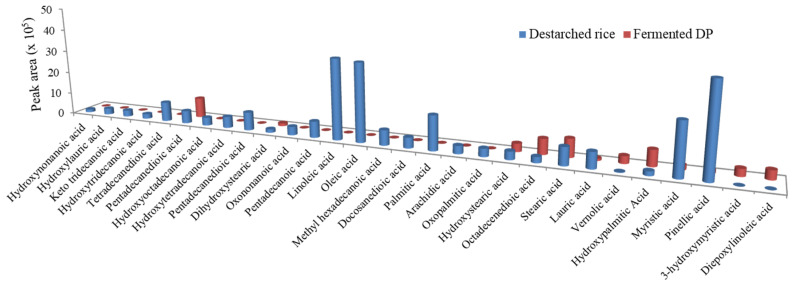
3.4. E. faecium EBD1fermentation Reduces Lipid Levels in Rice
Oxidation of lipids during fermentation results in the generation volatile compounds such as aldehydes and alcohols which contribute to flavor [42]. In this study, E. faecium EBD1fermentation caused a general reduction in the fatty acid levels in the rice sample (Figure 5). The levels of stearic acid (an antioxidant fatty acid) [43] slightly increased, while lauric acid (an antihypertensive fatty acid) [44] was still detectable in the fermentate. Our results are different from an earlier study which found no significant changes in lipid content during millet fermentation [45].
Figure 5.
The relative levels of fatty acids in destarched rice and fermented DP.
3.5. E. faecium EBD1fermented Rice Is Enriched with Antihypertensive Peptides
Lactic acid bacteria possess cell envelop proteinases that hydrolyze proteins in media into oligopeptides after which they are absorbed to meet their nutritional needs [9]. For this reason, we analyzed the peptides generated in the fermented samples and determined their potential functions by comparing them with similar peptides already reported in literature (Table 1). In all, 32 peptides were identified in the fermented rice samples among which 16 are reported in literature as antihypertensive peptides. Nine peptides had their carboxyl or amino-terminal amino acid sequences similar to reported antihypertensive peptides, while 3 peptides, namely VPL [46], MV, and HR [47] were found to be dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP IV) inhibitors. Many studies have shown the ability of DPP IV inhibitors to reduce hypertension [48,49]. One antioxidative peptide EL, was also found in the peptide profile of the fermented samples. The presence of these bioactive peptides in the fermented sample may contribute to the strong ACE inhibitory activity observed in this study. Meanwhile, functional analysis is required to confirm the antihypertensive activity of peptides in the fermented sample that contain sequences of already known antihypertensive peptides at their C and N terminals. Our findings are similar to other studies that reported that phenolic compounds [50,51] and bioactive peptides [52] in food can inhibit ACE activity.
Table 1.
Peptides identified in Enterococcus faecium EBD1 fermented DP.
| Retention Time | Peak Area | Adduct/Charge | Precursor Mass | Found at Mass | Formula Finder Results | Peptides | Similar Peptides Reported in Literature* | Peptide Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.93 | 221,600 | [M-H]- | 227.116 | 227.115 | C9H16N4O3 | GPG | GPG | Antihypertensive | [53] |
| 0.97 | 1,227,000 | [M-H]- | 516.206 | 516.2053 | C19H31N7O10 | QQQD | LQQQ | Antihypertensive | [54] |
| 1.31 | 506,800 | [M-H]- | 185.058 | 185.0572 | C7H10N2O4 | EG | EG | Antihypertensive | [55] |
| 3.16 | 501,500 | [M-H]- | 419.121 | 419.1206 | C18H20N4O8 | GGG | GGG | Antihypertensive | [56] |
| 8.22 | 292,200 | [M-H]- | 442.232 | 442.2311 | C19H33N5O7 | PKEA | VDKEA | Antihypertensive | [57] |
| 8.4 | 219,500 | [M-H]- | 426.237 | 426.2363 | C19H33N5O6 | GVGVP | Not found | - | - |
| 8.63 | 2,611,000 | [M-H]- | 227.105 | 227.1039 | C10H16N2O4 | EV | EV | Antihypertensive | [58] |
| 9.23 | 1,306,000 | [M-H]- | 291.1 | 291.0989 | C14H16N2O5 | EY | EY | Antihypertensive | [59] |
| 9.48 | 192,900 | [M-H]- | 544.228 | 544.2266 | C23H31N9O7 | WGGGGGG | GGG | Antihypertensive | [56] |
| 9.87 | 10,460 | [M-H]- | 293.116 | 293.1143 | C14H18N2O5 | DF | DF | Antihypertensive | [60] |
| 10.29 | 210,900 | [M-H]- | 326.209 | 326.2087 | C16H29N3O4 | VPL | VPL | DPP IV inhibitor | [46] |
| 10.6 | 1,264,000 | [M-H]- | 383.231 | 383.2305 | C18H32N4O5 | PLG | PLG | Antihypertensive | [61] |
| 11.56 | 195,100 | [M-H]- | 453.201 | 453.1996 | C20H30N4O8 | PDGA | Not found | - | - |
| 11.61 | 3,821,000 | [M-H]- | 241.121 | 241.1196 | C11H18N2O4 | EL | EL | Antioxidative | [62] |
| 11.81 | 432,500 | [M-H]- | 489.273 | 489.2725 | C25H38N4O6 | VLPY | VLPYP | Antihypertensive | [63] |
| 11.84 | 243,600 | [M-H]- | 518.227 | 518.2263 | C24H33N5O8 | DISW | ISW | Antihypertensive | [64] |
| 11.91 | 478,100 | [M-H]- | 395.195 | 395.1941 | C18H28N4O6 | YLS | YL | Antihypertensive | [65] |
| 11.92 | 267,600 | [M-H]- | 319.135 | 319.1335 | C13H24N2O5S | MG | MG | Antihypertensive | [66] |
| 12.12 | 249,800 | [M-H]- | 473.209 | 473.2079 | C20H34N4O7S | EMVP | MMVPI | Antihypertensive | [67] |
| 12.94 | 1,020,000 | [M-H]- | 489.237 | 489.2361 | C24H34N4O7 | GPLA | GPL | Antihypertensive | [68] |
| 13.0 | 471,200 | [M-H]- | 774.334 | 774.3331 | C44H49N5O6S | AW | AW | Antihypertensive | [69] |
| 13.3 | 187,800 | [M-H]- | 180.974 | 180.9733 | C2H2N2O8 | GG | GG | Antihypertensive | [58] |
| 13.41 | 1,627,000 | [M-H]- | 496.316 | 496.3145 | C24H43N5O6 | IVPVA | KPVAL | Antihypertensive | [70] |
| 13.42 | 1,415,000 | [M-H]- | 528.284 | 528.2836 | C27H39N5O6 | FPIV | GPFPIIV | Antihypertensive | [70] |
| 14.17 | 1,171,000 | [M-H]- | 510.331 | 510.3303 | C25H45N5O6 | GGGGG | GGG | Antihypertensive | [56] |
| 14.24 | 409,400 | [M-H]- | 482.263 | 482.2627 | C22H37N5O7 | VVPQ | VPQ | Antihypertensive | [71] |
| 15.88 | 153.2 | [M-H]- | 743.35 | 743.3477 | C33H56N6O9S2 | VMV | MV | DPP IV inhibitor | [47] |
| 17.11 | 14,500 | [M-H]- | 267.067 | 267.0646 | C8H16N2O6S | CE | Not found | - | - |
| 17.22 | 1,126,000 | [M-H]- | 310.165 | 310.1637 | C12H21N7O3 | HR | HR | DPP IV inhibitor | [47] |
| 17.8 | 360,400 | [M-H]- | 457.169 | 457.1688 | C17H34N2O8S2 | CC | CCD | Antihypertensive | [72] |
| 21.12 | 43,240 | [M-H]- | 474.264 | 474.2634 | C22H41N3O6S | ML | RML | Antihypertensive | [73] |
| 22.19 | 29,960 | [M-H]- | 473.284 | 473.2837 | C19H38N8O6 | KTAR | KTAP | Antihypertensive | [63] |
*Boldened alphabets represent amino acids sequences identified in this study and previous studies.
4. Conclusions
Using untargeted metabolomics, we found that Prozyme treatment and subsequent fermentation enhanced the generation of organic acids (flavor compounds) and essential amino acids. The fermented DP samples also contained known antihypertensive phenolic compounds as well as antihypertensive peptides which make the sample a promising material for developing cheap antihypertensive foods. Despite the antihypertensive potential of the fermented product, further studies regarding the ability of Enterococcus faecium EBD1 fermented Prozyme-treated destarched rice to reduce high blood pressure in vivo is warranted.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/9/8/1007/s1. Table S1: Procedure for assay of ACE activity. Table S2: Organic acids and volatile compounds in destarched rice, Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP) and fermented DP. Table S3: Amino acids in destarched rice, Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP) and fermented DP. Table S4: Phenolic compounds in destarched rice, Prozyme treated destarched rice (DP) and fermented DP.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.B.-M.D. and D.-H.O.; Formal analysis, E.B.-M.D. and J.-R.K.; Investigation, F.K.O.; Methodology, R.C. and D.Y.; Resources, J.-H.K.; Supervision, D.-H.O.; Writing—original draft, E.B.-M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture and Forestry. Grant number 119014032SB010.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Zhu F. Anthocyanins in cereals: Composition and health effects. Food Res. Int. 2018;109:232–249. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Das A.J., Das G., Miyaji T., Deka S.C. In vitro antioxidant activities of polyphenols purified from four plant species used in rice beer preparation in Assam India. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016;19:636–651. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2015.1038835. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stagos D. Antioxidant activity of polyphenolic plant extracts. Antioxidants. 2020;9:19. doi: 10.3390/antiox9010019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Qu W., Du G.-L., Feng B., Shao H. Effects of oxidative stress on blood pressure and electrocardiogram findings in workers with occupational exposure to lead. Int. J. Med. Res. 2019;47:2461–2470. doi: 10.1177/0300060519842446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Montezano A.C., Touyz R.M. Molecular mechanisms of hypertension—Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants: A basic science update for the clinician. Can. J. Cardiol. 2012;28:288–295. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2012.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Alaaeddine R., Elkhatib M.A., Mroueh A., Fouad H., Saad E.I., El-Sabban M.E., Plane F., El-Yazbi A.F. Impaired endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization underlies endothelial dysfunction during early metabolic challenge: Increased ROS generation and possible interference with NO function. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019;371:567–582. doi: 10.1124/jpet.119.262048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mathew E., Mukkadan J. Clinical disparity of oxidative stress with blood pressure. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019:3. doi: 10.3126/jbs.v6i3.26821. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kruger R., Schutte R., Huisman H., Van Rooyen J., Malan N., Fourie C., Louw R., Van der Westhuizen F., Van Deventer C., Malan L. Associations between reactive oxygen species, blood pressure and arterial stiffness in black South Africans: The SABPA study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2012;26:91–97. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2010.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Daliri E.B.-M., Lee B.H., Oh D.H. Current perspectives on antihypertensive probiotics. Probiotics Antimicrob. 2017;9:91–101. doi: 10.1007/s12602-016-9241-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Daliri E.B.-M., Lee B.H., Oh D.H. Current trends and perspectives of bioactive peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018;58:2273–2284. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1319795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dong J., Xu X., Liang Y., Head R., Bennett L. Inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme activity by polyphenols from tea (Camellia sinensis) and links to processing method. Food Funct. 2011;2:310–319. doi: 10.1039/c1fo10023h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Persson I.A.-L., Persson K., Andersson R.G. Effect of Vaccinium myrtillus and its polyphenols on angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in human endothelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009;57:4626–4629. doi: 10.1021/jf900128s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Al Shukor N., Van Camp J., Gonzales G.B., Staljanssens D., Struijs K., Zotti M.J., Raes K., Smagghe G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory effects by plant phenolic compounds: A study of structure activity relationships. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013;61:11832–11839. doi: 10.1021/jf404641v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kontani N., Omae R., Kagebayashi T., Kaneko K., Yamada Y., Mizushige T., Kanamoto R., Ohinata K. Characterization of Ile-His-Arg-Phe, a novel rice-derived vasorelaxing peptide with hypotensive and anorexigenic activities. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014;58:359–364. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201300334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen J., Liu S., Ye R., Cai G., Ji B., Wu Y. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory tripeptides from rice protein hydrolysate: Purification and characterization. J. Funct. Foods. 2013;5:1684–1692. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2013.07.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pinciroli M., Aphalo P., Nardo A.E., Añón M.C., Quiroga A.V. Broken rice as a potential functional ingredient with inhibitory activity of renin and angiotensin-converting enzyme. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019;74:405–413. doi: 10.1007/s11130-019-00754-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Aluko R.E. Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015;6:235–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-022814-015520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oboh G., Ademiluyi A., Akindahunsi A. Changes in polyphenols distribution and antioxidant activity during fermentation of some underutilized legumes. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2009;15:41–46. doi: 10.1177/1082013208101022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rubak Y.T., Nuraida L., Iswantini D., Prangdimurti E. Production of antihypertensive bioactive peptides in fermented food by lactic acid bacteria—A review. Carpath. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019;11:29–44. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhao S., Zhao J., Bu D., Sun P., Wang J., Dong Z. Metabolomics analysis reveals large effect of roughage types on rumen microbial metabolic profile in dairy cows. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014;59:79–85. doi: 10.1111/lam.12247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goldansaz S.A., Guo A.C., Sajed T., Steele M.A., Plastow G.S., Wishart D.S. Livestock metabolomics and the livestock metabolome: A systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0177675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yang Y., Dong G., Wang Z., Wang J., Zhang Z., Liu J. Rumen and plasma metabolomics profiling by UHPLC-QTOF/MS revealed metabolic alterations associated with a high-corn diet in beef steers. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0208031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Metsalu T., Vilo J. ClustVis: A web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using principal component analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:W566–W570. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pinkard B.R., Gorman D.J., Rasmussen E.G., Maheshwari V., Kramlich J.C., Reinhall P.G., Novosselov I.V. Raman spectroscopic data from formic acid decomposition in subcritical and supercritical water. Data Brief. 2020;29:105312. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.105312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tung L. Method of calculating molecular weight distribution function from gel permeation chromatograms. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1966;10:375–385. doi: 10.1002/app.1966.070100303. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Berente B., De la Calle García D., Reichenbächer M., Danzer K. Method development for the determination of anthocyanins in red wines by high-performance liquid chromatography and classification of German red wines by means of multivariate statistical methods. J. Chromatogr. A. 2000;871:95–103. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(99)01272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhou Z., Robards K., Helliwell S., Blanchard C. Composition and functional properties of rice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002;37:849–868. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2621.2002.00625.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Suwannapan O., Wachirattanapongmetee K., Thawornchinsombut S., Katekaew S. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from Thai jasmine rice bran protein hydrolysates. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020;55:2441–2450. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.14495. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cirlini M., Ricci A., Galaverna G., Lazzi C. Application of lactic acid fermentation to elderberry juice: Changes in acidic and glucidic fractions. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020;118:108779. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108779. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang L., Zhu Q., Lu A., Liu X., Zhang L., Xu C., Liu X., Li H., Yang T. Sodium butyrate suppresses angiotensin II-induced hypertension by inhibition of renal (pro)renin receptor and intrarenal renin–angiotensin system. J. Hypertens. 2017;35:1899–1908. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bays H.E., Maccubbin D., Meehan A.G., Kuznetsova O., Mitchel Y.B., Paolini J.F. Blood pressure-lowering effects of extended-release niacin alone and extended-release niacin/laropiprant combination: A post hoc analysis of a 24-week, placebo-controlled trial in dyslipidemic patients. Clin. Ther. 2009;31:115–122. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dai T., Chen J., McClements D.J., Hu P., Ye X., Liu C., Li T. Protein–polyphenol interactions enhance the antioxidant capacity of phenolics: Analysis of rice glutelin–procyanidin dimer interactions. Food Func. 2019;10:765–774. doi: 10.1039/C8FO02246A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kumar S., Prahalathan P., Raja B. Antihypertensive and antioxidant potential of vanillic acid, a phenolic compound in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats: A dose-dependence study. Redox Rep. 2011;16:208–215. doi: 10.1179/1351000211Y.0000000009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Peixoto-Neves D., Wang Q., Leal-Cardoso J.H., Rossoni L.V., Jaggar J.H. Eugenol dilates mesenteric arteries and reduces systemic BP by activating endothelial cell TRPV 4 channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015;172:3484–3494. doi: 10.1111/bph.13156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Saravanakumar M., Raja B. Veratric acid, a phenolic acid attenuates blood pressure and oxidative stress in L-NAME induced hypertensive rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011;671:87–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.08.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jin L., Piao Z.H., Sun S., Liu B., Kim G.R., Seok Y.M., Lin M.Q., Ryu Y., Choi S.Y., Kee H.J. Gallic acid reduces blood pressure and attenuates oxidative stress and cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:1–14. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15925-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Luo D., Xu J., Chen X., Zhu X., Liu S., Li J., Xu X., Ma X., Zhao J., Ji X. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) attenuates salt-induced hypertension and renal injury in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61794-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sui H., Yan W. Effect of apigenin on SBP of spontaneous hypertension rats and its mechanism. J. Environ. Health. 2009;26:112–113. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yusuf M.A., Singh B.N., Sudheer S., Kharwar R.N., Siddiqui S., Abdel-Azeem A.M., Fernandes Fraceto L., Dashora K., Gupta V.K. Chrysophanol: A natural anthraquinone with multifaceted biotherapeutic potential. Biomolecules. 2019;9:68. doi: 10.3390/biom9020068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chandrasekara A., Shahidi F. Bioaccessibility and antioxidant potential of millet grain phenolics as affected by simulated in vitro digestion and microbial fermentation. J. Funct. Foods. 2012;4:226–237. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2011.11.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dey T.B., Kuhad R.C. Enhanced production and extraction of phenolic compounds from wheat by solid-state fermentation with Rhizopus oryzae RCK2012. Biotech. Rep. 2014;4:120–127. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2014.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Liptáková D., Matejčeková Z., Valík L. Lactic acid bacteria and fermentation of cereals and pseudocereals. Ferment. Process. 2017;10:65459. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang Z.J., Liang C.L., Li G.M., Yu C.Y., Yin M. Stearic acid protects primary cultured cortical neurons against oxidative stress4. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2007;28:315–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Alves N.F.B., de Queiroz T.M., de Almeida Travassos R., Magnani M., de Andrade Braga V. Acute treatment with lauric acid reduces blood pressure and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017;120:348–353. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Antony U., Sripriya G., Chandra T. The effect of fermentation on the primary nutrients in foxtail millet (Setaria italica) Food Chem. 1996;56:381–384. doi: 10.1016/0308-8146(95)00186-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Umezawa H., Aoyagi T., Ogawa K., Naganawa H., Hamada M., Takeuchi T. Diprotins A and B, inhibitors of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV, produced by bacteria. J. Antibiot. 1984;37:422–425. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lan V.T.T., Ito K., Ohno M., Motoyama T., Ito S., Kawarasaki Y. Analyzing a dipeptide library to identify human dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor. Food Chem. 2015;175:66–73. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cosenso-Martin L.N., Giollo-Junior L.T., Vilela-Martin J.F. DPP-4 inhibitor reduces central blood pressure in a diabetic and hypertensive patient: A case report. Medicine. 2015;94 doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pacheco B.P., Crajoinas R.O., Couto G.K., Davel A.P.C., Lessa L.M., Rossoni L.V., Girardi A.C. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition attenuates blood pressure rising in young spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int. J. Hypertens. 2011;29:520–528. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328341939d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang Y., Pechan T., Chang S.K.C. Antioxidant and angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory activities of phenolic extracts and fractions derived from three phenolic-rich legume varieties. J. Funct. Foods. 2018;42:289–297. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.12.060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Santos M.C., Toson N.S.B., Pimentel M.C.B., Bordignon S.A.L., Mendez A.S.L., Henriques A.T. Polyphenols composition from leaves of Cuphea spp. and inhibitor potential, in vitro, of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020;255:112781. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wang X., Chen H., Fu X., Li S., Wei J. A novel antioxidant and ACE inhibitory peptide from rice bran protein: Biochemical characterization and molecular docking study. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017;75:93–99. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2016.08.047. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wang X., Wang J., Lin Y., Ding Y., Wang Y., Cheng X., Lin Z. QSAR study on angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor oligopeptides based on a novel set of sequence information descriptors. J. Mol. Model. 2011;17:1599–1606. doi: 10.1007/s00894-010-0862-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yano S., Suzuki K., Funatsu G. Isolation from α-zein of thermolysin peptides with angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996;60:661–663. doi: 10.1271/bbb.60.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cheung H.-S., Wang F.-L., Ondetti M.A., Sabo E.F., Cushman D.W. Binding of peptide substrates and inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Importance of the COOH-terminal dipeptide sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 1980;255:401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zhou P., Yang C., Ren Y., Wang C., Tian F. What are the ideal properties for functional food peptides with antihypertensive effect? A computational peptidology approach. Food Chem. 2013;141:2967–2973. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.05.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hernández-Ledesma B., Recio I., Ramos M., Amigo L. Preparation of ovine and caprine β-lactoglobulin hydrolysates with ACE-inhibitory activity. Identification of active peptides from caprine β-lactoglobulin hydrolysed with thermolysin. Int. Dairy J. 2002;12:805–812. doi: 10.1016/S0958-6946(02)00080-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Castellano P., Aristoy M.-C., Sentandreu M.Á., Vignolo G., Toldrá F. Peptides with angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity generated from porcine skeletal muscle proteins by the action of meat-borne Lactobacillus. J. Proteom. 2013;89:183–190. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.06.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wu H., He H.-L., Chen X.-L., Sun C.-Y., Zhang Y.-Z., Zhou B.-C. Purification and identification of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from shark meat hydrolysate. Process Biochem. 2008;43:457–461. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2008.01.018. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ichimura T., Hu J., Aita D.Q., Maruyama S. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity and insulin secretion stimulative activity of fermented fish sauce. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003;96:496–499. doi: 10.1016/S1389-1723(03)70138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Byun H.-G., Kim S.-K. Structure and activity of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from Alaskan pollack skin. BMB Rep. 2002;35:239–243. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2002.35.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Suetsuna K., Ukeda H., Ochi H. Isolation and characterization of free radical scavenging activities peptides derived from casein. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2000;11:128–131. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2863(99)00083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kohmura M., Nio N., Kubo K., Minoshima Y., Munekata E., Ariyoshi Y. Inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme by synthetic peptides of human β-casein. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989;53:2107–2114. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gu Y., Majumder K., Wu J. QSAR-aided in silico approach in evaluation of food proteins as precursors of ACE inhibitory peptides. Food Res. Int. 2011;44:2465–2474. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.01.051. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Tauzin J., Miclo L., Gaillard J.-L. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from tryptic hydrolysate of bovine αS2-casein. FEBS Lett. 2002;531:369–374. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03576-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Nogata Y., Nagamine T., Yanaka M., Ohta H. Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides produced by autolysis reactions from wheat bran. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009;57:6618–6622. doi: 10.1021/jf900857w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Escudero E., Sentandreu M.A., Arihara K., Toldra F. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides generated from in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of pork meat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010;58:2895–2901. doi: 10.1021/jf904204n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.He R., Malomo S.A., Girgih A.T., Ju X., Aluko R.E. Glycinyl-histidinyl-serine (GHS), a novel rapeseed protein-derived peptide has blood pressure-lowering effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013;61:8396–8402. doi: 10.1021/jf400865m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Nakahara T., Sano A., Yamaguchi H., Sugimoto K., Chikata H., Kinoshita E., Uchida R. Antihypertensive effect of peptide-enriched soy sauce-like seasoning and identification of its angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory substances. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010;58:821–827. doi: 10.1021/jf903261h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Del Mar Contreras M., Carrón R., Montero M.J., Ramos M., Recio I. Novel casein-derived peptides with antihypertensive activity. Int. Dairy J. 2009;19:566–573. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2009.05.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Minervini F., Algaron F., Rizzello C., Fox P., Monnet V., Gobbetti M. Angiotensin I-converting-enzyme-inhibitory and antibacterial peptides from Lactobacillus helveticus PR4 proteinase-hydrolyzed caseins of milk from six species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003;69:5297–5305. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.9.5297-5305.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Udenigwe C.C., Adebiyi A.P., Doyen A., Li H., Bazinet L., Aluko R.E. Low molecular weight flaxseed protein-derived arginine-containing peptides reduced blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats faster than amino acid form of arginine and native flaxseed protein. Food Chem. 2012;132:468–475. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wu J., Aluko R.E., Nakai S. Structural requirements of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: Quantitative structure− activity relationship study of di-and tripeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006;54:732–738. doi: 10.1021/jf051263l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.